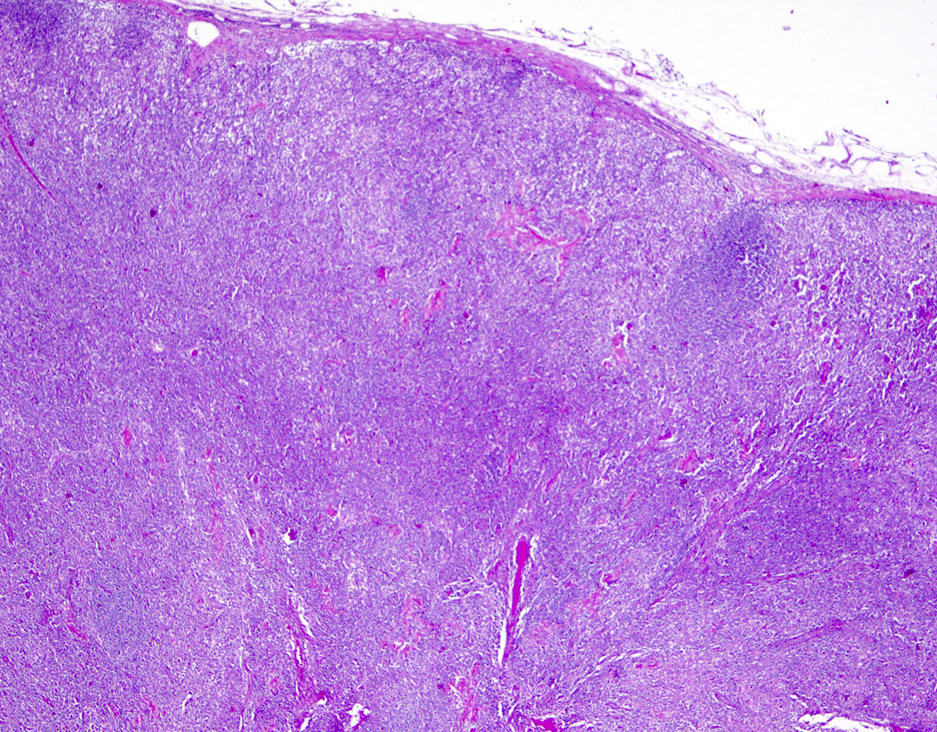
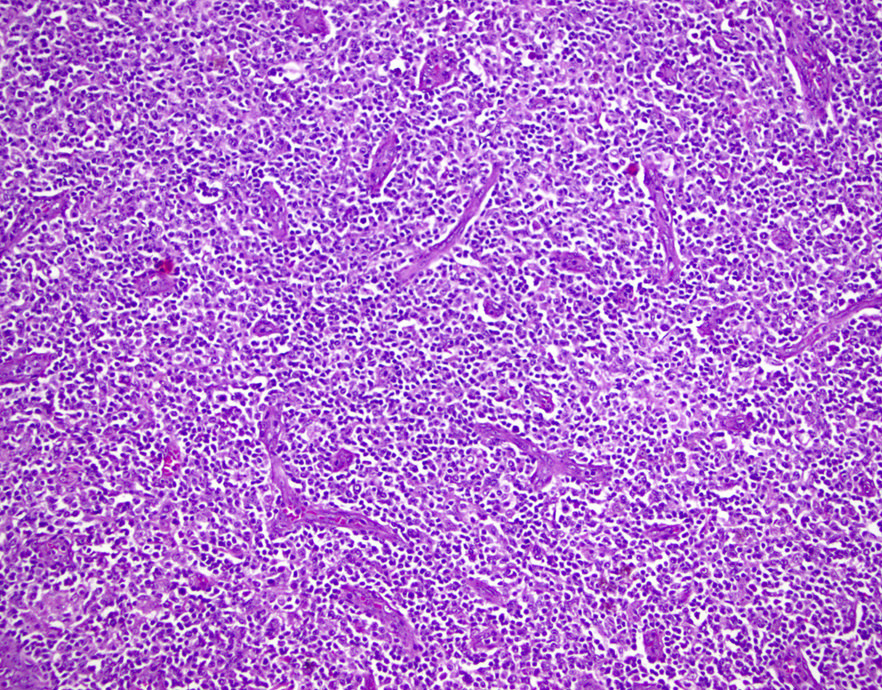
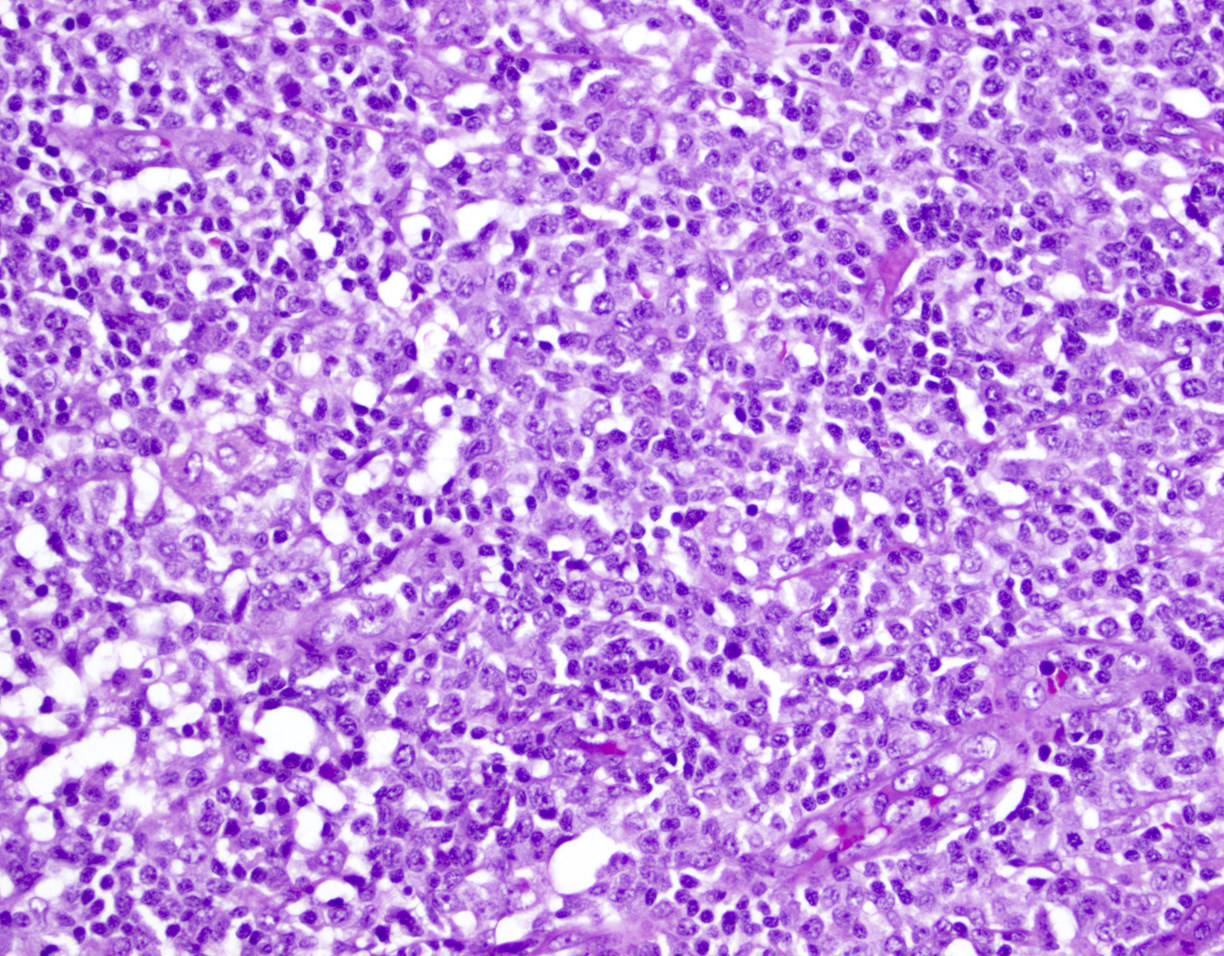
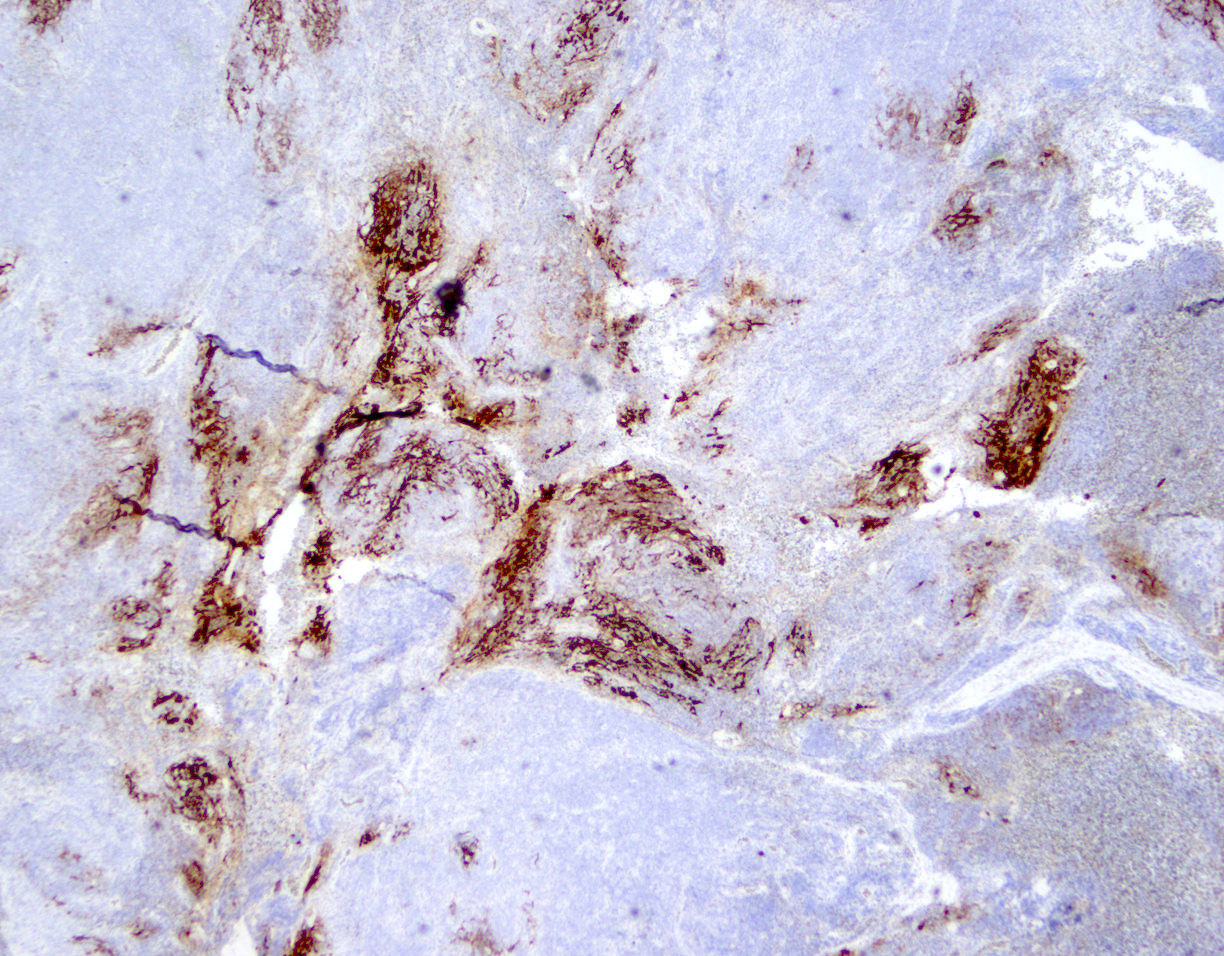
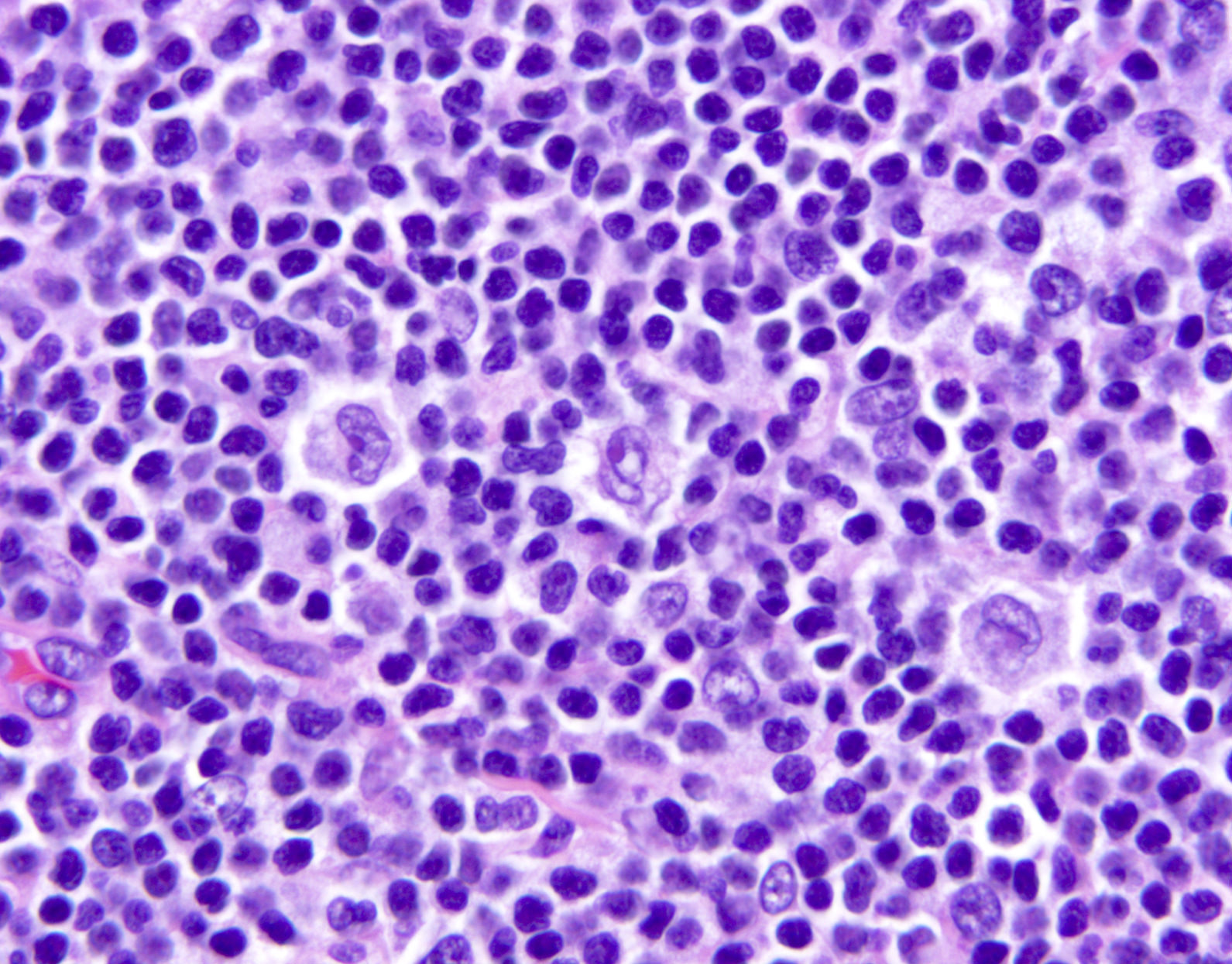
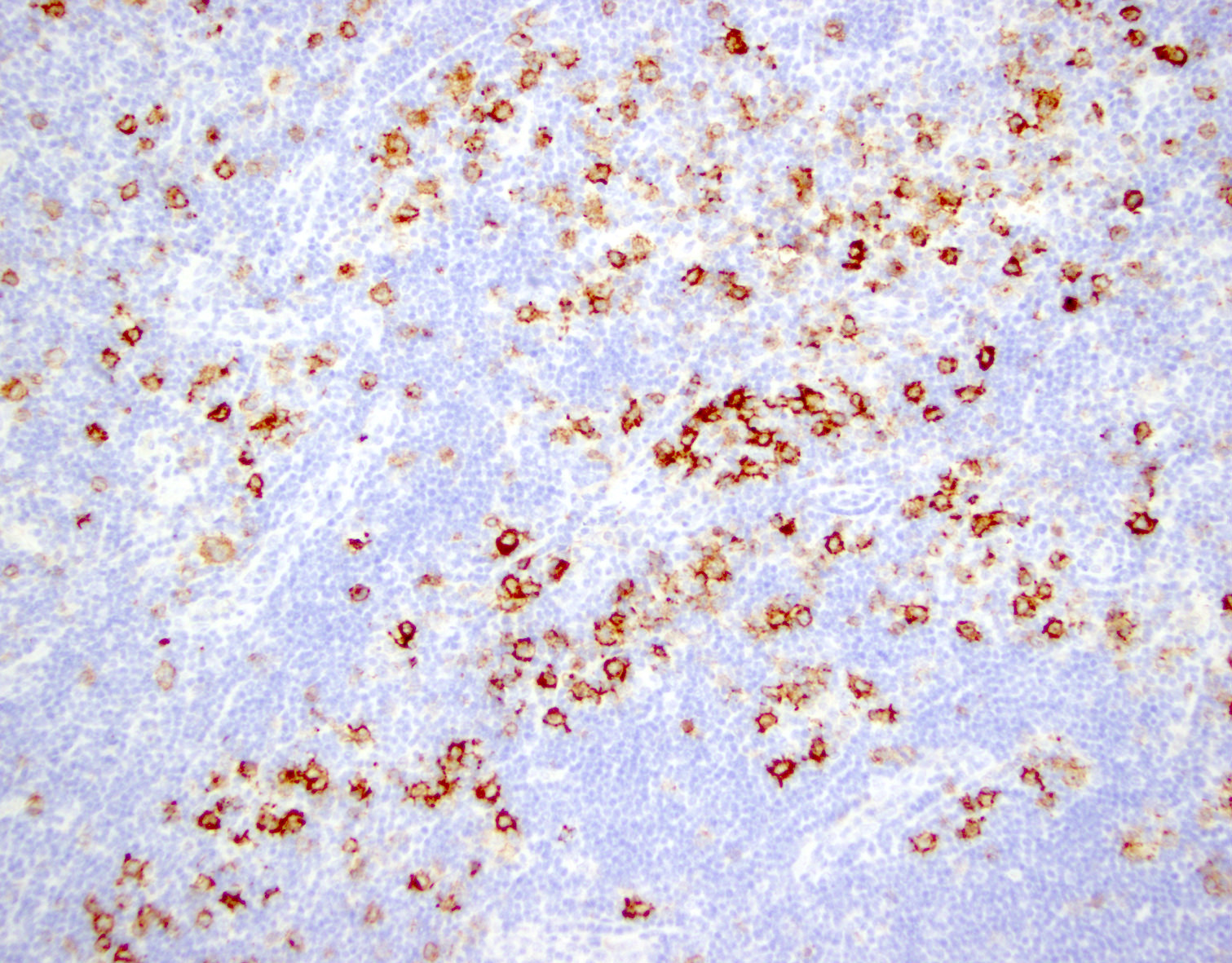
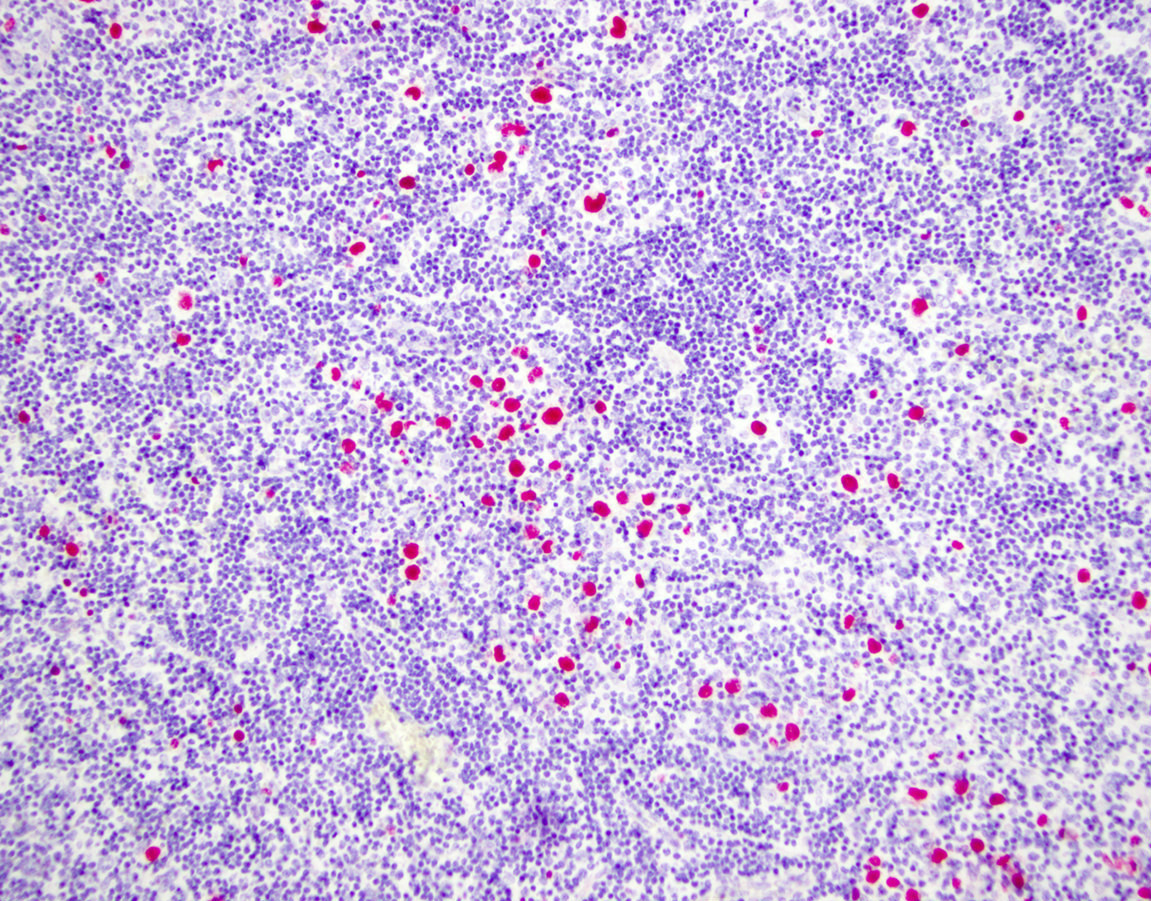
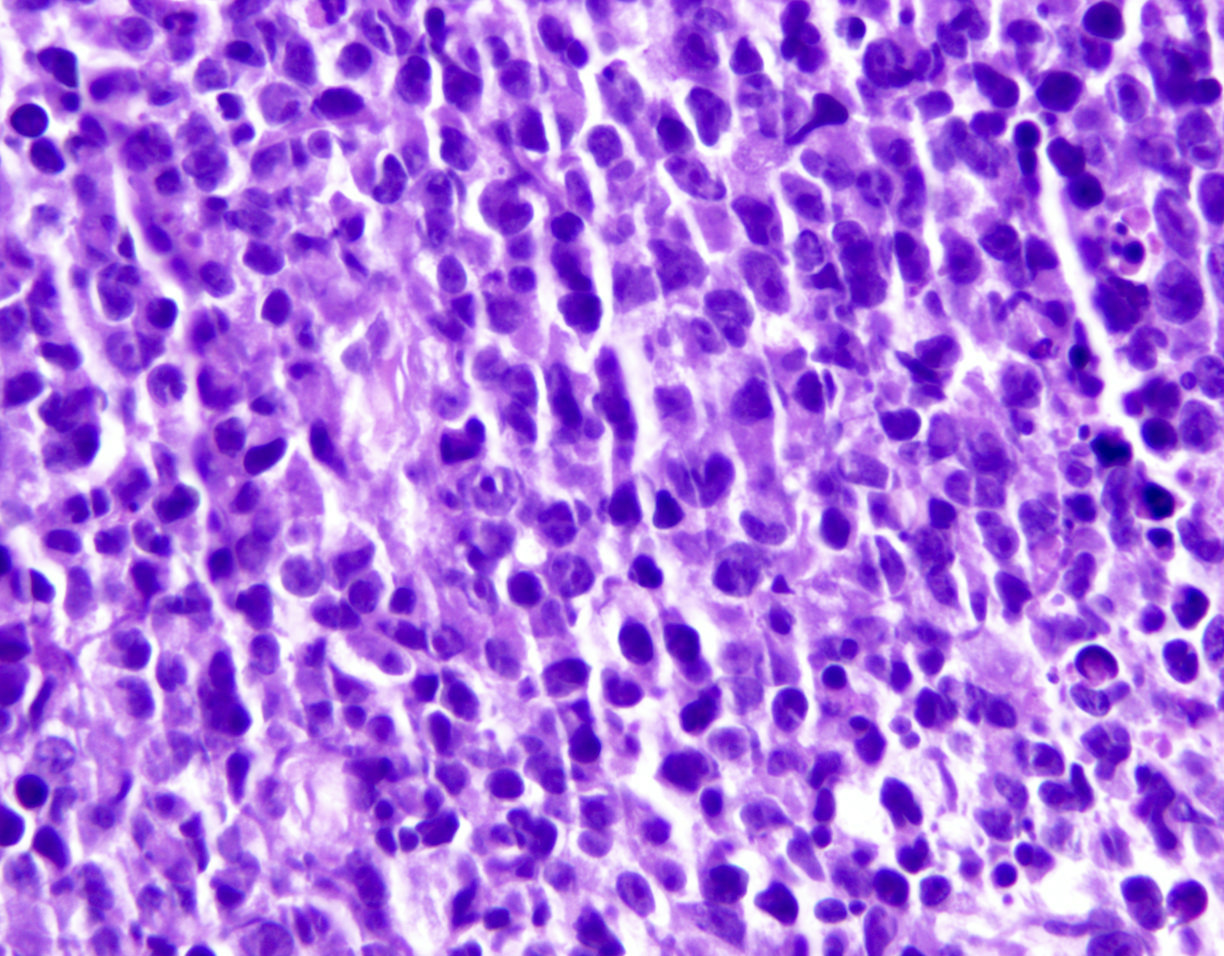
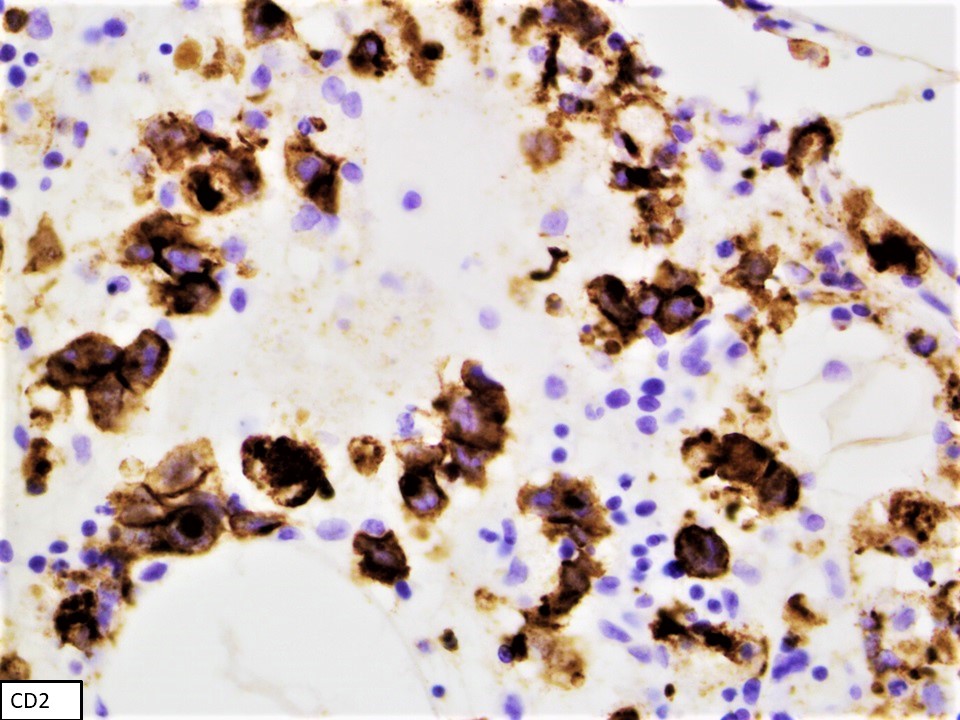
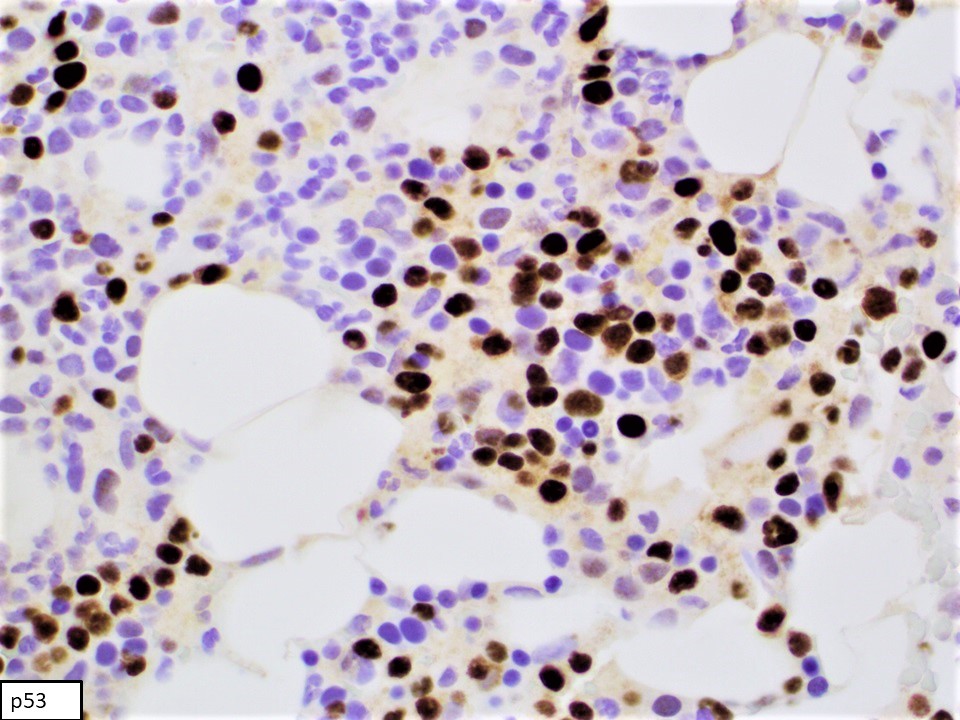
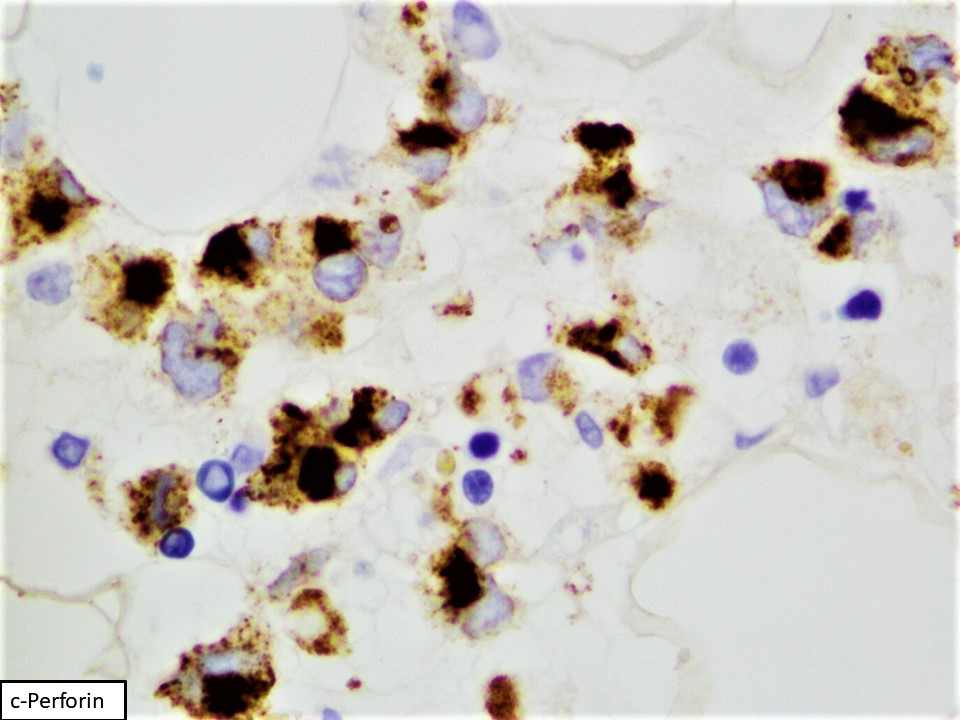
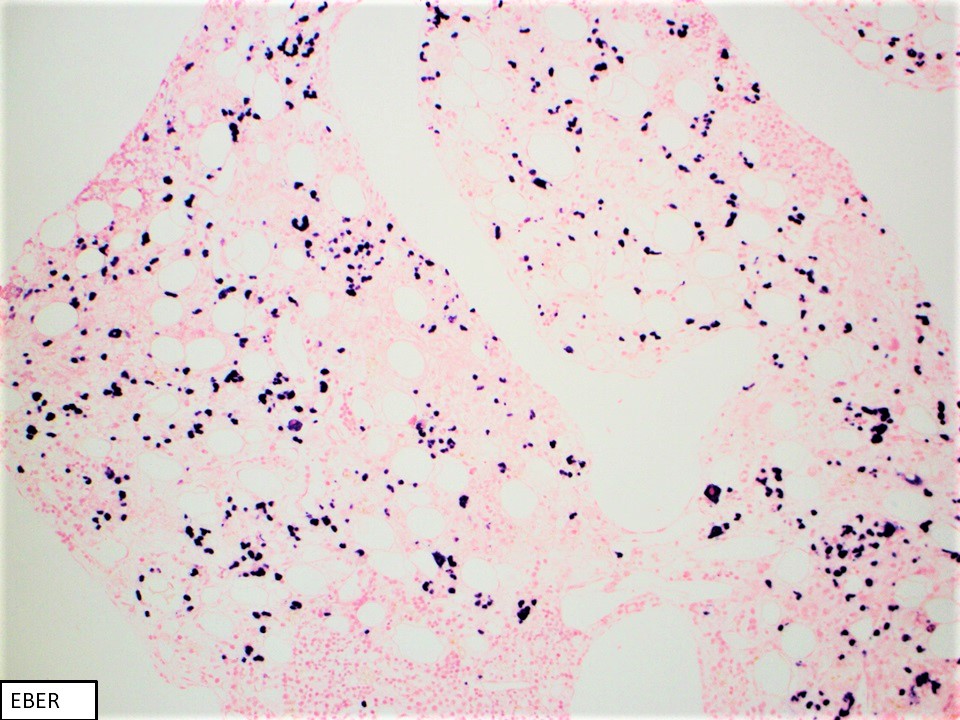
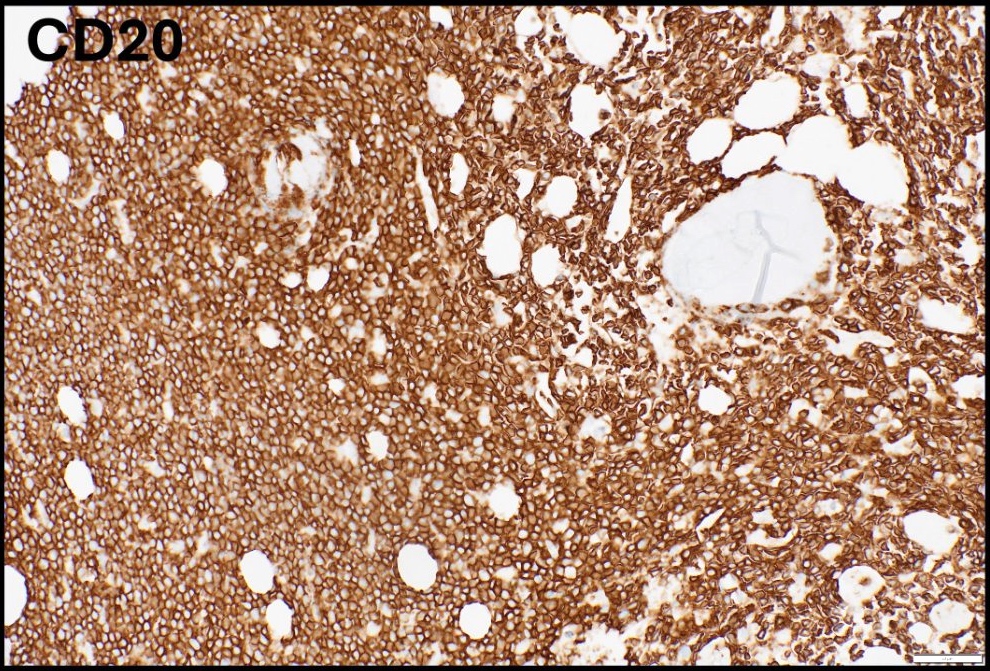
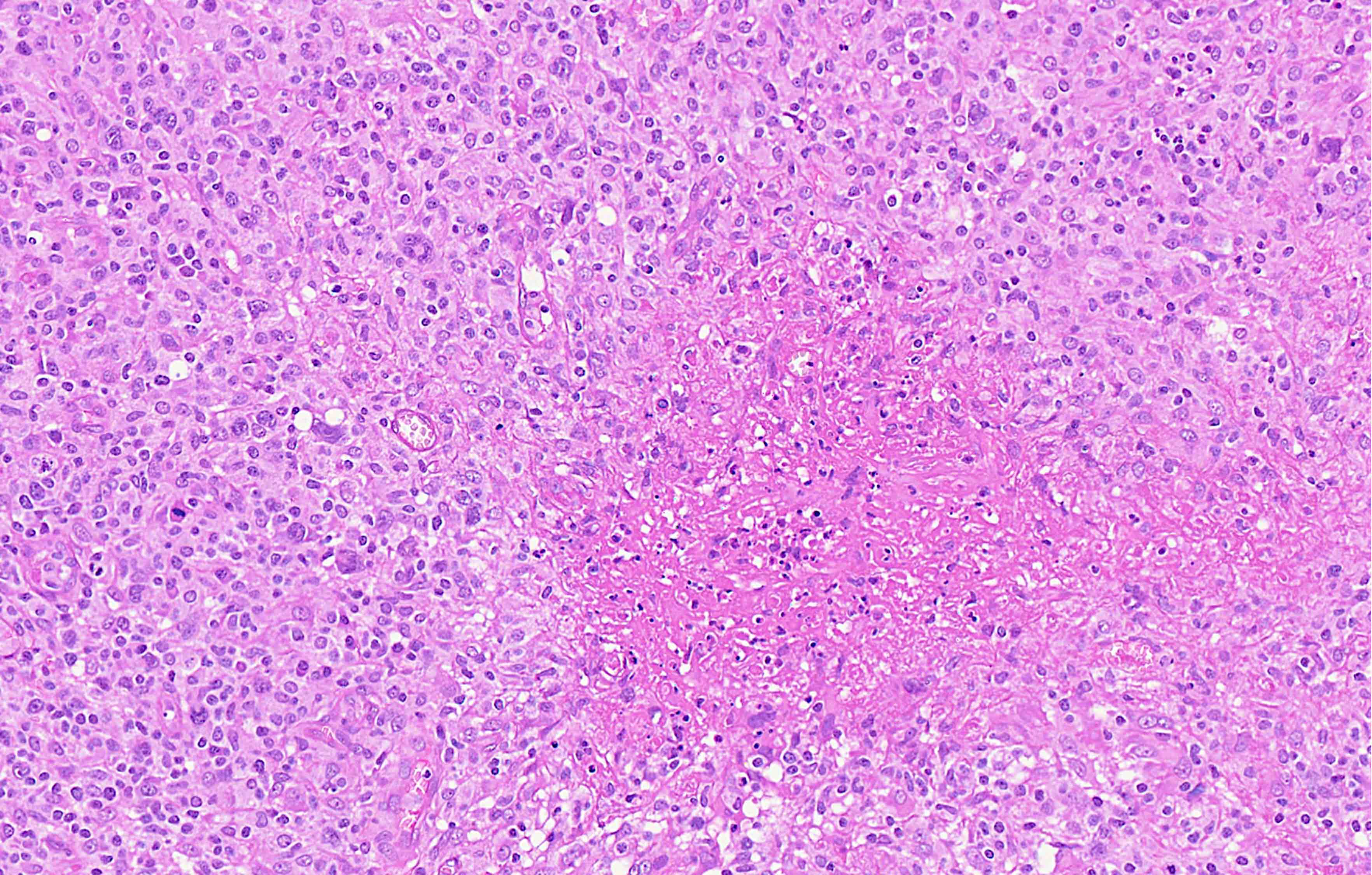
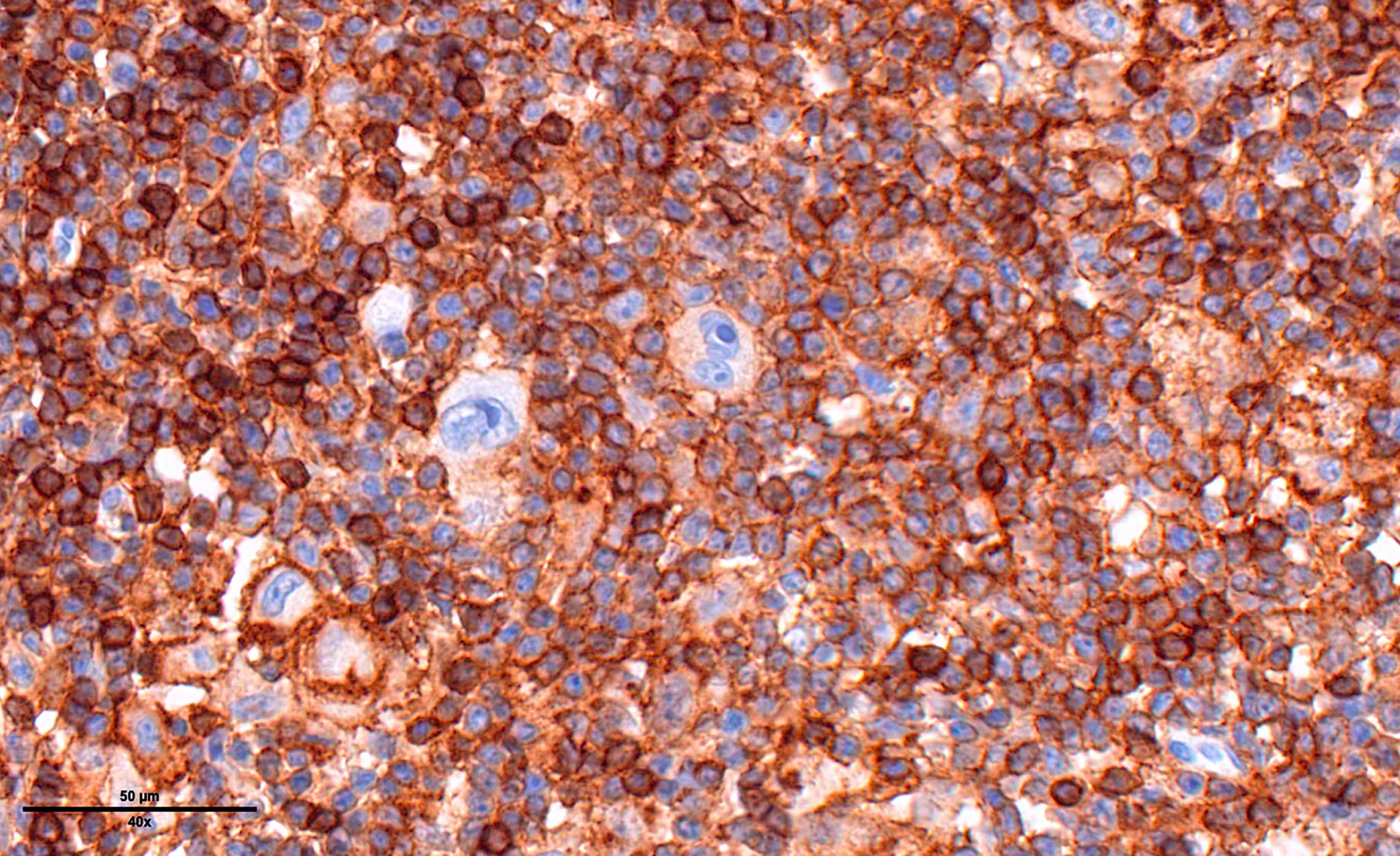
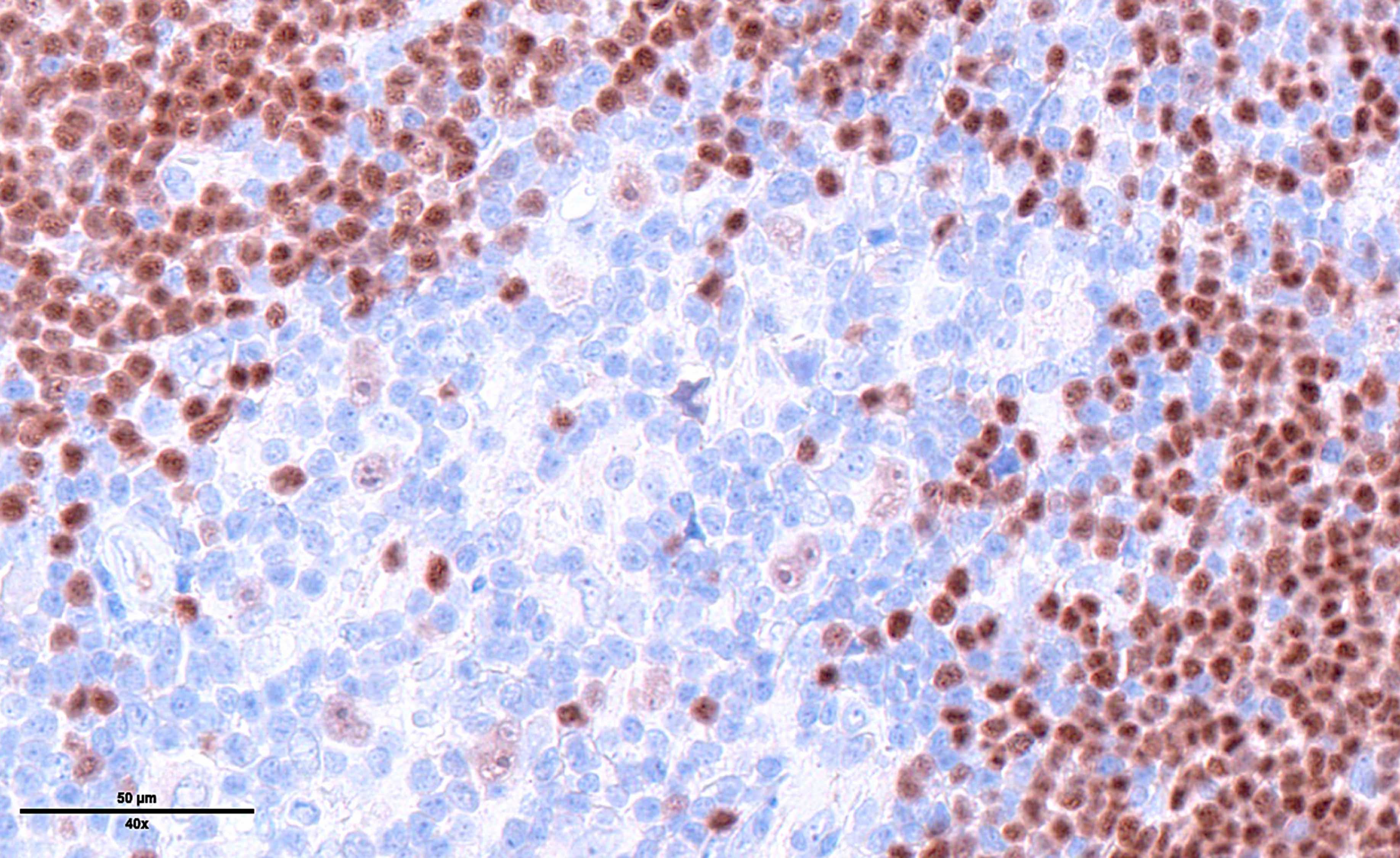
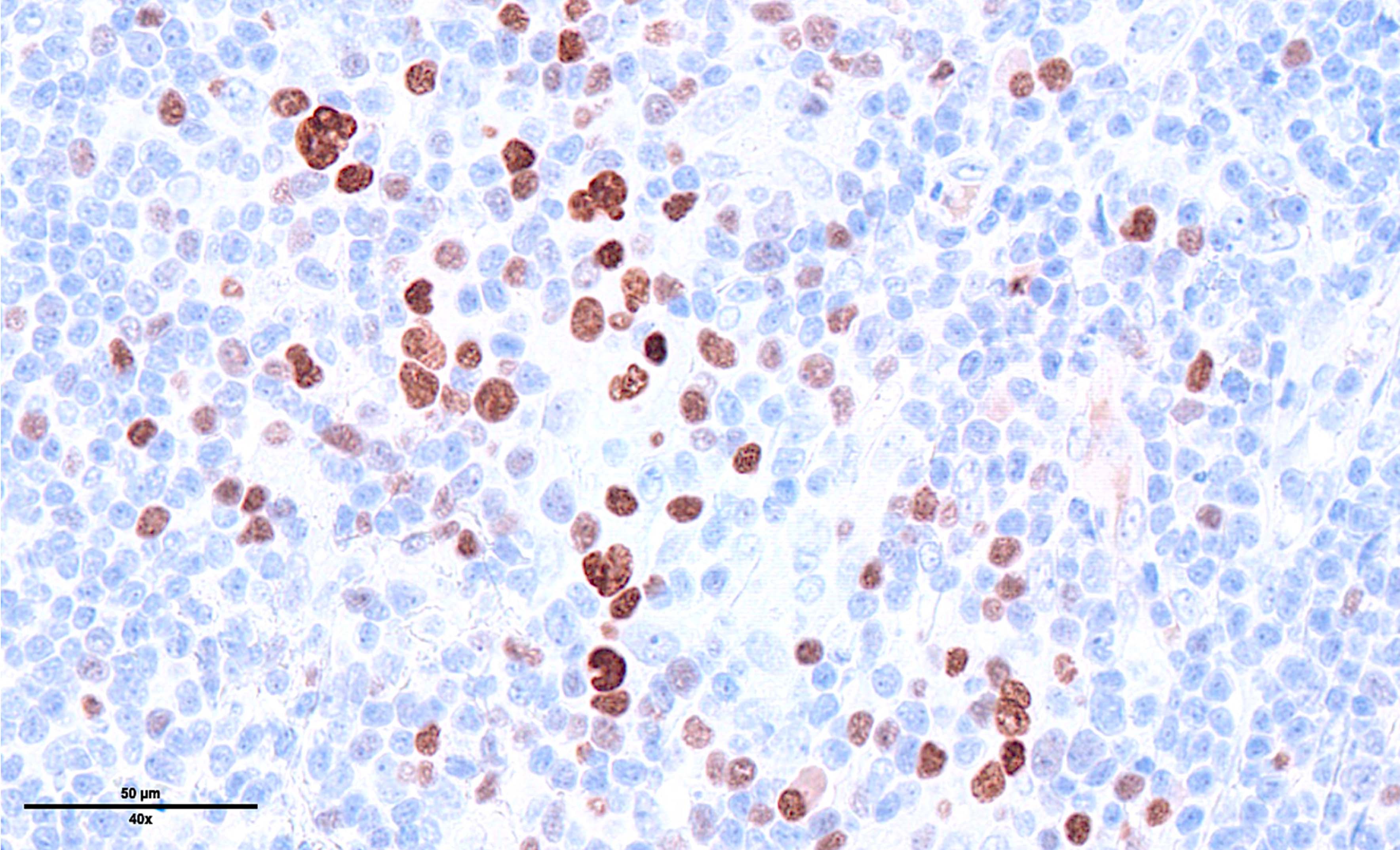
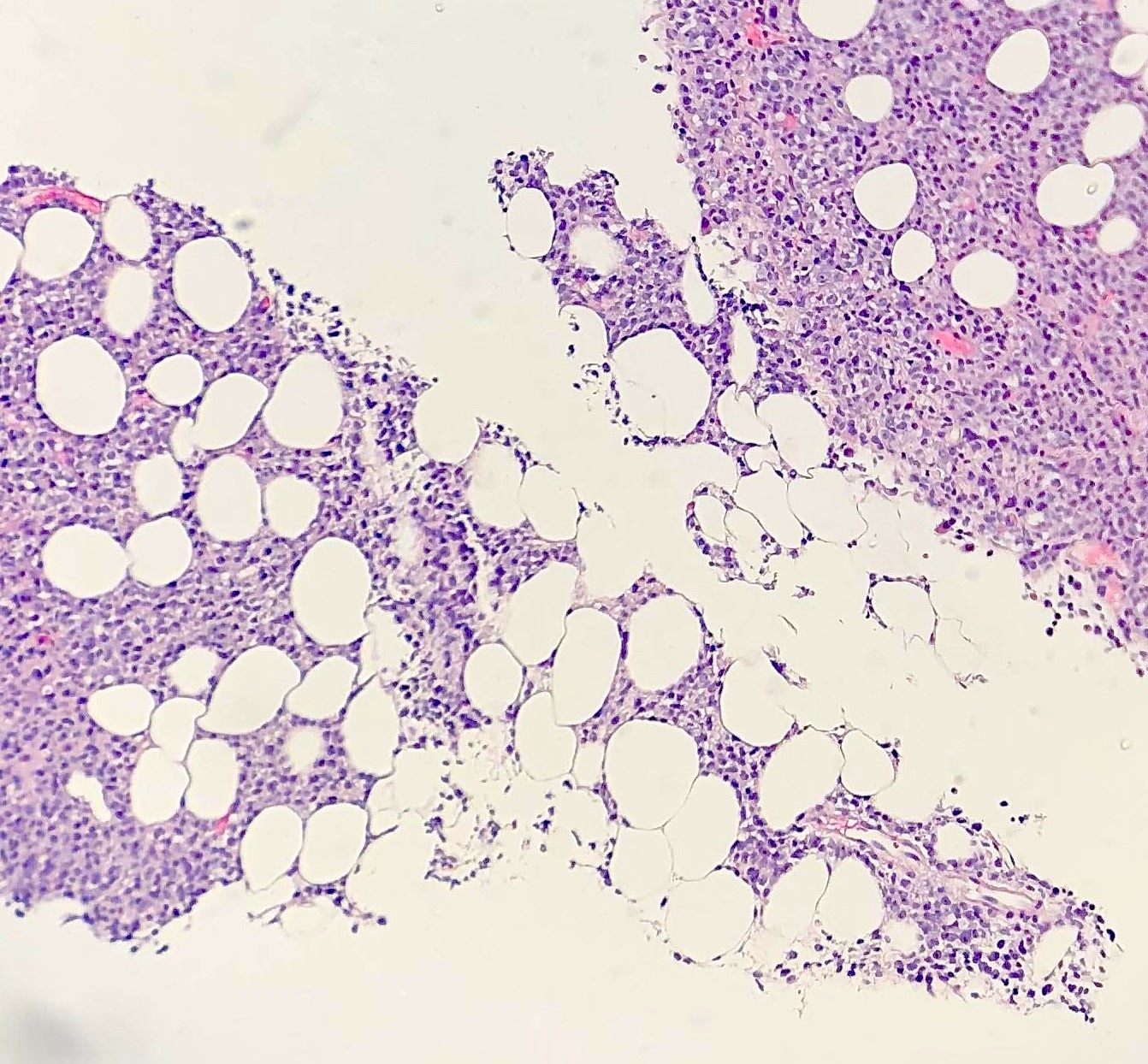
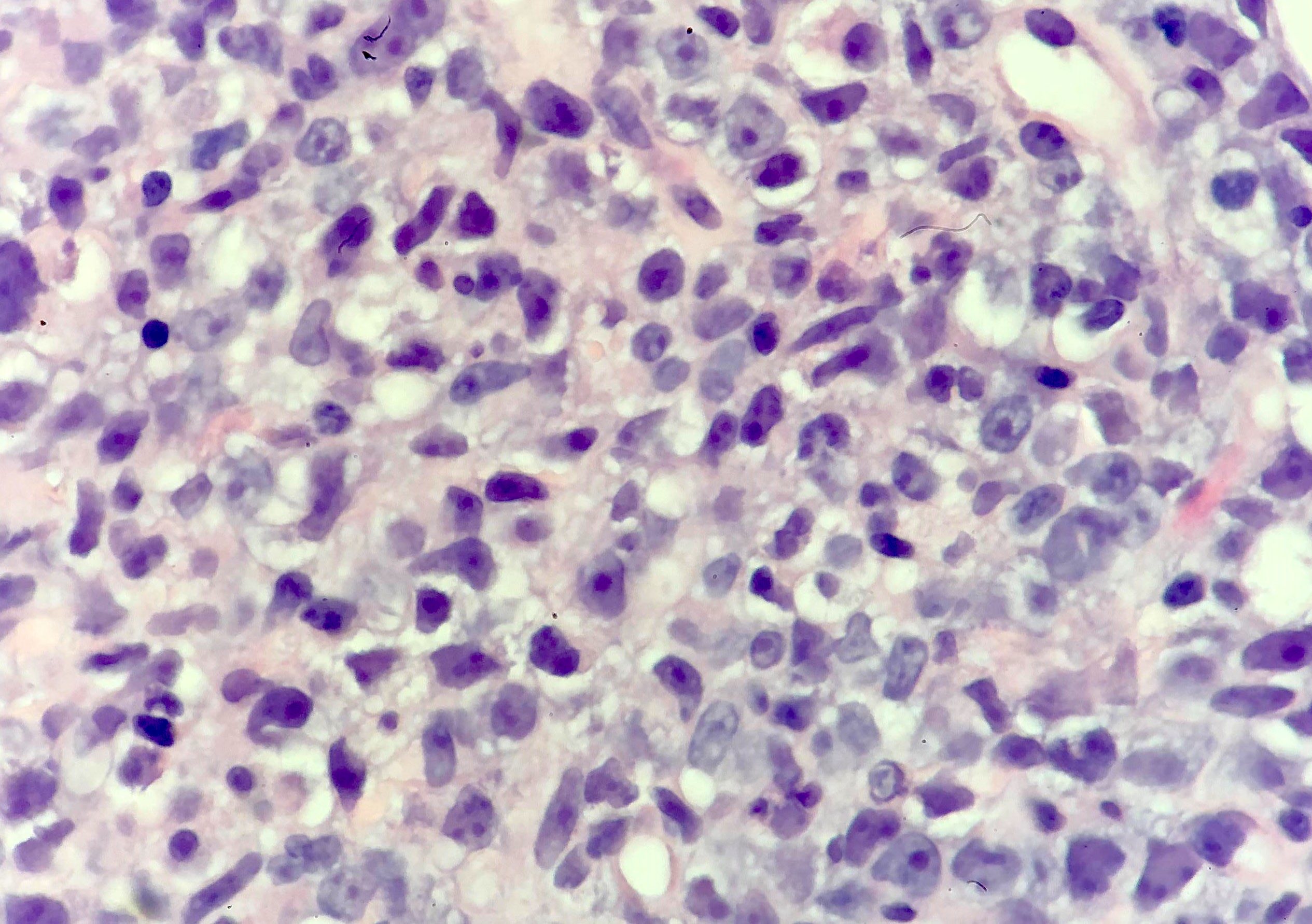
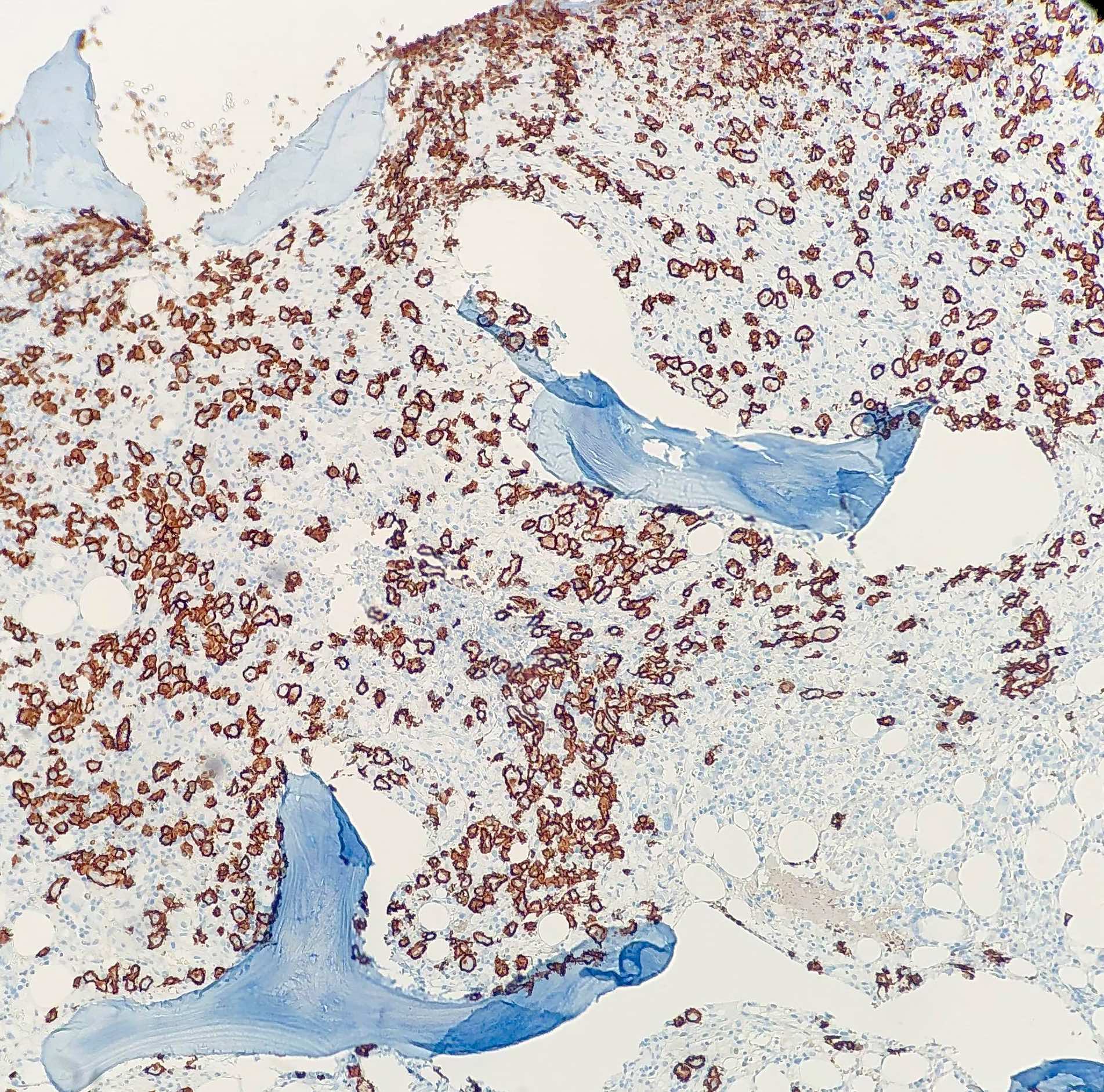
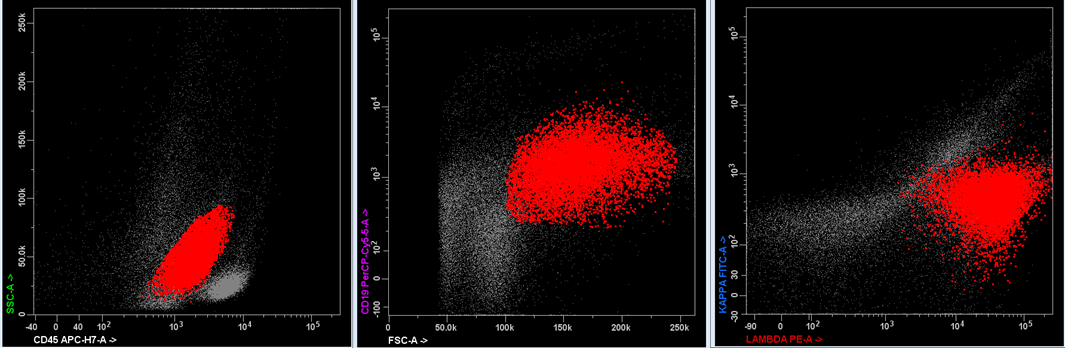
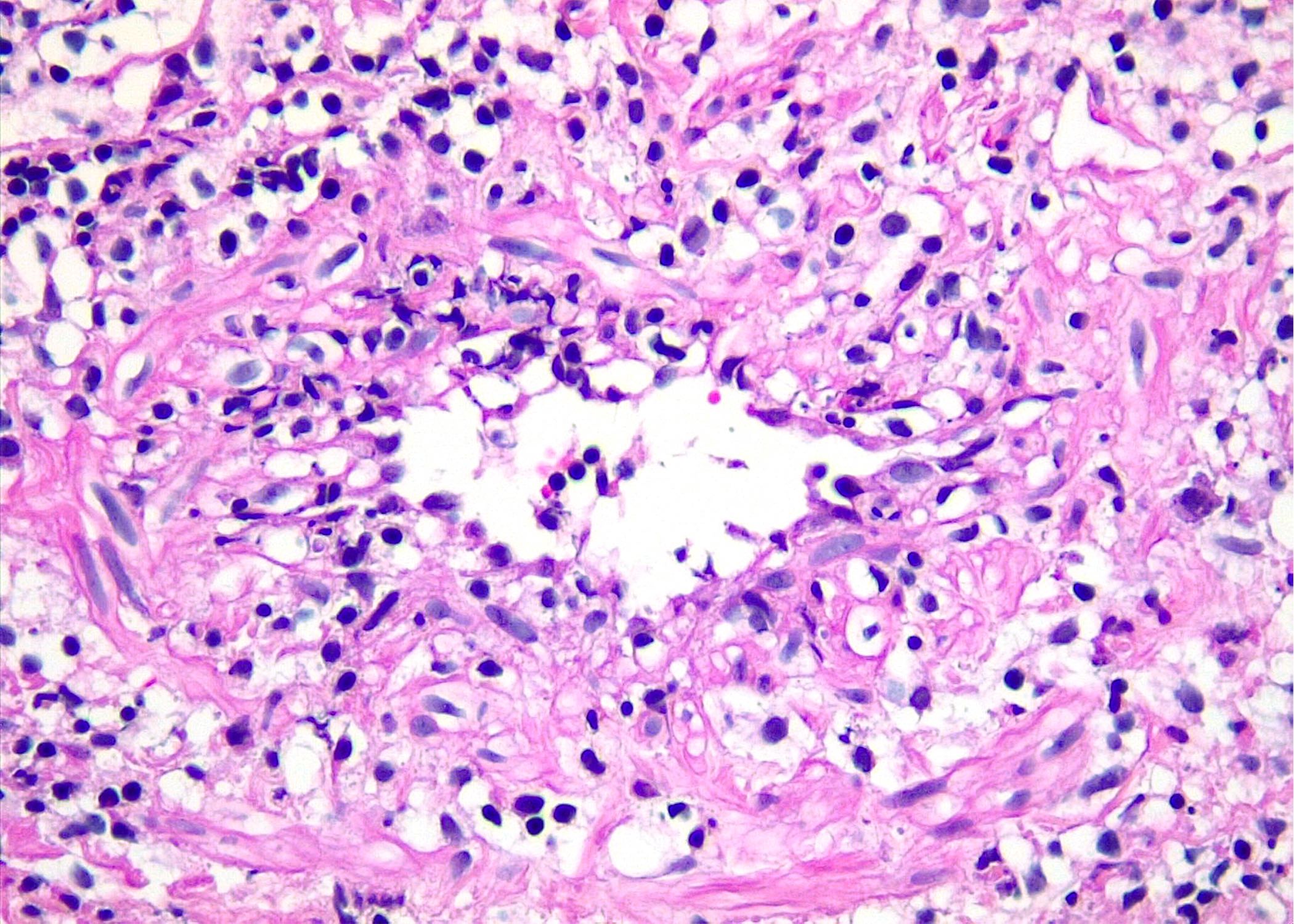
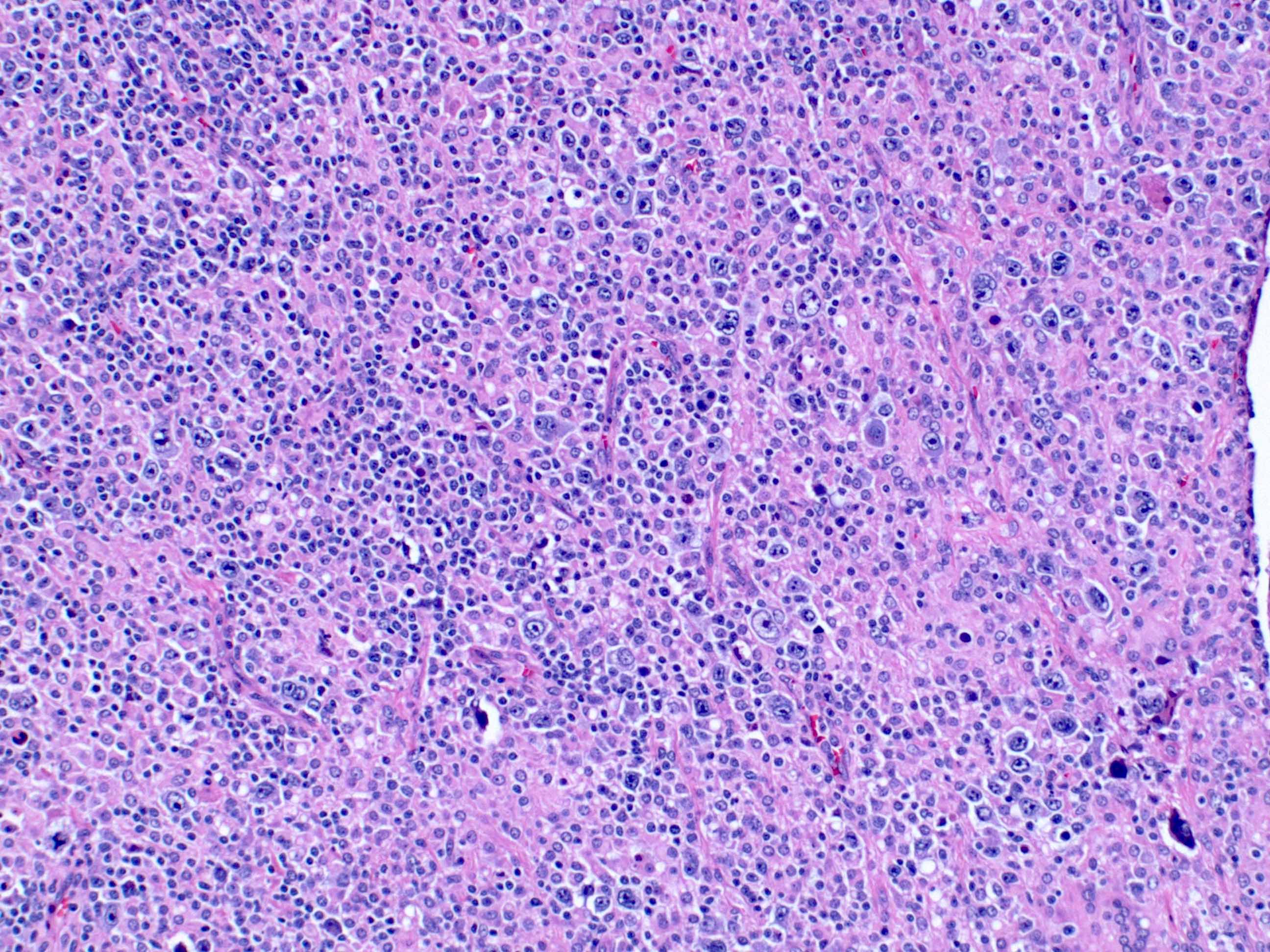
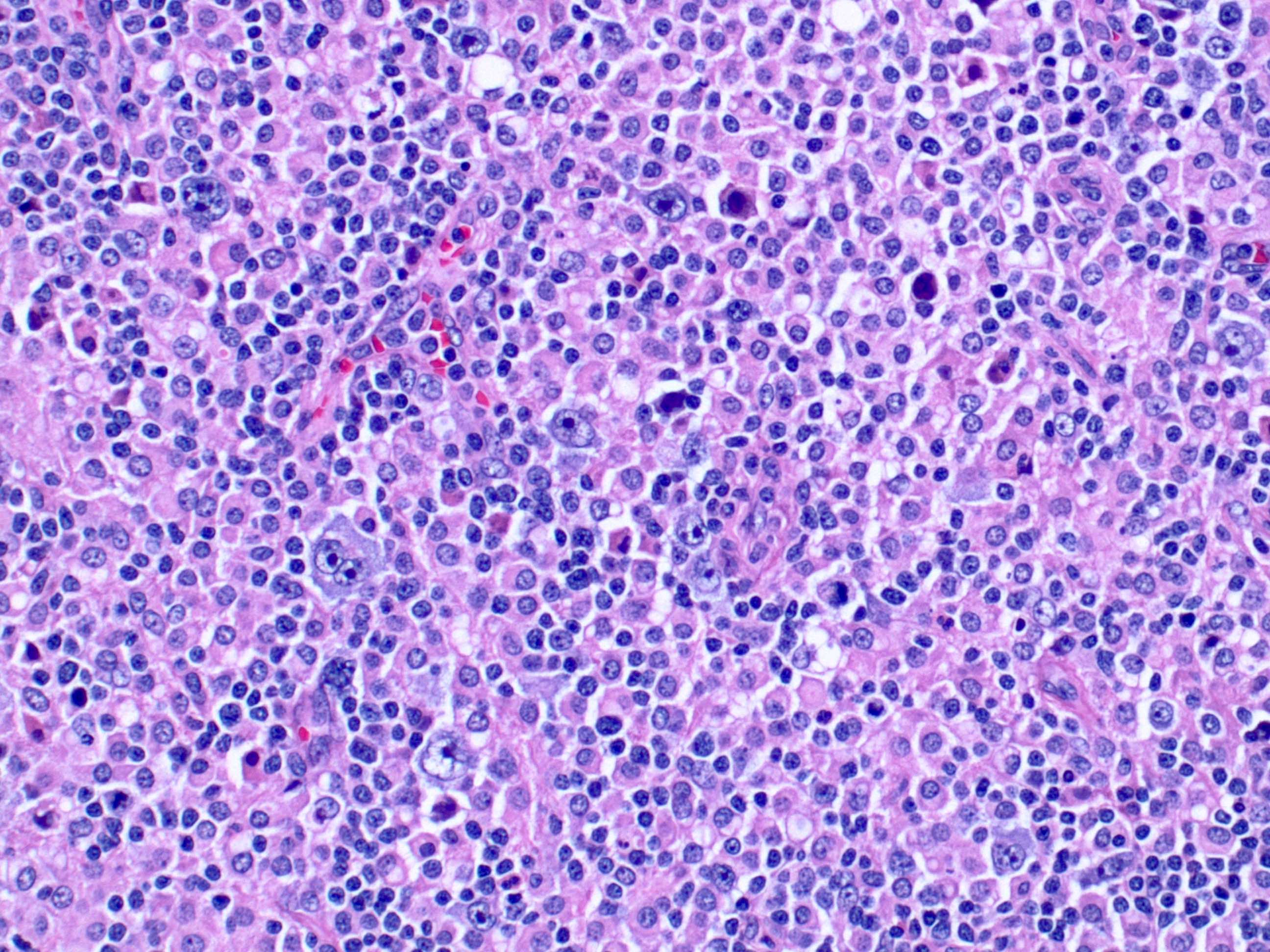
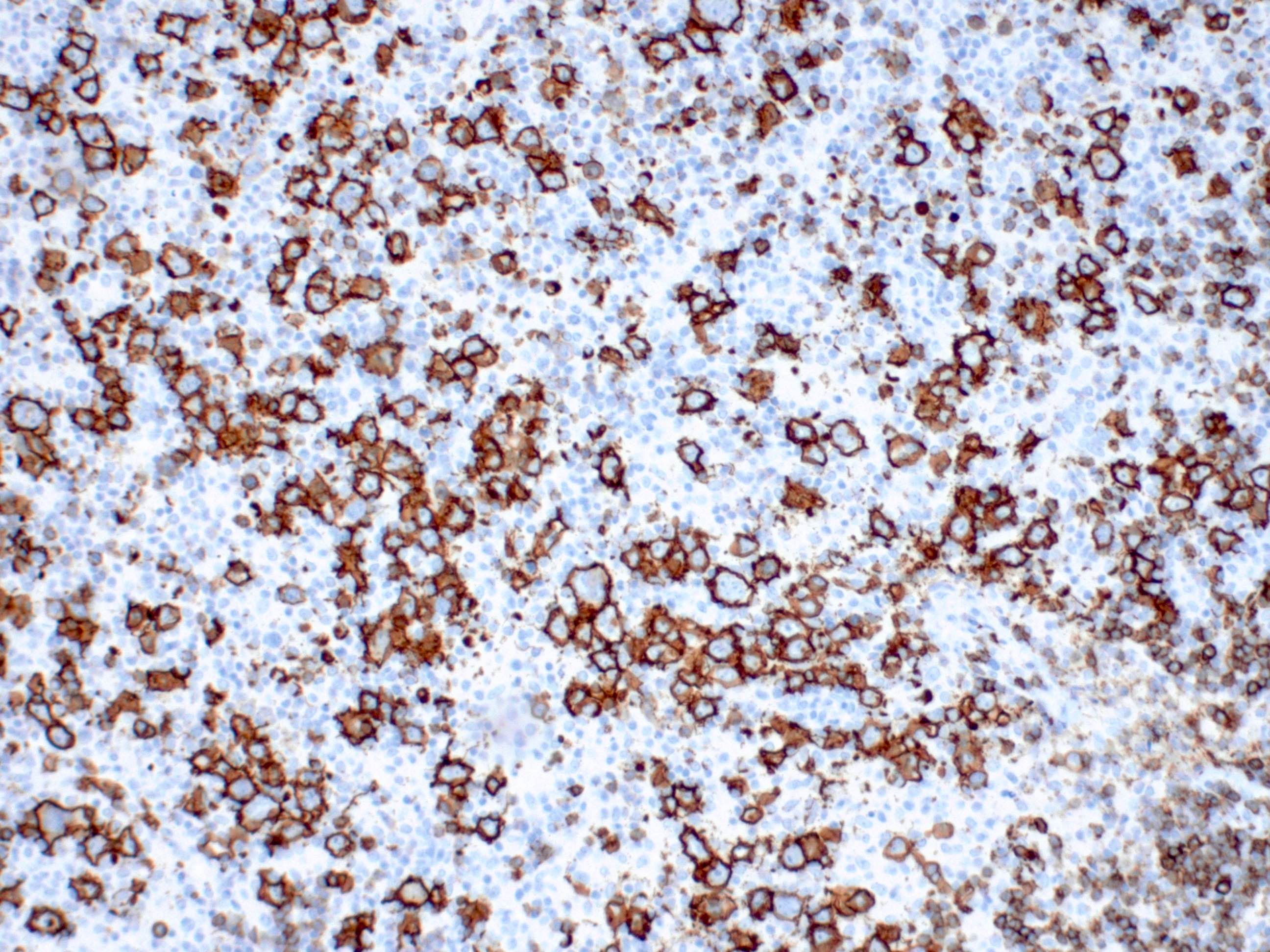
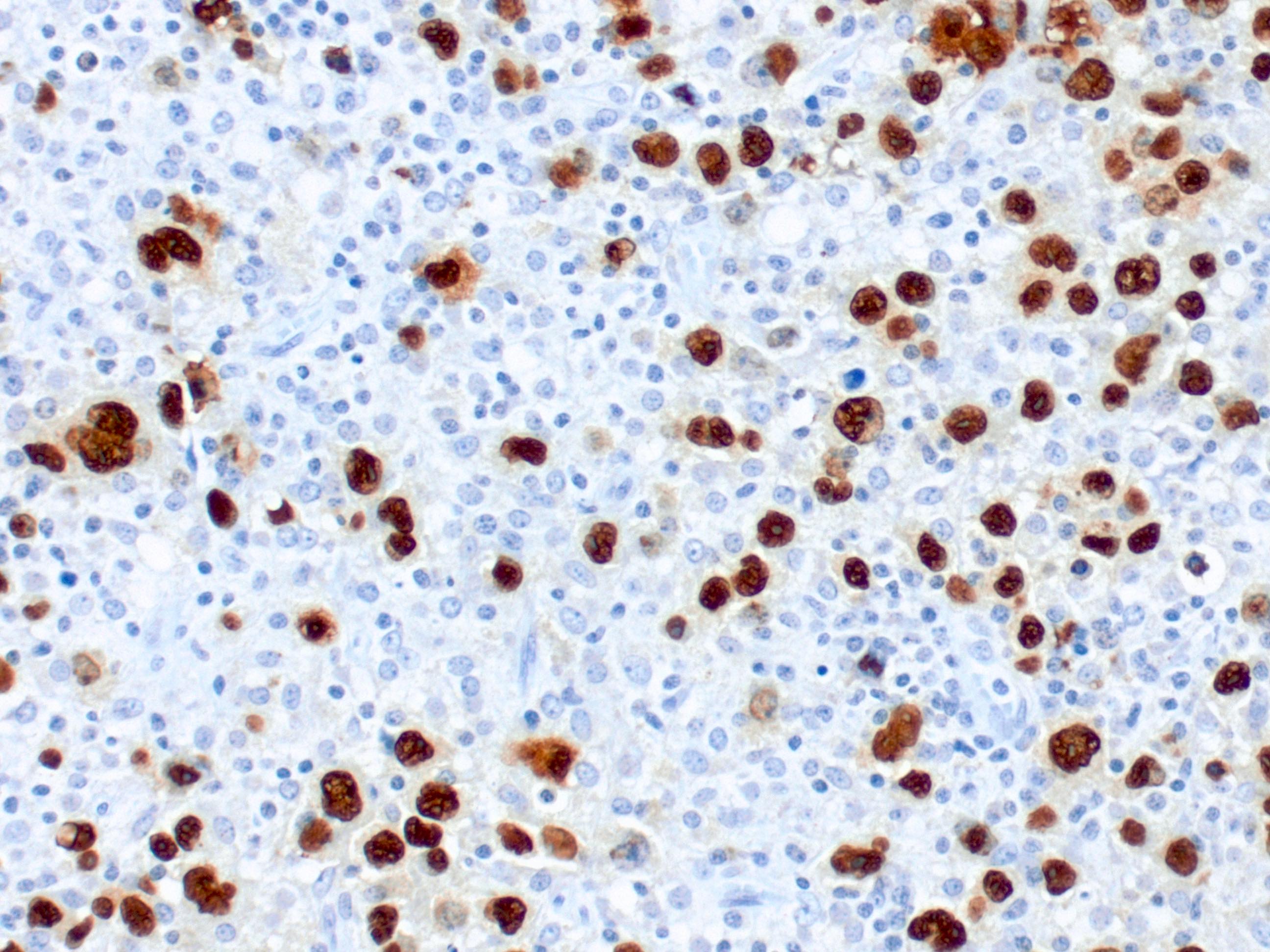
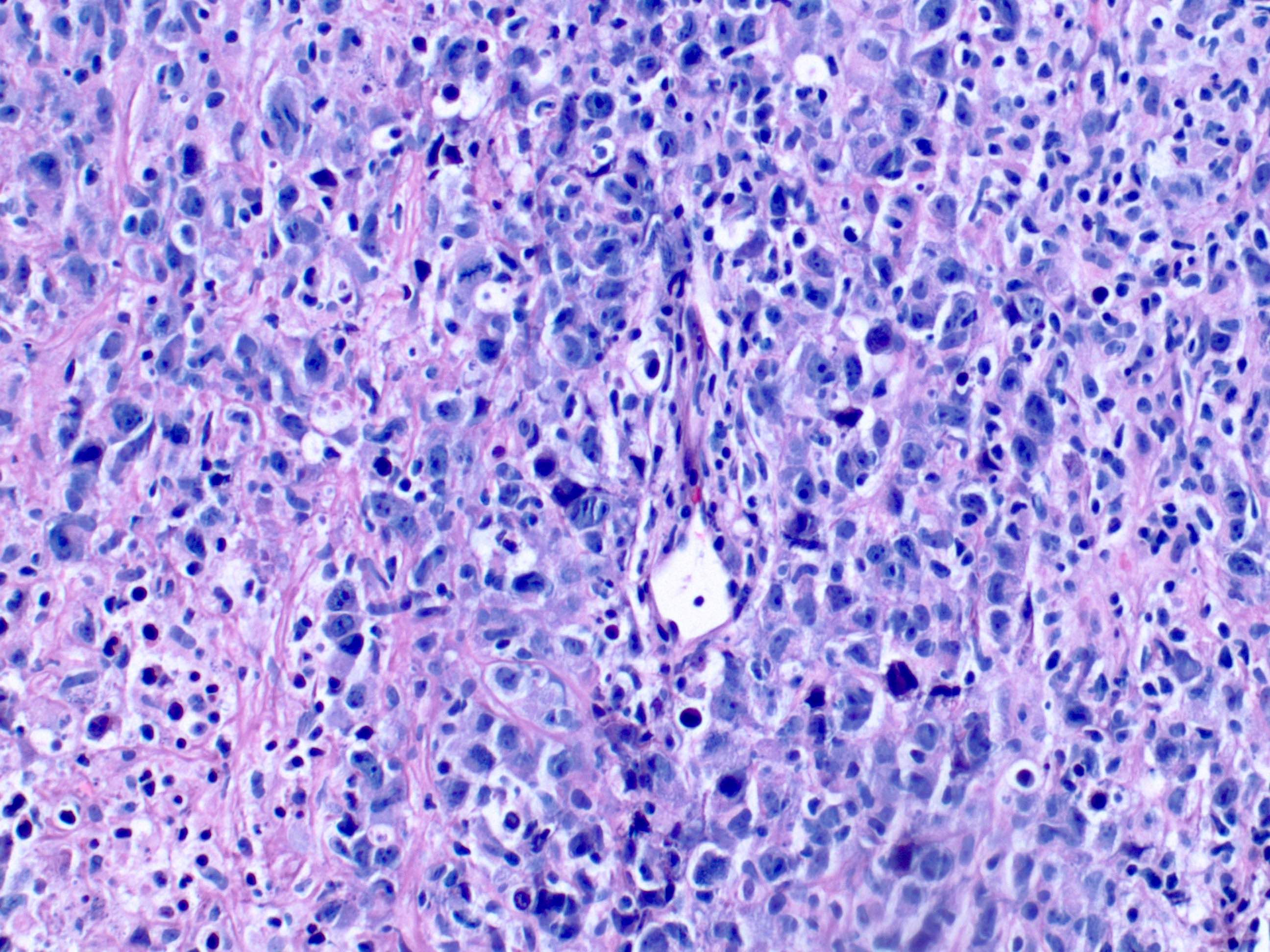
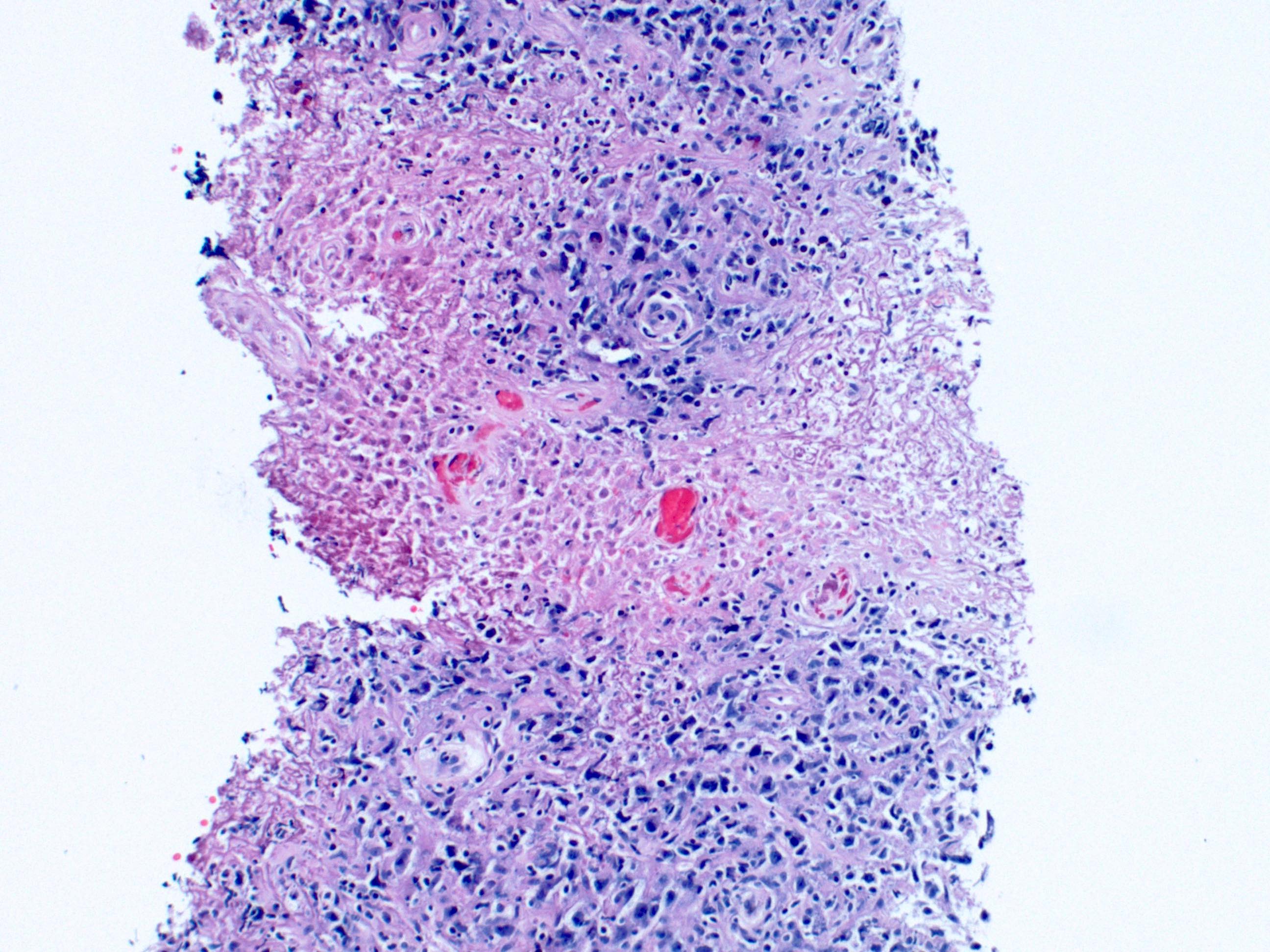
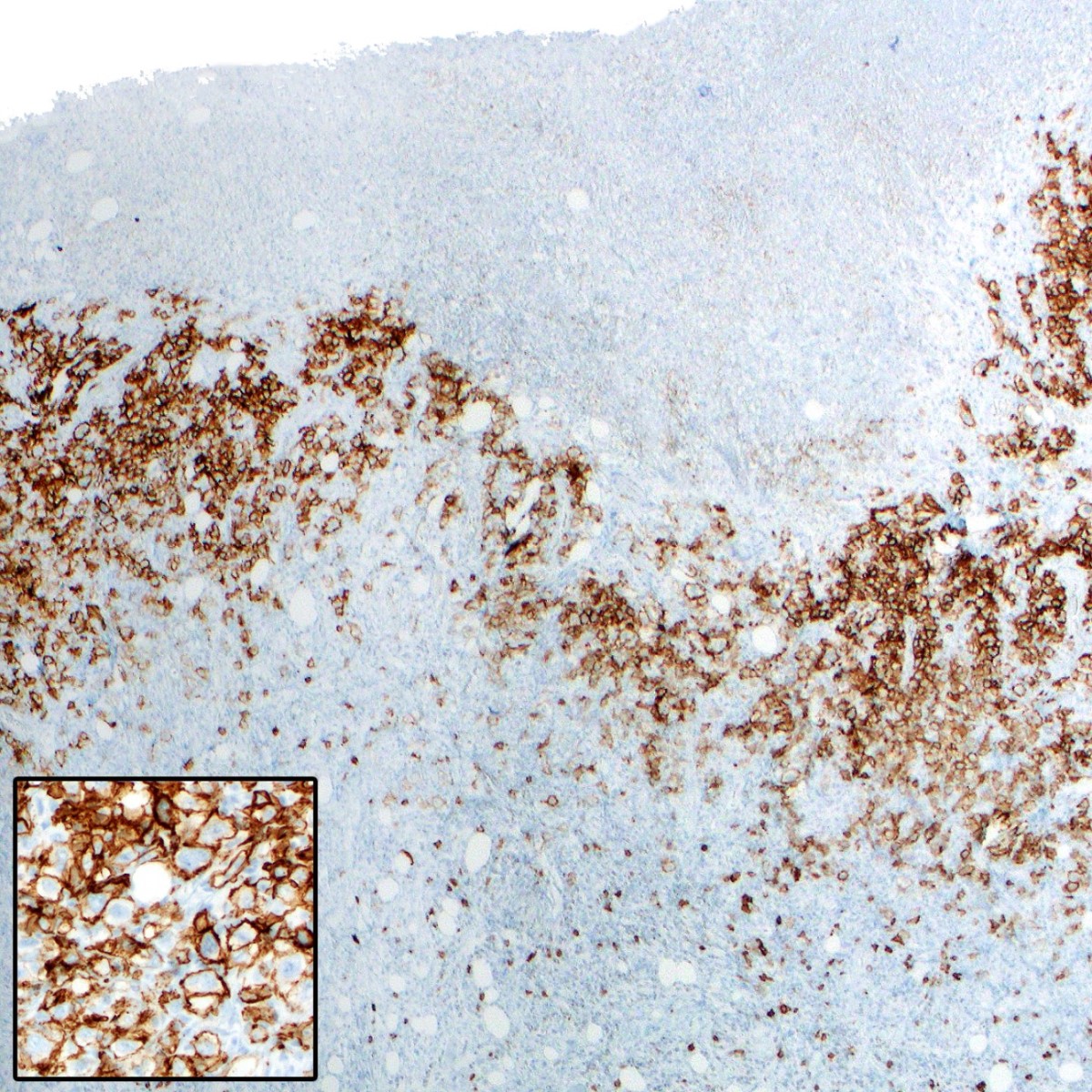
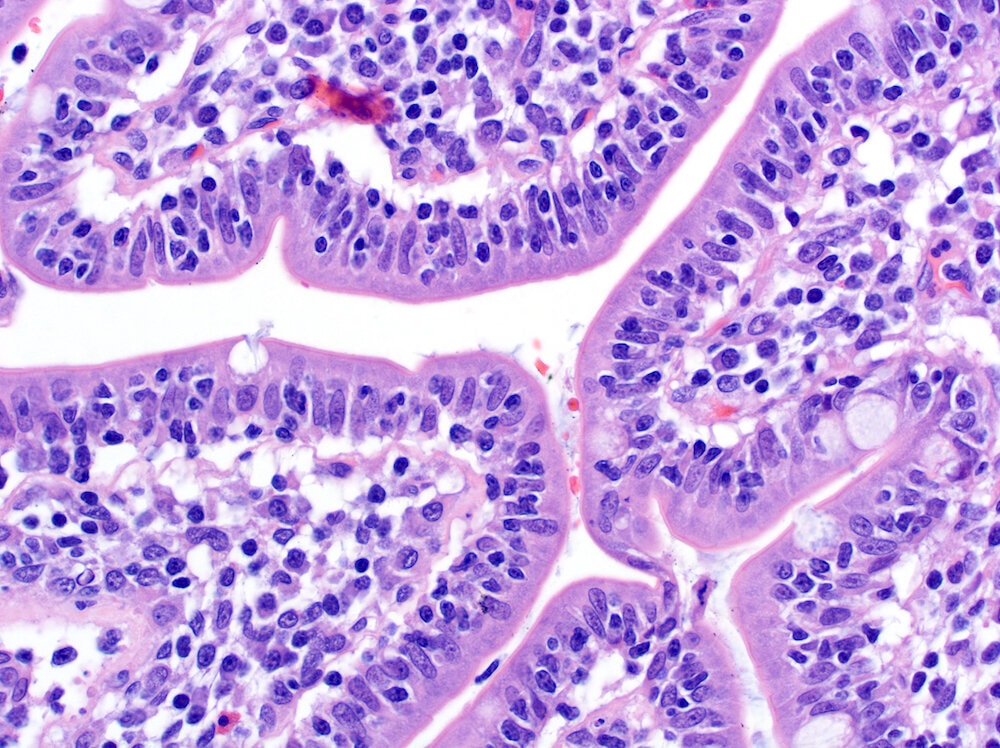
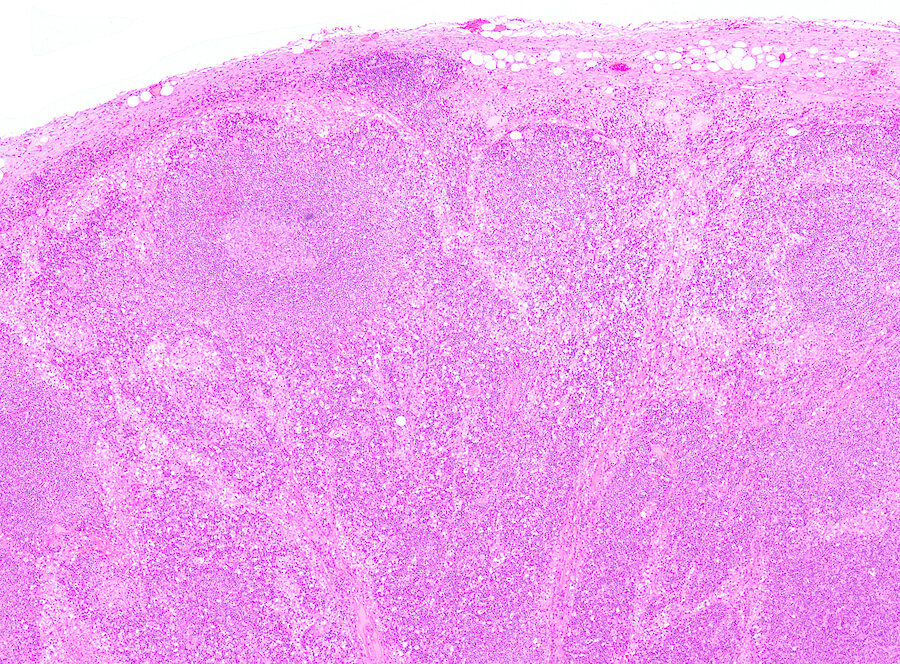
