Table of Contents
CD20 | CD21 | CD22 | CD23 | CD24 | CD25 | CD26 | CD27 | CD28 | CD29 | Diagrams / tables | Microscopic (histologic) imagesCite this page: Pernick N. CD20-29. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cdmarkerscd20to29.html. Accessed March 28th, 2025.
CD20
- See CD20
CD21
- See CD21
CD22
- Pan B cell marker helpful for diagnosis of hairy cell leukemia
- Also called B lymphocyte cell adhesion molecule (BL-CAM), Sialic acid binding immunoglobulin-like lectin / Siglec-2
- Pathophysiology:
- Inhibits B cell receptor signaling via alpha 2,6 sialic acid ligand binding activity (Front Immunol 2012;2:96); also binds CD45 and has adhesion properties of a lectin (J Exp Med 2002;195:1207)
- May localize B cells in lymphoid tissues
- Ligand is CD75
- CD22 internalizes within the cell and recycles (Traffic 2014;15:255)
- Clinical features:
- Shows variability in flow cytometry expression between specimens from same patient, may be due to delayed processing (Am J Clin Pathol 2002;117:615, Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2011;80:83)
- Leukemic cells from infants with newly diagnosed preB leukemia may express CD22 with exon 12 deletion (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010;107:16852)
- Epratuzumab and other anti-CD22 antibodies may have therapeutic value as part of radioimmunotherapy
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (J Clin Oncol 2010;28:3709, Blood 2011;118:4053), including relapsed / resistant hairy cell leukemia (J Clin Oncol 2012;30:1822)
- ALL (Cancer 2013;119:2728, Lancet Oncol 2012;13:403)
- SLE and other autoimmune diseases (Blood 2013;122:3020)
- CD22 may be a component of immunotoxins (Eur J Immunol 2012;42:2792)
- Uses by pathologists:
- Pan B cell marker; helpful for diagnosis of hairy cell leukemia
- Aberrant CD22 expression is useful to detect monoclonal B cells of CLL admixed with benign polyclonal B cells (Am J Clin Pathol 2005;123:826)
- Positive staining - normal: B cells (considered a pan B cell antigen), dendritic cells and basophils
- Positive staining - disease:
- Hairy cell leukemia; also pre B ALL
- Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2009;76:237)
- Staining of other B cell leukemias / lymphomas is variable (Am J Clin Pathol 2002;117:615)
- Negative staining:
- Myeloblasts, plasma cells
- Lung carcinoma (Cancer Res 2014;74:263, Cancer Res 2012;72:5556)
- Reference: OMIM: 107266 [Accessed 7 May 2021]
CD23
- See CD23
CD24
- Glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor protein involved in cell adhesion and tumor metastasis
- Putative cancer stem cell marker
- Also called heat stable antigen homologue (HAS)
- Pathophysiology: small glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor protein with mucin-like adhesion properties; promotes antigen dependent proliferation of B cells and prevents differentiation into plasma cells
- Clinical features:
- Ligand of P selectin on tumor cells that is associated with in vitro invasiveness and metastasis (Tumour Biol 2002;23:139, Cancer Res 2005;65:10783)
- Expressed in many solid tumors, promotes tumor growth,invasion and metastasis and confers resistance to some chemotherapeutic drugs (Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2013;17:1709)
- Marker of disseminated tumor cells in malignant pleural effusions (Int J Cancer 2013;133:2925)
- Breast cancer cells with CD44+ / CD24- phenotype are associated with:
- Stem cell properties (Mod Pathol 2012;25:185)
- Poor prognosis in triple negative (Hum Pathol 2012;43:364)
- Other breast tumors (Oncol Rep 2014;31:1127)
- Cancer stem cells: cells within tumor that possesses the capacity to self-renew and to cause the heterogeneous lineages of cancer cells that comprise the tumor
- Cancer stem cell hypothesis: a small subpopulation of cancer cells drives tumor initiation, growth and metastasis (Oncol Rep 2014;31:1127)
- Alleles / polymorphisms associated with autoimmune disease risk / progression, including:
- Inflammatory bowel disease (Int J Biol Markers 2014;29:e62)
- Multiple sclerosis (Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003;100:15041, Am J Transl Res 2012;4:347)
- CD24 polymorphism may serve as poor prognostic marker in esophageal cancer (Int J Biol Markers 2014;29:49)
- Uses by pathologists:
- Strong expression is a poor prognostic factor in carcinomas of:
- Bile duct (Cancer Lett 2006;235:34)
- Bladder (Oncol Lett 2013;6:96)
- Breast (with CD44) (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2012;133:979, PLoS One 2012;7:e43110)
- Colorectum (Clin Cancer Res 2005;11:6574)
- Gallbladder (Med Oncol 2012;29:1879)
- Liver (Clin Cancer Res 2009;15:5518)
- Lung: nonsmall (Br J Cancer 2003;88:231)
- Ovary (Am J Pathol 2002;161:1215)
- Pancreas (Pancreas 2014;43:380)
- Poor prognostic marker in glioma, osteosarcoma (J Biomed Biotechnol 2012;2012:517172, Clin Transl Oncol 2013;15:541)
- Strong expression is a poor prognostic factor in carcinomas of:
- Positive staining - normal:
- All B cells, granulocytes
- Also apocrine sweat glands, epithelial cells, fallopian tube, kidney cells, muscle, nucleus pulposus of intervertebral discs and some neurons (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006;103:6374)
- Positive staining - disease:
- Apocrine metaplasia of breast, exosomes (membrane vesicles 40 - 100 nm released by different cell types from a late endosomal cellular compartment) (Mol Oncol 2009;3:220, J Transl Med 2011;9:86)
- Most pre-B-ALL / lymphoblastic lymphoma, virtually all B cell lymphomas
- Breast cancer: ductal type has cytoplasmic expression, invasive micropapillary has strong expression with typical inverted apical membrane pattern (Breast 2012;21:165)
- Chordoma (Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005;338:1890)
- Various solid carcinomas (Pathol Res Pract 2005;201:479)
- Biliary tract dysplasia / carcinoma (Hum Pathol 2010;41:1558)
- Lung cancer (J Clin Pathol 2013;66:256)
- Pancreatic ductal carcinoma and IPMN (Hum Pathol 2010;41:1466)
- Pleomorphic adenoma (salivary gland) (Histopathology 2013;62:1075)
- Wilm tumor (Hum Pathol 1990;21:536)
- Negative staining: plasma cells, T cells, monocytes, mast cells, red blood cells, platelets; also ovarian epithelium, multiple myeloma and chondrosarcoma
- Reference: OMIM: 600074 [Accessed 7 May 2021]
CD25
- Marker for hairy cell leukemia and systemic mastocytosis
- Also called IL-2 receptor alpha chain, IL2RA and TAC antigen (OMIM: 147730 [Accessed 7 May 2021])
- Pathophysiology:
- Exists in at least 3 forms: a high affinity dimer, an intermediate affinity monomer (beta subunit) and a low affinity monomer (alpha subunit)
- Considered an activation antigen (also CD30)
- CD4+ CD25+ cells are regulatory T cells (Treg) that (Cancer Res 2012;72:2162):
- Suppress the activation of self reactive T cells and prevent autoimmunity
- May prevent cytotoxic T cells from killing tumor cells (J Hepatol 2006;45:254, Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2006;14:119)
- CD4+ CD25+ cells also suppress NK cells (Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006;103;5460, J Immunol 2006;176:1582)
- May act directly on B cells (Blood 2006;107:3925)
- Clinical features:
- High levels of Treg by flow cytometry are associated with advanced stage in esophageal and gastric cancer (Cancer Immunol Immunother 2006;55:1064, Oncol Lett 2012;4:755)
- CD25 expression in advanced cutaneous T cell lymphoma associated with response to denileukin diftitox therapy, a recombinant fusion protein of diphtheria toxin and IL-2, which binds to CD25 (J Invest Dermatol 2006;126:575, Leuk Lymphoma 2013;54:69)
- Uses by pathologists:
- Marker for hairy cell leukemia but CD103 and CD123 may be more useful (Am J Clin Pathol 2011;136:625)
- Loss of CD25 distinguishes hairy cell leukemia from variant hairy cell leukemia or other disorders (Am J Clin Pathol 2009;131:586)
- Diagnose systemic mastocytosis (Mod Pathol 2012;25:516)
- Also specific in GI mucosal mast cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:1669)
- CD25+ cutaneous mast cells in urticaria pigmentosa may predict subsequent systemic mastocytosis (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:139)
- Part of diagnostic criteria for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis is soluble CD25 / IL2 receptor ≥ 2,400 U/ml (Pediatr Blood Cancer 2007;48:124)
- Marker for hairy cell leukemia but CD103 and CD123 may be more useful (Am J Clin Pathol 2011;136:625)
- Positive staining - normal: activated B and T cells, macrophages, osteoblasts; some thymocytes, some myeloid precursors and some oligodendocytes; basophils have dim staining by flow cytometry (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2008;132:813)