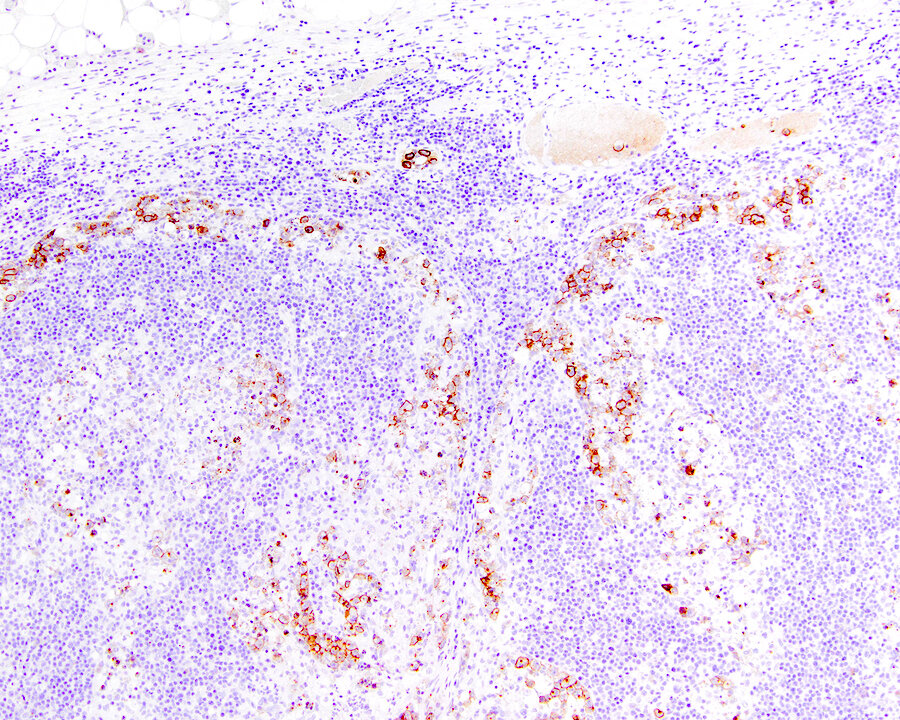
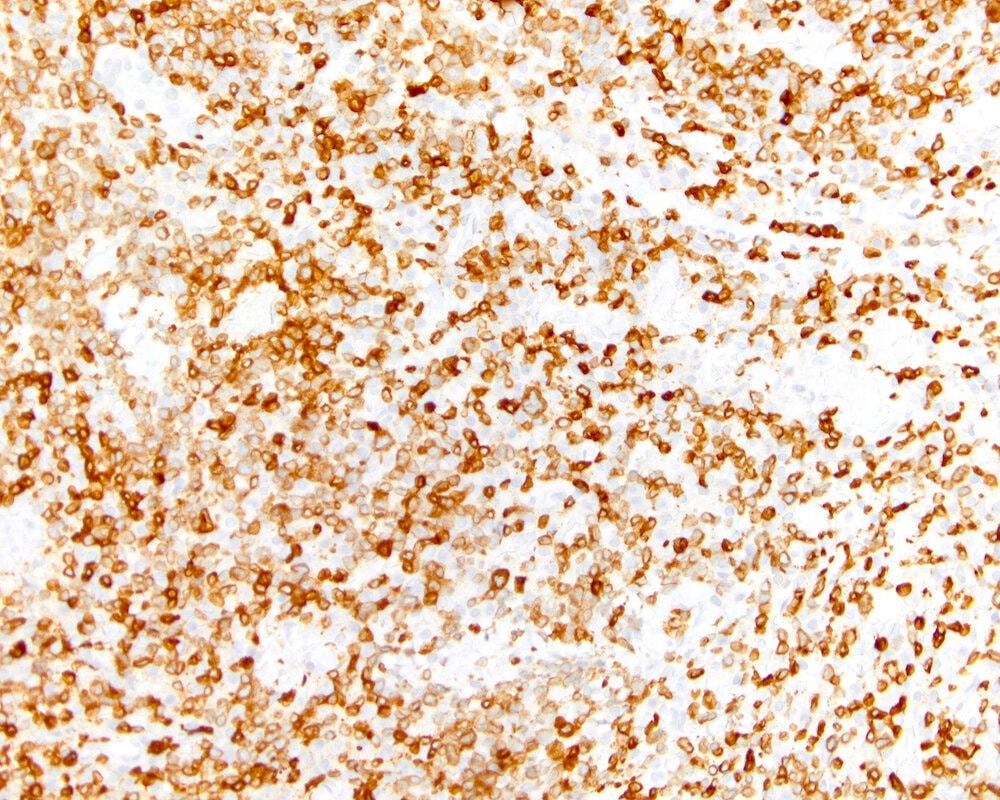
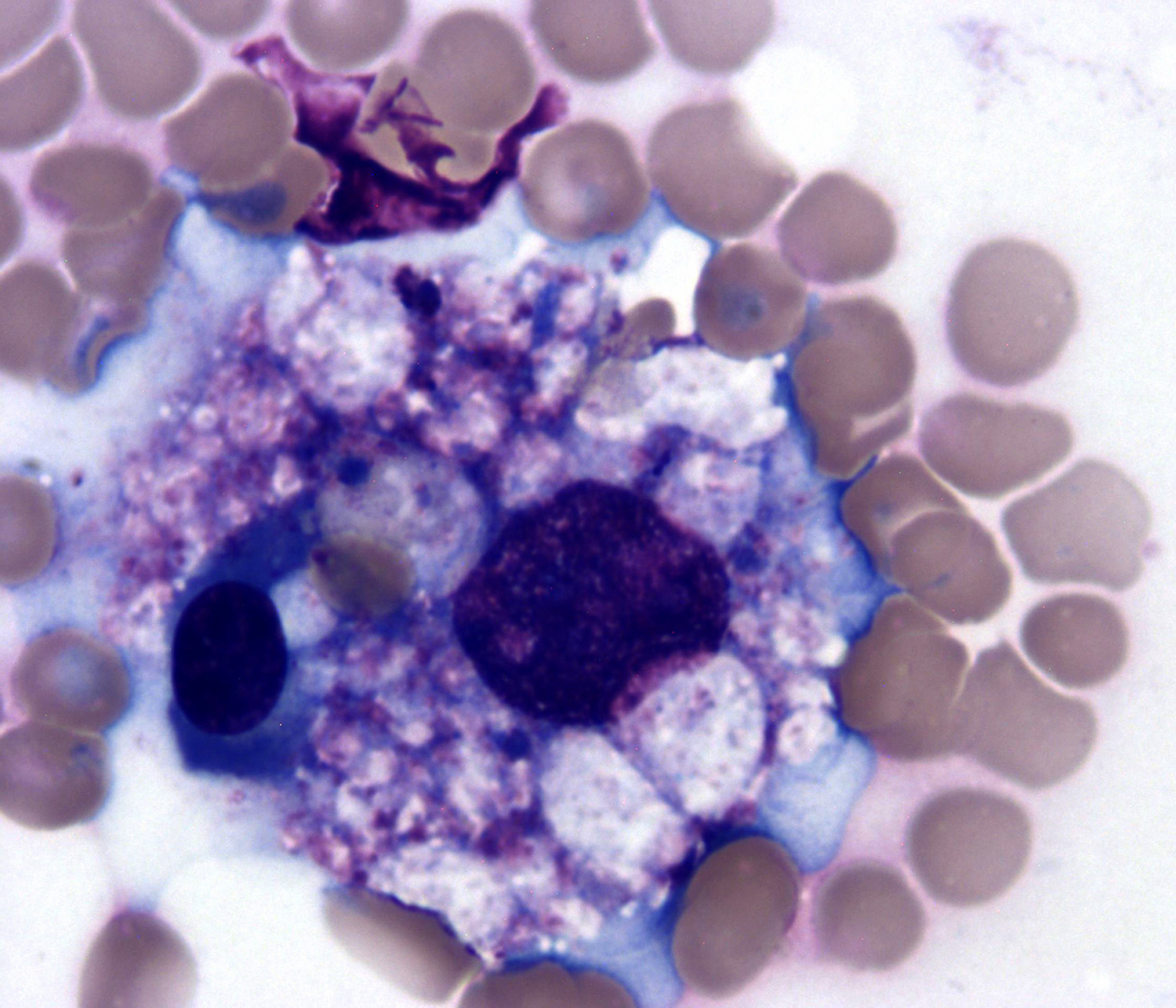
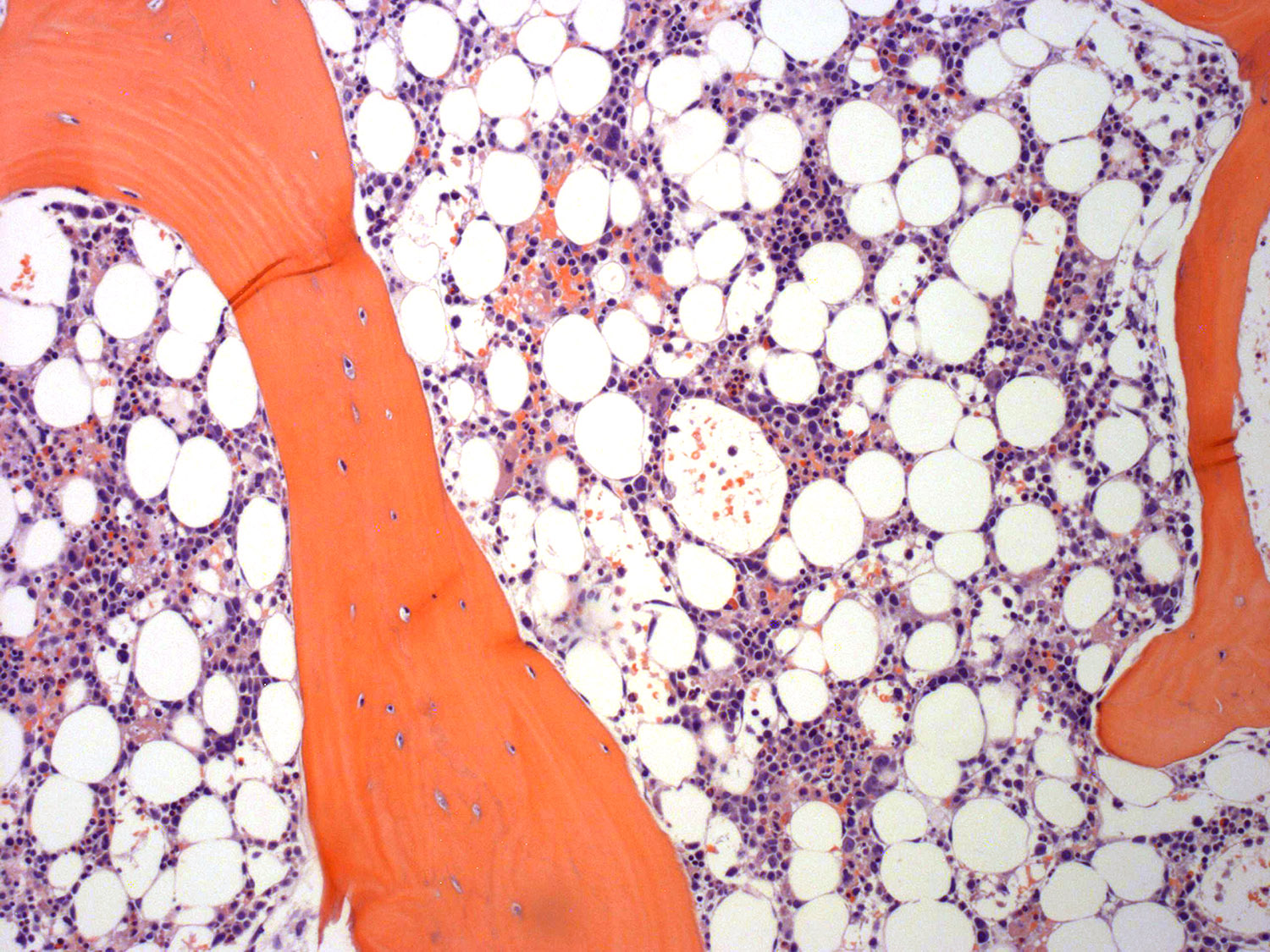
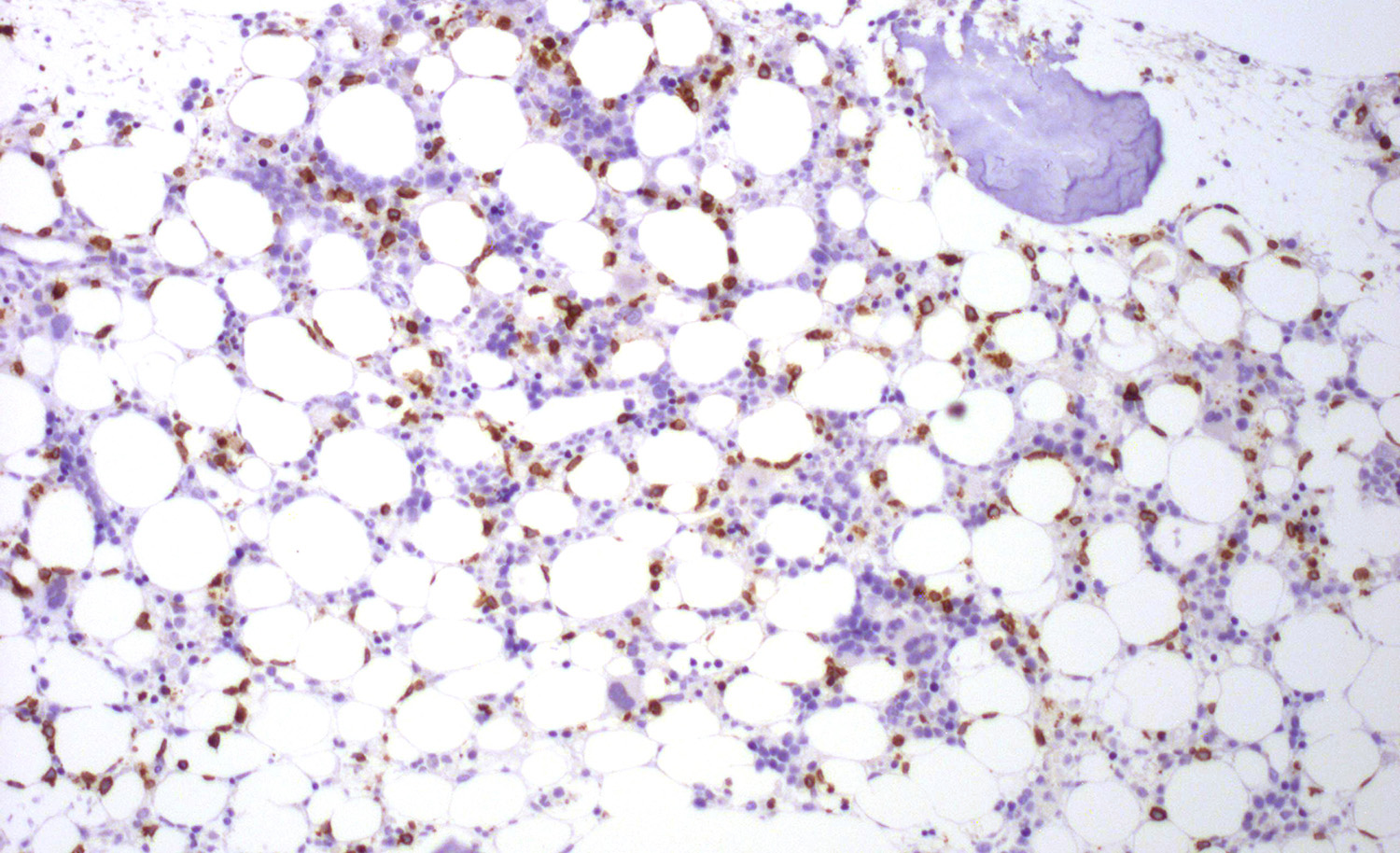
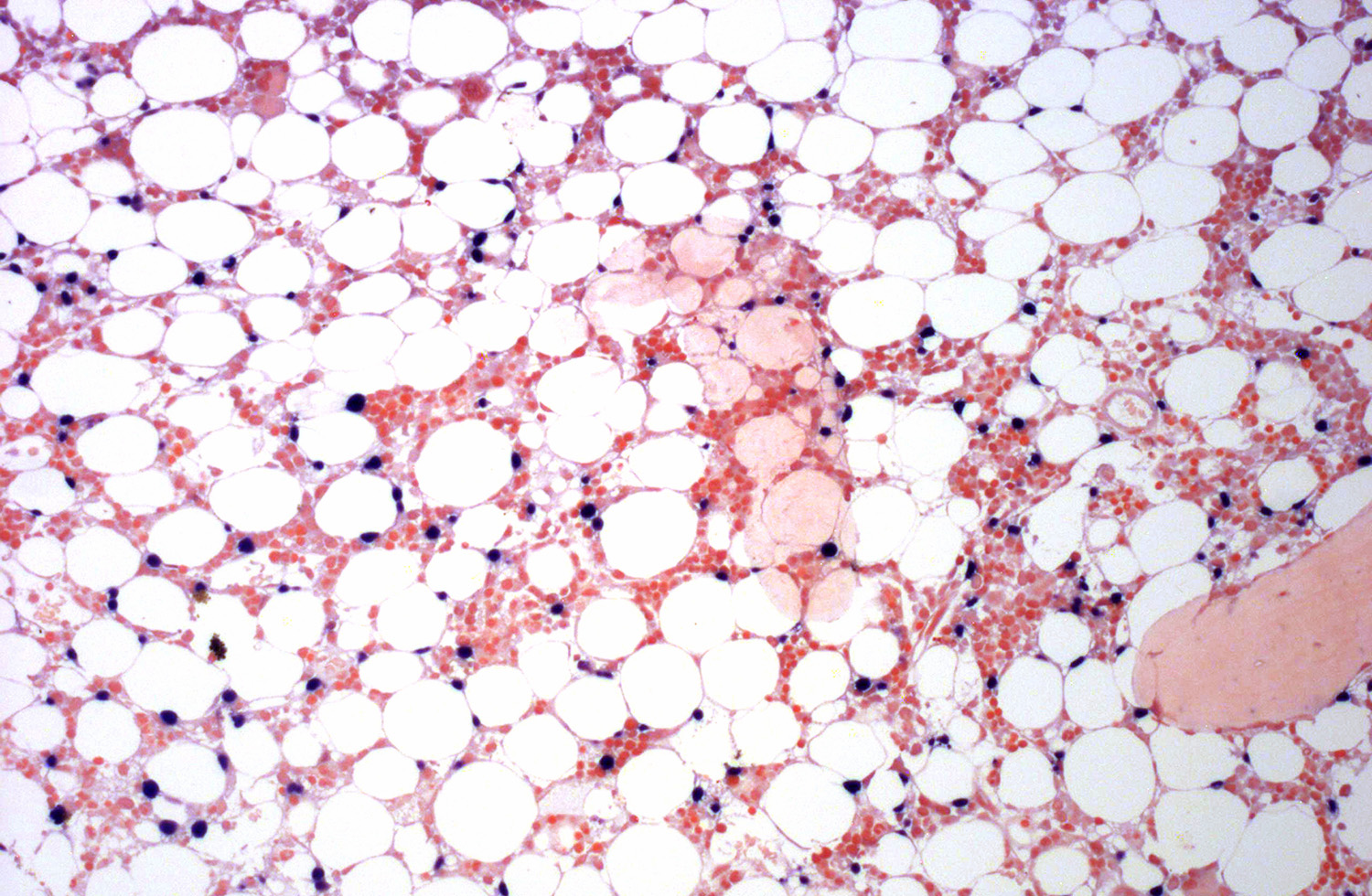
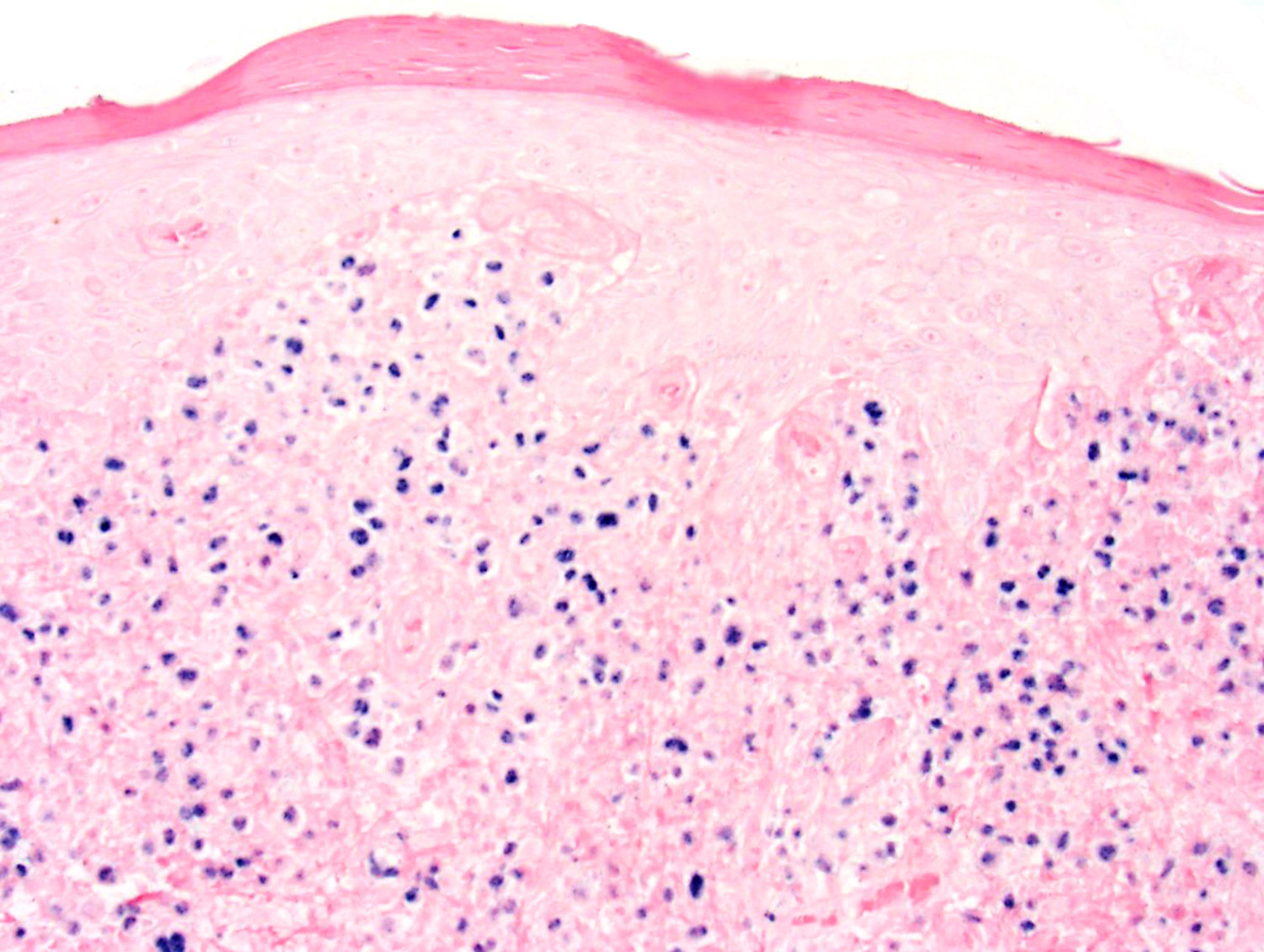
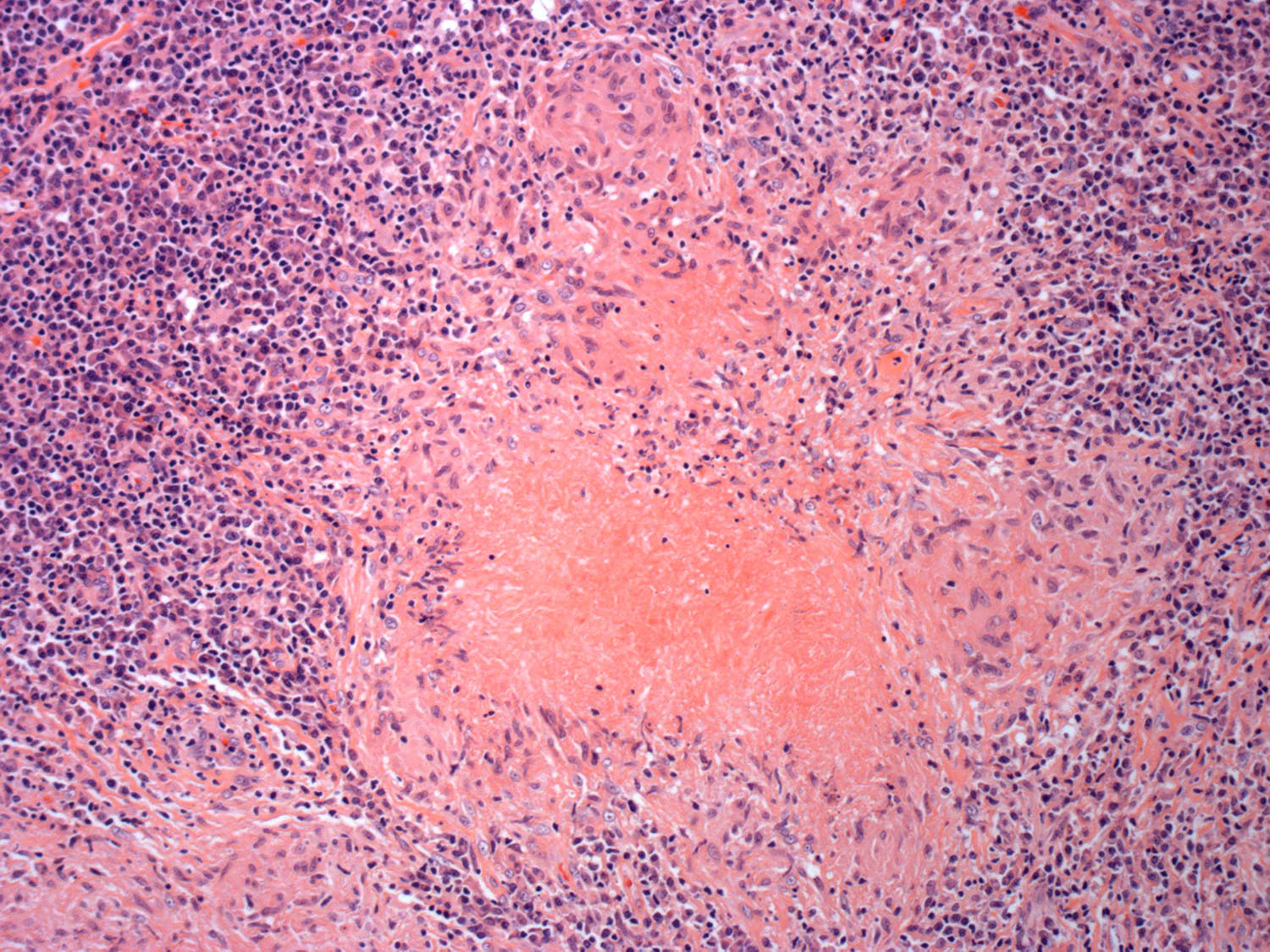
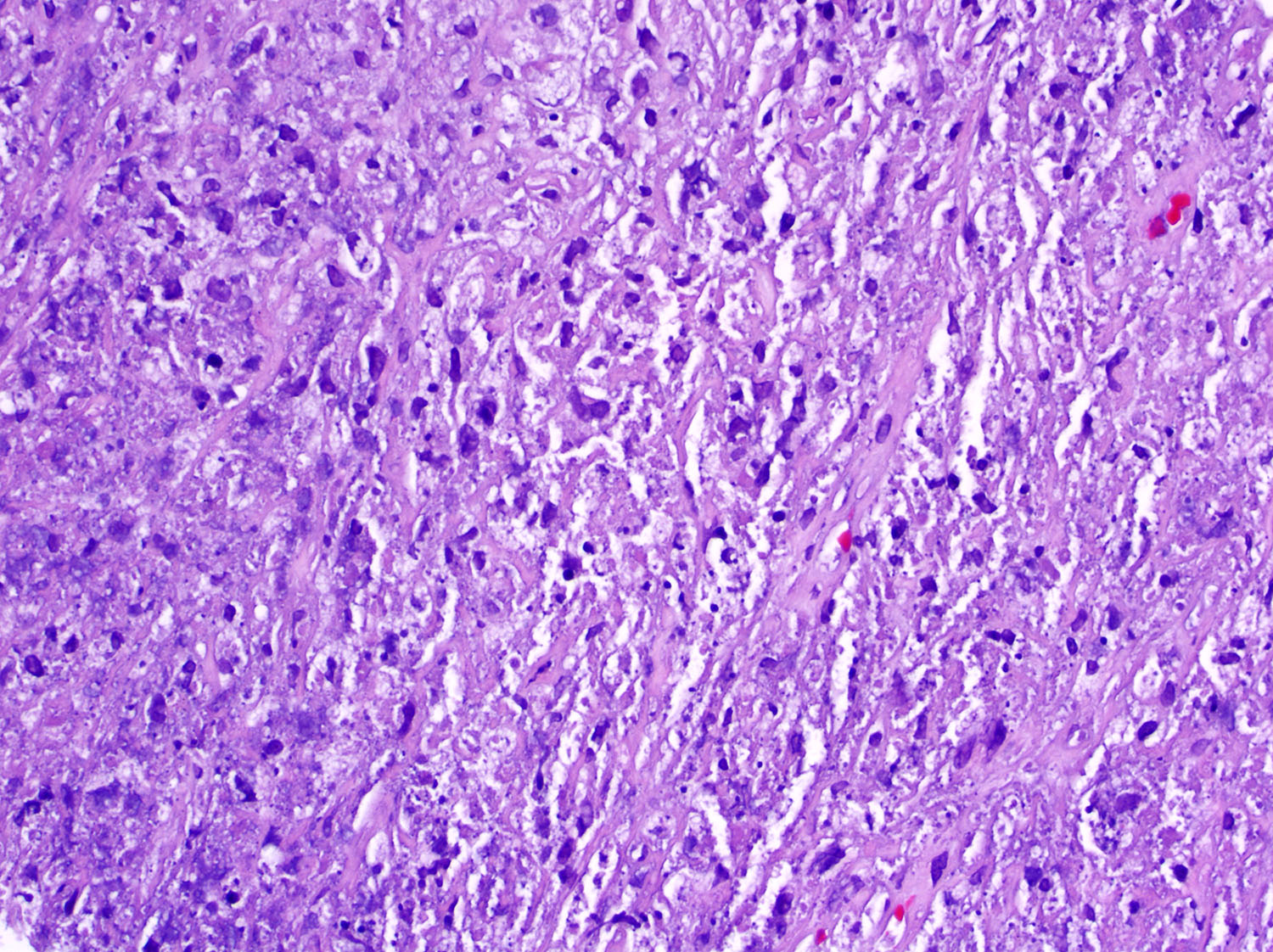
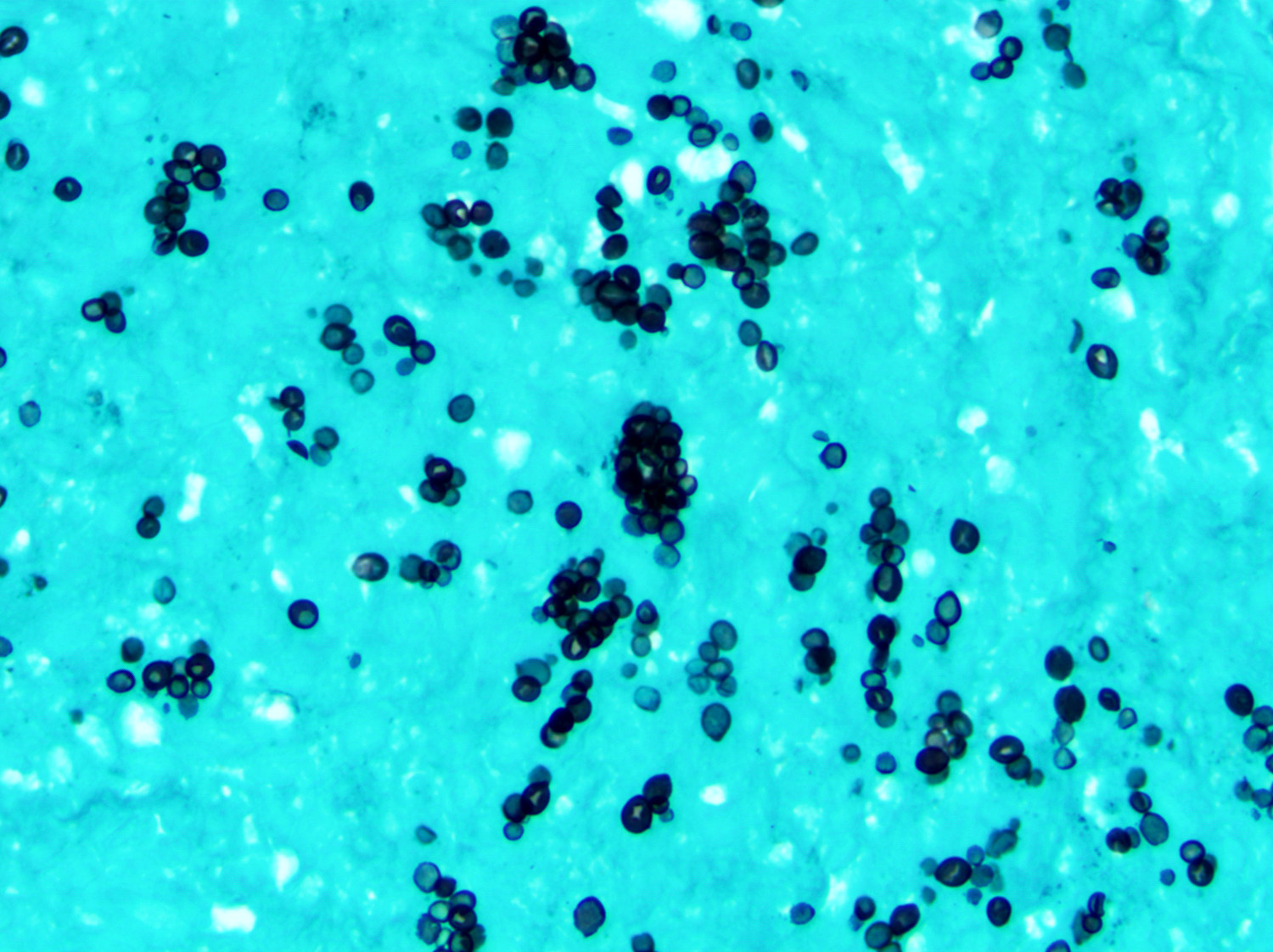
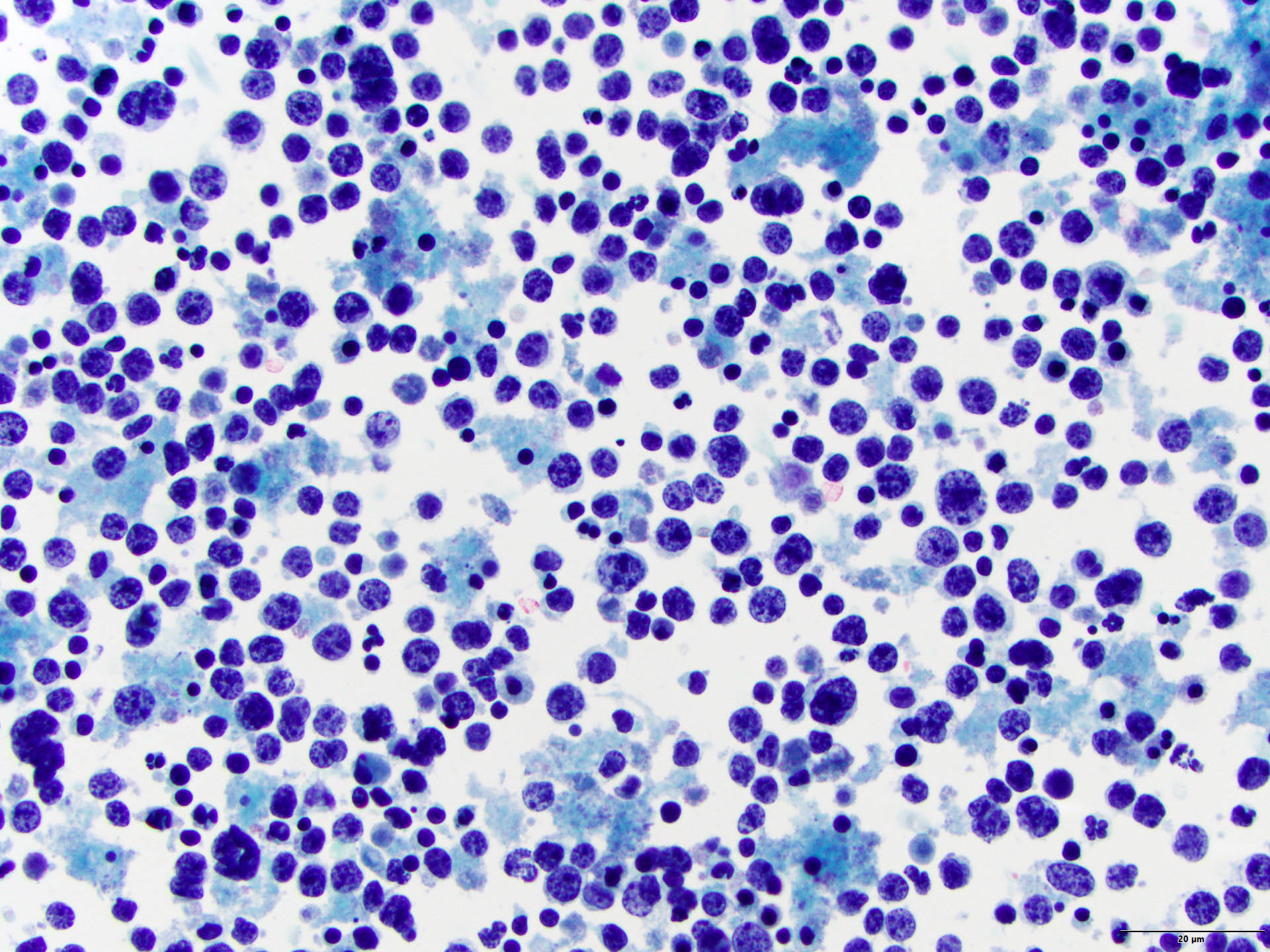
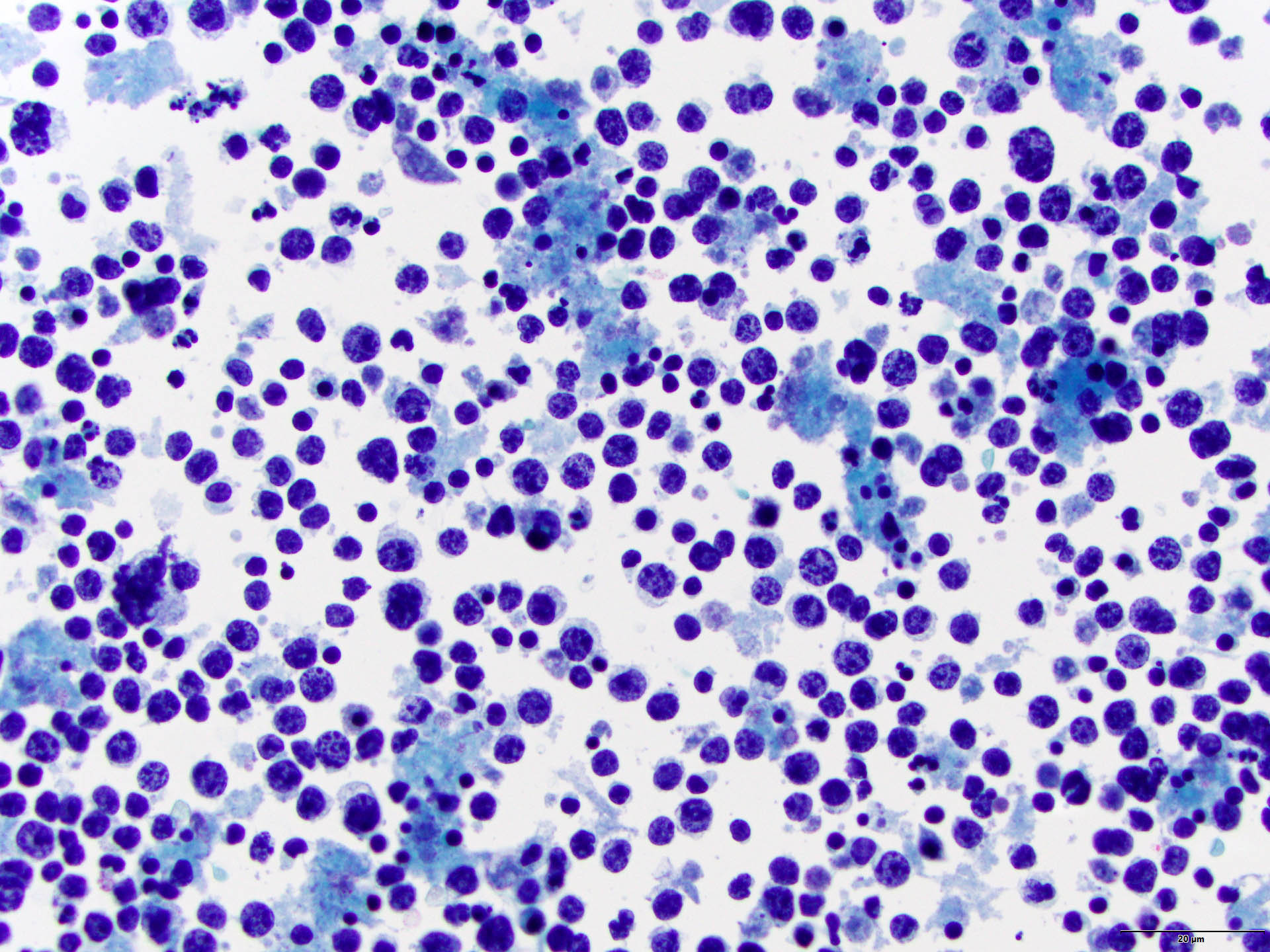
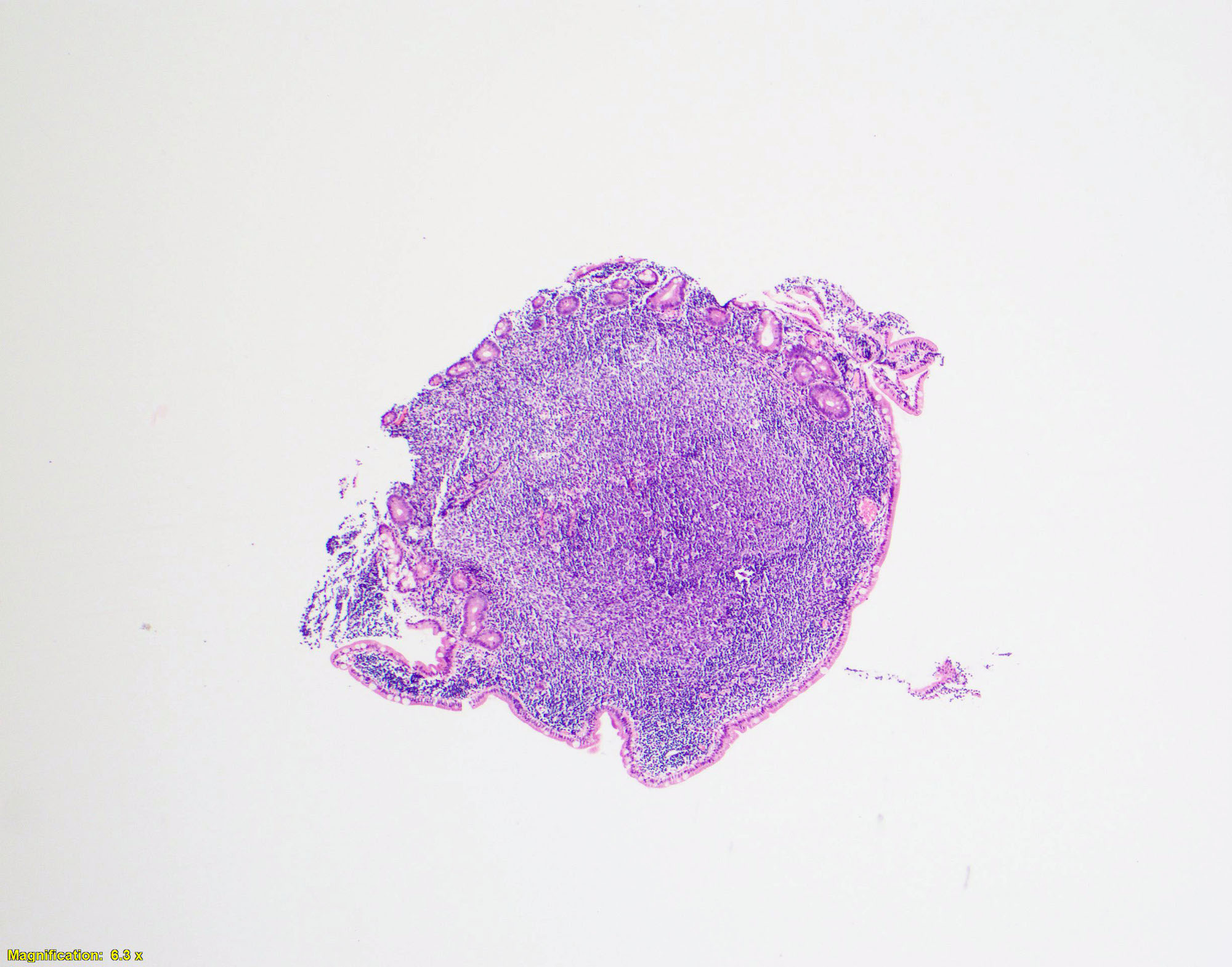
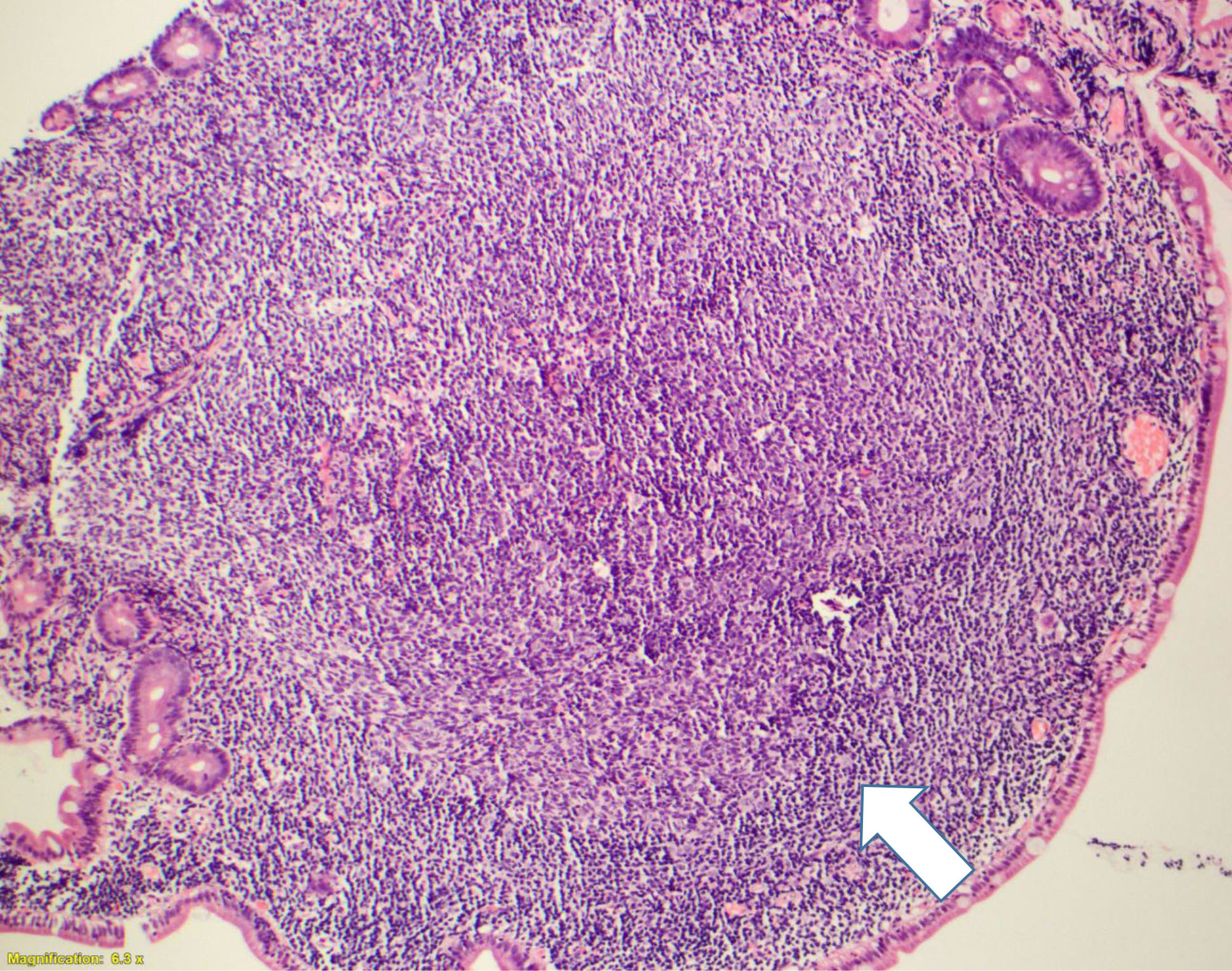
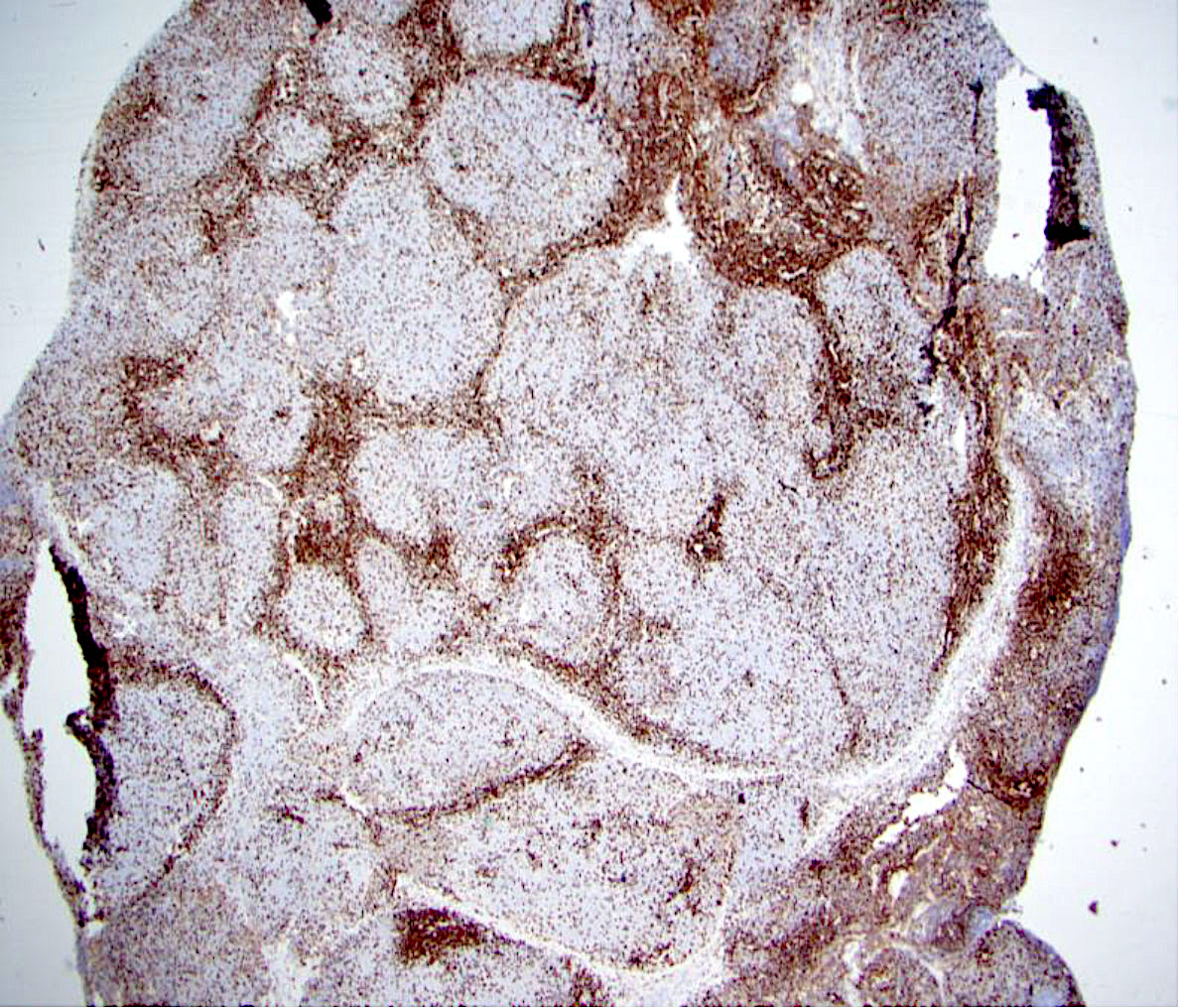
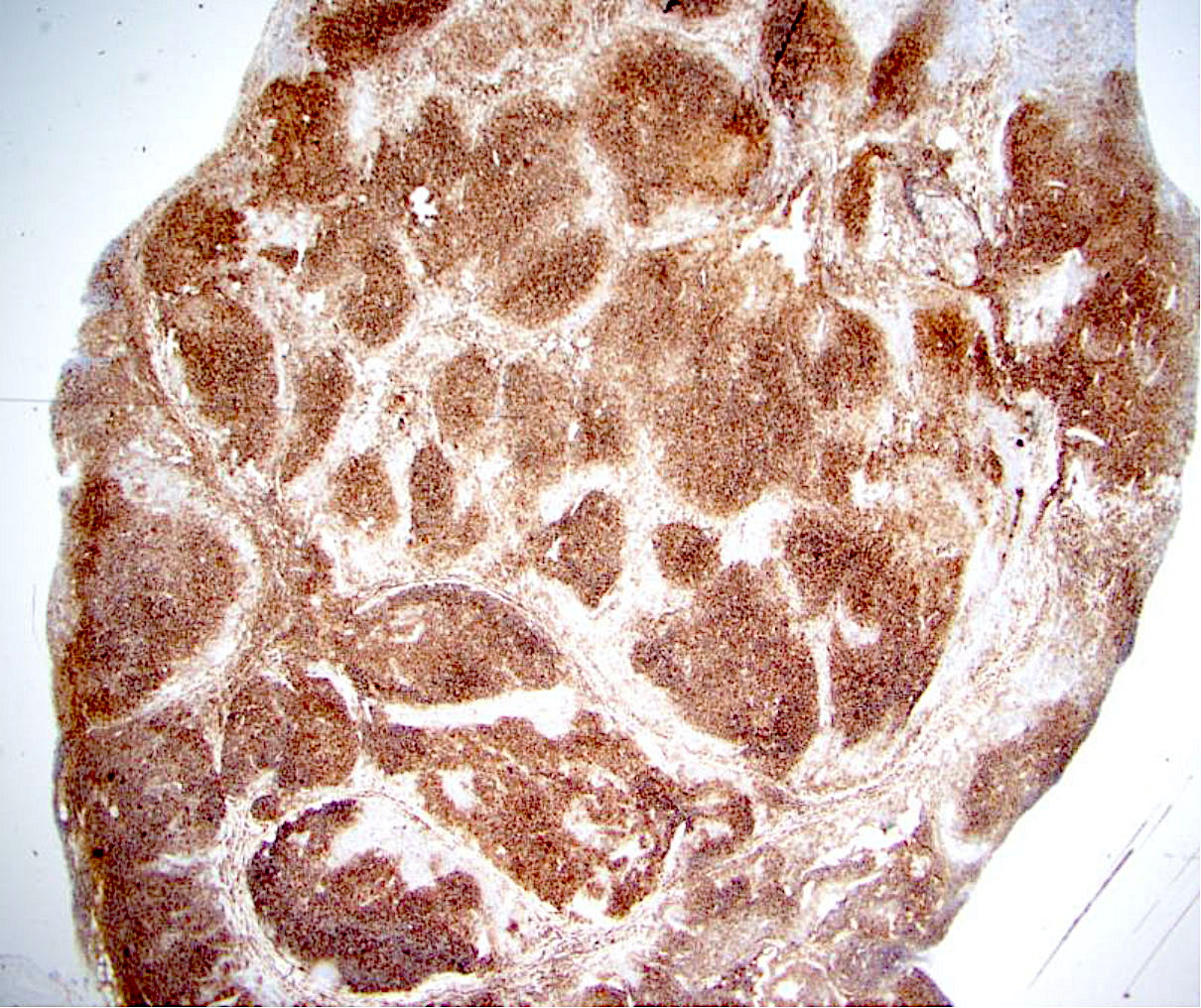
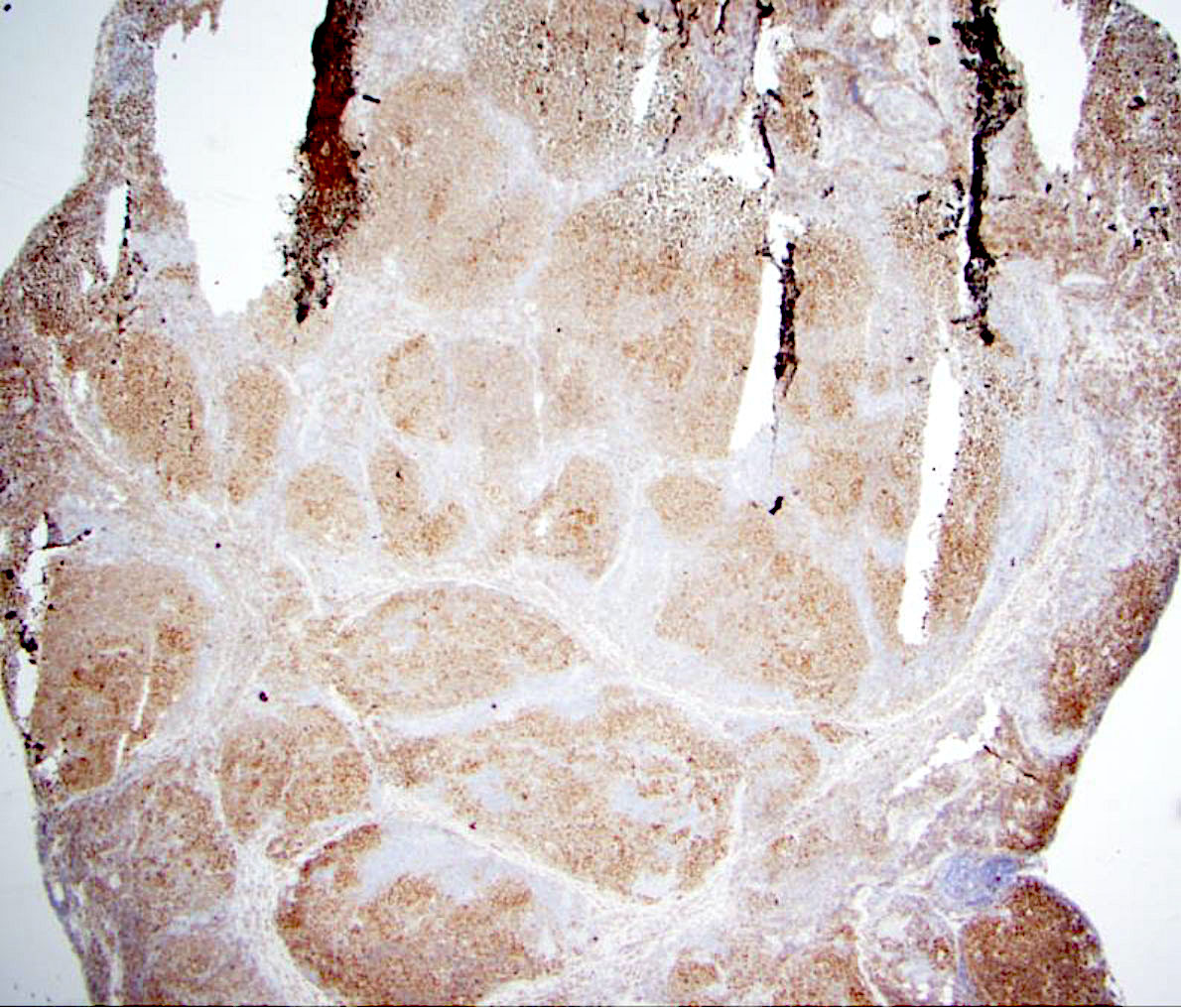
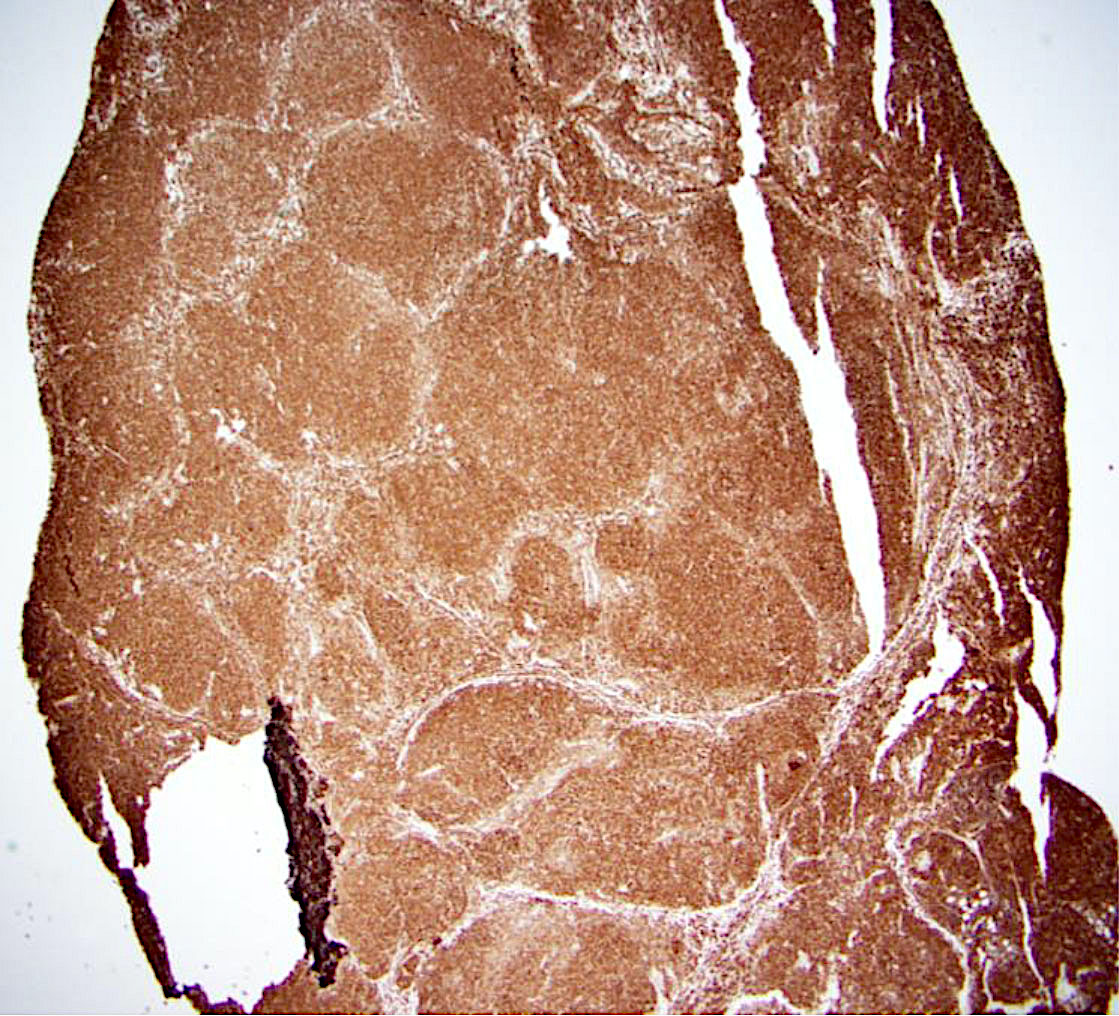
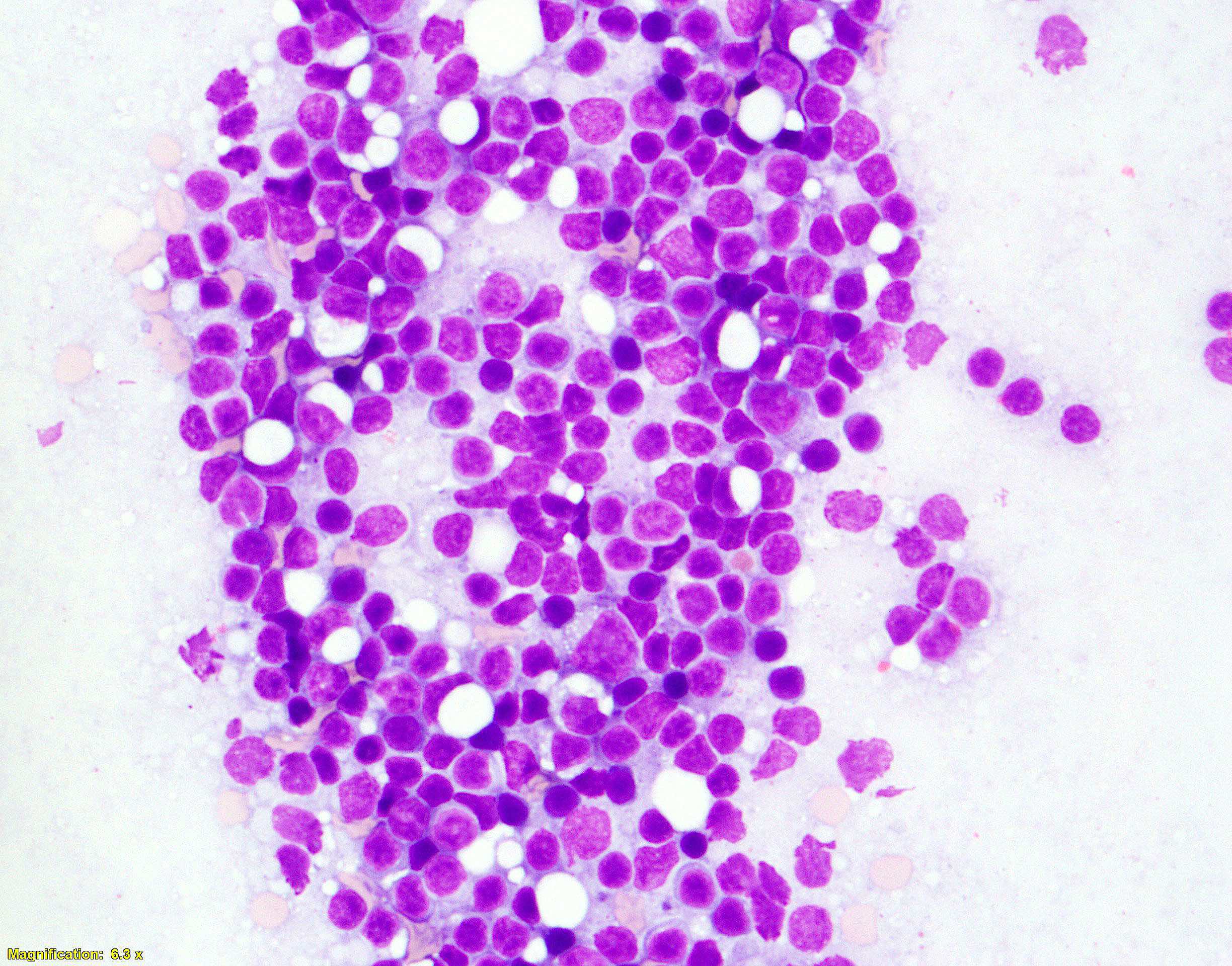
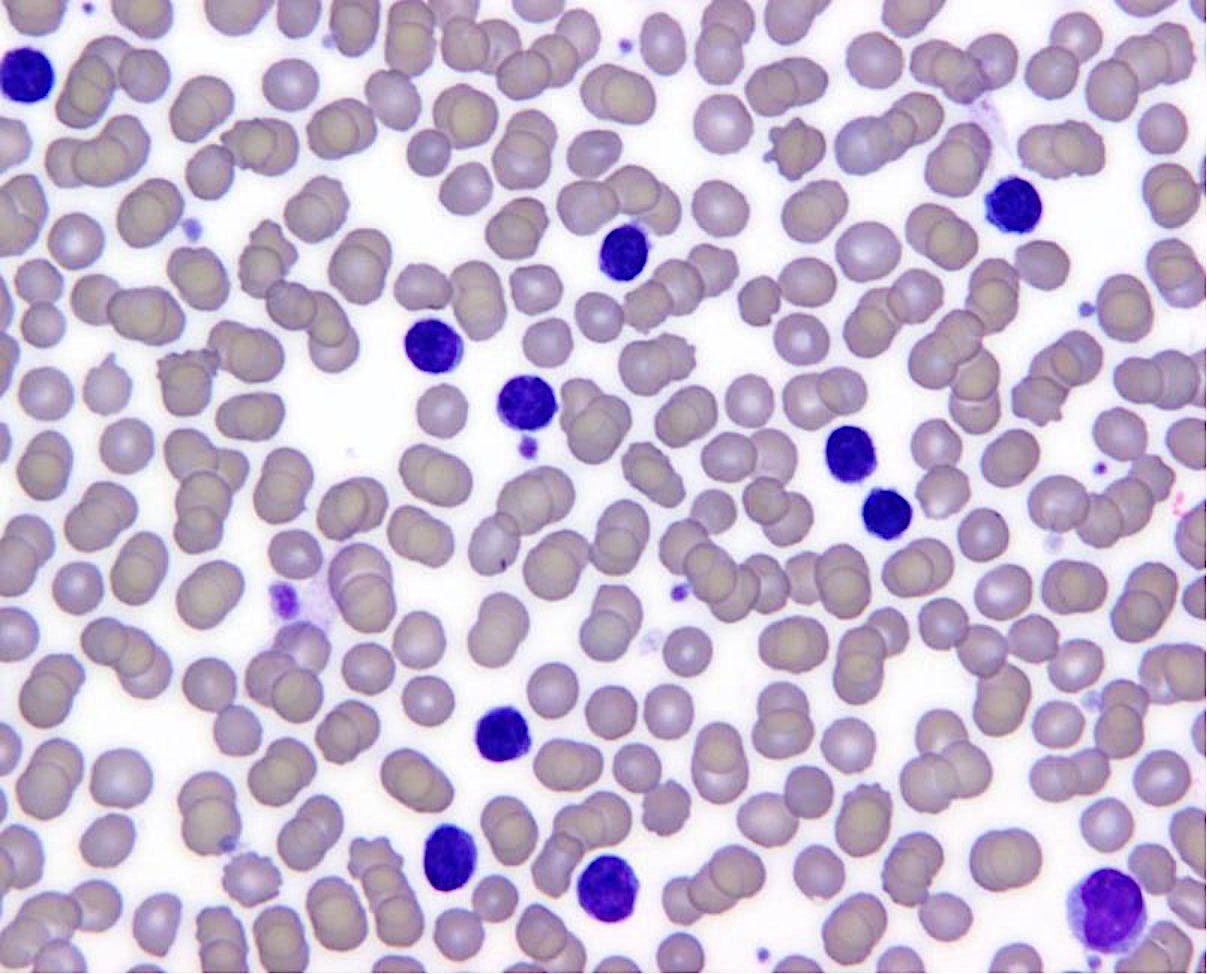
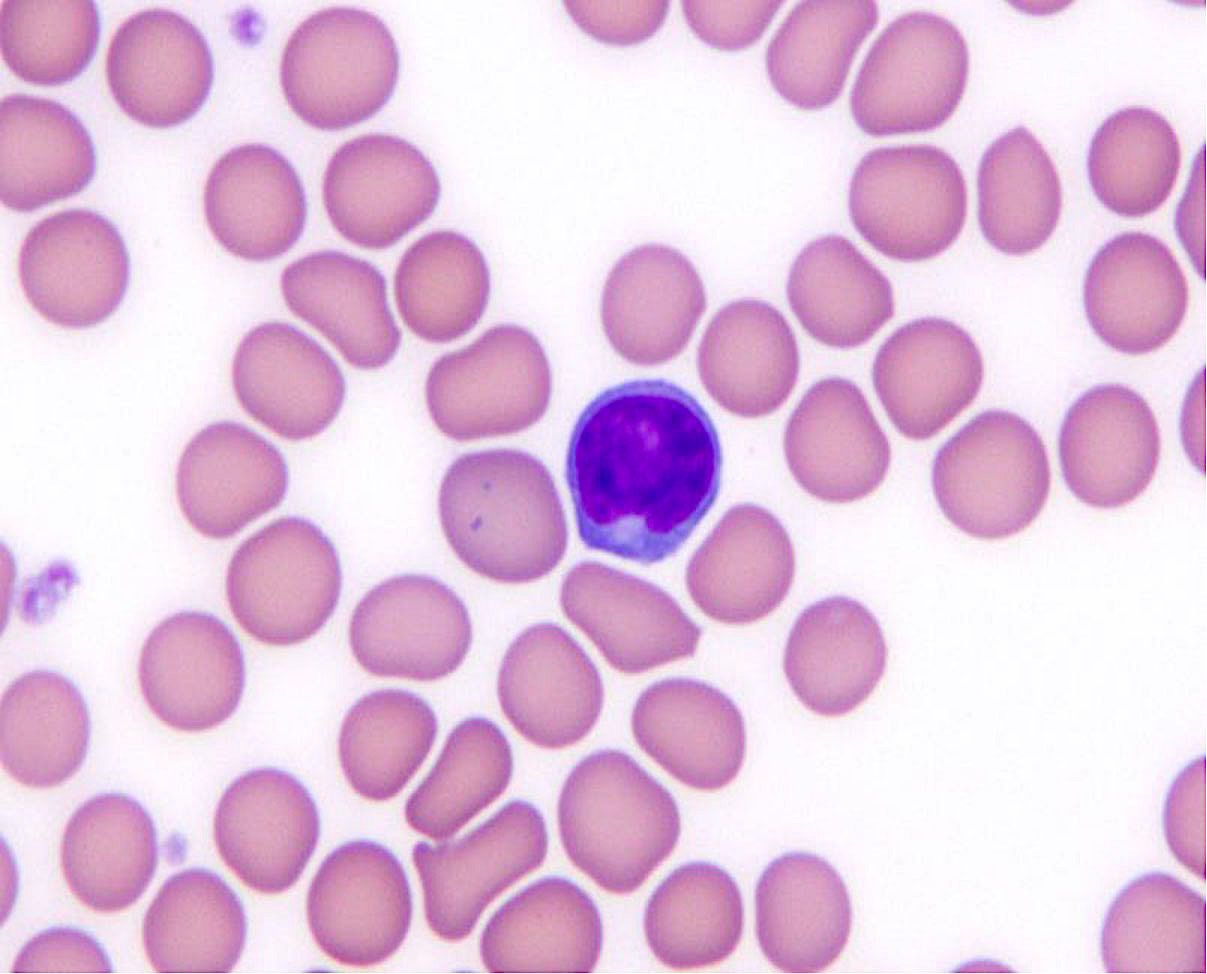
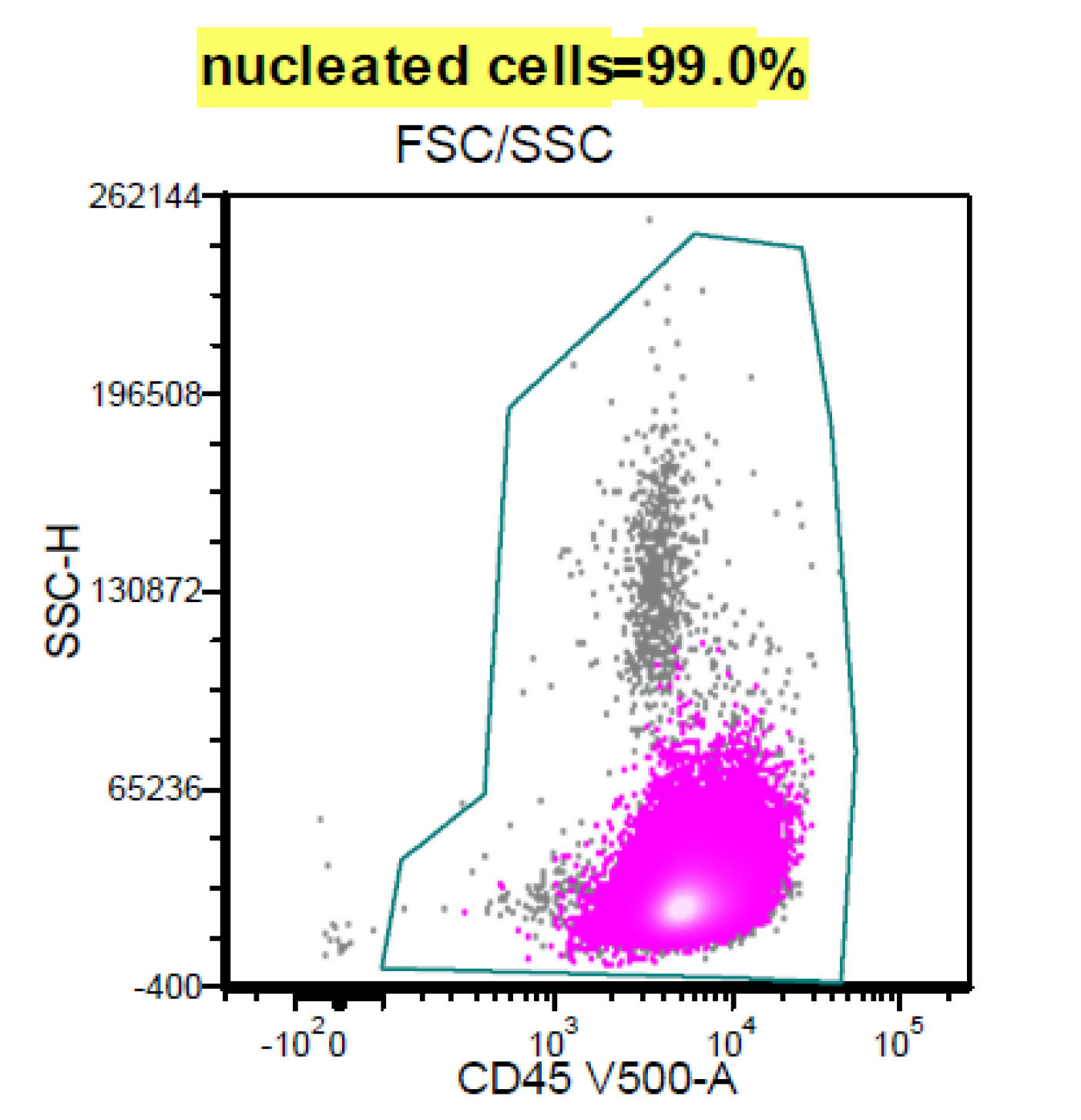
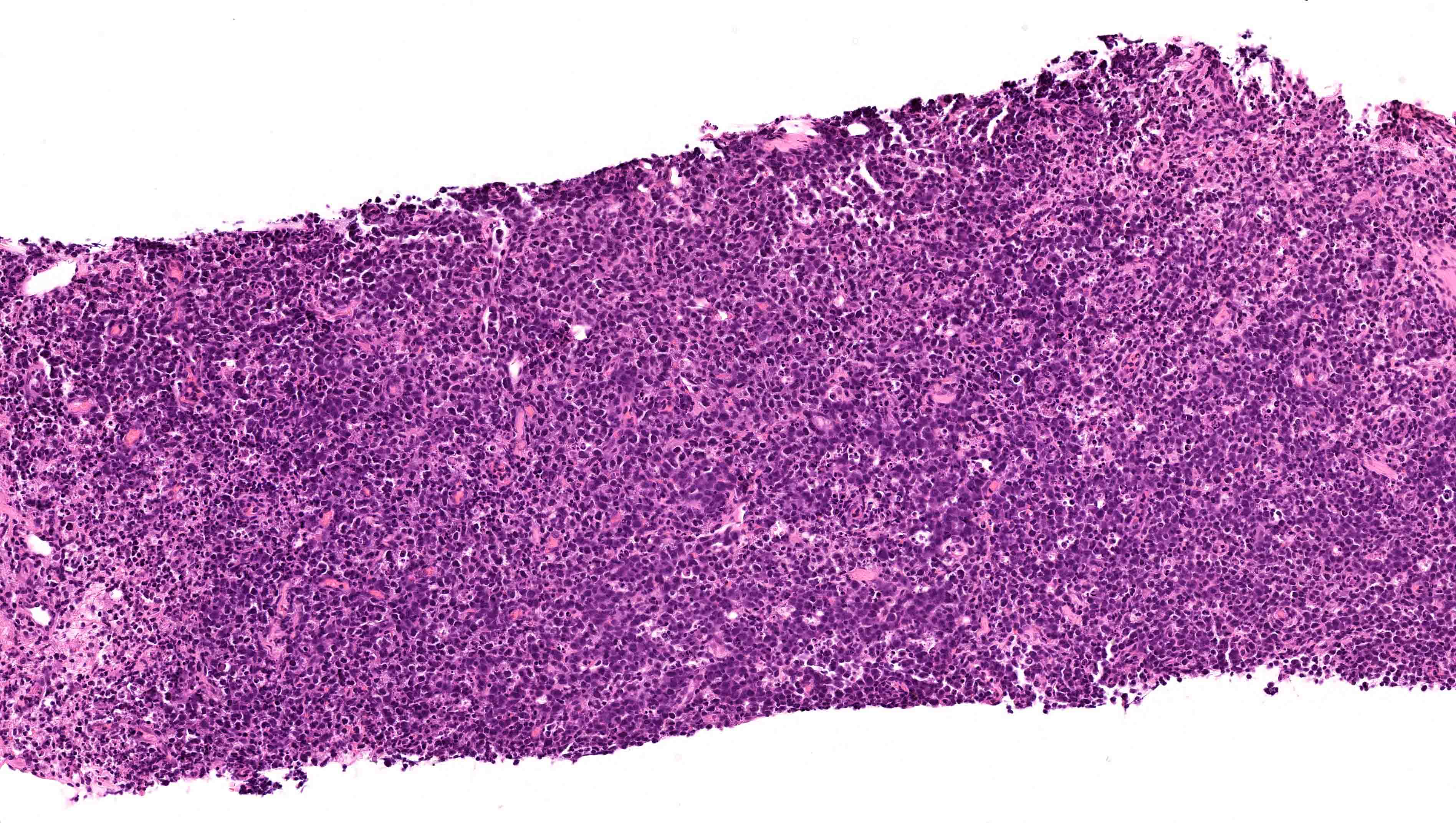
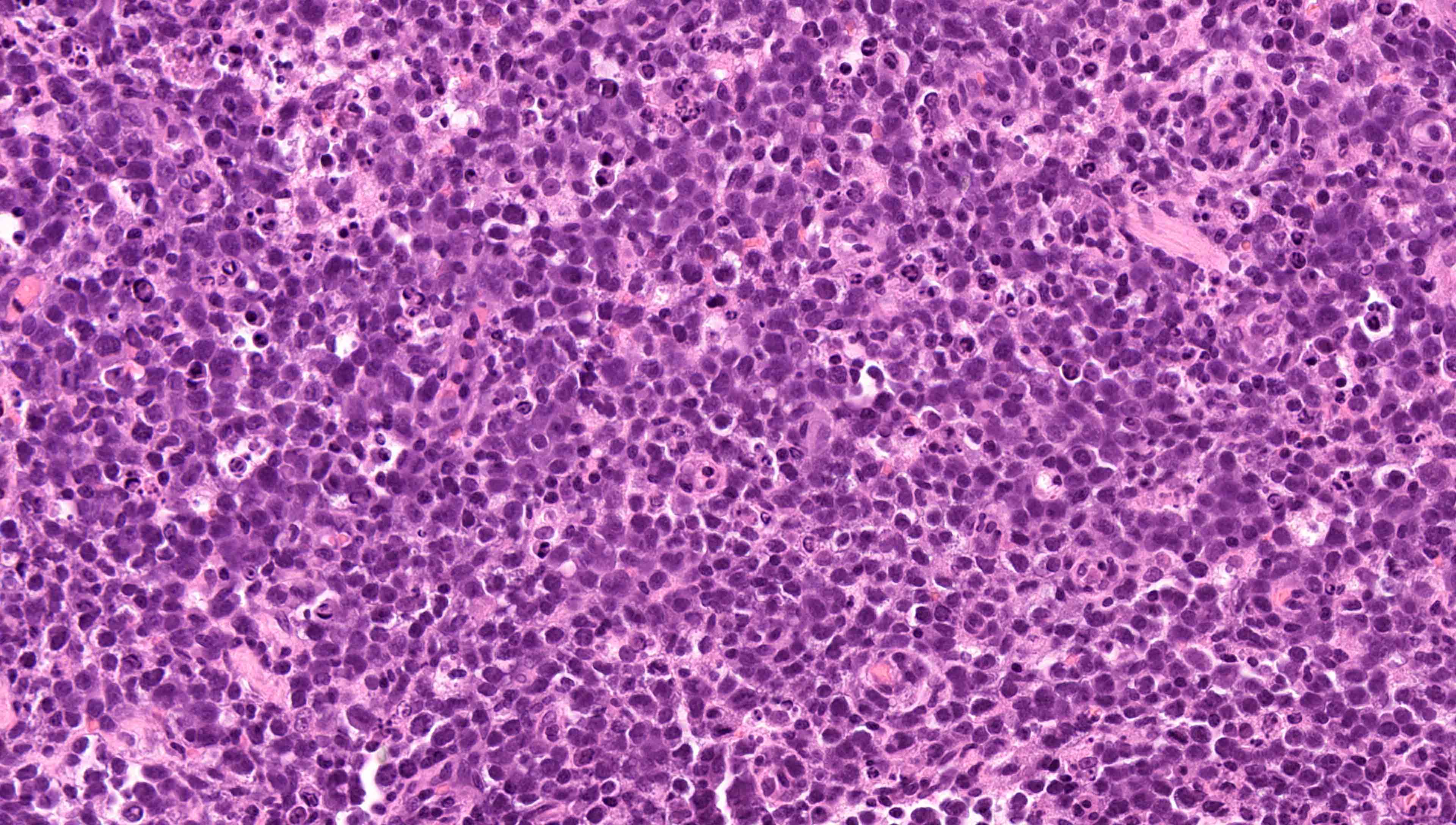
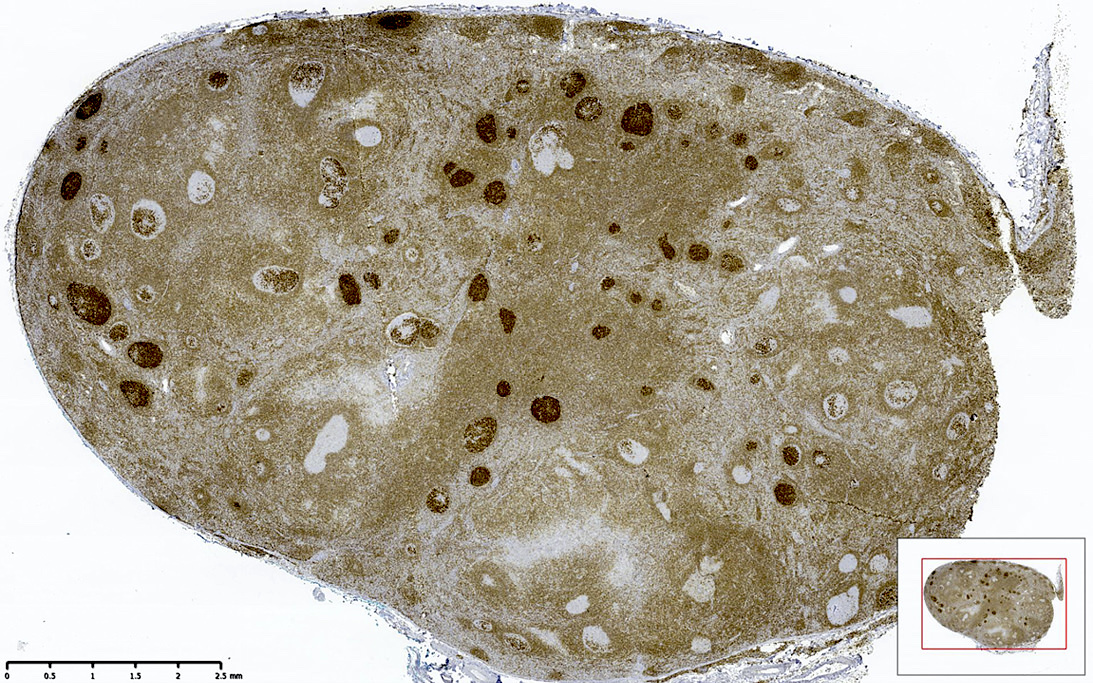
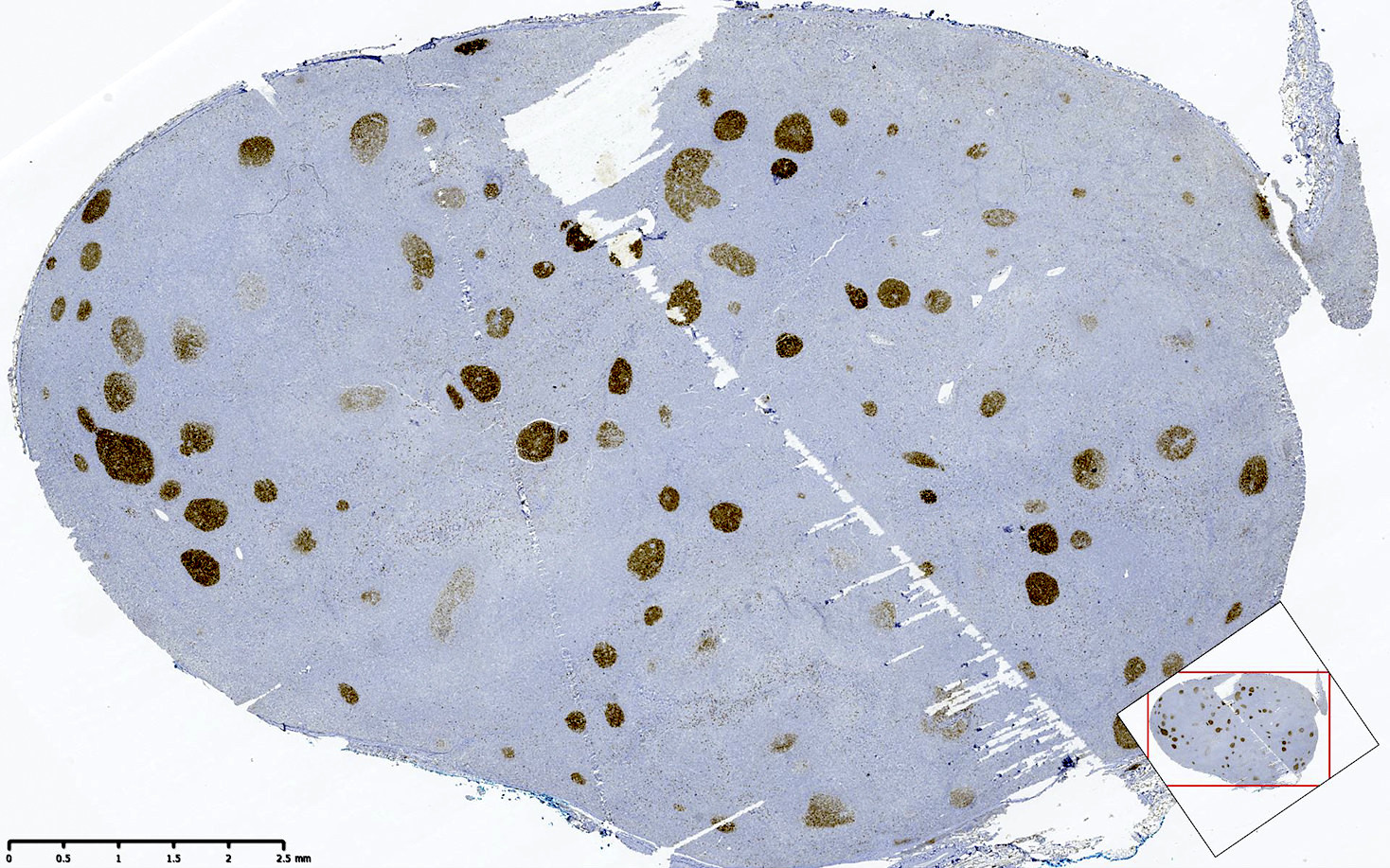
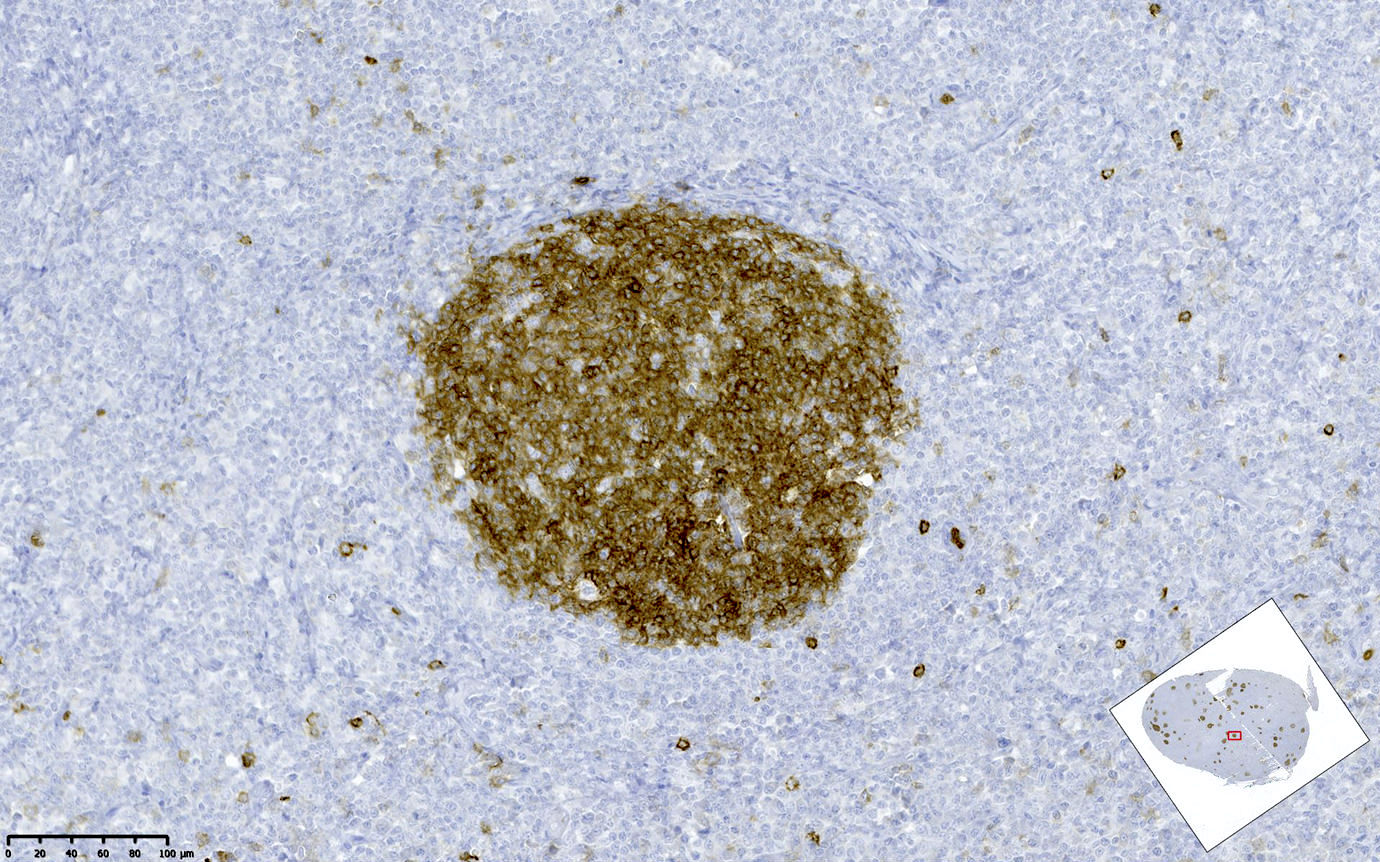
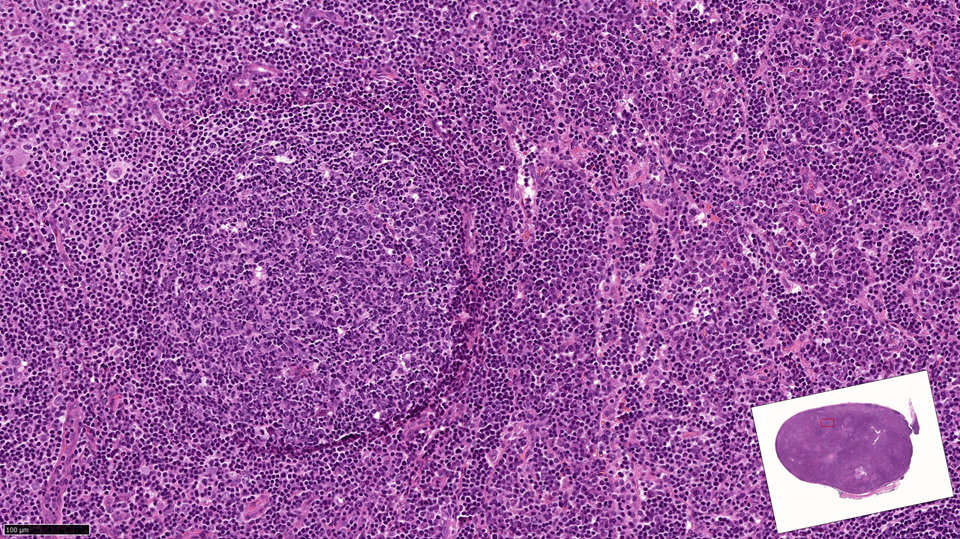
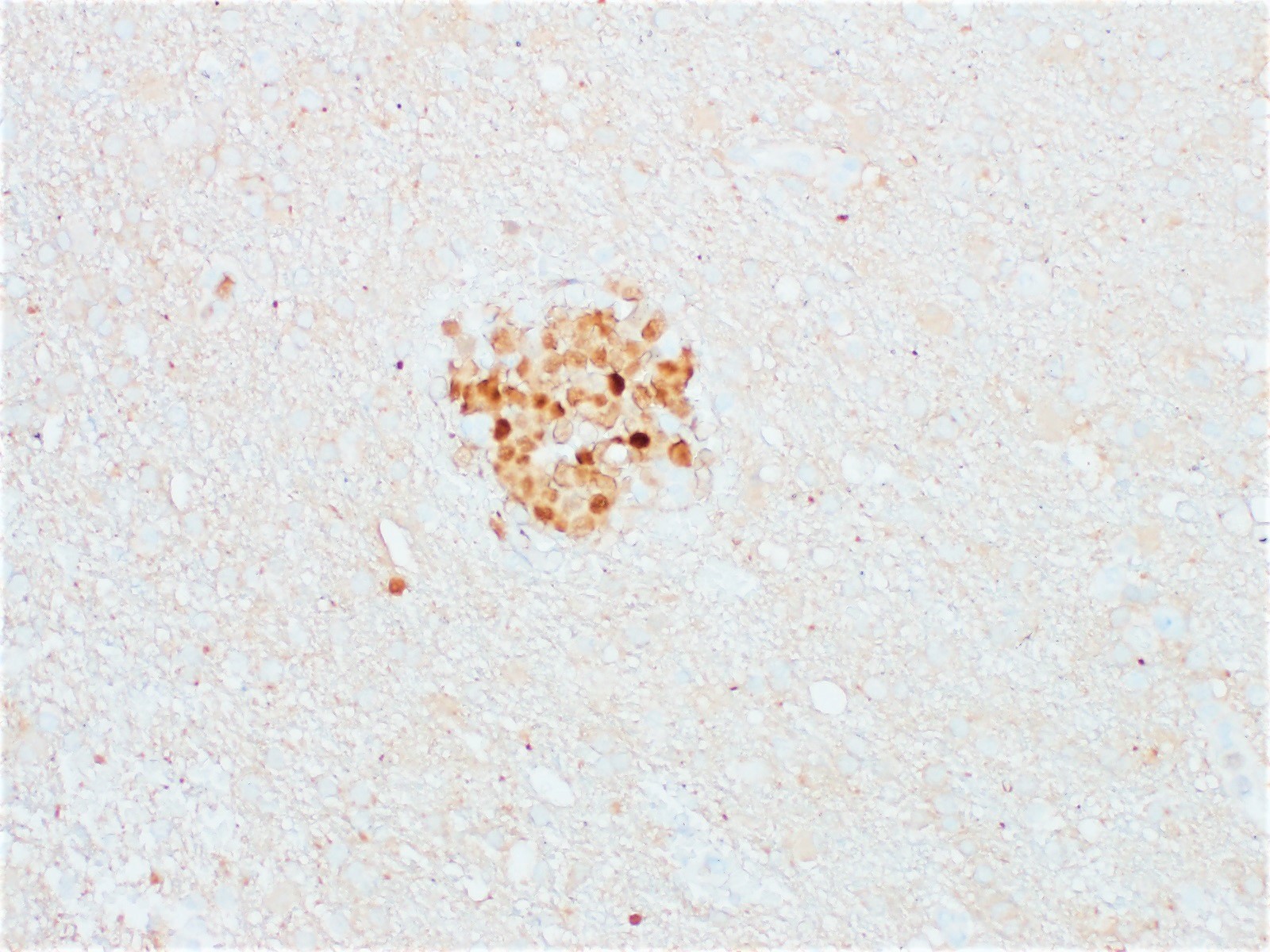
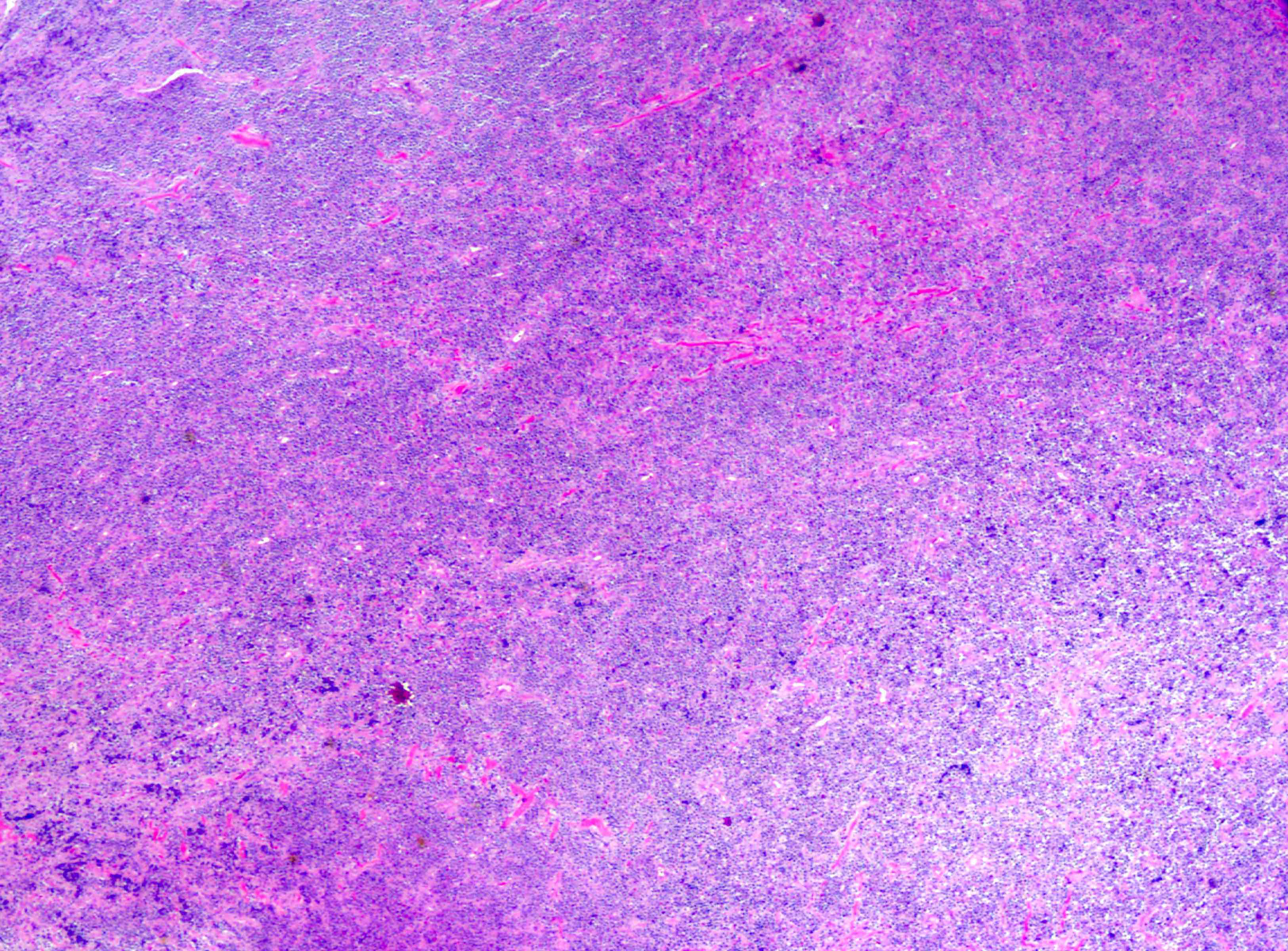
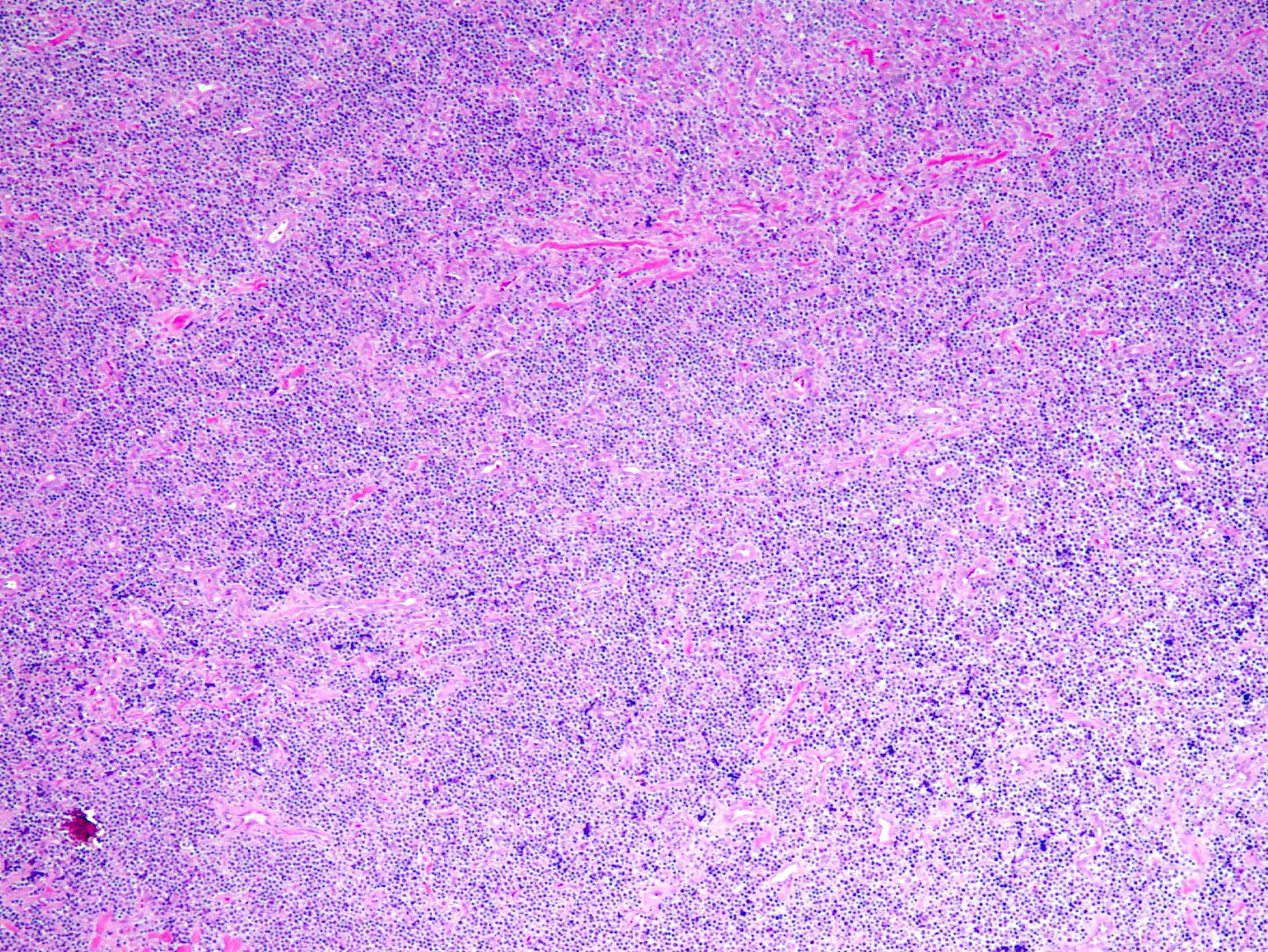