- Positive staining - disease:
- Hairy cell leukemia (most, Am J Clin Path 2006;125:251)
- Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (Am J Clin Path 2003;119:205)
- Most B cell neoplasms, adult T cell leukemia / lymphoma (Am J Clin Pathol 2010;133:592)
- Reed-Sternberg-like cells in peripheral T cell lymphoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:1513)
- Hodgkin lymphoma (most), some AML
- Systemic mastocytosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:832)
- Acquired ocular toxoplasmosis (Arq Bras Oftalmol 2010;73:443)
- Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis (Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:482)
- Neuroblastoma
- Negative staining:
- Nonneoplastic mast cells (Am J Clin Path 2004;122:560)
- Marginal zone B cell lymphoma (Am J Clin Path 1996;105:277)
- T cell large granular leukemia / lymphoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:935)
- Often / usually variant hairy cell leukemia (Am J Clin Path 2005;123:132)
CD26
- Widely expressive dipeptidase with various clinical features (see below)
- Also called dipeptidyl-peptidase IV, DPP4, DDPIV, adenosine deaminase complexing protein 2 (OMIM: 102720 [Accessed 7 May 2021])
- Pathophysiology:
- Costimulatory molecule in T cell activation and proliferation
- Also regulates various chemokines and cytokines
- Cleaves amino-terminal dipeptides
- Key role in cell adhesion and invasion, plays a role in cell spreading and migration (BMC Cancer 2013;13:517)
- Either soluble in plasma or present on cell surface
- Clinical features:
- Acute kidney transplant rejection: associated with increased serum CD26 and CD26 inhibition reduces acute and accelerated rejection (Adv Exp Med Biol 2003;524:133)
- Colorectal carcinoma: marker of poor prognosis (PLoS One 2014;9:e98582, PLoS One 2014;9:e107470)
- Endometrial carcinoma: reduced expression (Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;188:670)
- HIV infection: may have protective role (Virol J 2010;7:343)
- Lung: soluble CD26 in serum/pleural fluid may distinguish pleural mesothelioma (lower values) from pulmonary adenocarcinoma (PLoS One 2014;9:e115647)
- Lung: may function as tumor suppressor in non small cell lung carcinoma (Int J Cancer 2004;109:855)
- Lymphoma, T cell: absence of CD26 staining on peripheral blood CD4+ T cells by flow cytometry may be useful for diagnosis (Am J Clin Pathol 2001;115:885, Am J Clin Pathol 2008;129:146)
- Pregnancy: blastocyst implantation may occur by binding of endometrial CD26 to embryonal fibronectin (Mol Hum Reprod 2006;12:491)
- Prostate cancer: possible poor prognostic marker (J Res Med Sci 2013;18:647)
- Thyroid carcinoma: increased expression (Diagn Cytopathol 2002;26:366, Am J Clin Pathol 1991;96:306)
- In initial study, CD26high T cells elicit tumor immunity against multiple malignancies via enhanced migration and persistence (Nat Commun 2017;8:1961)
- No significant uses by pathologists
- Positive staining - normal:
- Activated T and B cells, basophils, macrophages, NK cells, thymocytes (mature)
- Epithelium: endometrium, hepatocytes, lung, prostate, renal proximal tubular cells, small intestine
- Also cytotrophoblast and extravillous trophoblast (J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002;87:4287)
- Biliary canaliculae, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, mesothelial cells (Oncology 2002;63:158)
- Splenic sinus lining cells
- Positive staining - disease:
- Esophageal adenocarcinoma and Barrett's metaplasia (Hum Pathol 1999;30:1291)
- Prostate carcinoma, thyroid anaplastic carcinoma (reduced expression in undifferentiated versus differentiated areas (Am J Clin Pathol 2006;125:399)
- Wilm's tumor (Hum Pathol 1990;21:536)
- Negative staining: normal thyroid gland, T cells in peripheral blood of mycosis fungoides / cutaneous T cell lymphoma (40%) (BMC Clin Pathol 2002;2:5)
CD27
- See CD27
CD28
- Receptor important in CD4+ T cell activation, IL2 production and T helper 2 development (OMIM #186760)
- Plays a critical role in controlling the adaptive arm of the immune response (Blood 2005;105:13)
- Pathophysiology:
- T cells require 2 signals for full activation: (1) binding of the antigen / MHC complex on the antigen presenting cell to the T cell receptor; (2) interaction of CD28 with its ligands CD80 (B7-1) or CD86 (B7-2), found on activated B cells and called a costimulation signal