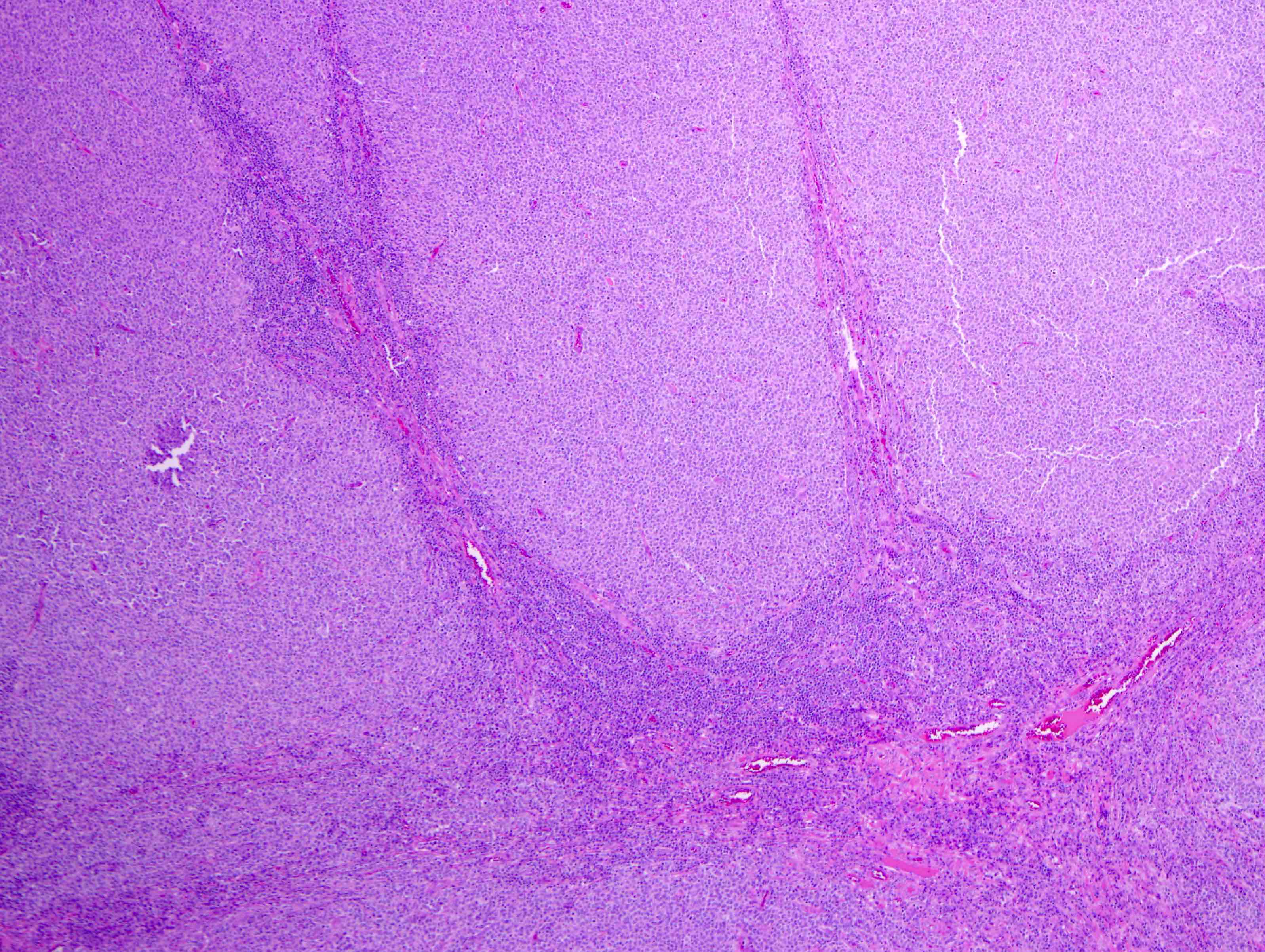
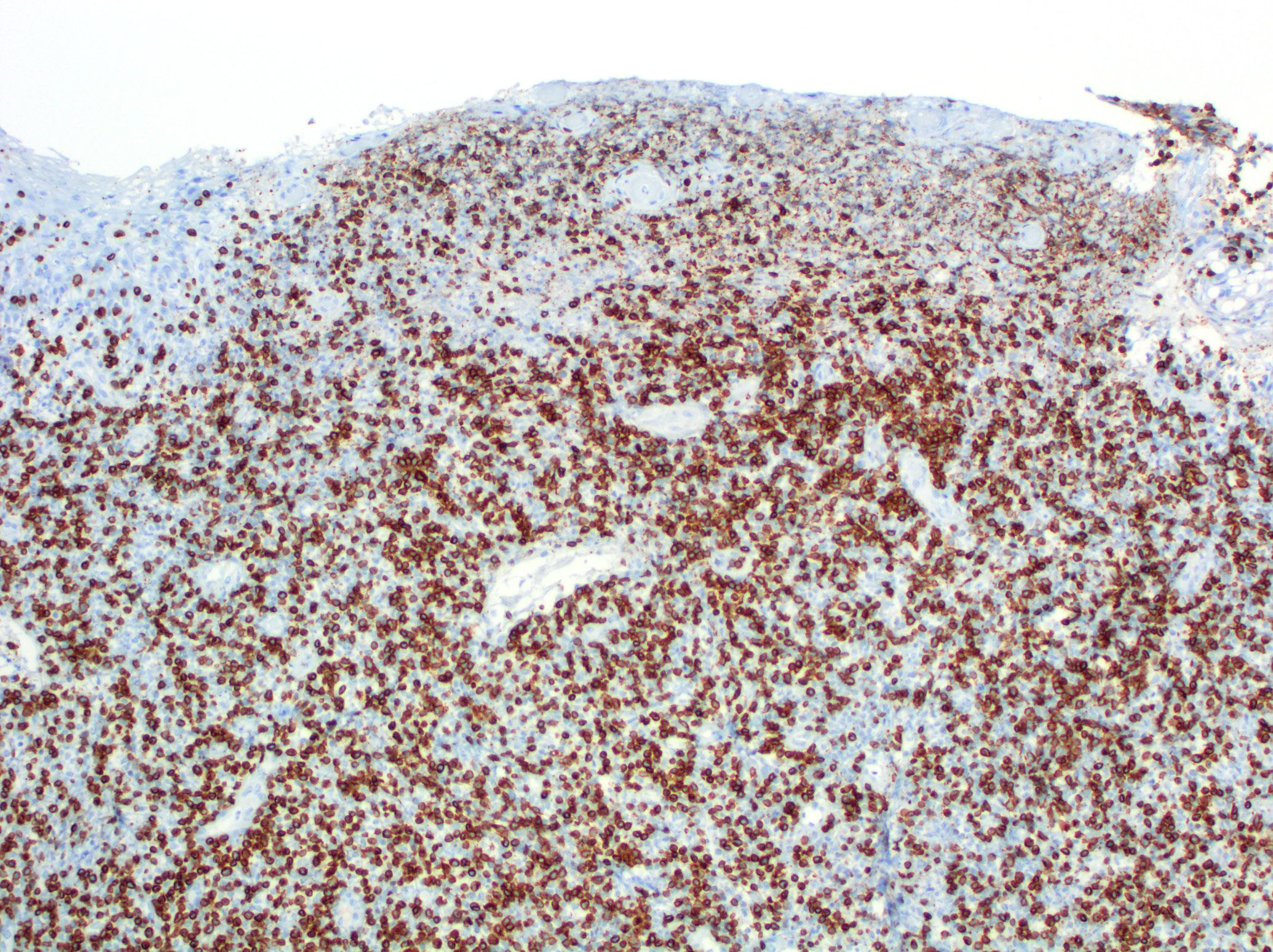
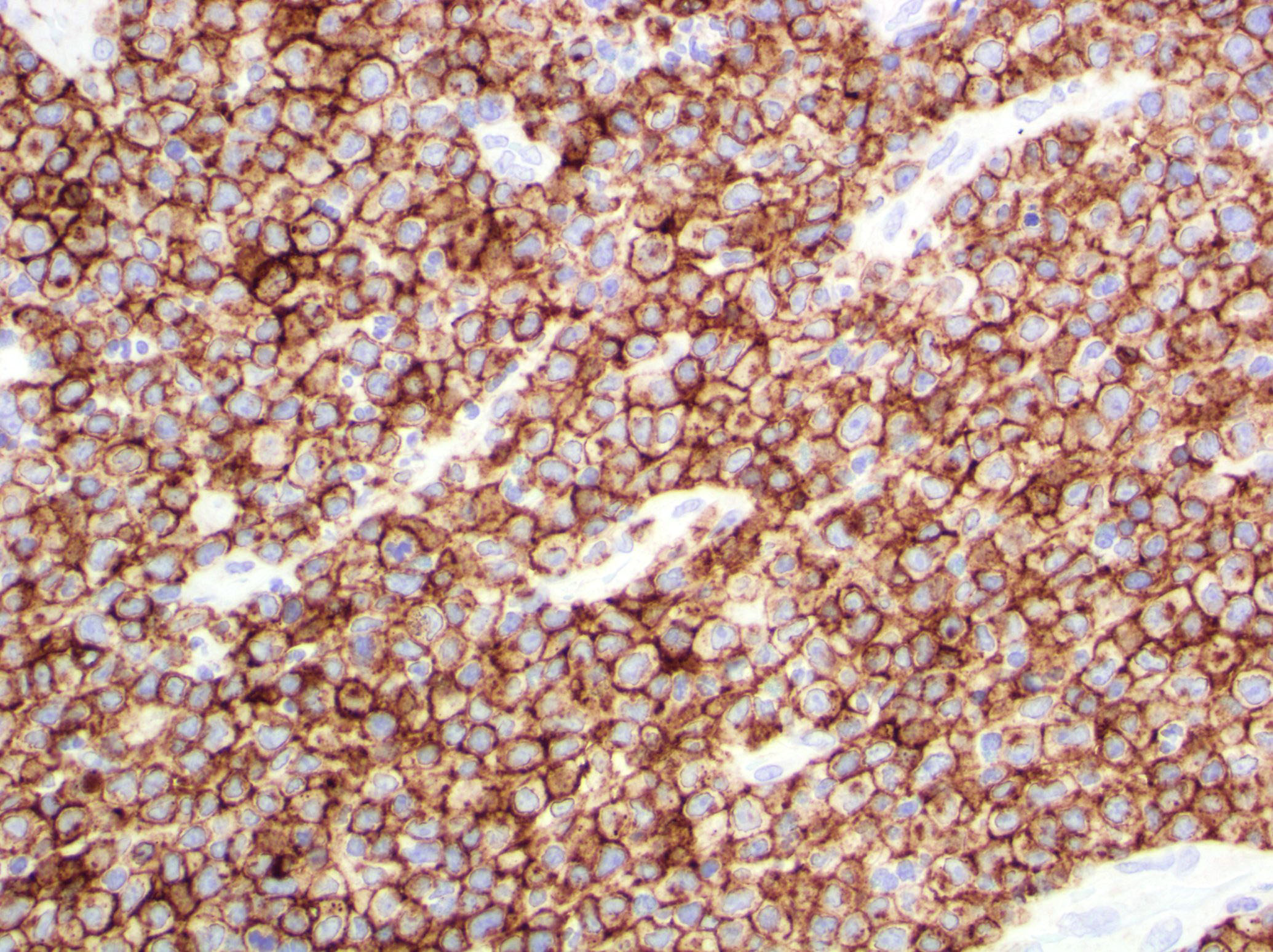
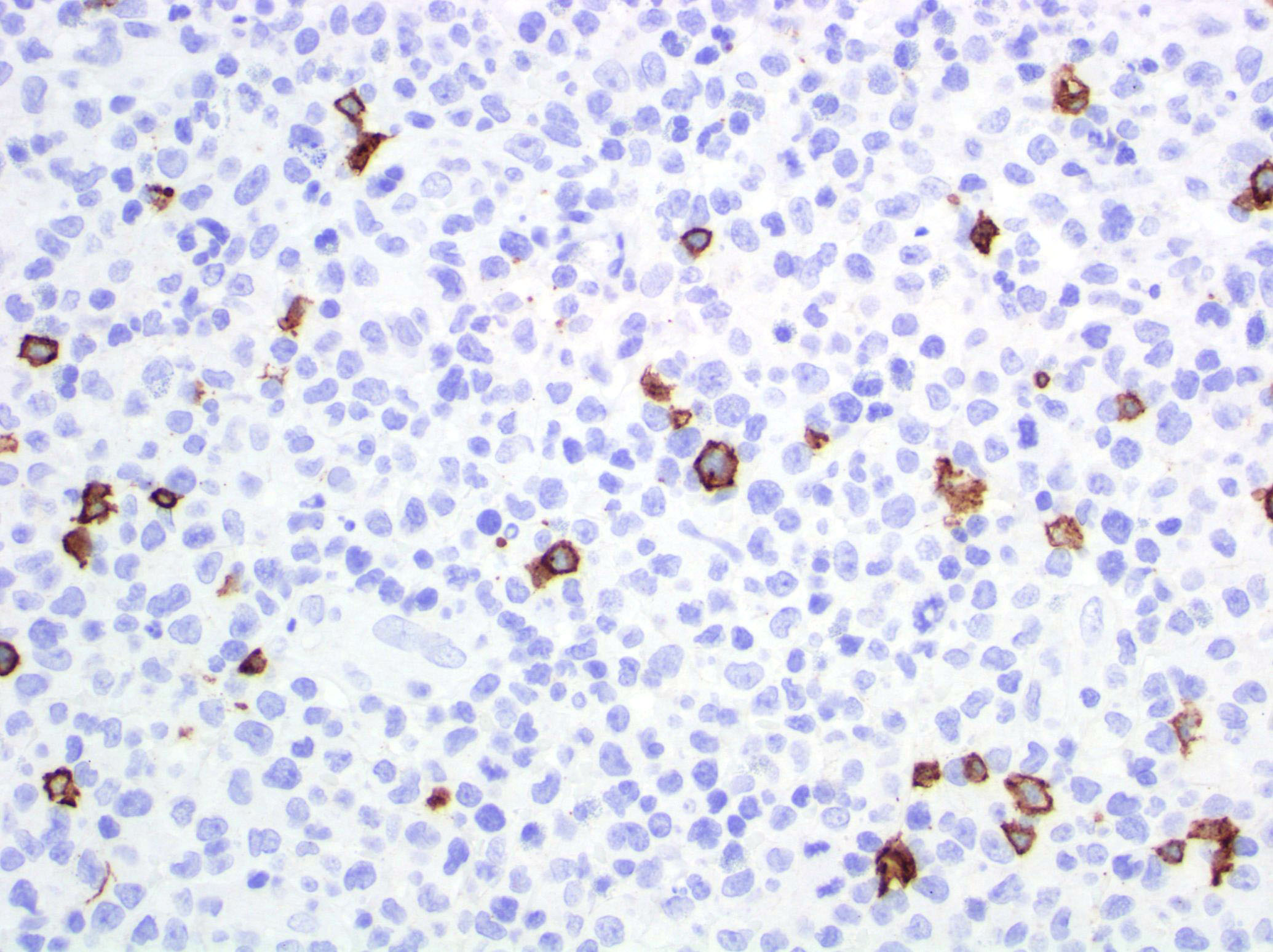
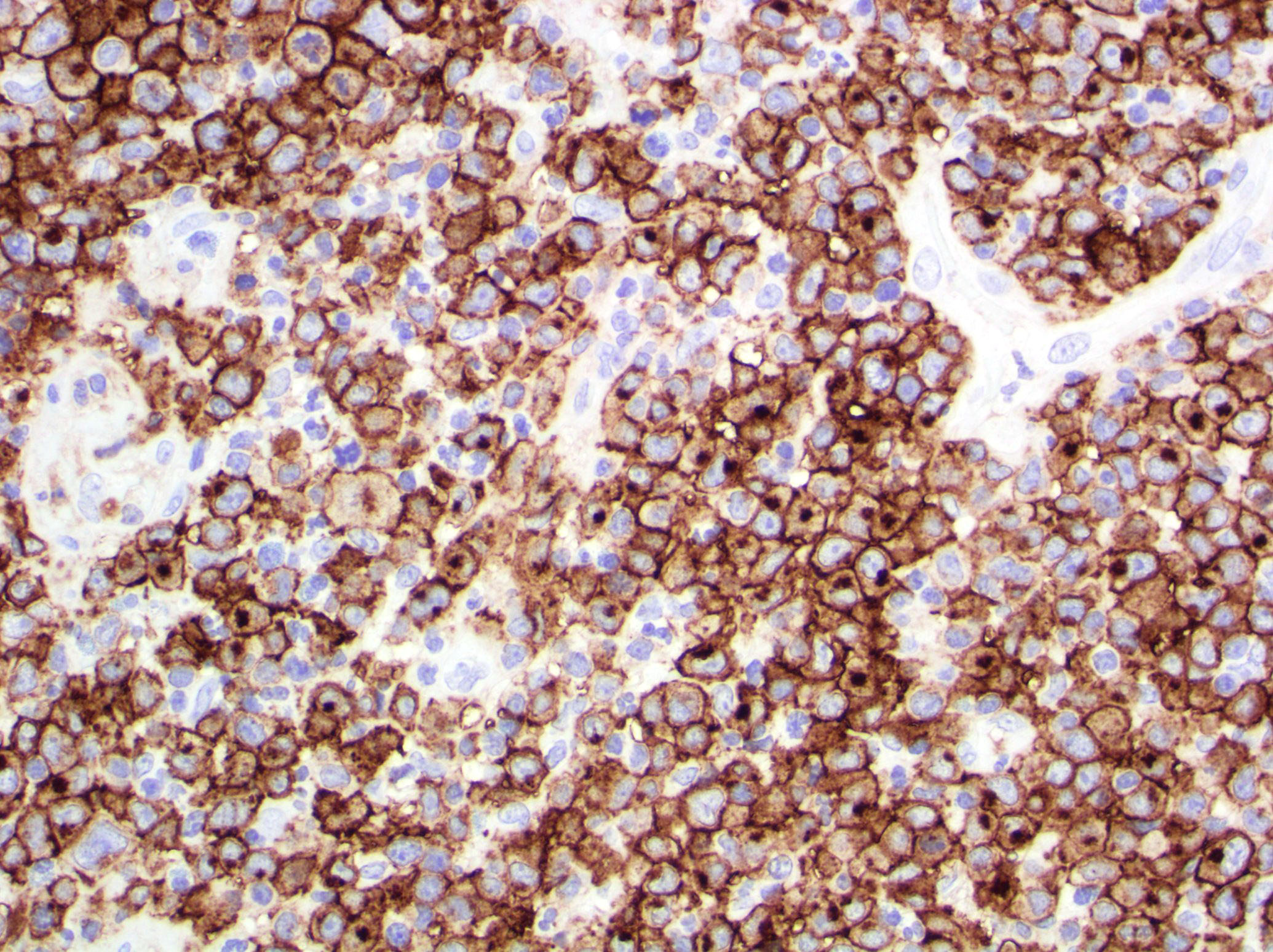
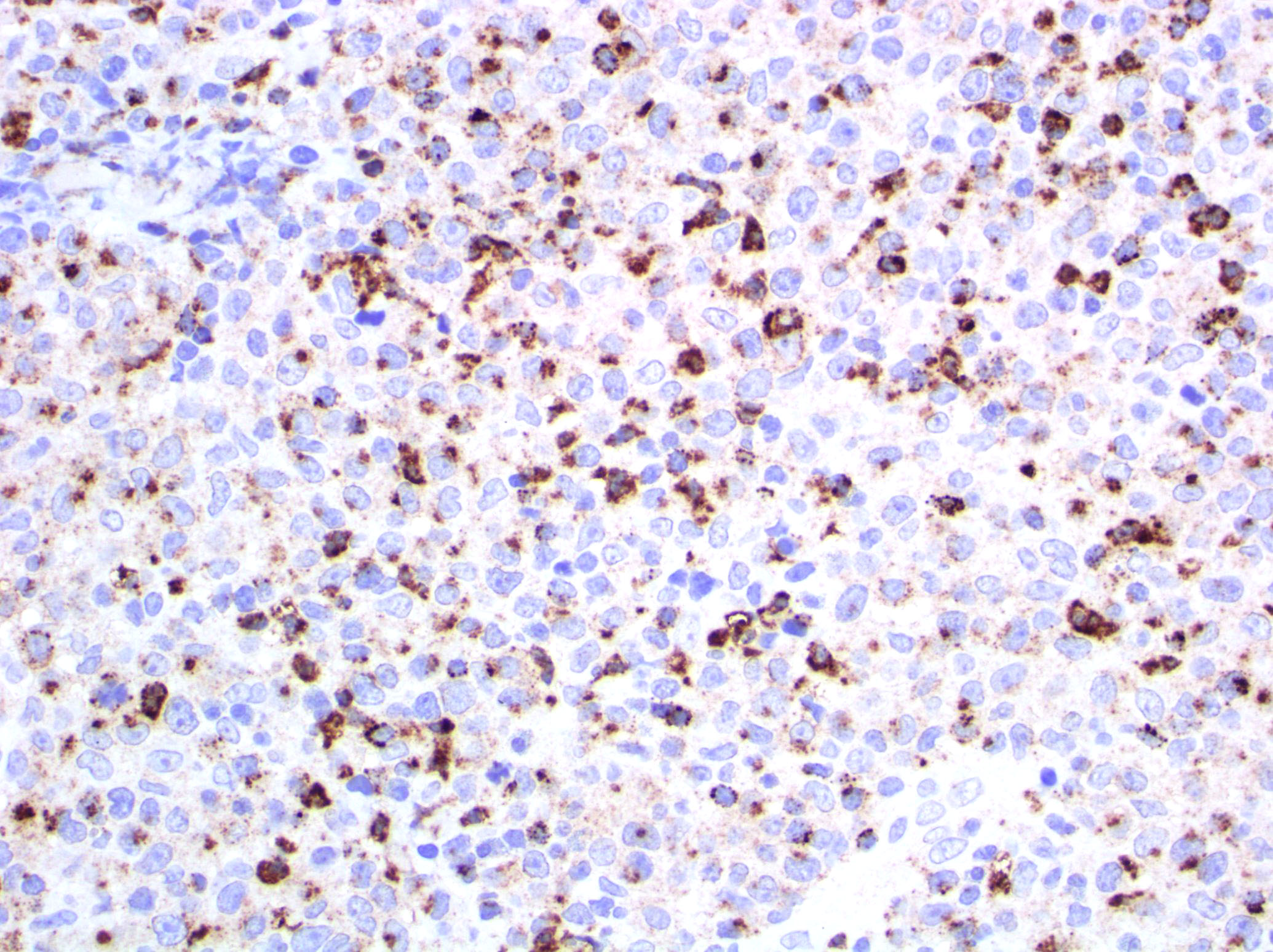
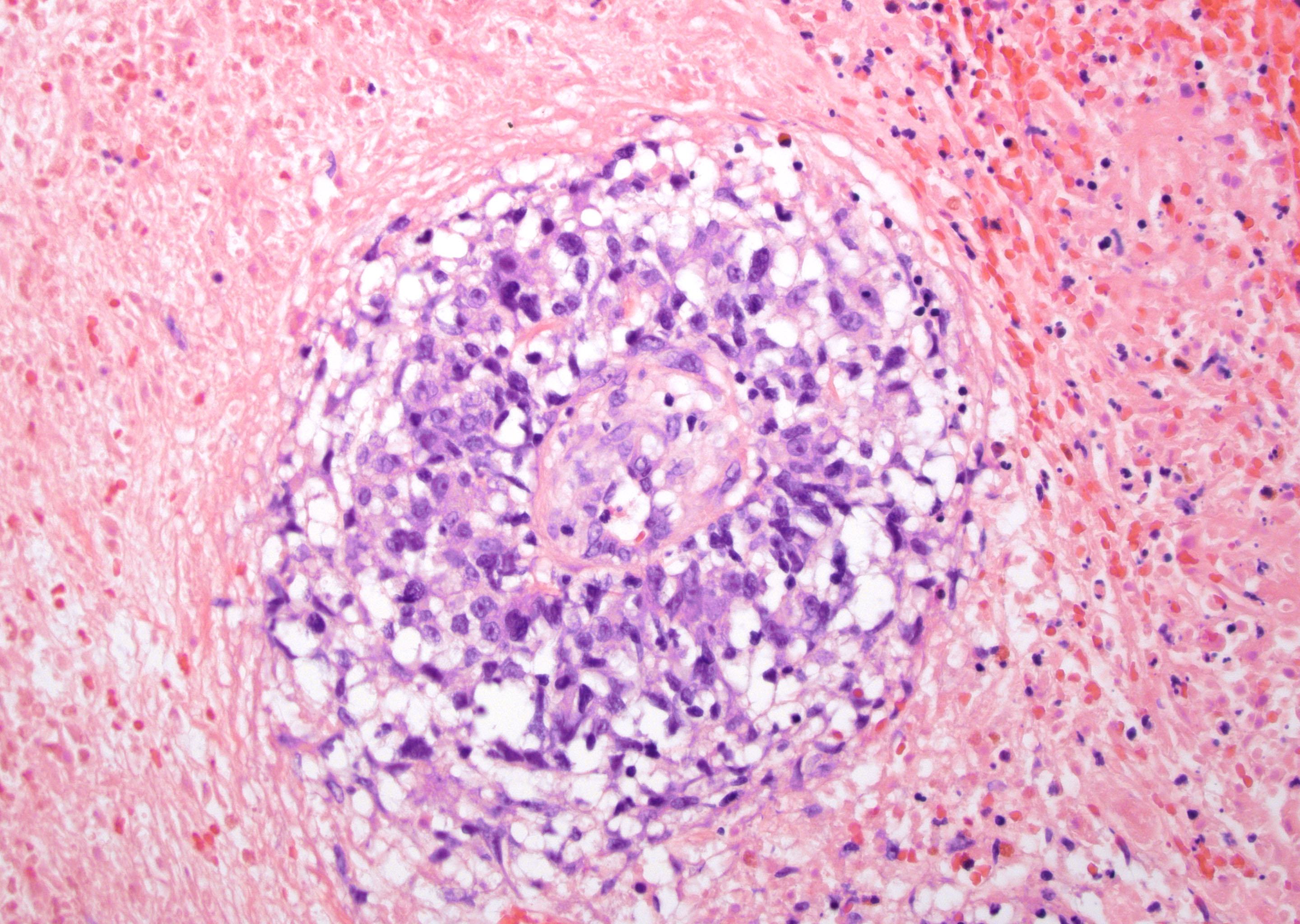
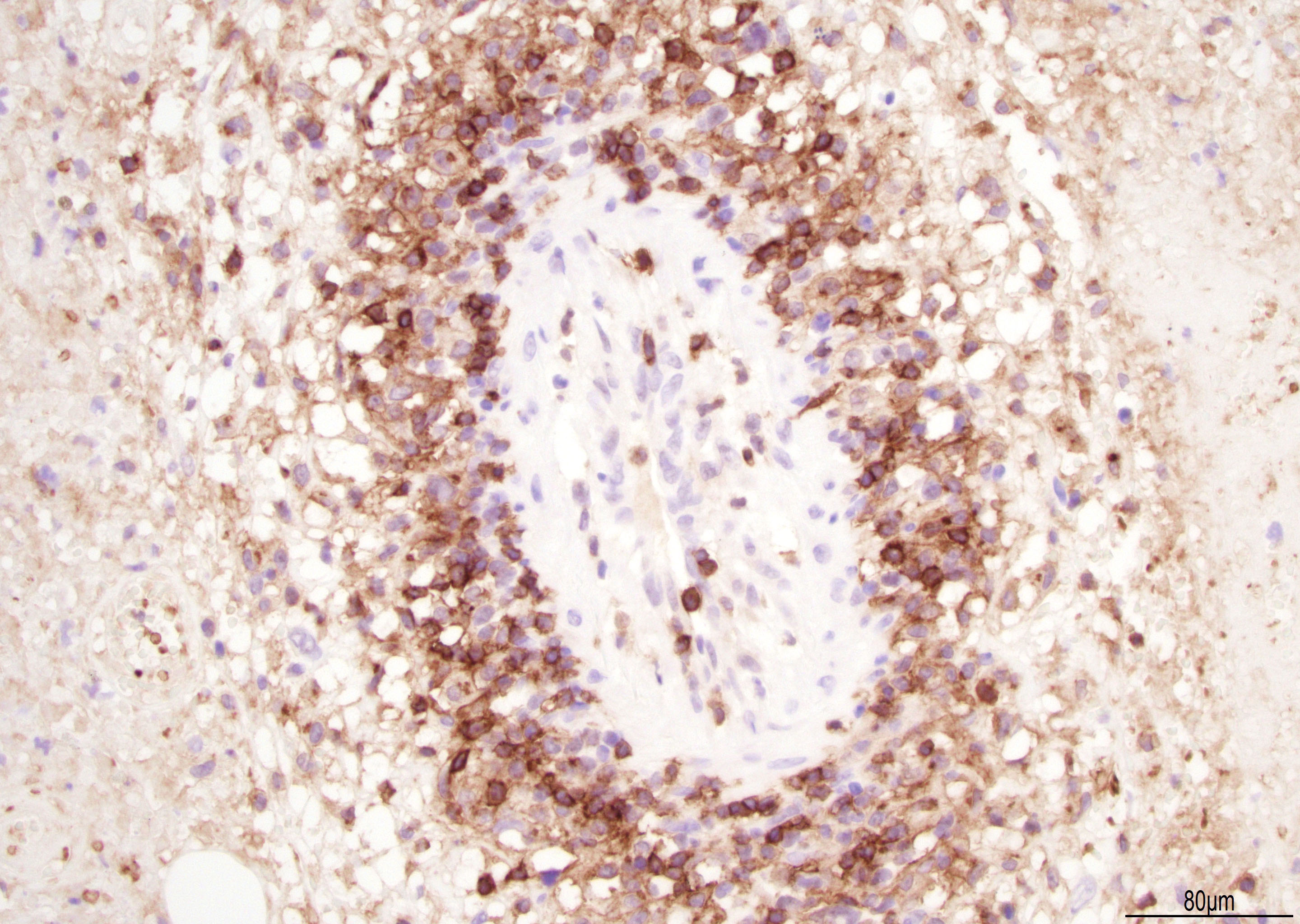
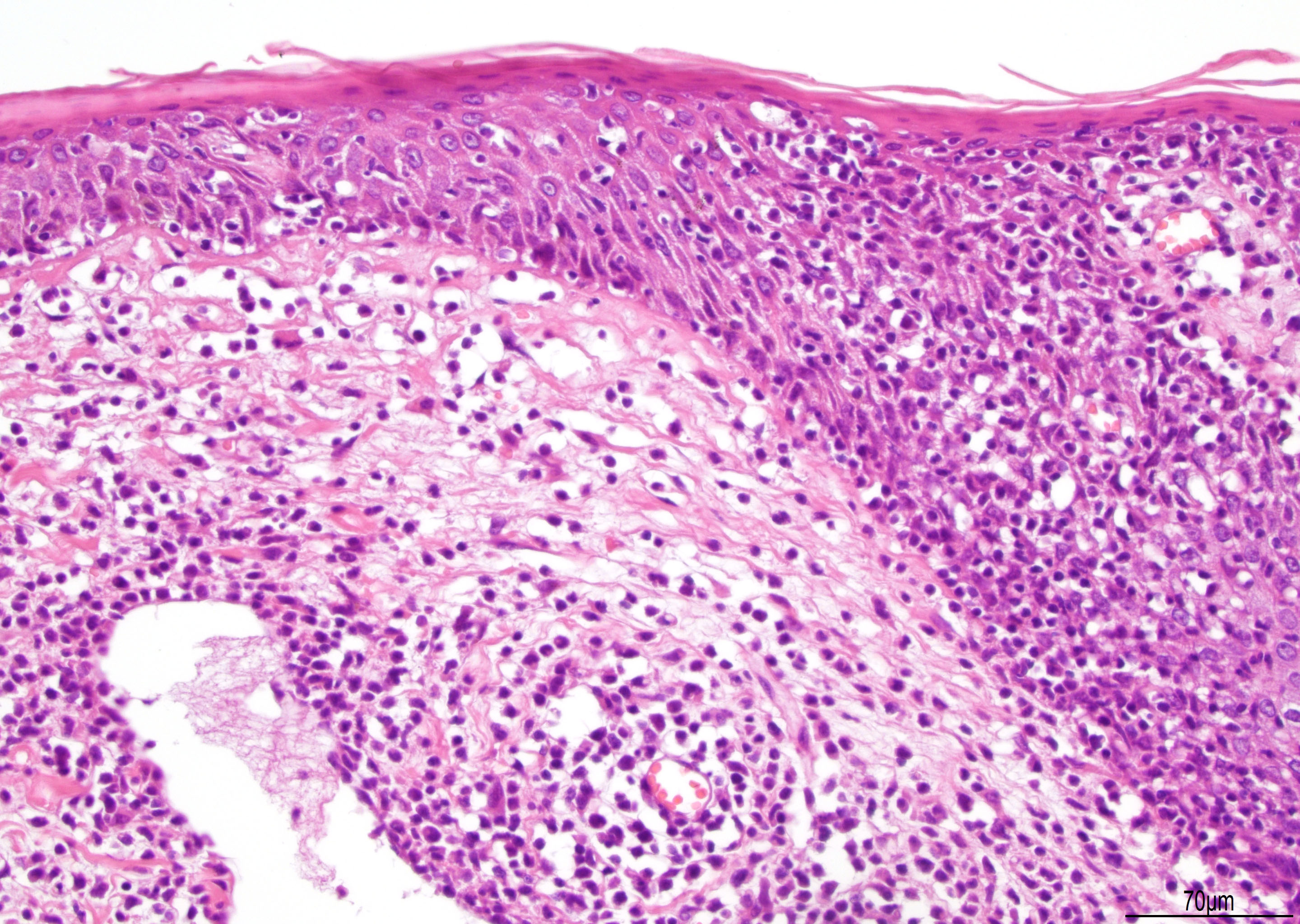
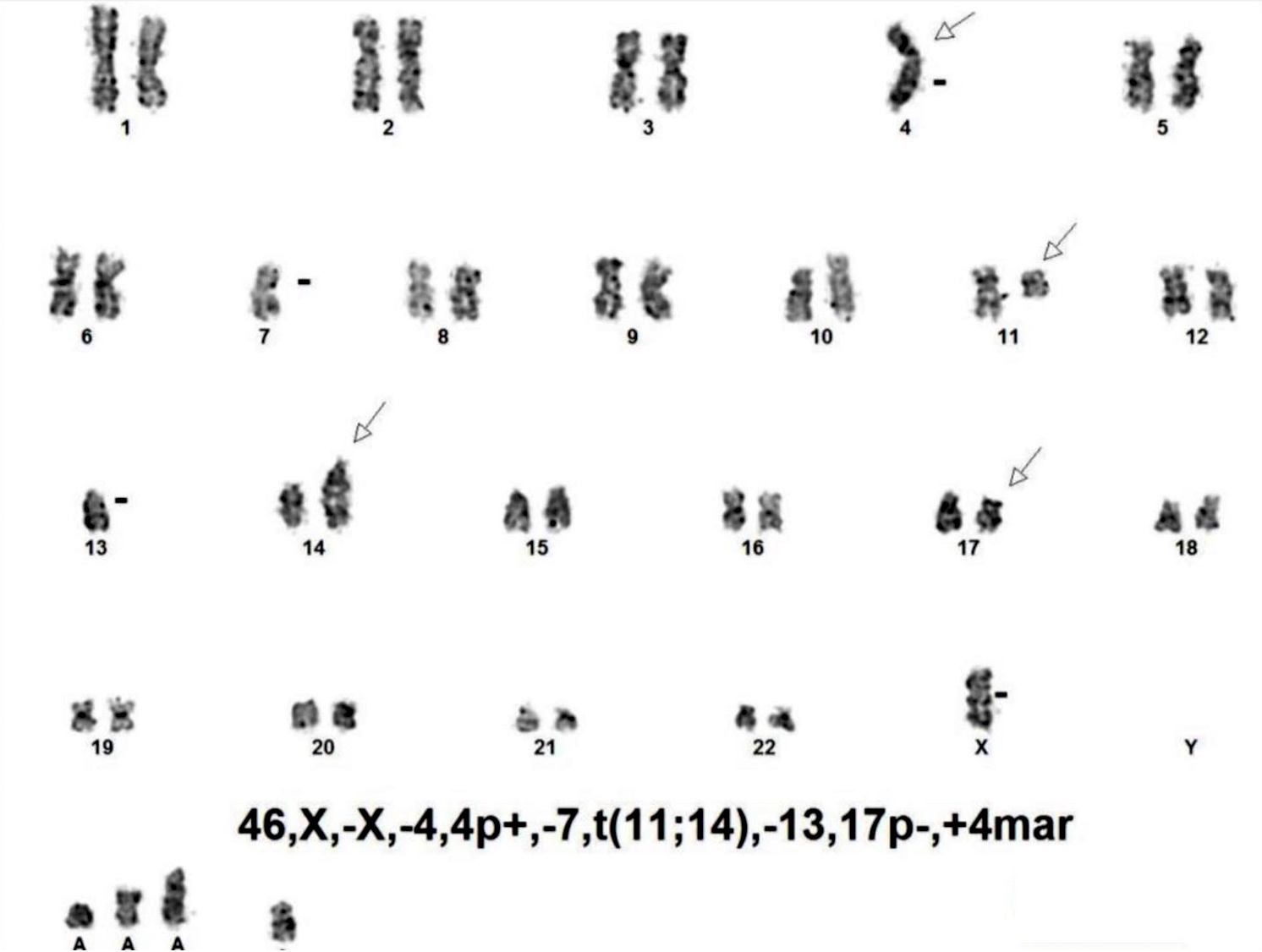
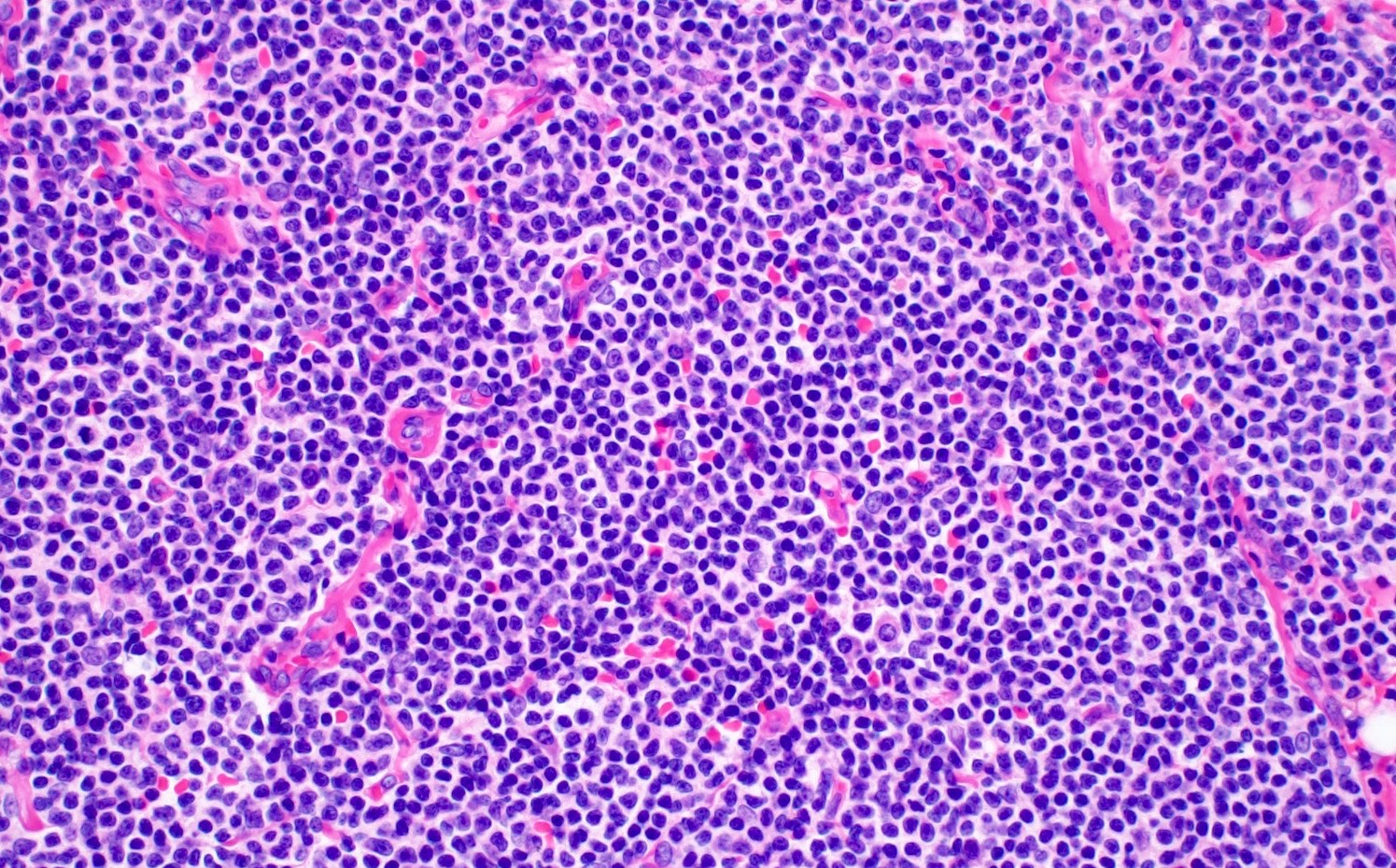
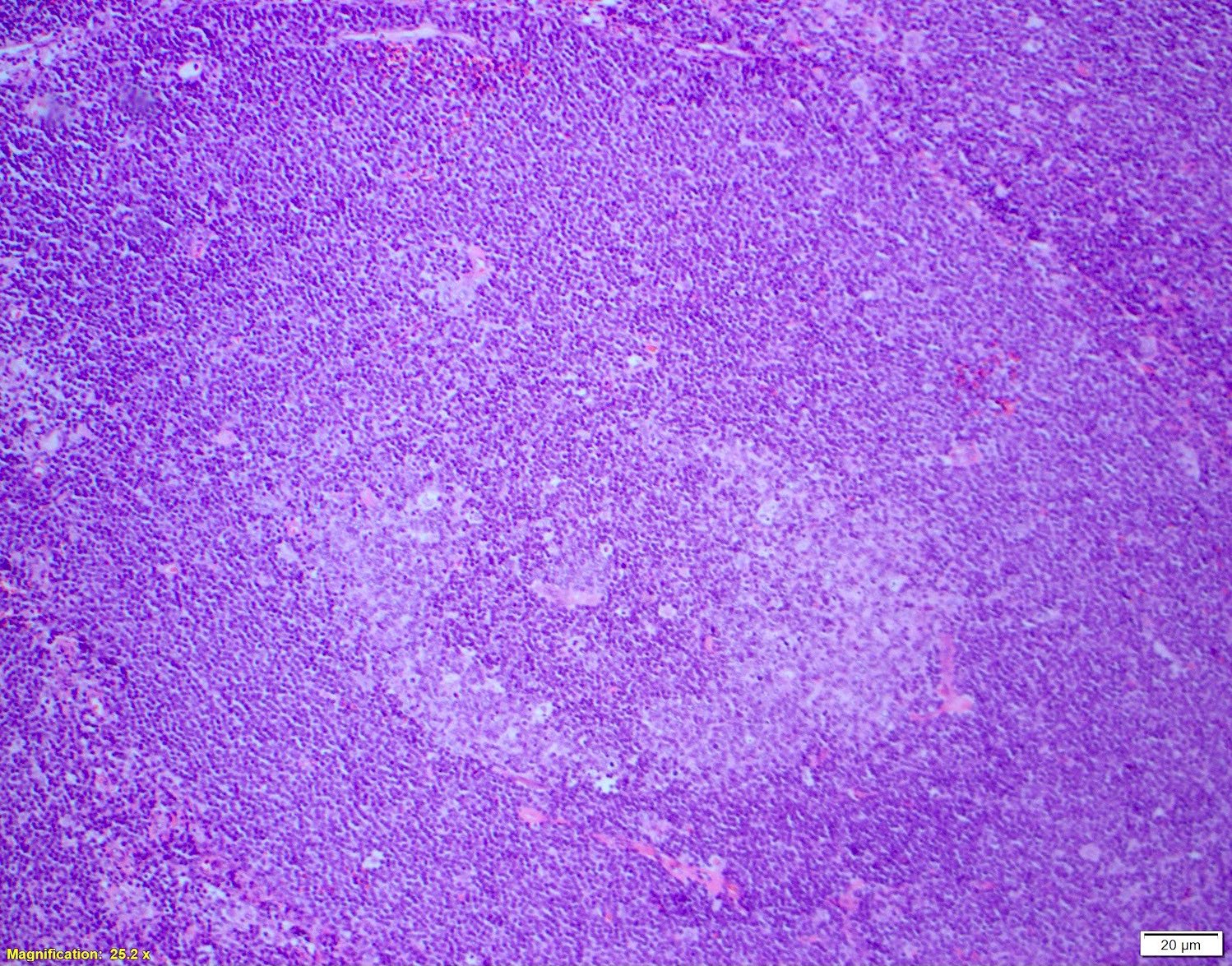
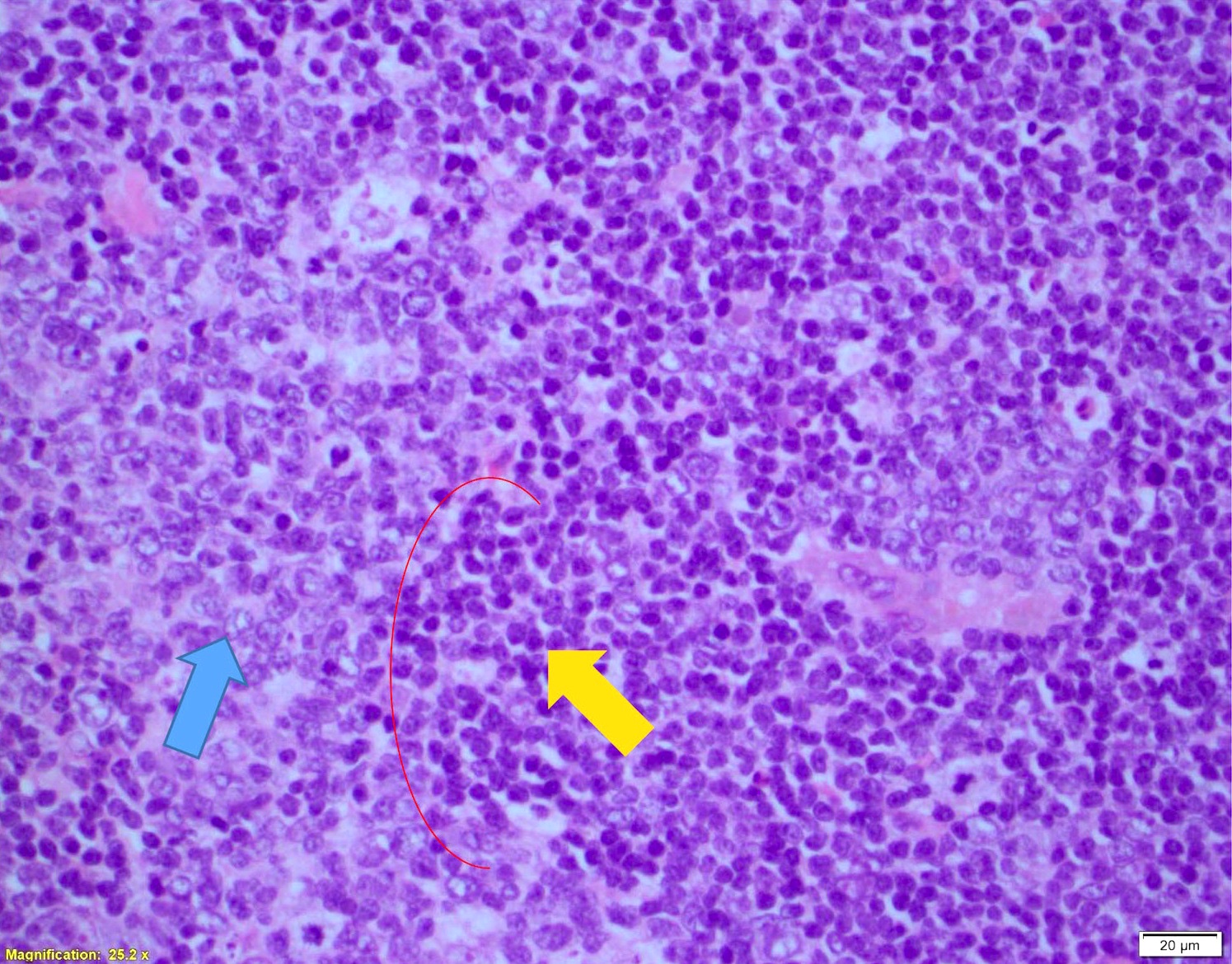
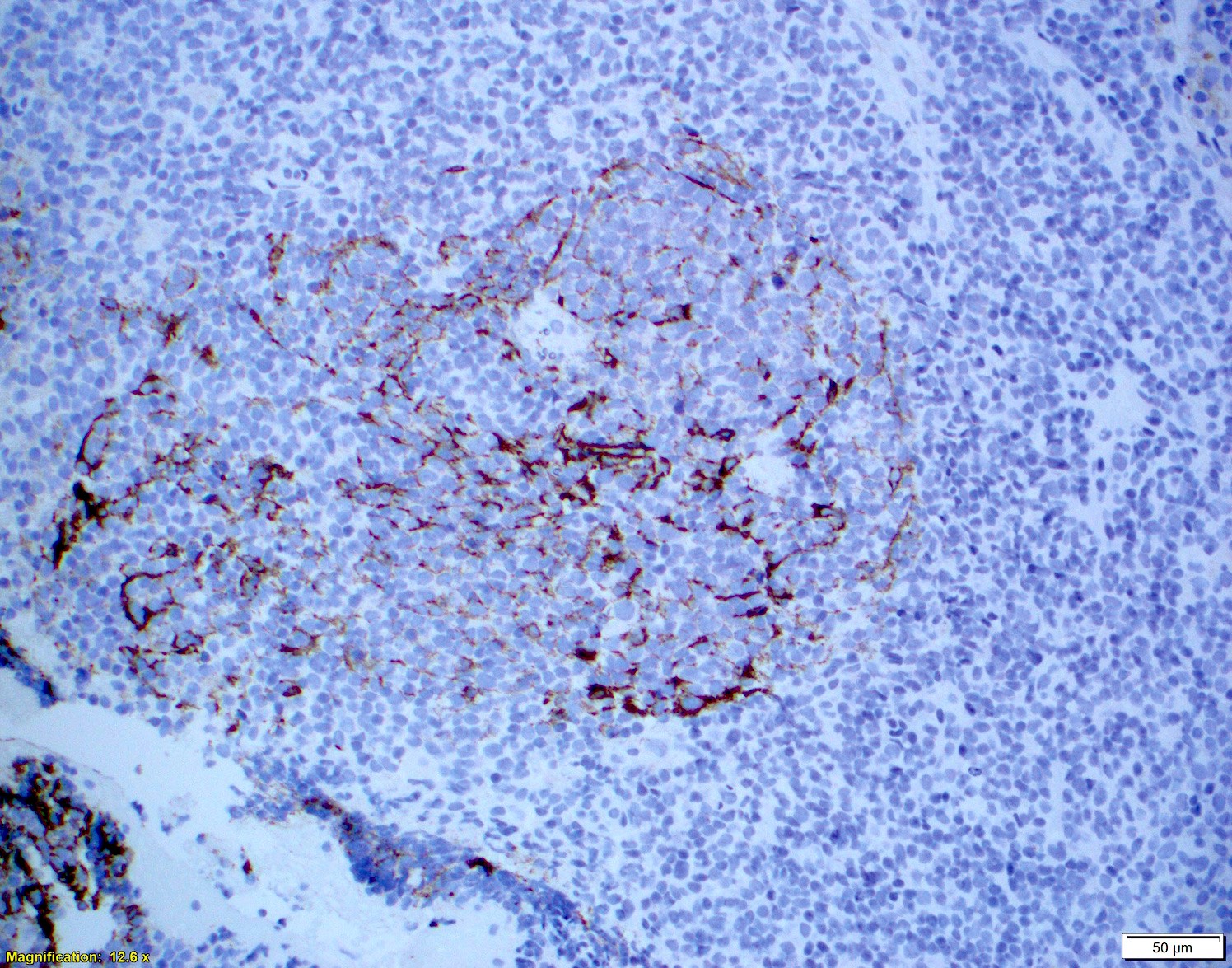
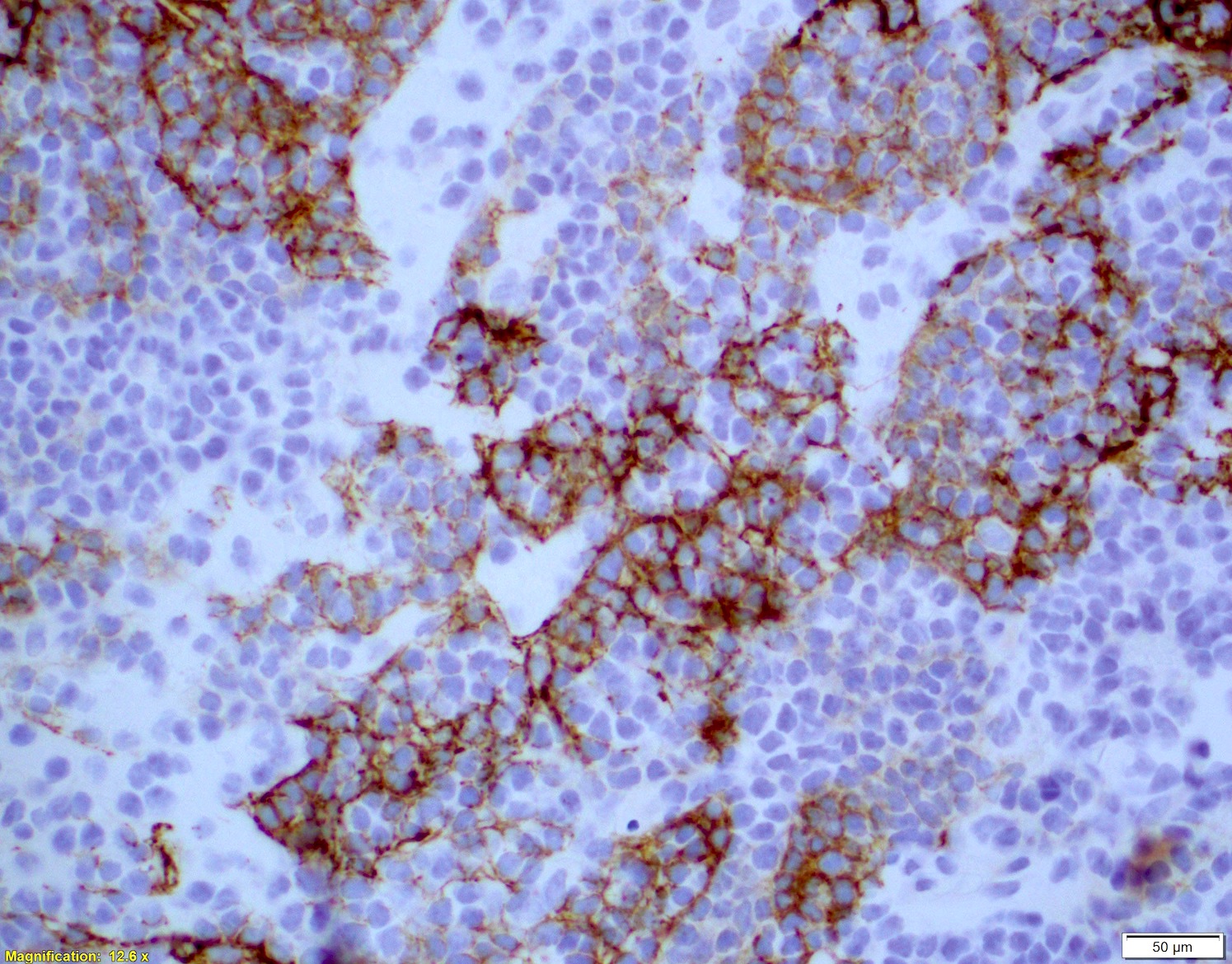
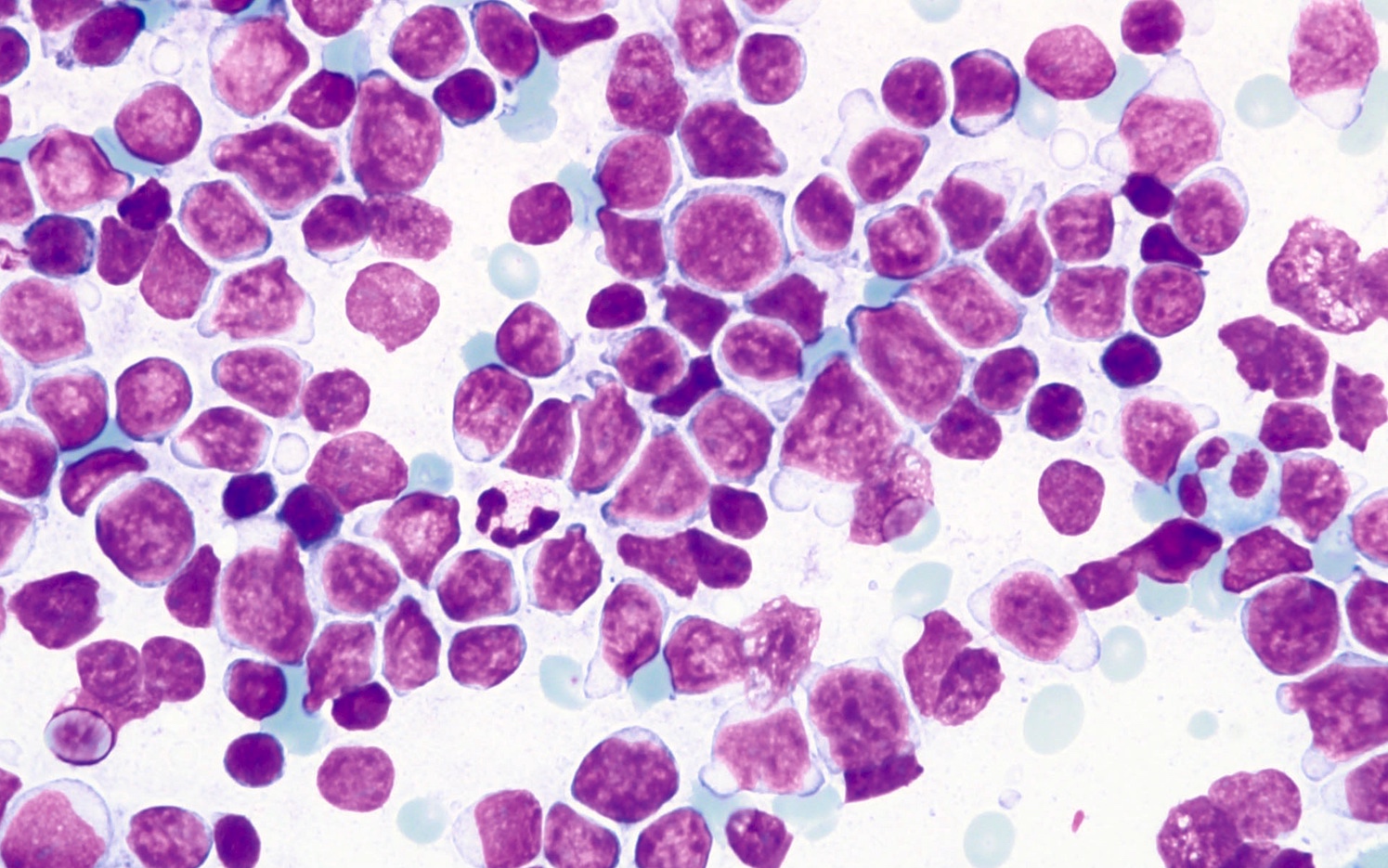
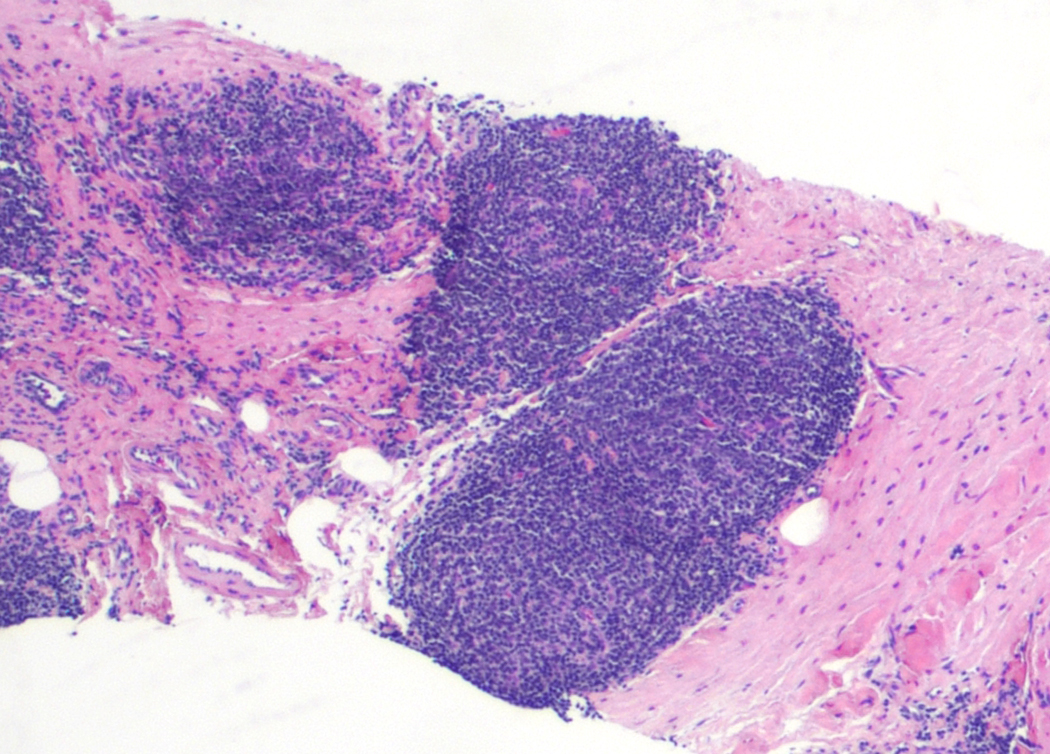
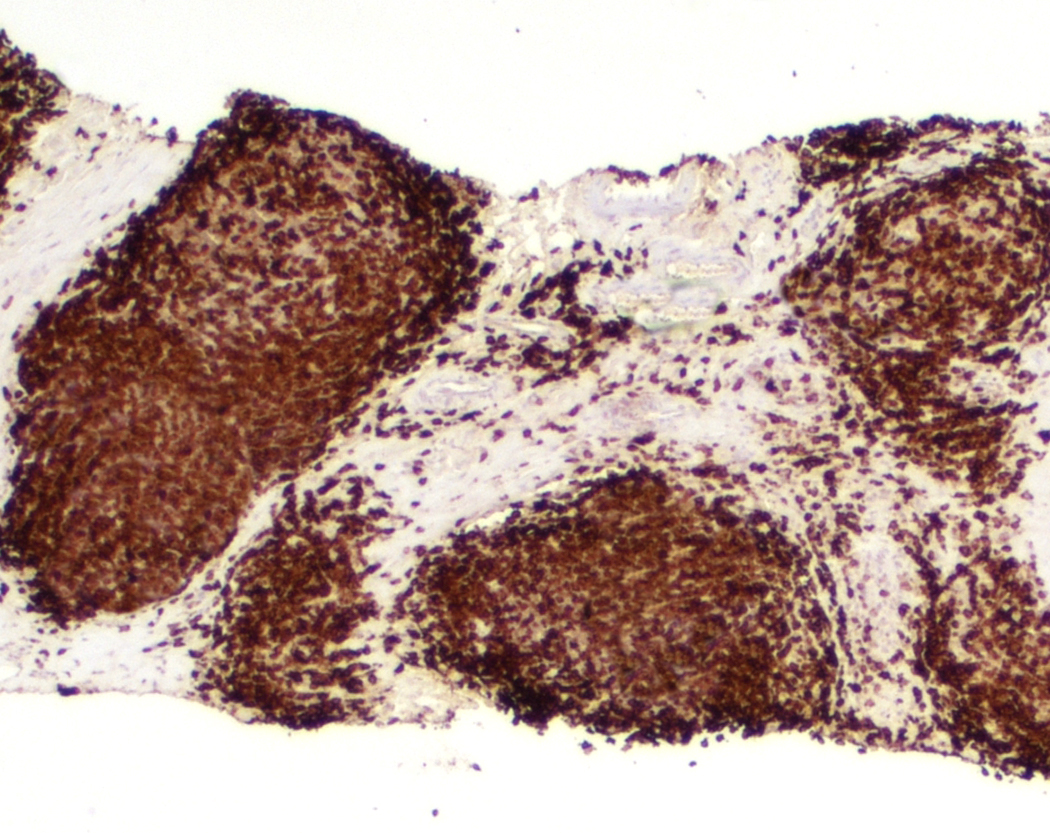
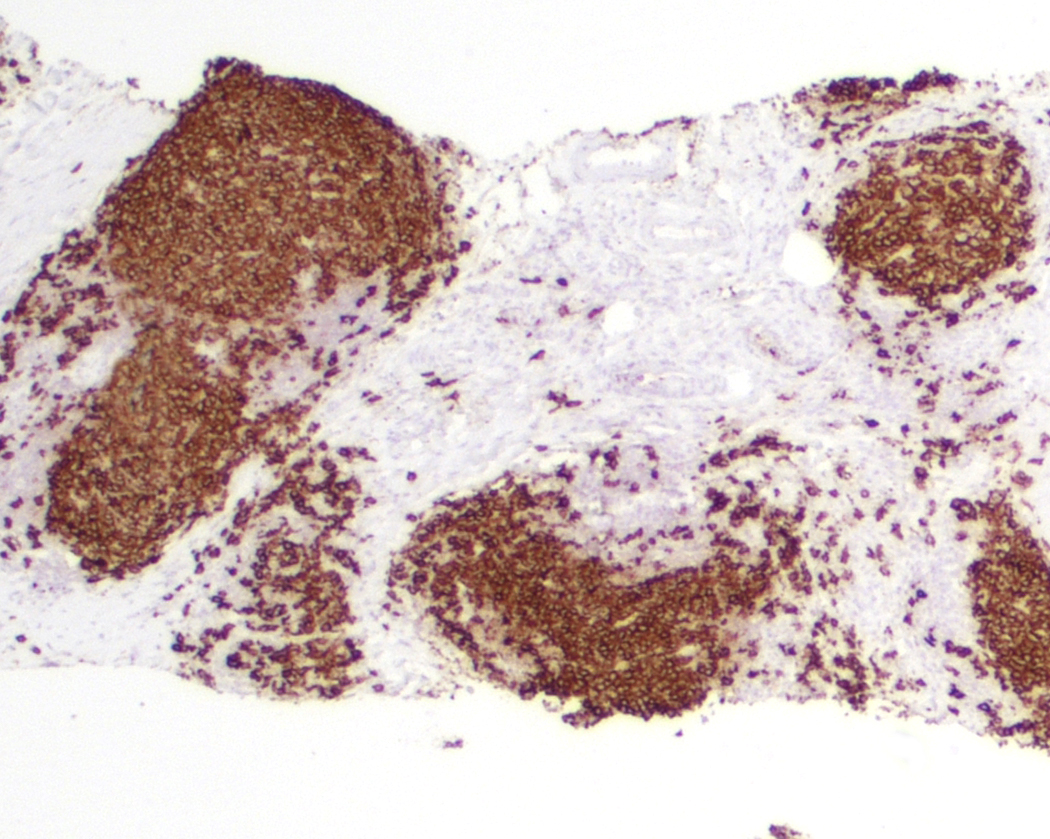
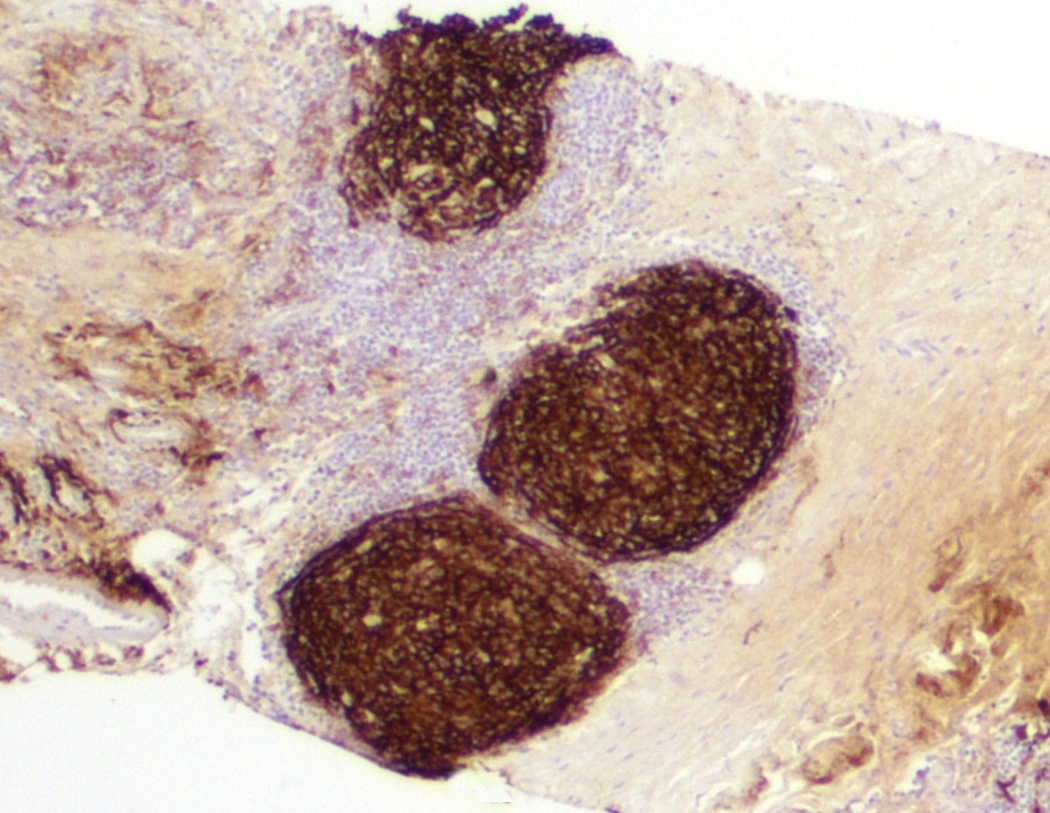
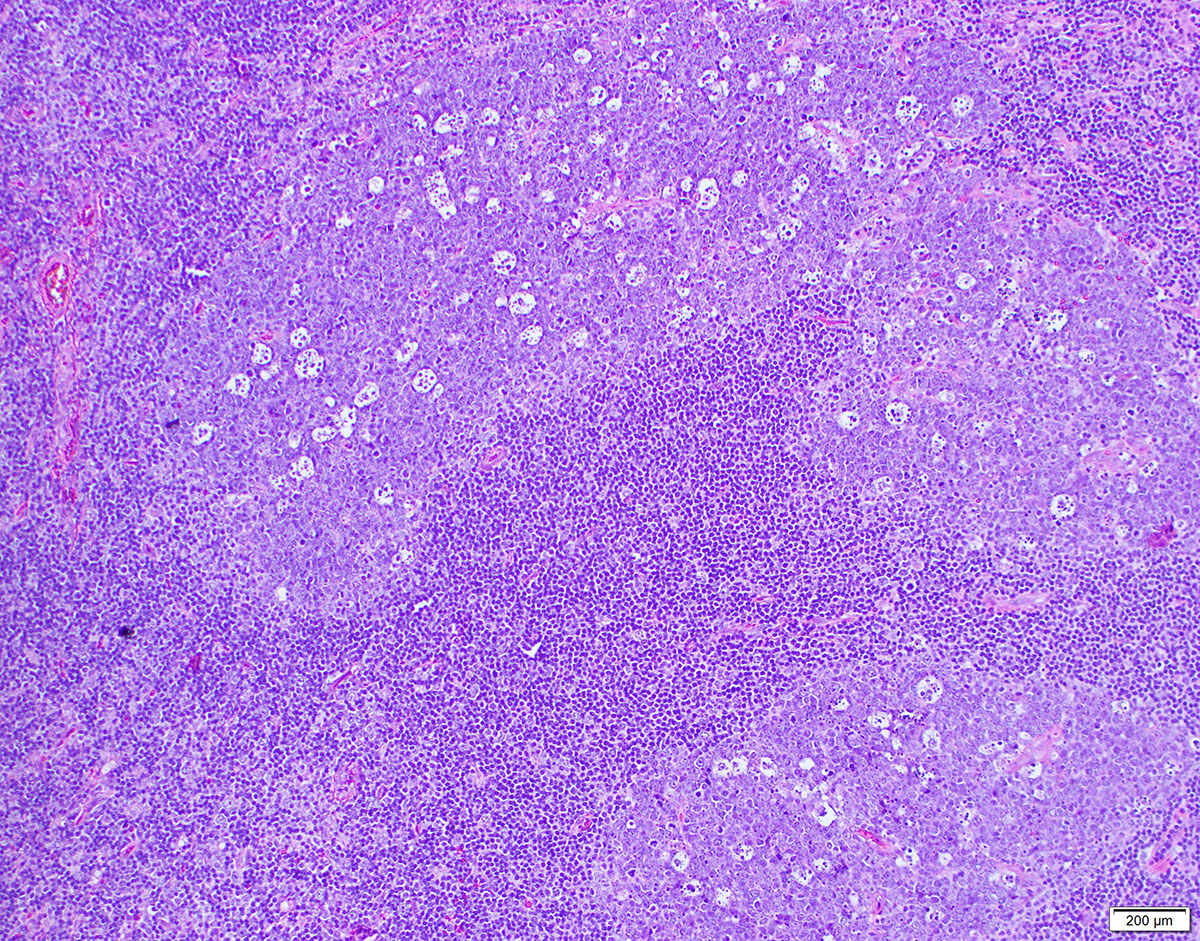
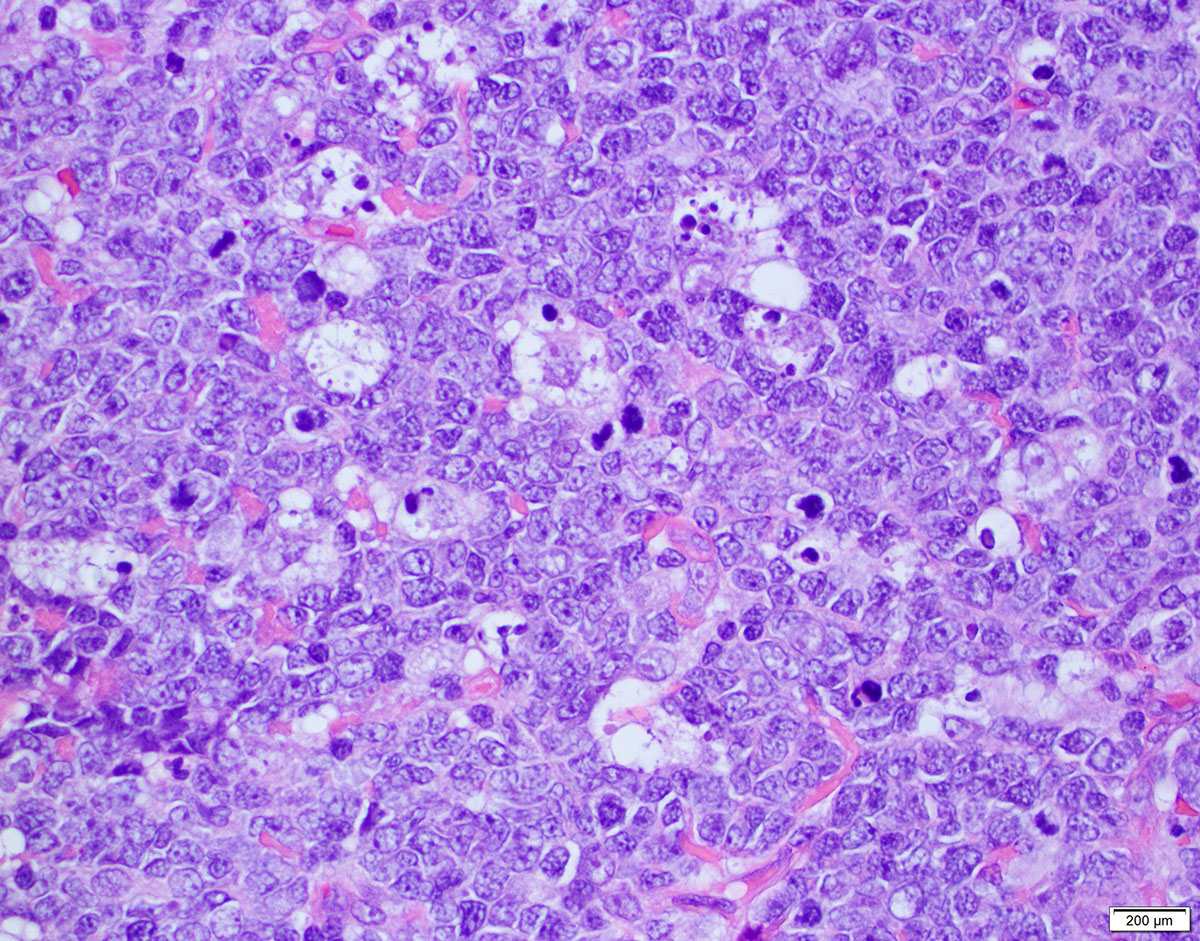
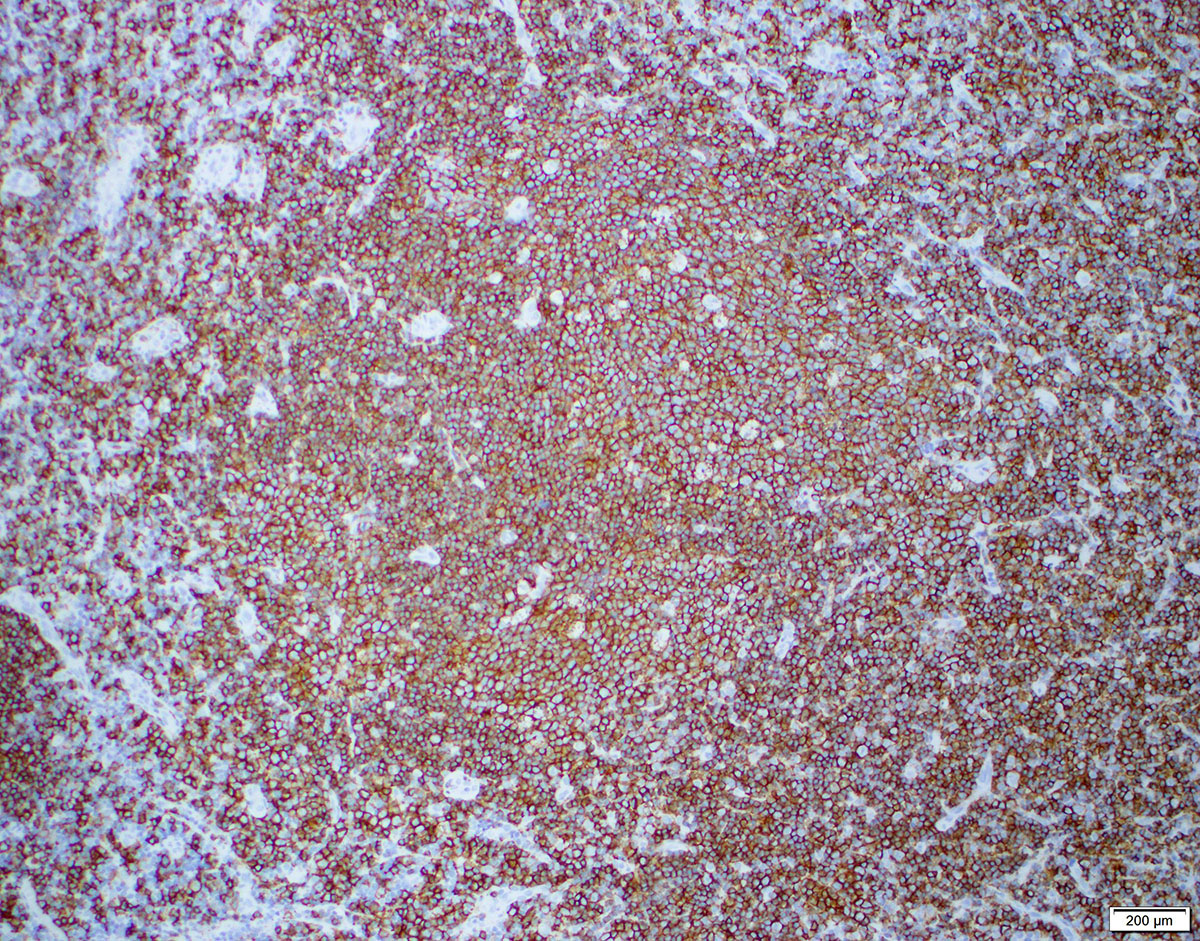
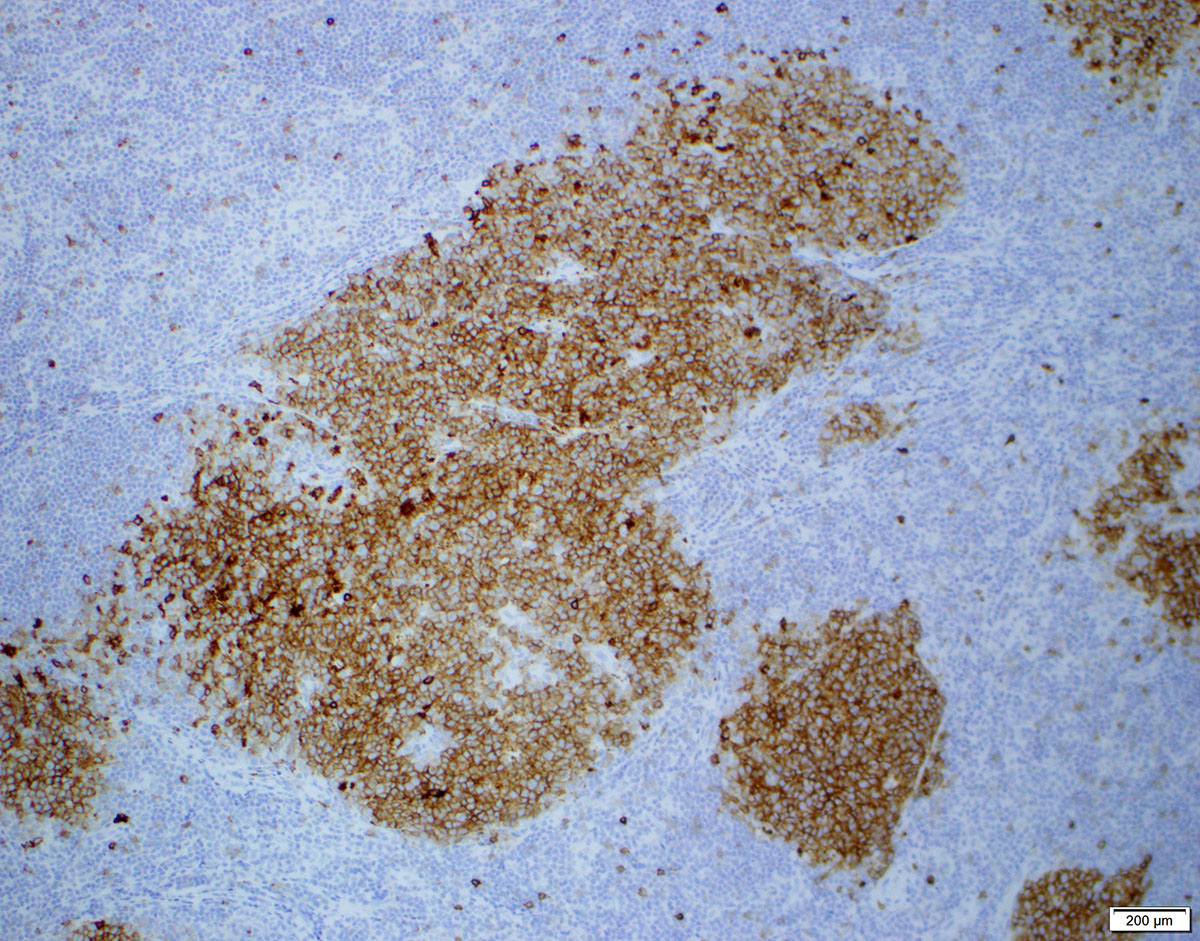
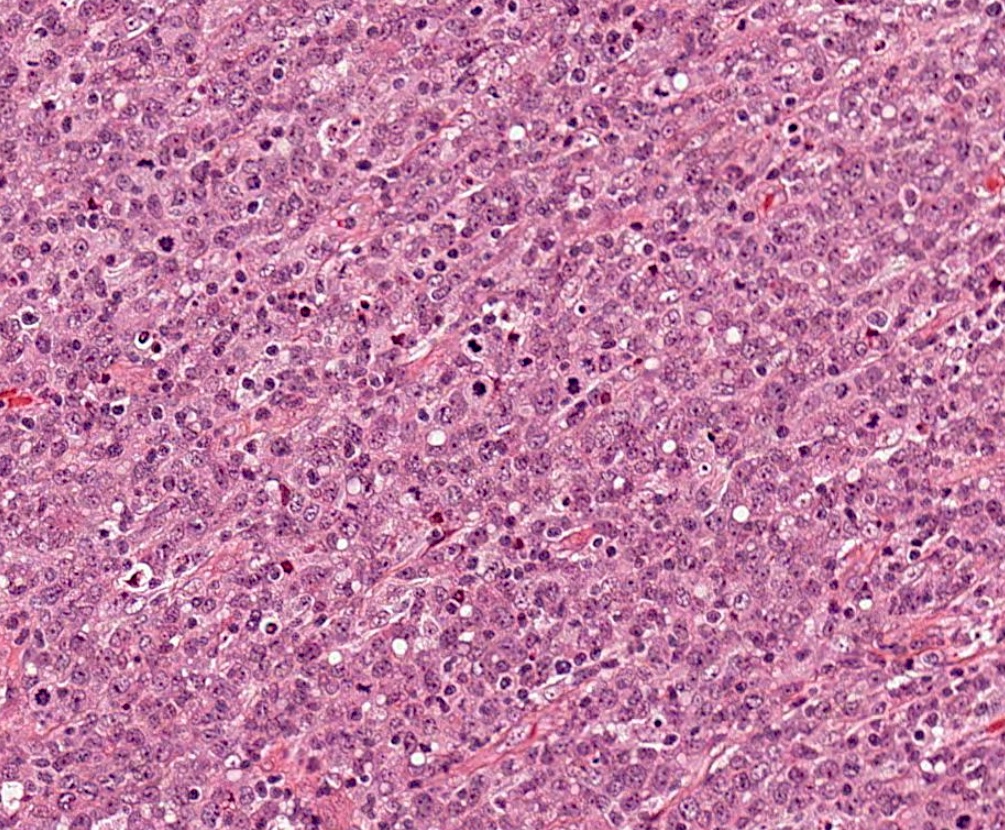
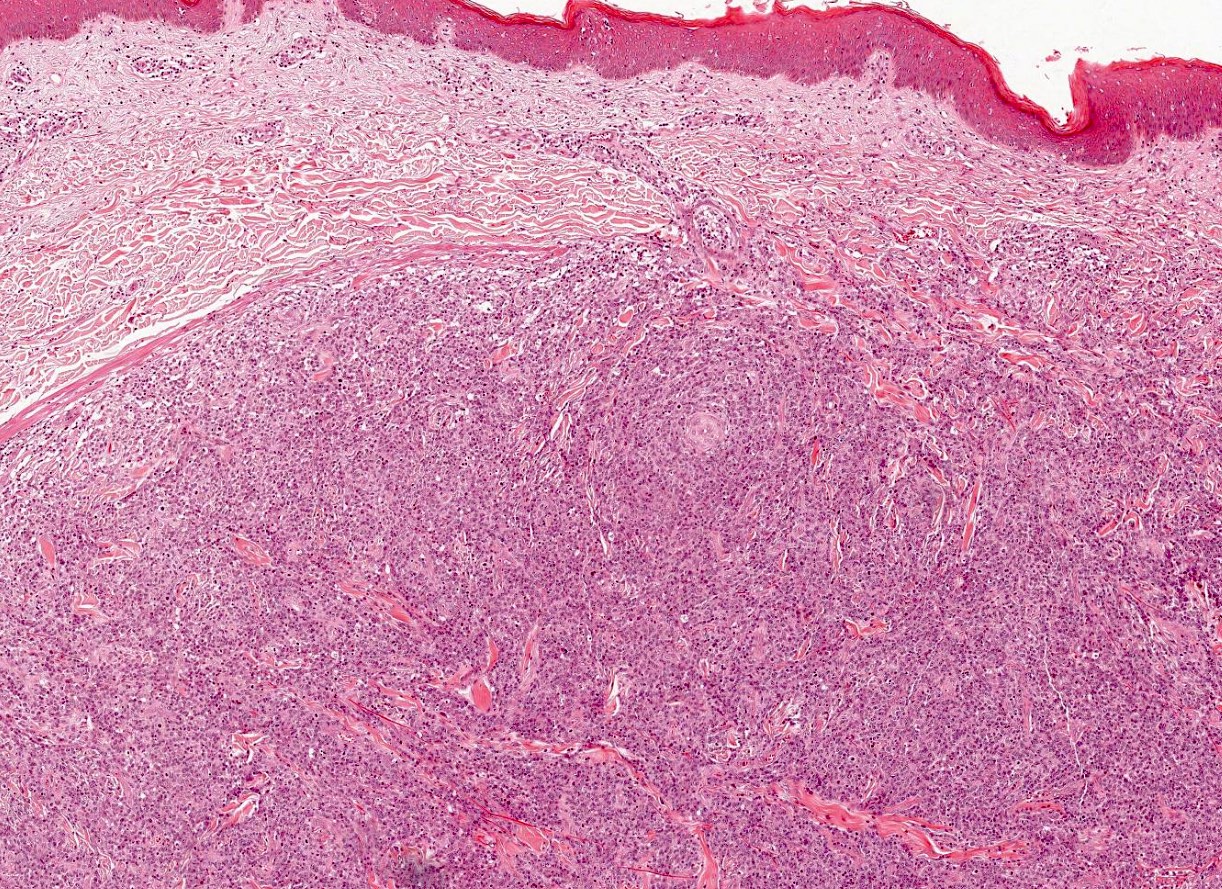
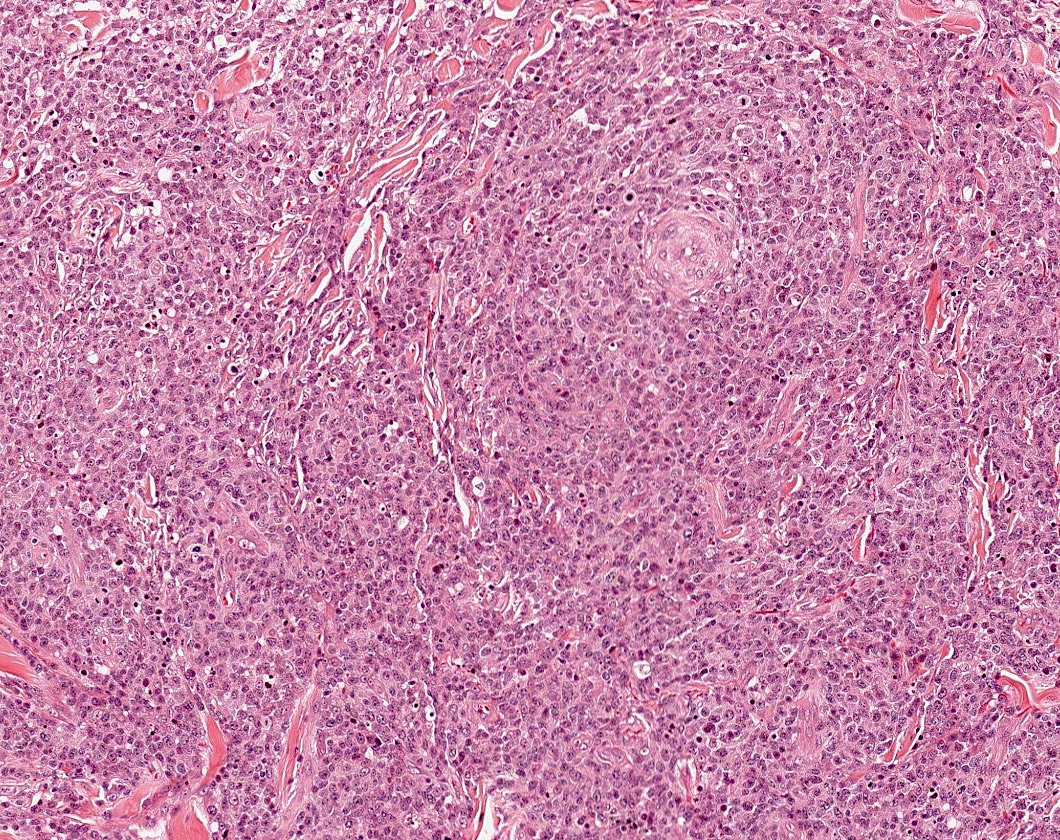
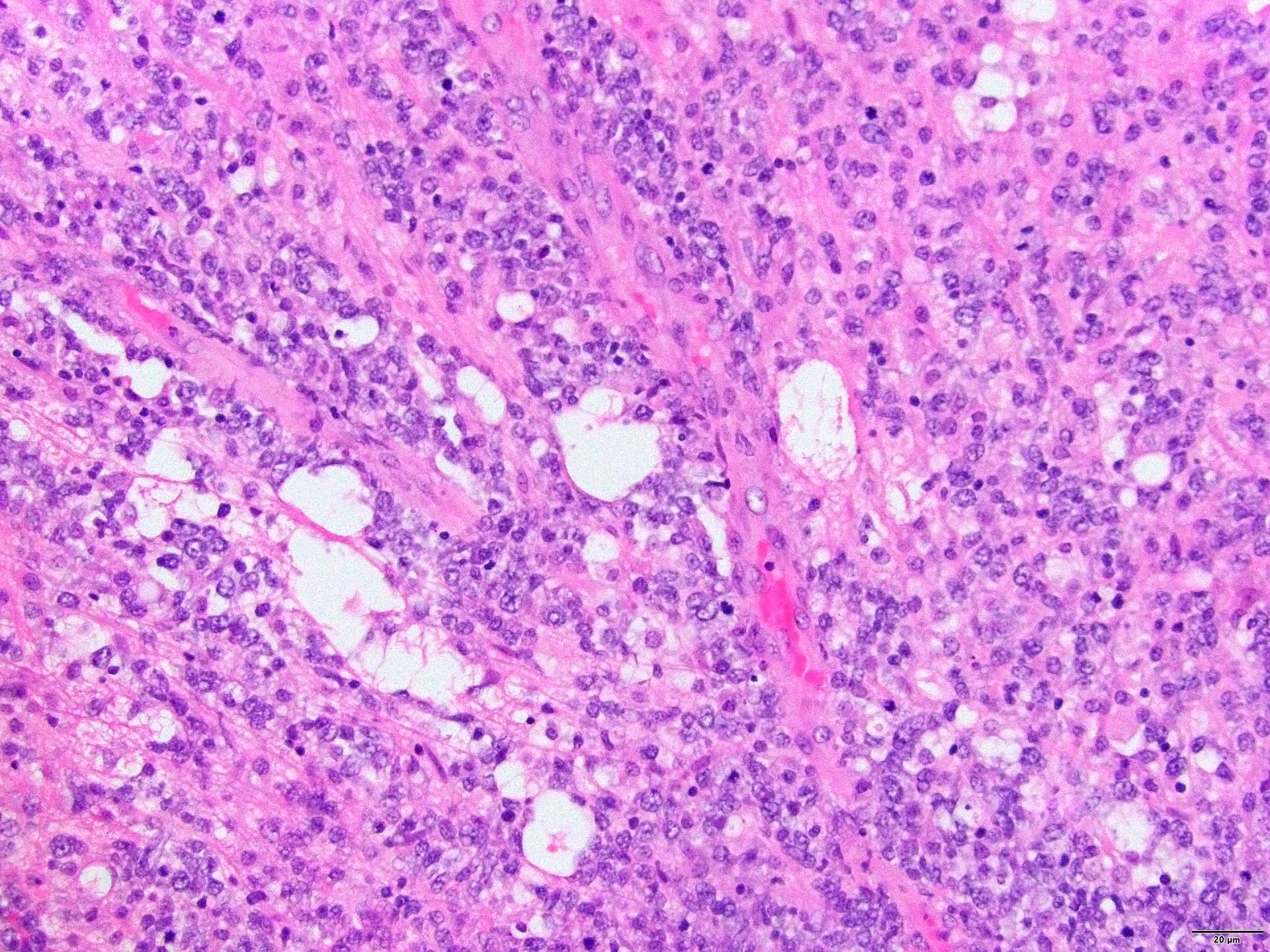
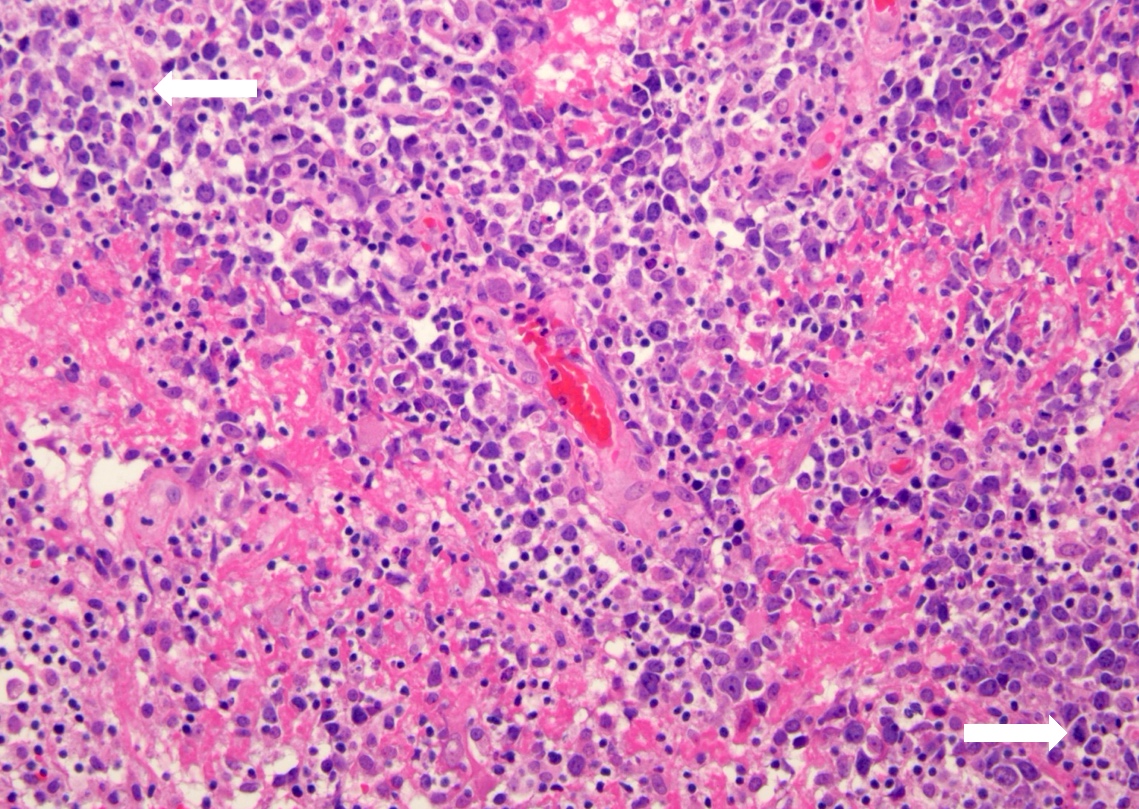
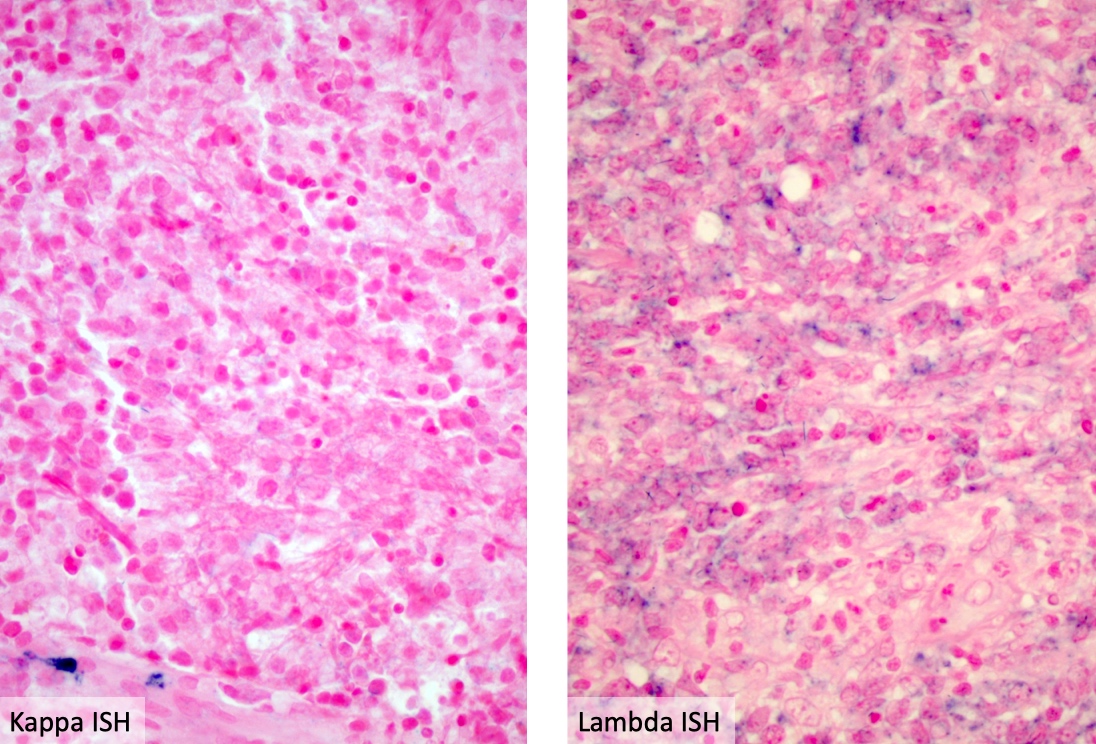
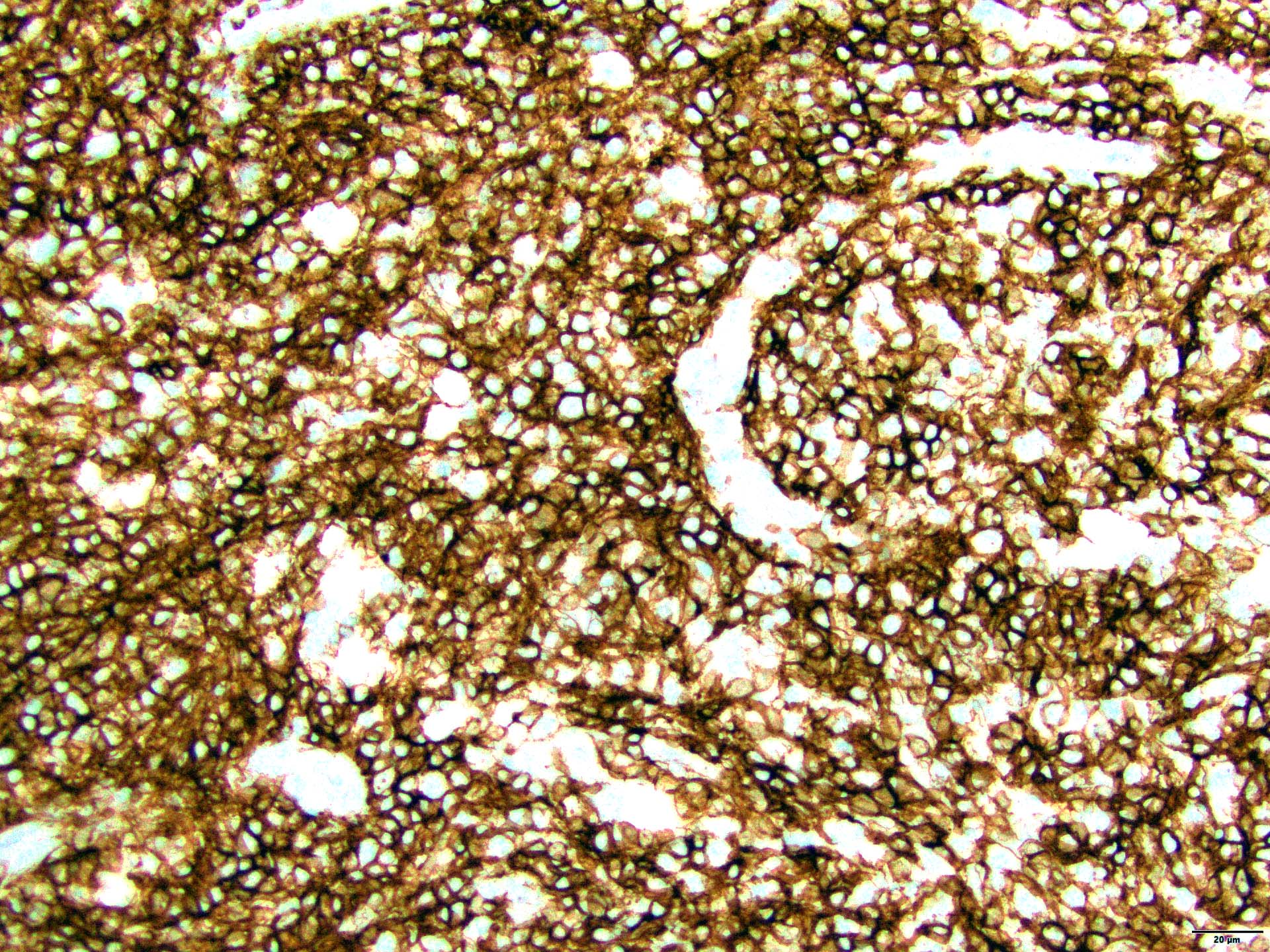
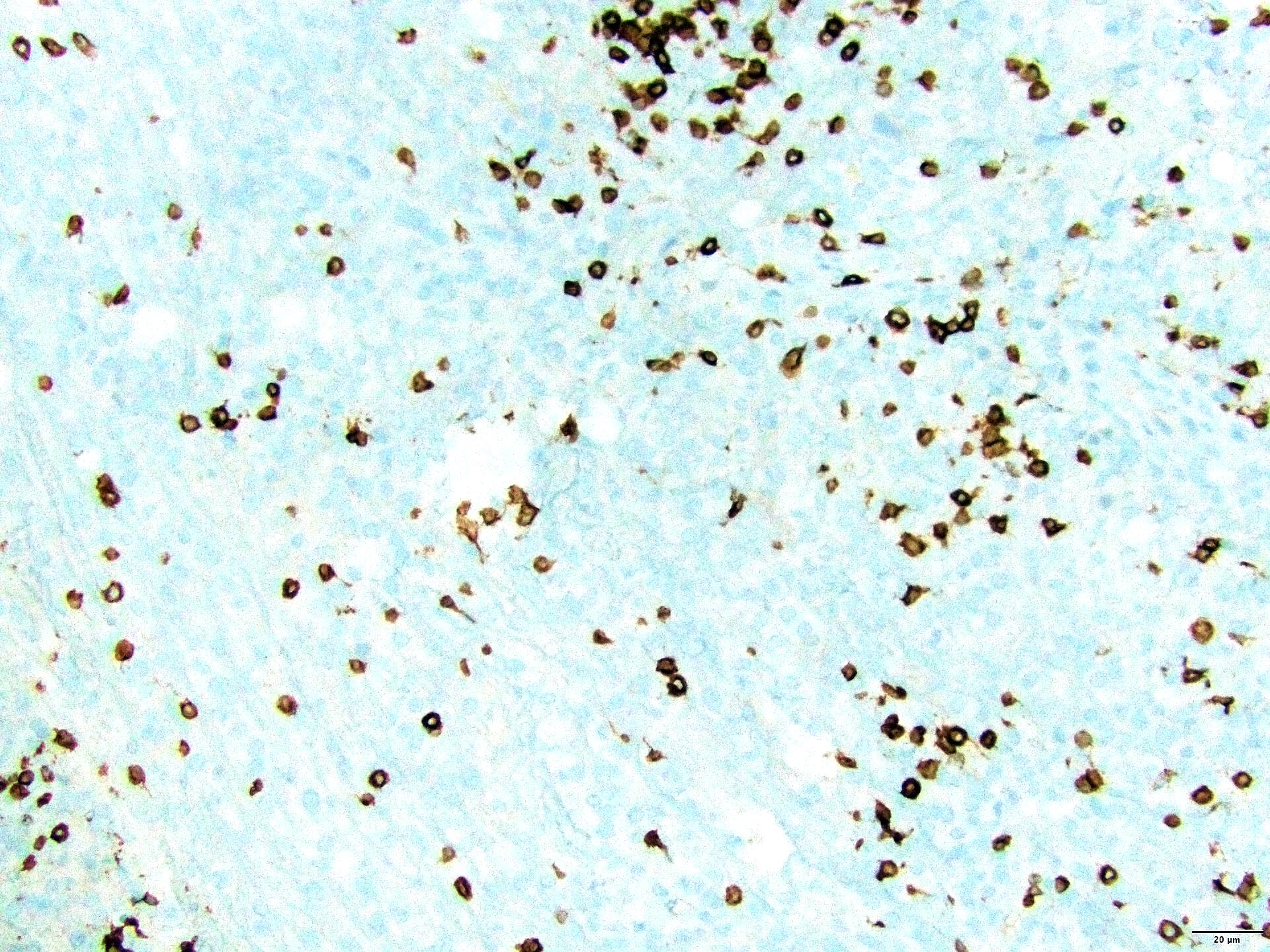
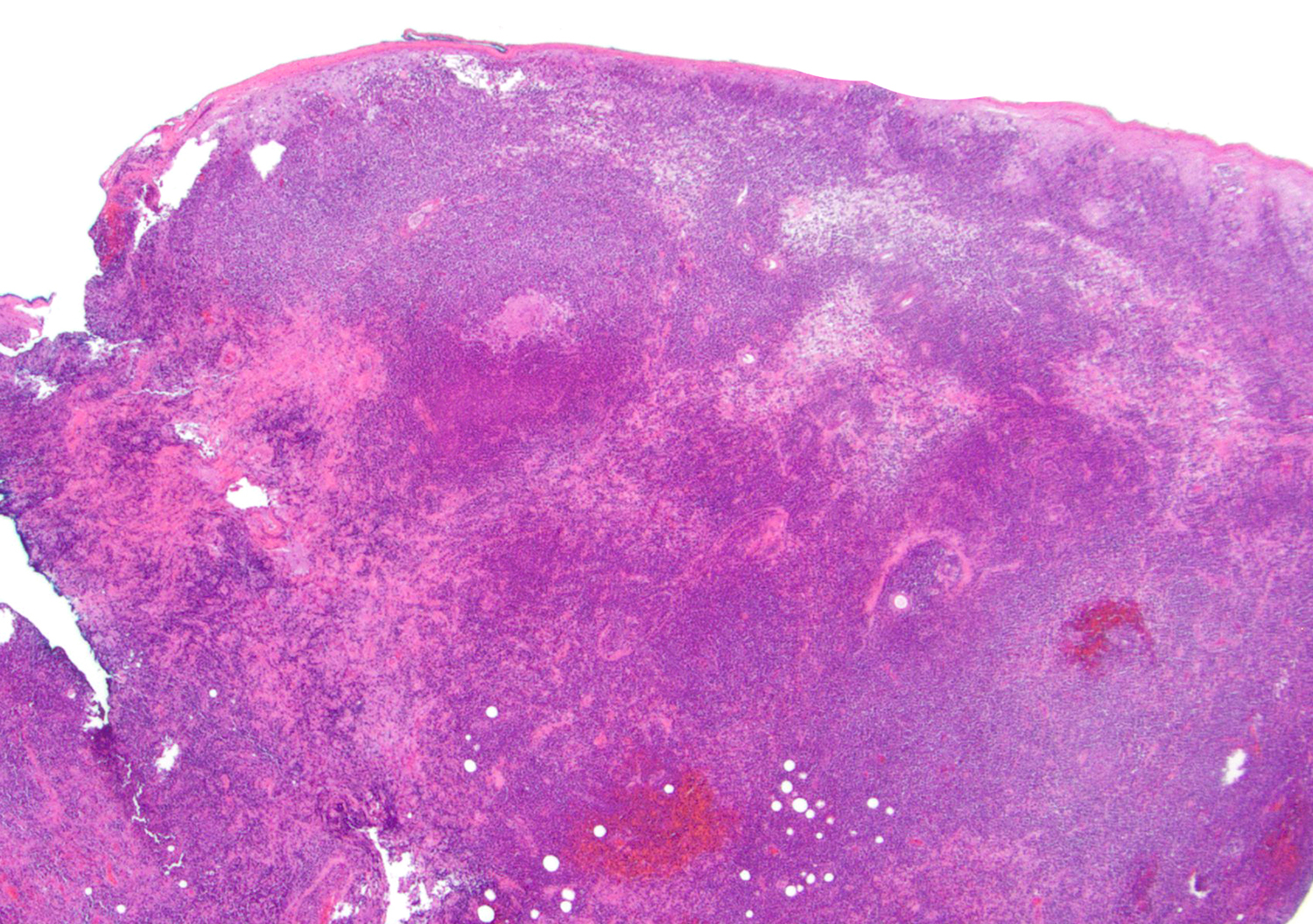
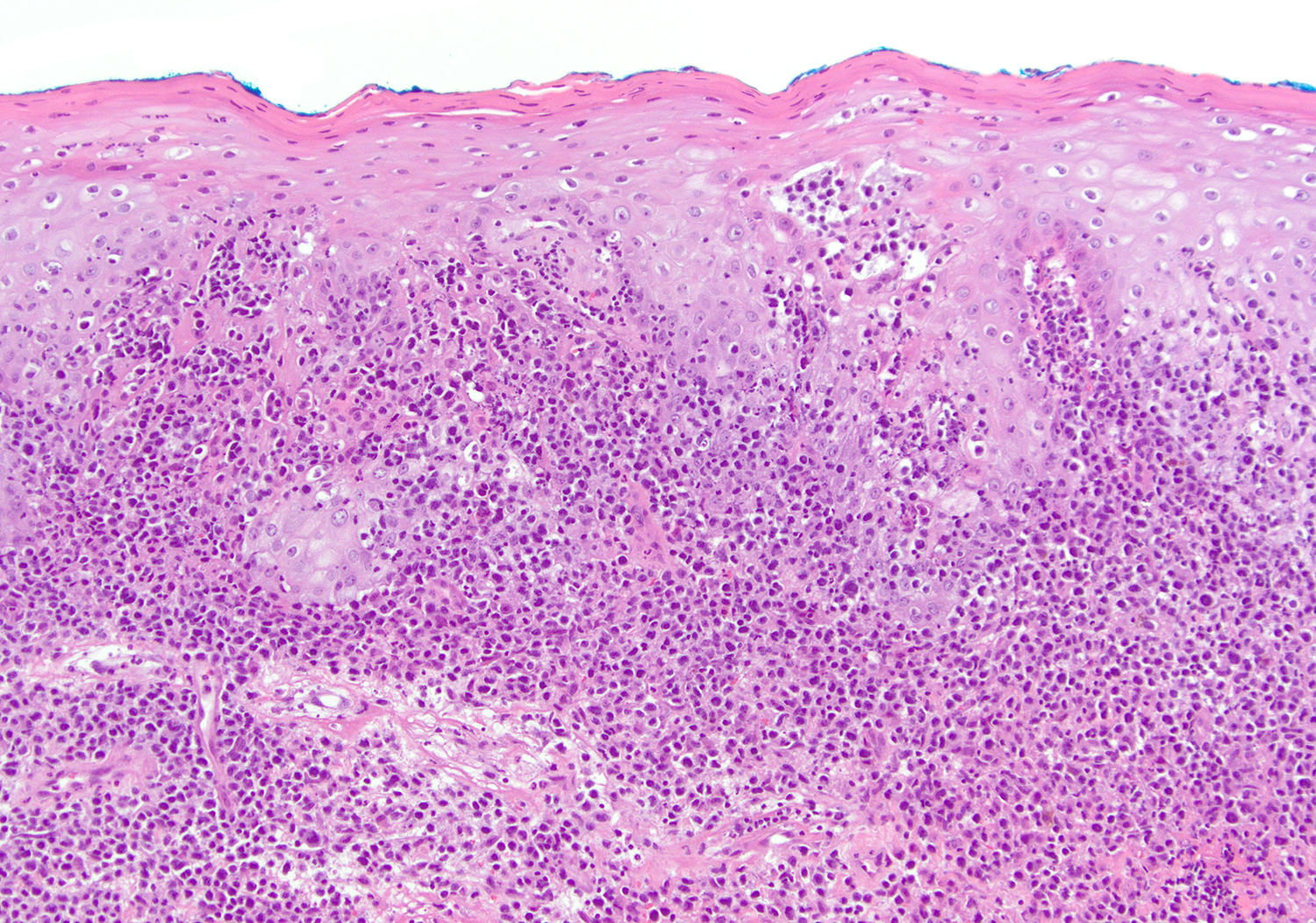
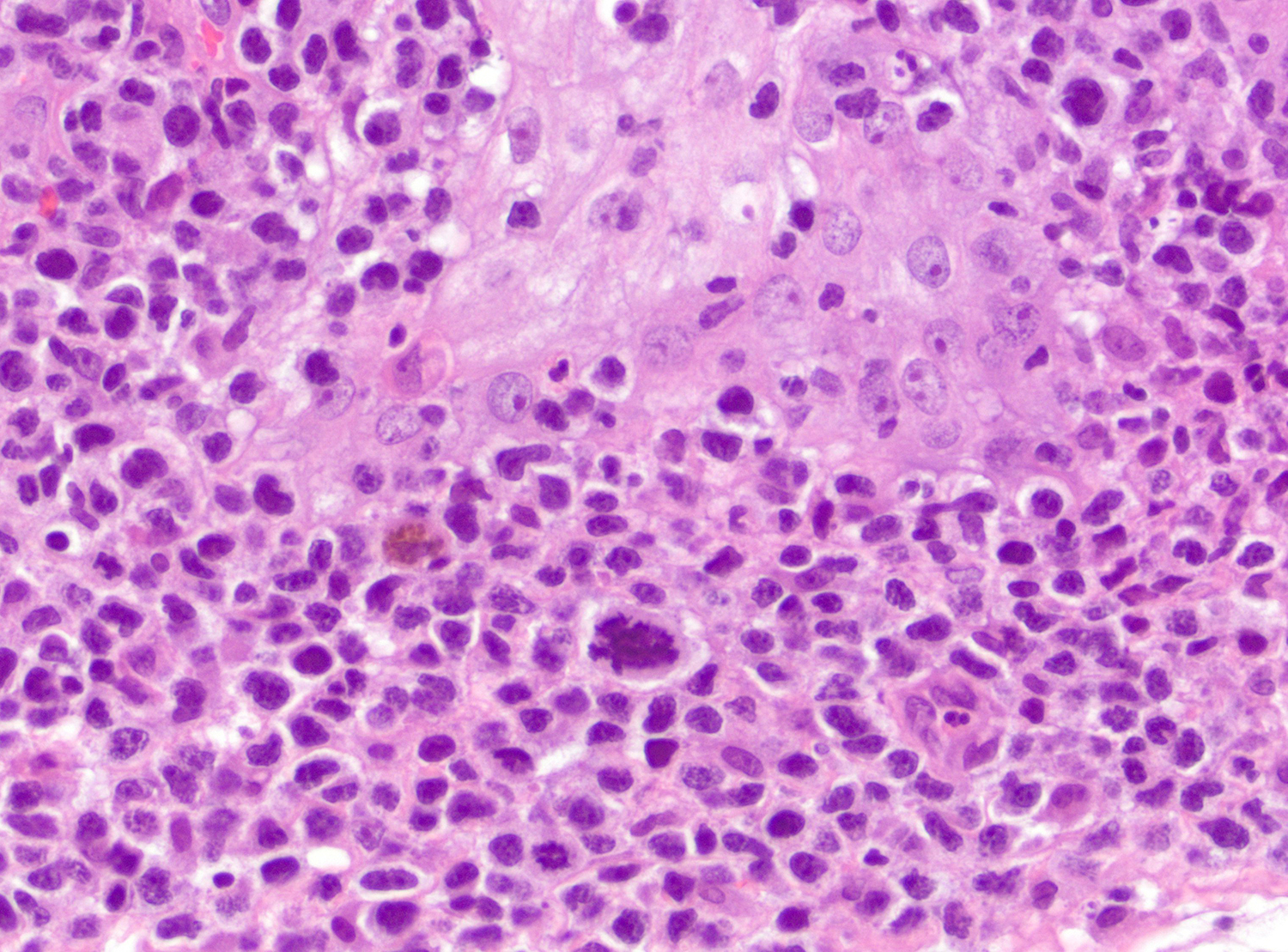
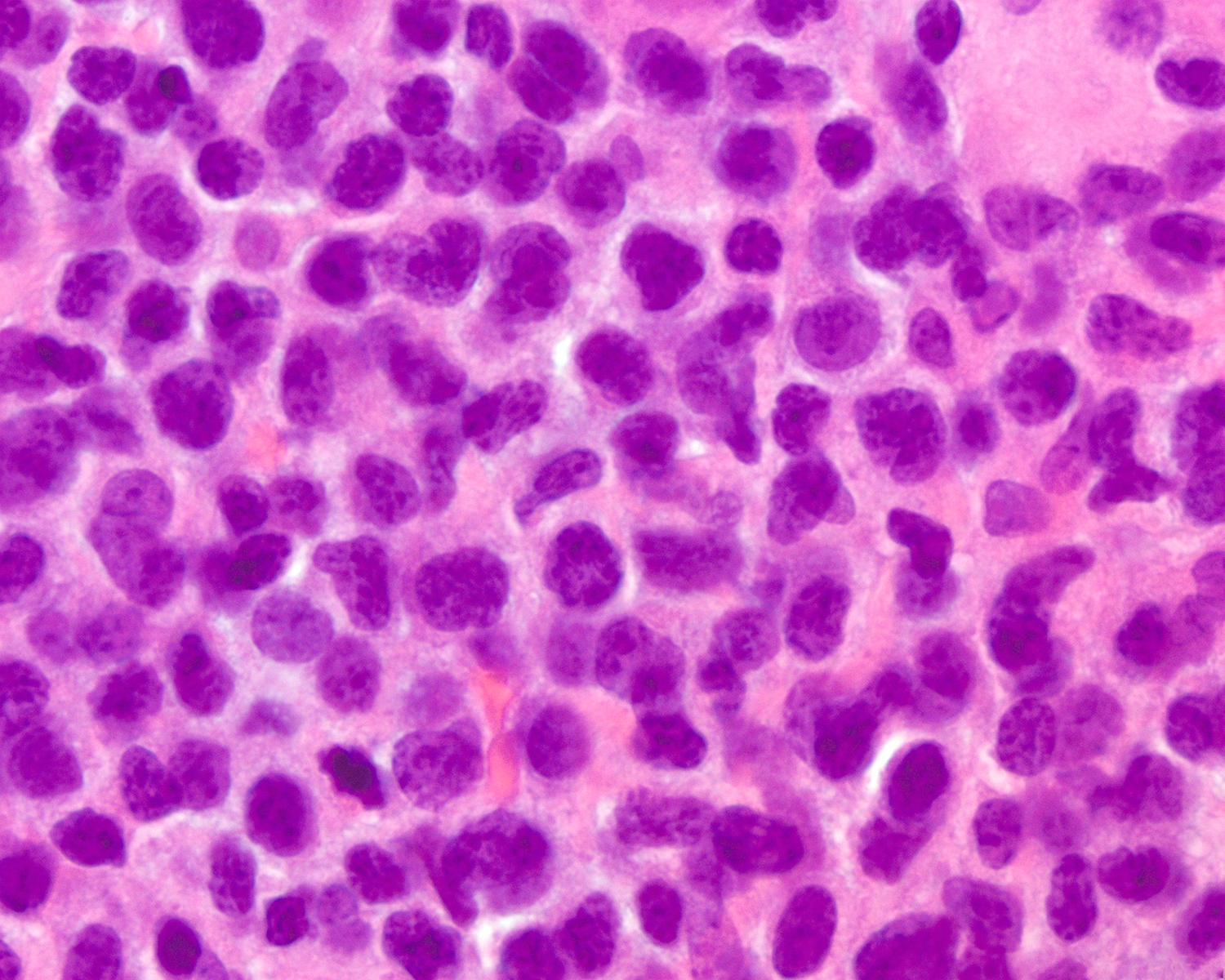
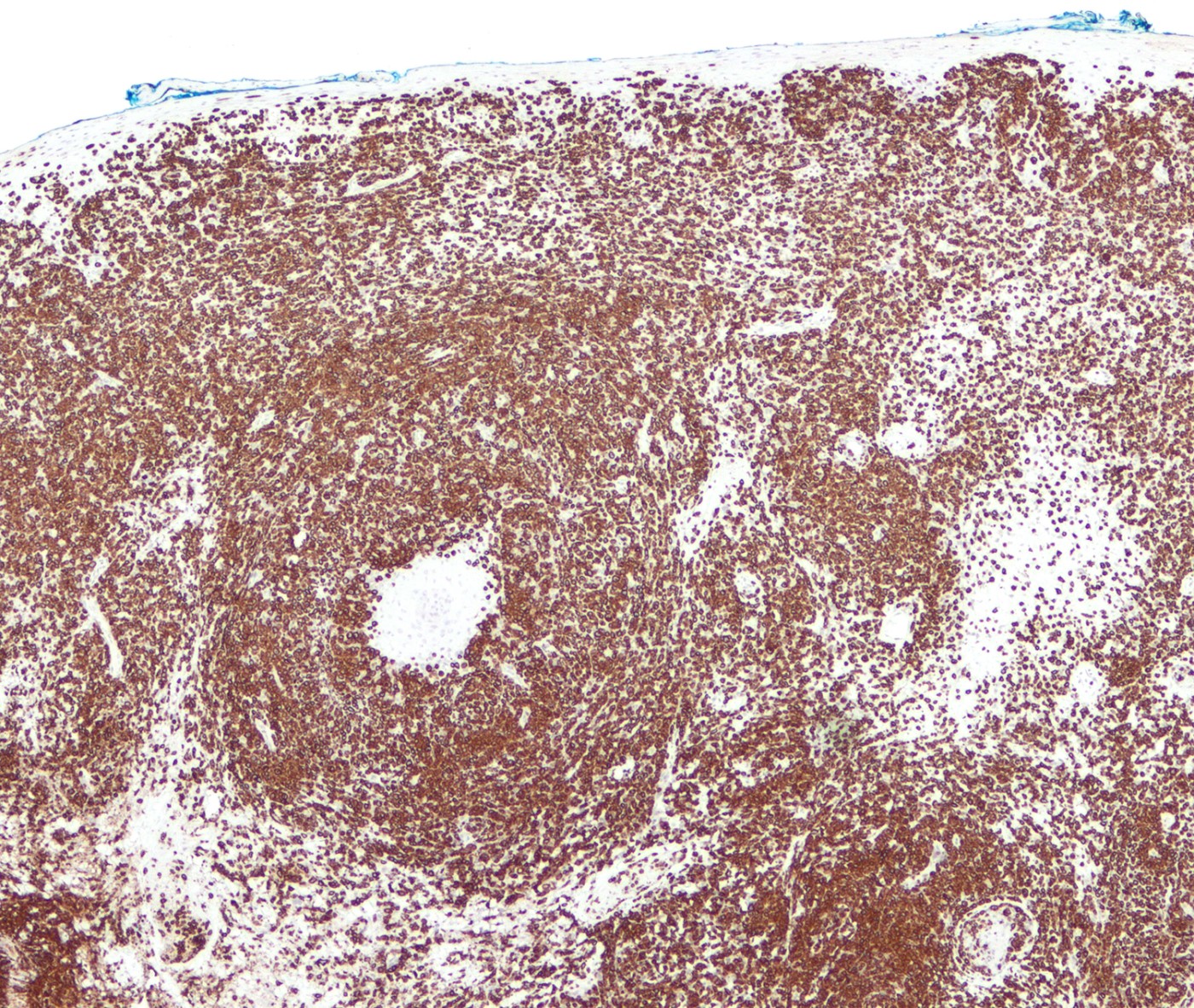
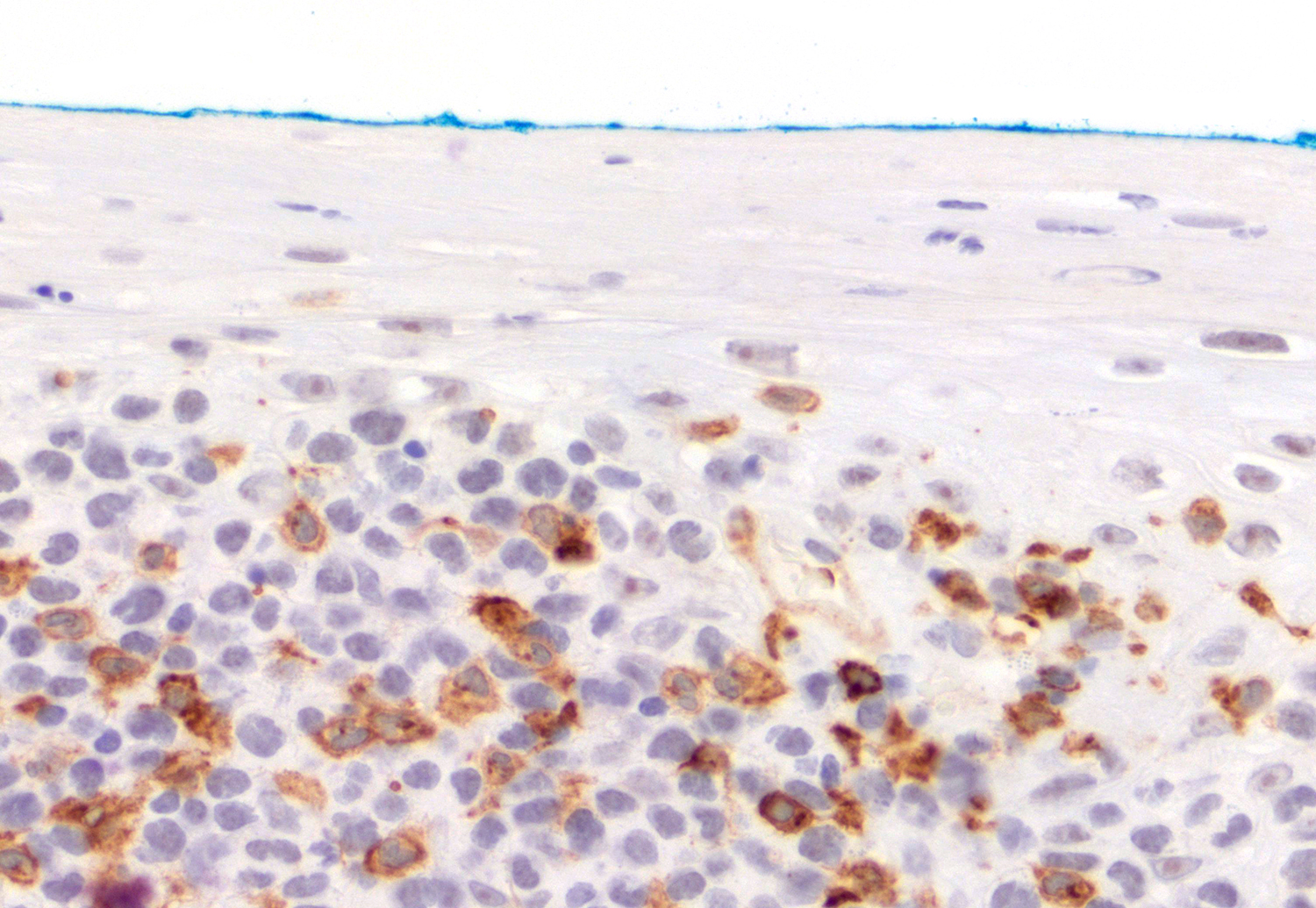
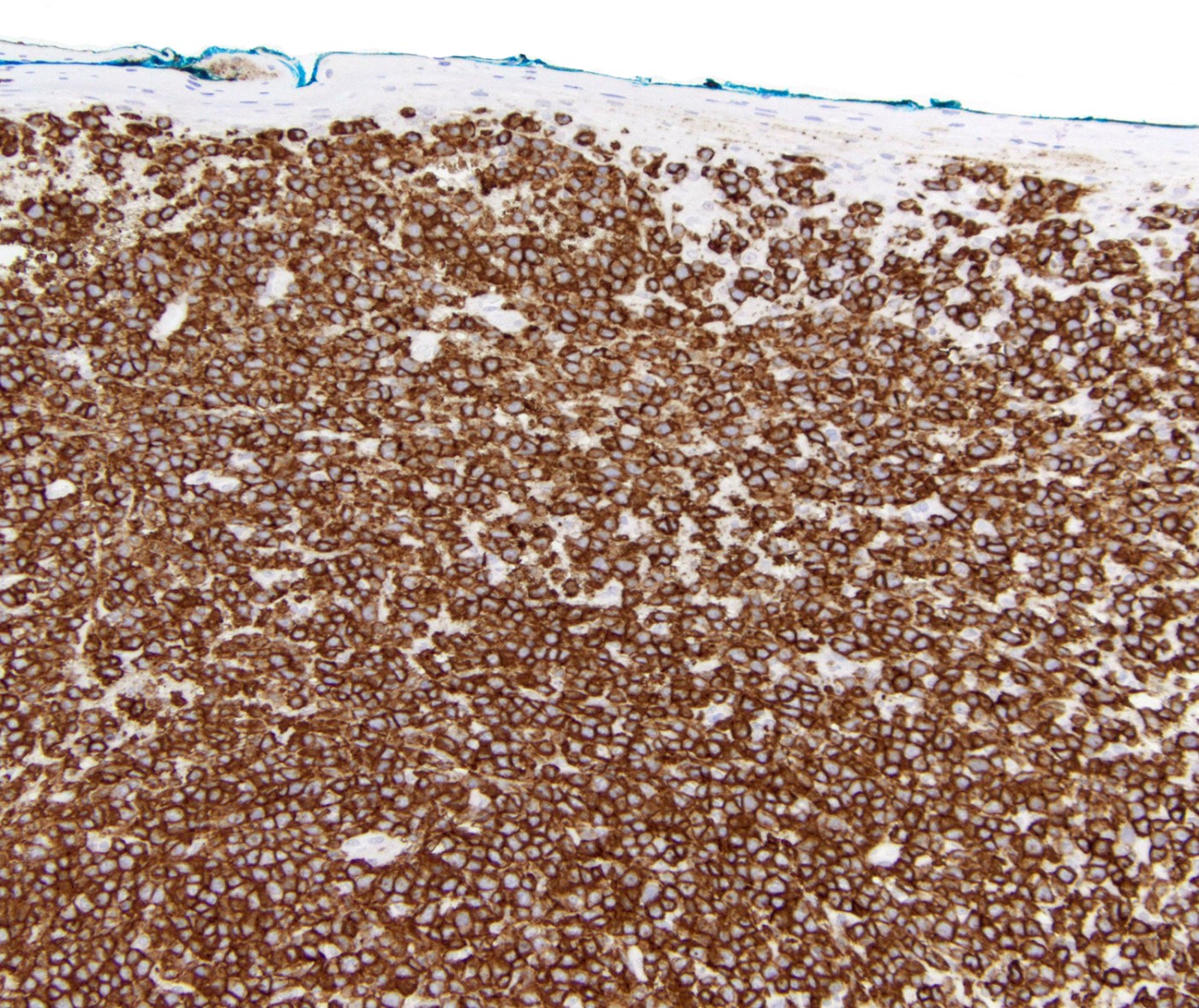
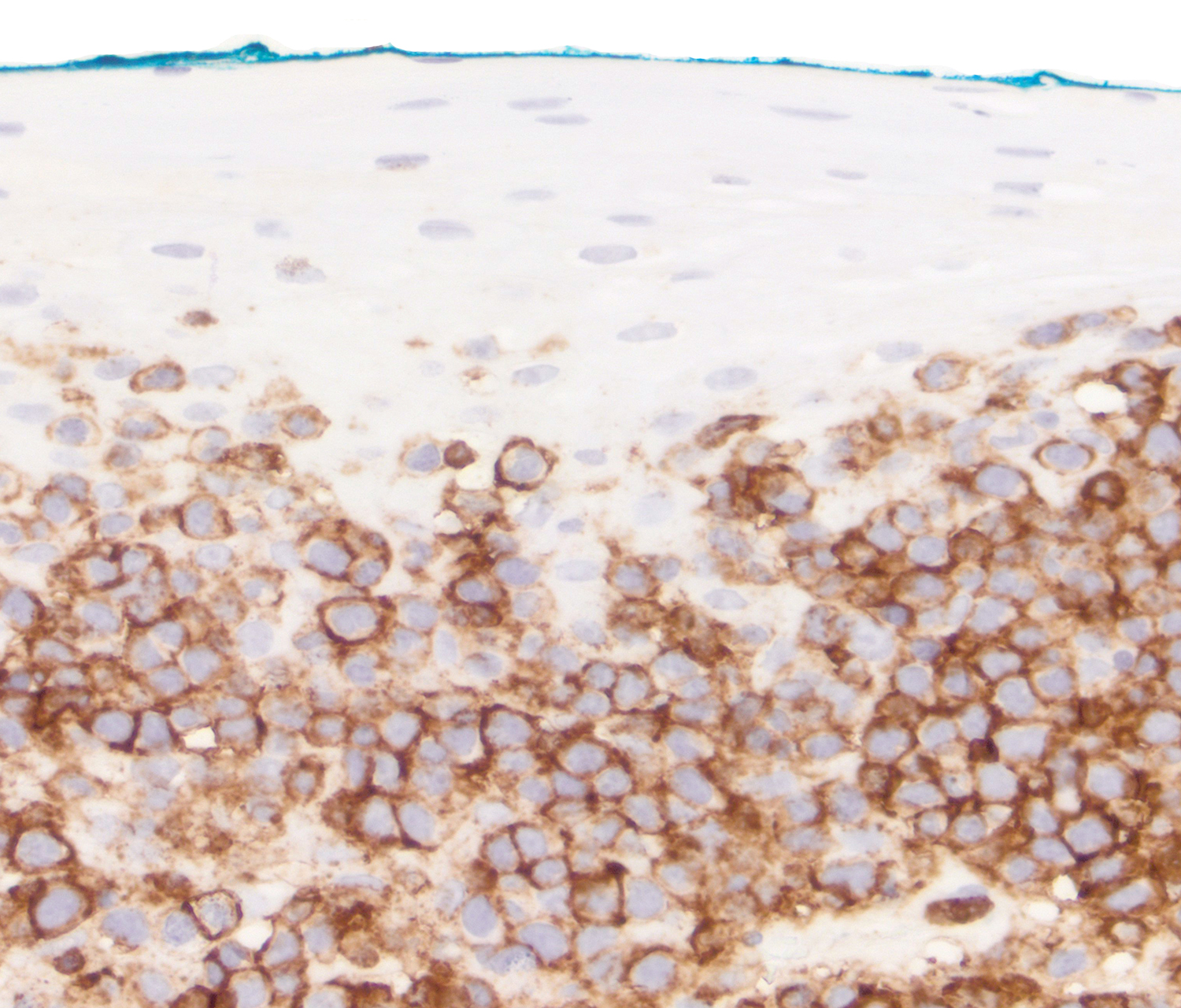
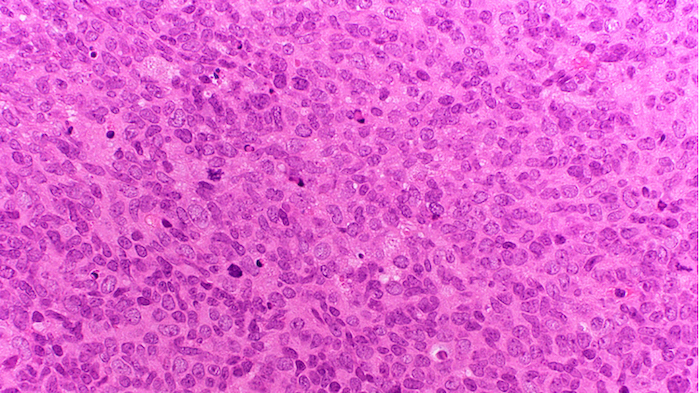
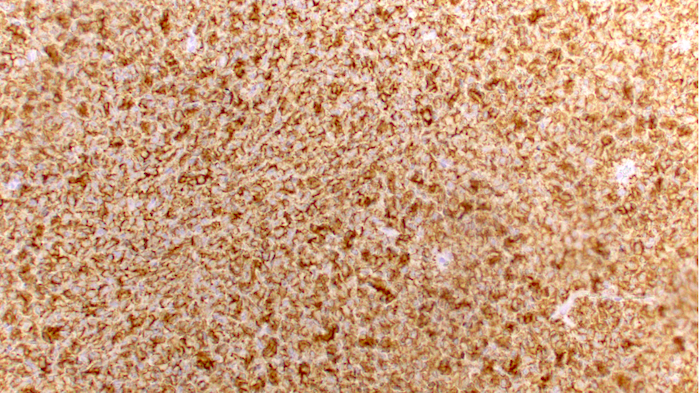
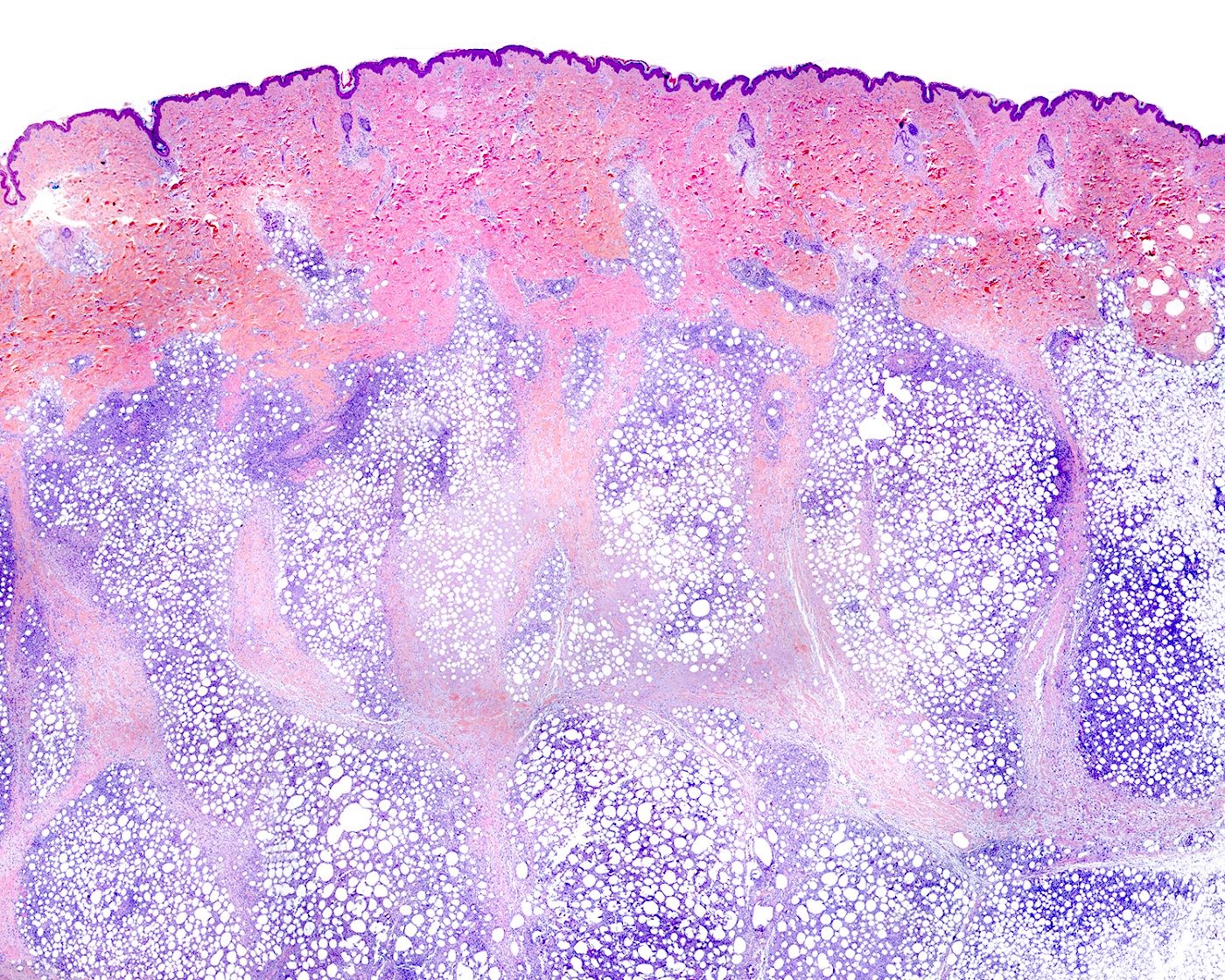
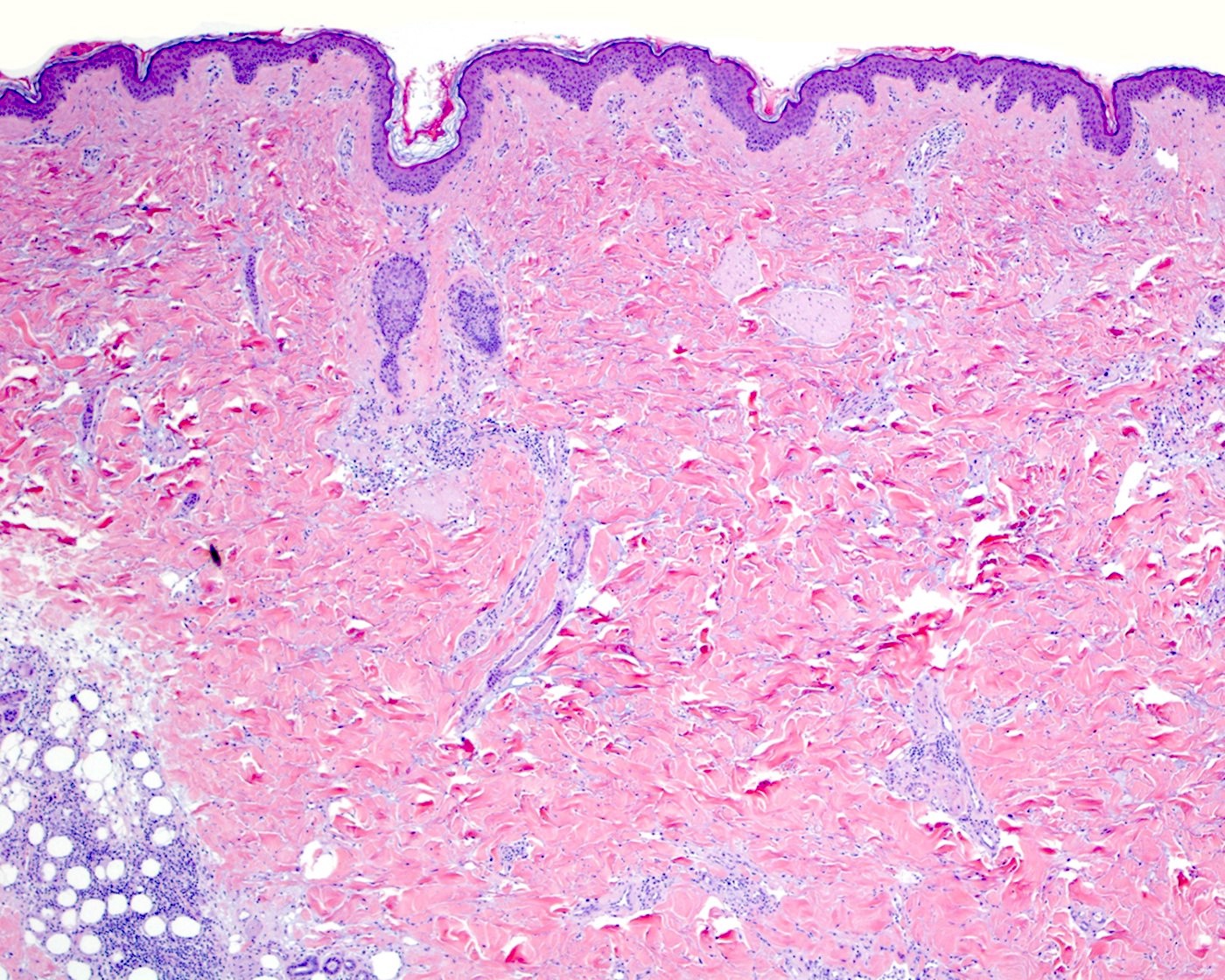
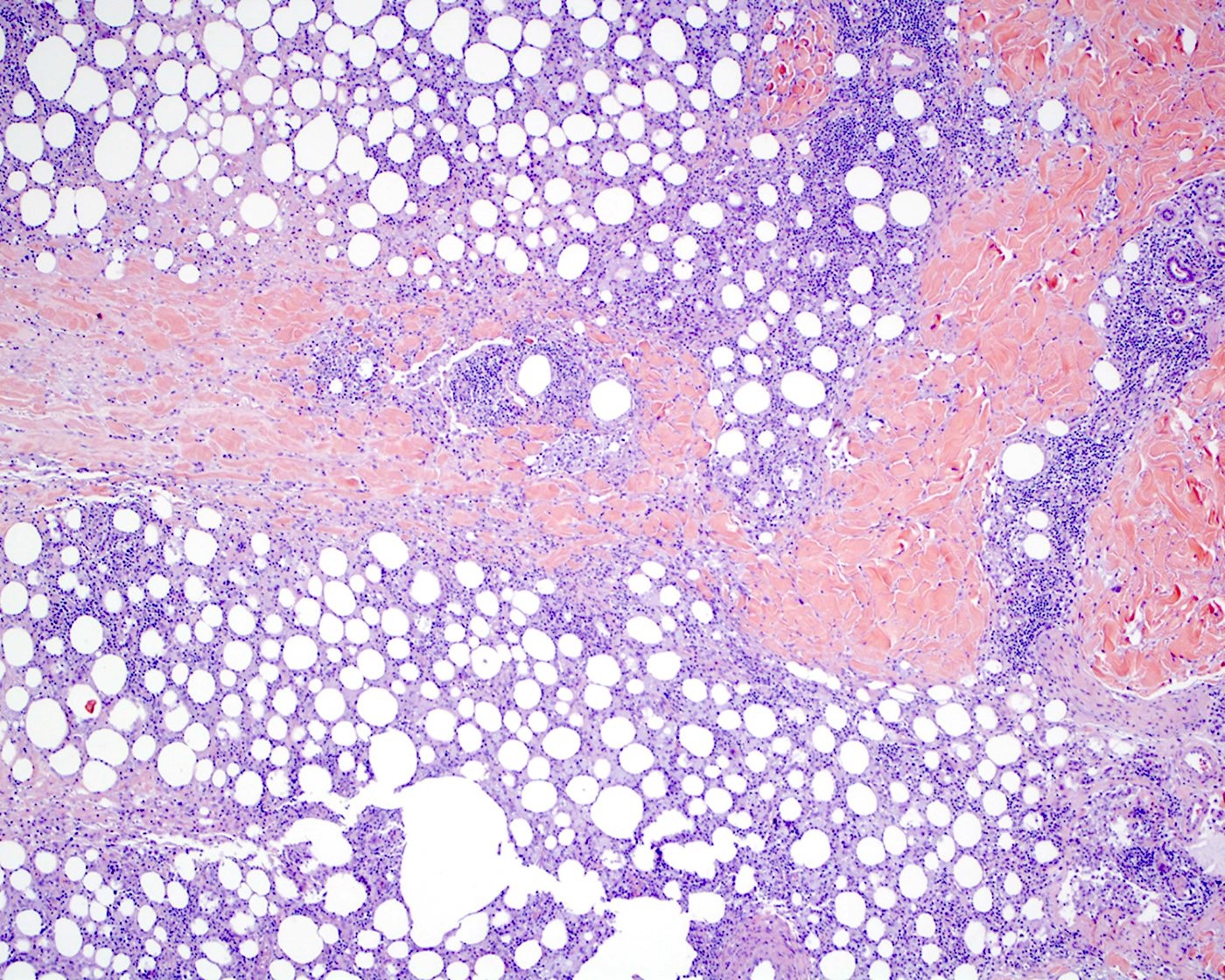
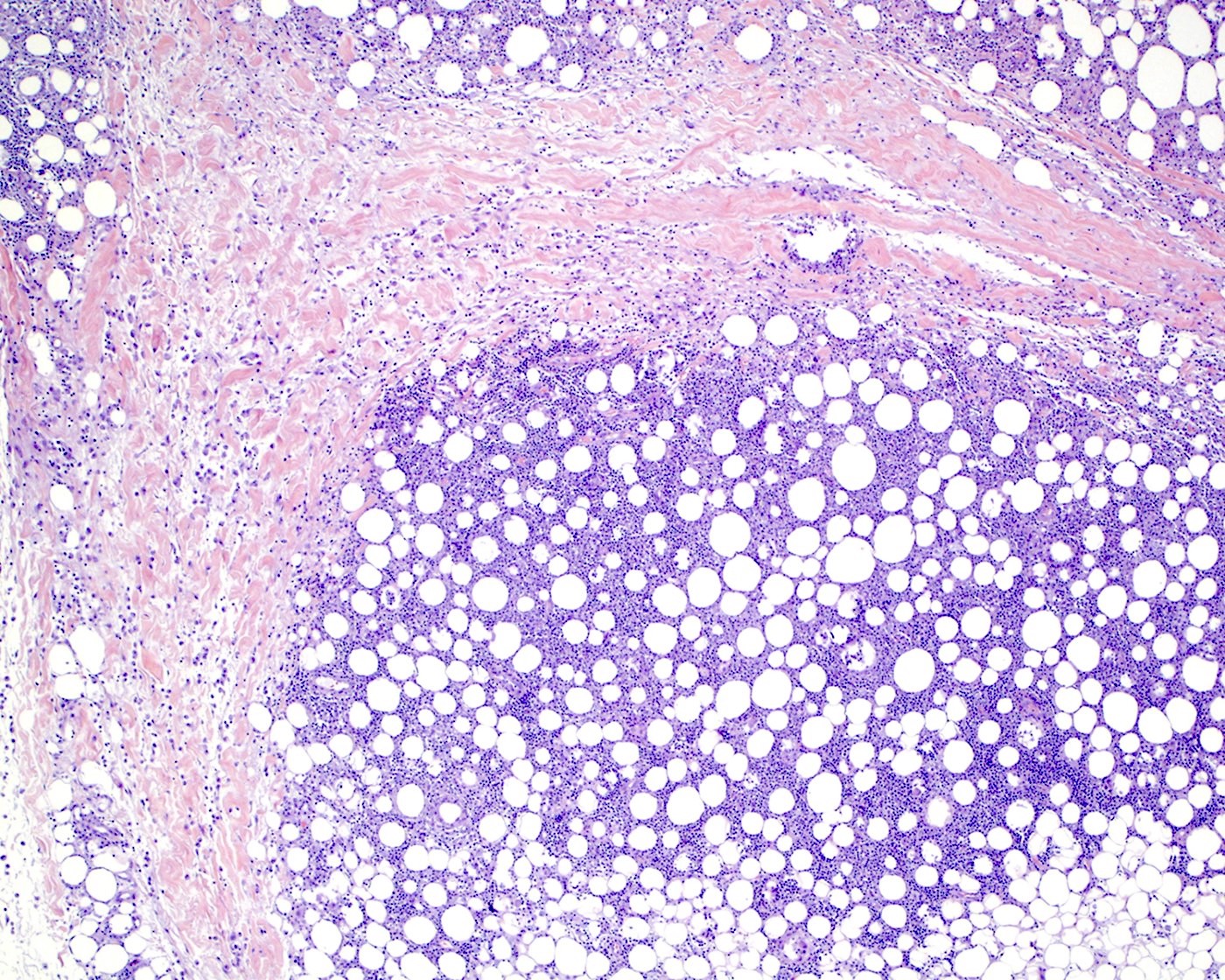
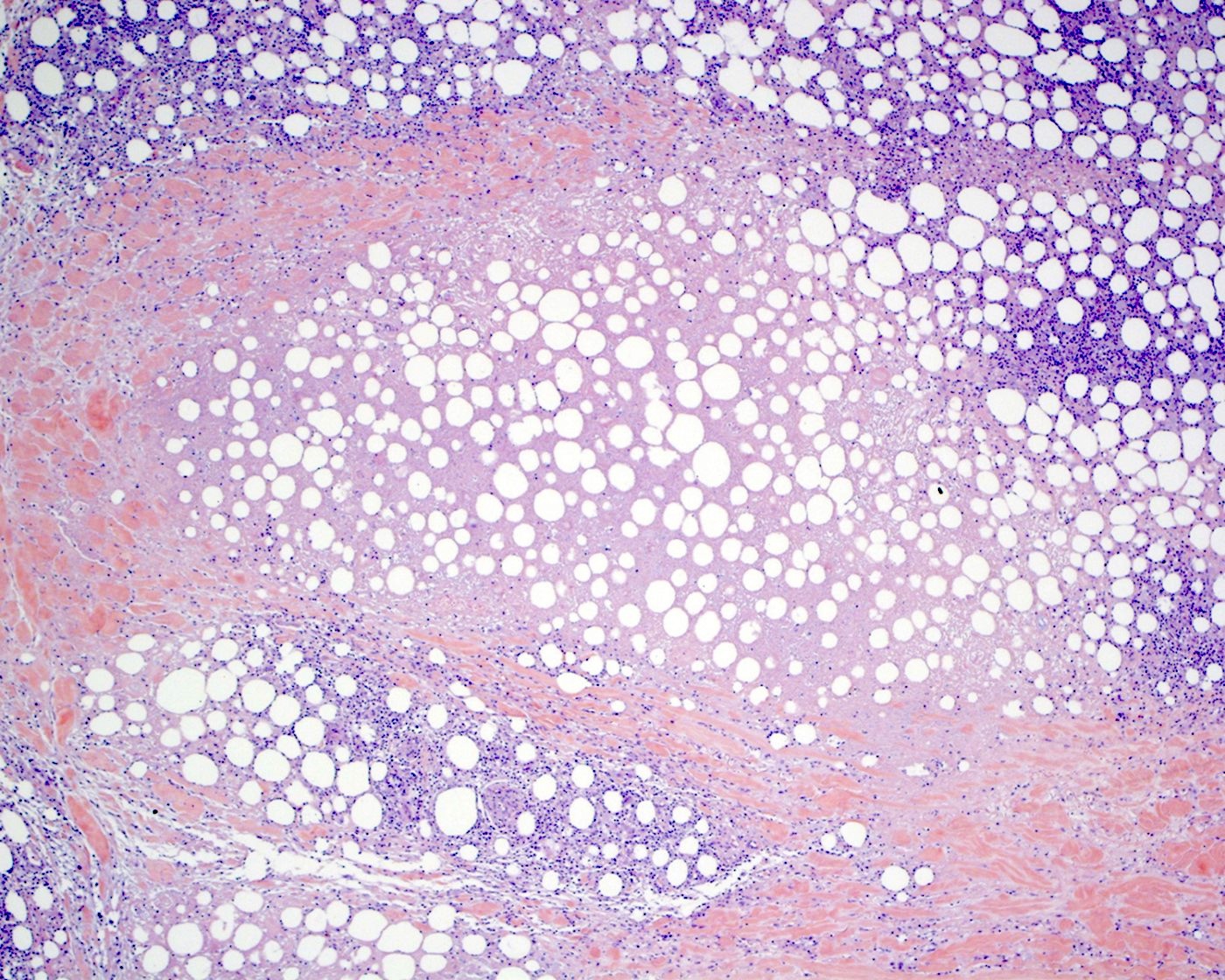
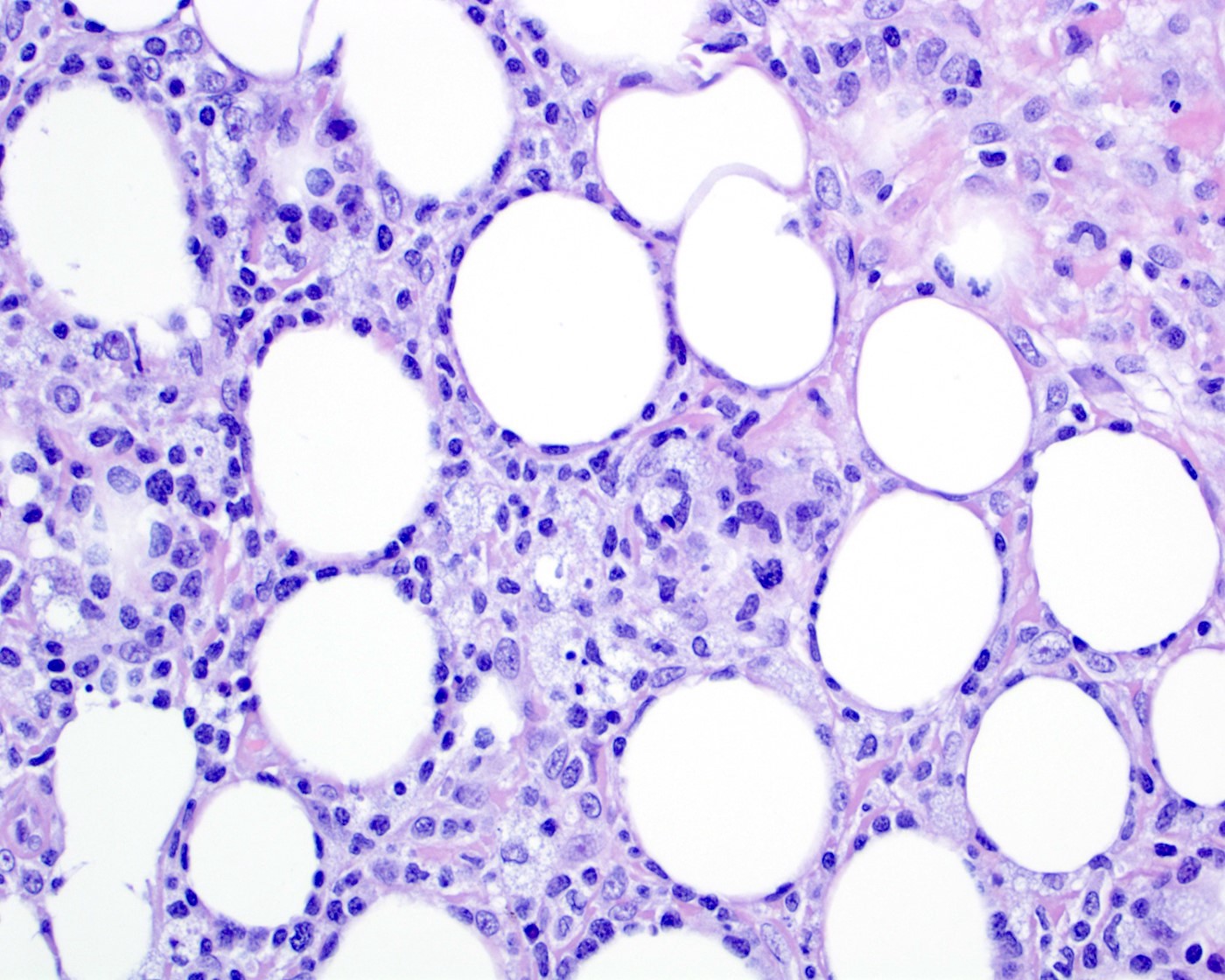
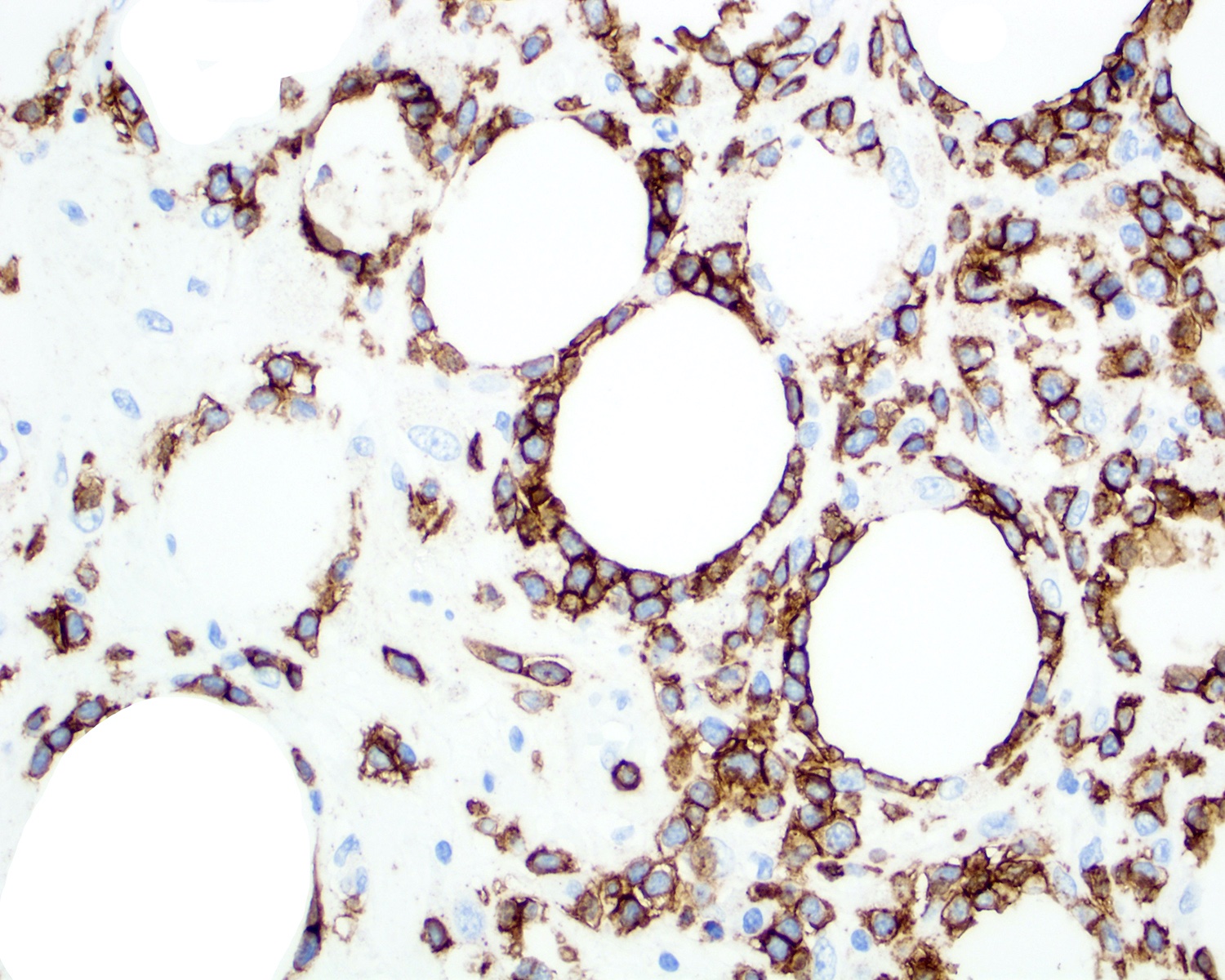
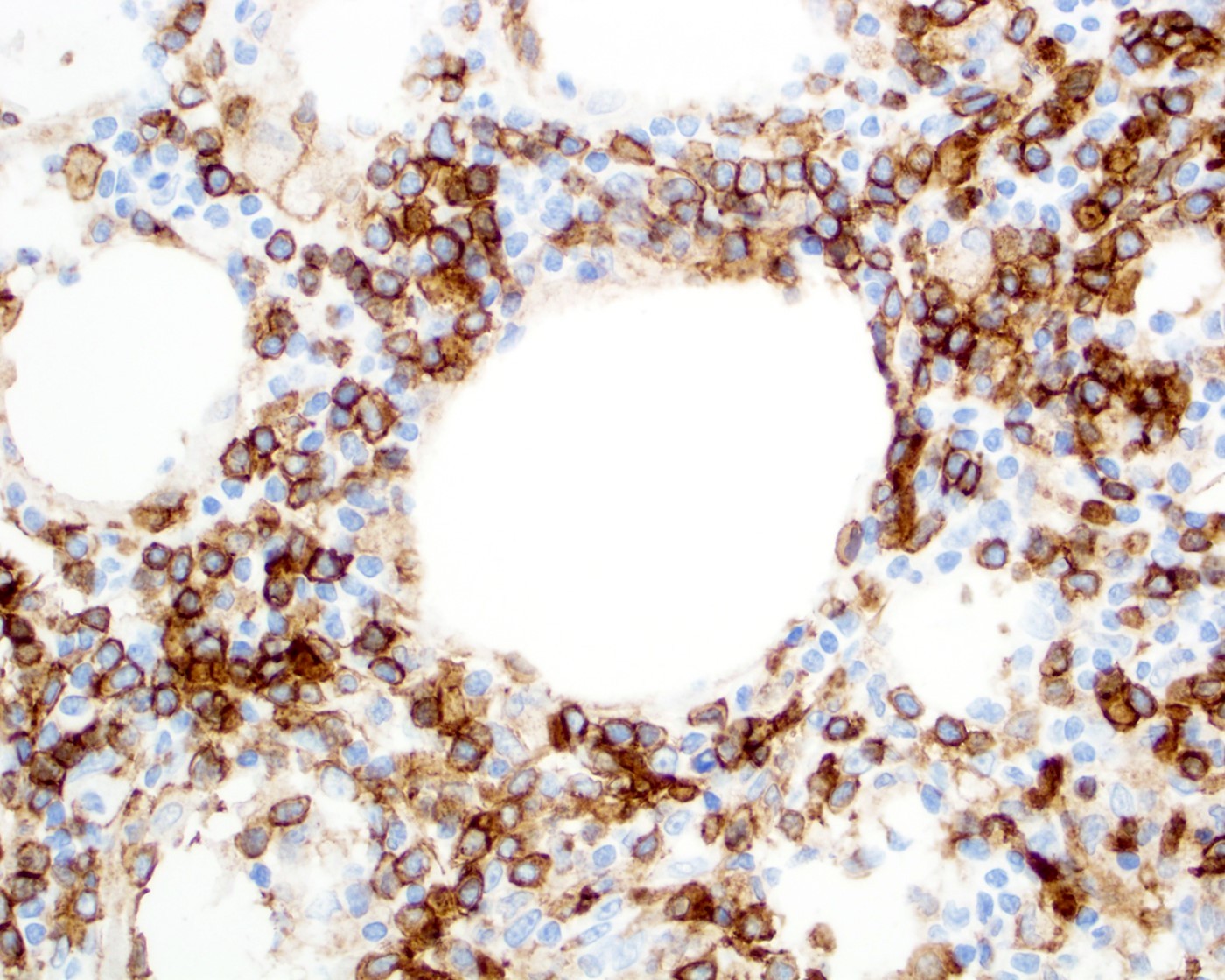
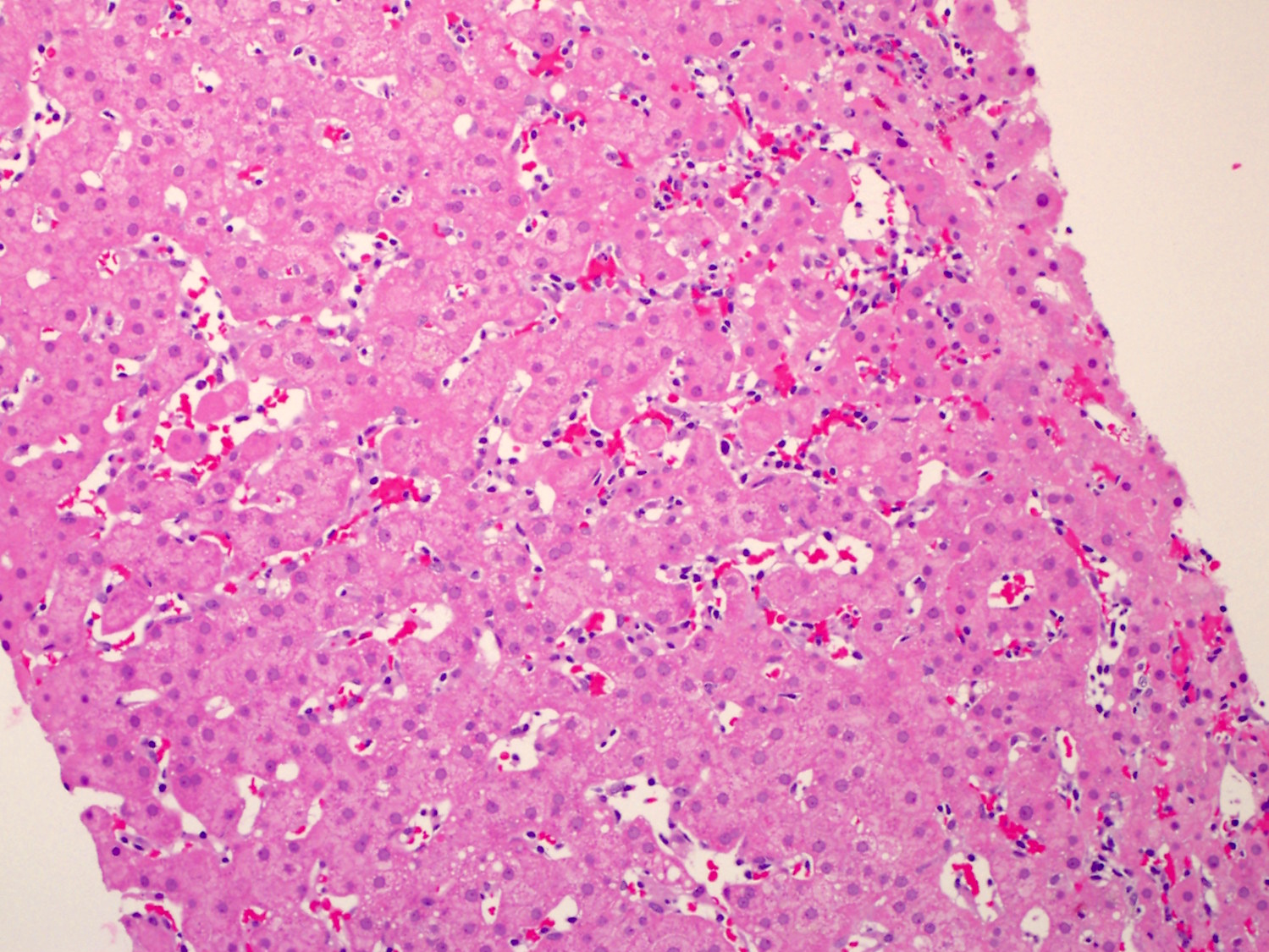
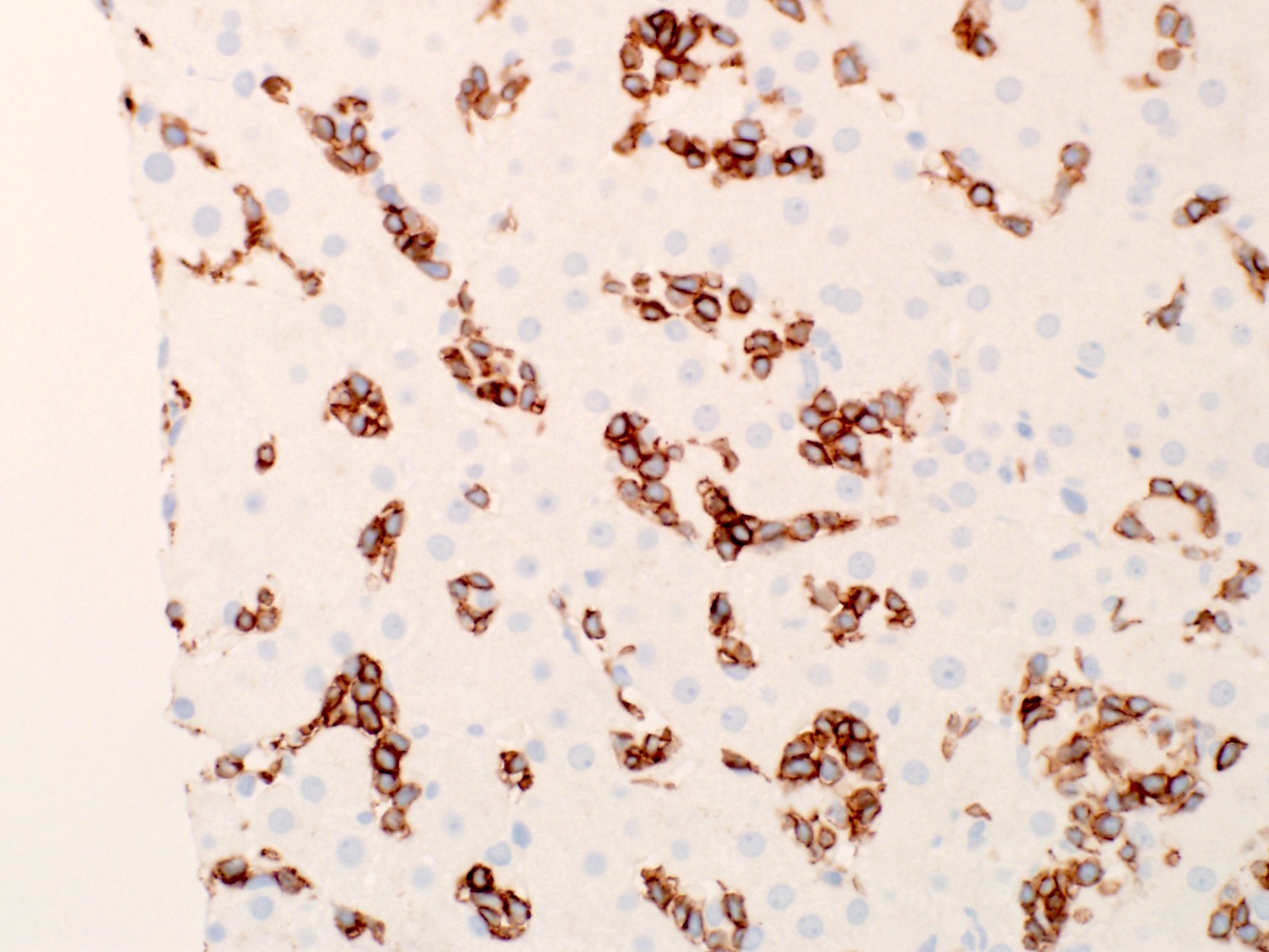
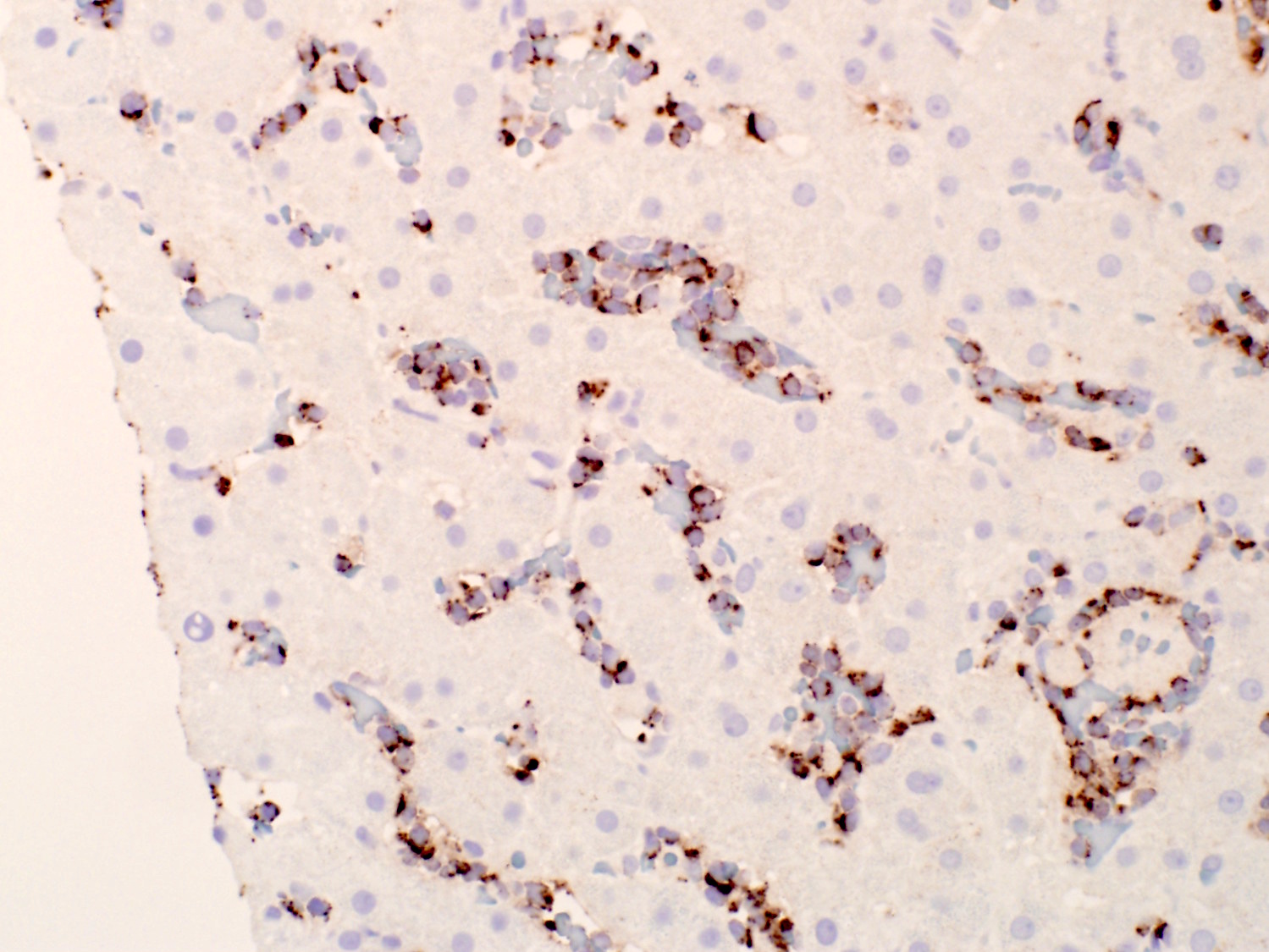
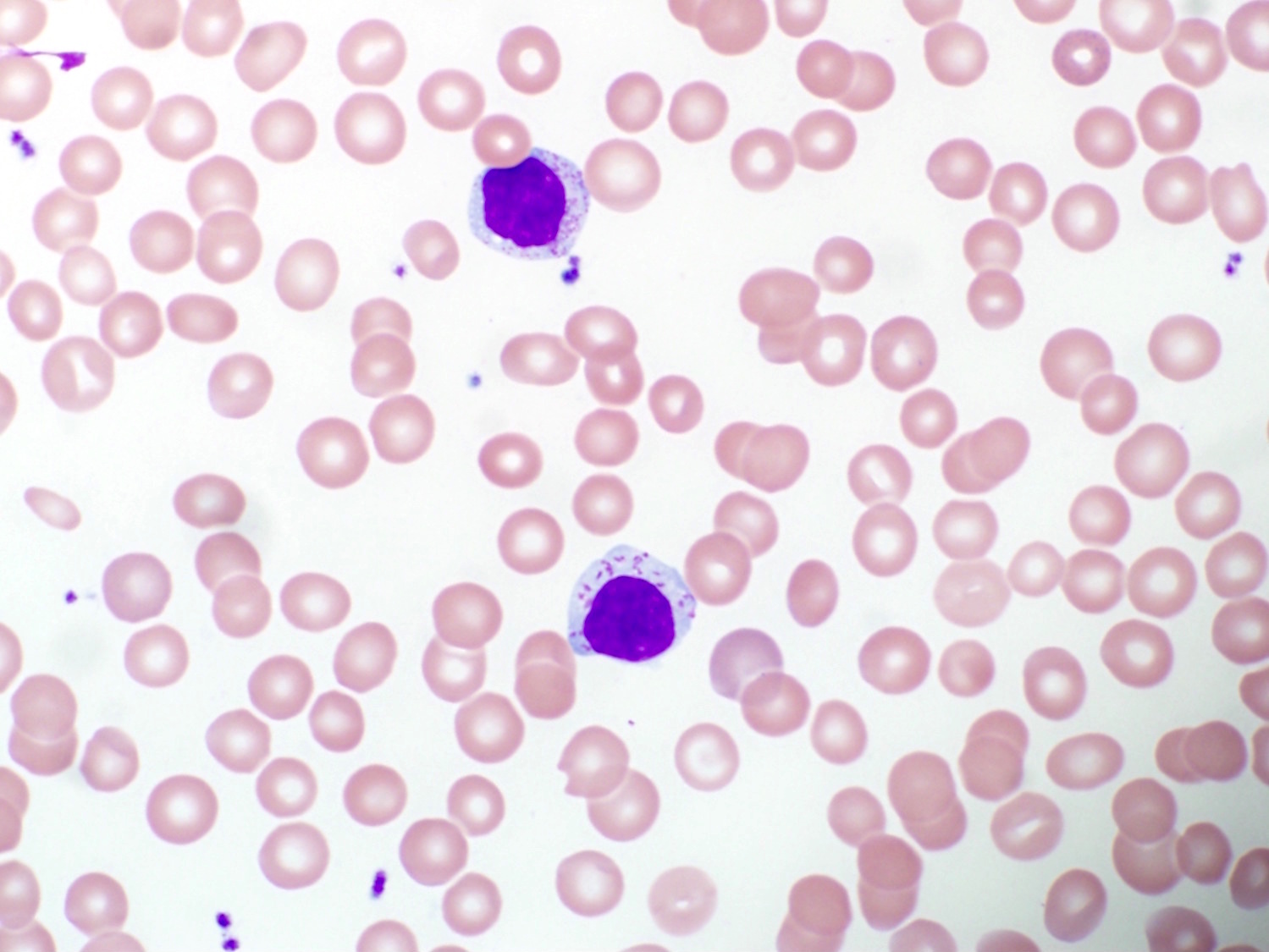
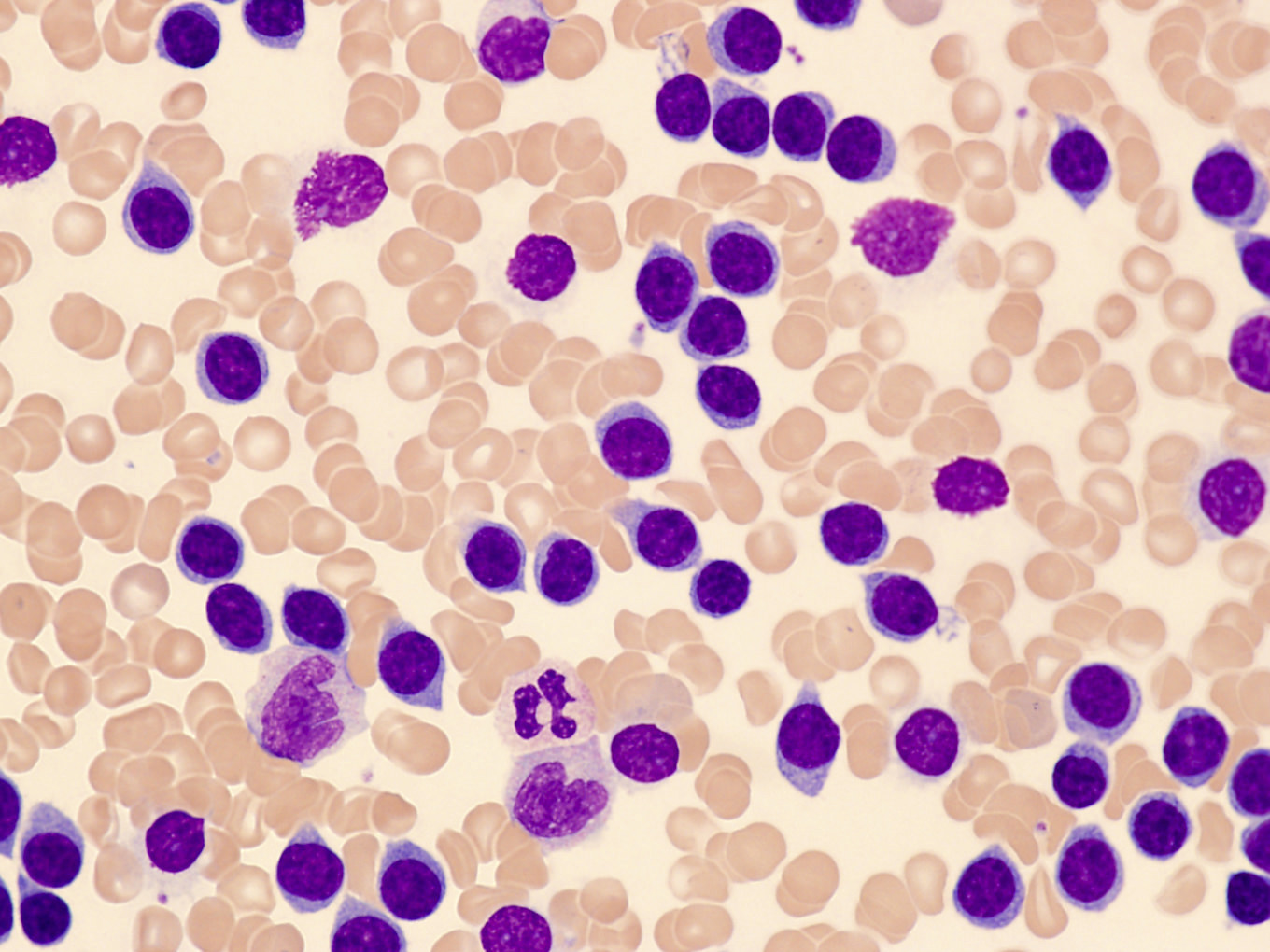
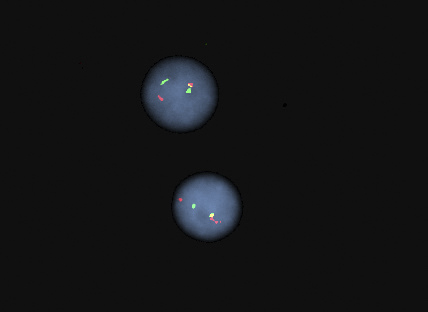
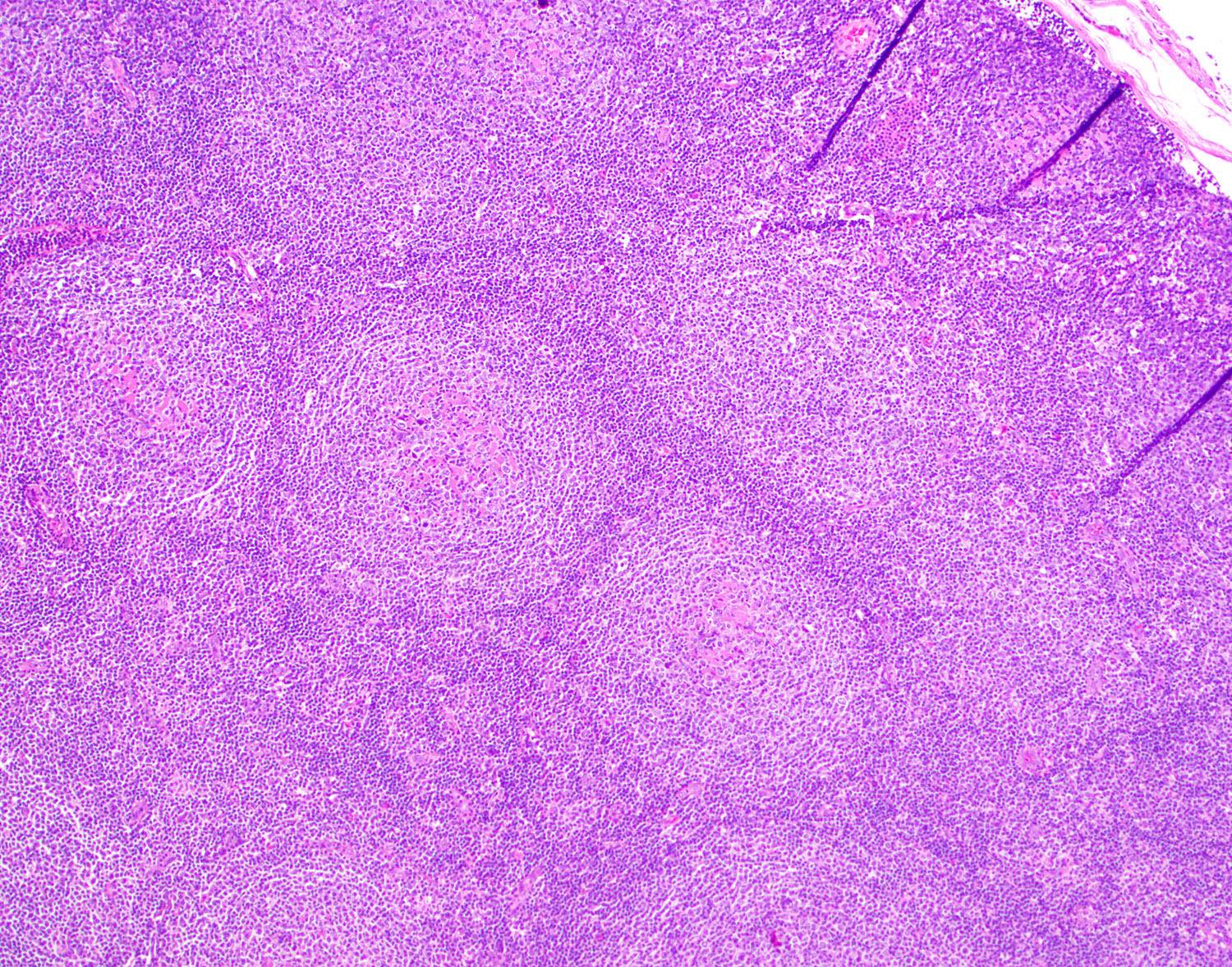
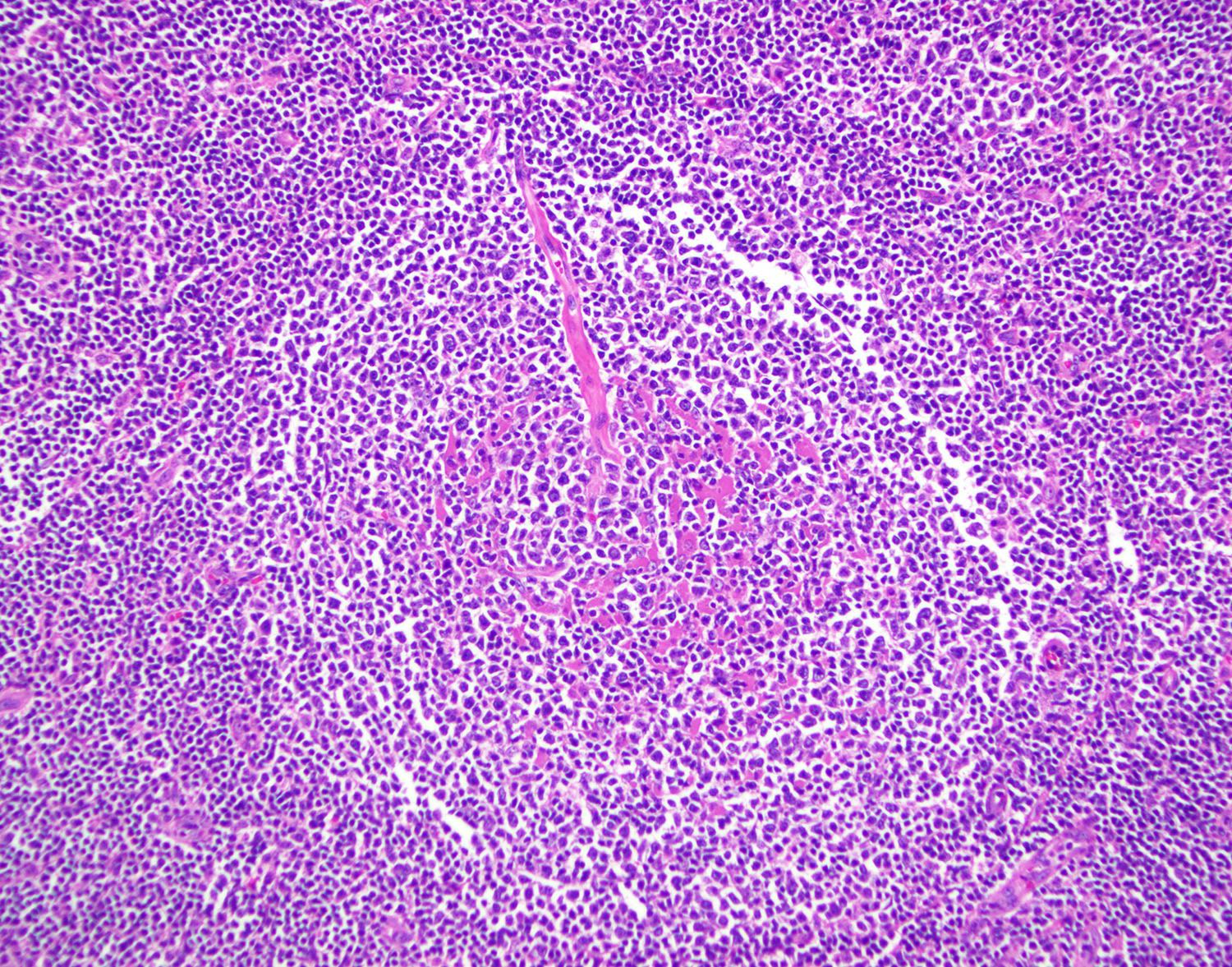
Superpage - Images
Superpage Topics
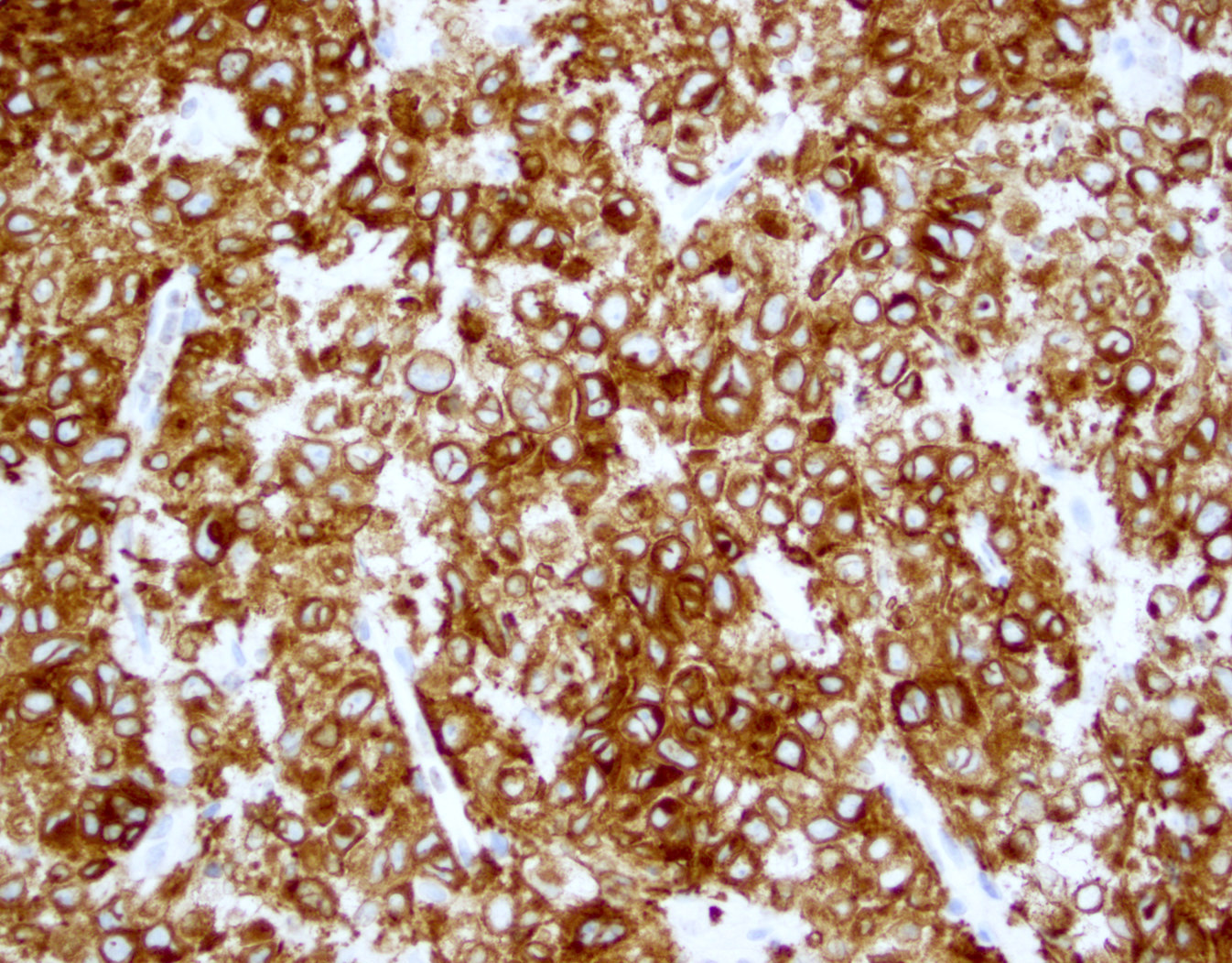
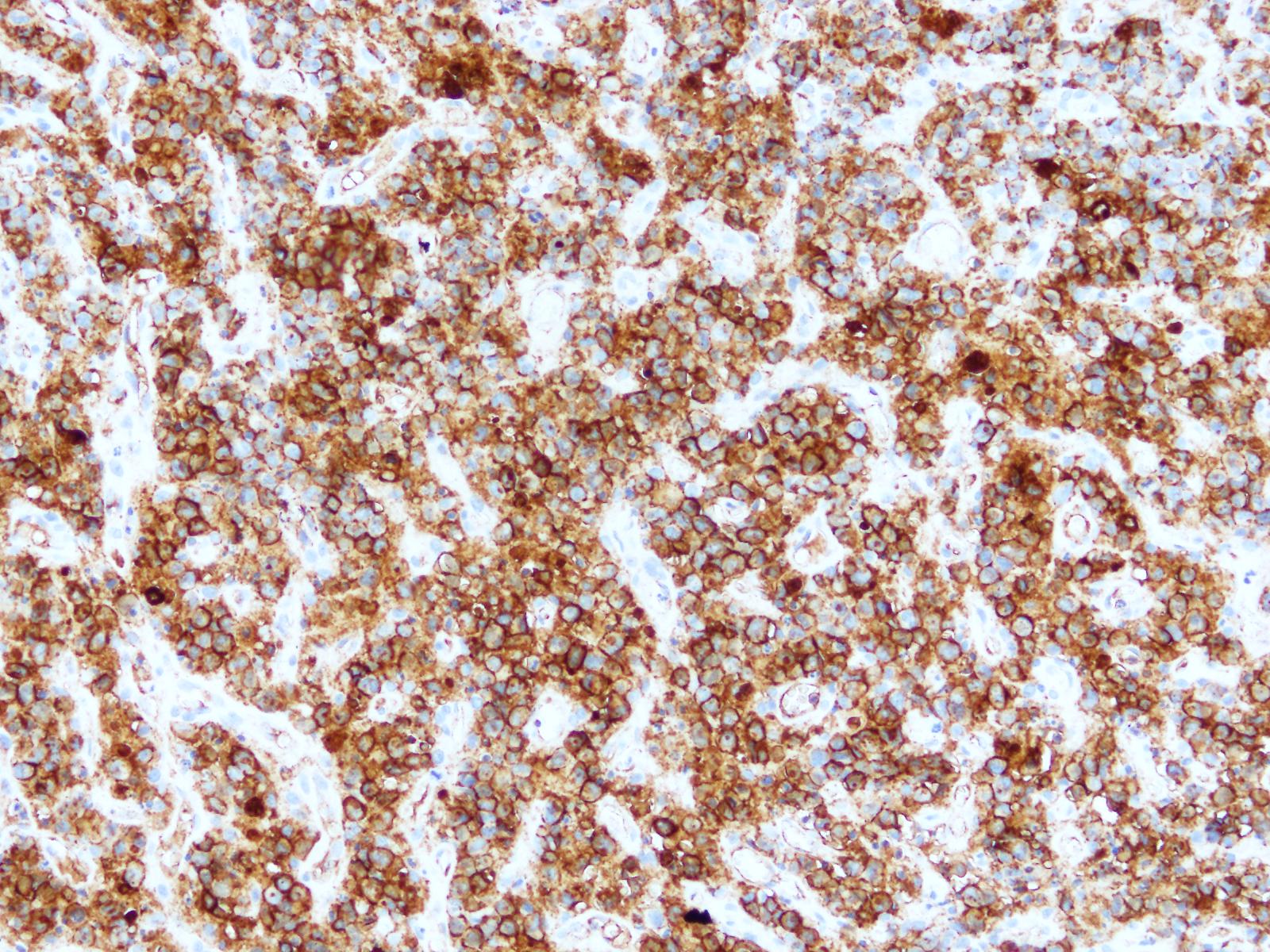
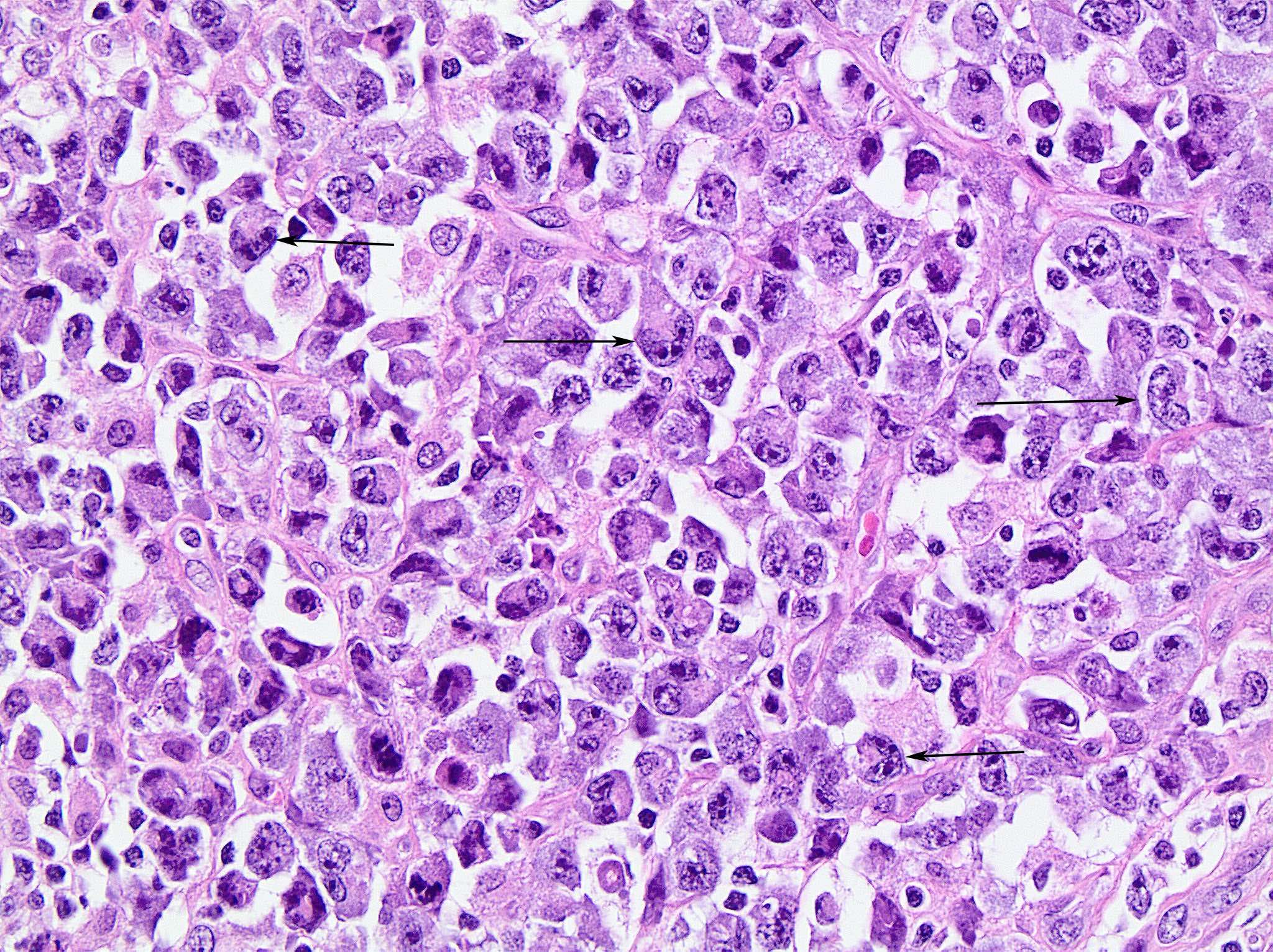
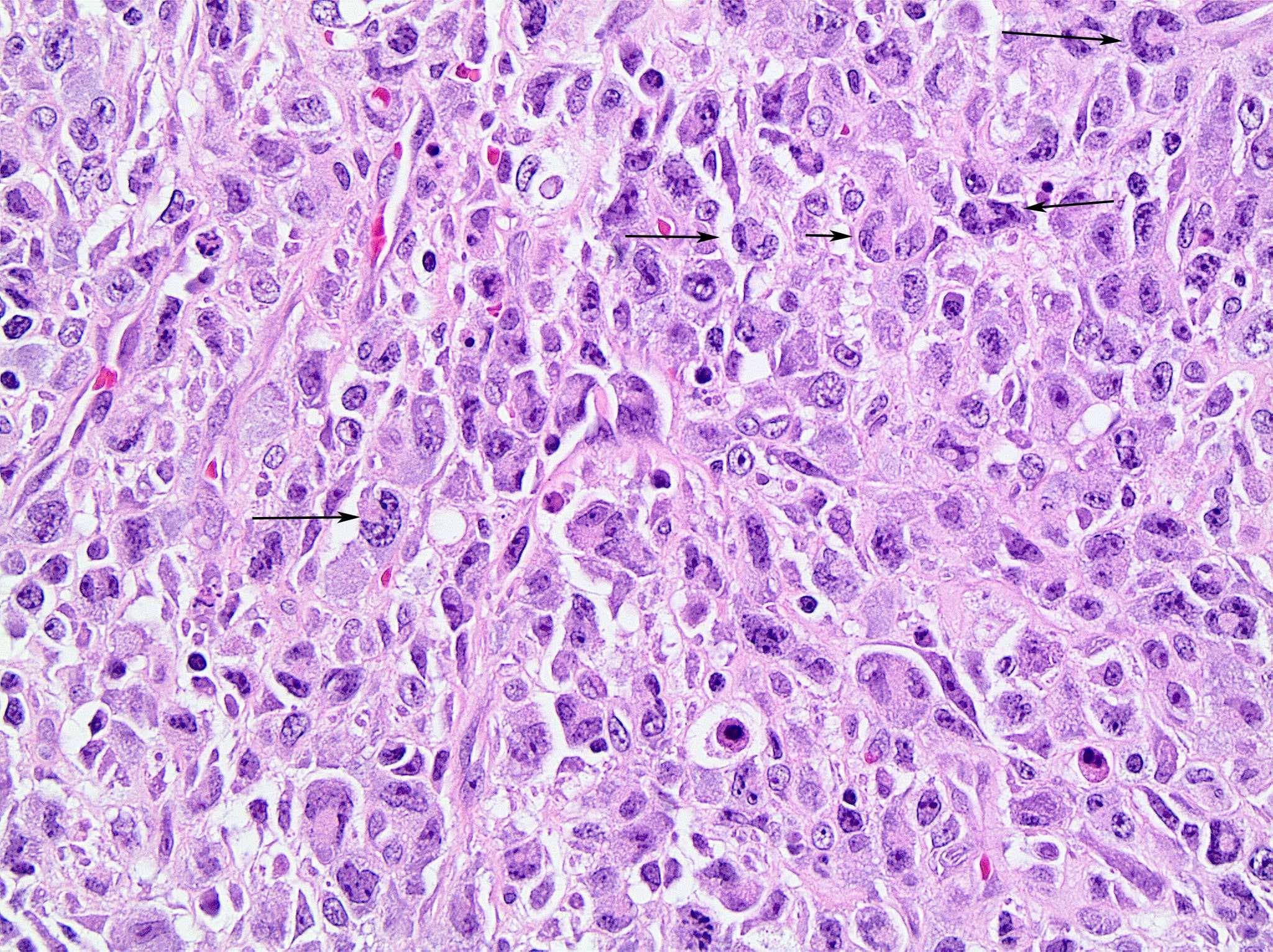
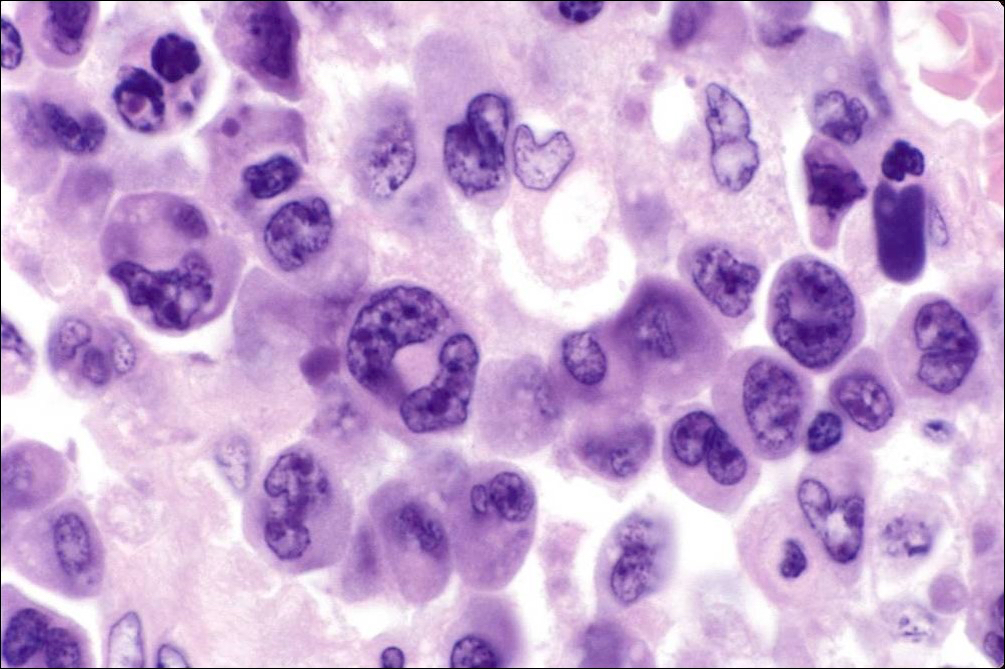
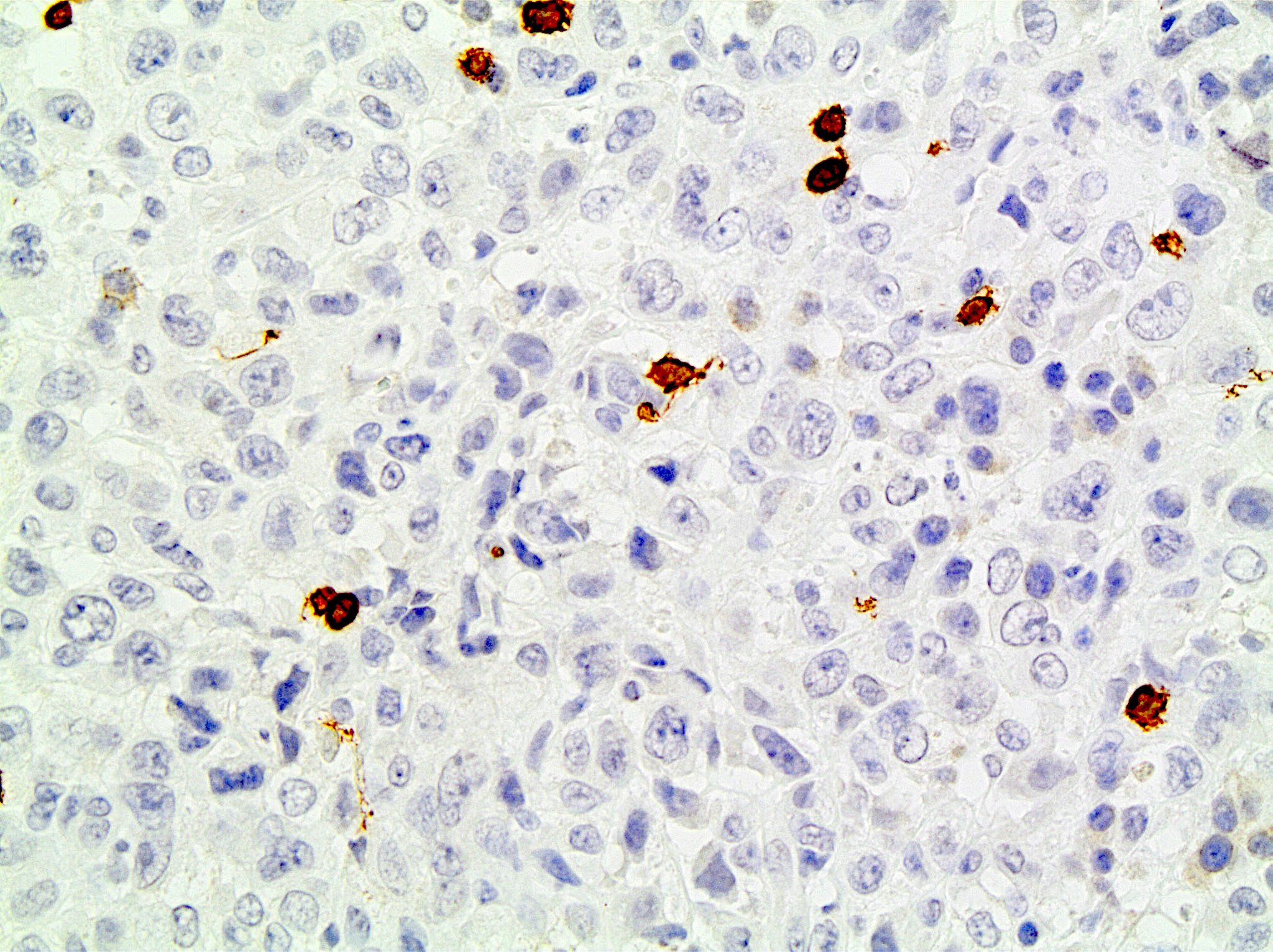
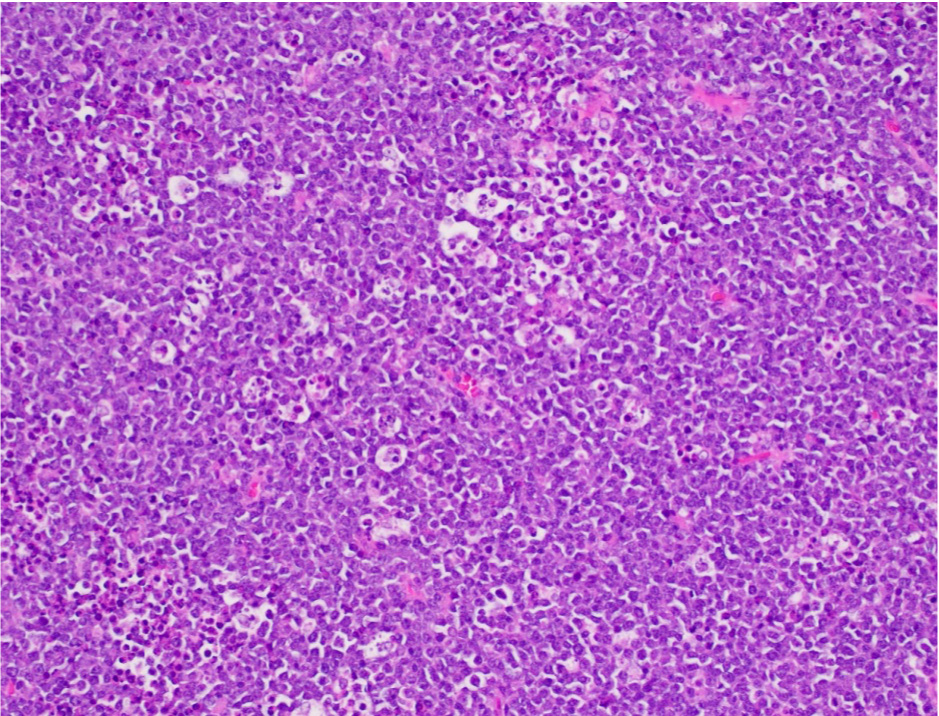
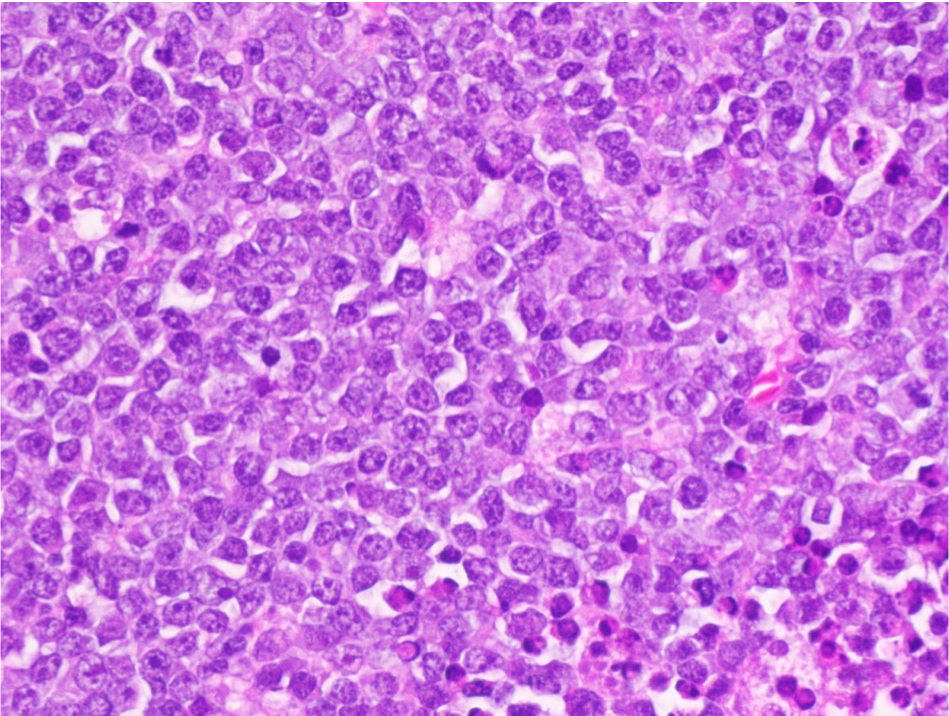
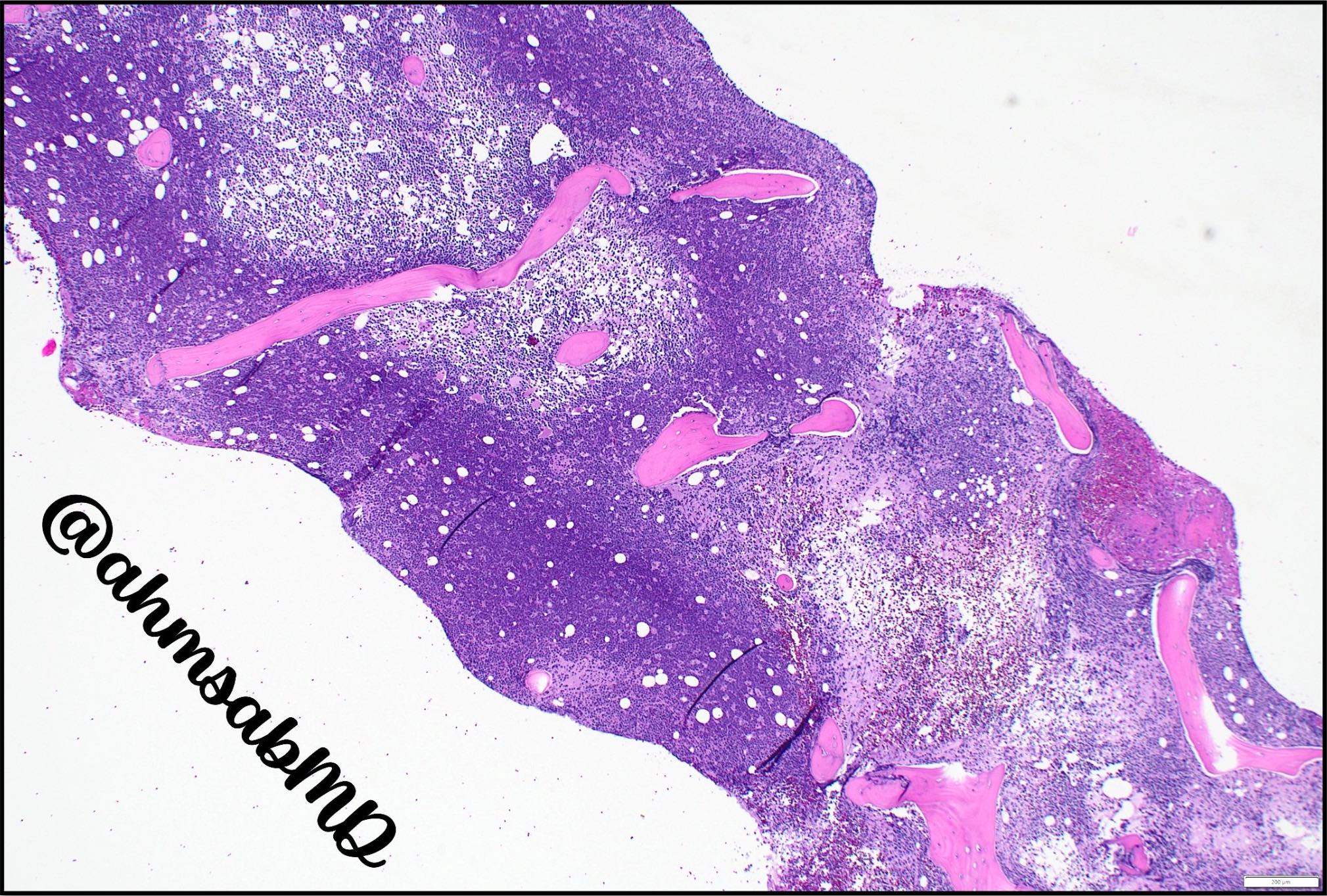
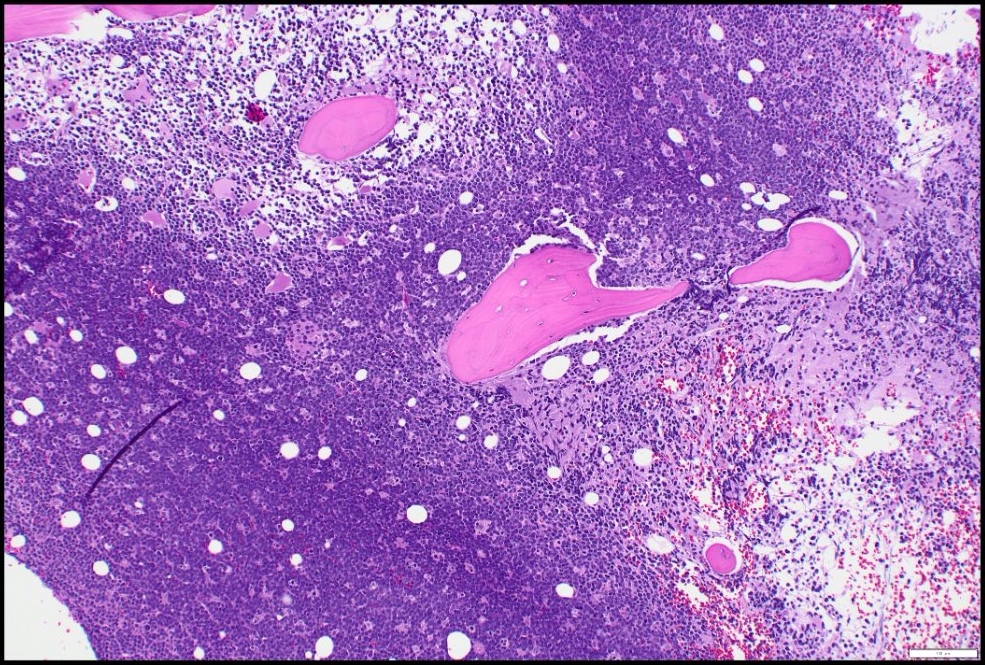
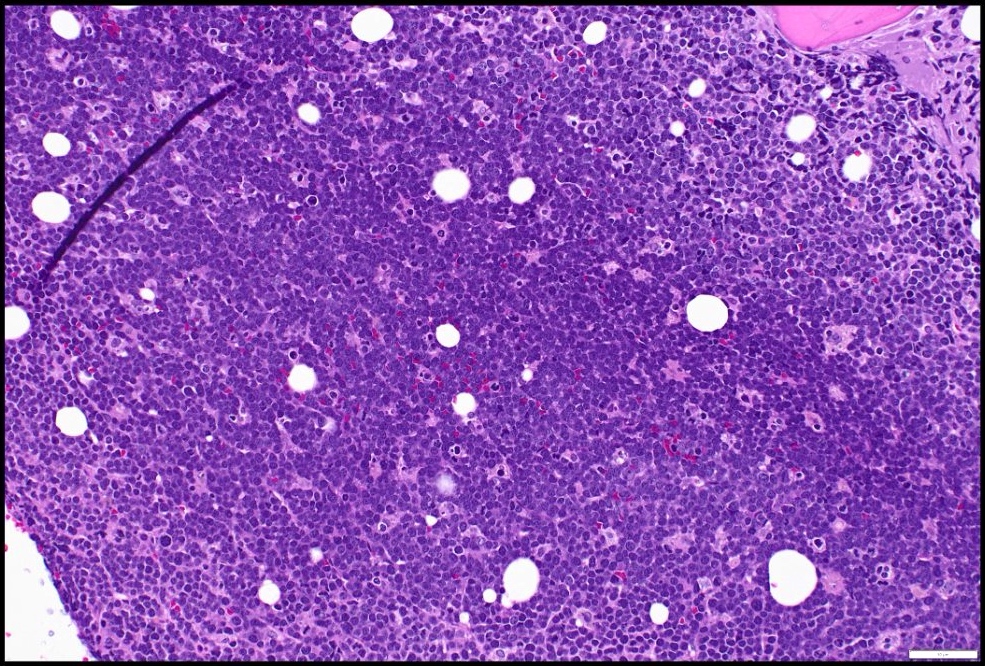
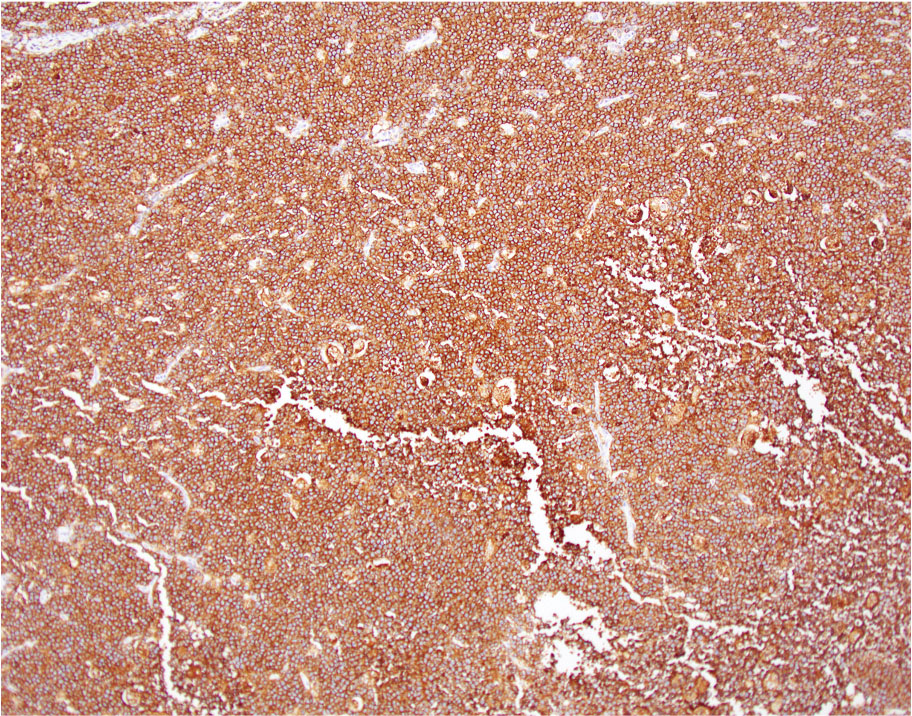
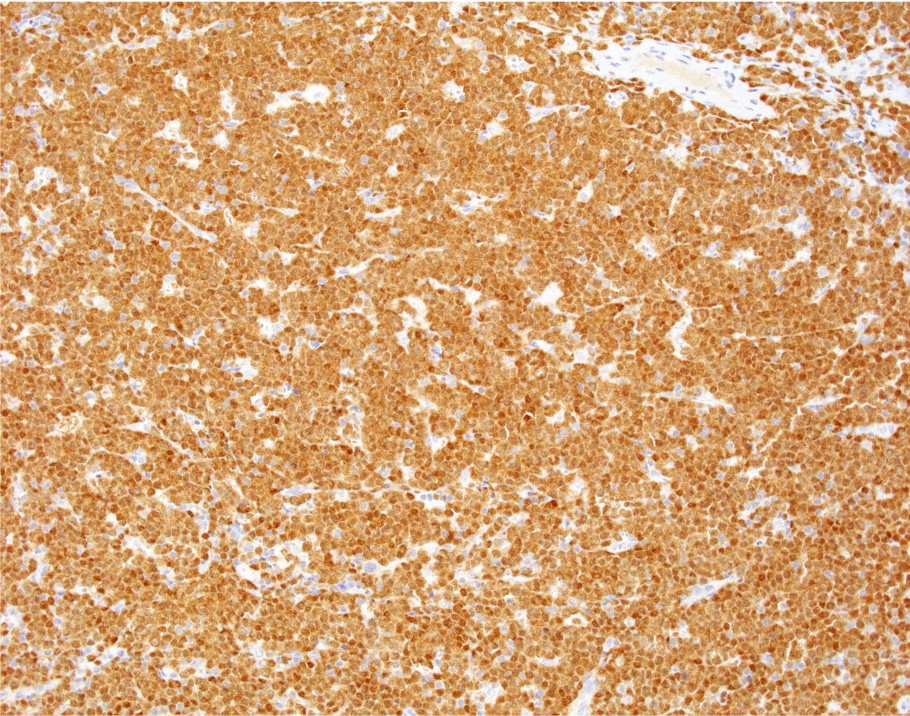
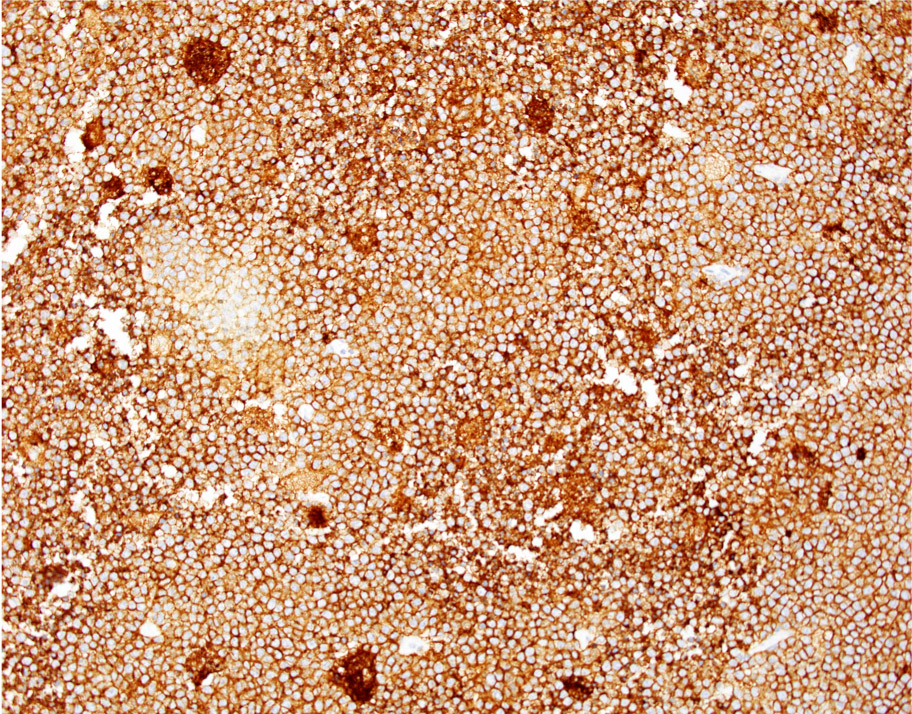
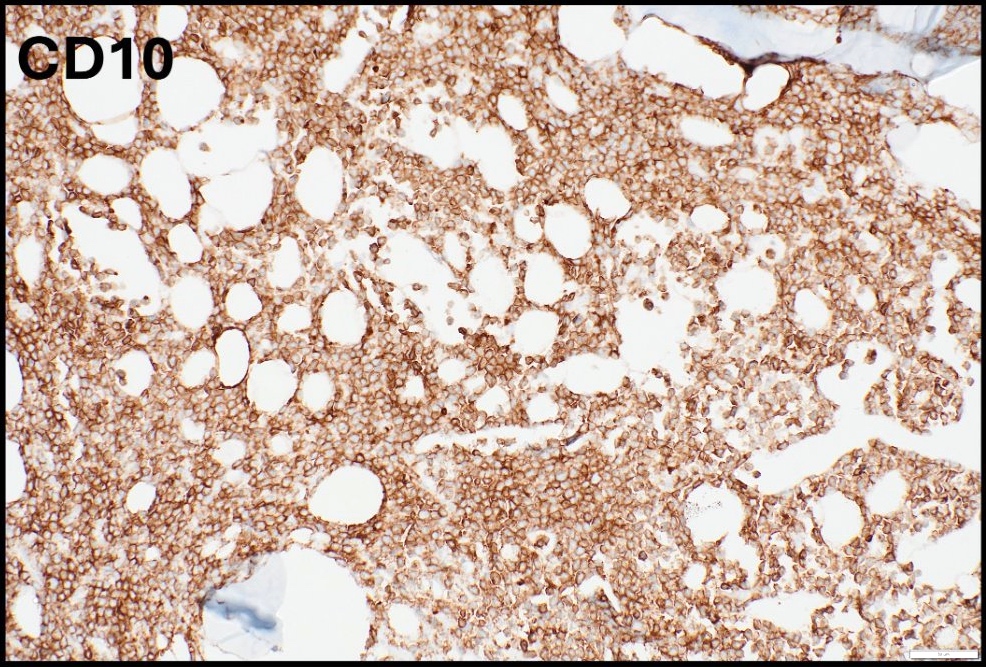
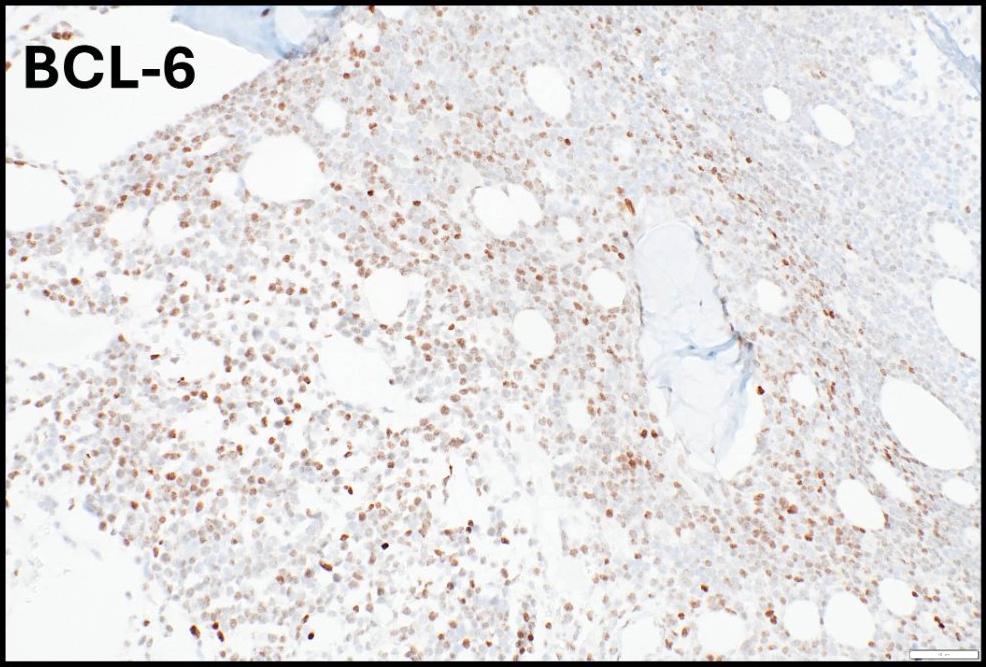
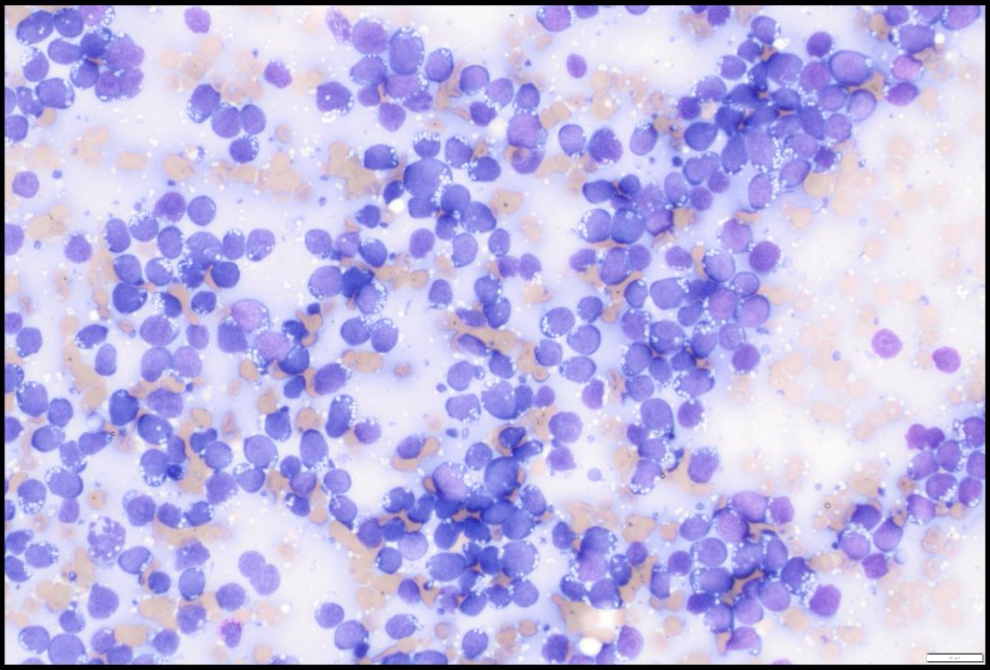
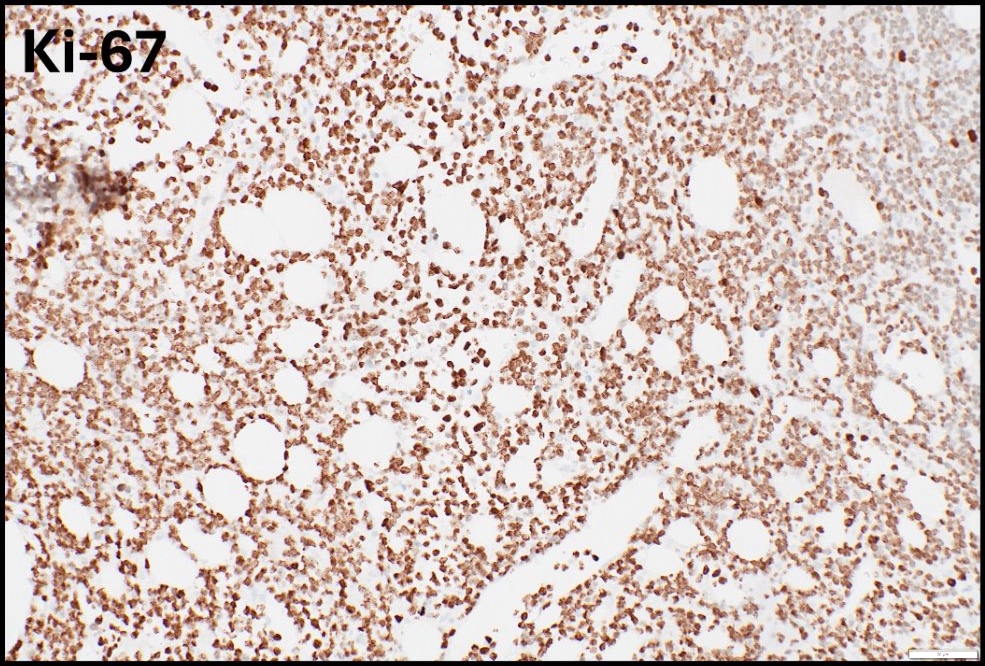
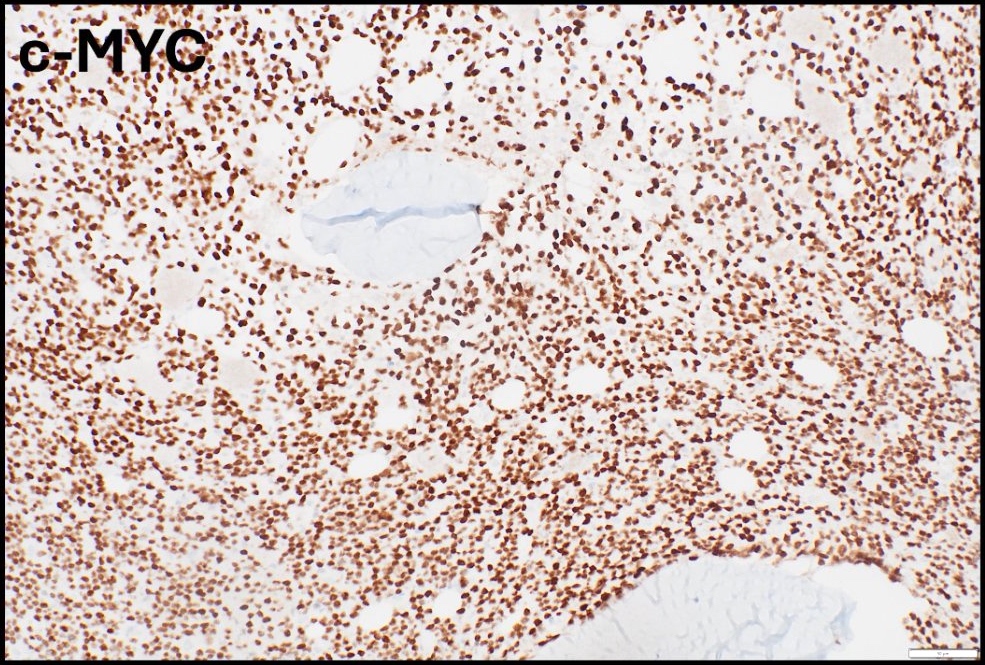
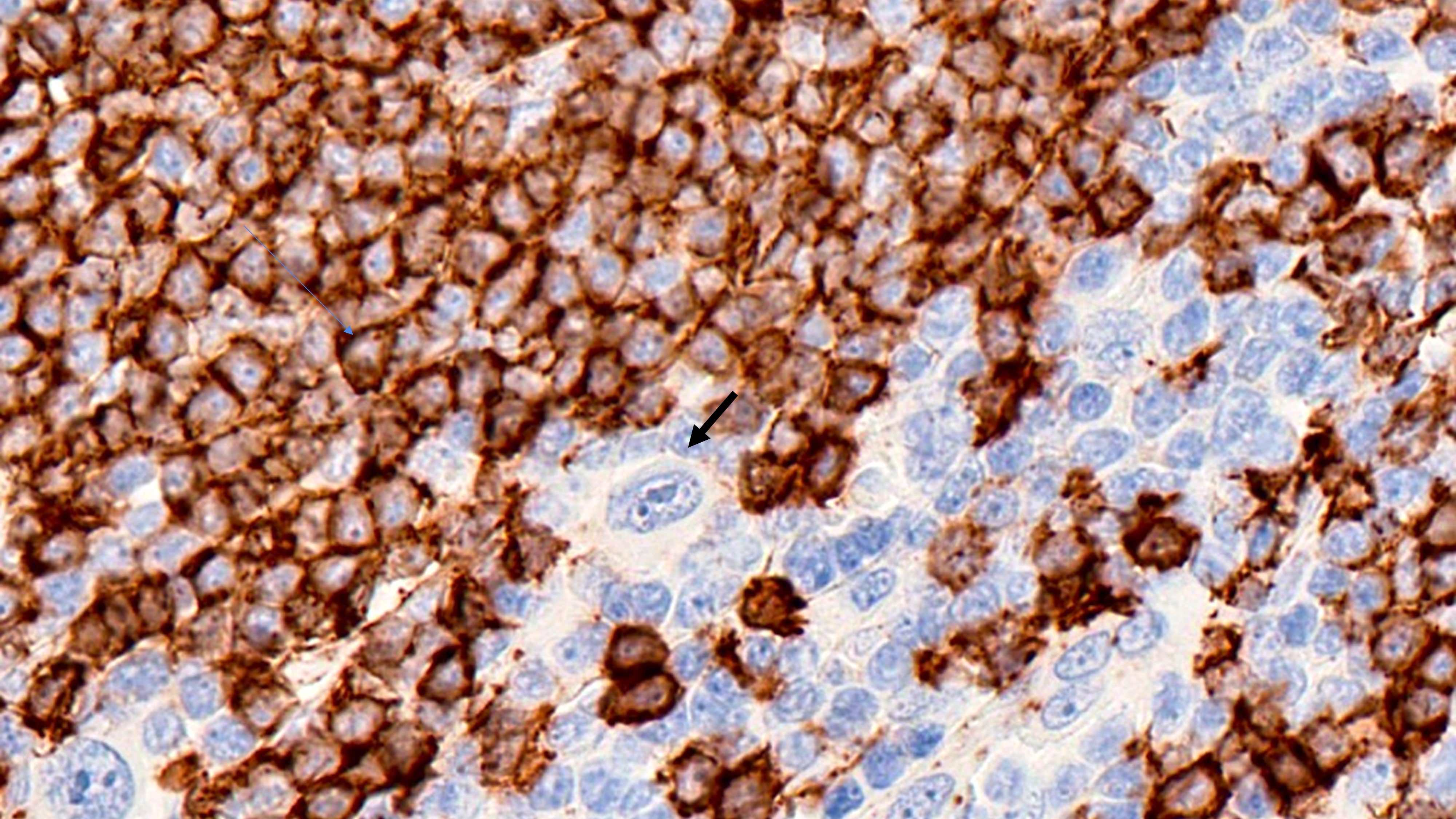
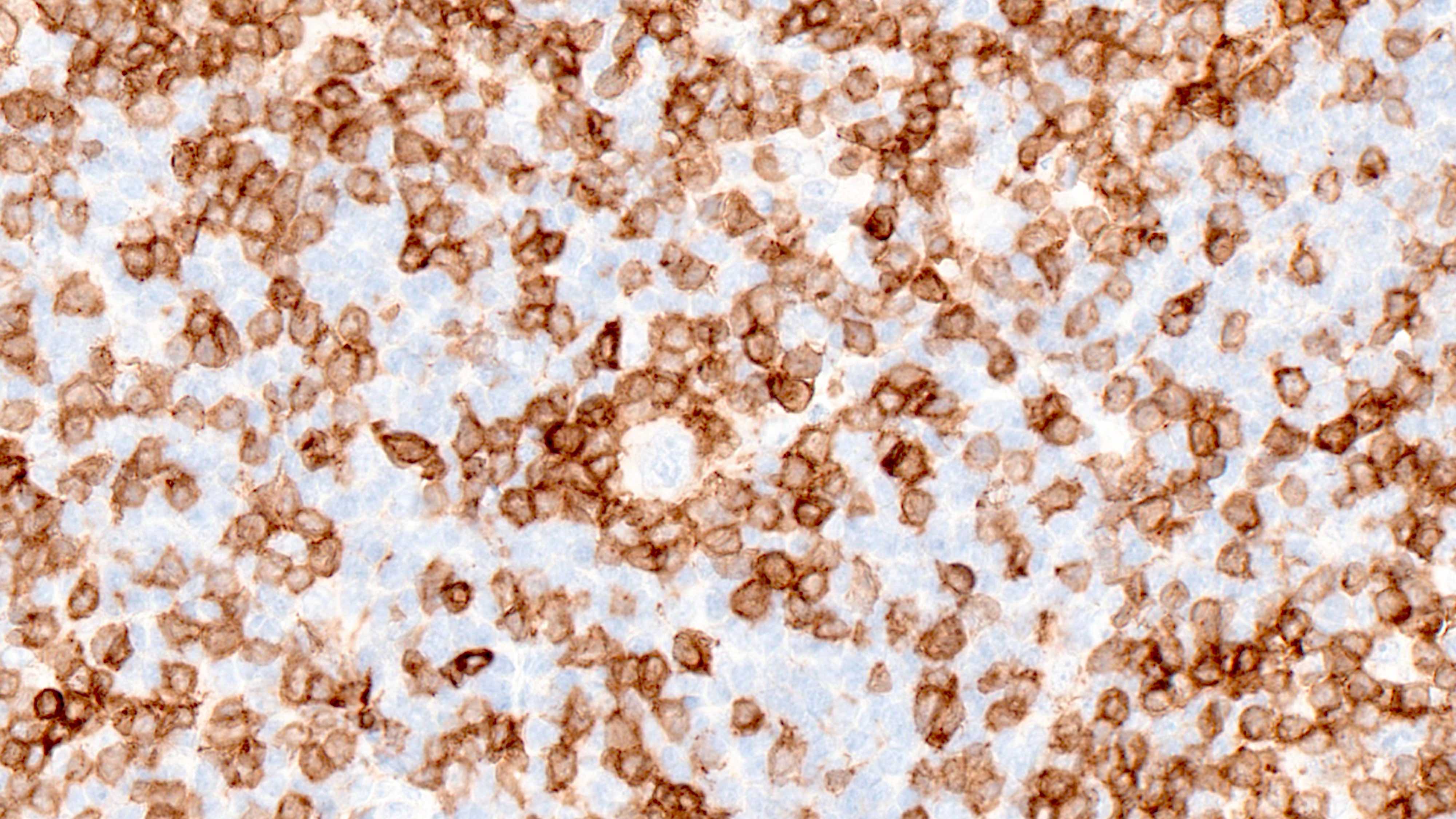
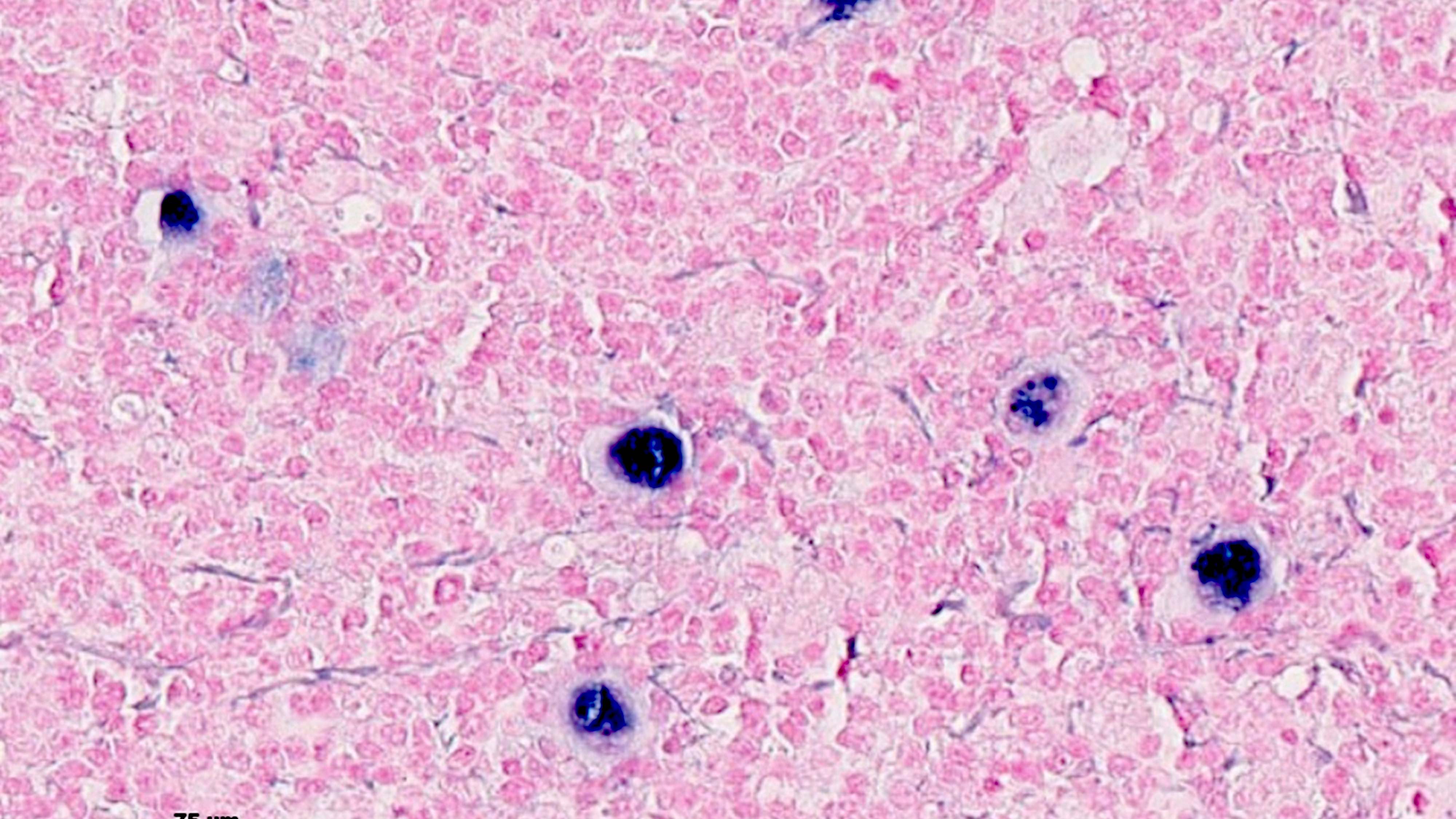
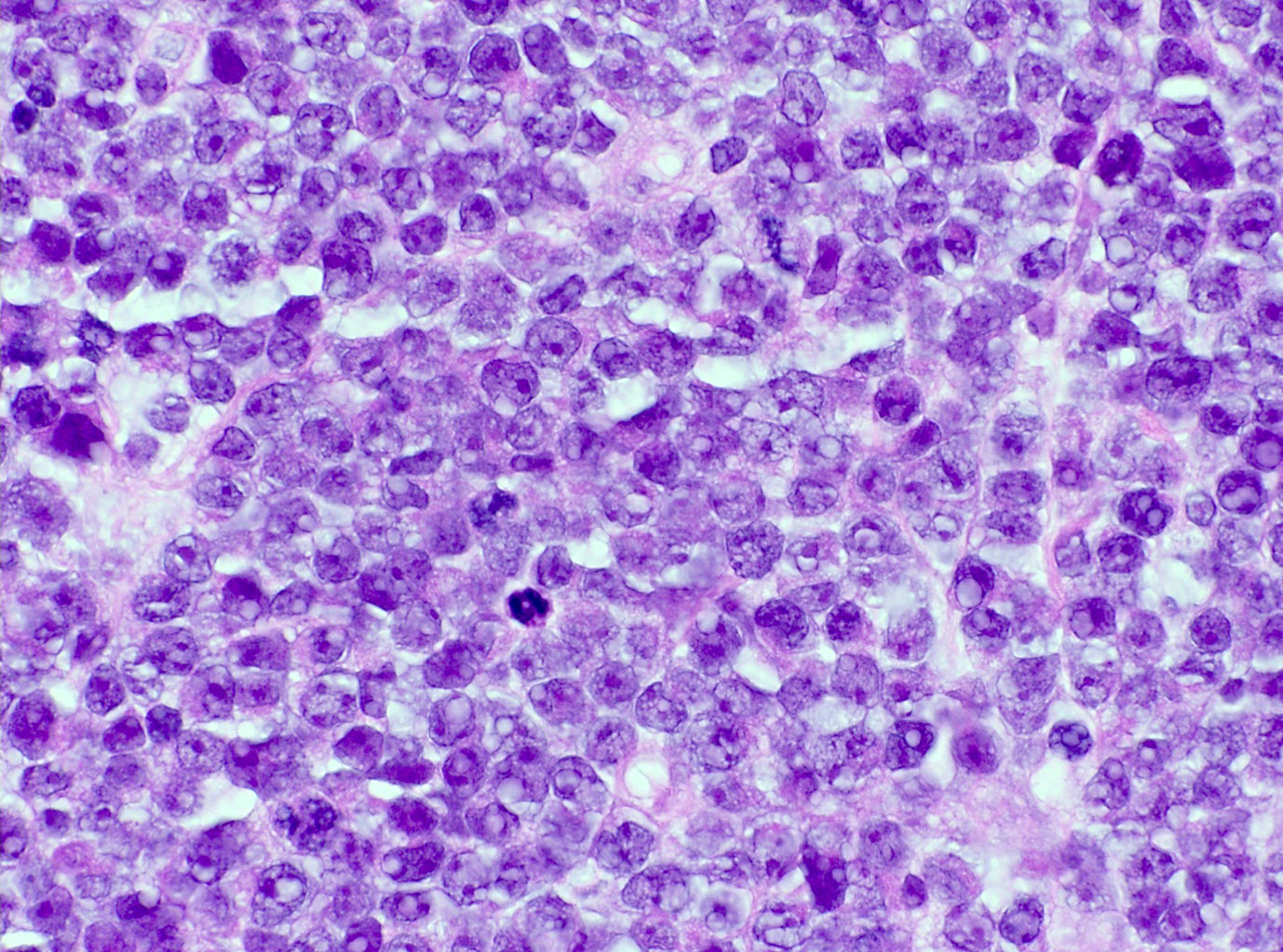
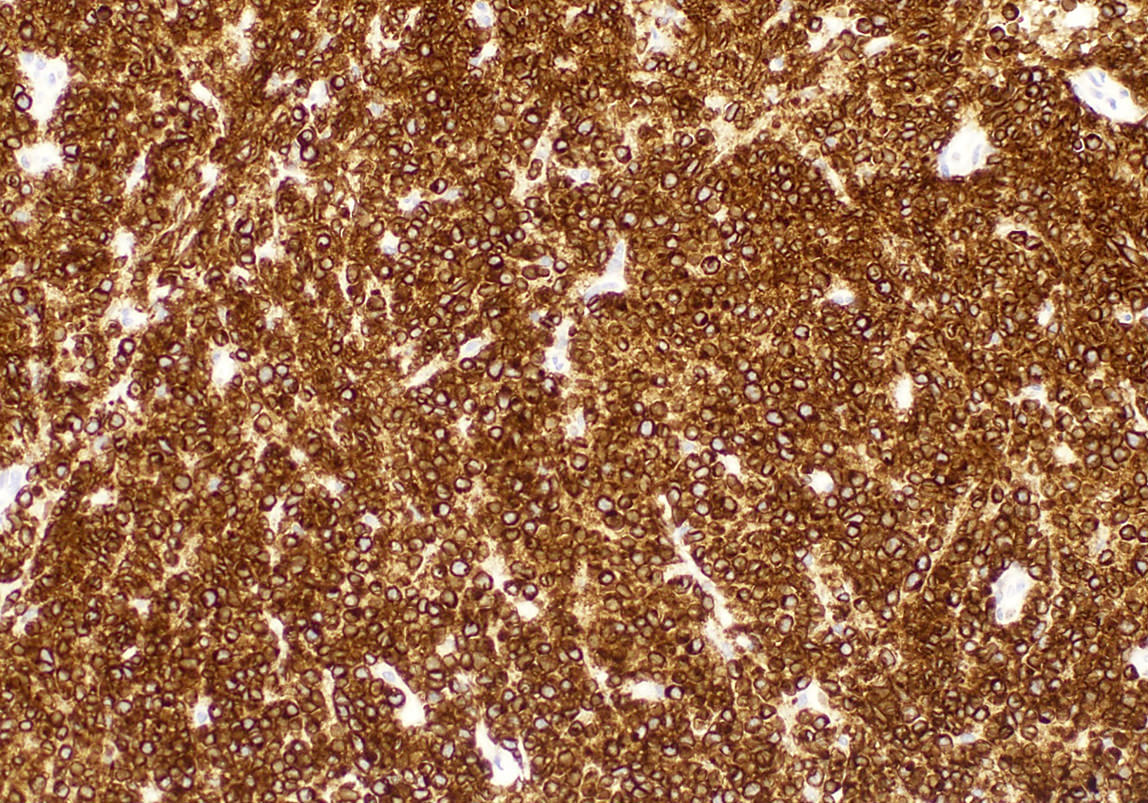
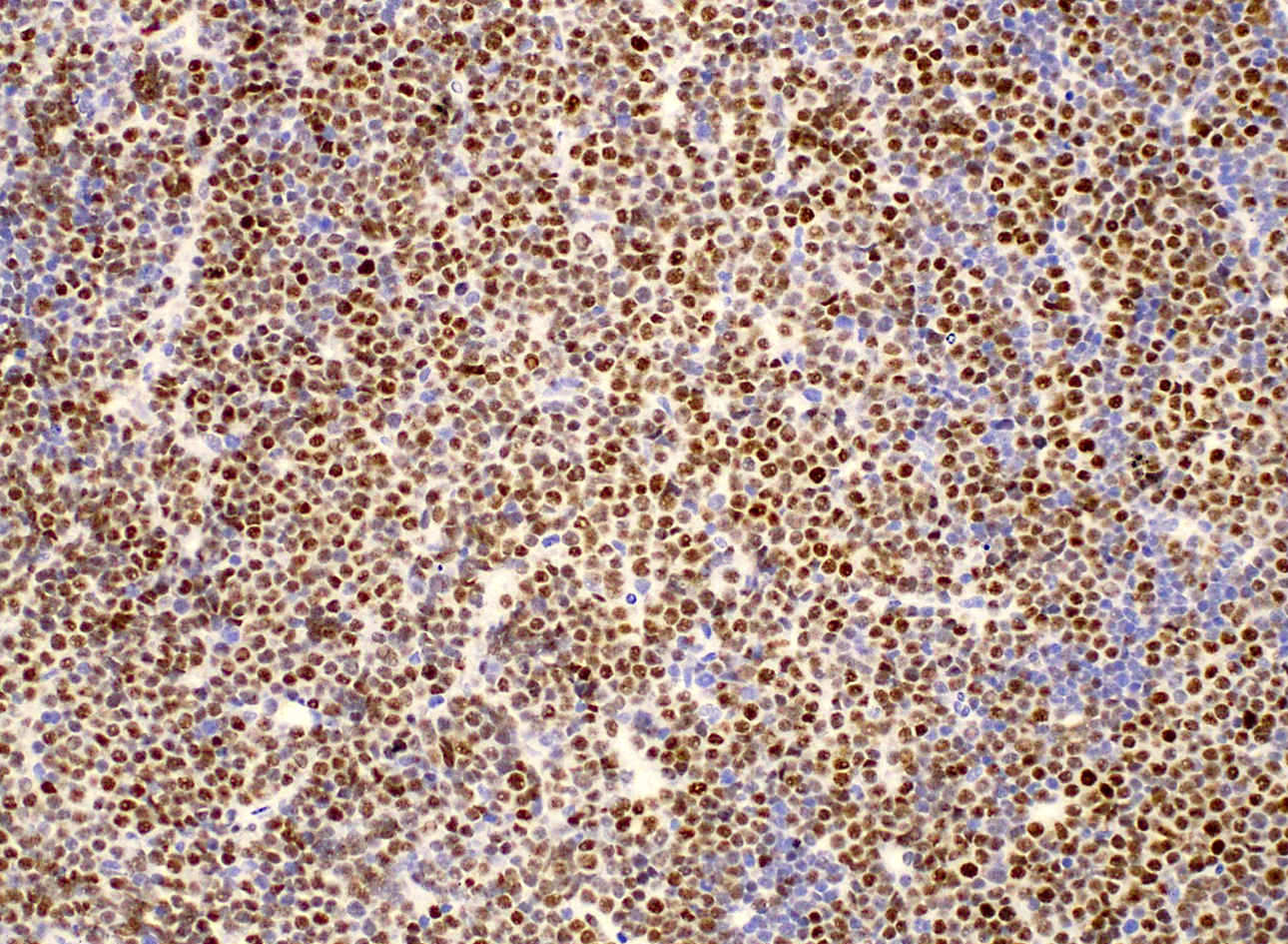
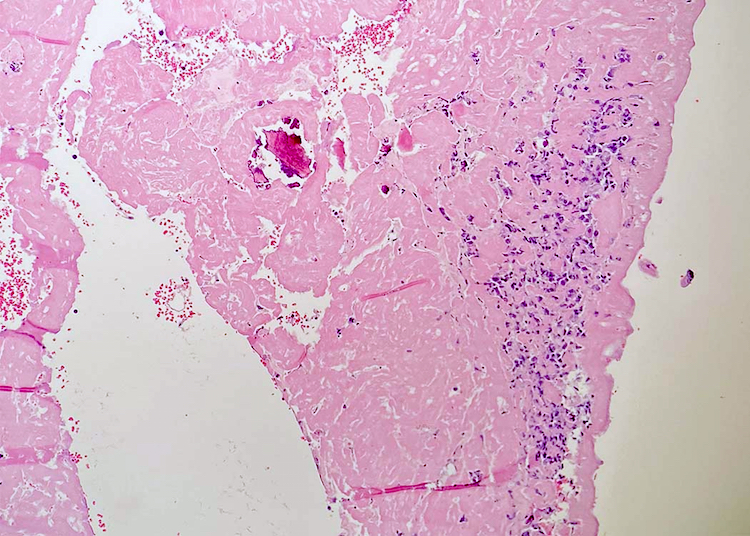
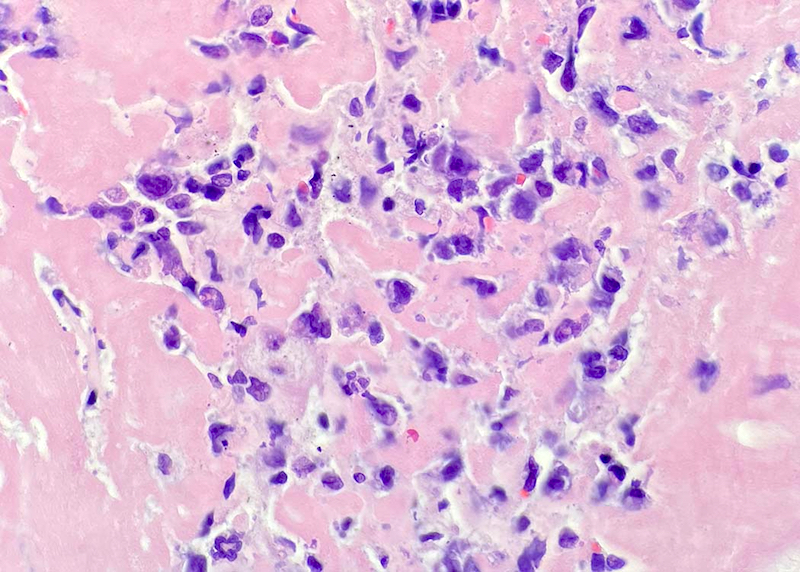
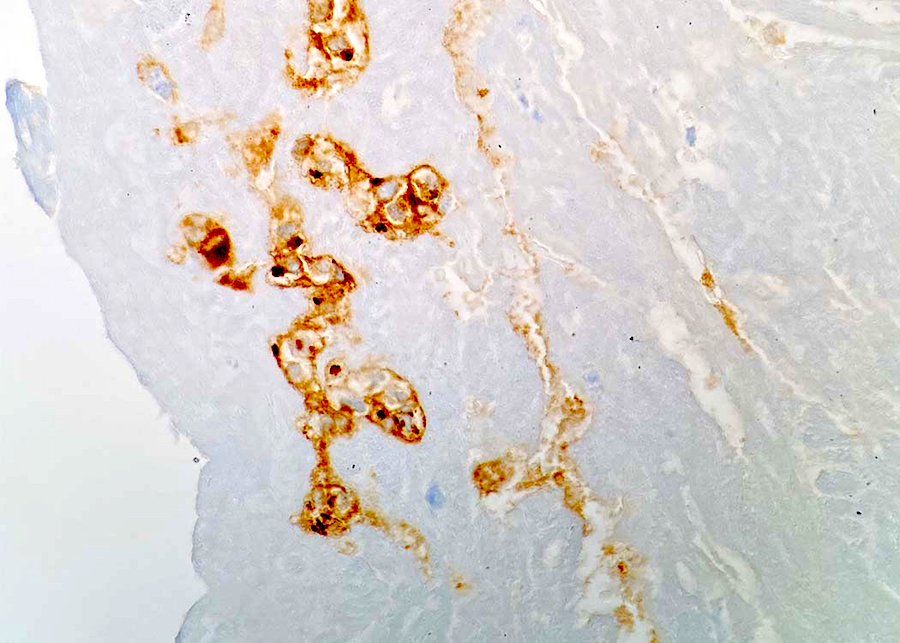
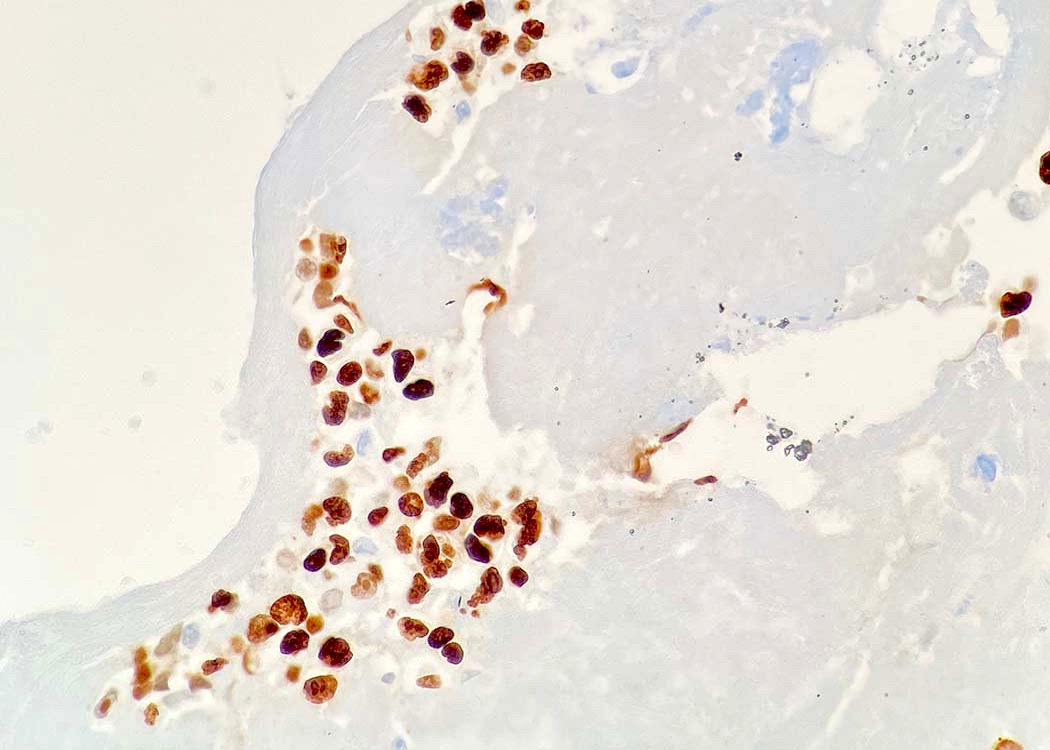
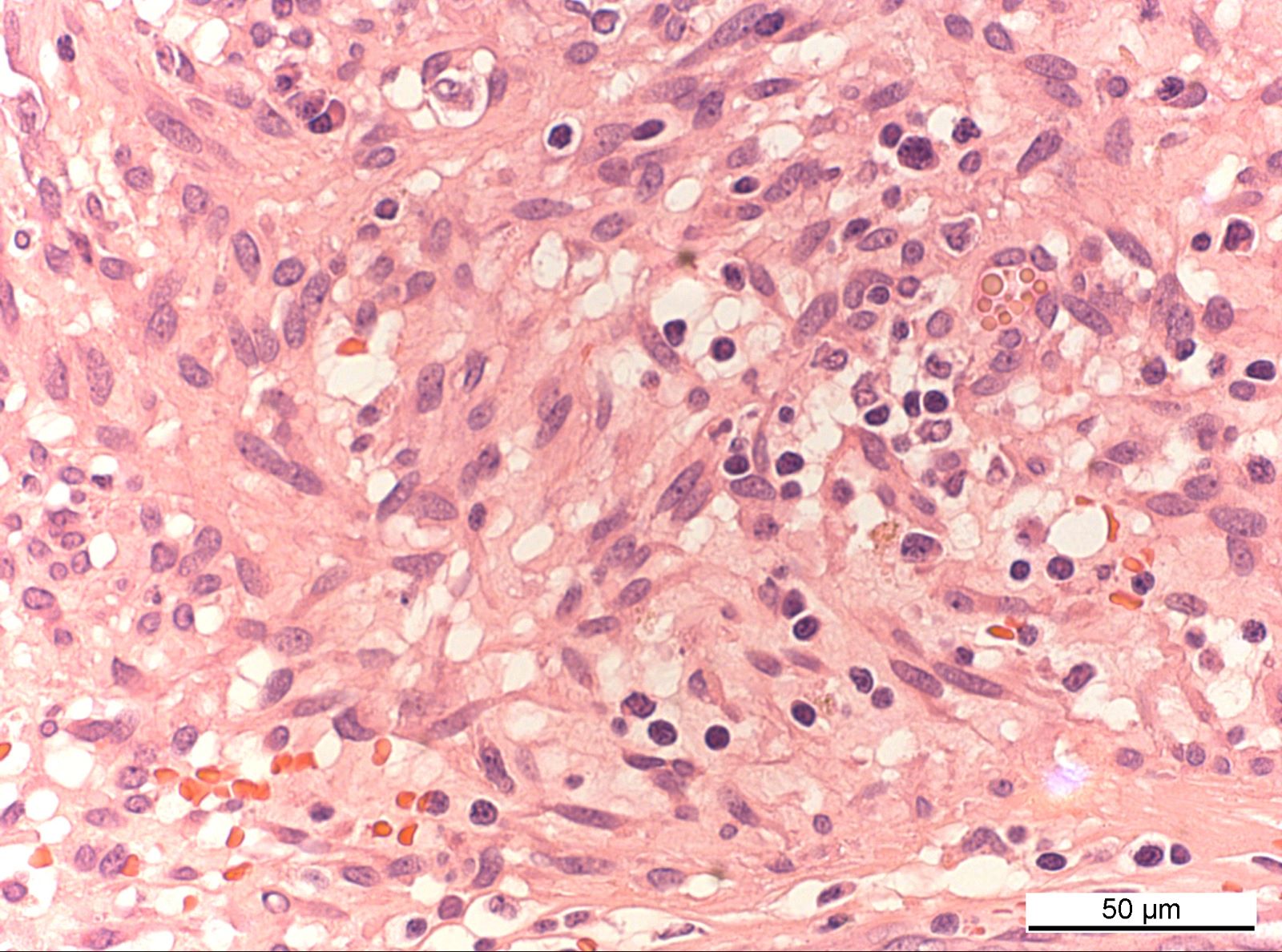
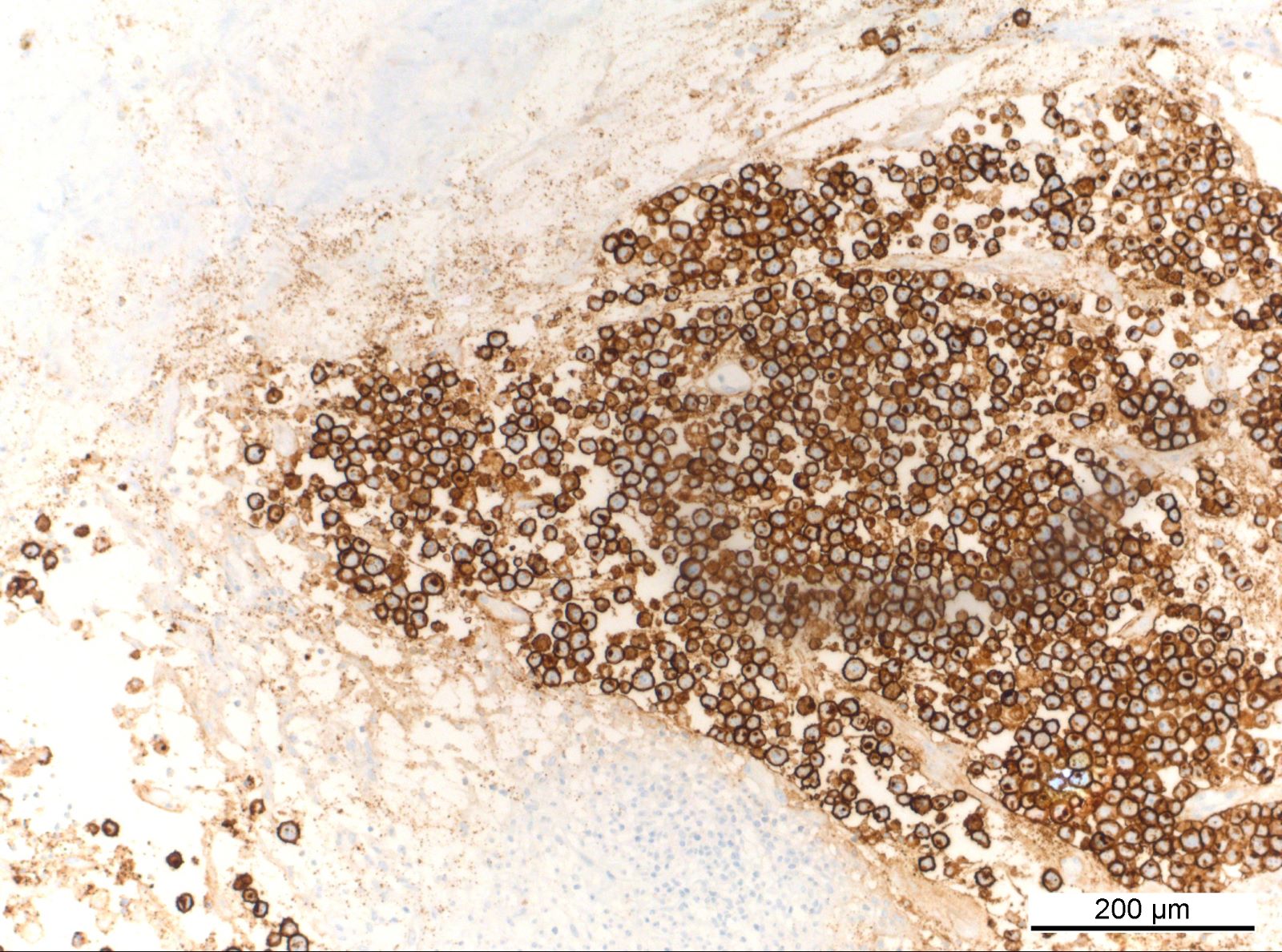
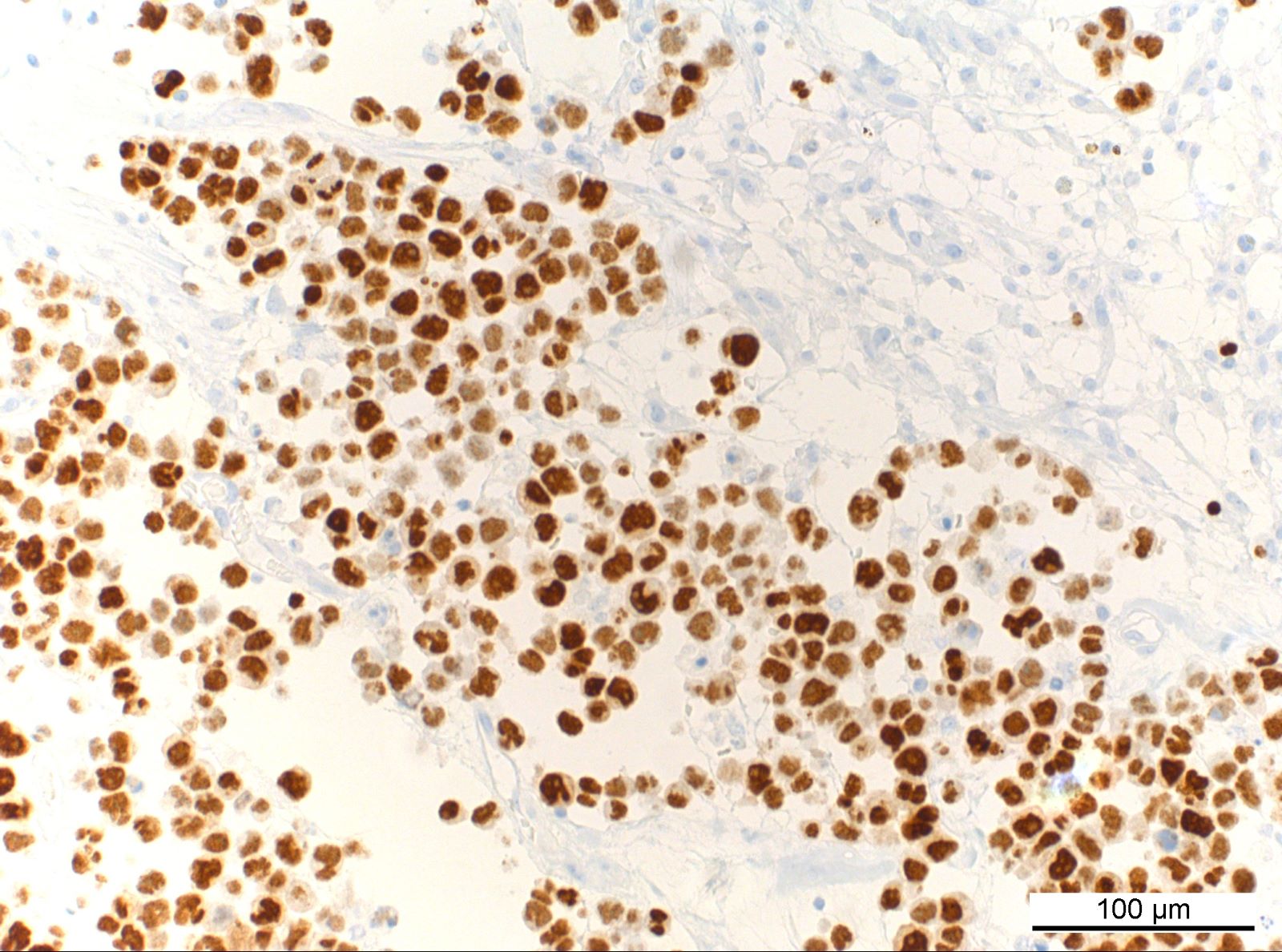
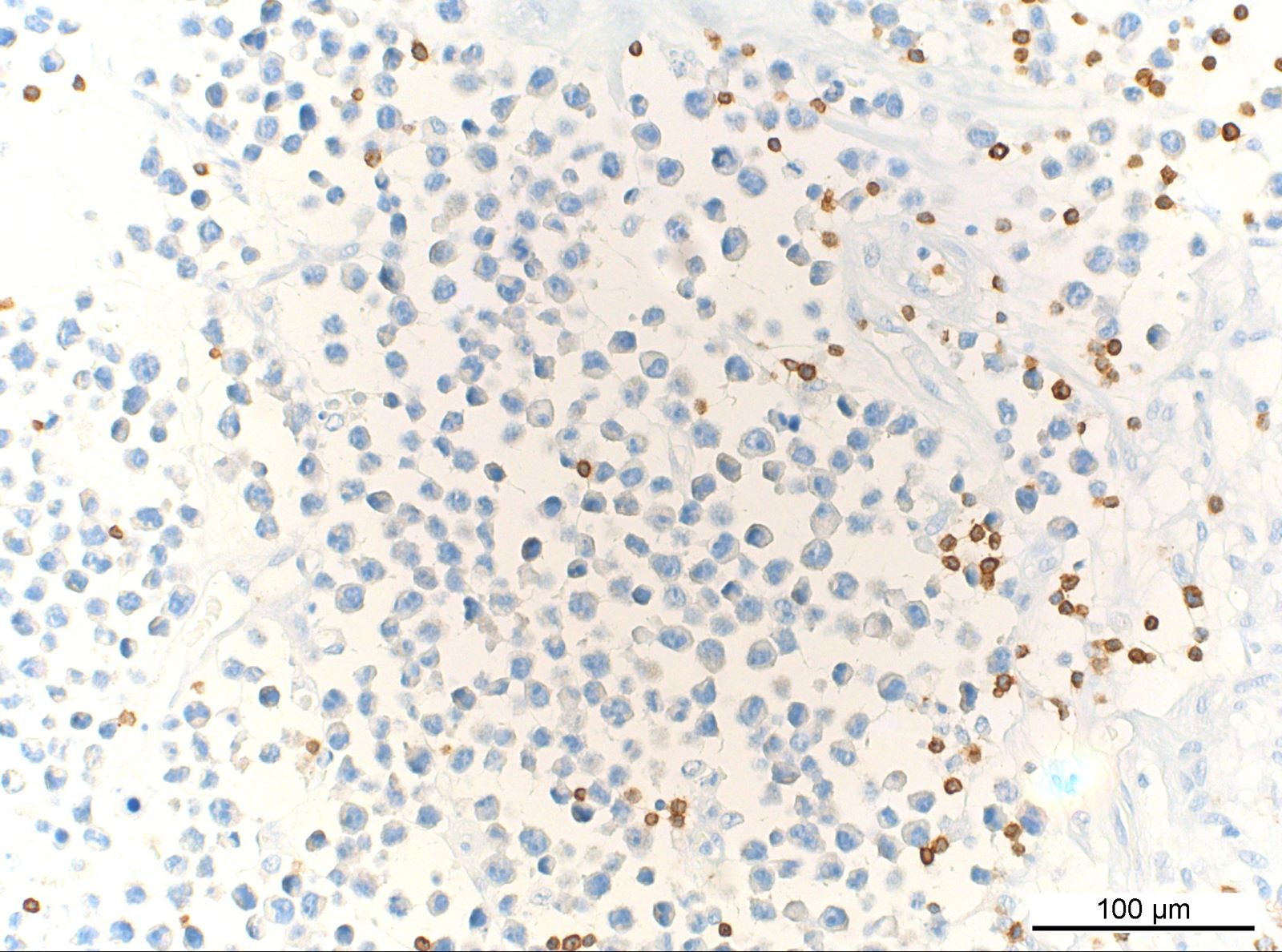
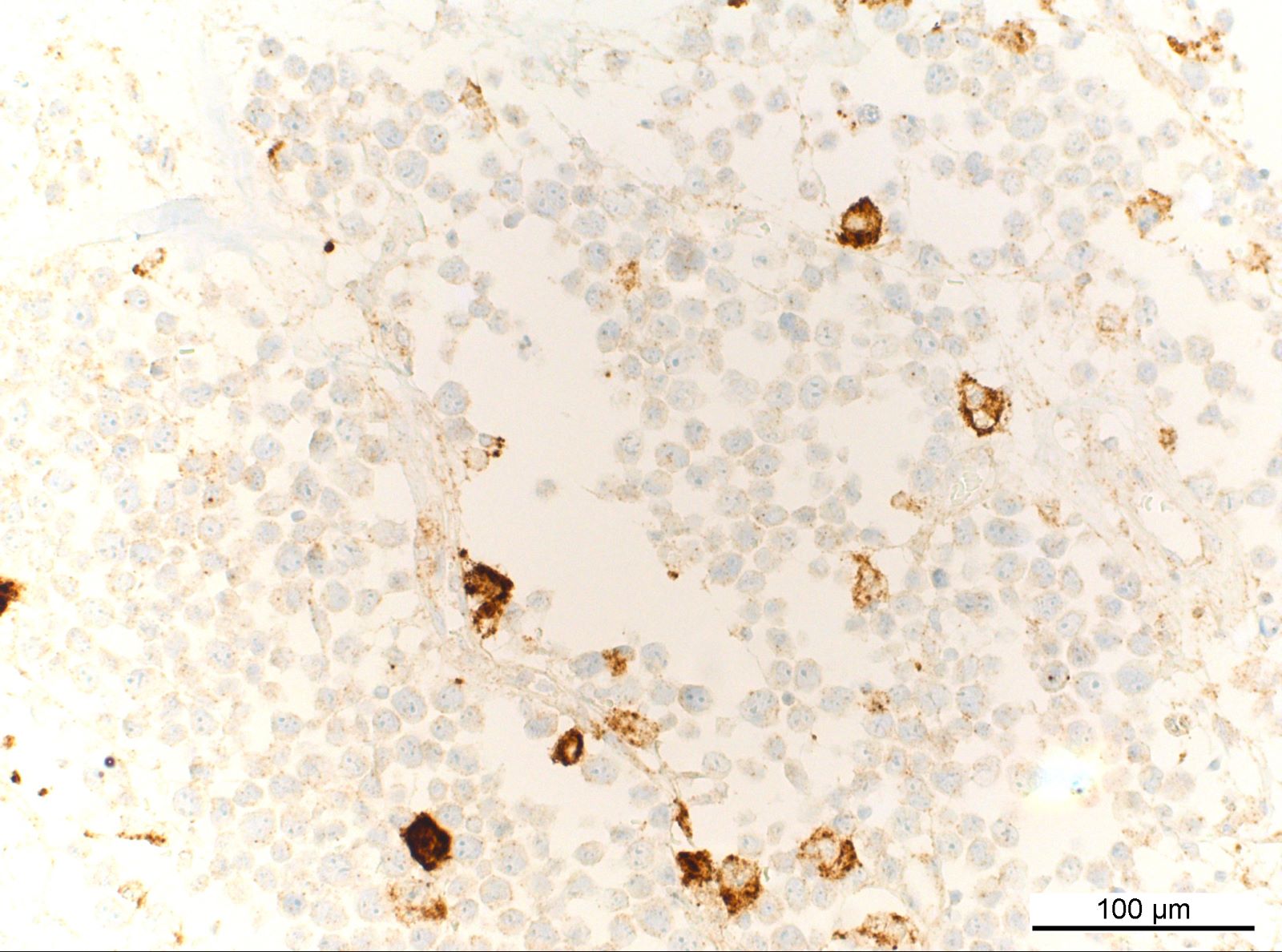
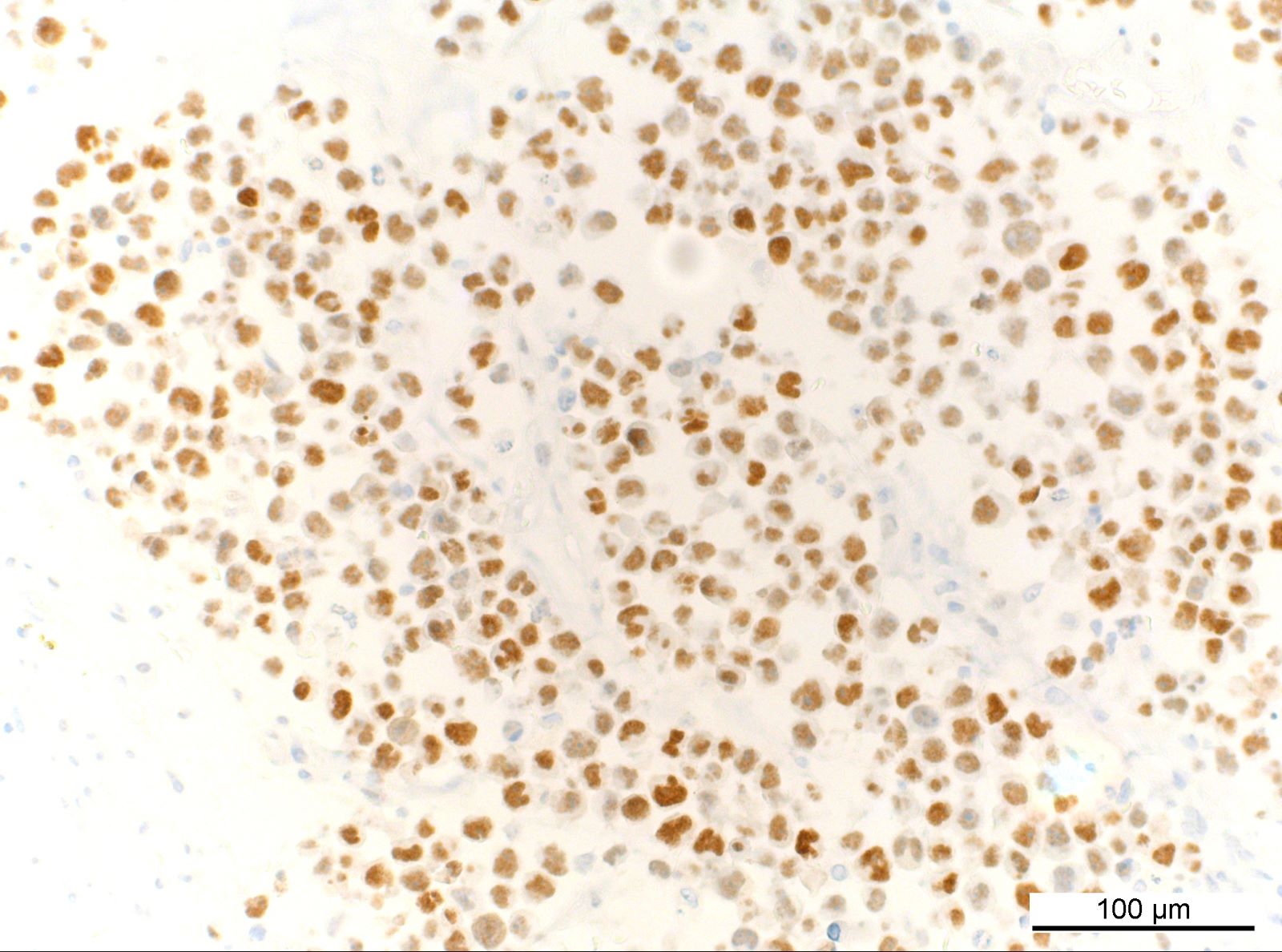
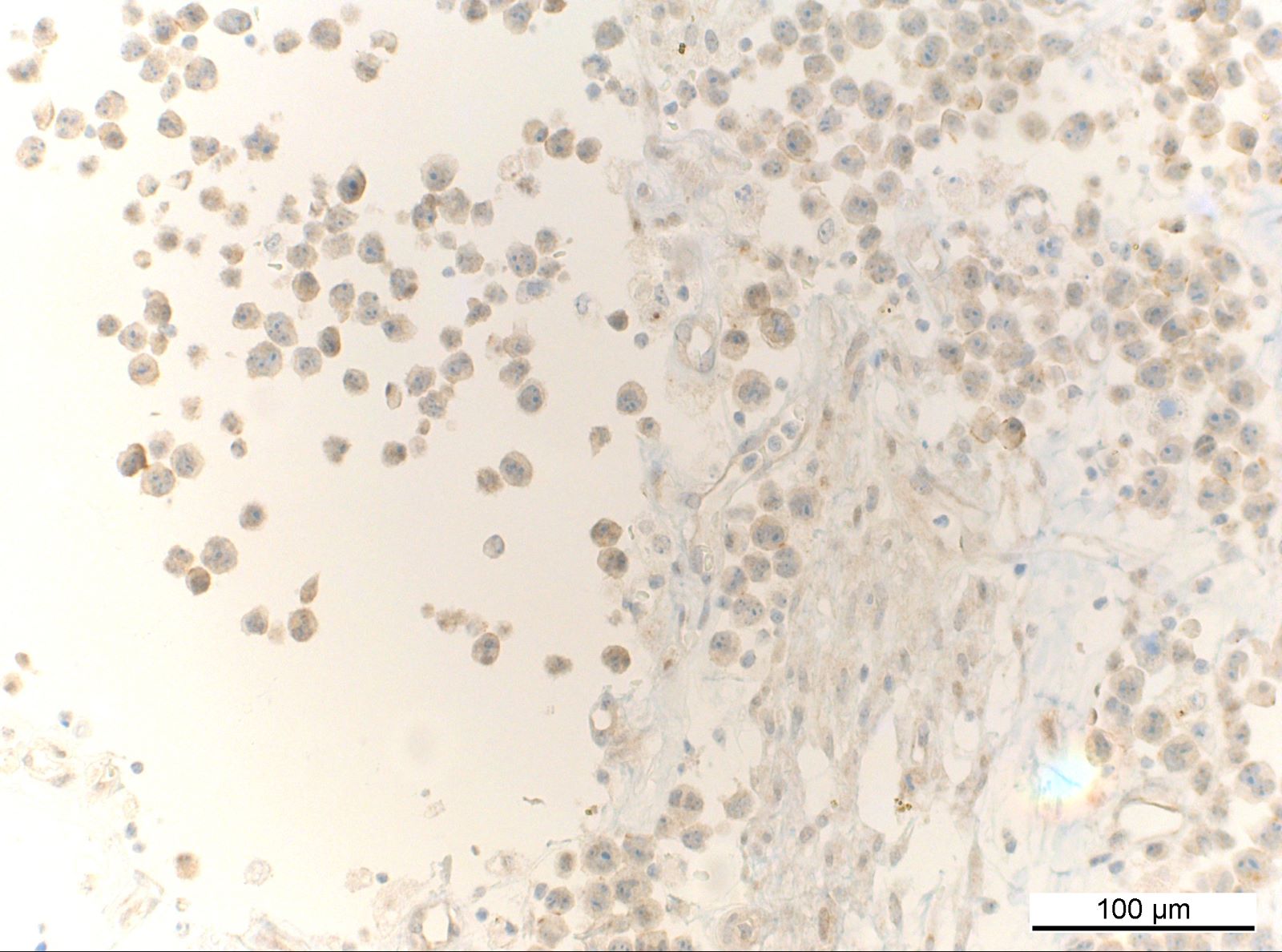
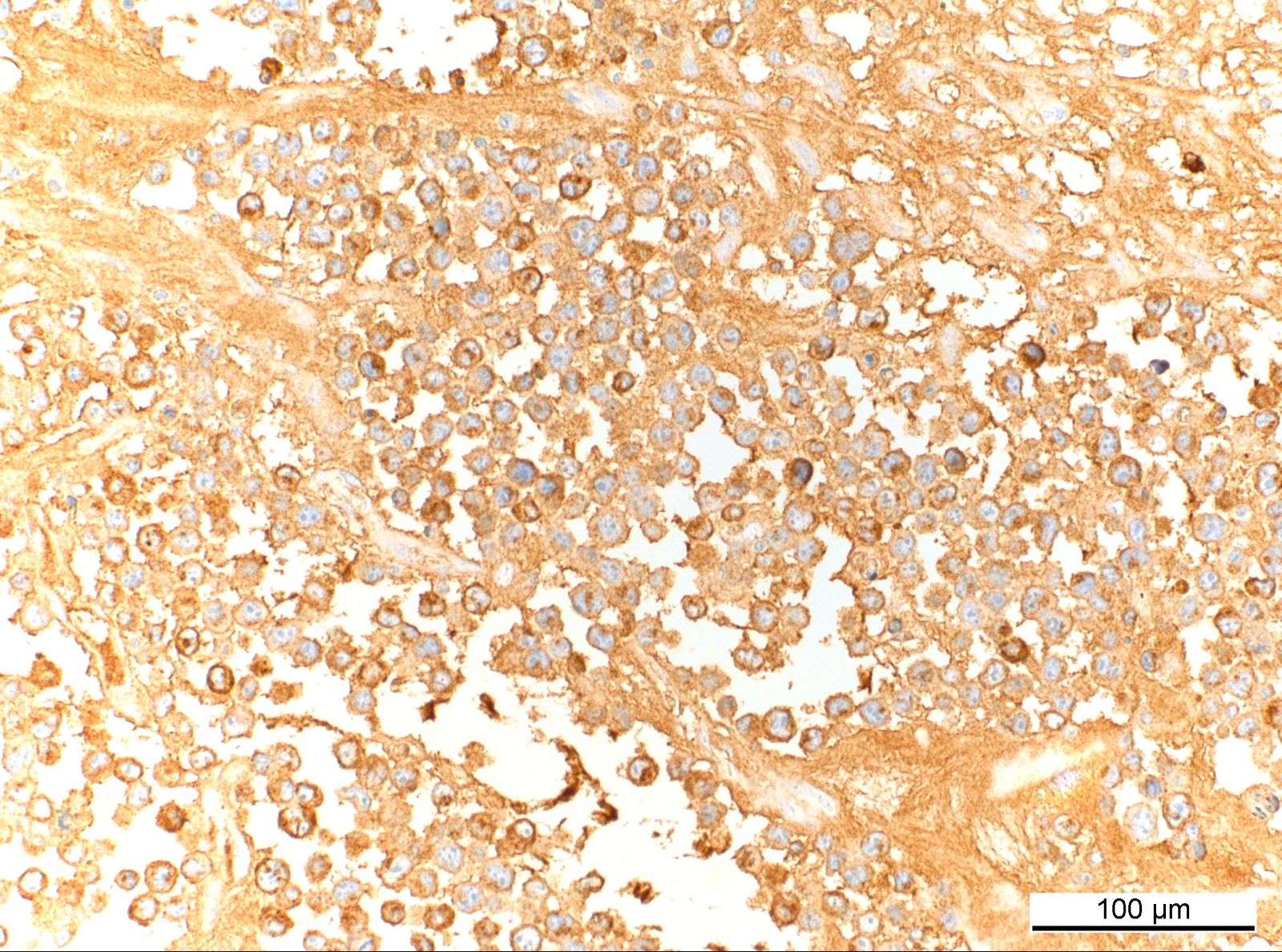
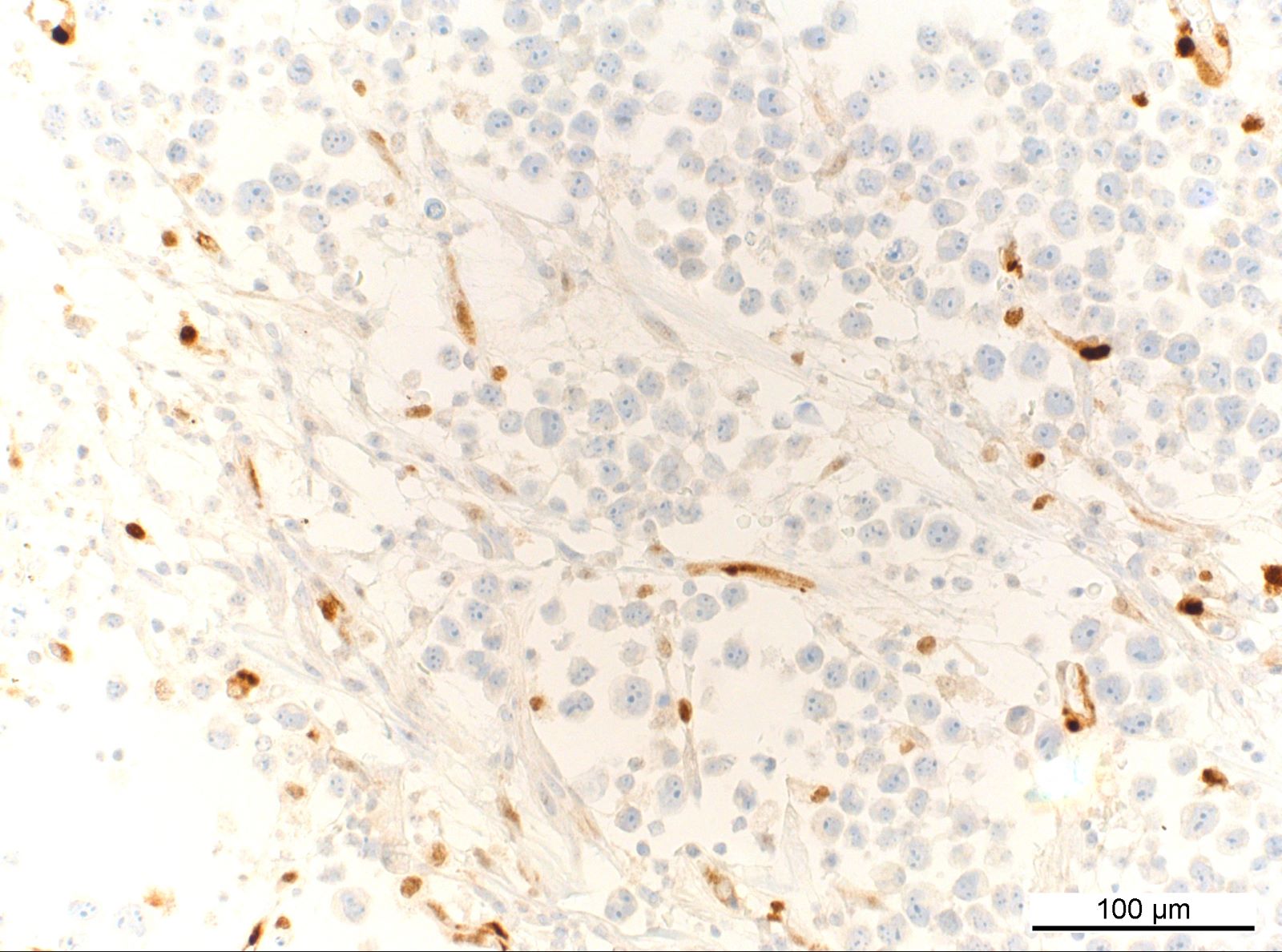
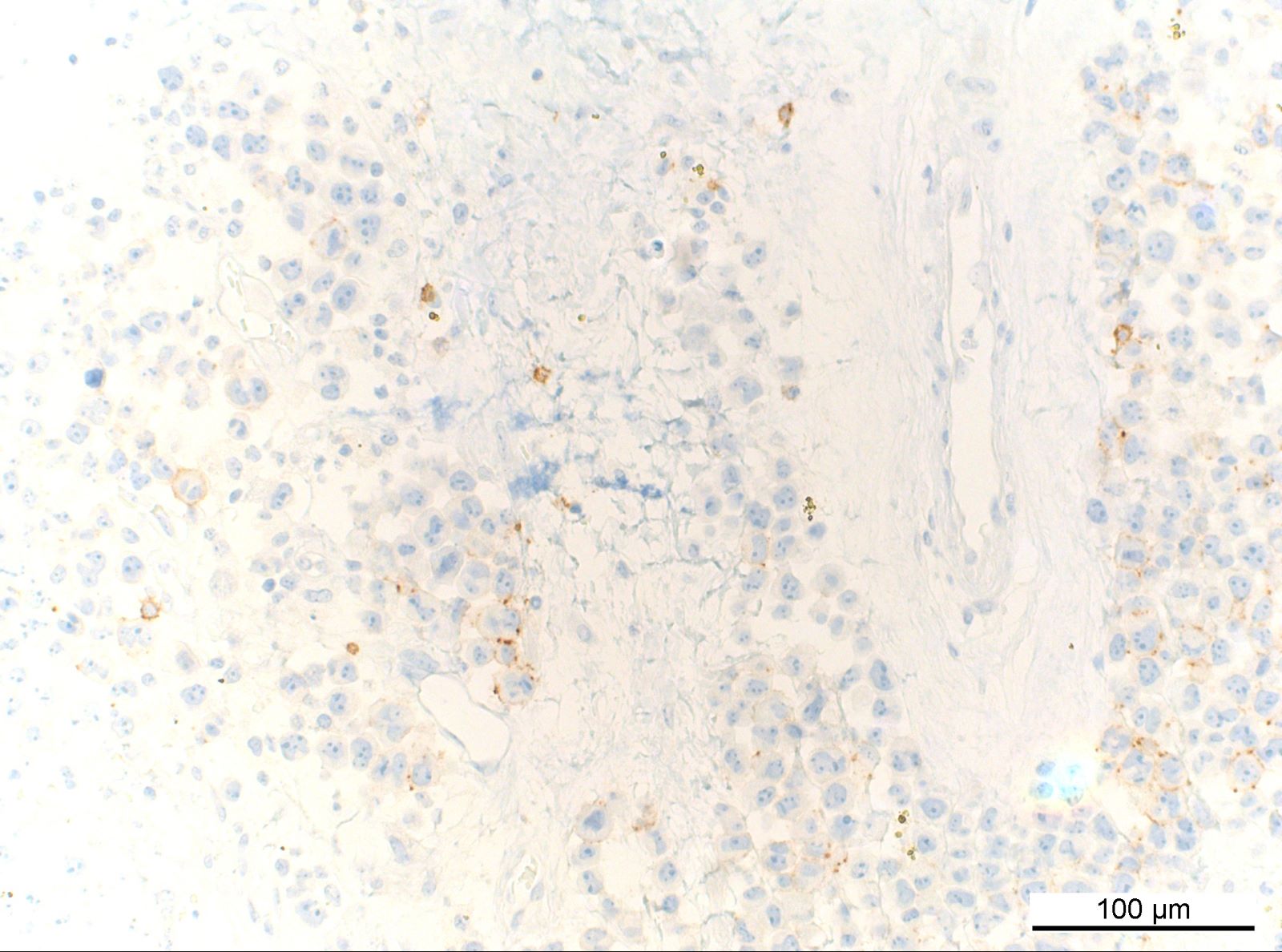
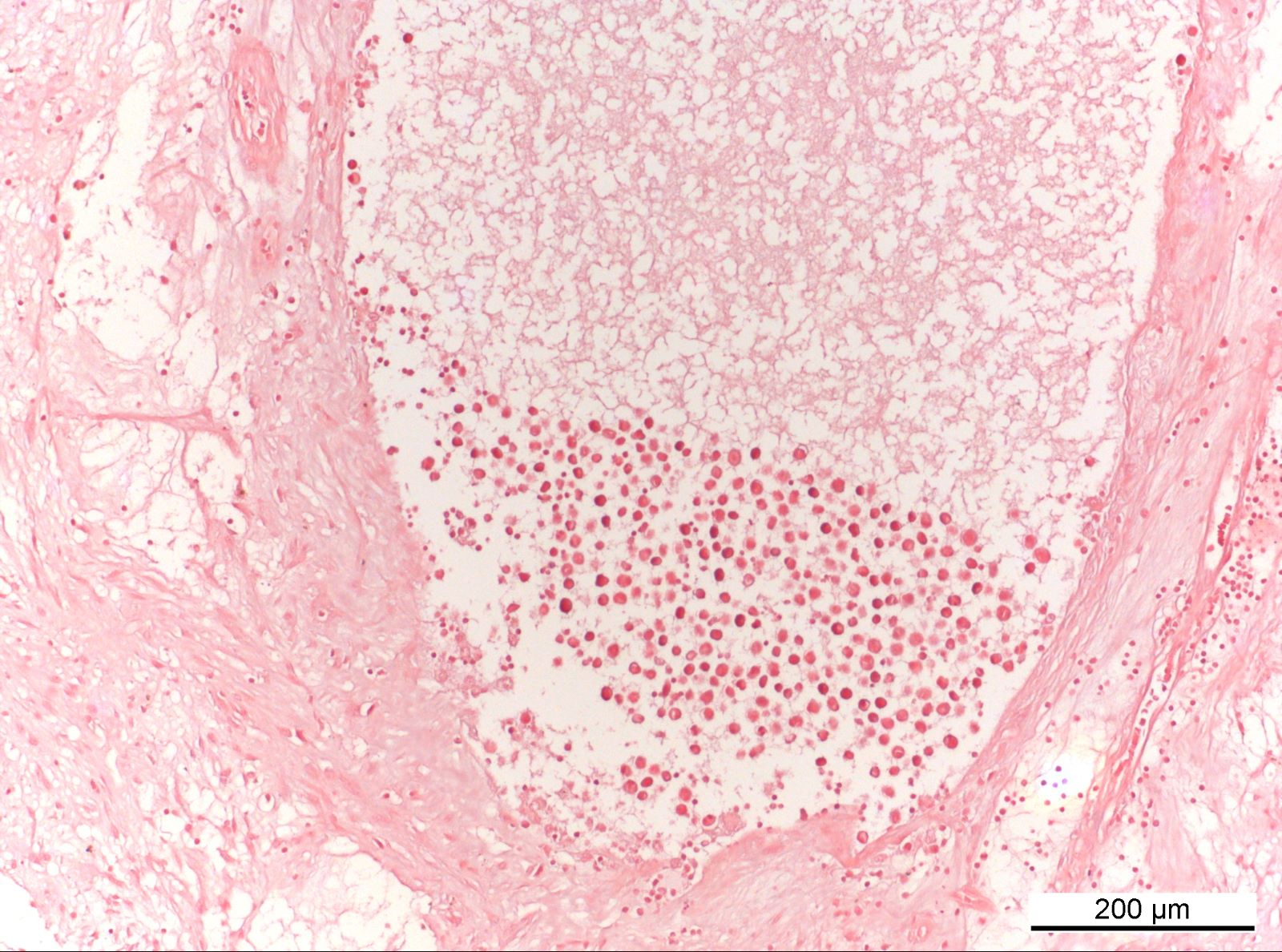
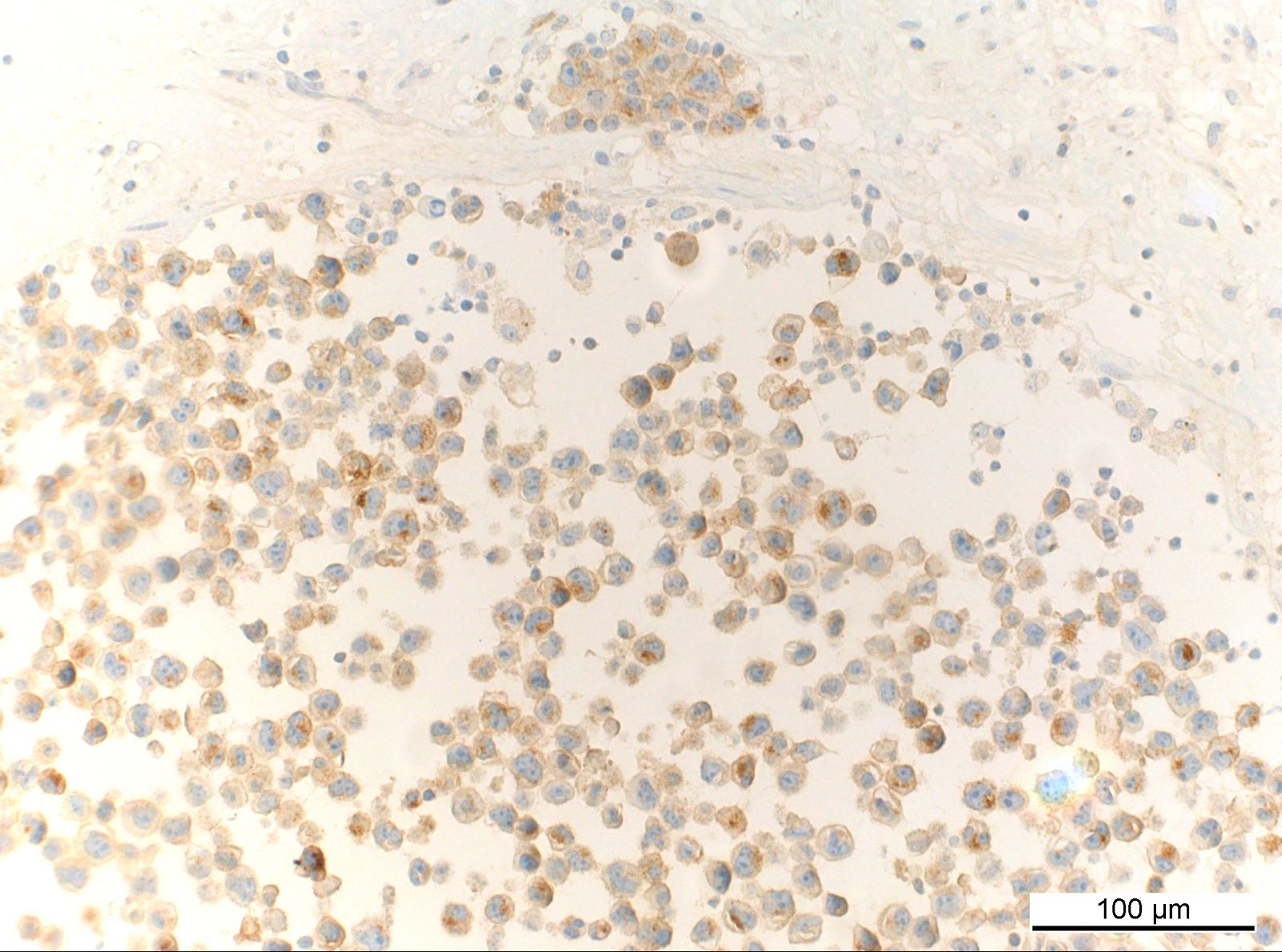
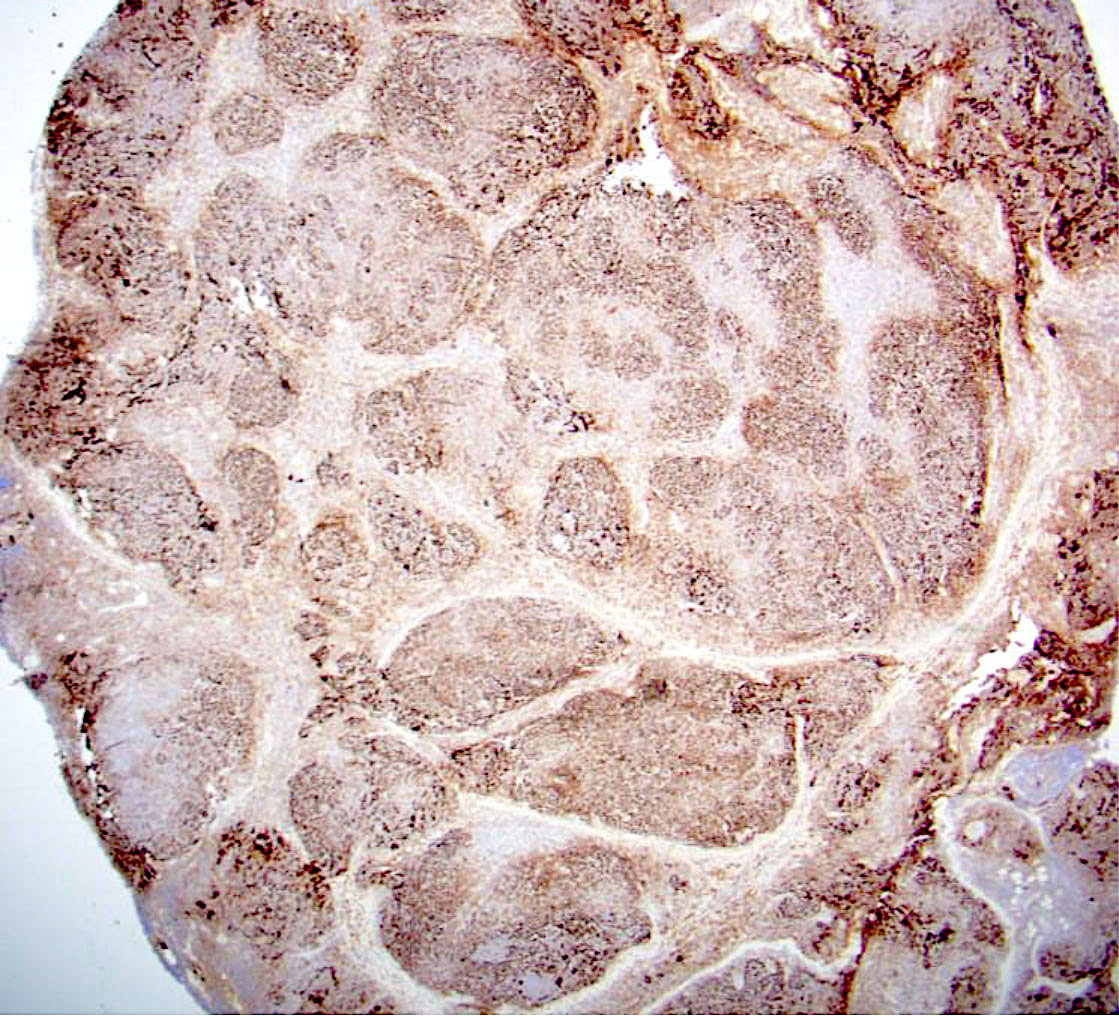
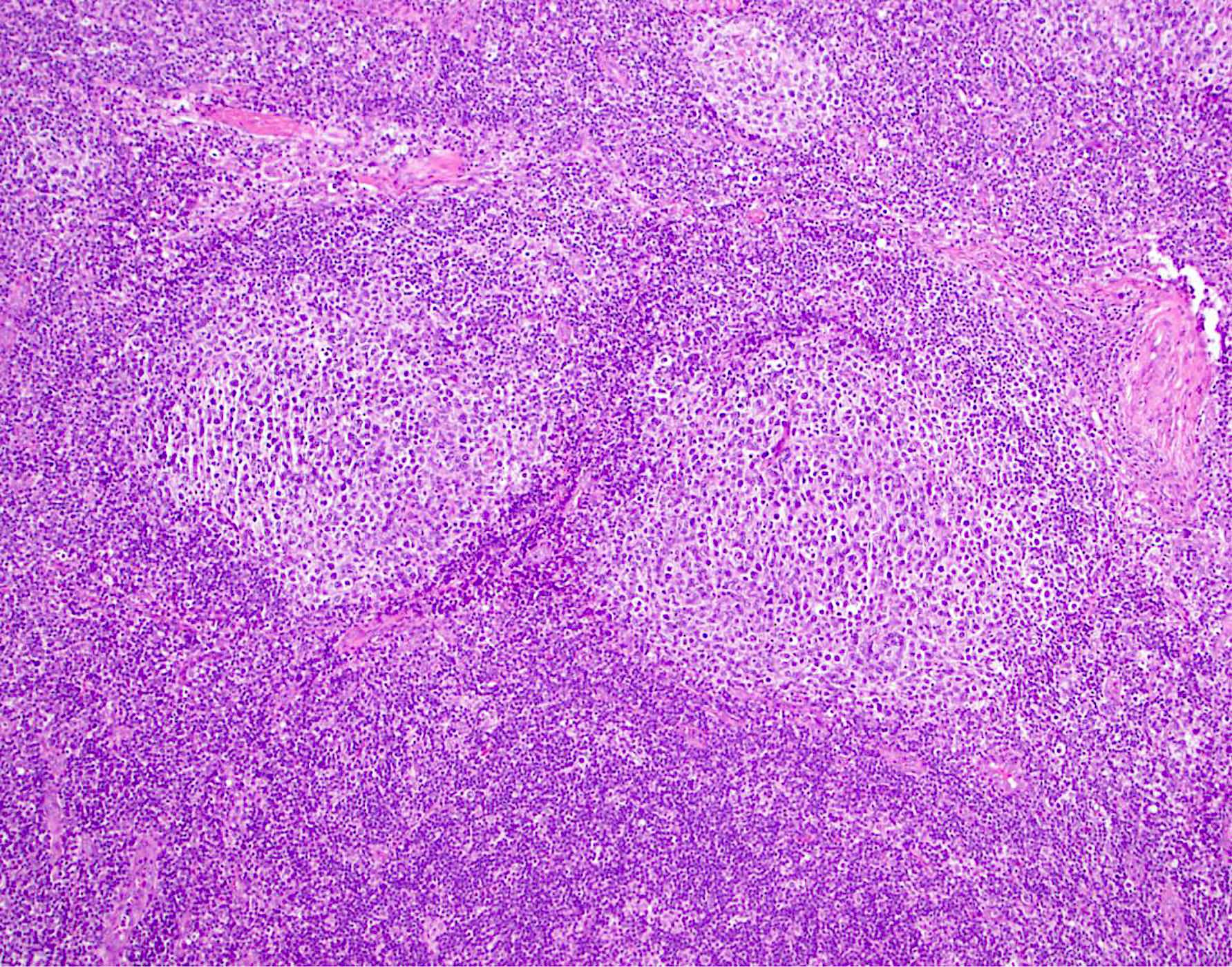
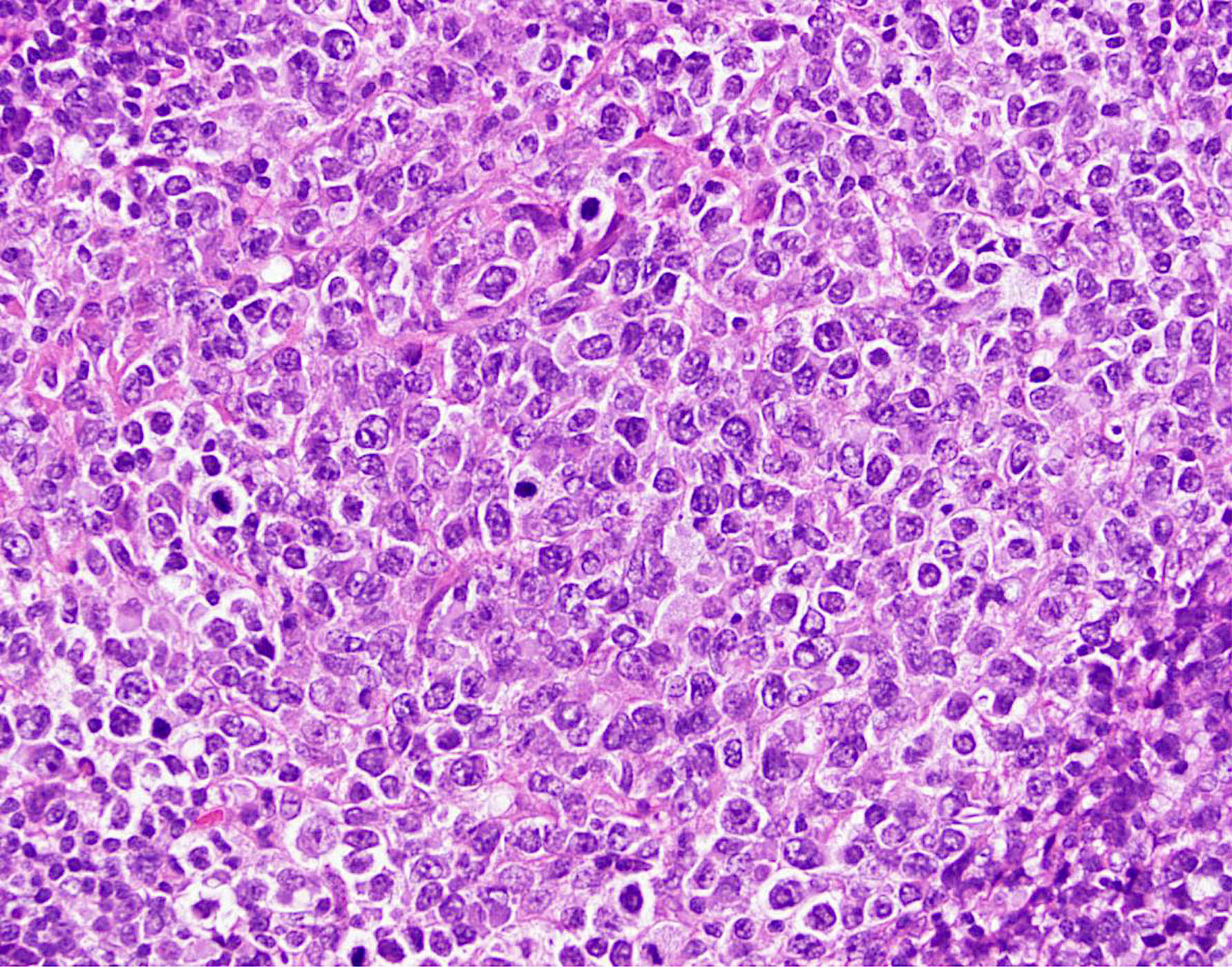
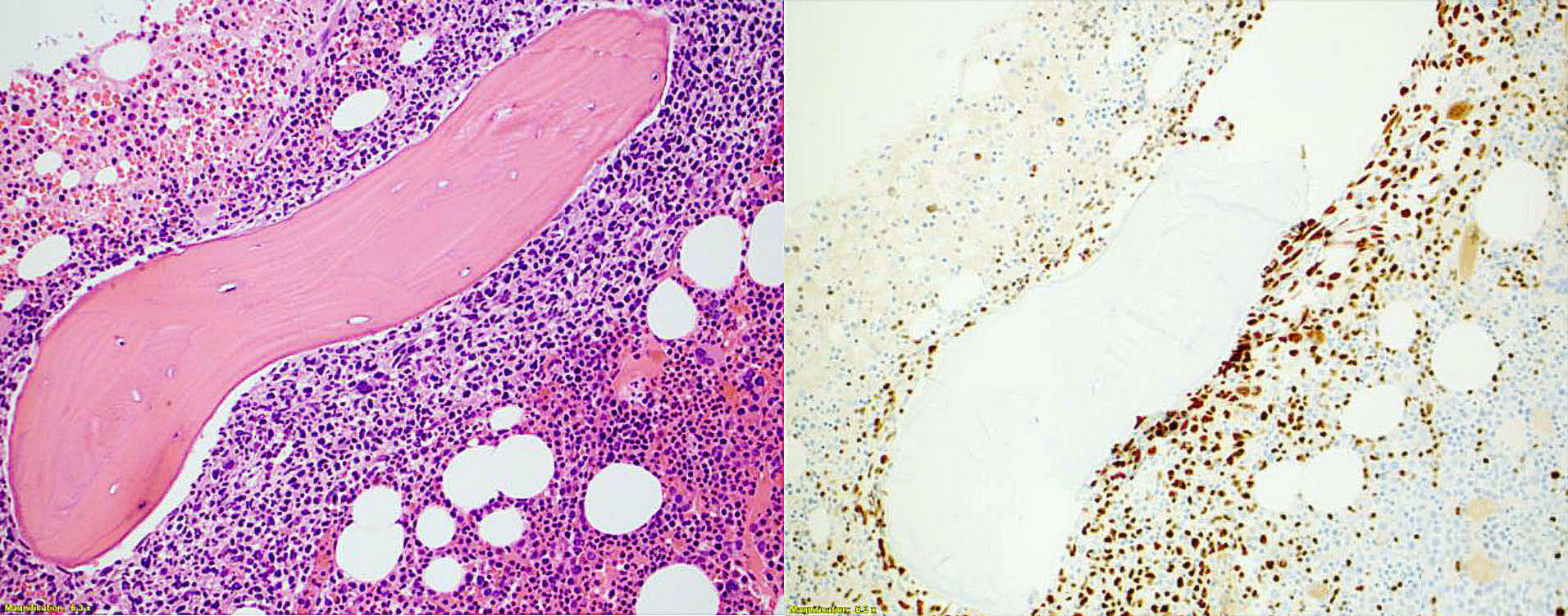
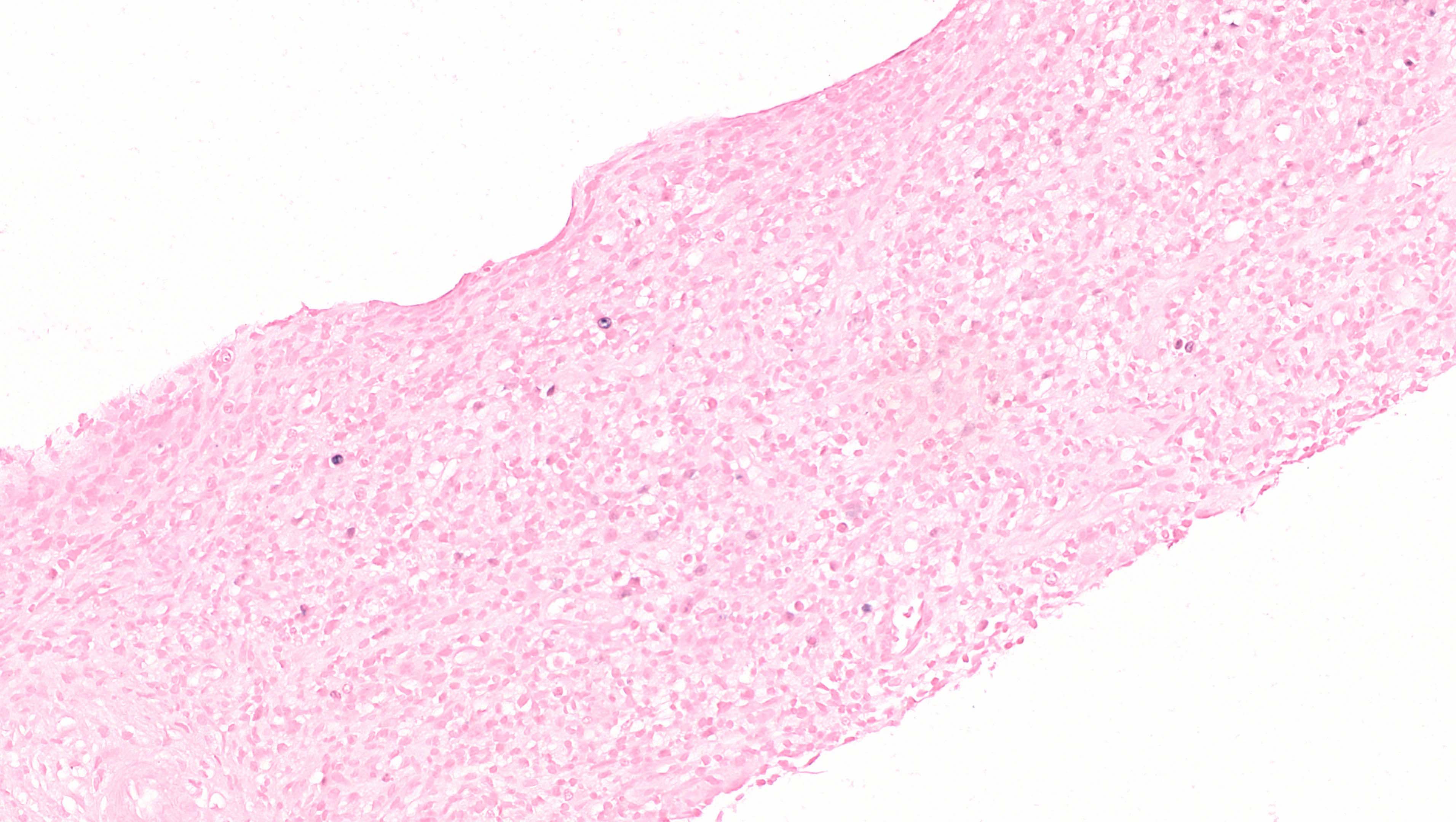
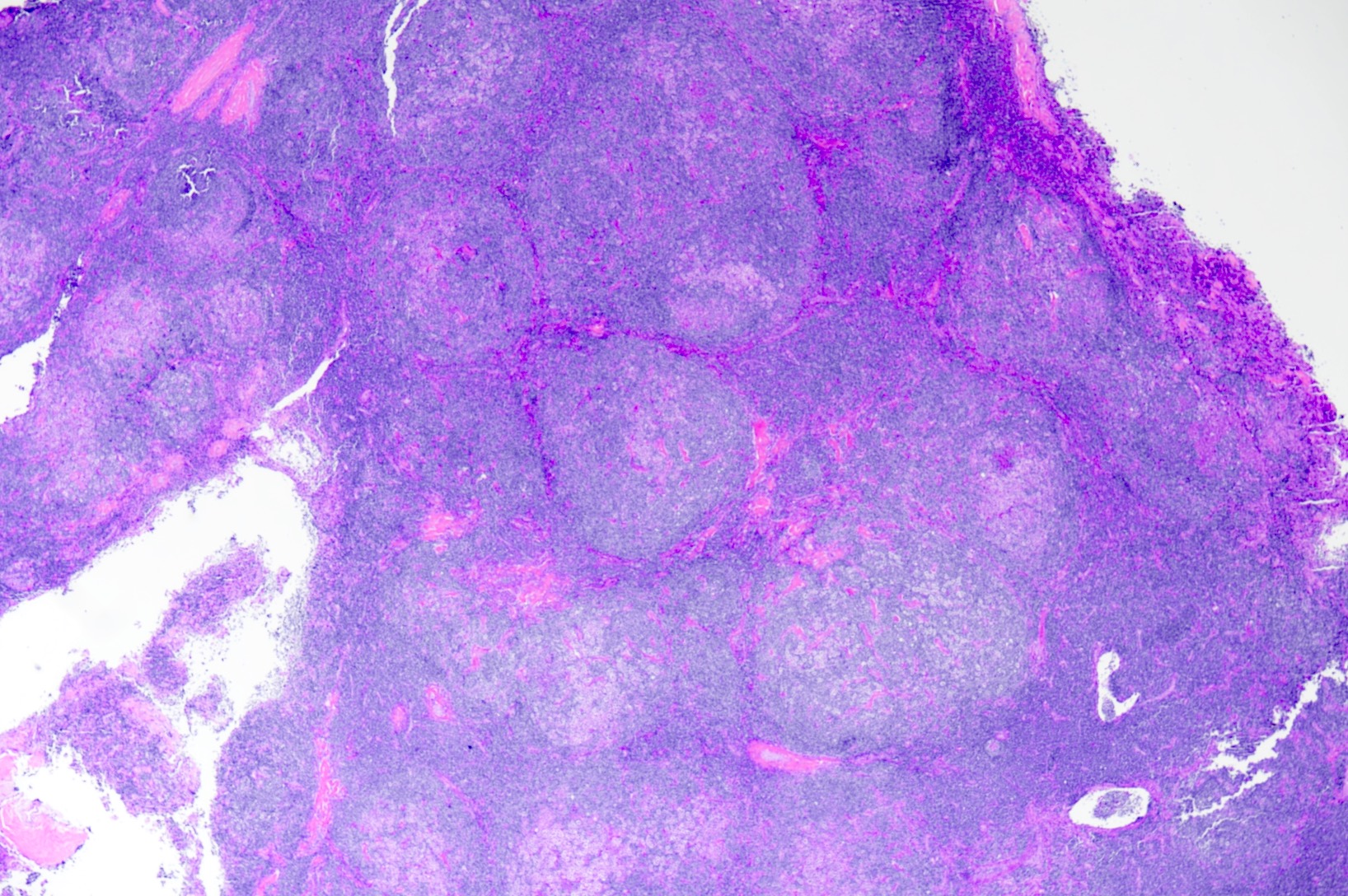
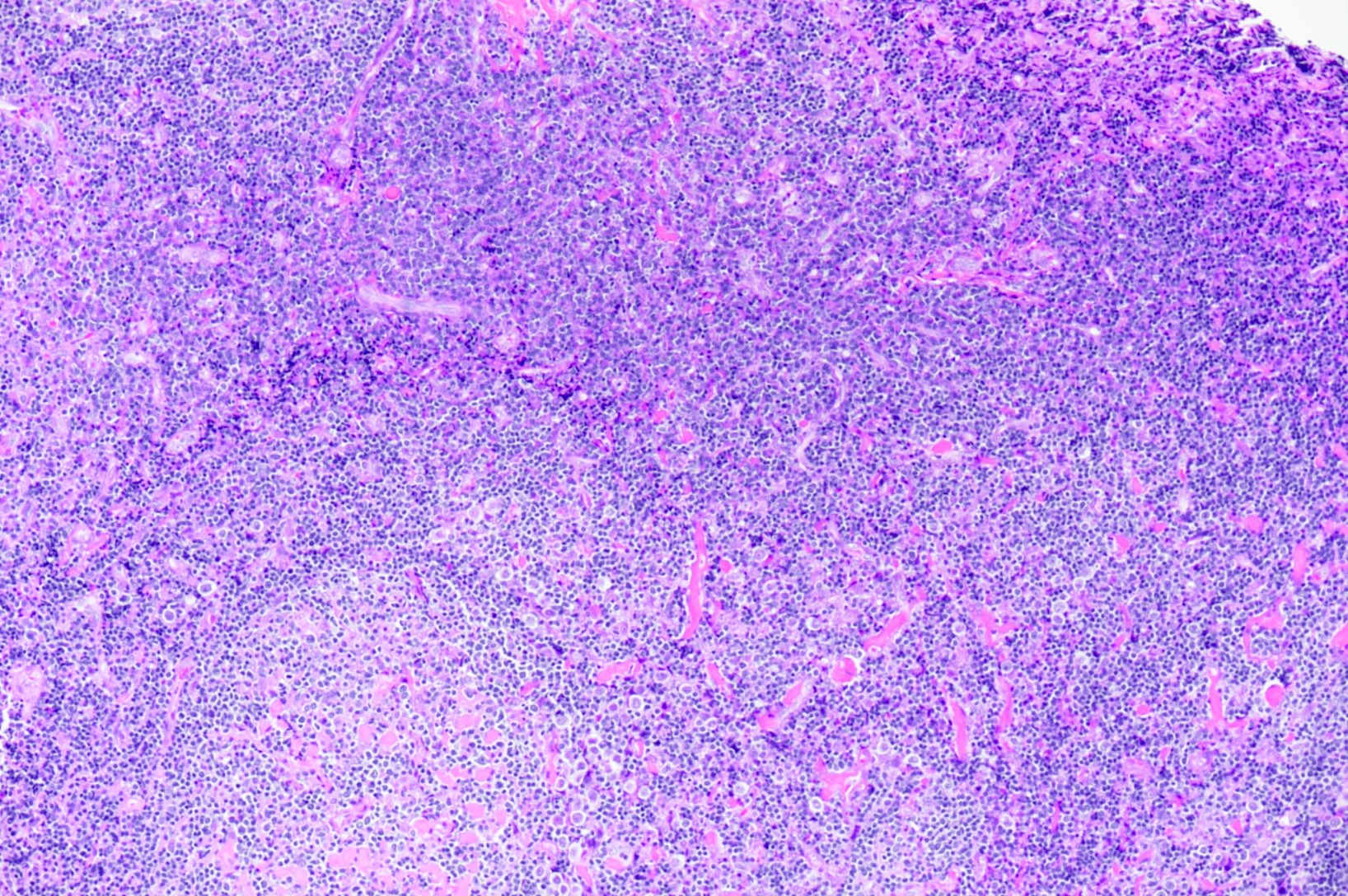
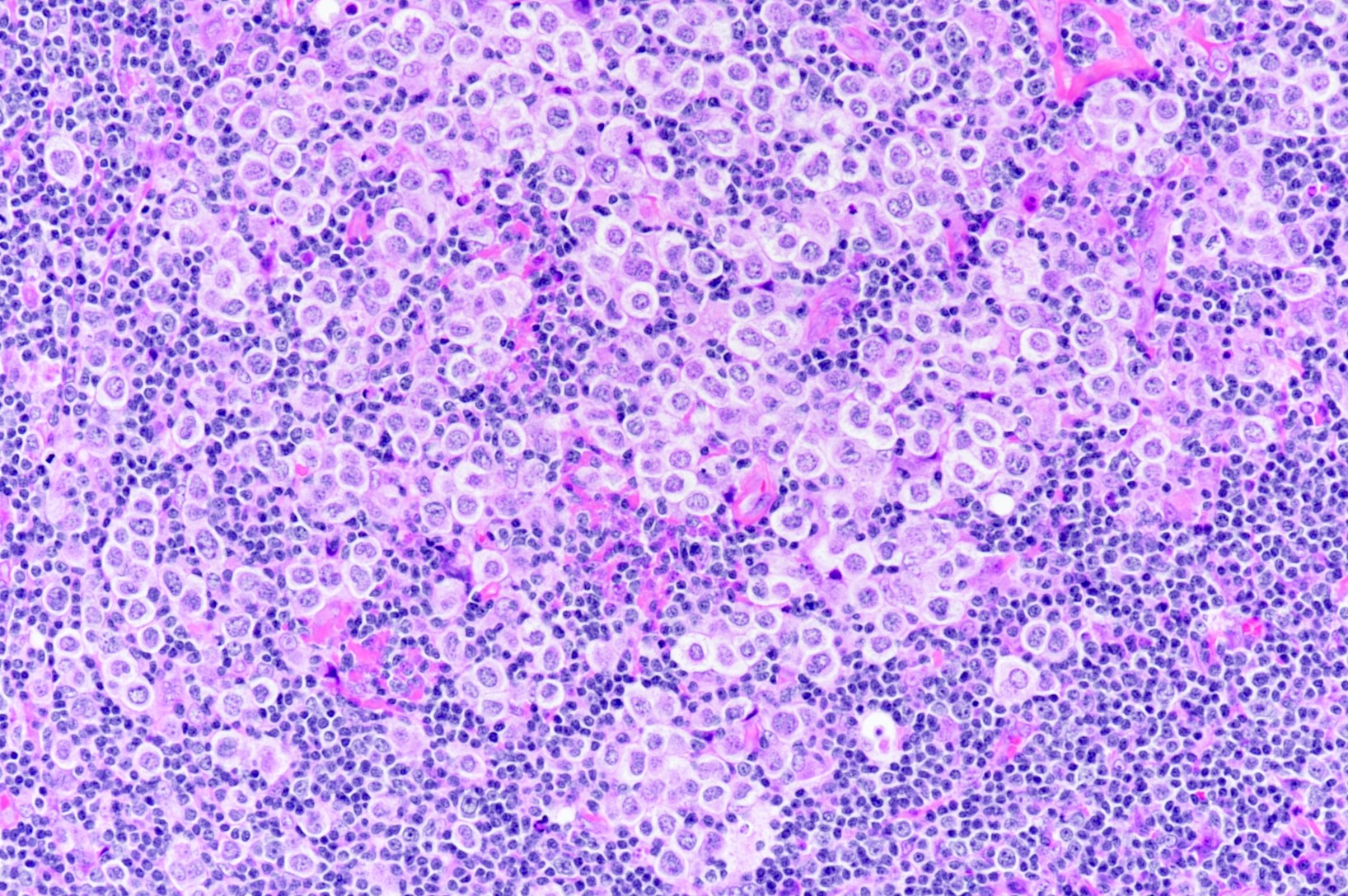
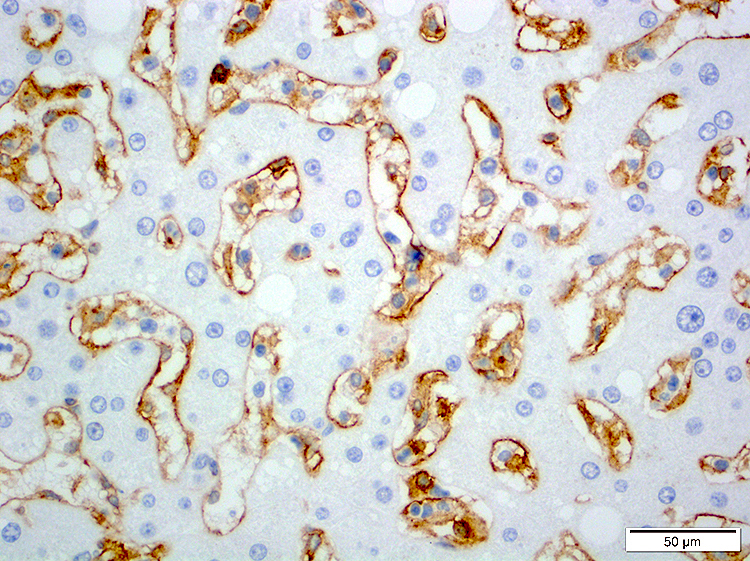
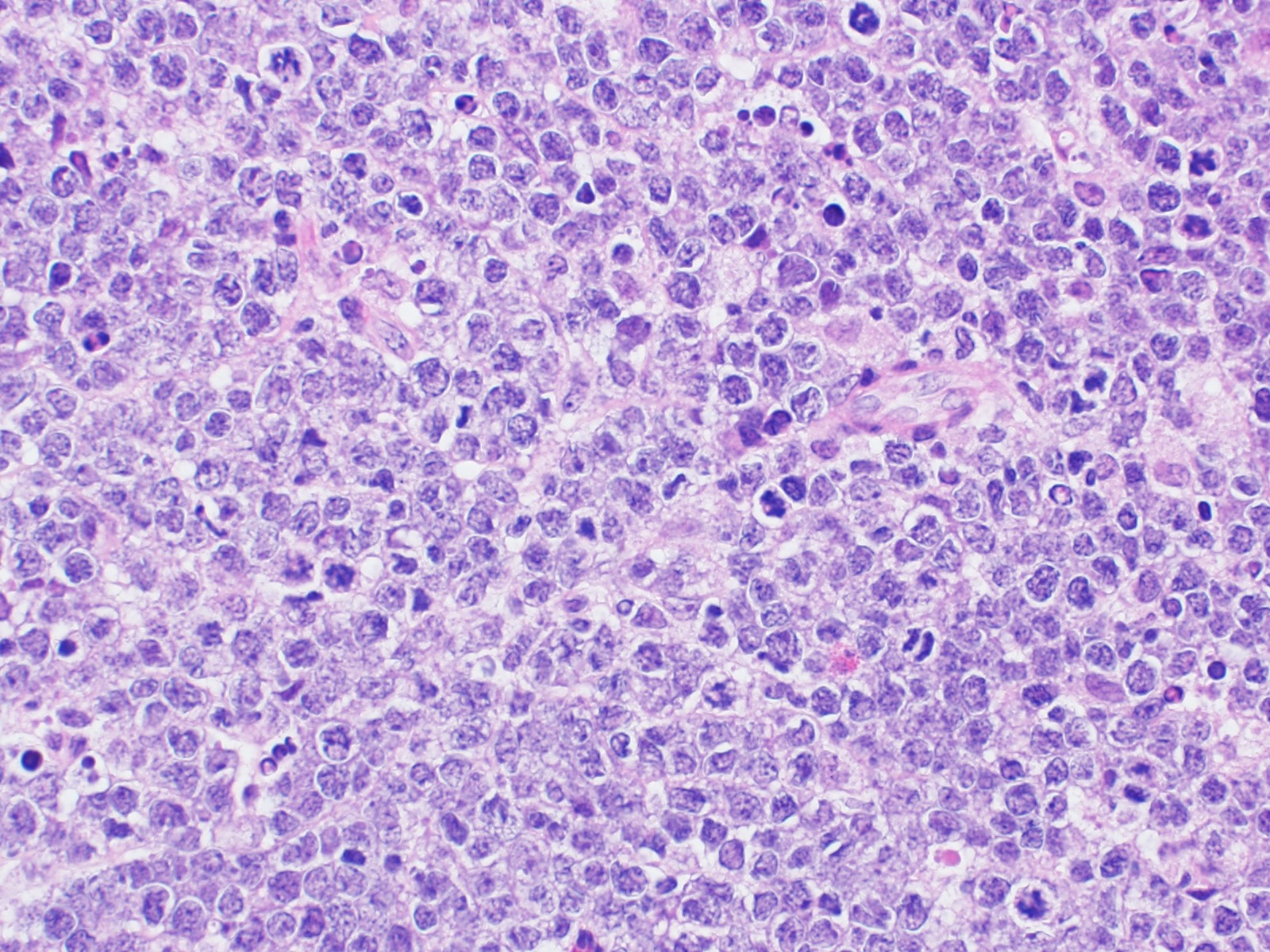
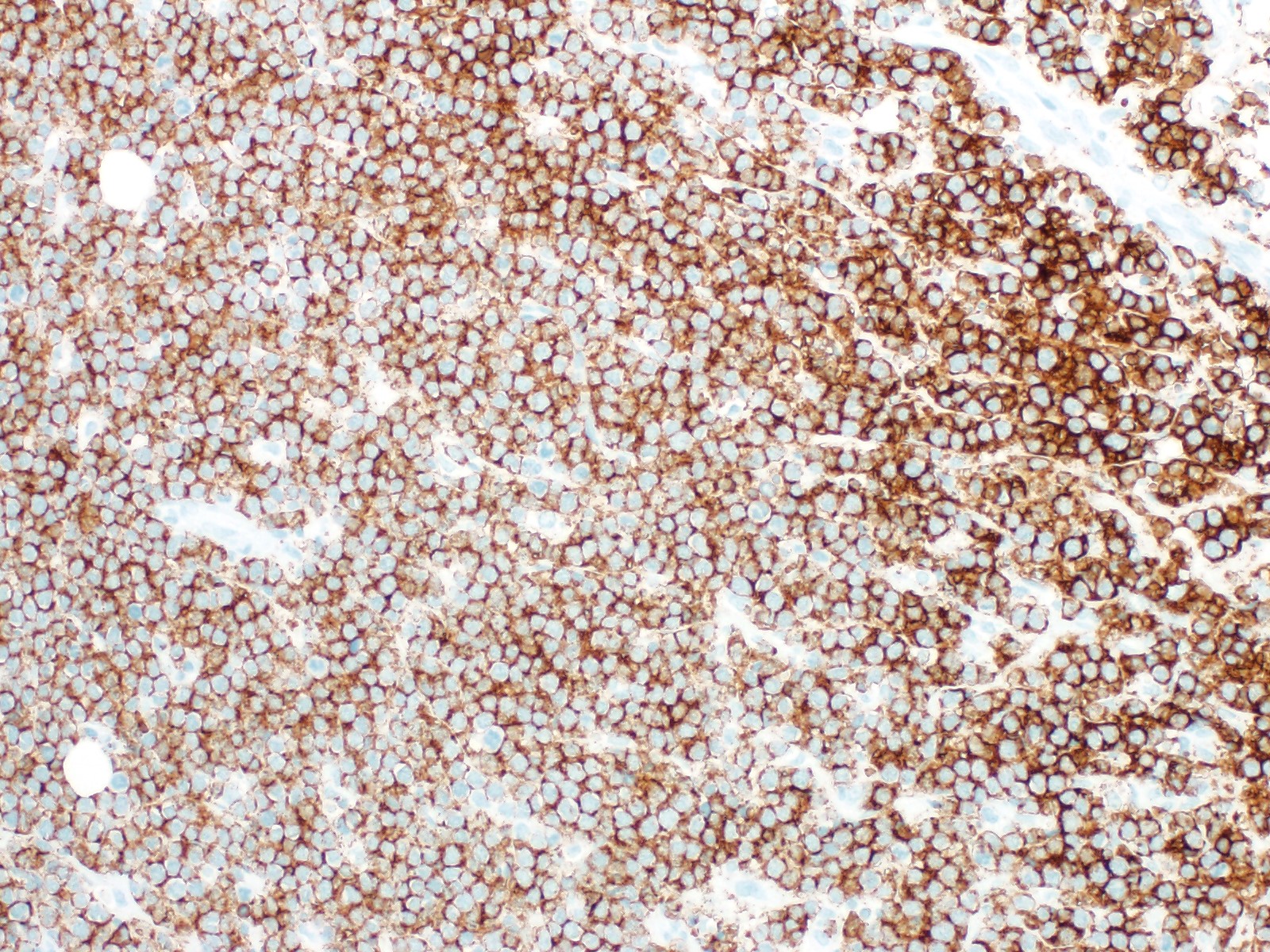
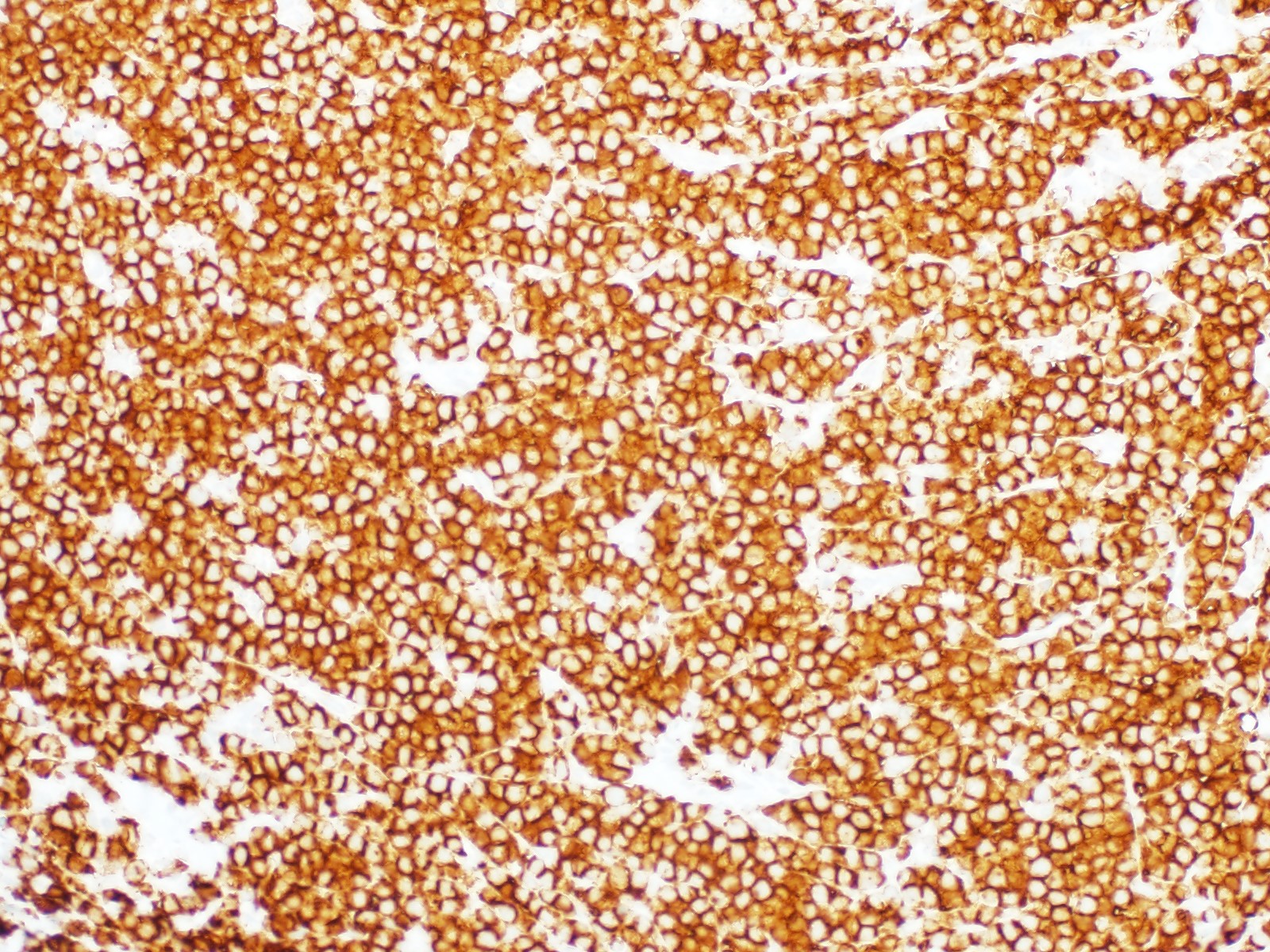
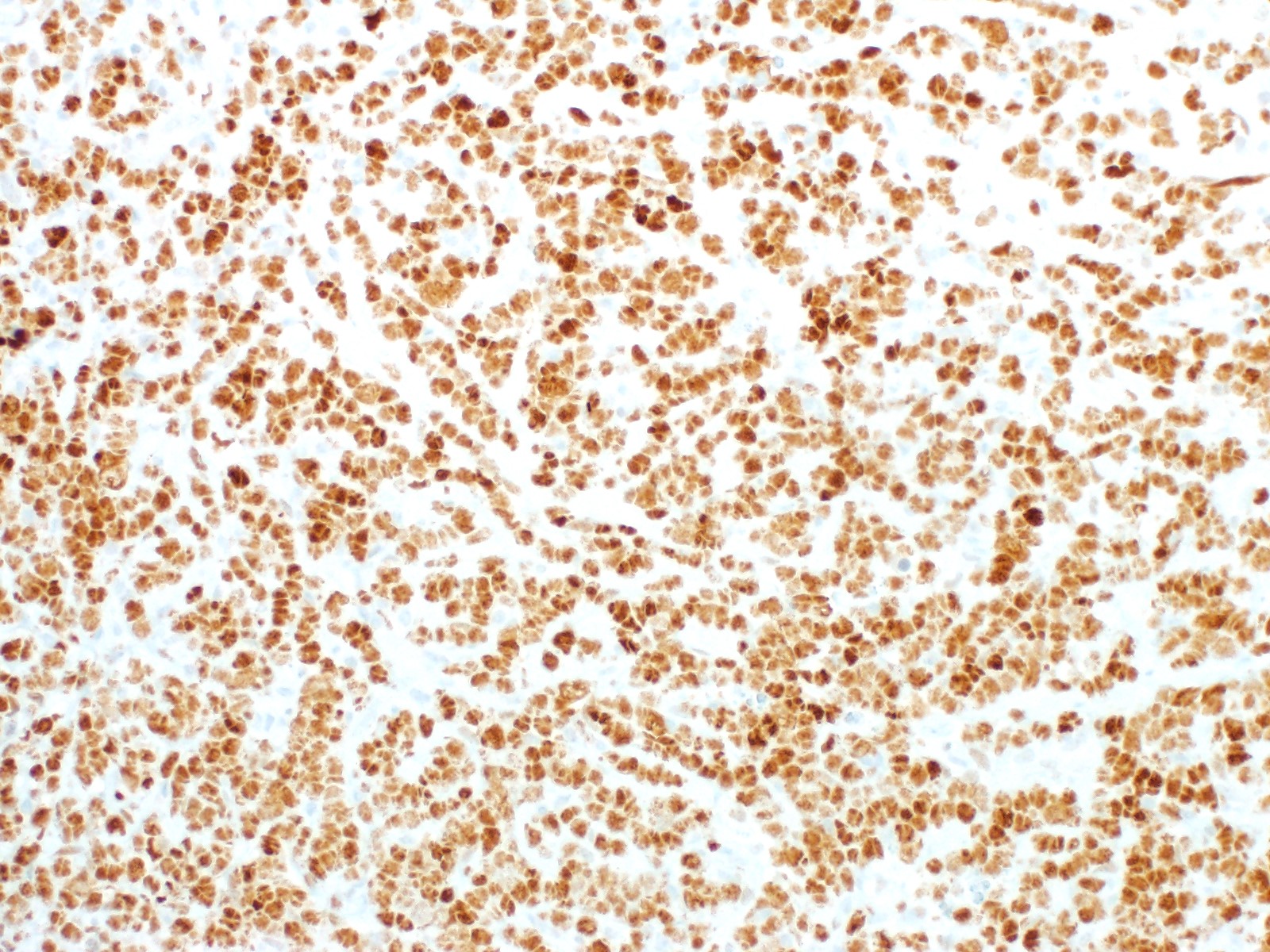
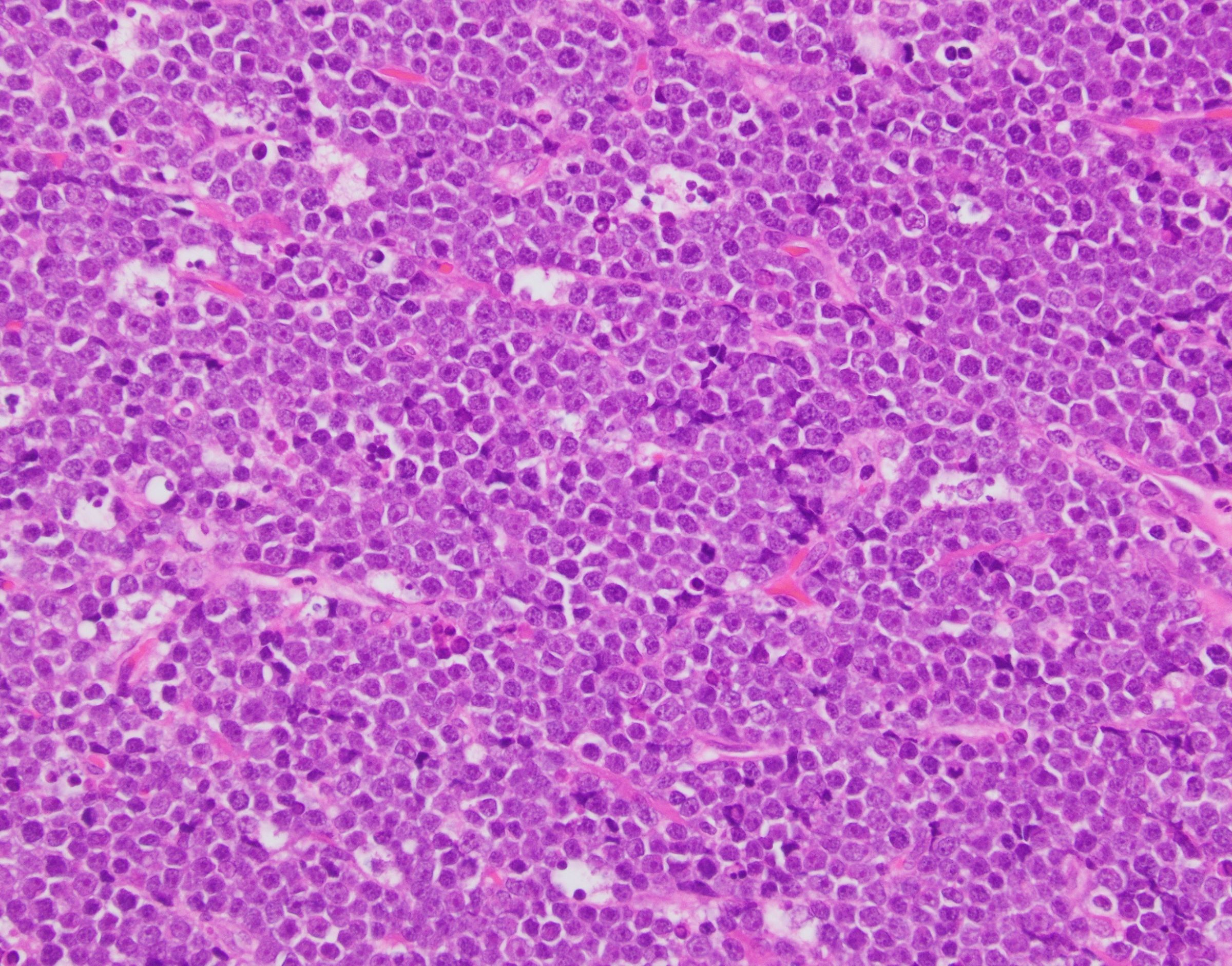
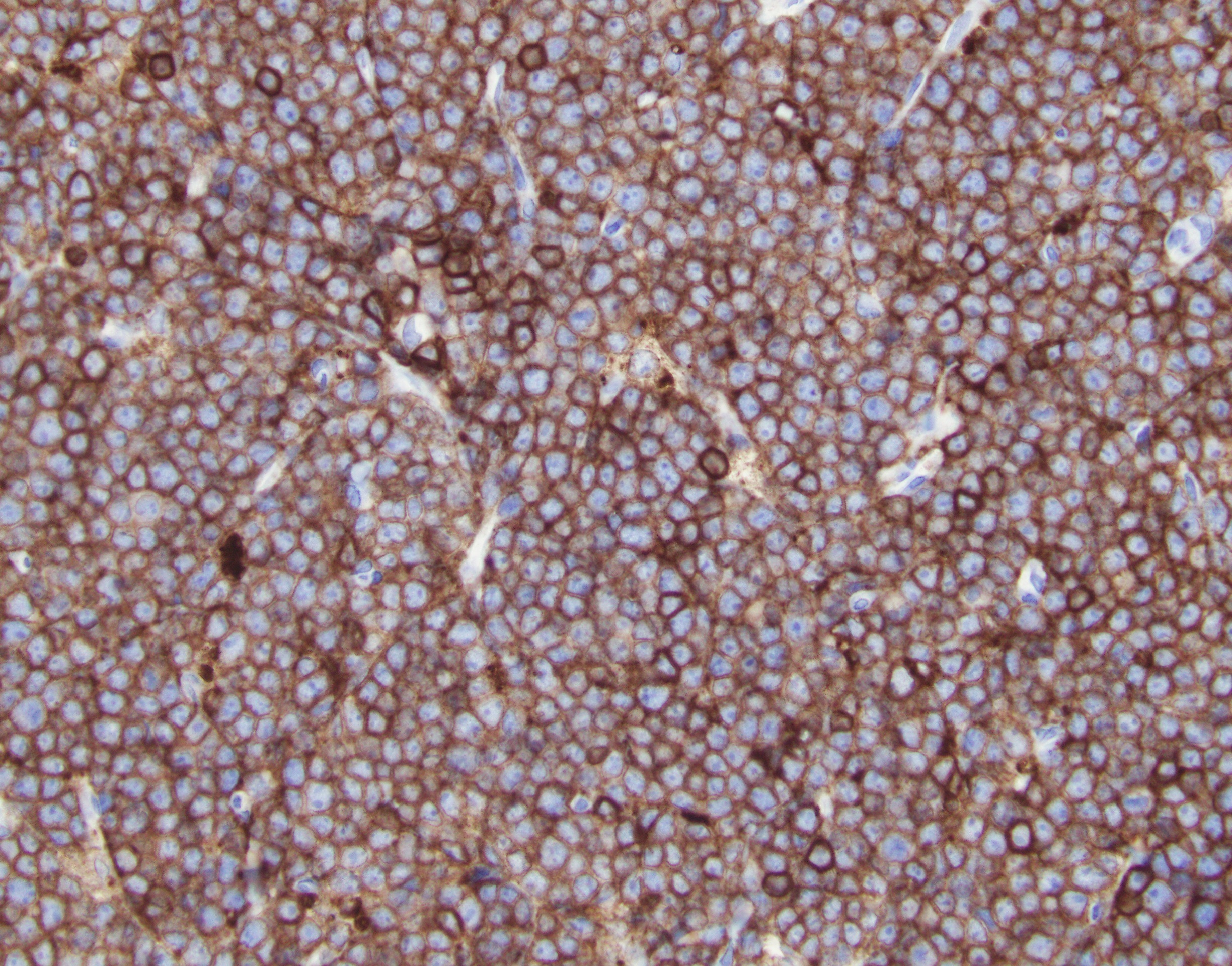
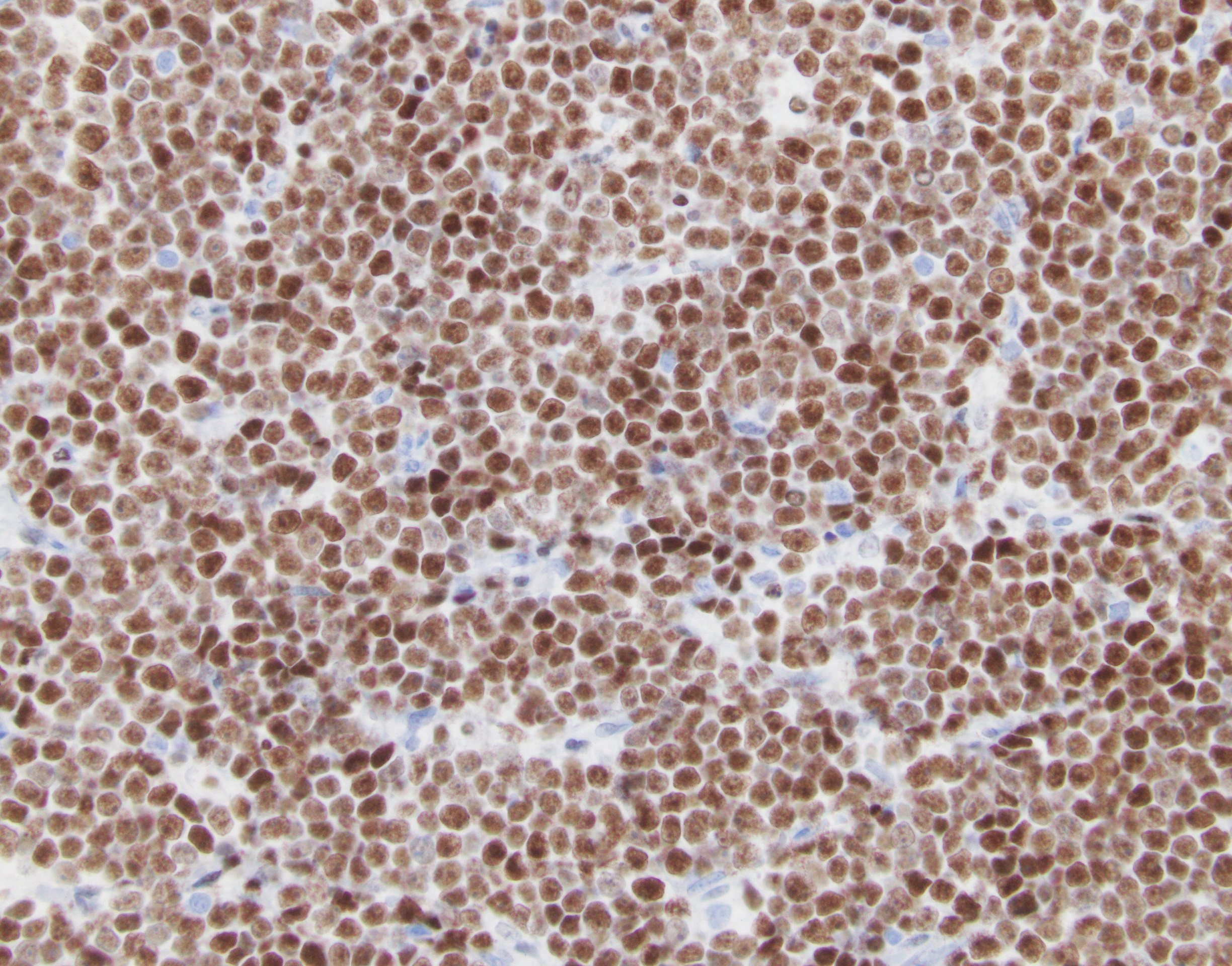
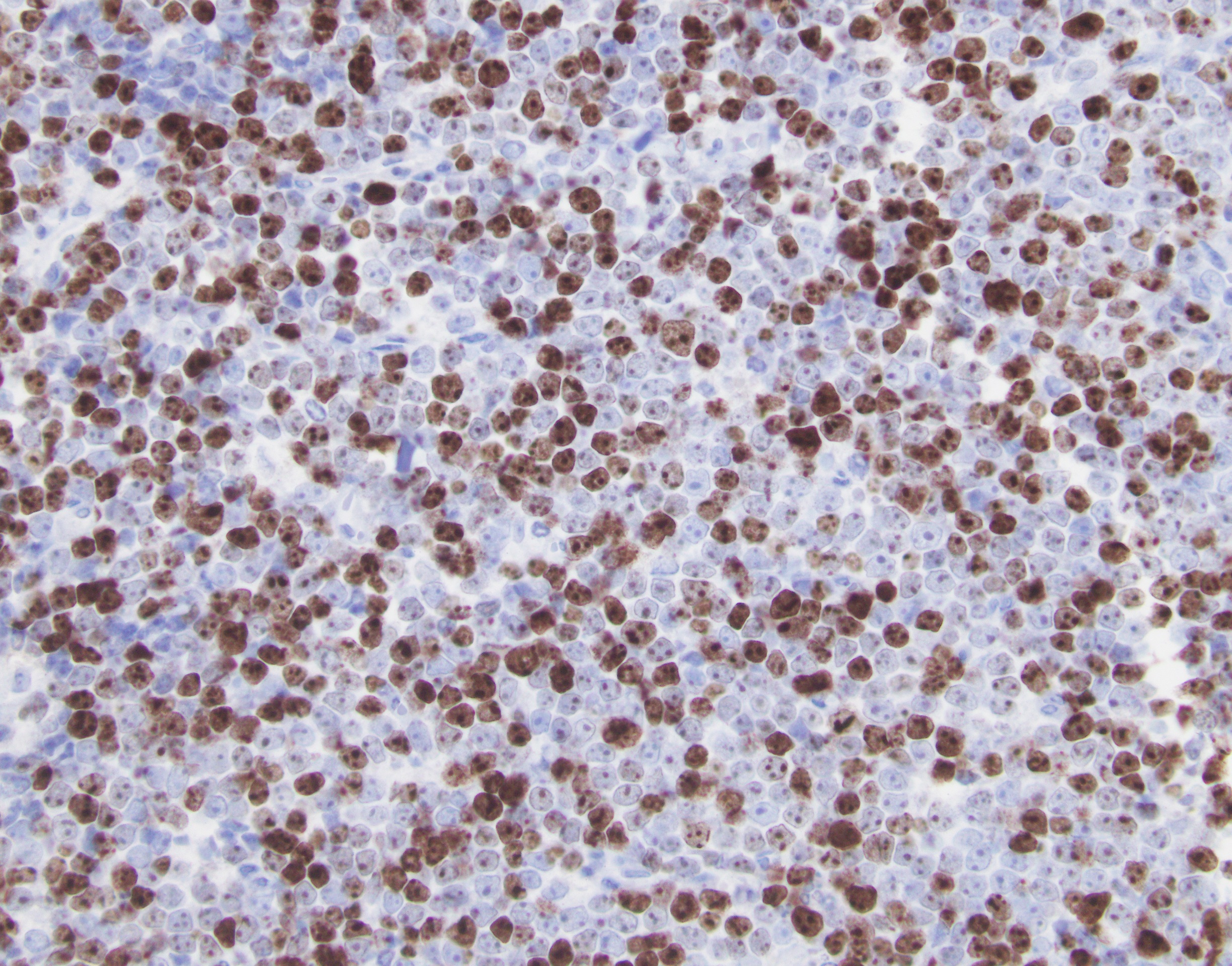
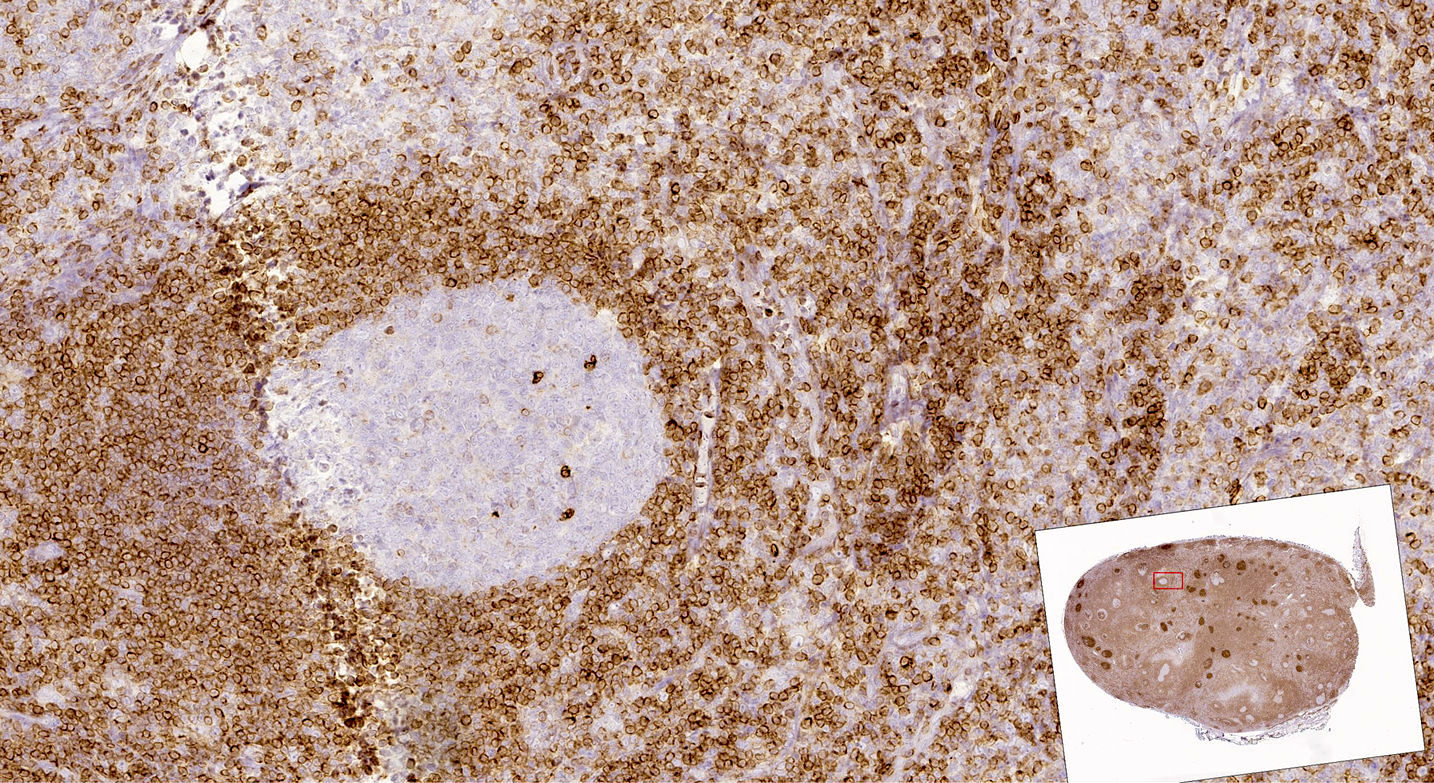
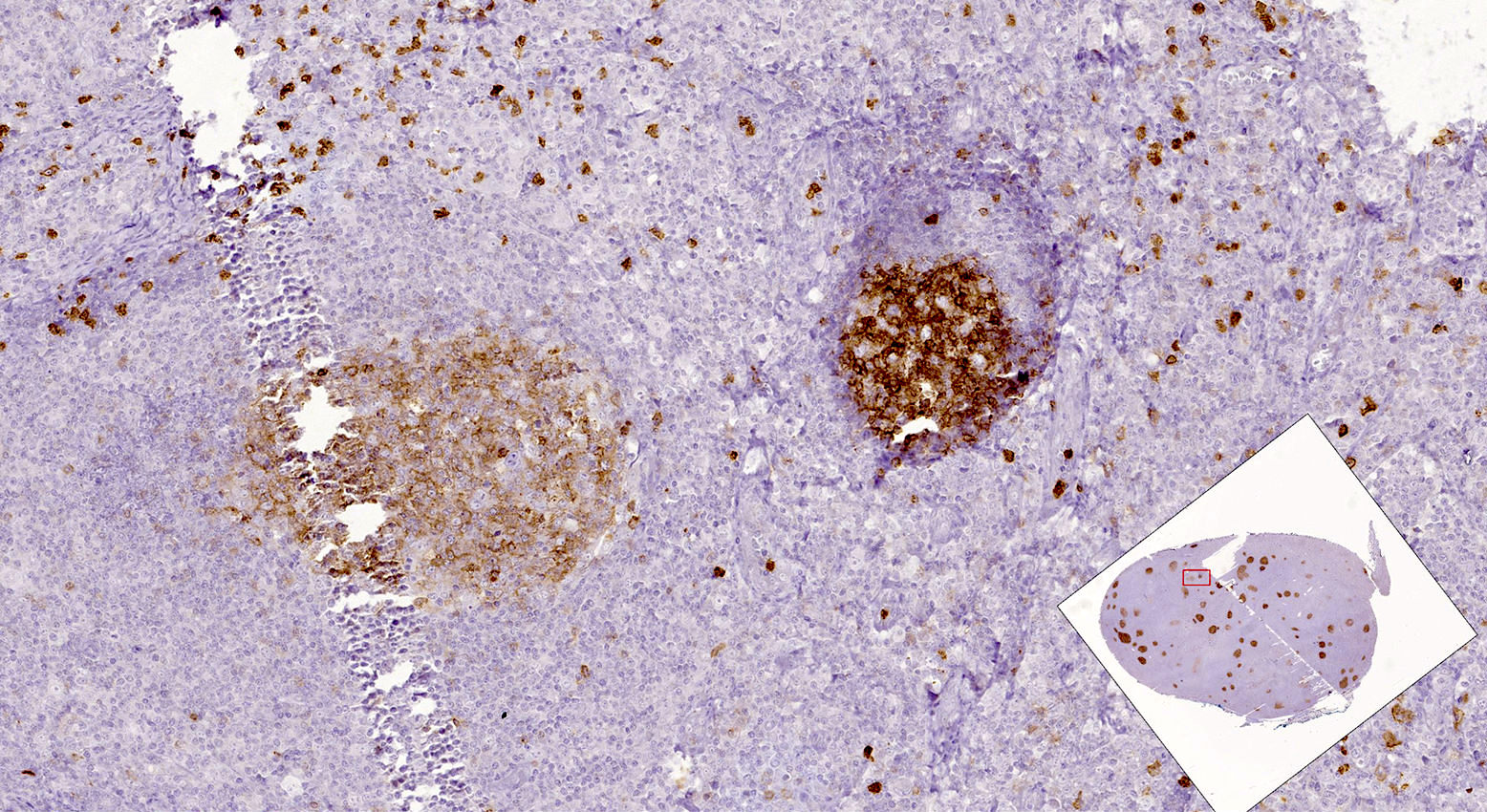
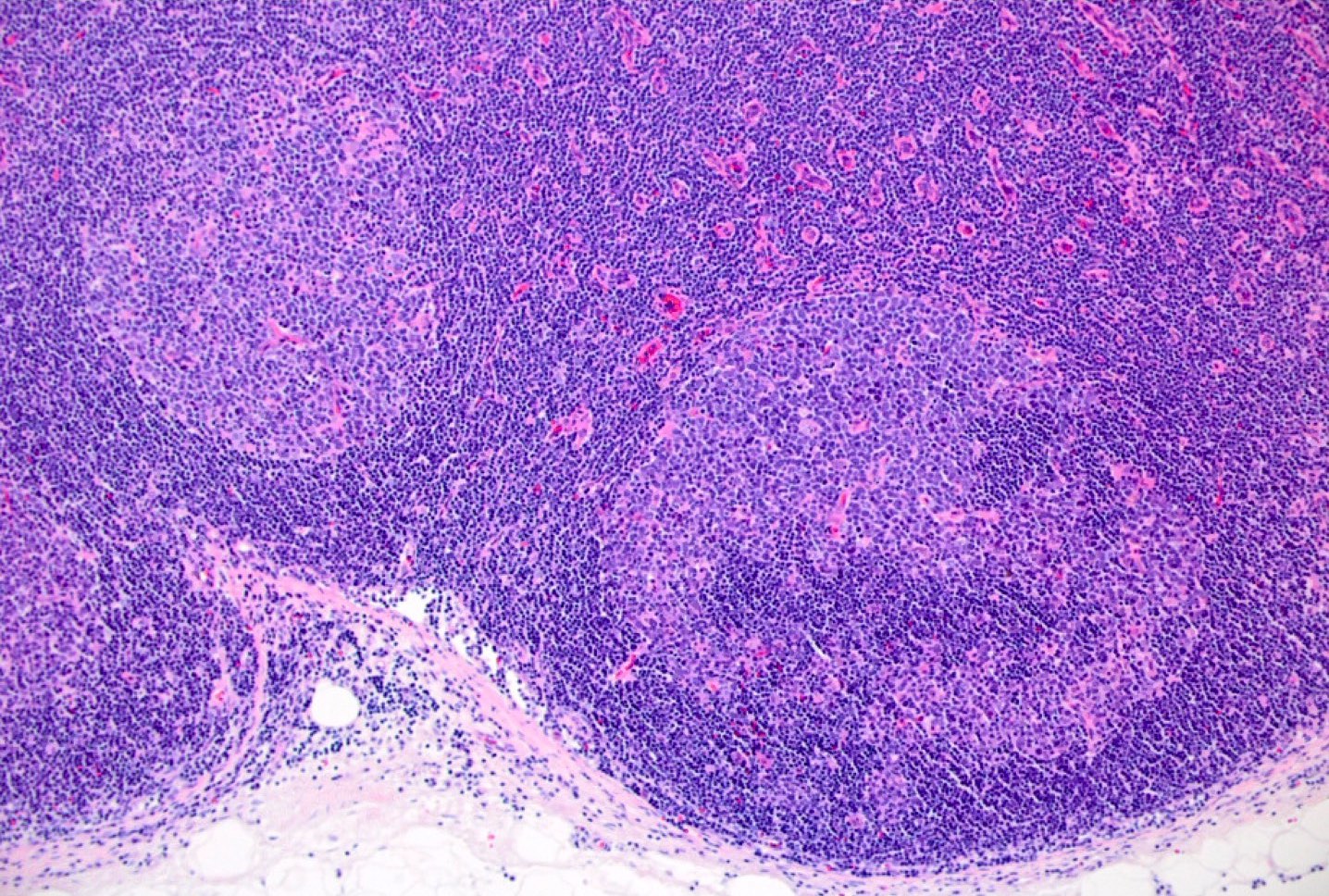
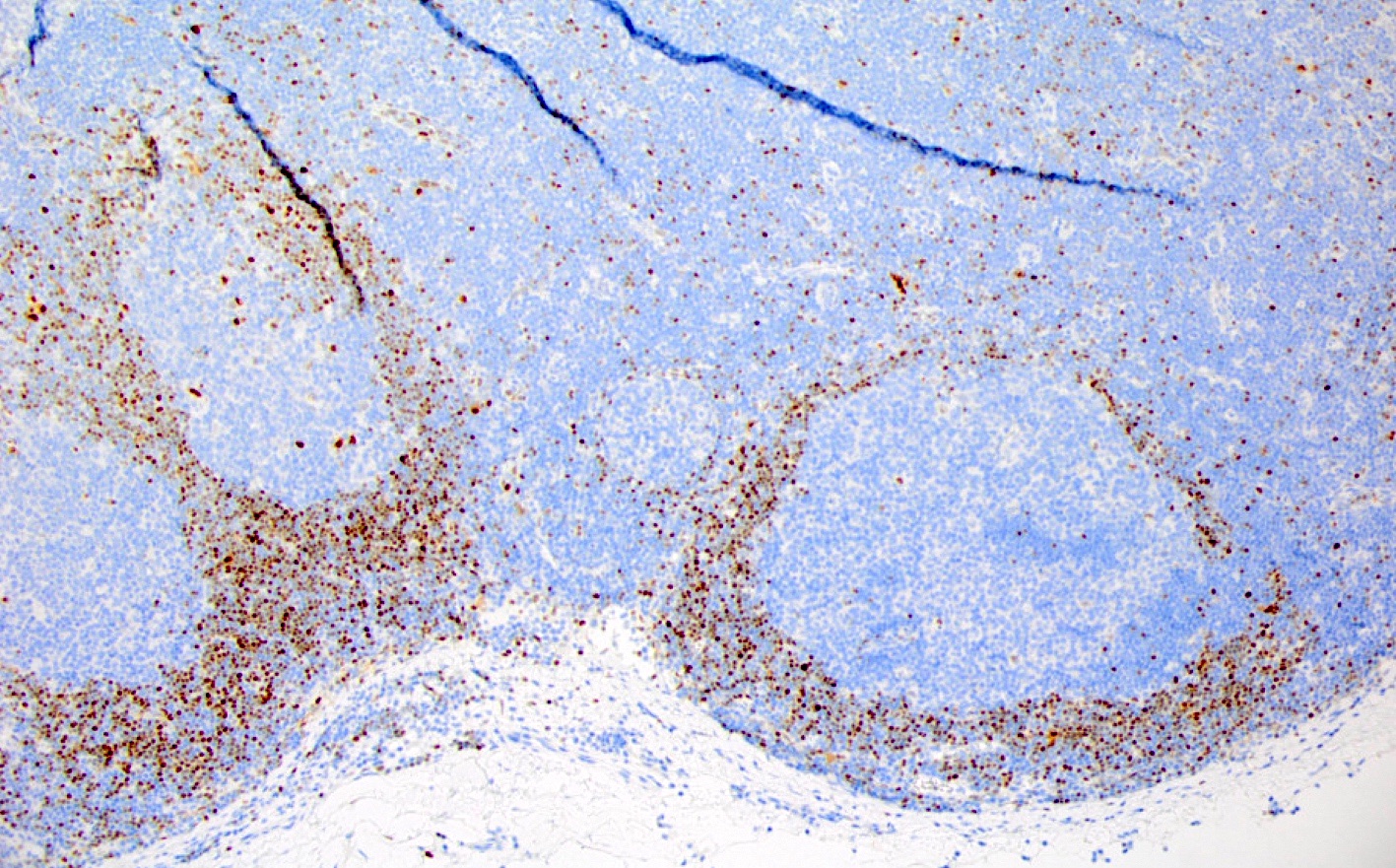
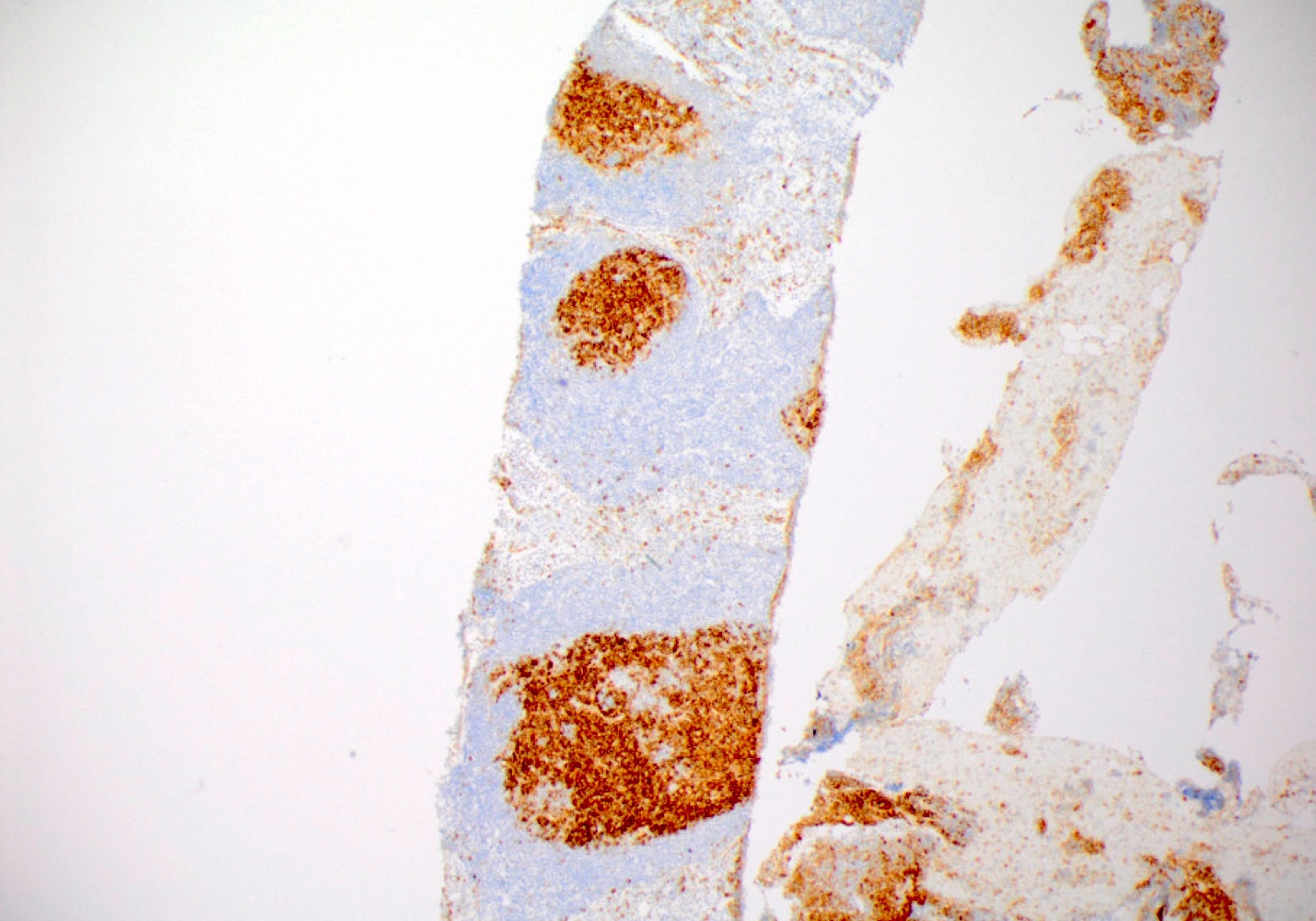
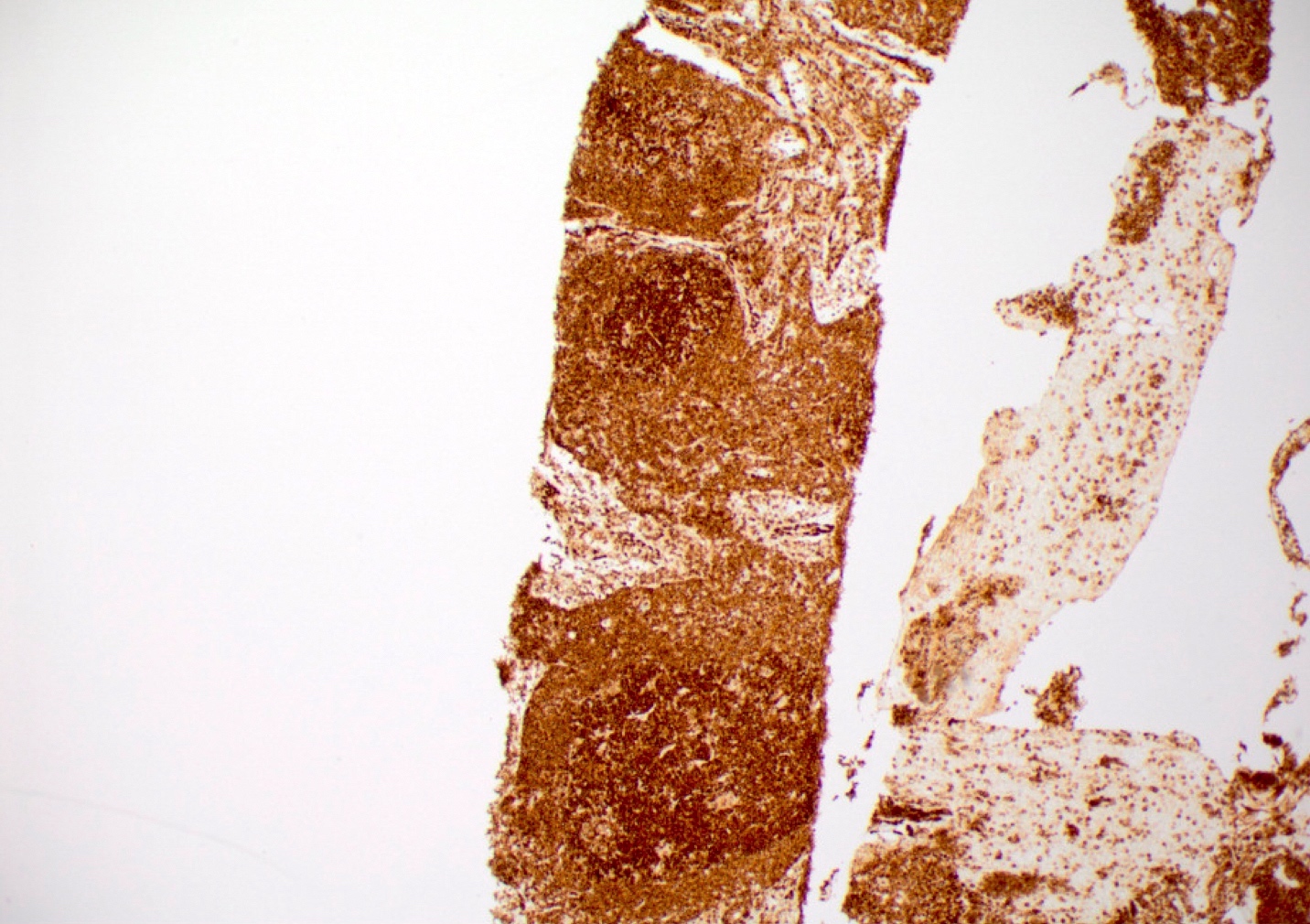
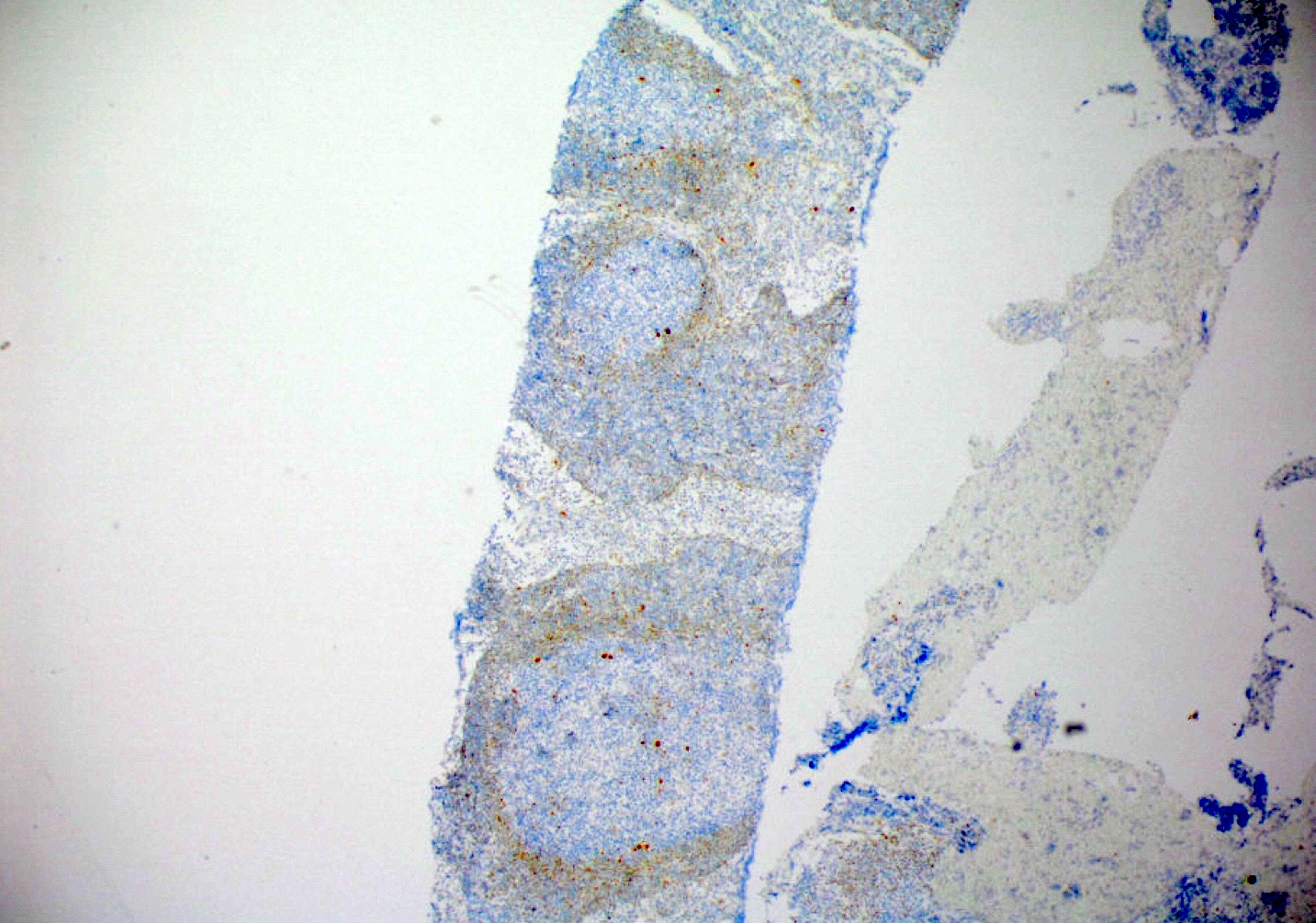
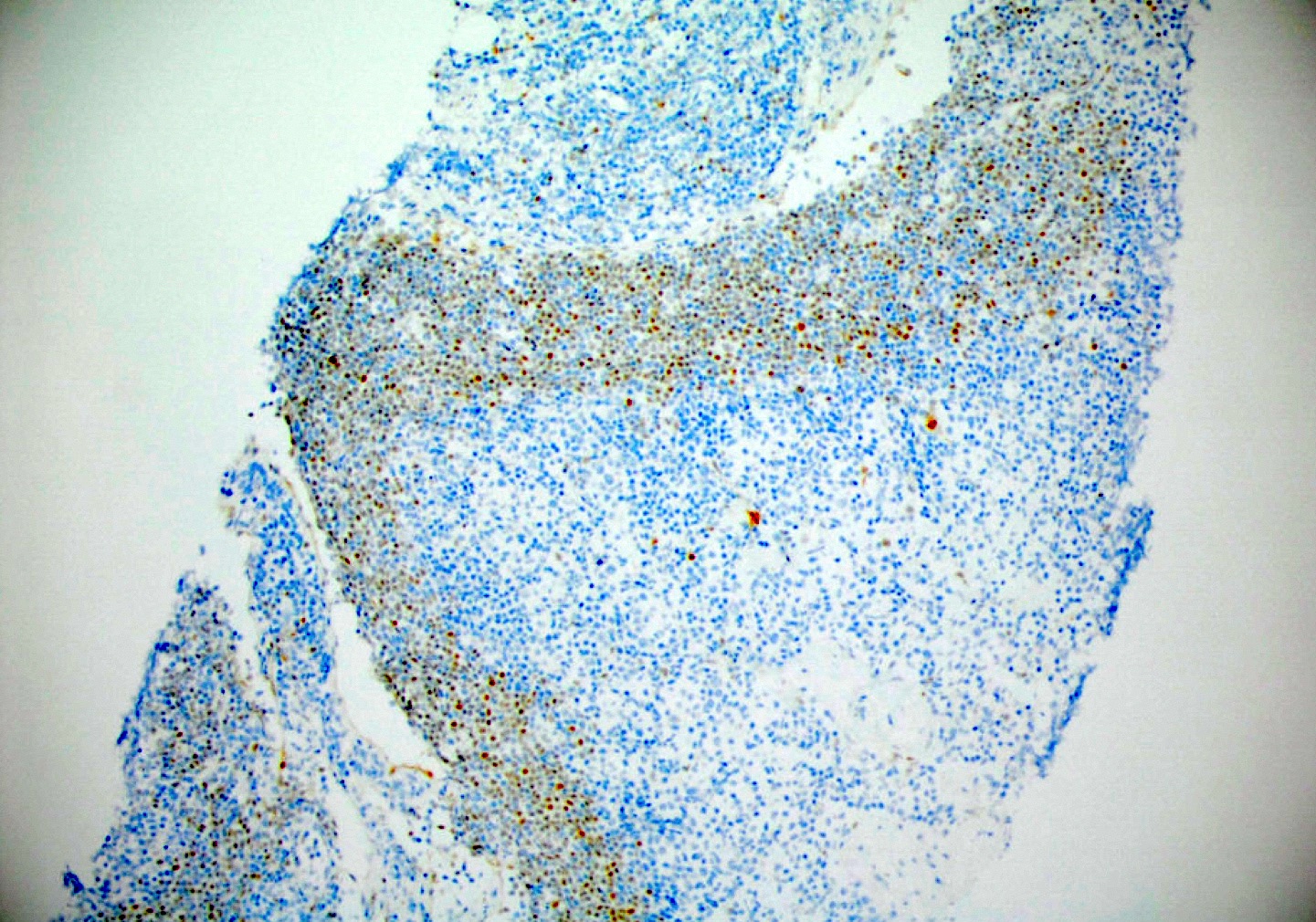
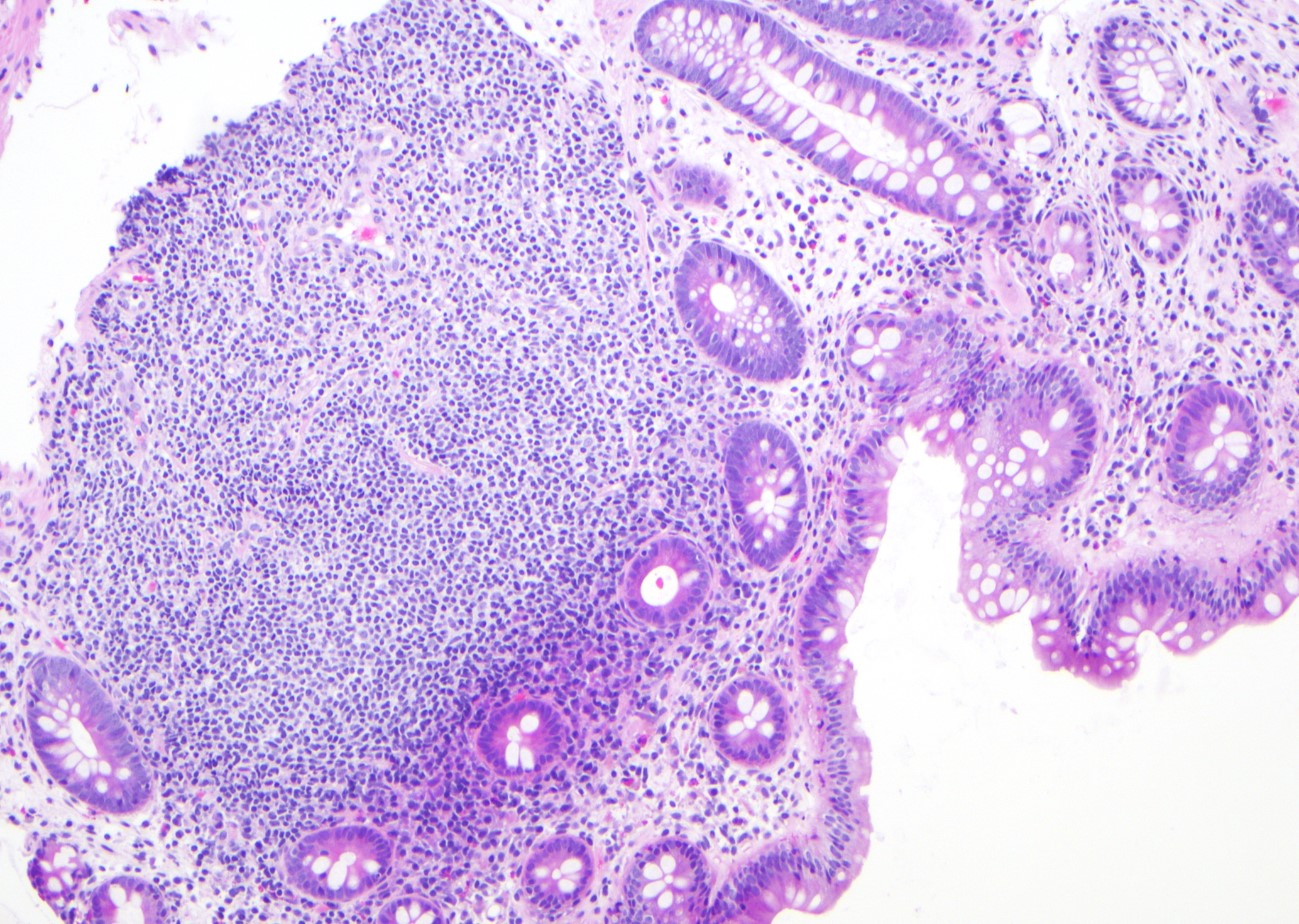
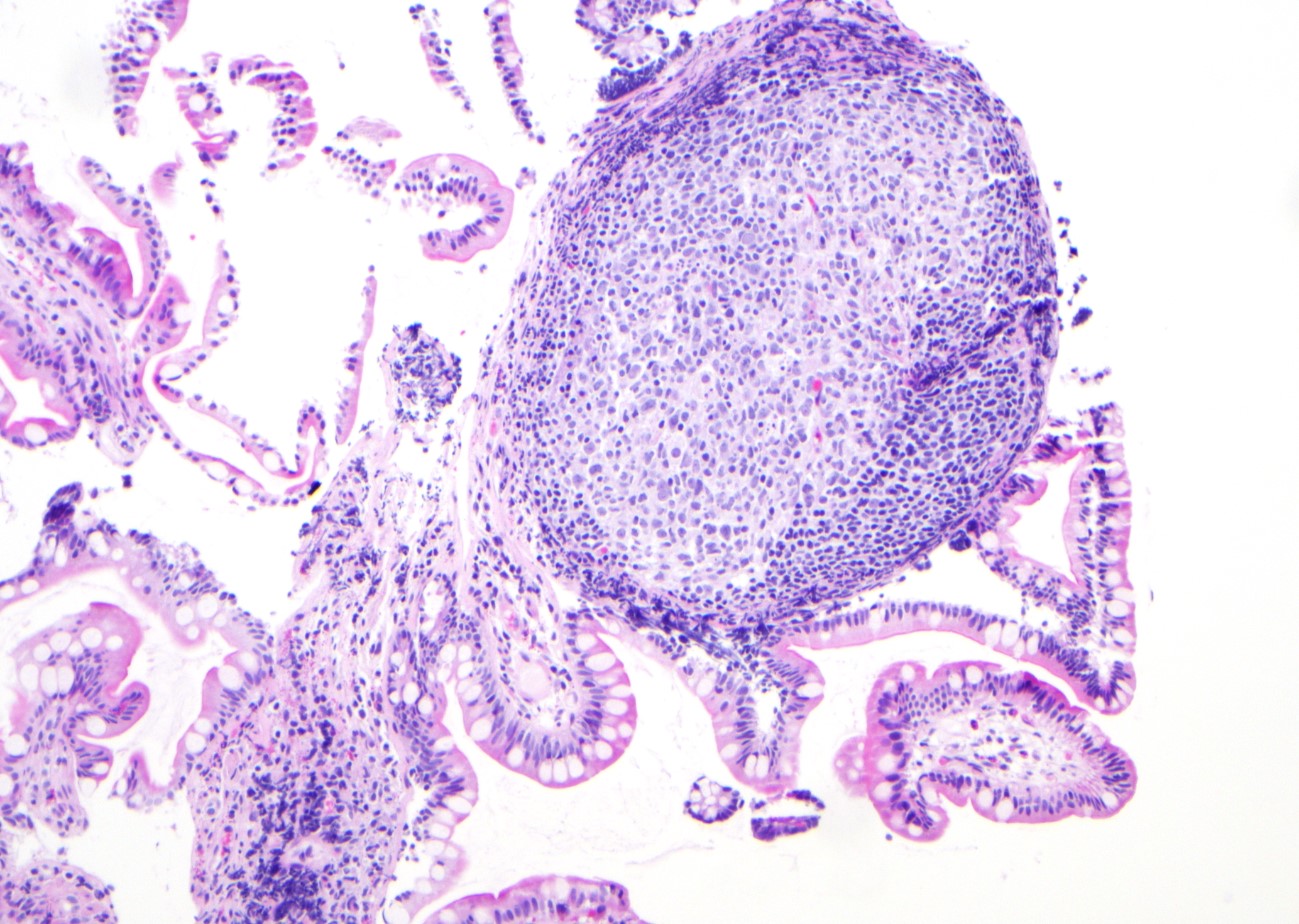
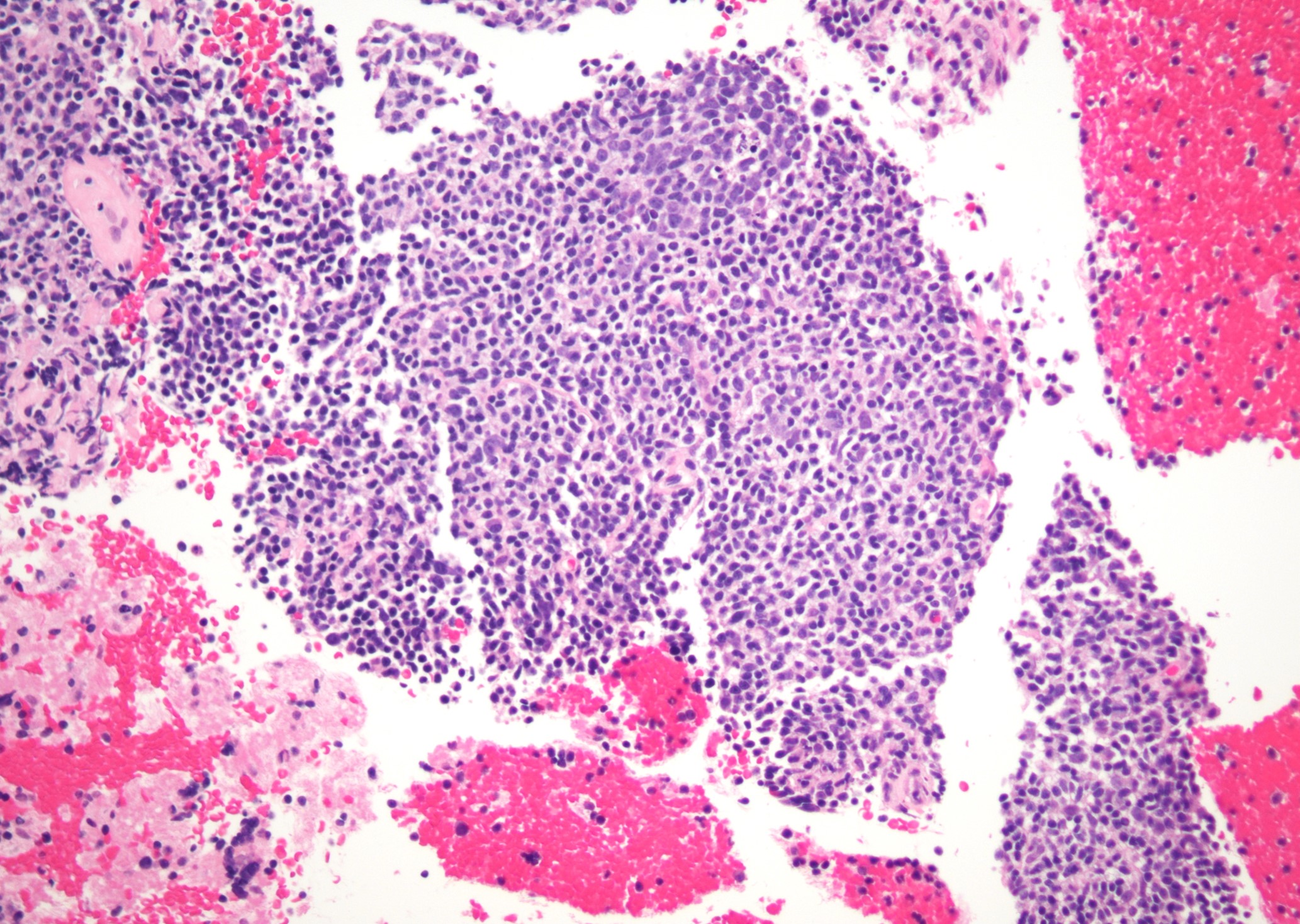
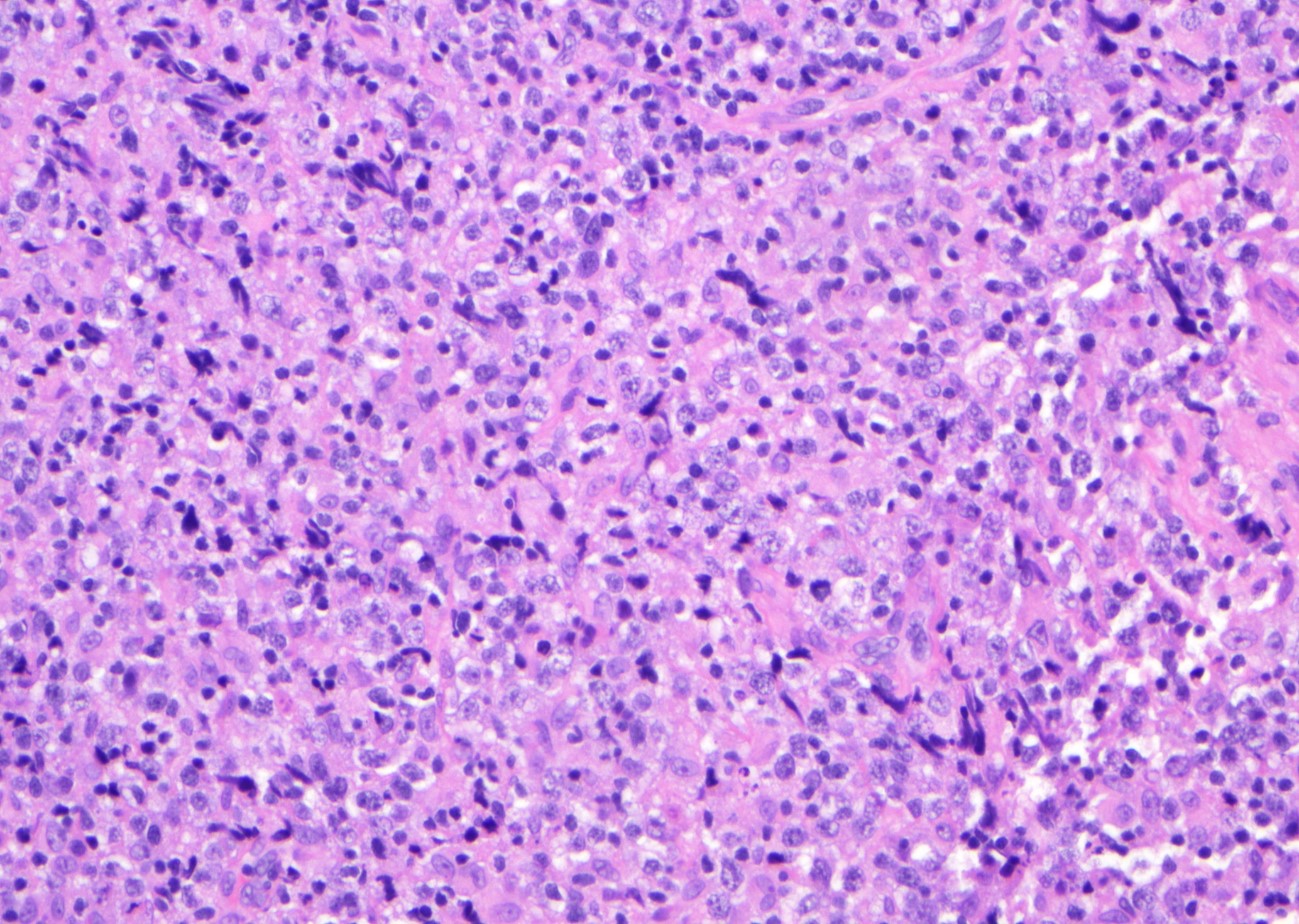
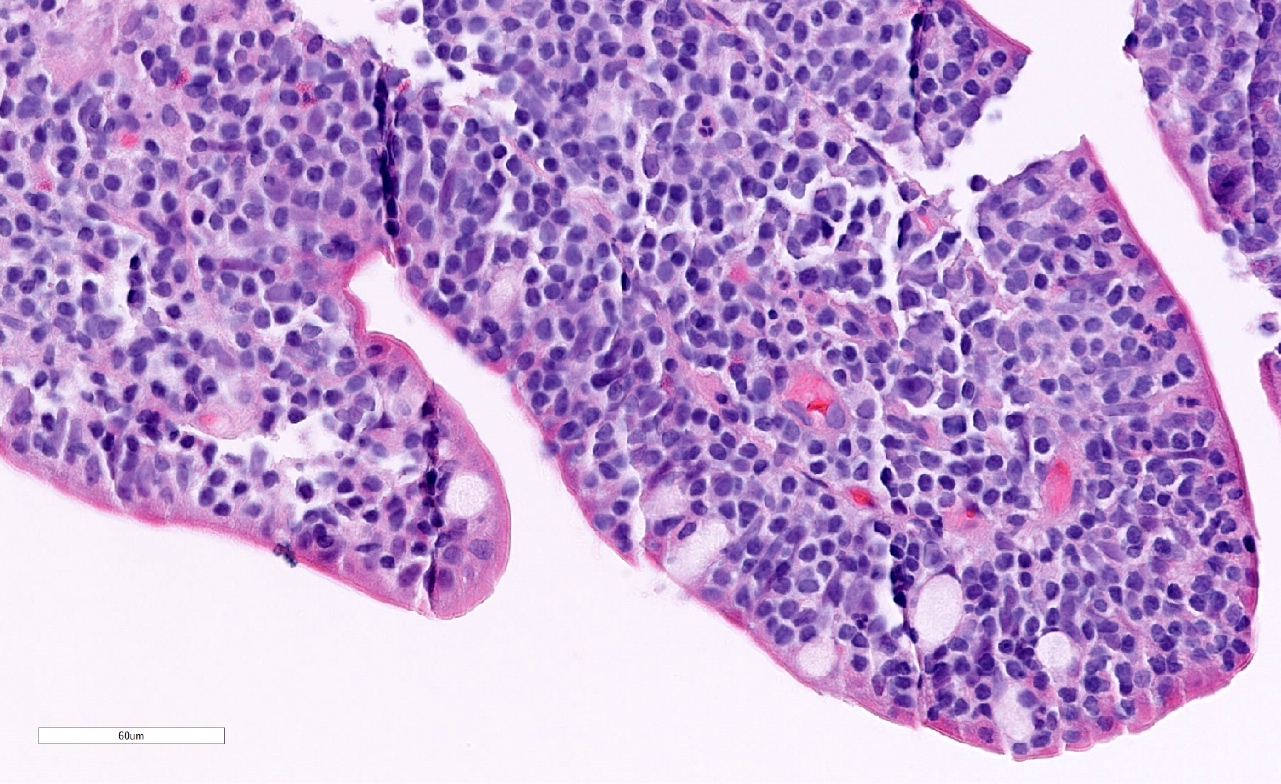
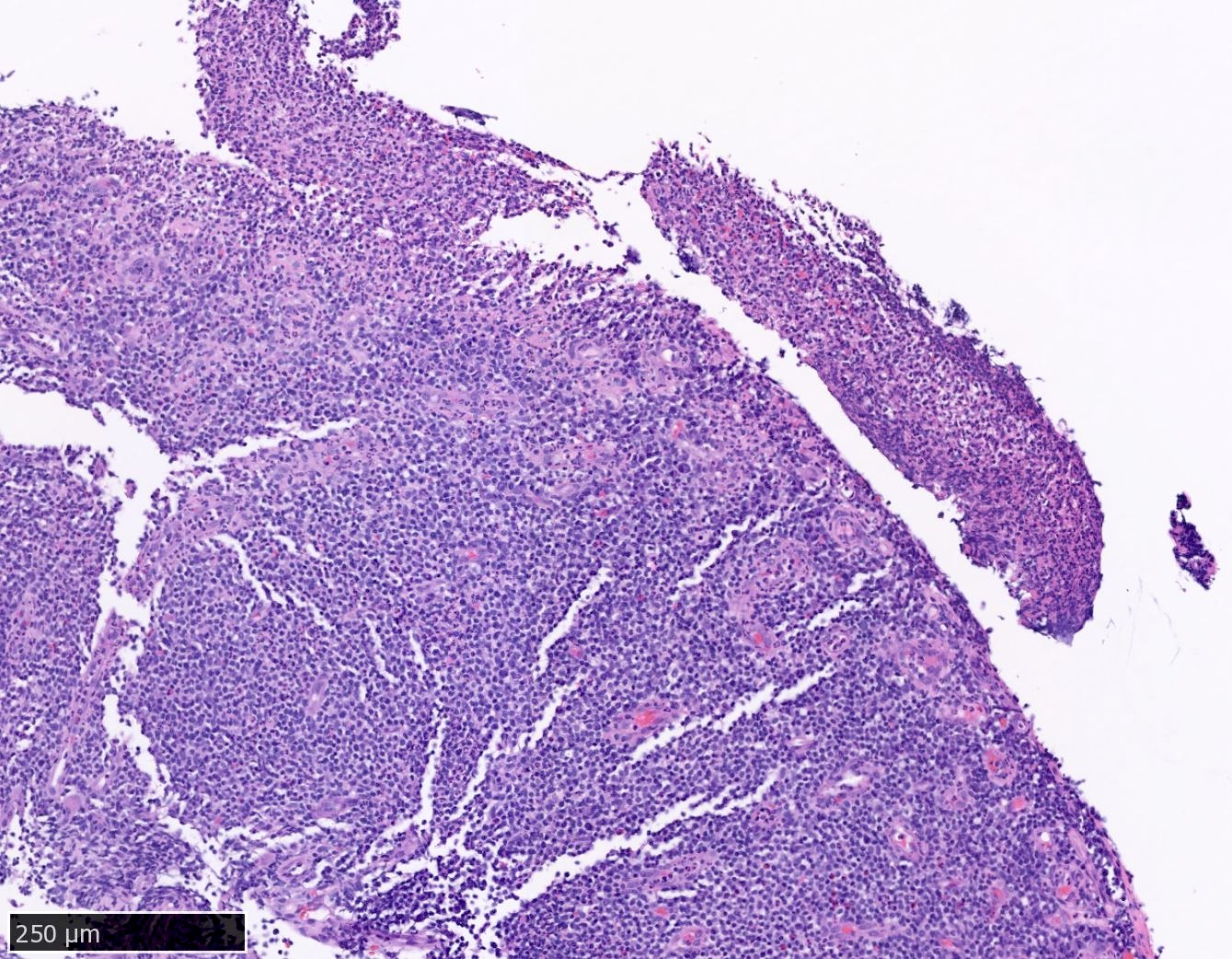
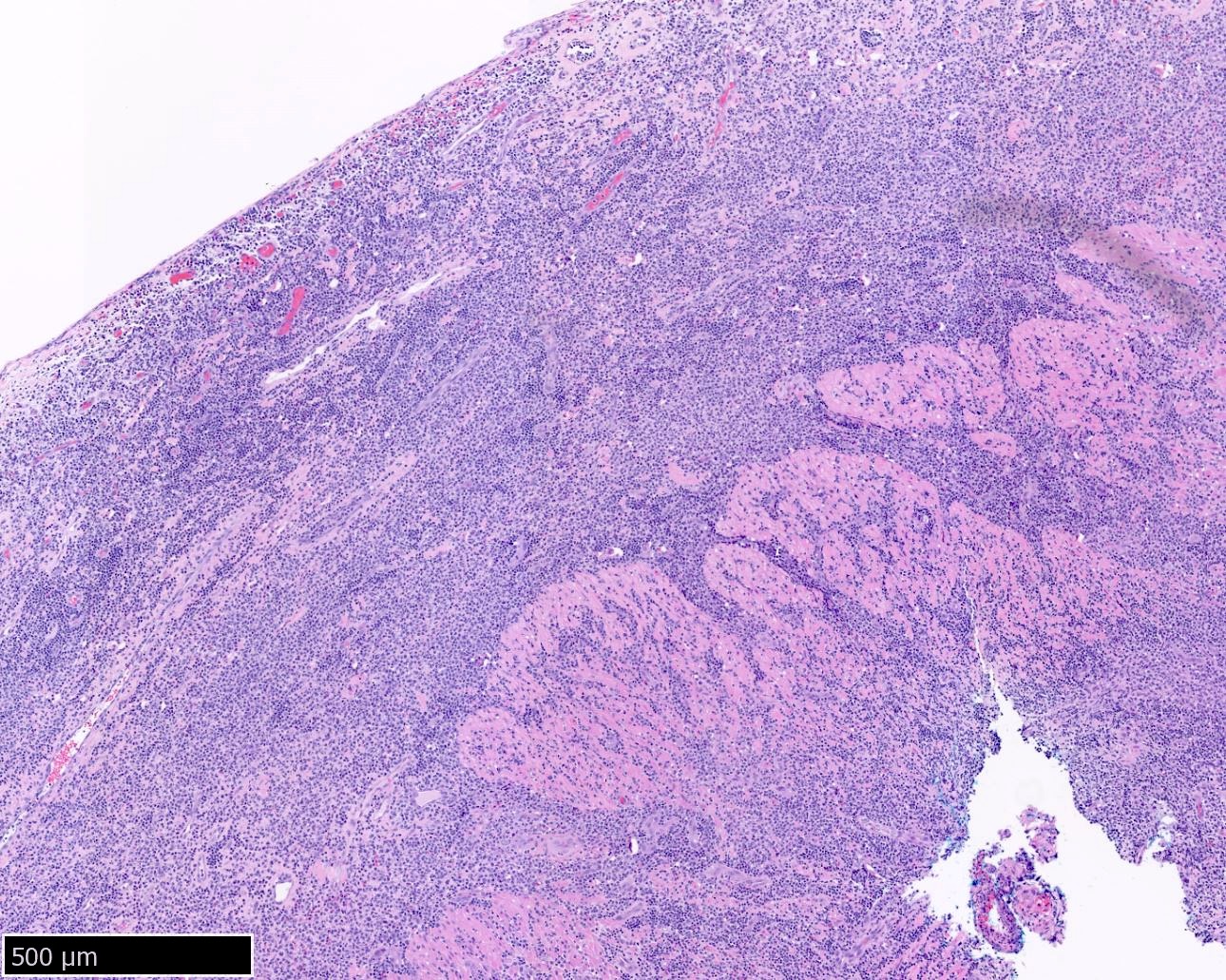
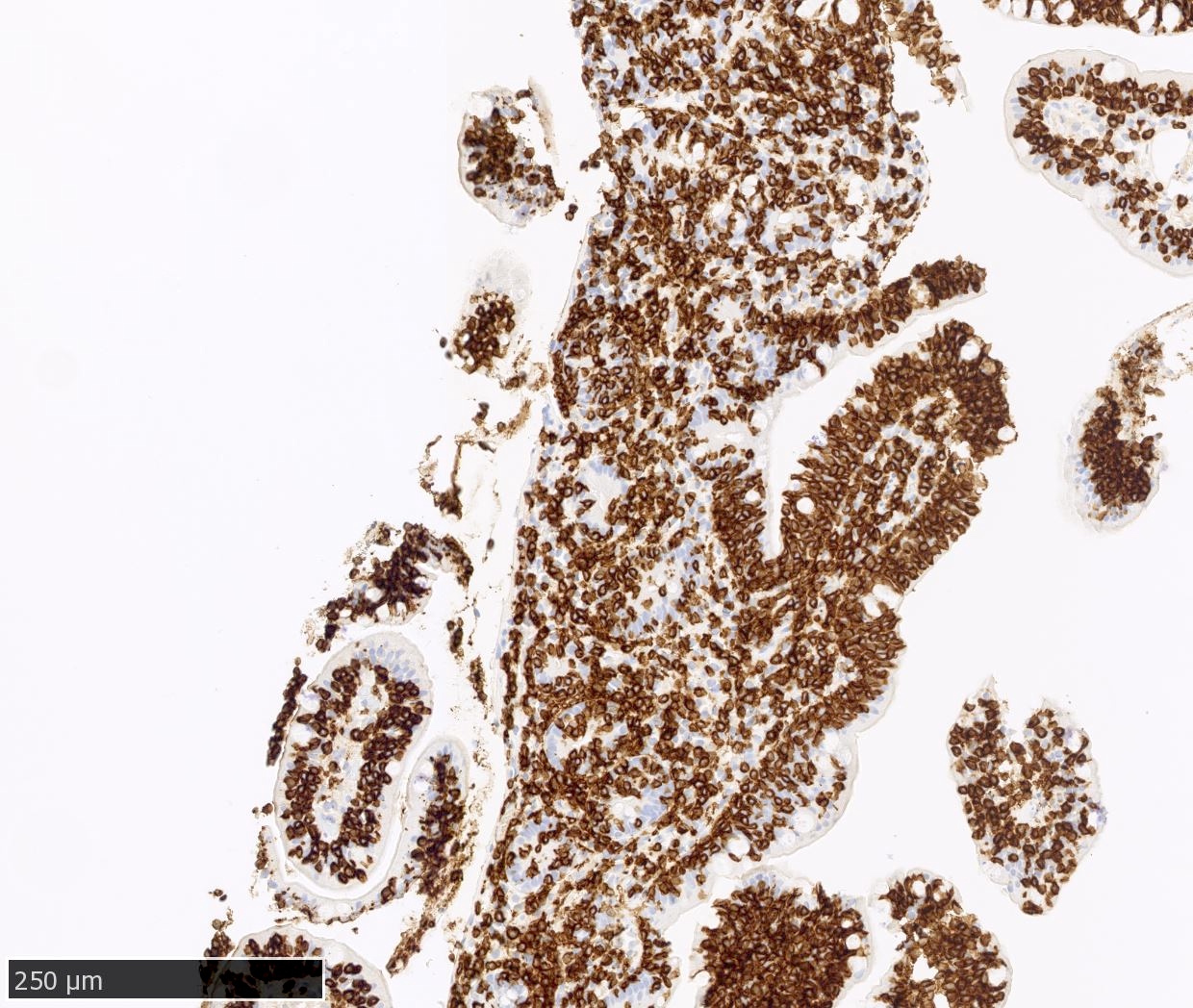
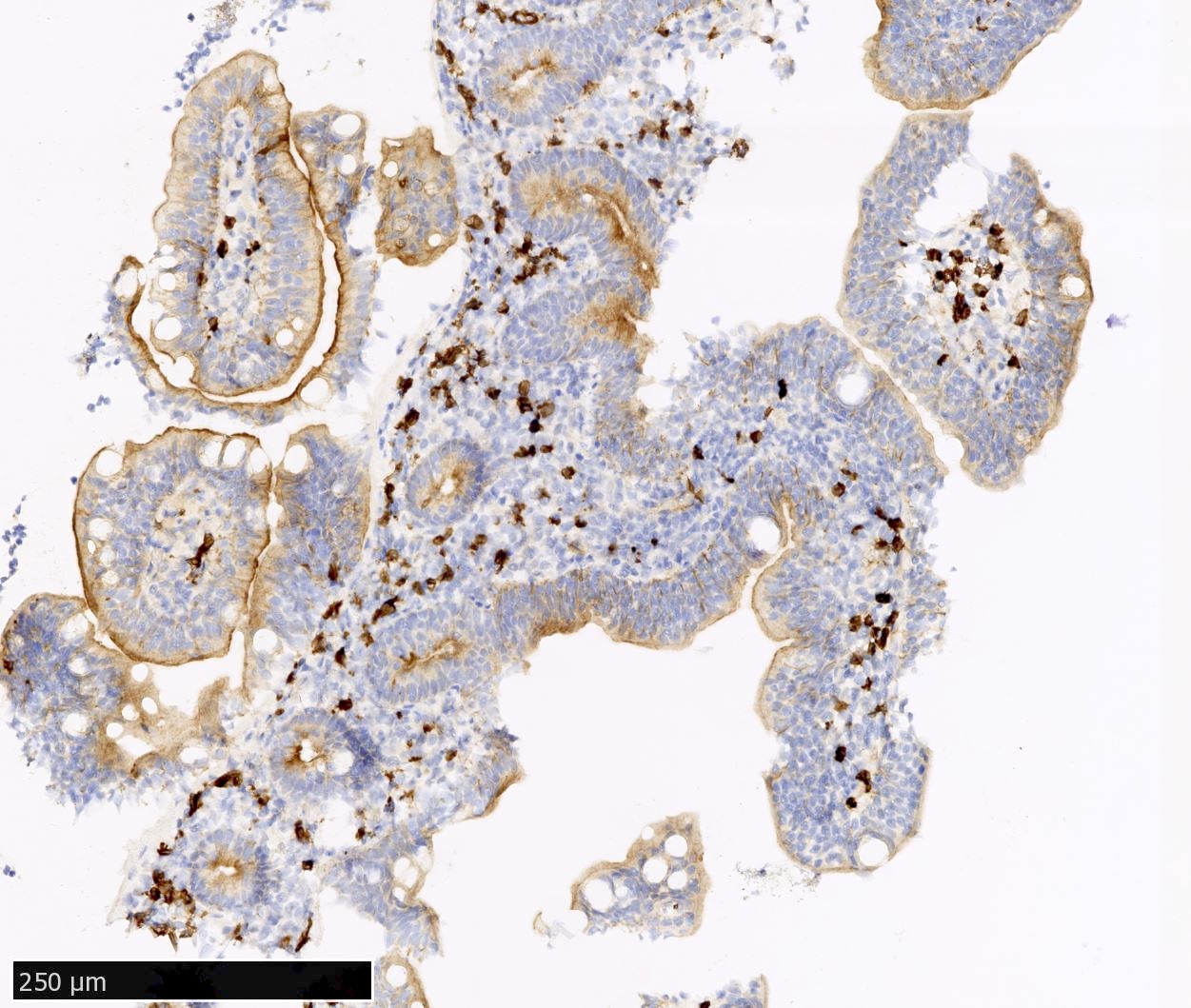
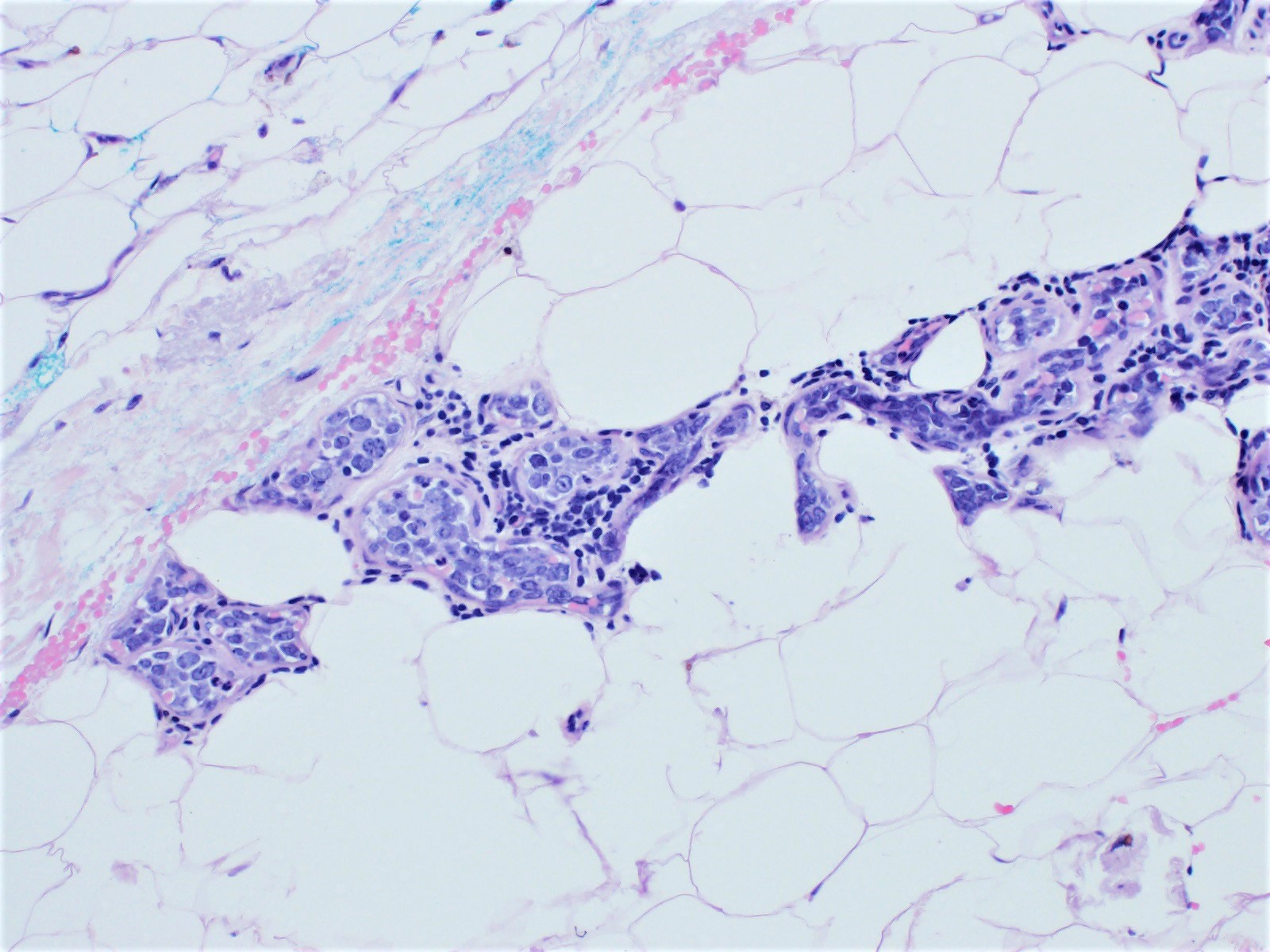
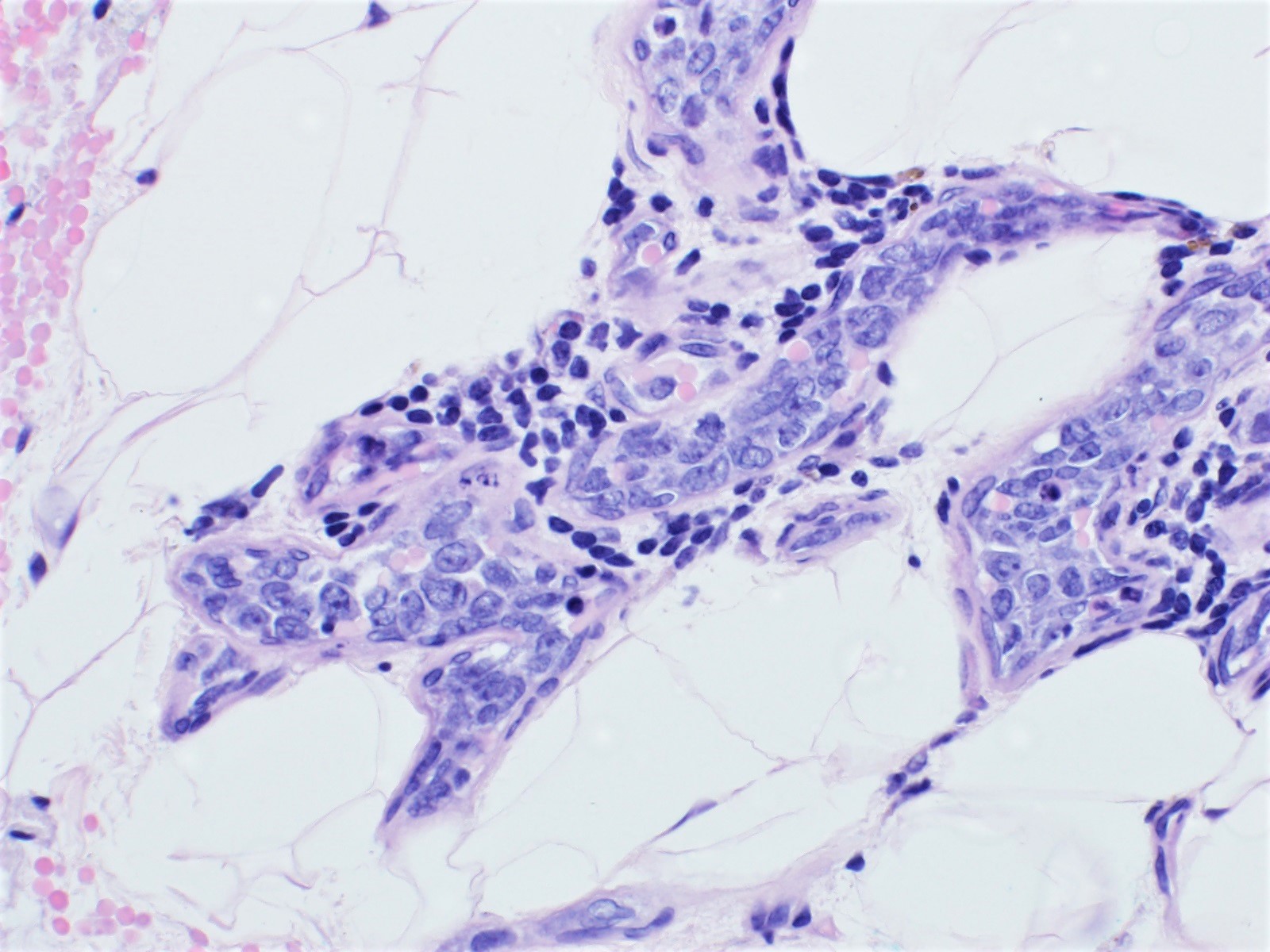
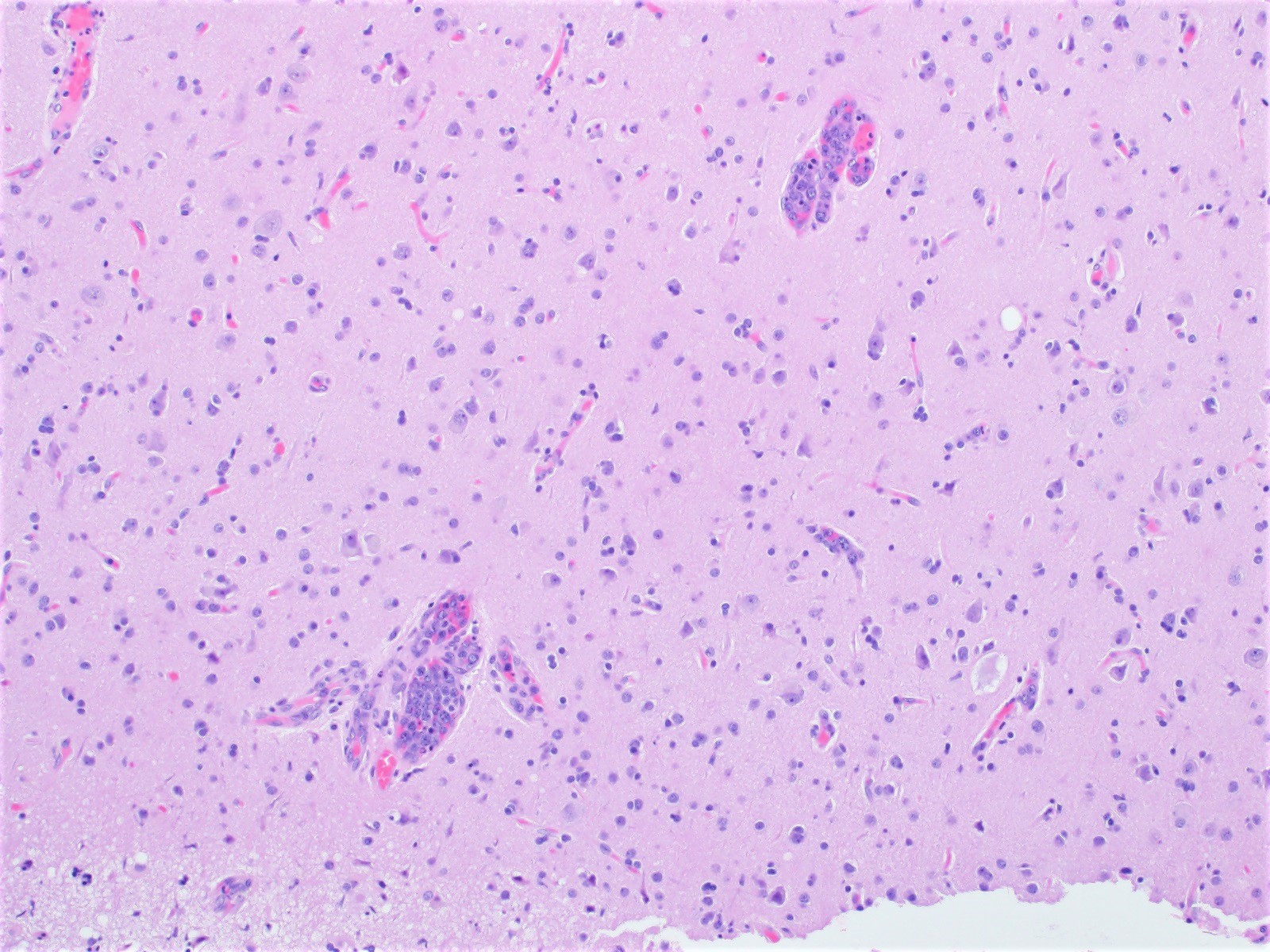
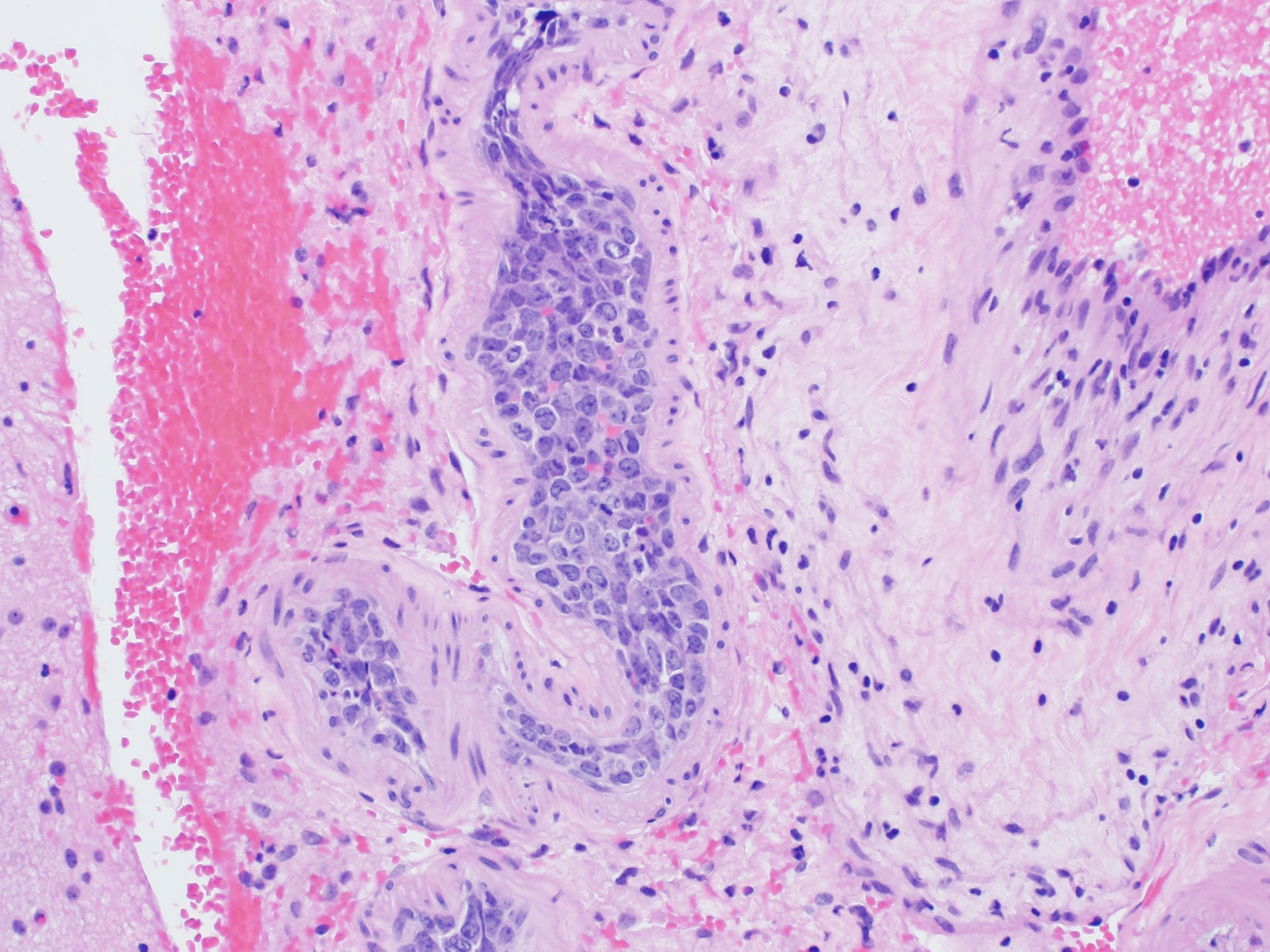
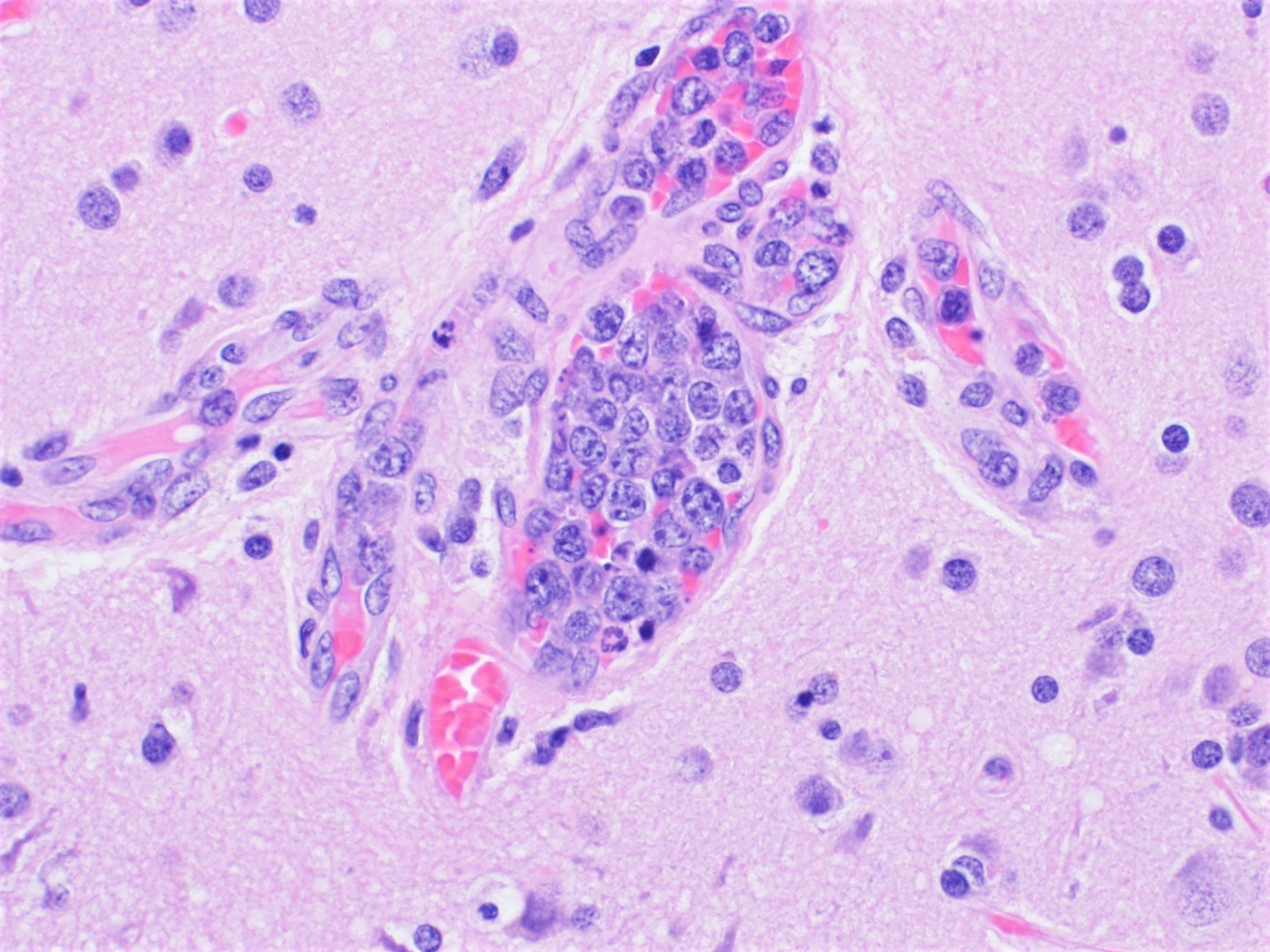
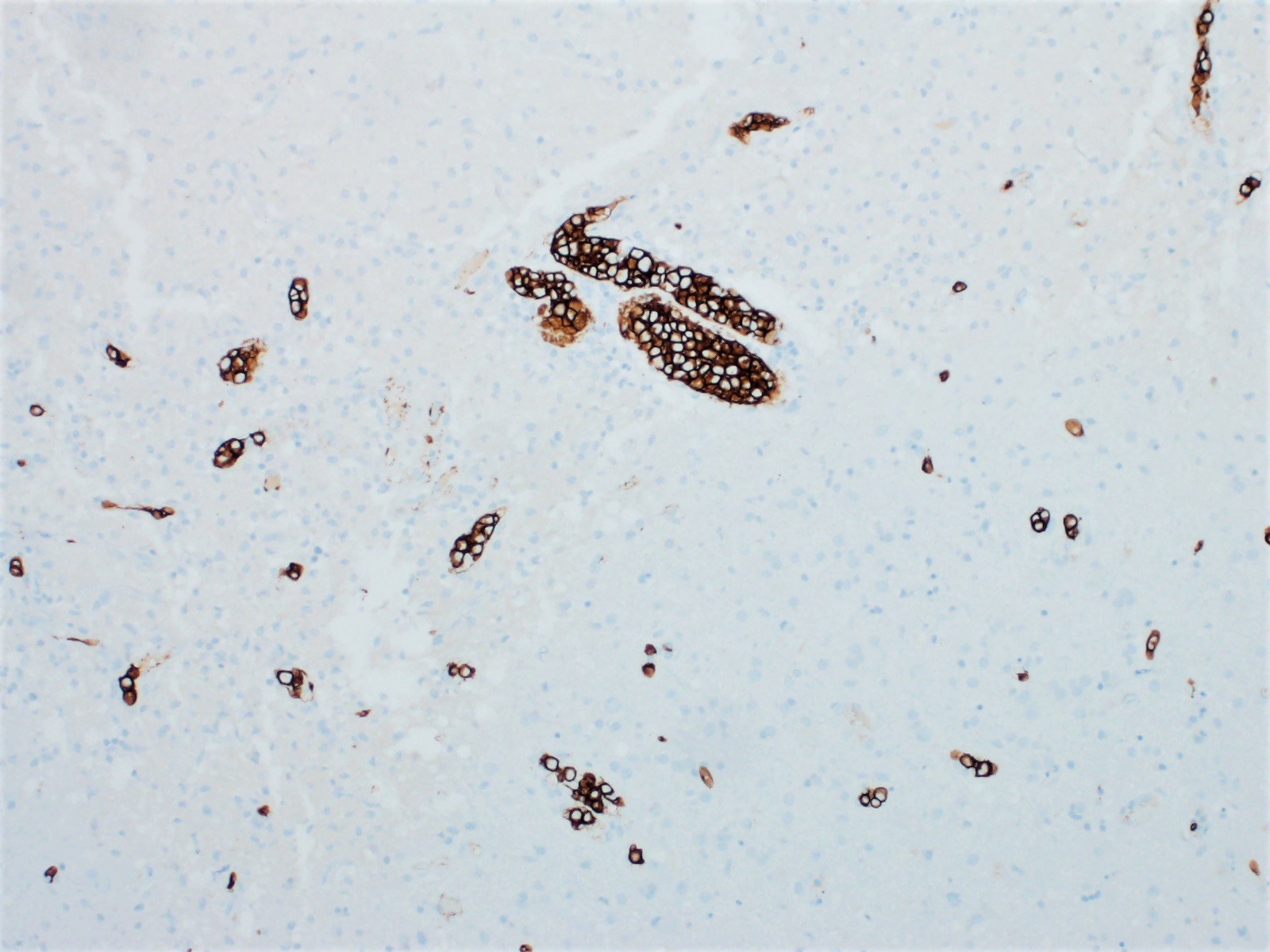
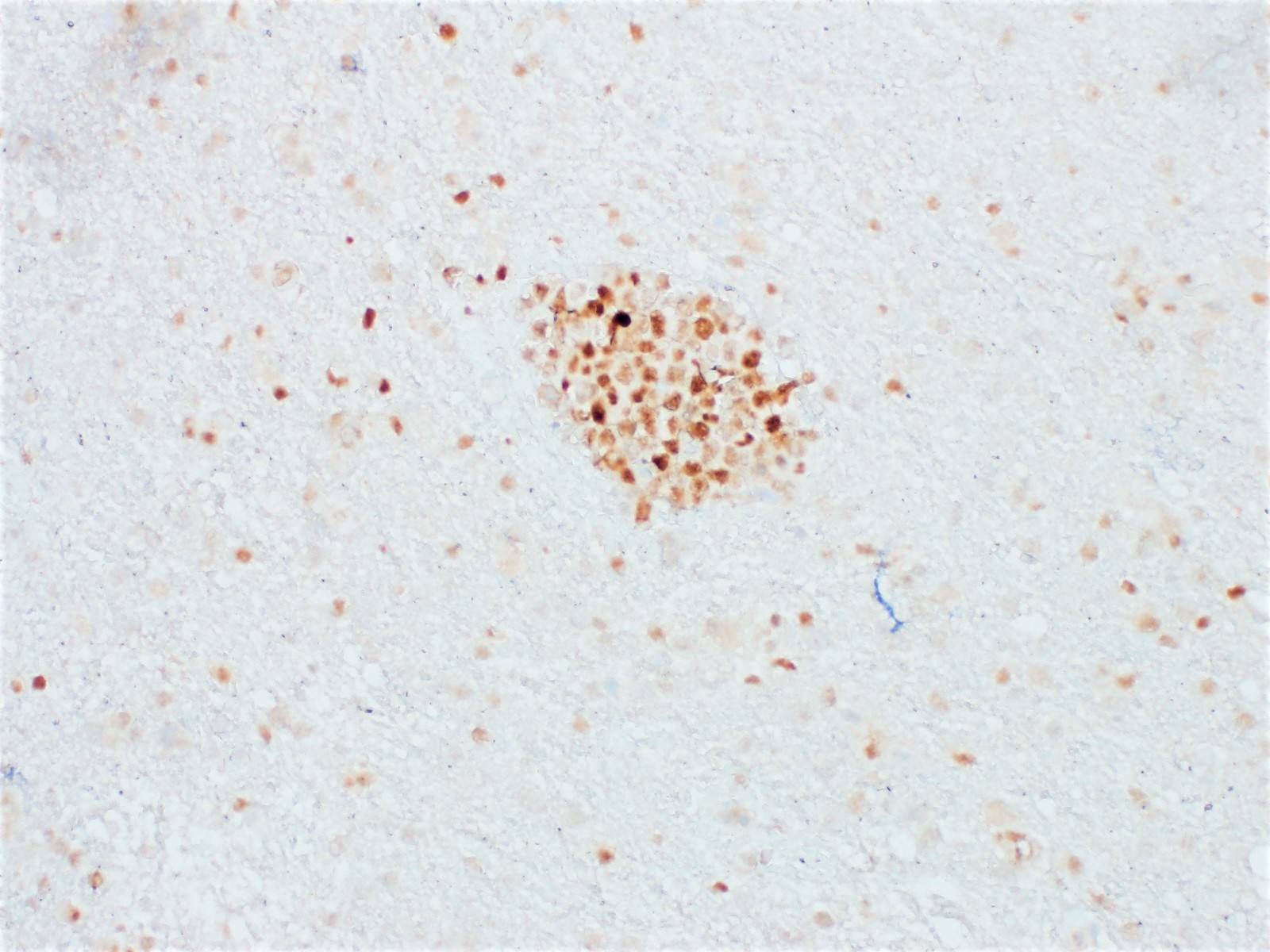
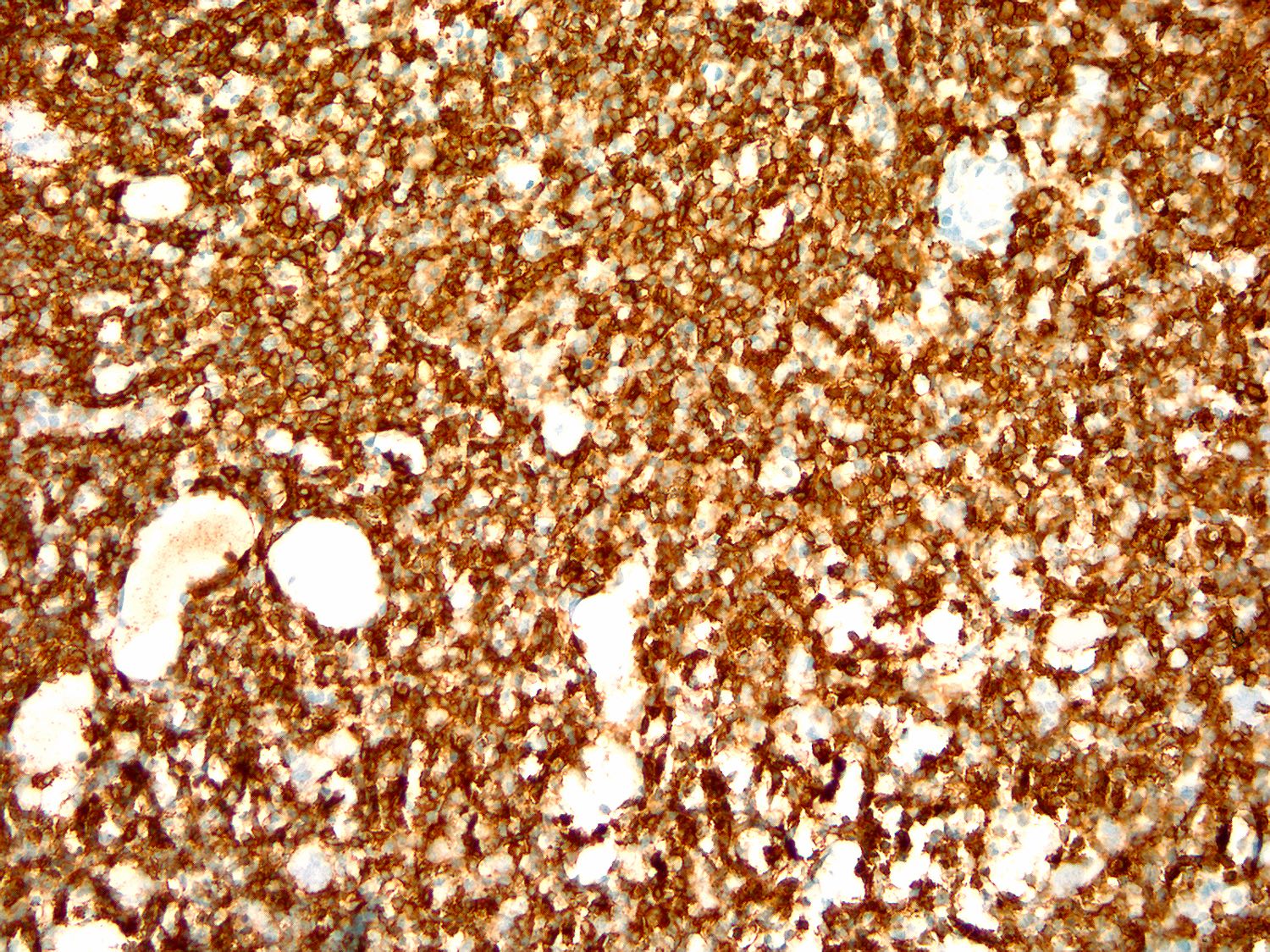
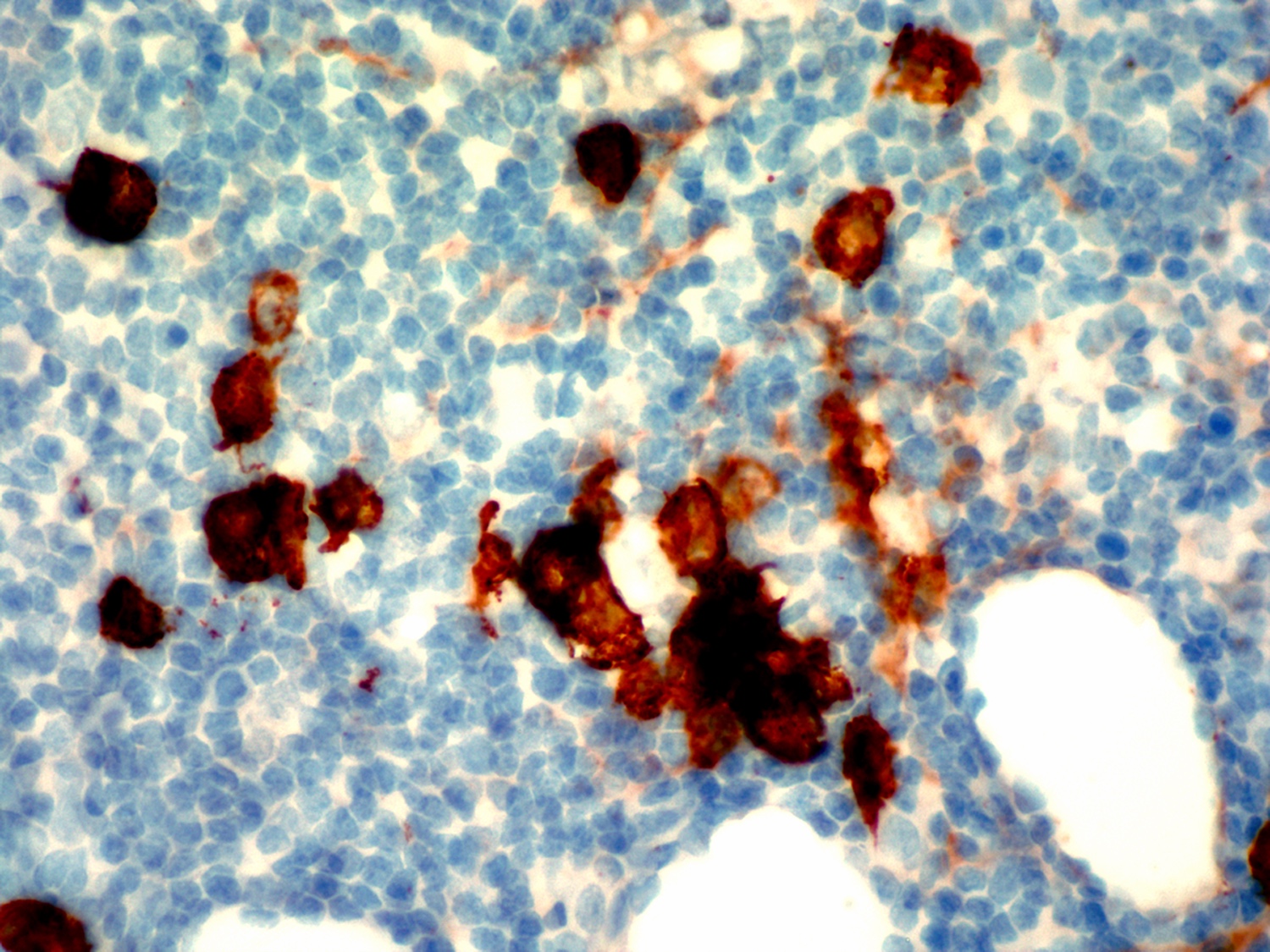
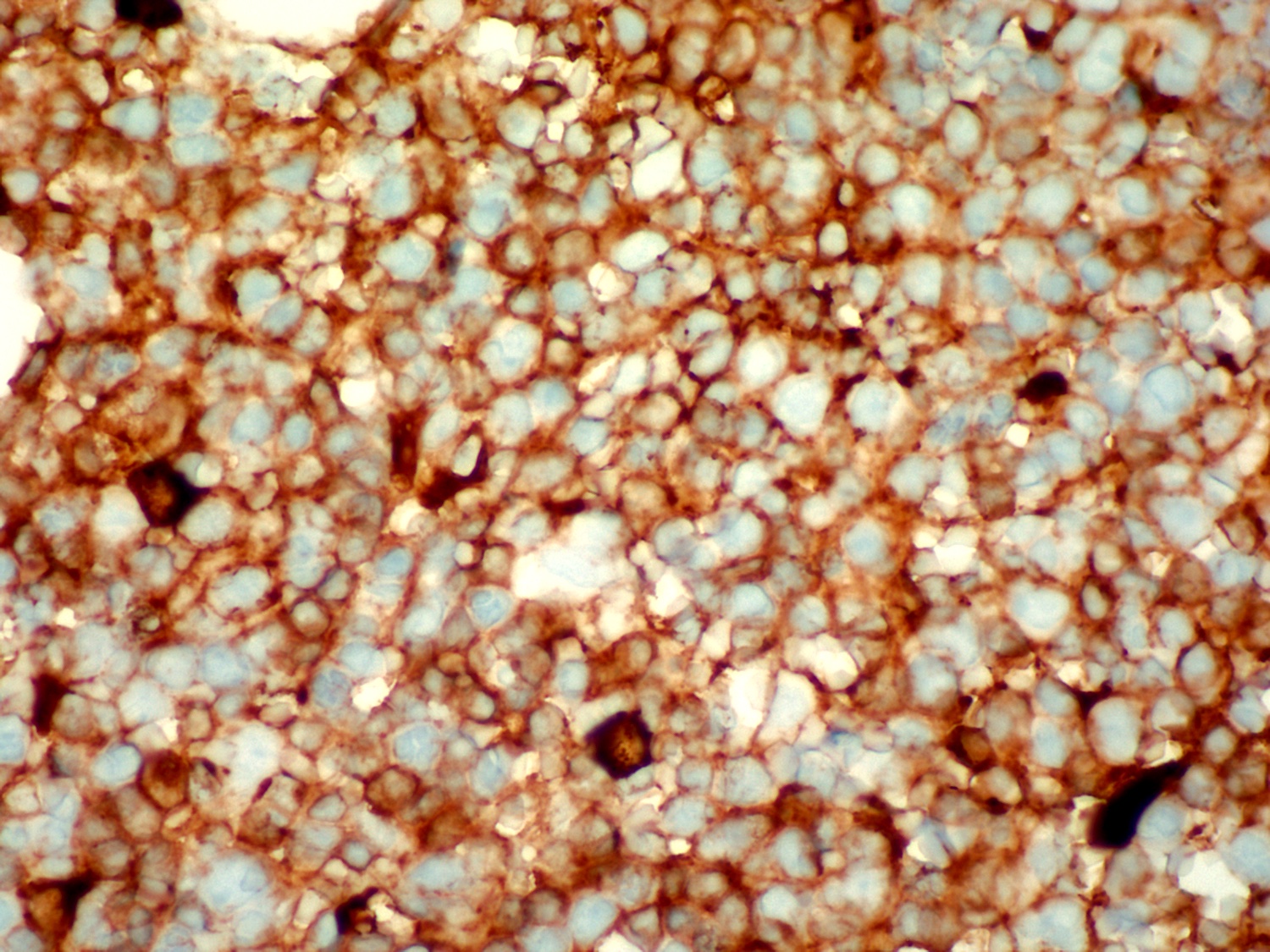
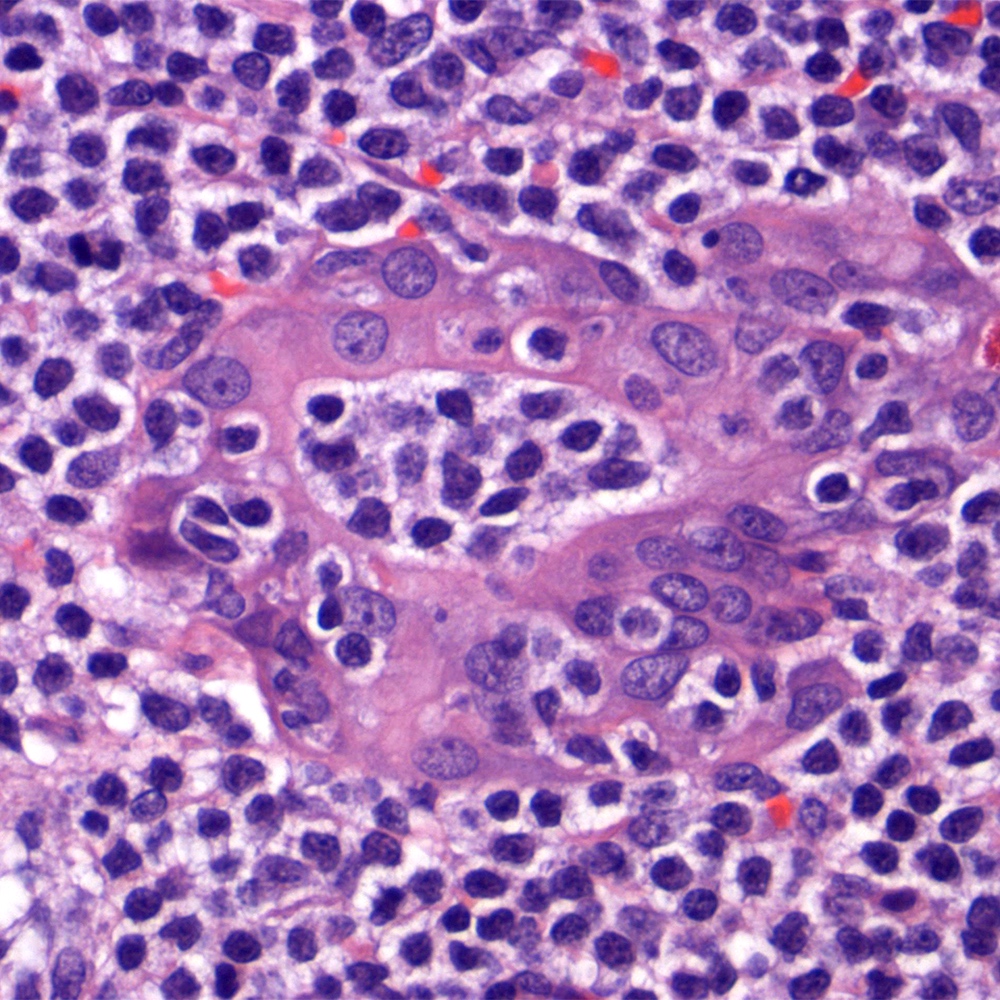
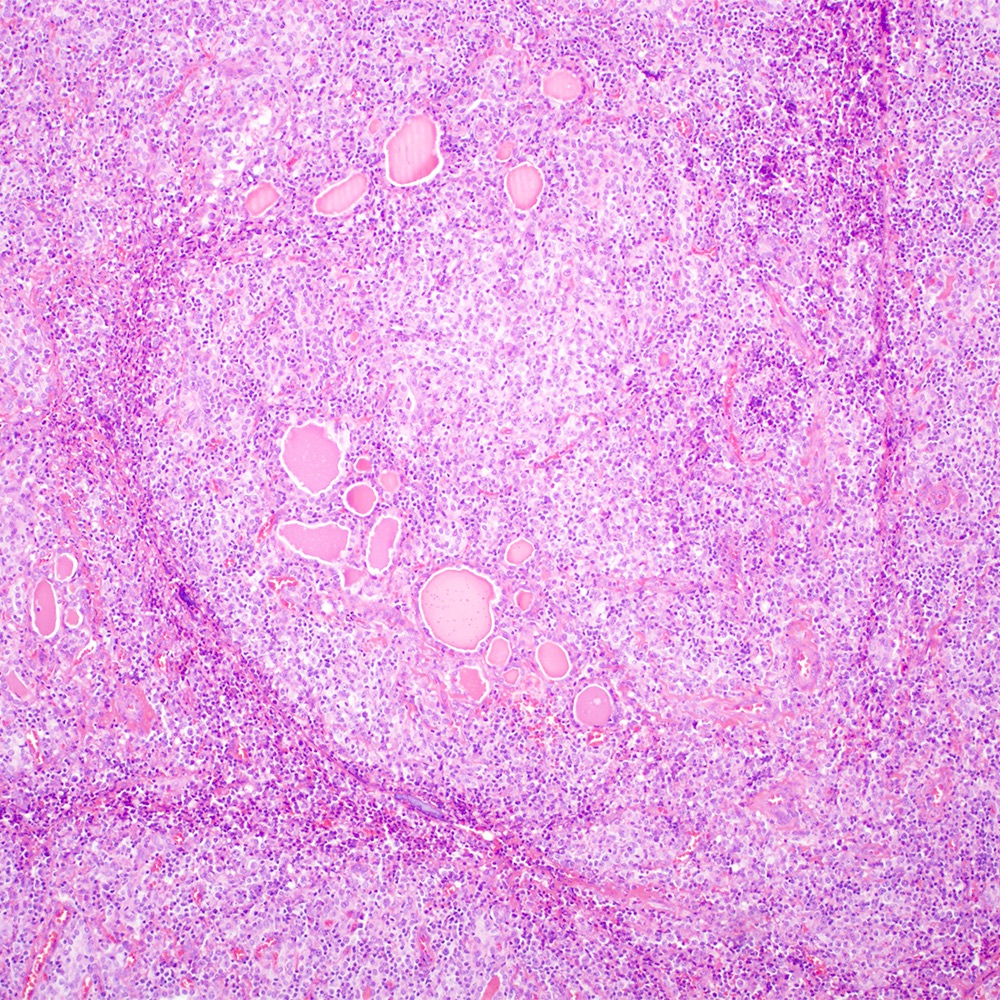
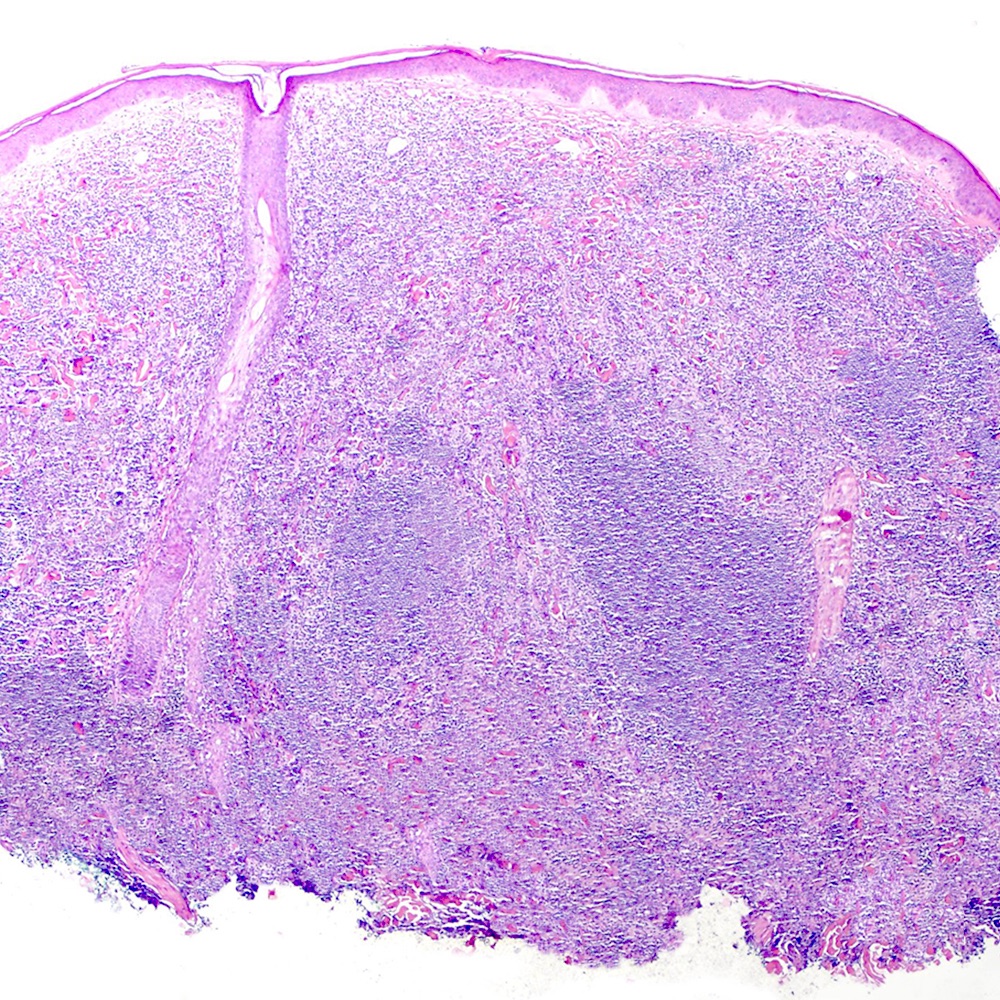
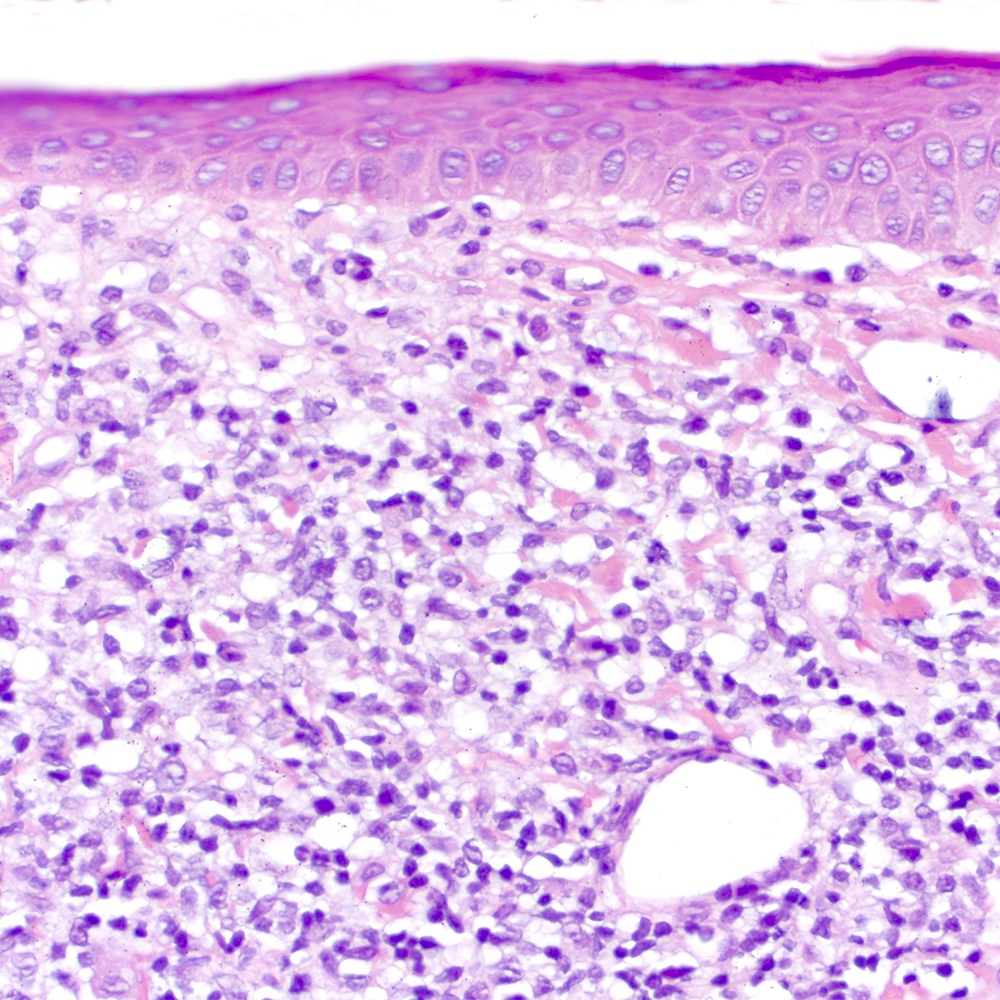
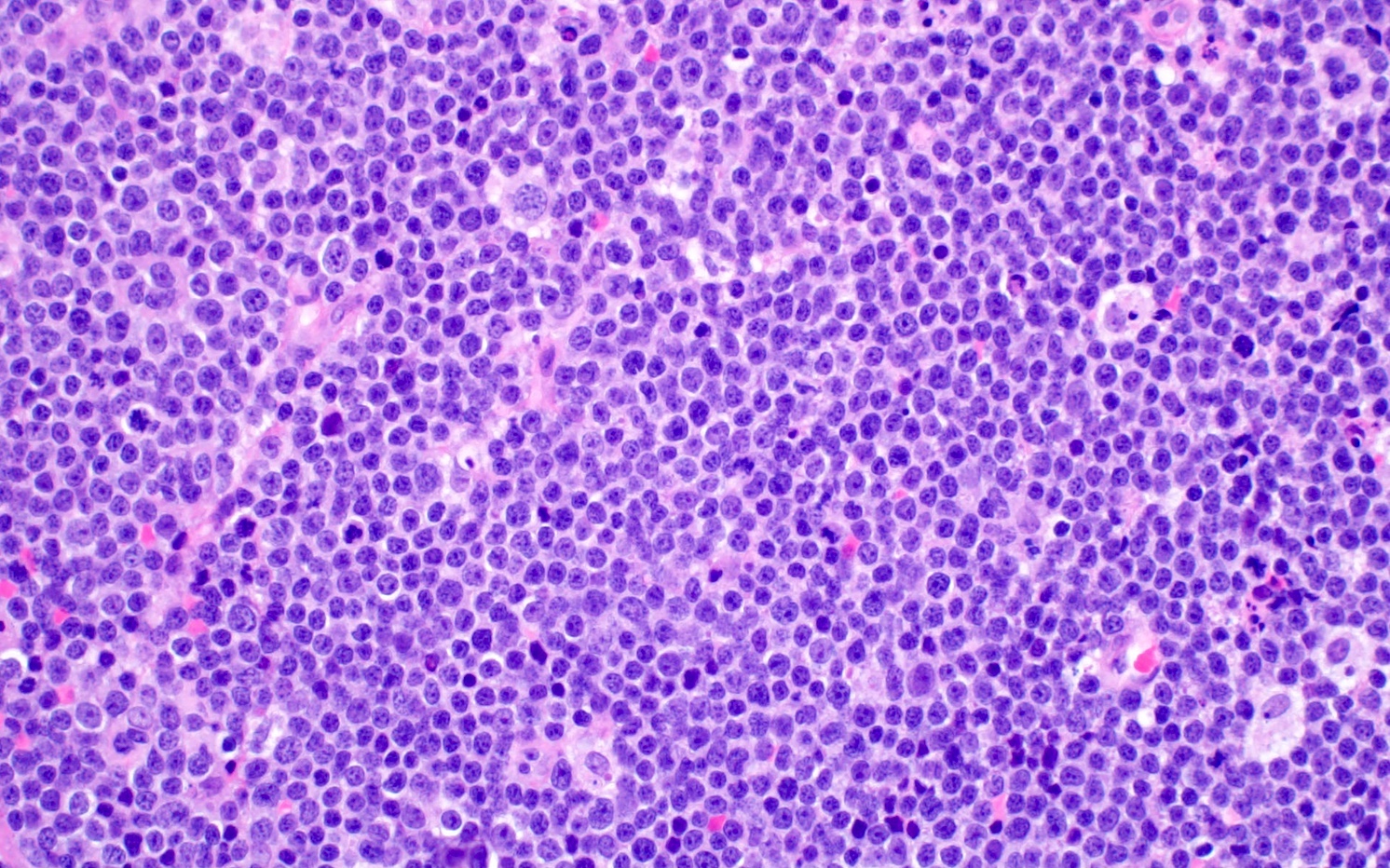
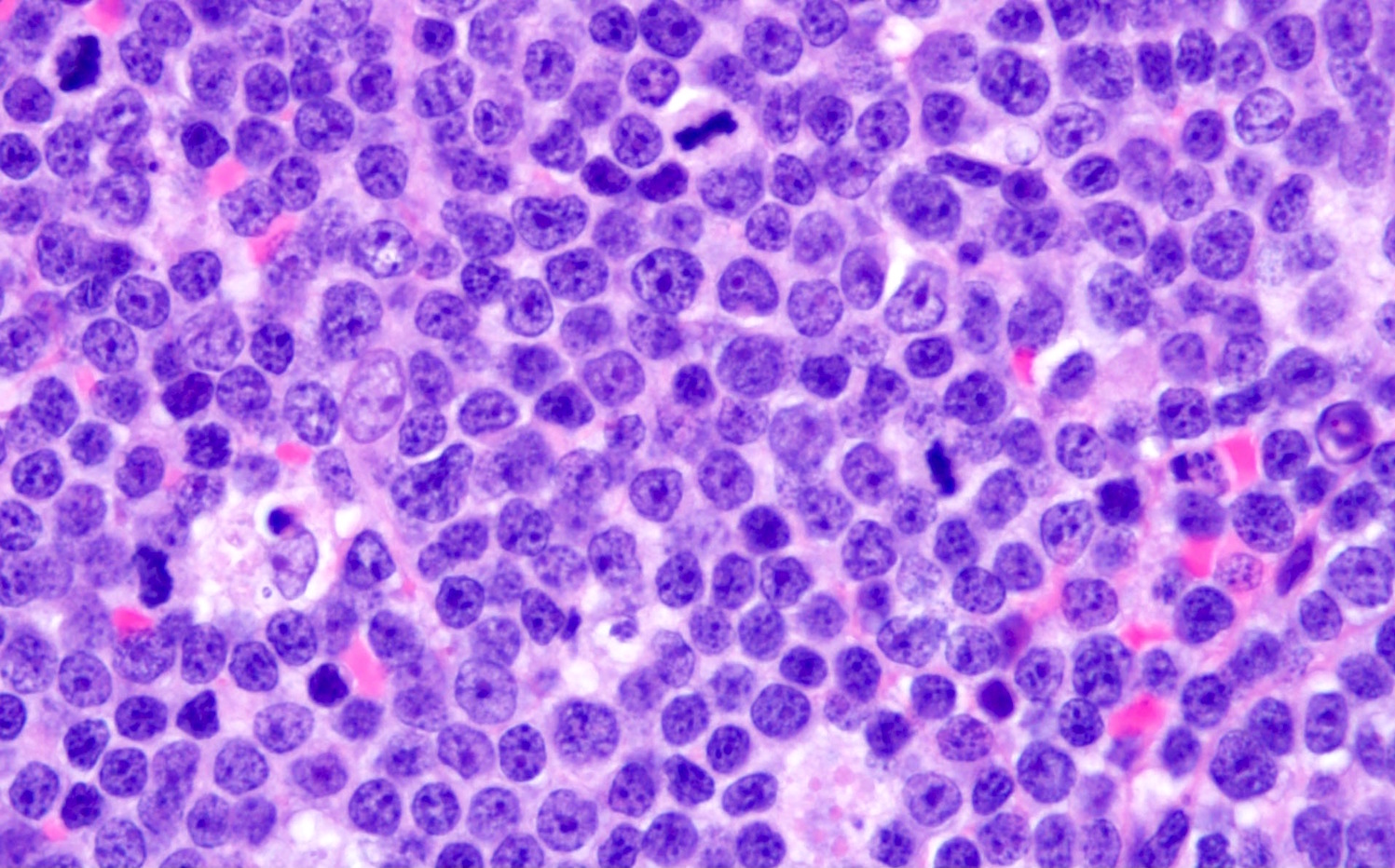
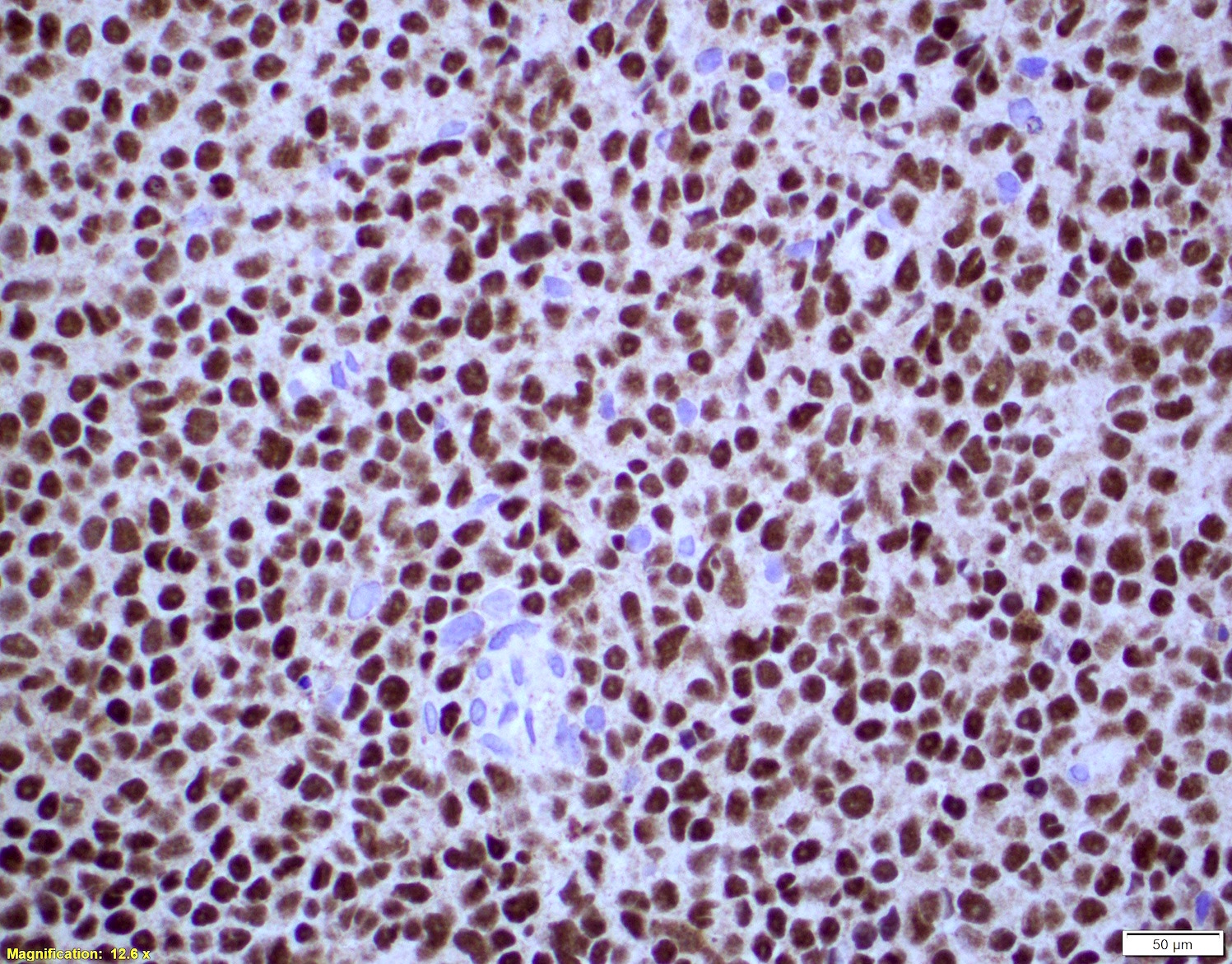
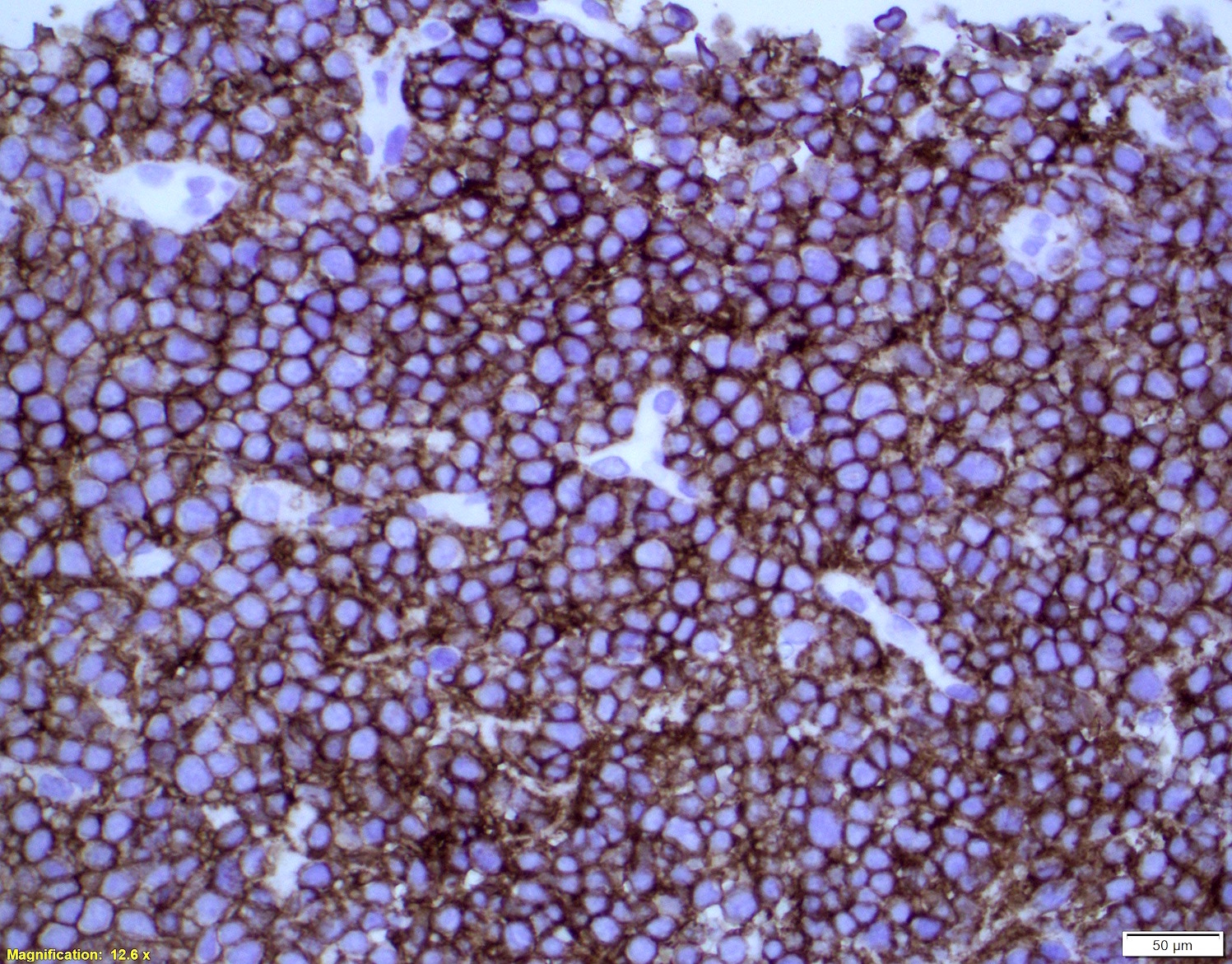
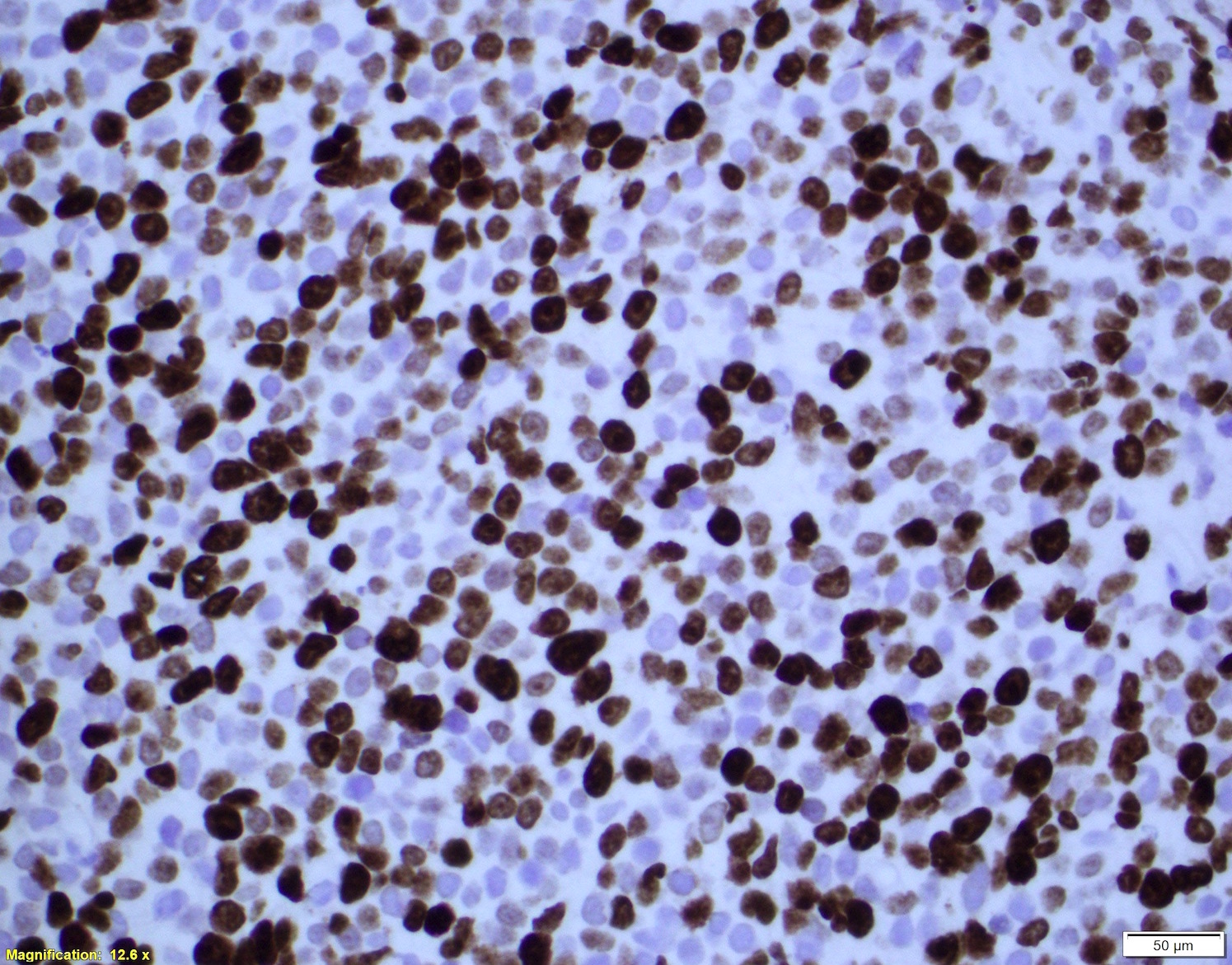
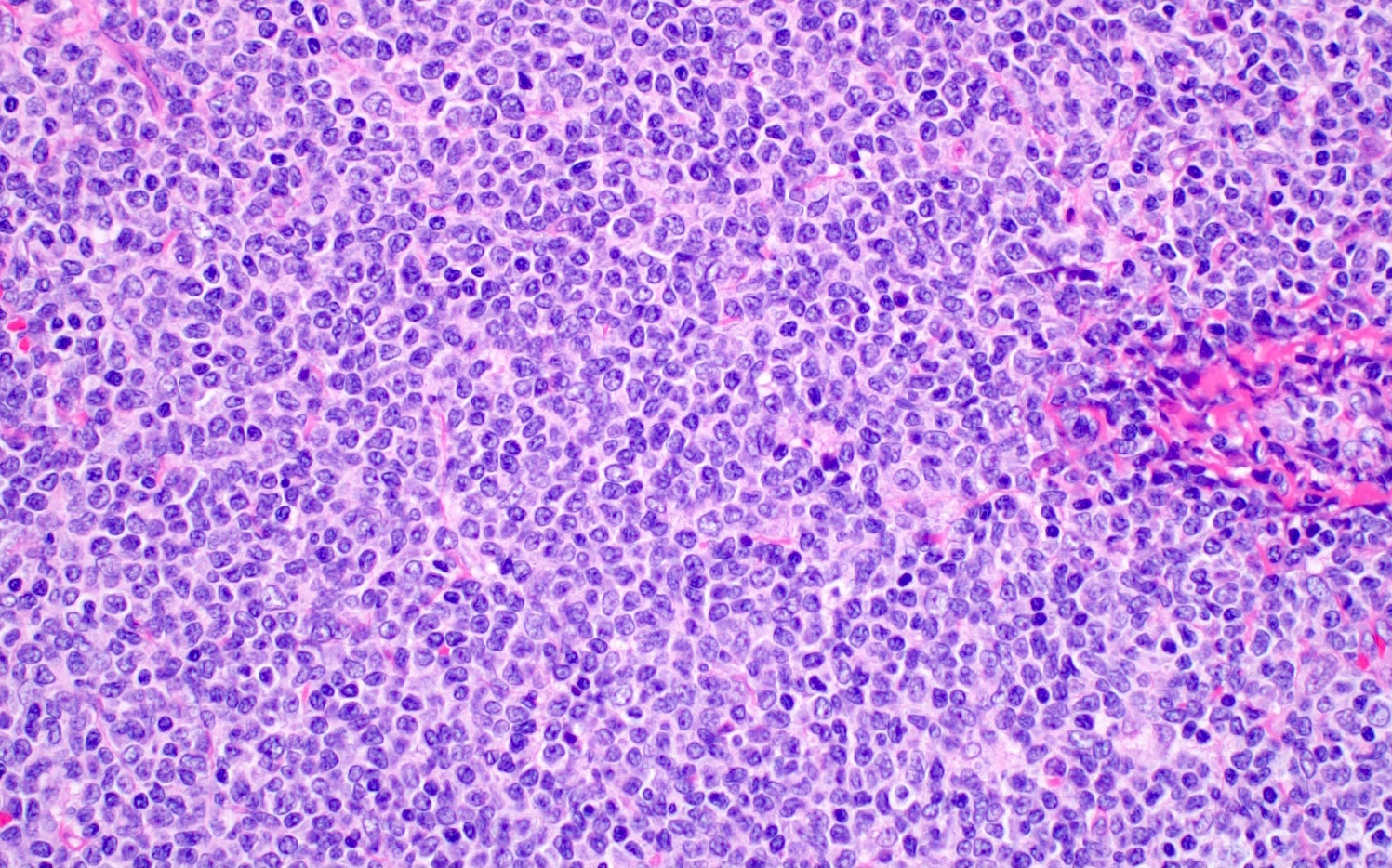
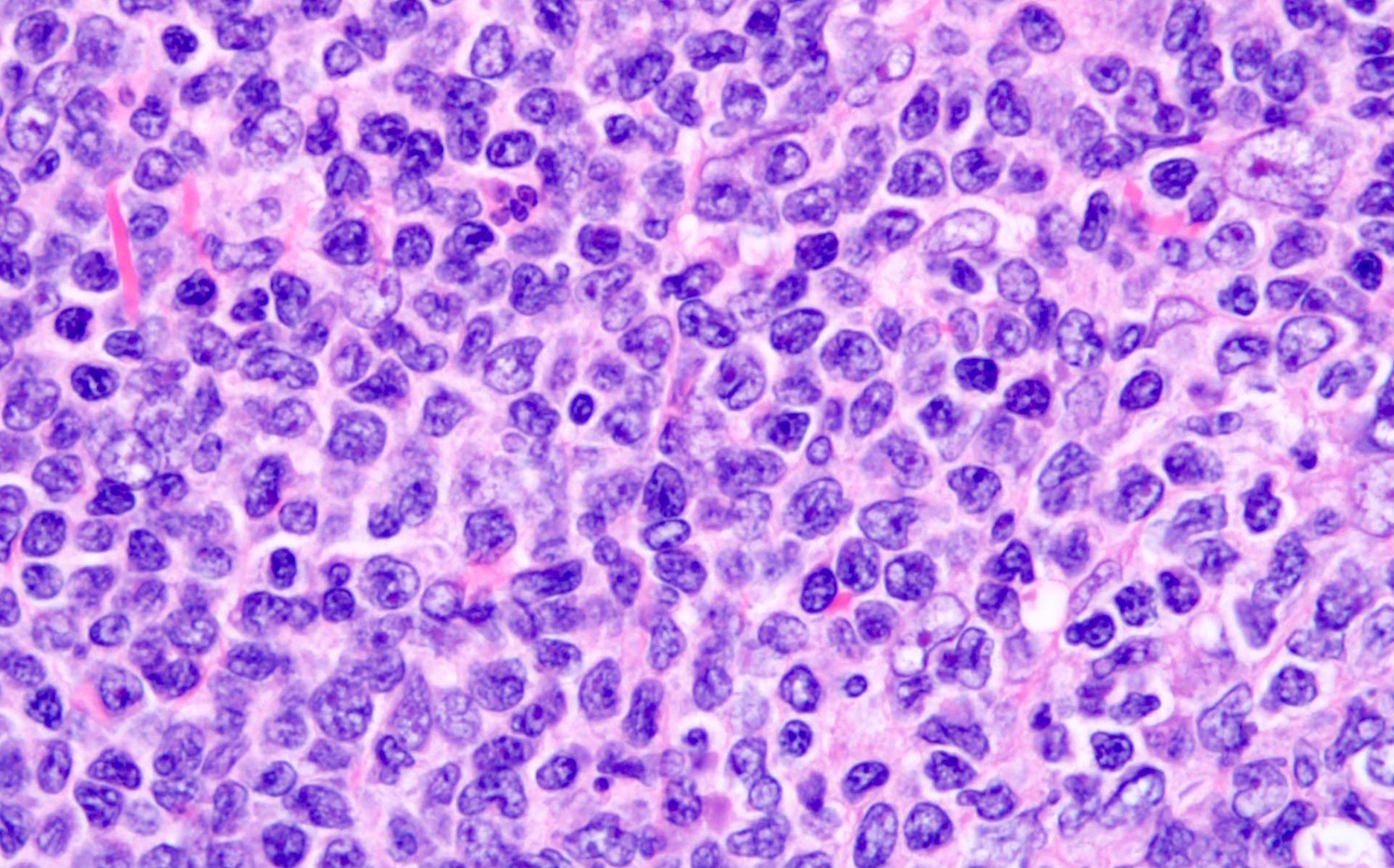
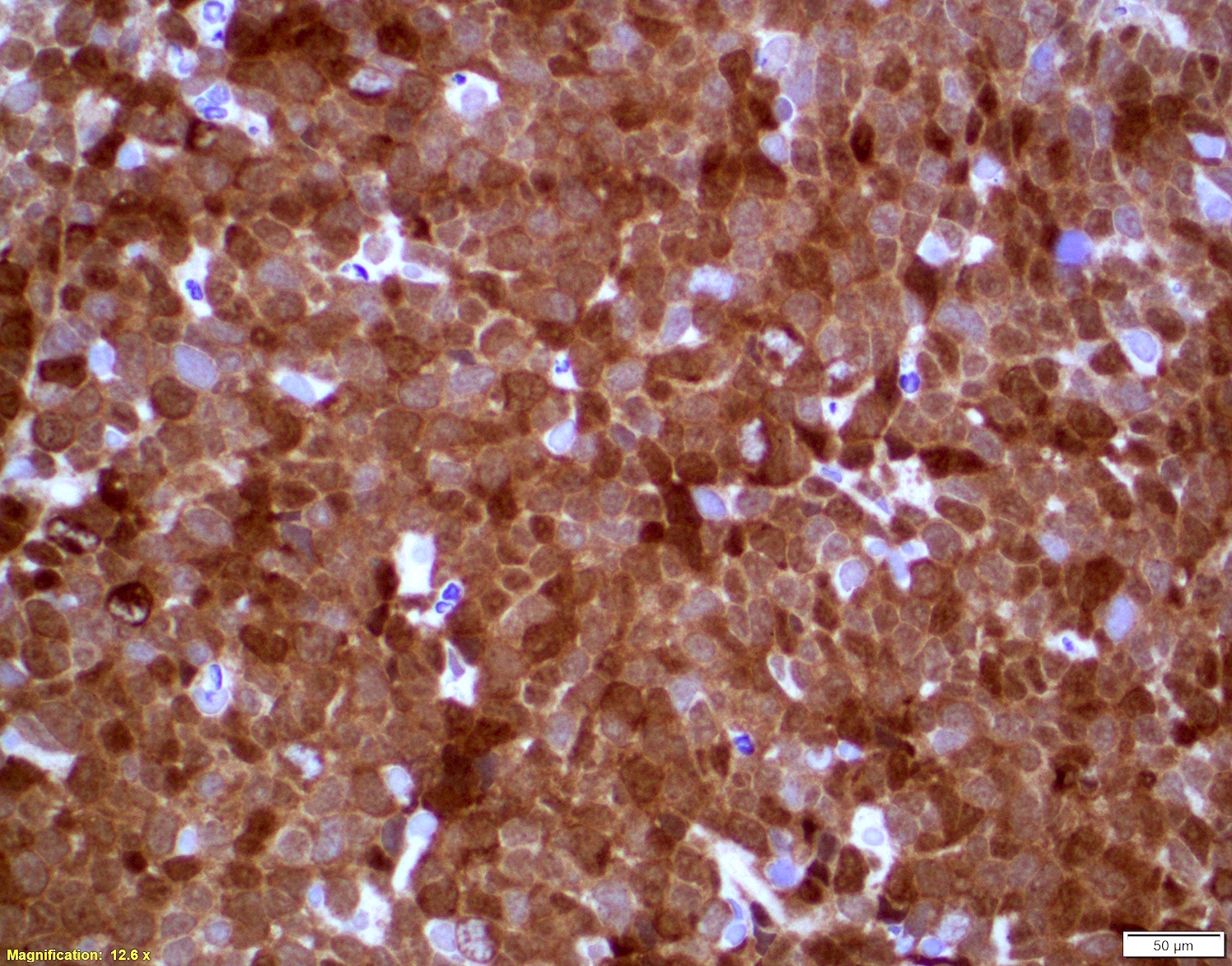
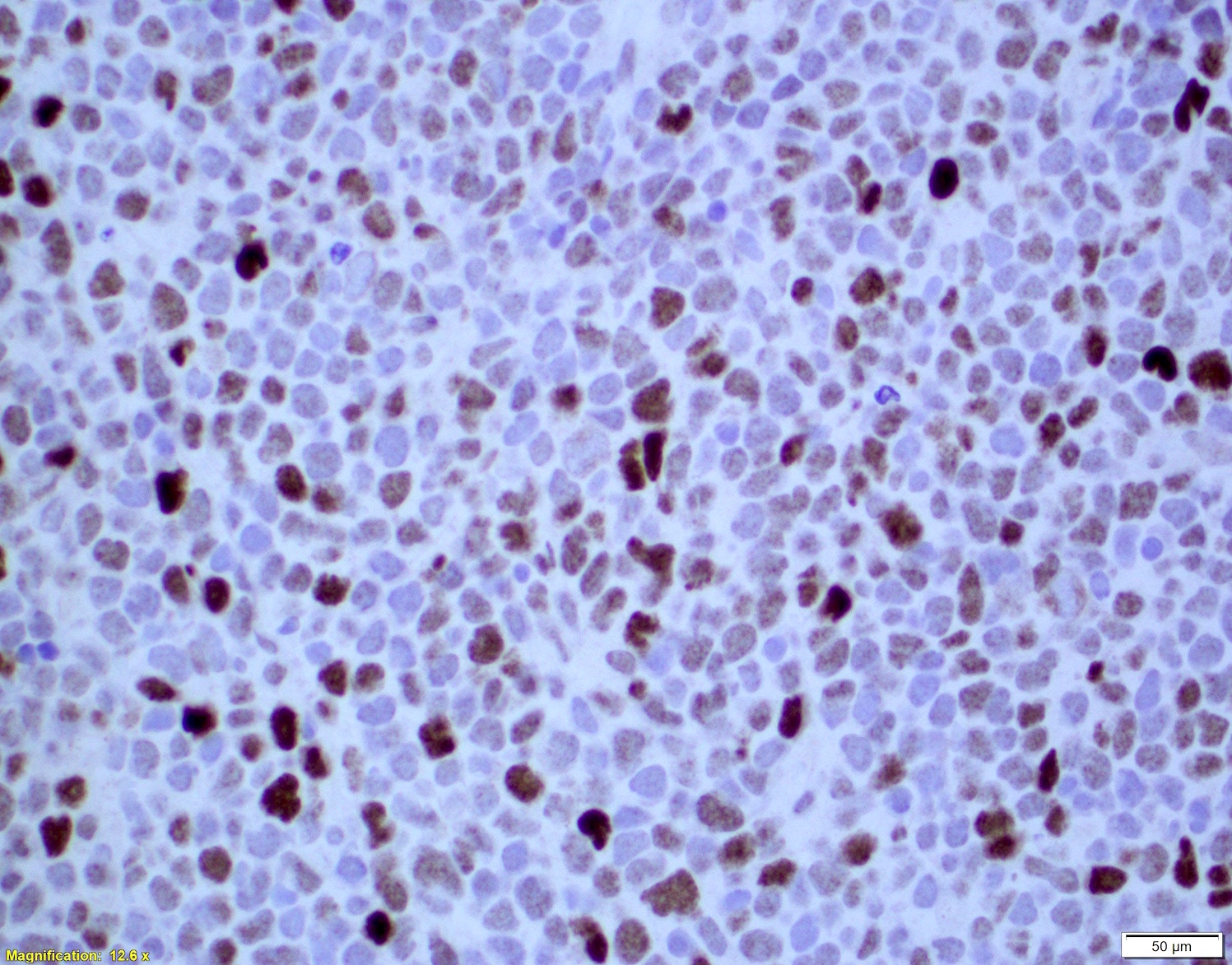
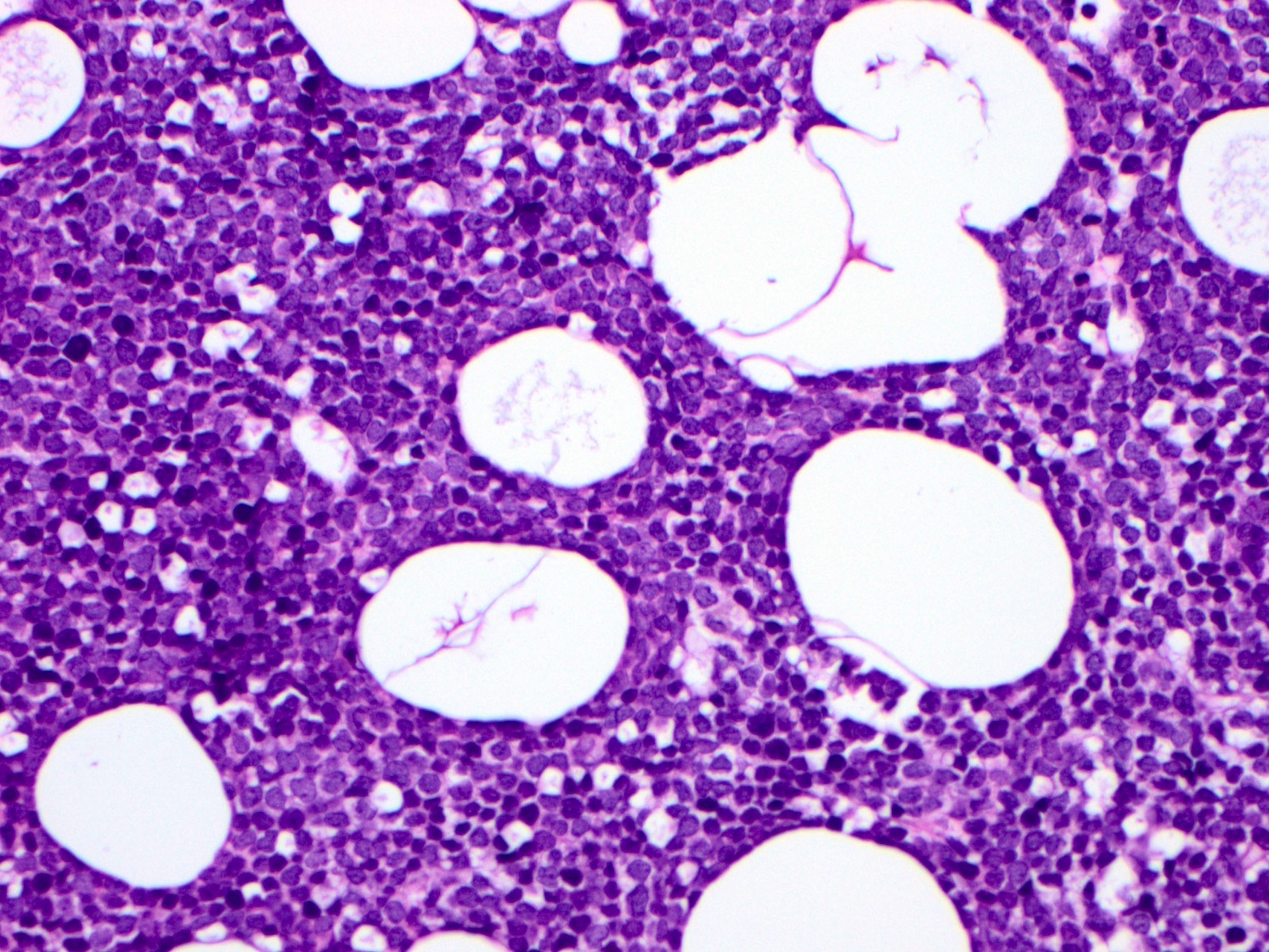
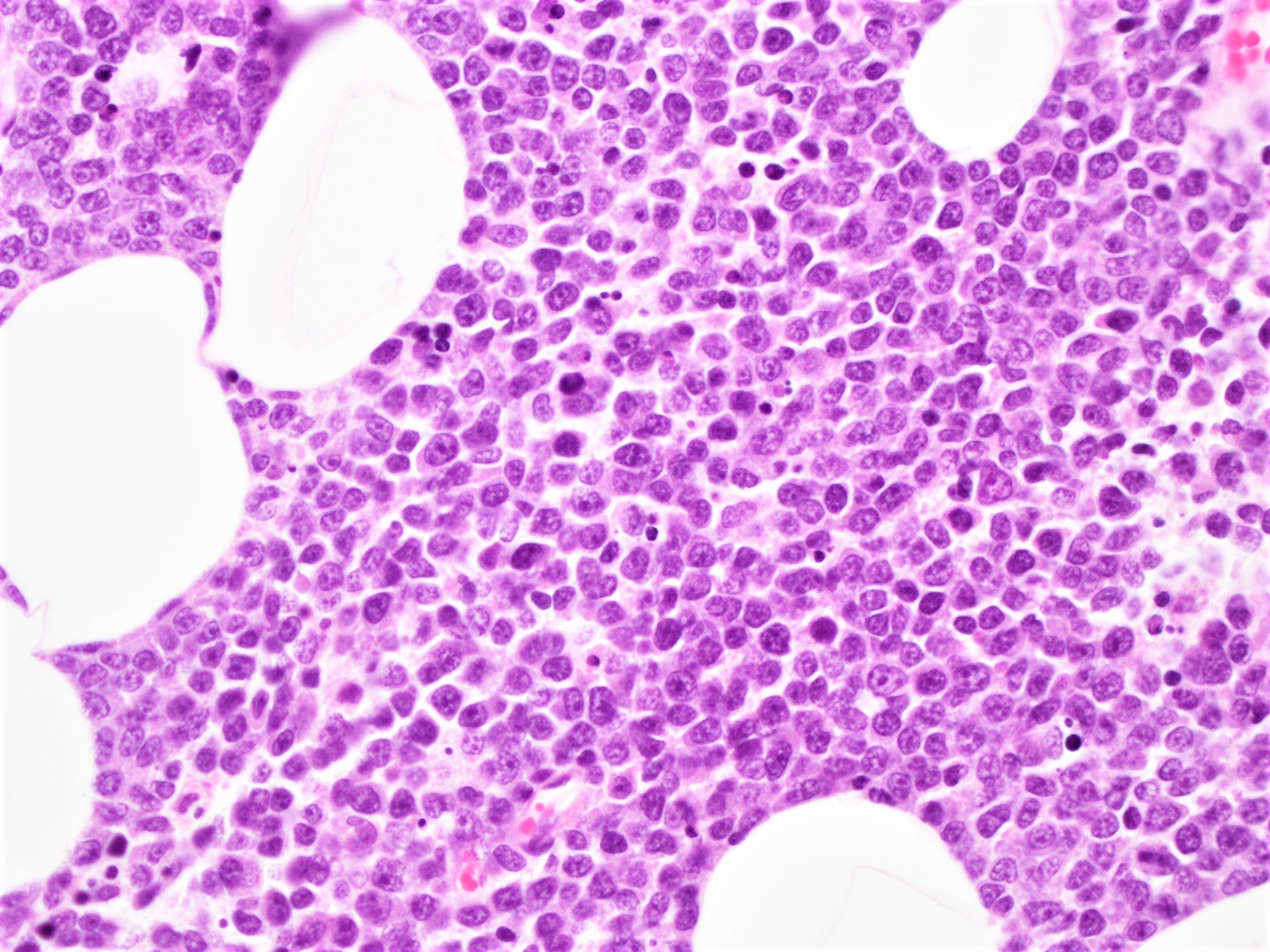
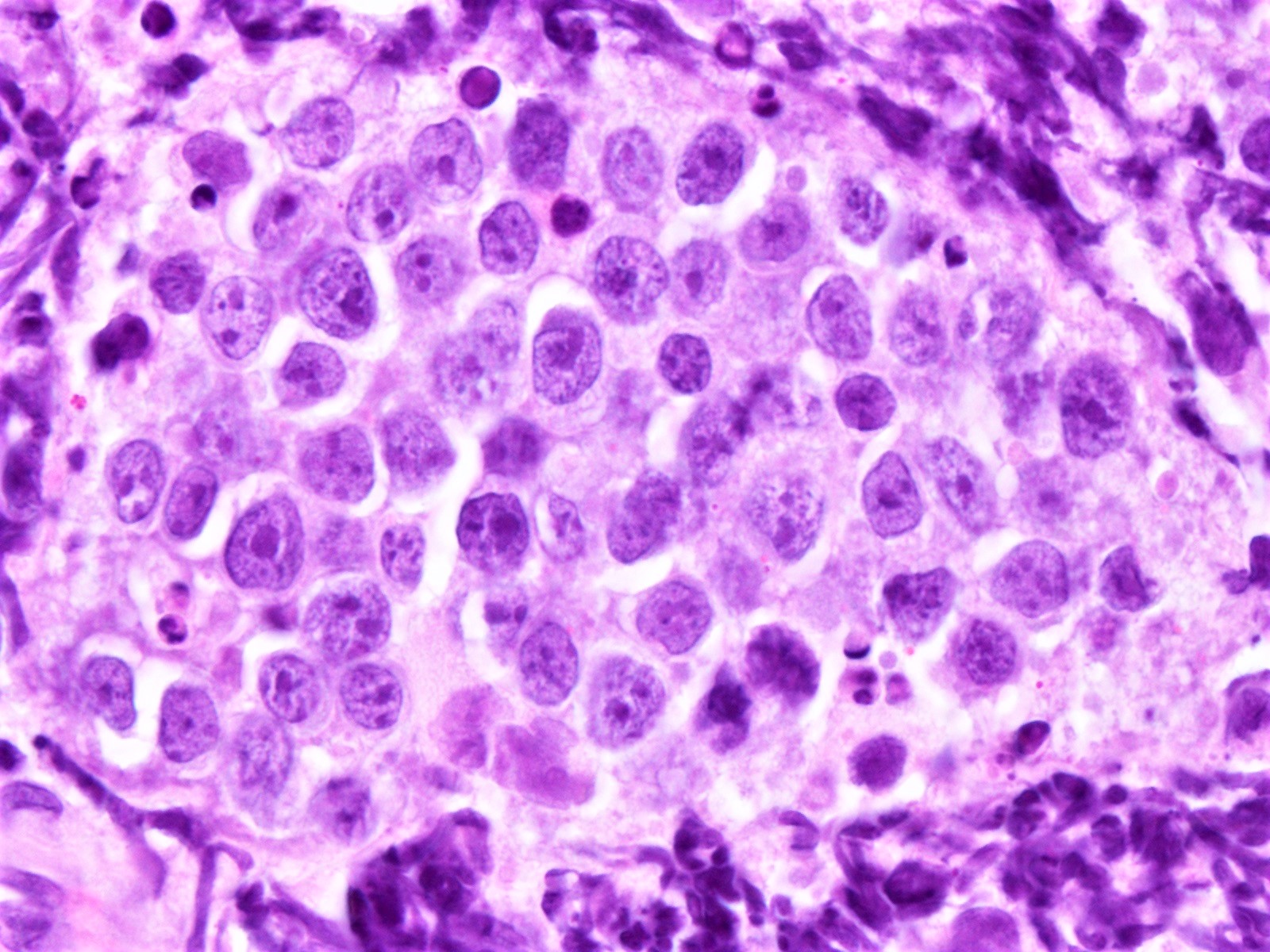
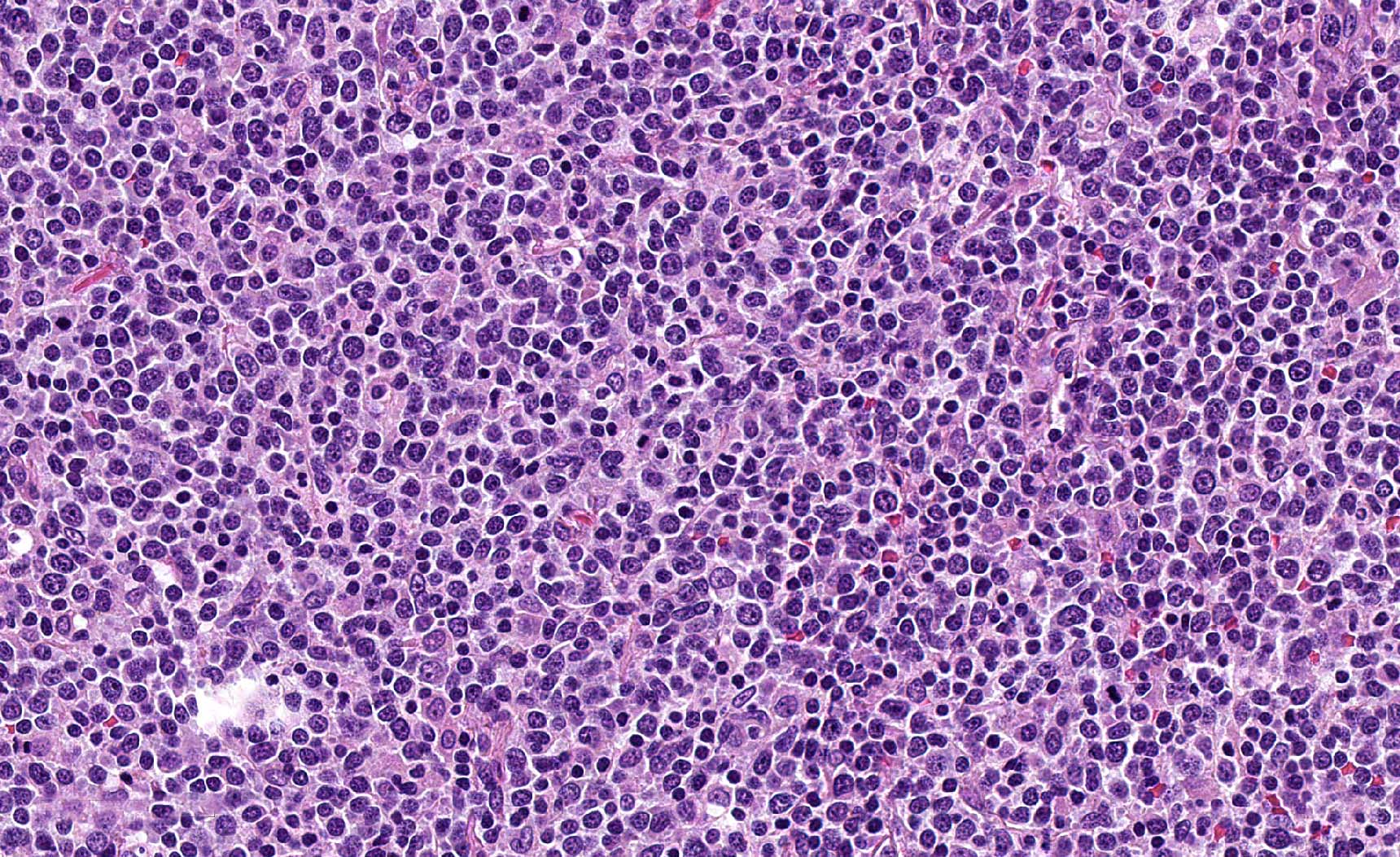
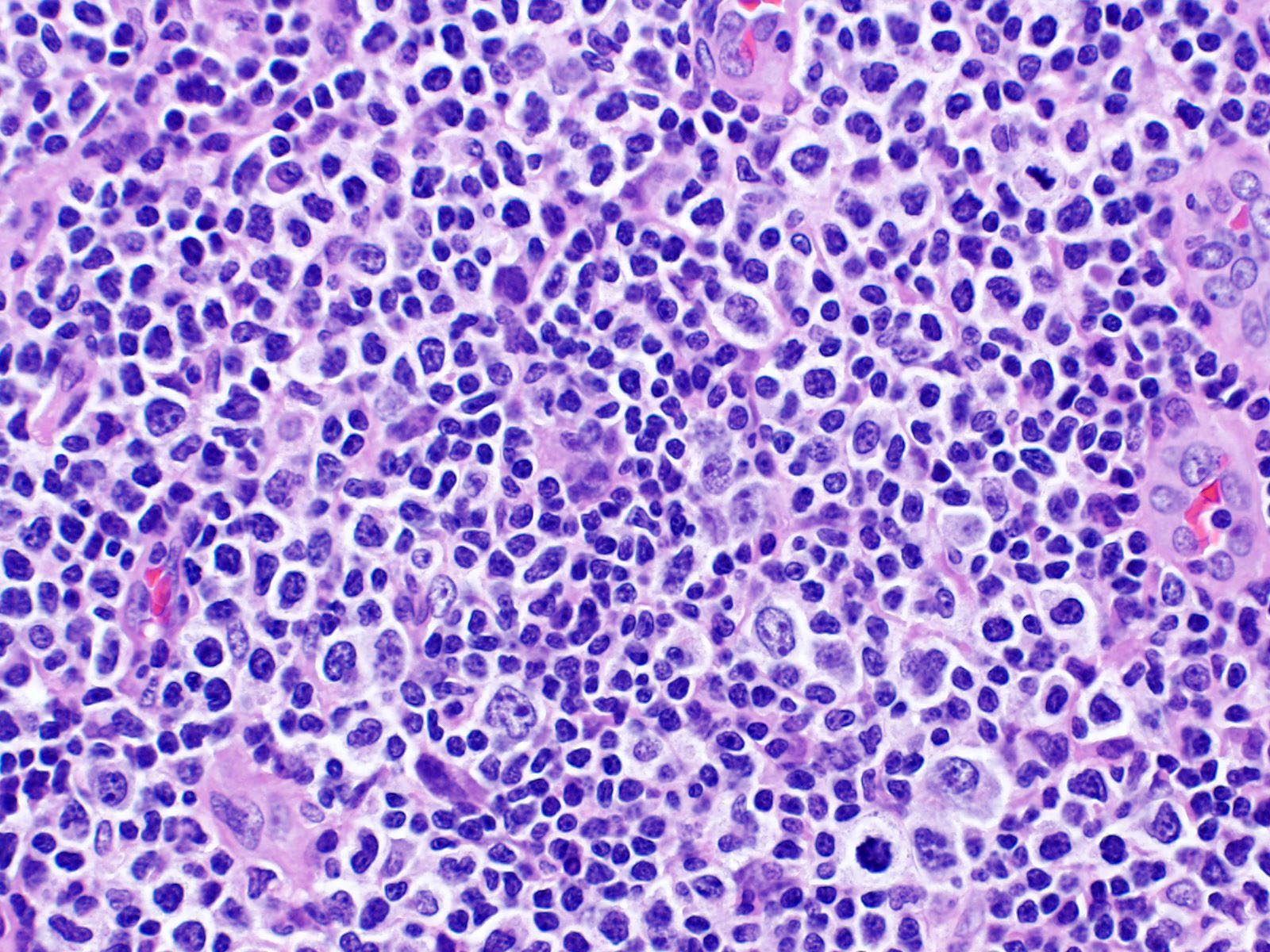
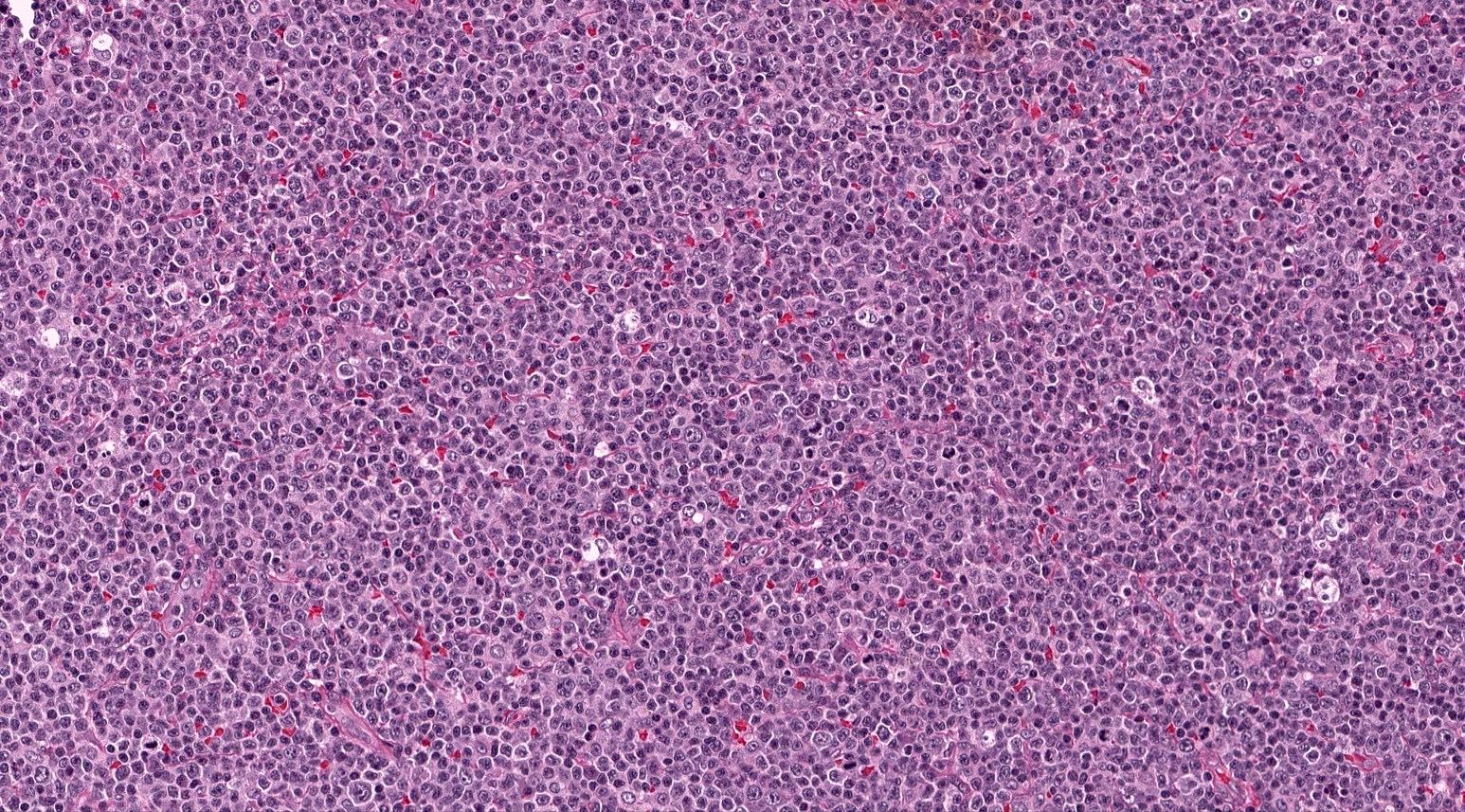
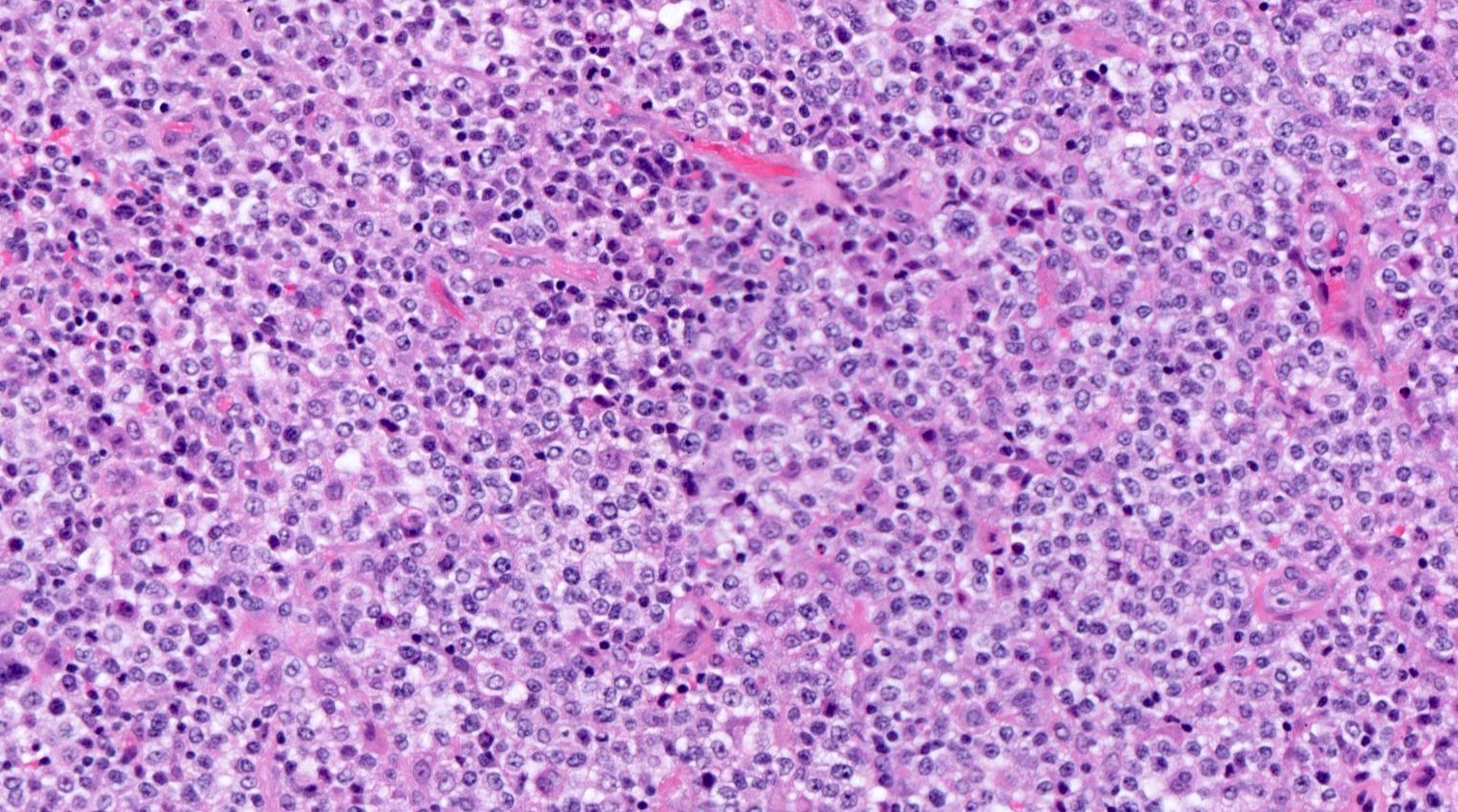
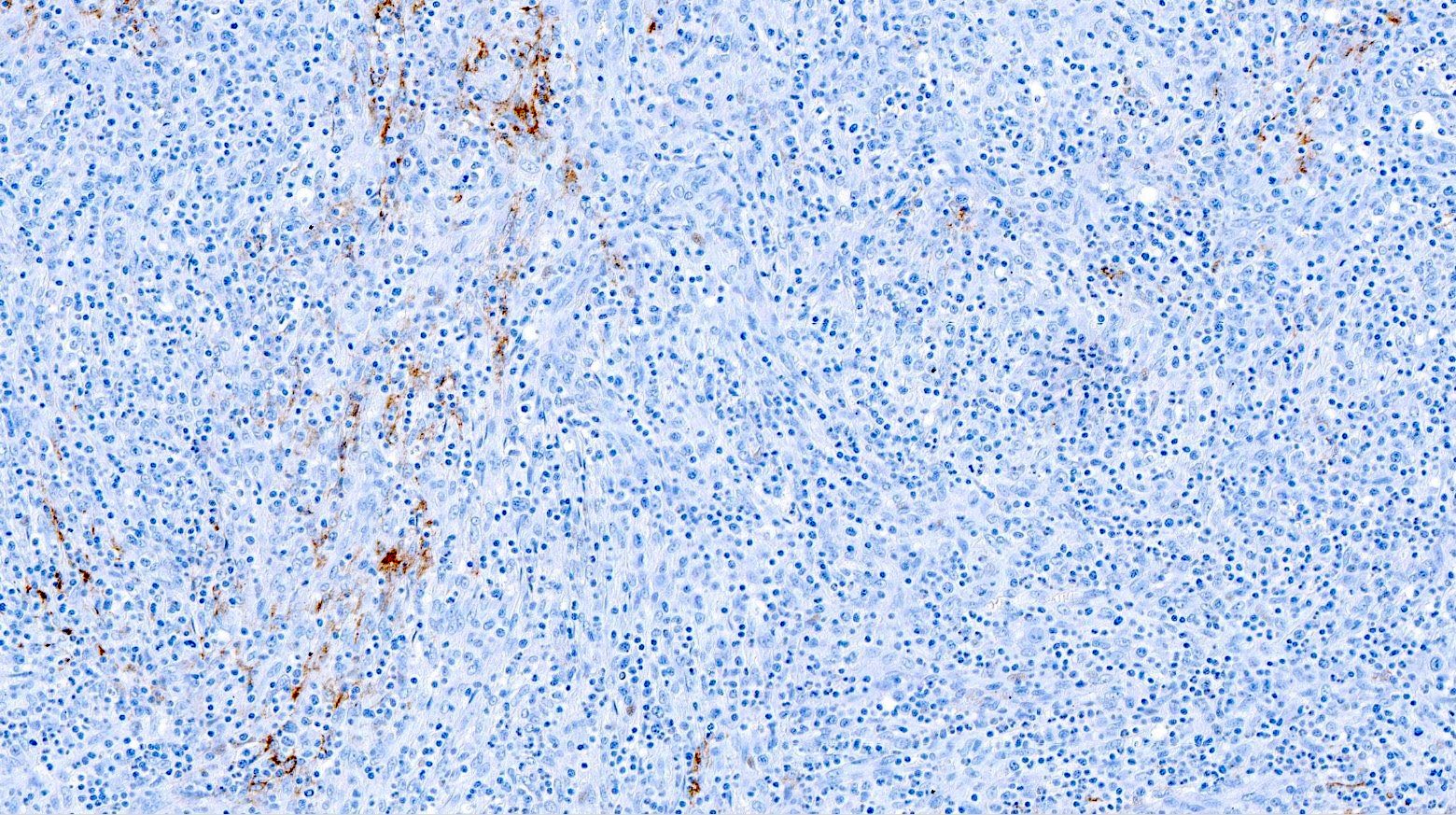
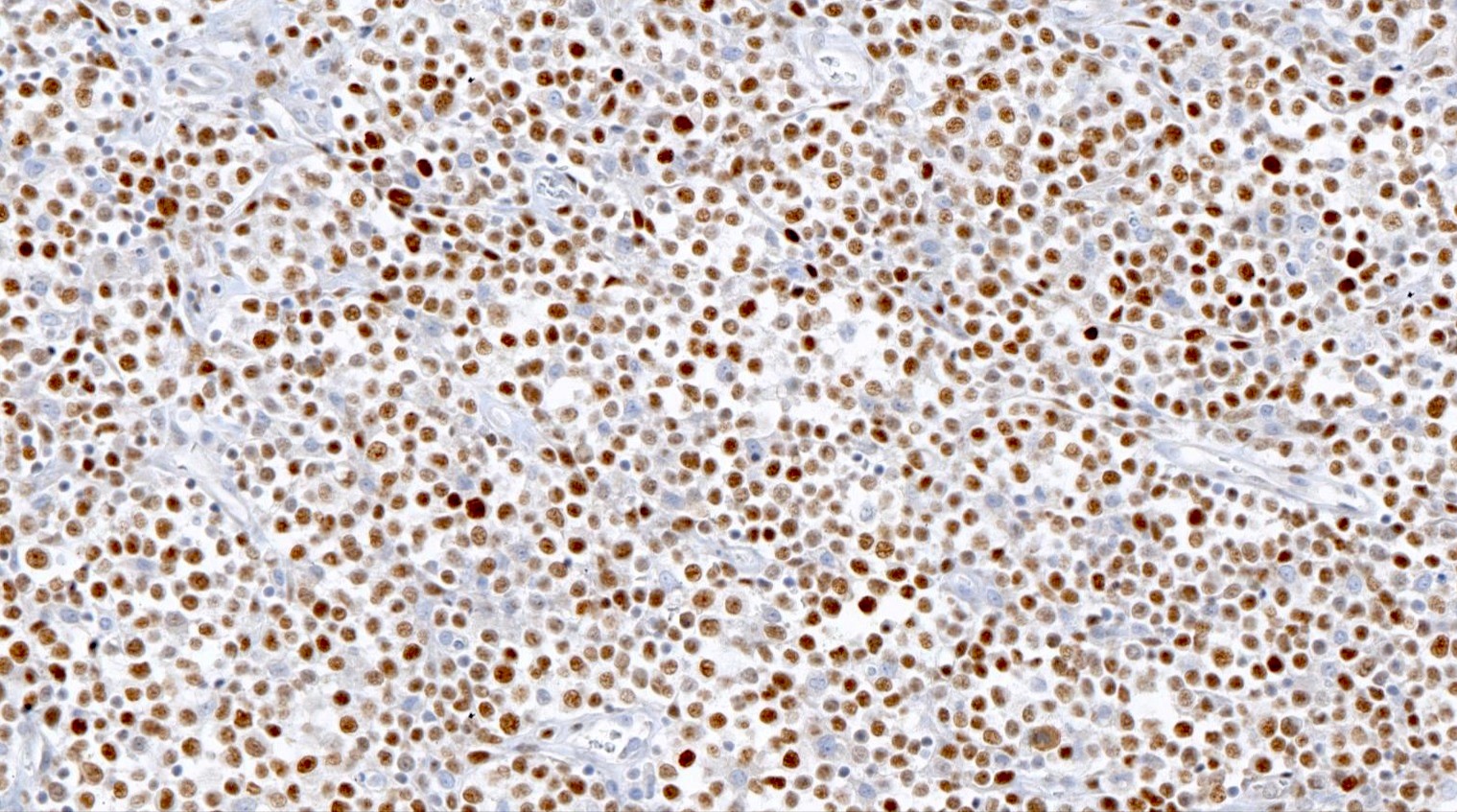
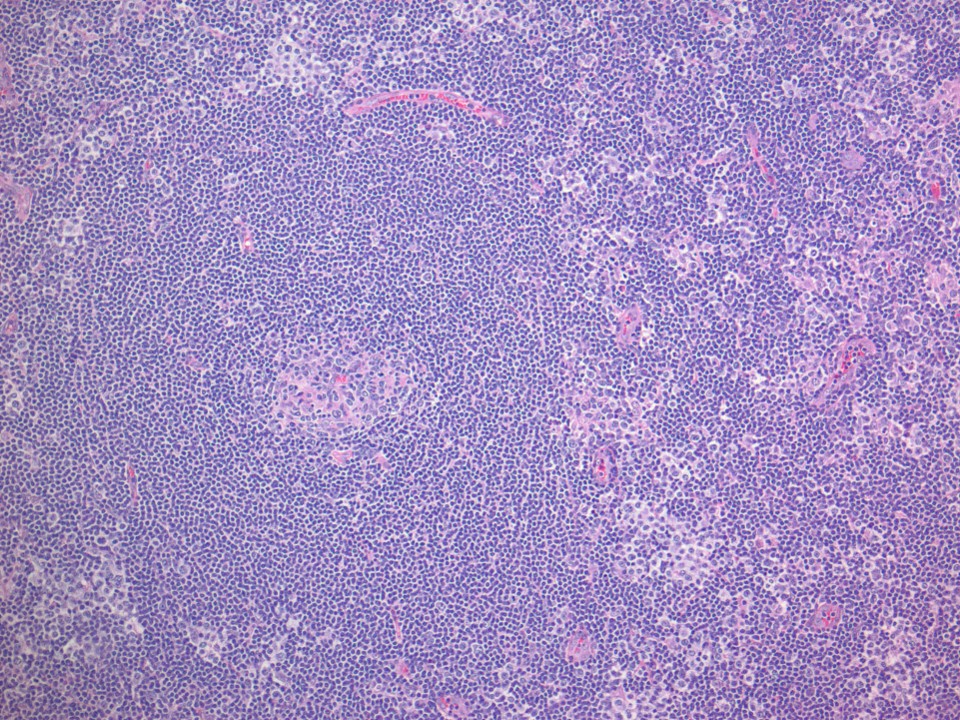
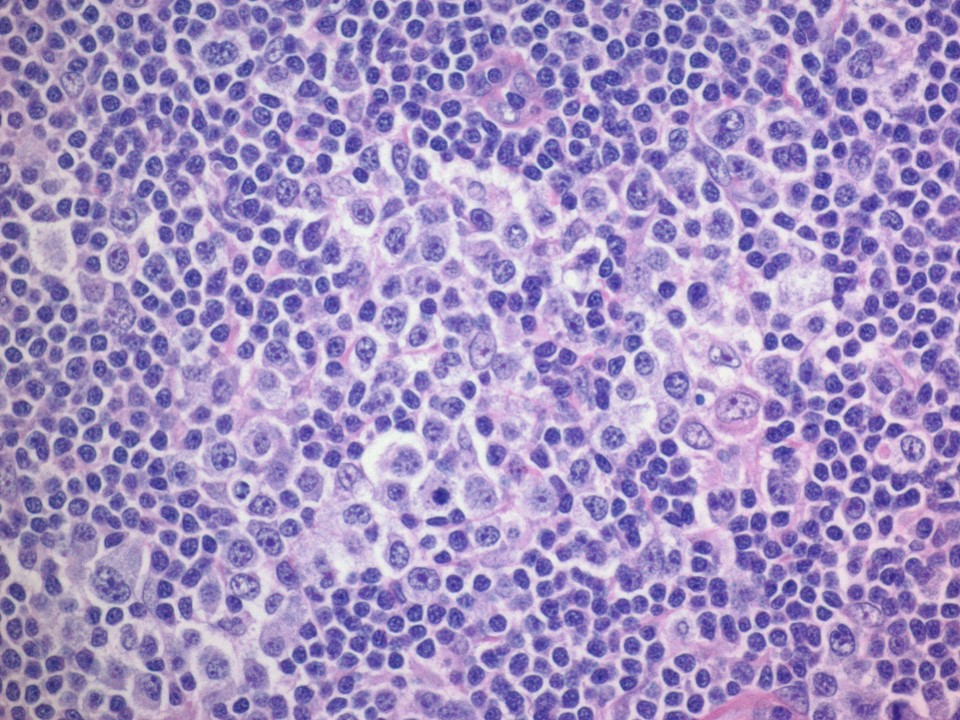
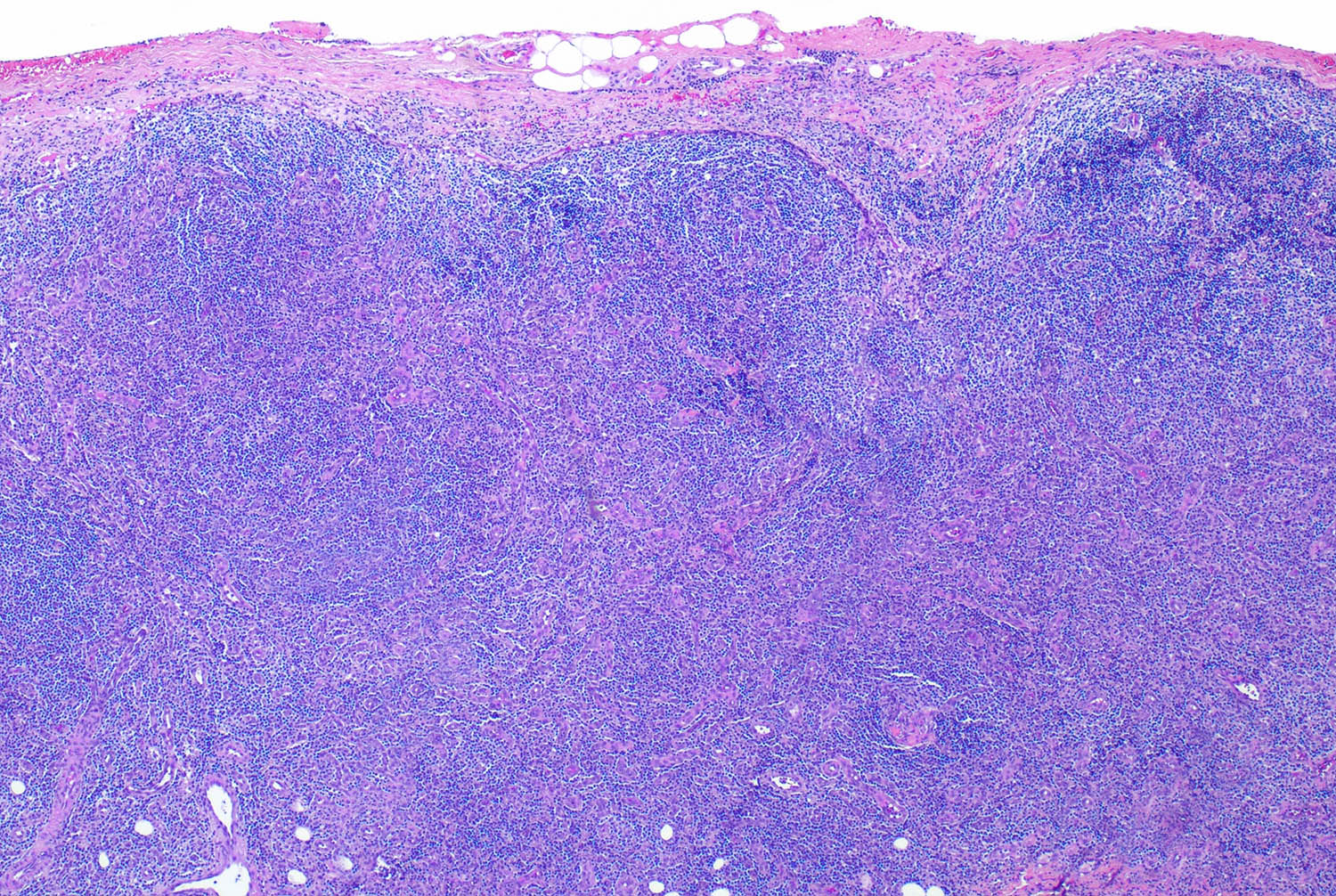
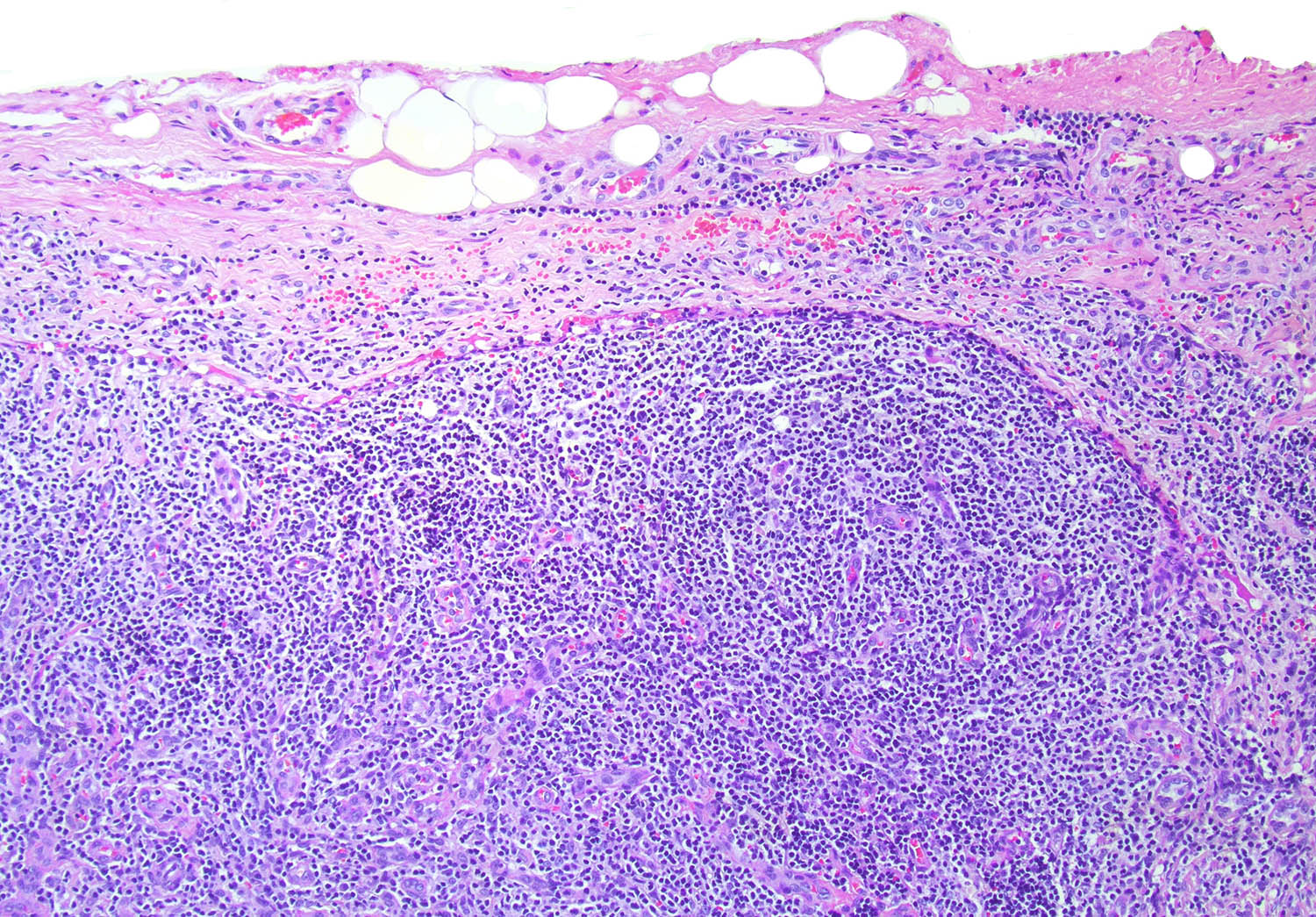
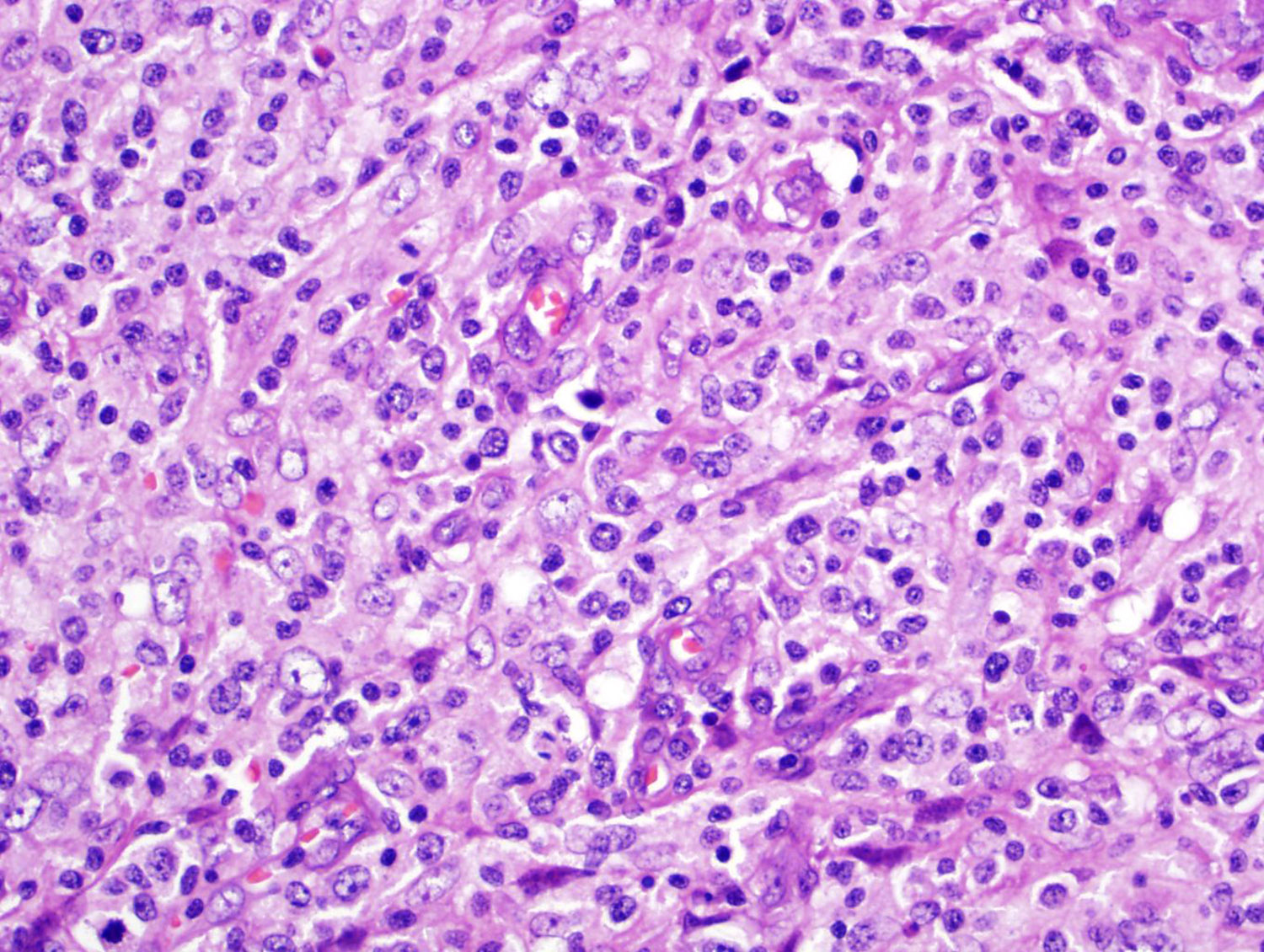
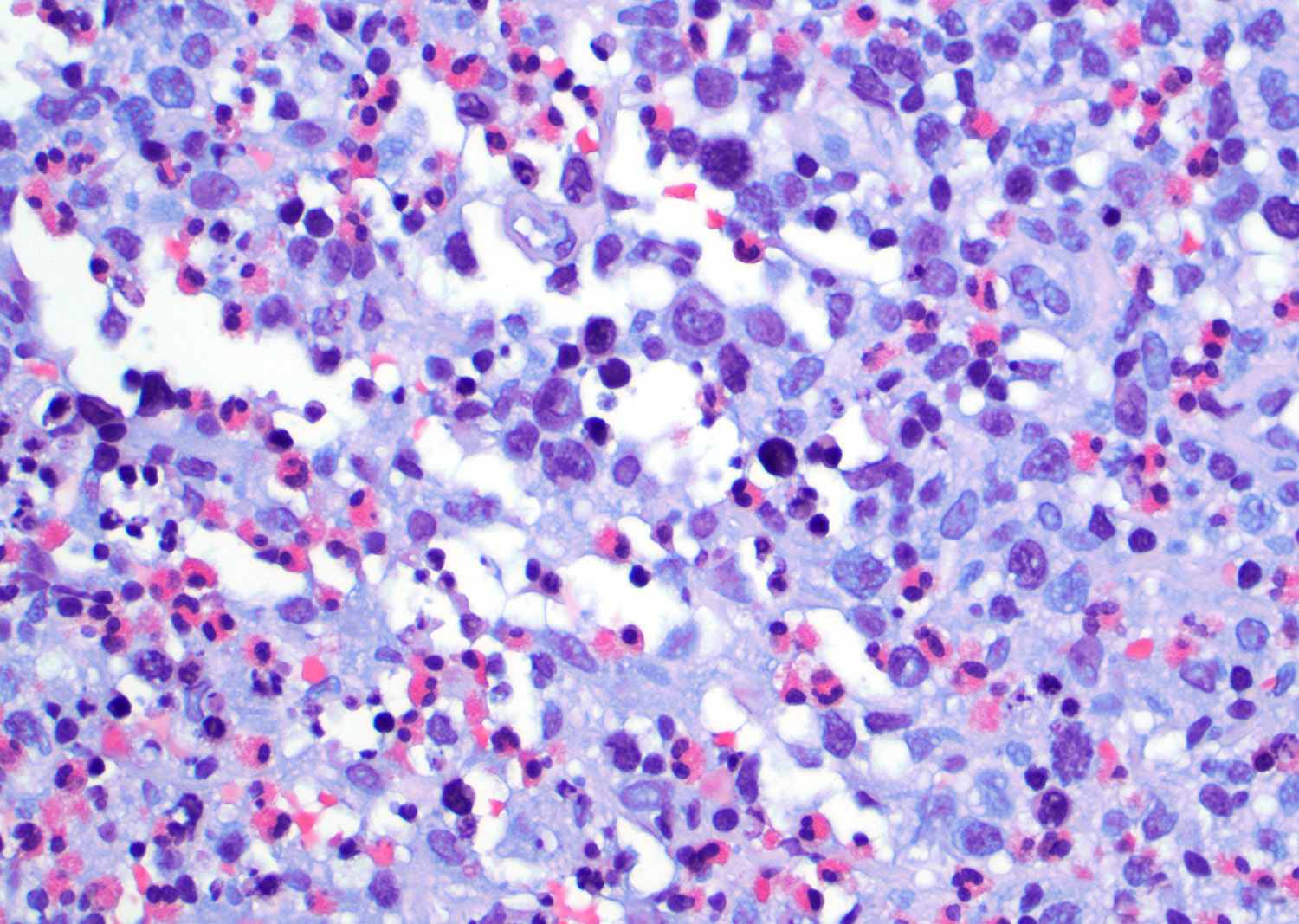
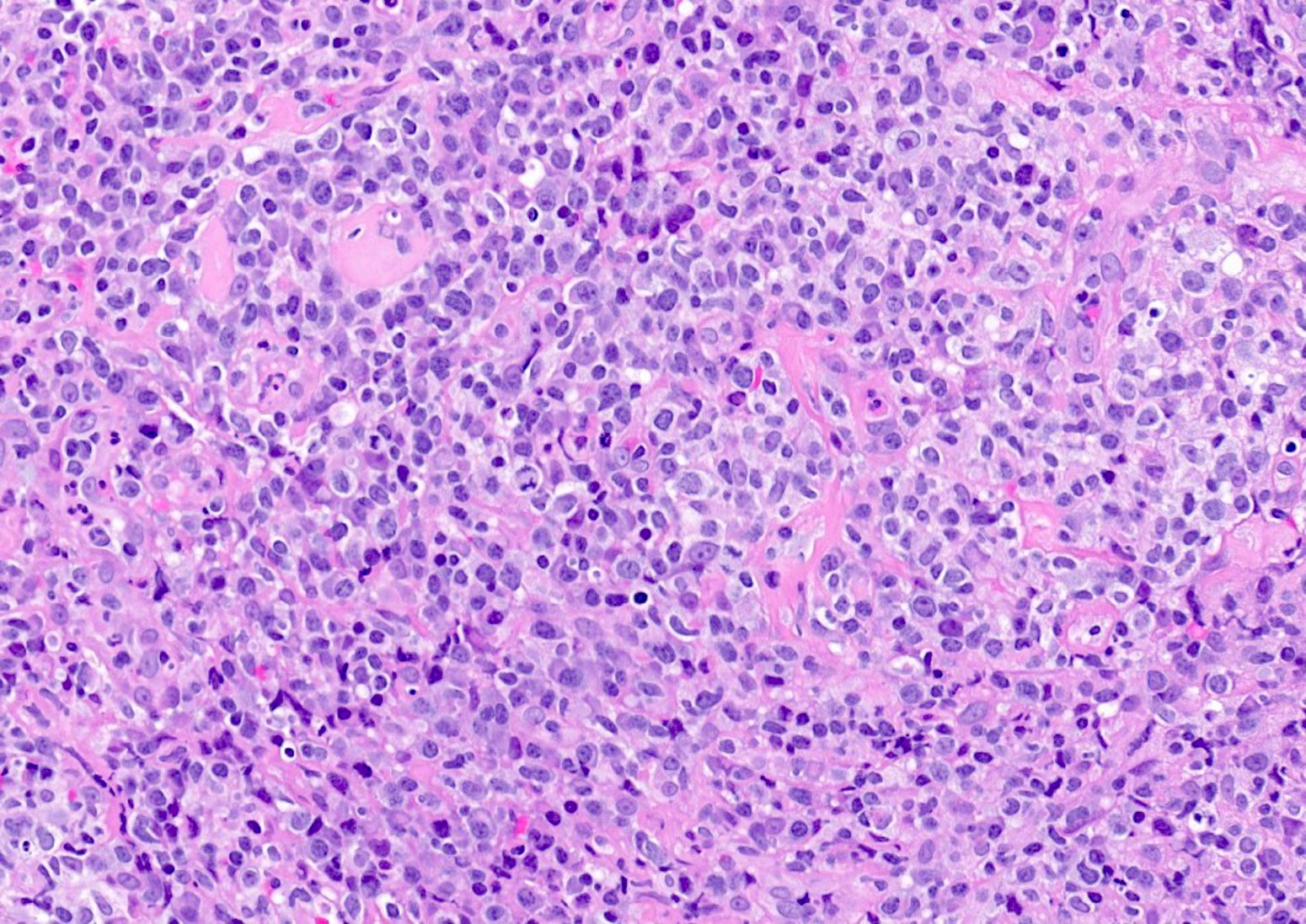
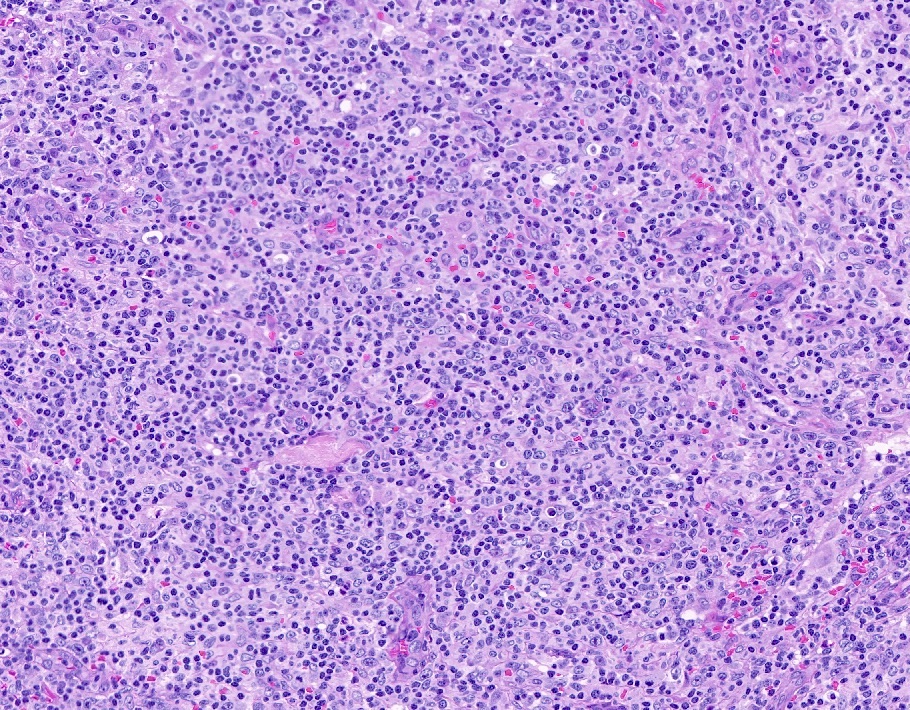
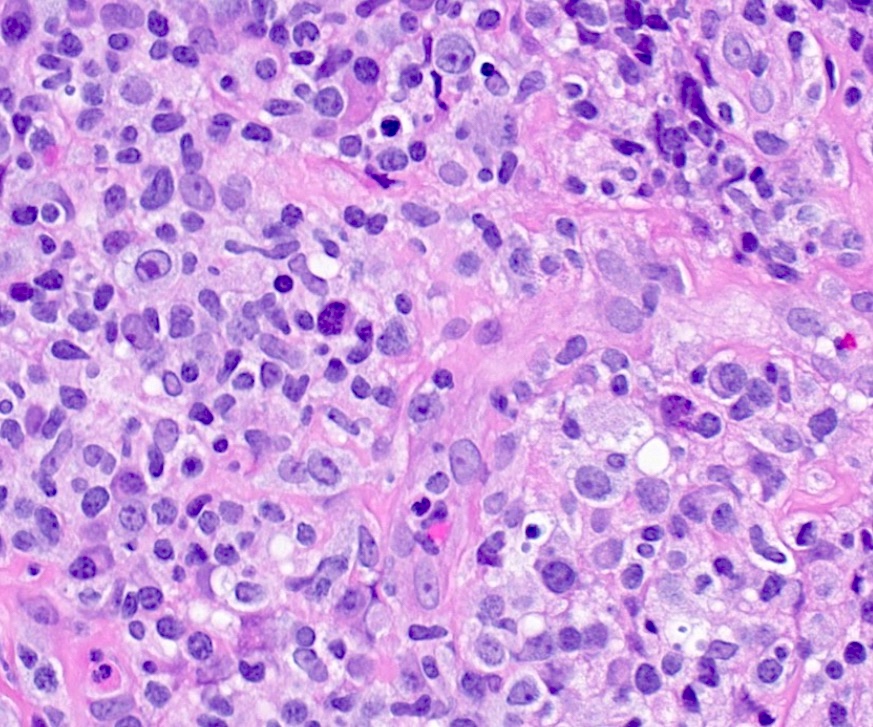
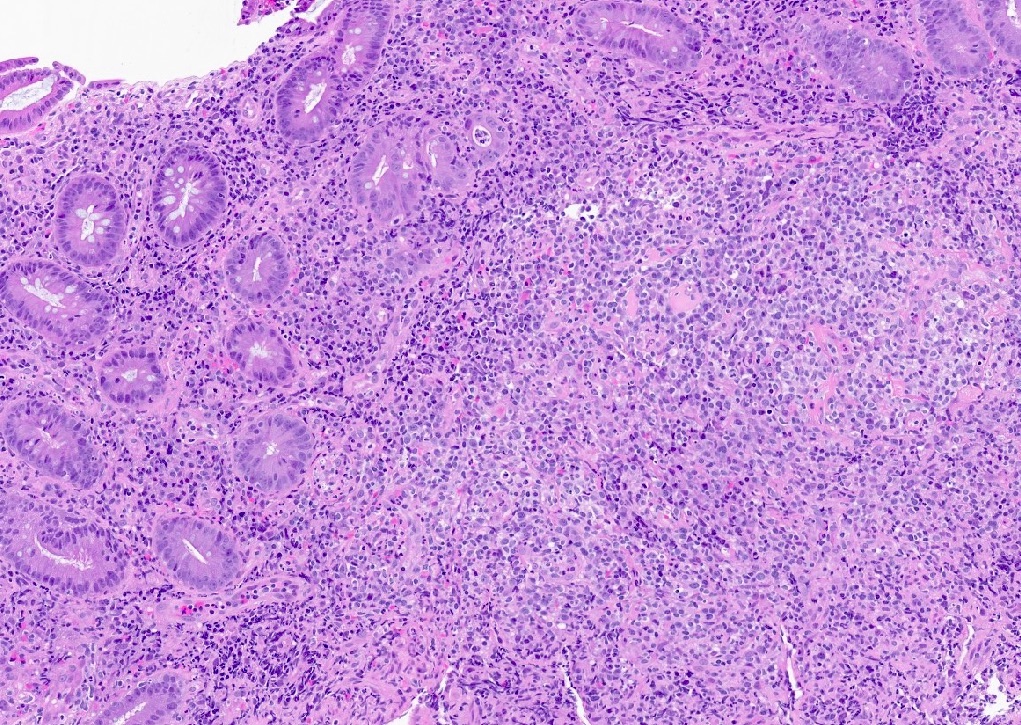
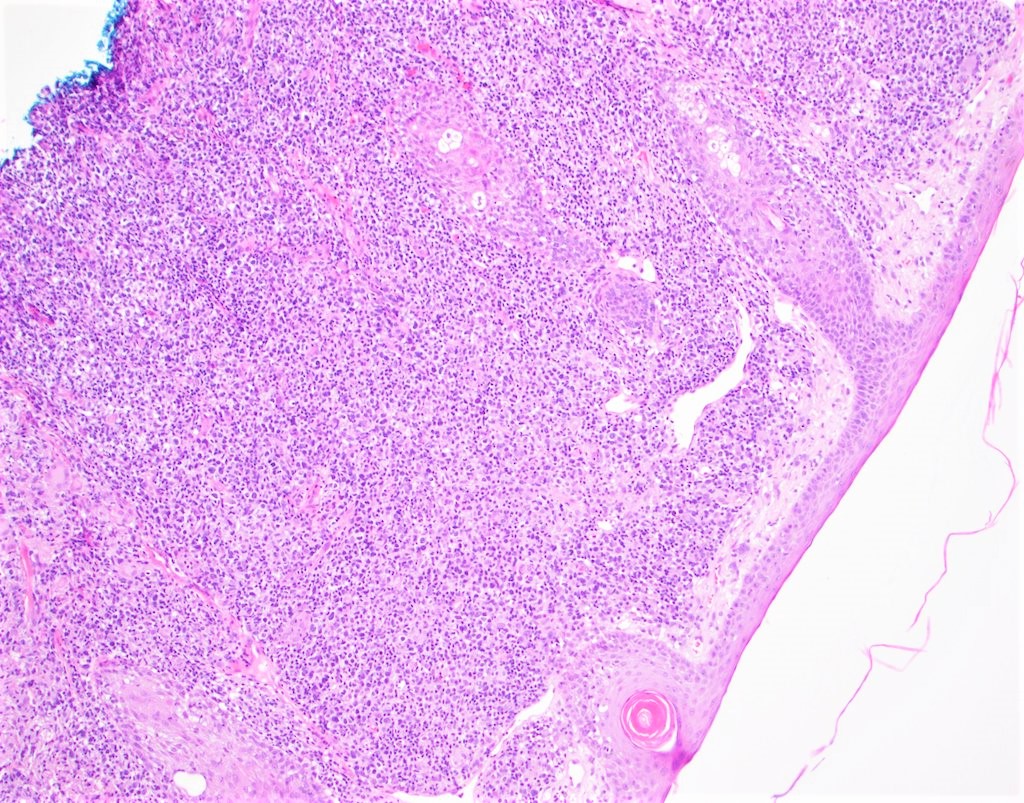
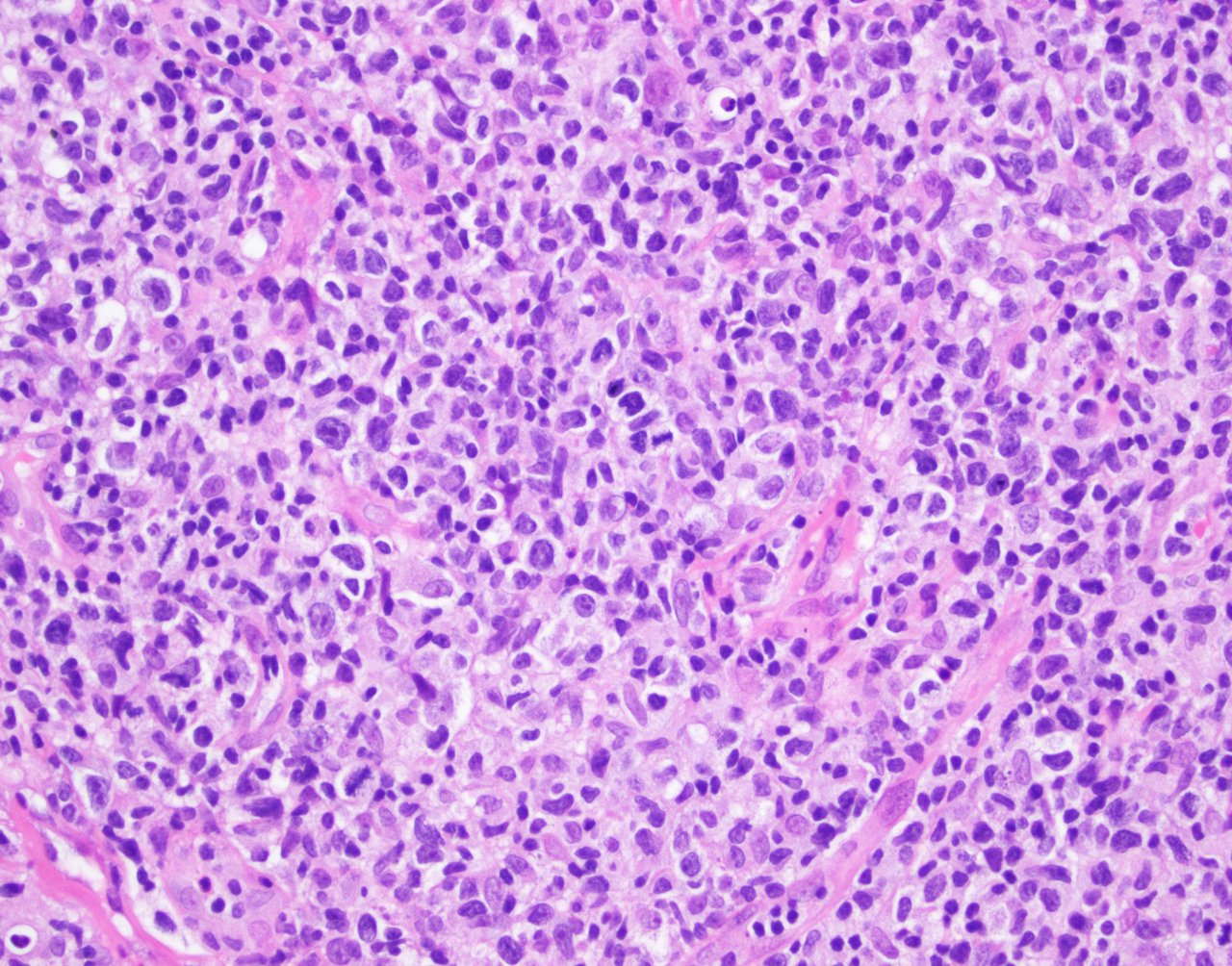
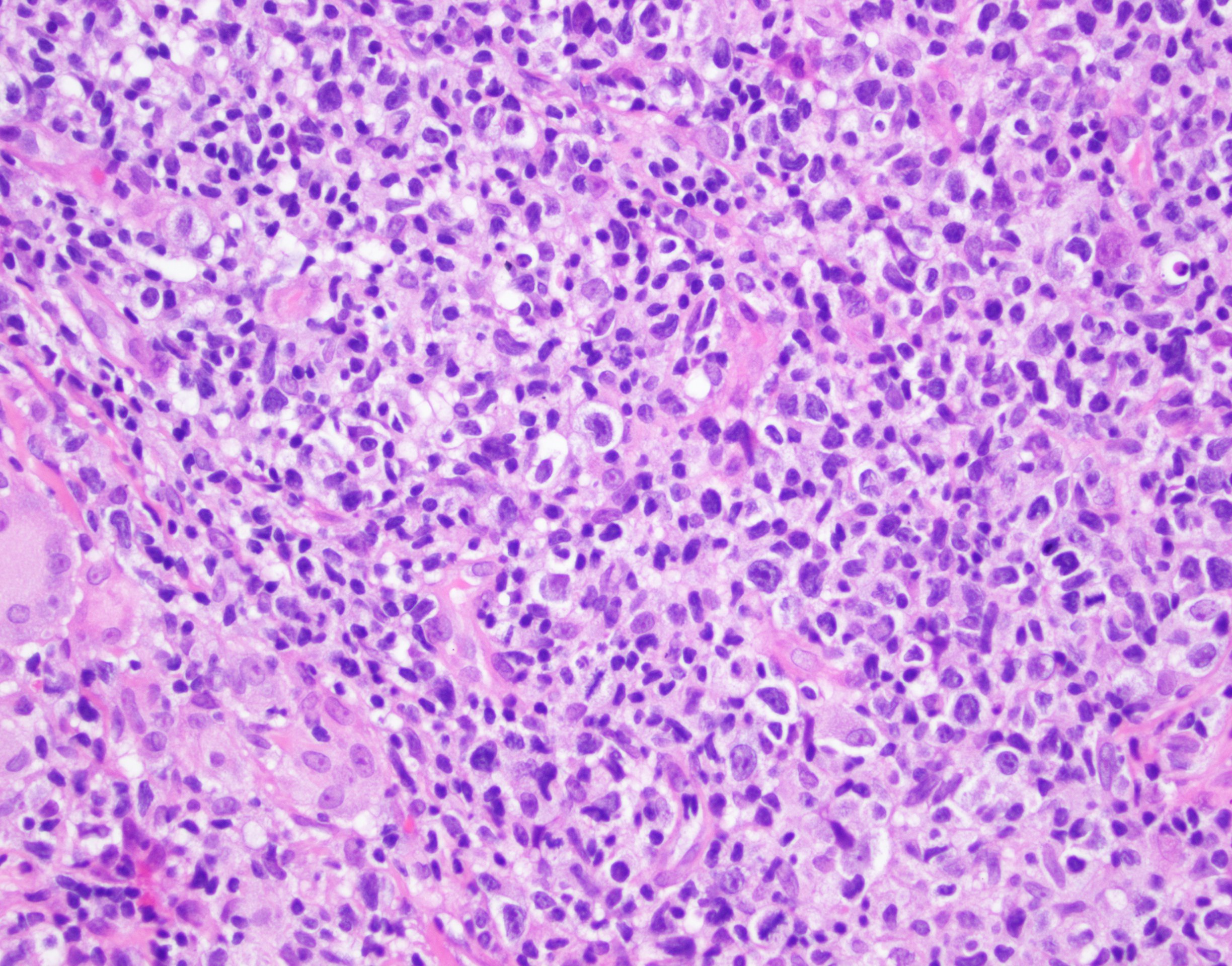
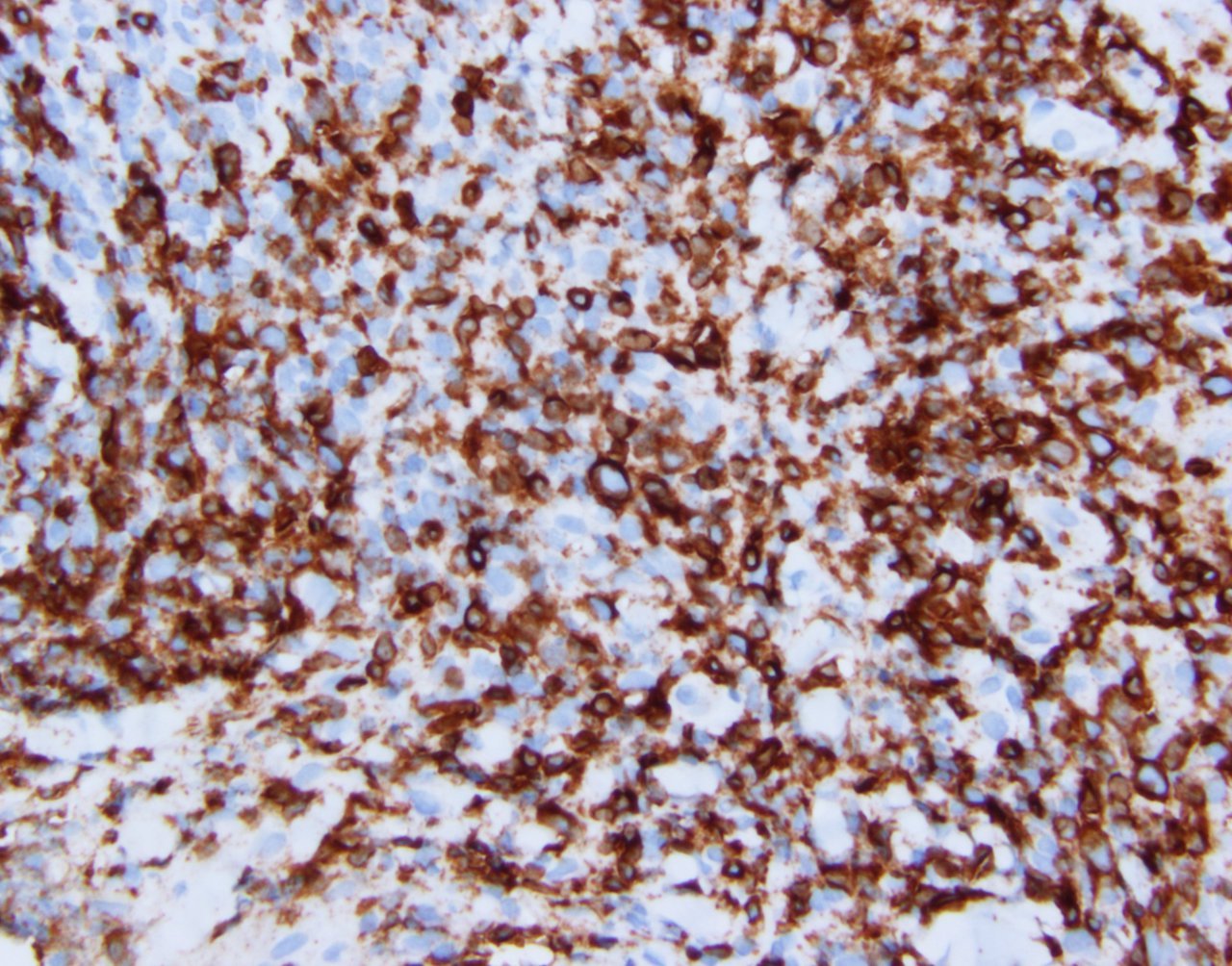
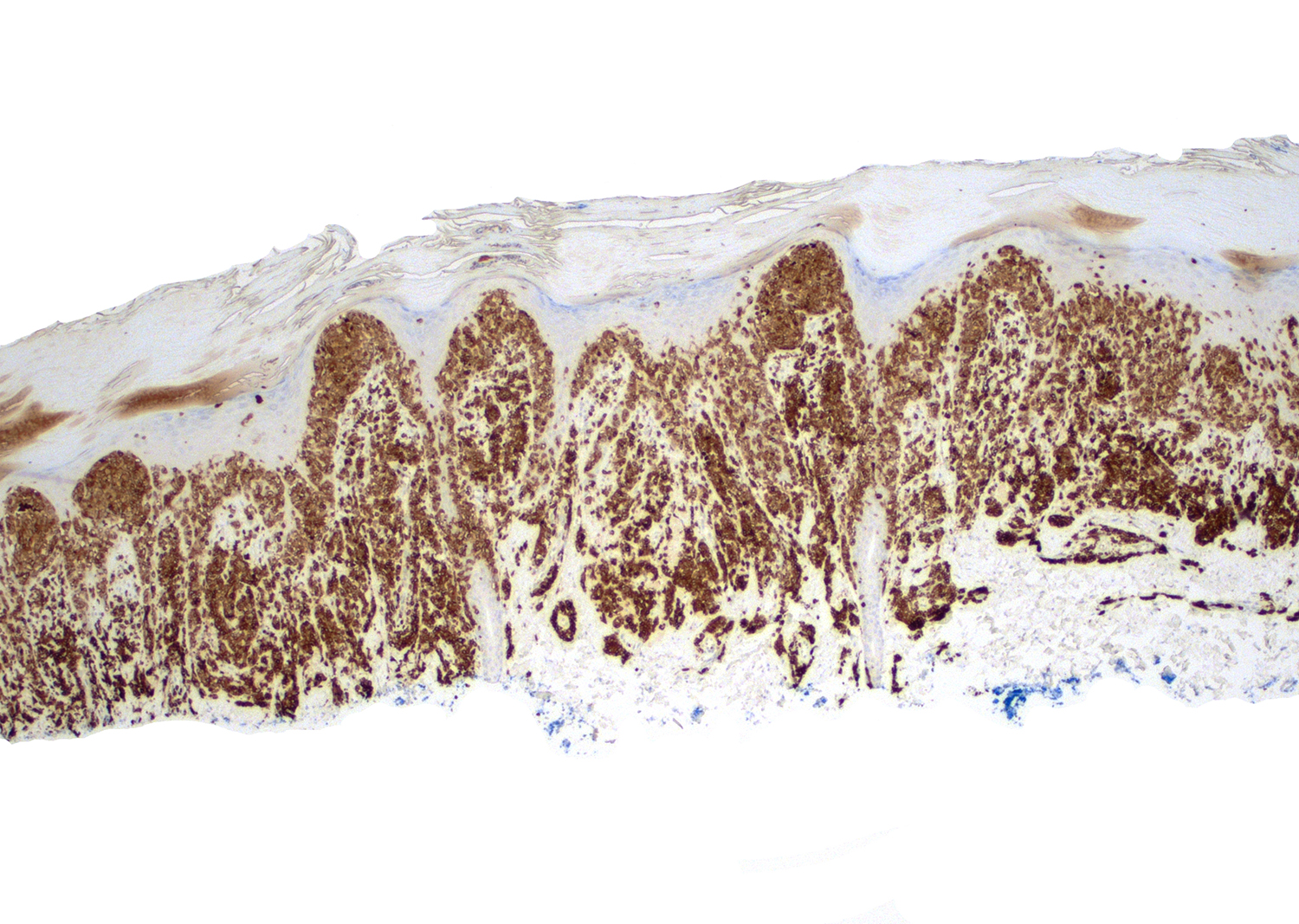
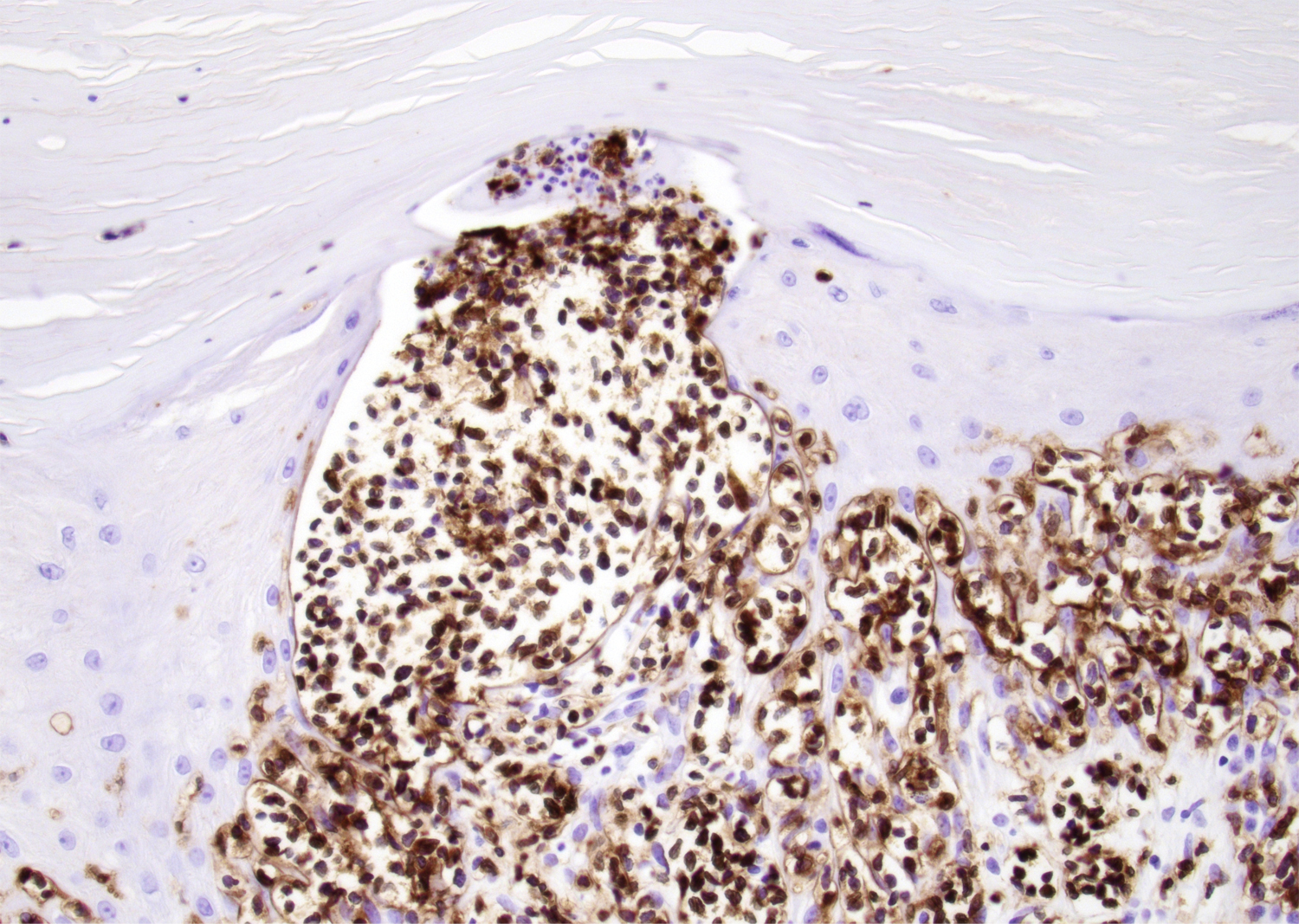
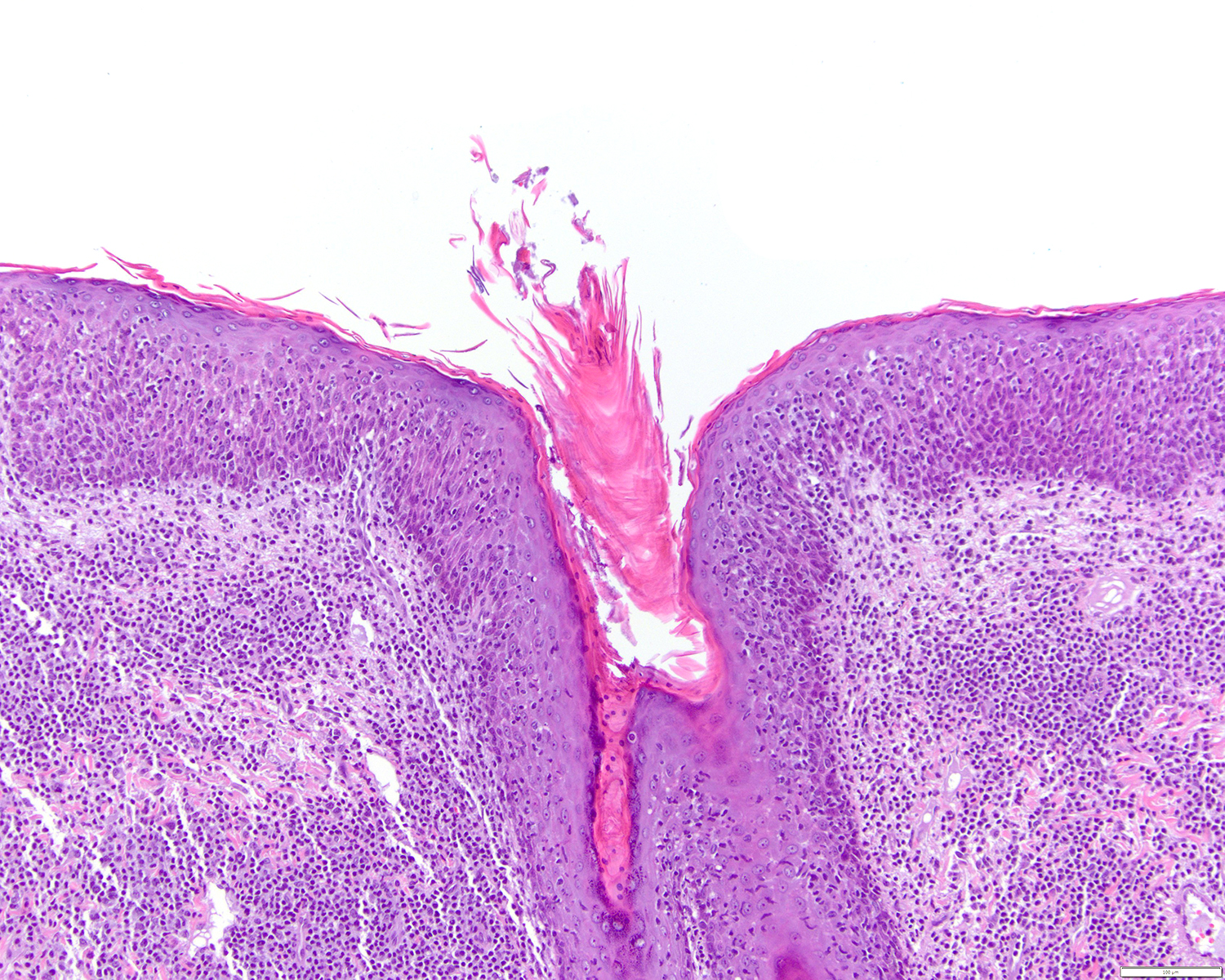
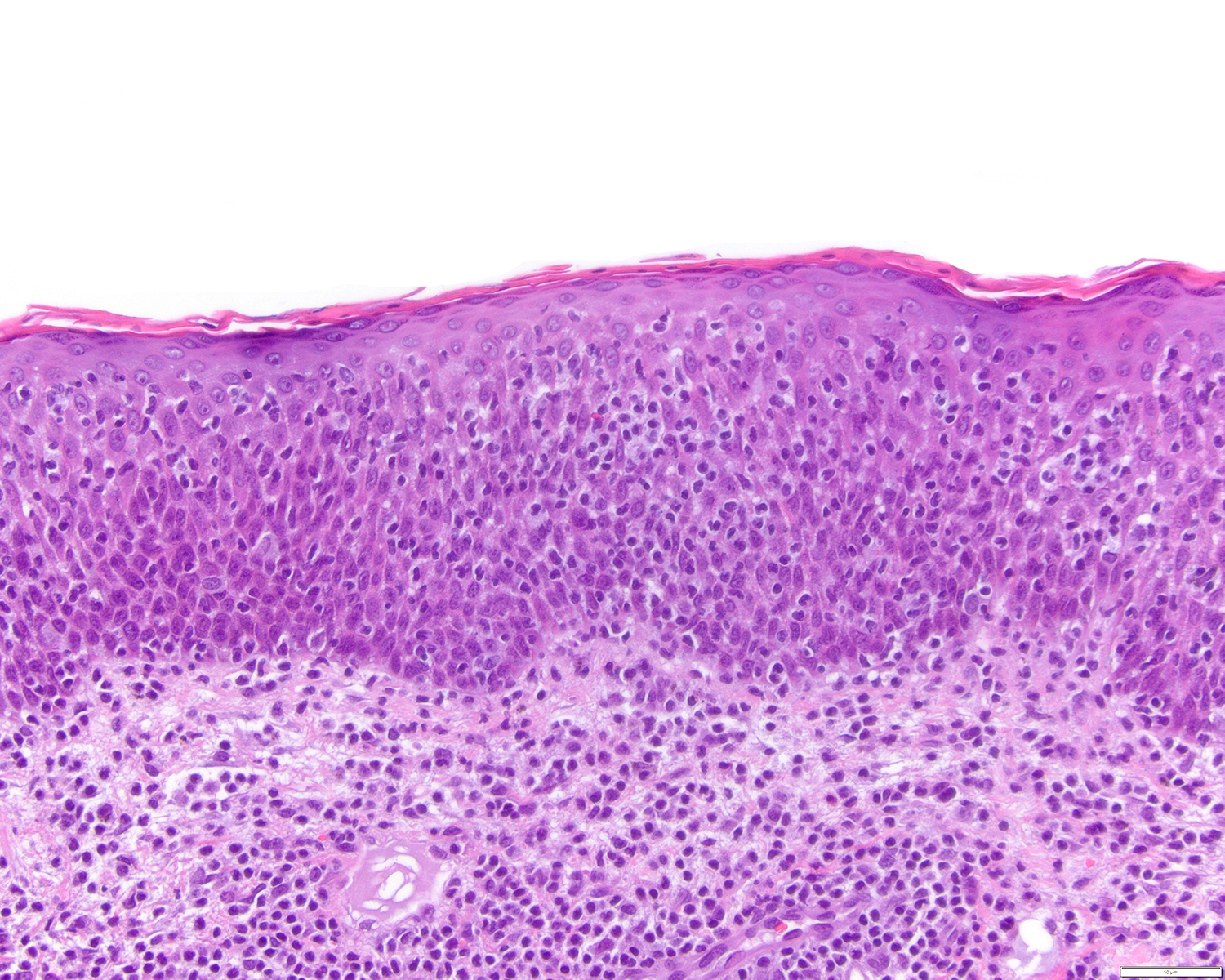
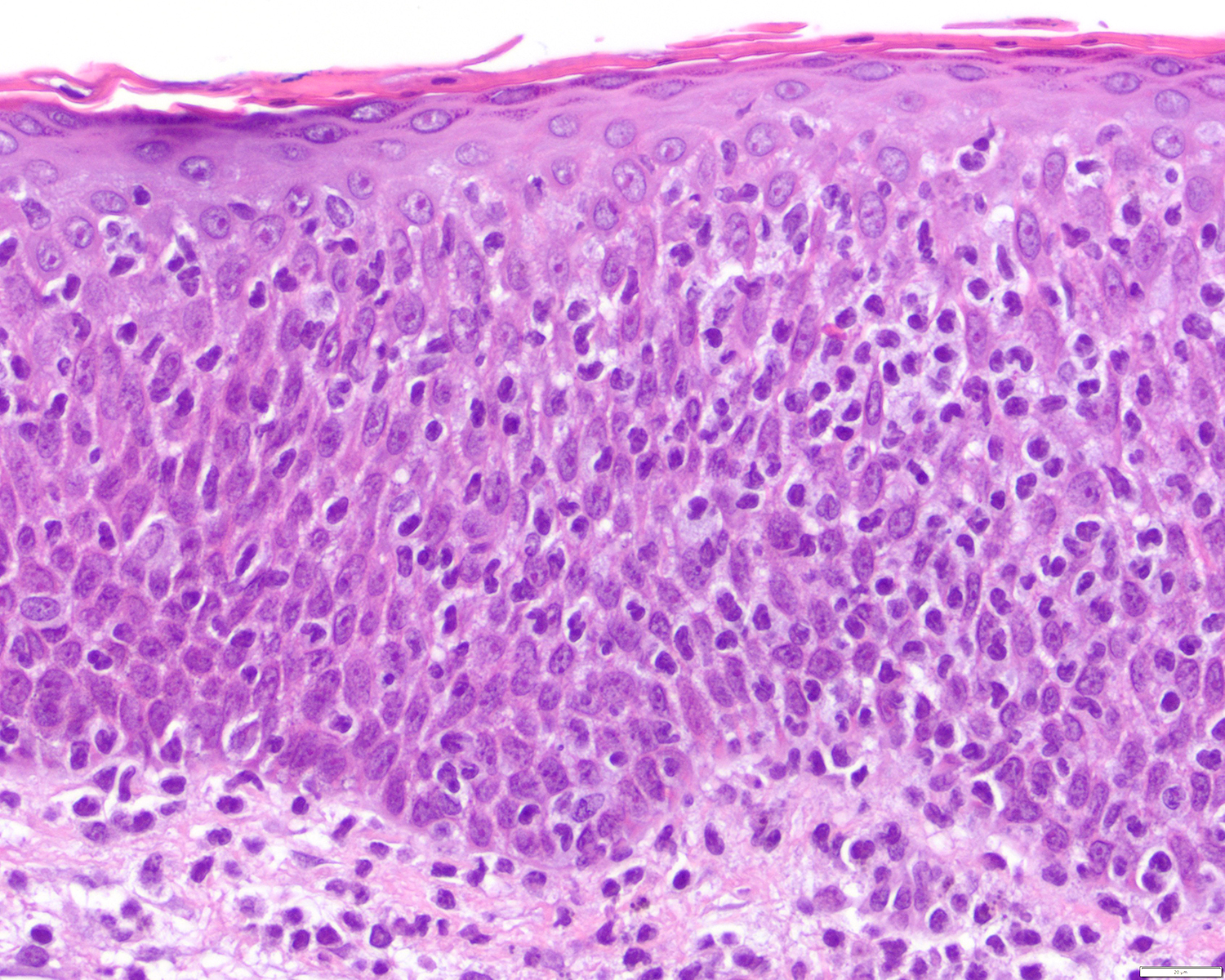
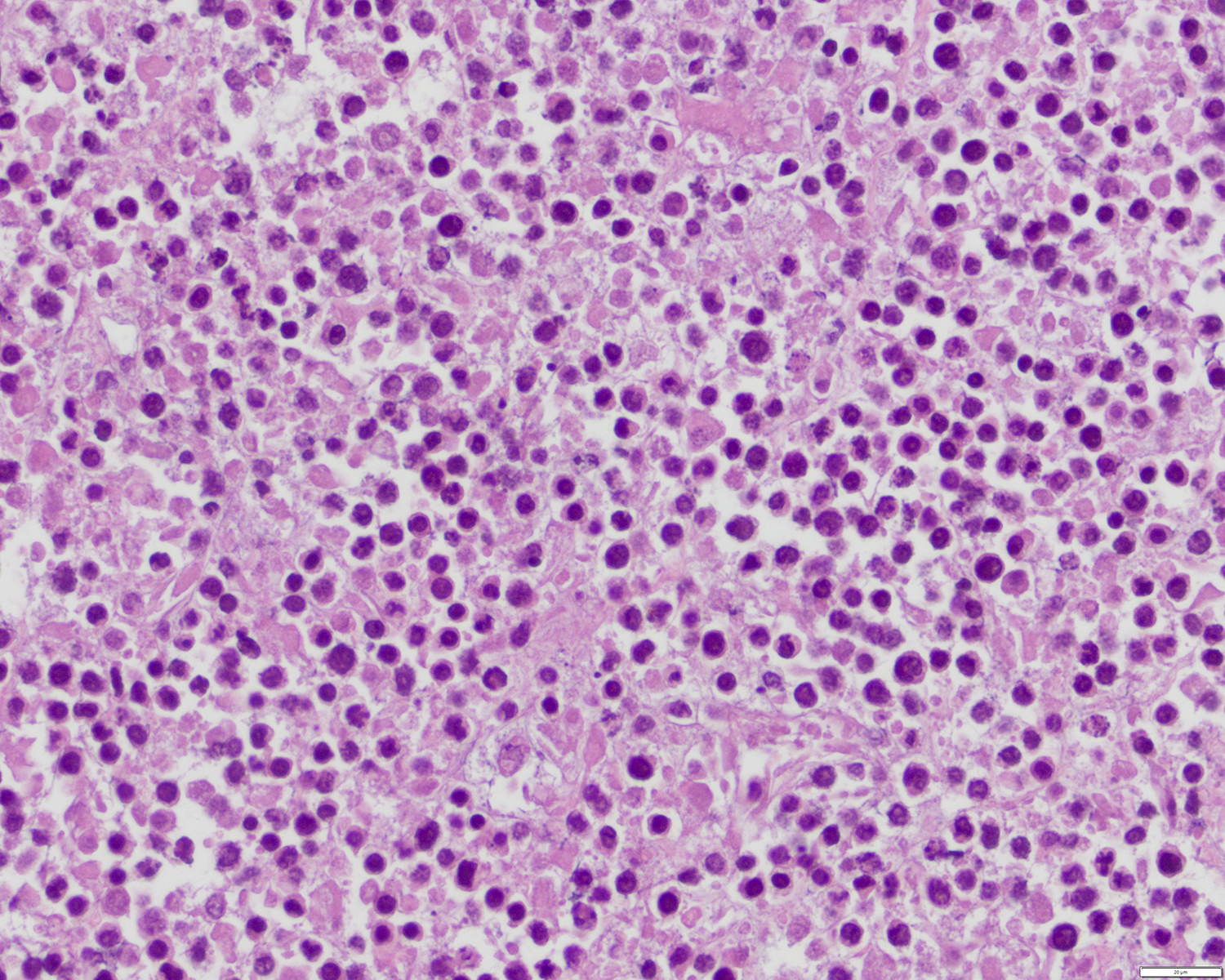
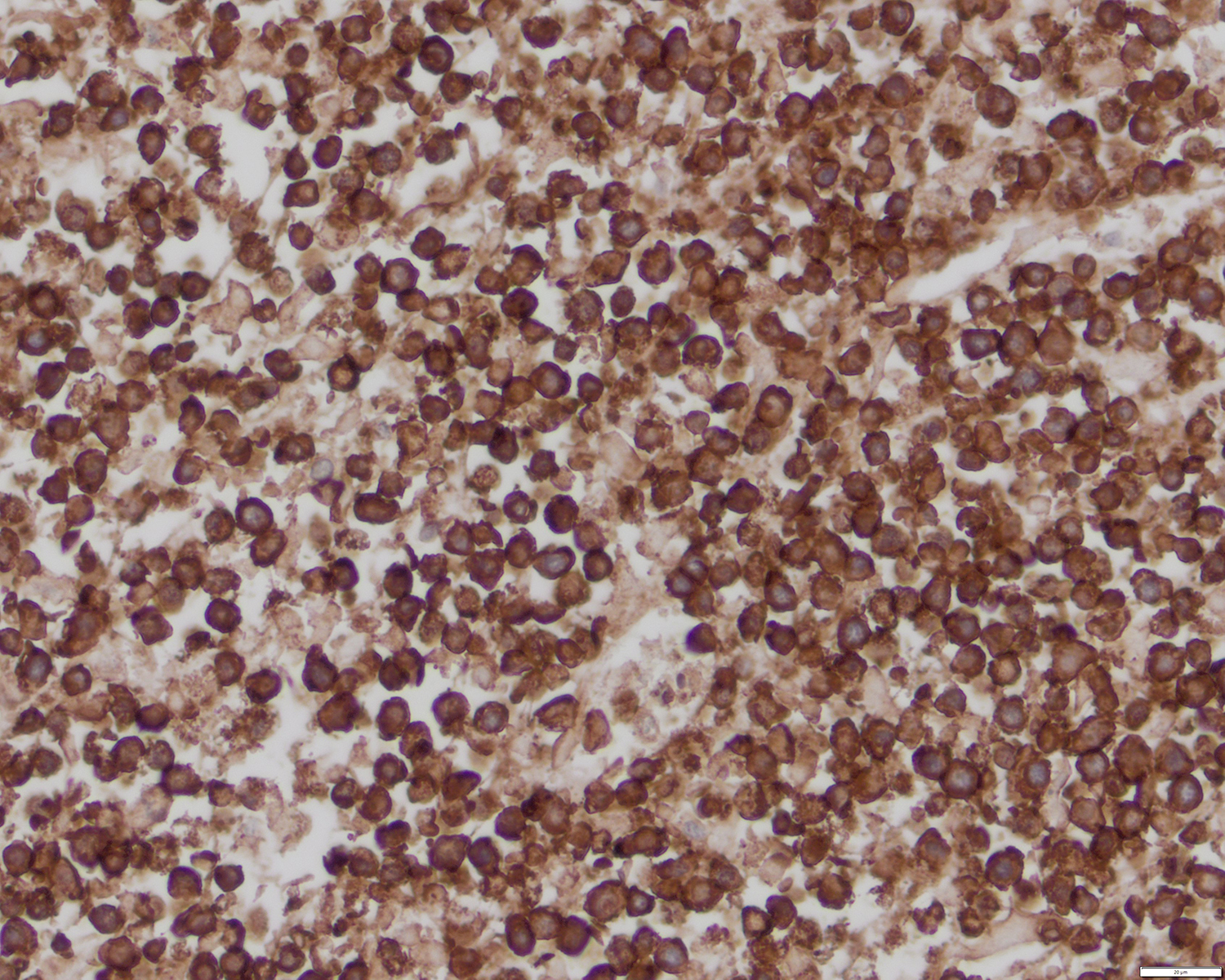
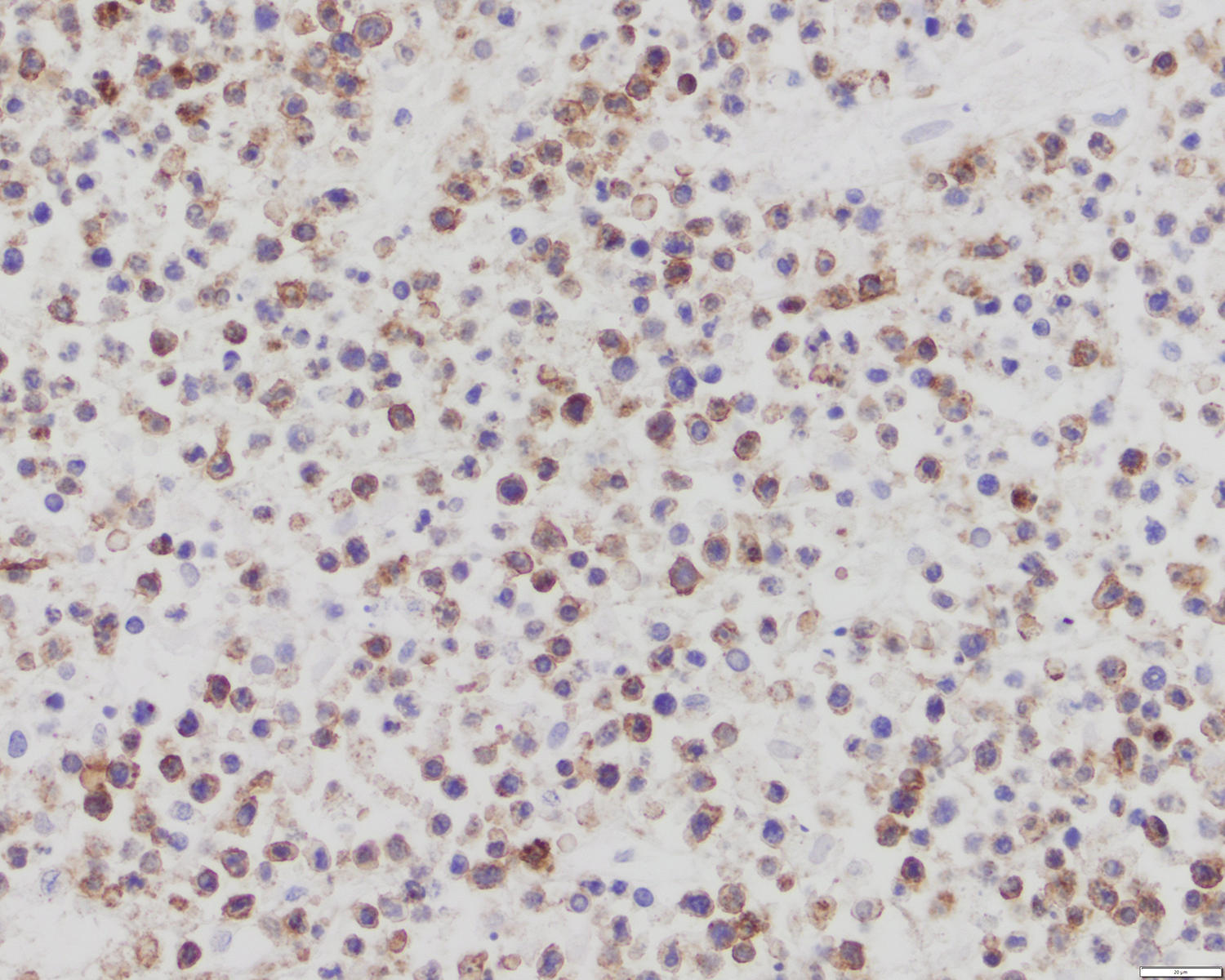