- Costimulatory signal induces T cell activation and survival, interleukin 2 production, T helper type 2 development and clonal expansion
- CD28 is a constitutive, high abundance, low affinity receptor; its binding also increases expression of CTLA4 (CD152), a structurally related cell surface receptor on T cells which competes with CD28 for the same ligands but has opposite effects (J Clin Immunol 2002;22:1, Curr Pharm Des 2006;12:149)
- CD8+, CD28+ T cells are antigen specific cytotoxic T cells (class I restricted) and constitute 90% of CD8+ T cells
- CD8+, CD28- T cells are suppressor T cells; loss of CD28 expression in T cells is associated with various infectious and autoimmune diseases and aging:
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis (Gastroenterology 2014;147:221)
- Hashimoto thyroiditis (BMC Endocr Disord 2013;13:34)
- Chronic hepatitis B virus infection (Biomed Rep 2014;2:270)
- Chronic bone infection (Clin Exp Immunol 2014;176:49)
- Unexplained spontaneous abortion and unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion (Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2006;93:123)
- Aging; the frequency of CD28(null) T cells predicts immune incompetence in elderly; these T cells are functionally active and long lived but have no / limited proliferative capacity (Trends Immunol 2009;30:306)
- Clinical features:
- Contributes to genetic susceptibility to type 1 diabetes (Gene 2014;533:420)
- CD4+ CD28(null) cells are an independent predictor of mortality in heart failure (Atherosclerosis 2013;230:414)
- No significant clinical use by pathologists
- Positive staining - normal: CD4+ T cells (95%), CD8+ T cells (50%); activated B cells, thymocytes and plasma cells (some)
- Positive staining - disease: myeloma (95%) (Blood 2014;123:3770)
CD29
- Integrin component that mediates adhesion and is involved in homing to sites of inflammation
- Also called glycoprotein IIa (GP IIa), integrin beta-1 (ITGB1), fibronectin receptor beta subunit, VLA (CD49) beta chain
- Pathophysiology:
- Common beta subunit of integrins VLA1 to VLA6, which are also composed of alpha subunits alpha 1 to alpha 6 (CD49a - f)
- Combines with CD49a to form a receptor for collagen and laminin; this receptor may also be involved in cell to cell adhesion and play a role in inflammation and fibrosis
- Involved in lymphocyte and endothelial adhesion; important for lymphocyte trafficking and transvascular migration
- Promotes or inhibits apoptosis, depending on the ligands and apoptotic insults (Cancer Res 2003;63:8302)
- May help define neural lineage differentiation of stem cells (Stem Cells 2009;27:2928)
- Uses by pathologists: myoepithelial marker, although established markers (SMA, CD10, p63, S100, maspin, calponin, GFAP, smooth muscle myosin) are more commonly used
- Positive staining - normal: fibroblasts, platelets, T cells, monocytes, granulocytes (low), mast cells, endothelial cells and myoepithelium; also other diverse cell types
- Positive staining - disease:
- Bile duct epithelium in alcoholic liver disease (16%) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1999;123:411)
- Breast metaplastic carcinoma (90%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:347)
- Breast sarcoma NOS if CD10+ (43%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:450)
- Liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 2010;18:353)
- Lung cancer (PLoS One 2013;8:e55714)
- Myeloma in bone marrow (Br J Haematol 2002;119:70)
- T cells in asthma (Pol Arch Med Wewn 2012;122:585)
- Trophoblasts in malignant gestational trophoblastic disease (Int J Gynecol Cancer 2013;23:749)
- Negative staining:
- Red blood cells, spermatogonia (Syst Biol Reprod Med 2013;59:233)
- Intravascular lymphomatosis (Hum Pathol 2000;31:220)
- References: OMIM: 135630 [Accessed 7 May 2021], Wikipedia: CD29, Cell Biochem Biophys 2014;70:601
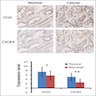
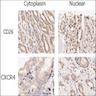
Diagrams / tables
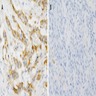
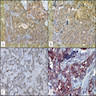
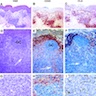
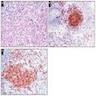
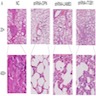
Microscopic (histologic) images
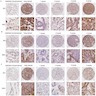
Images hosted on other servers: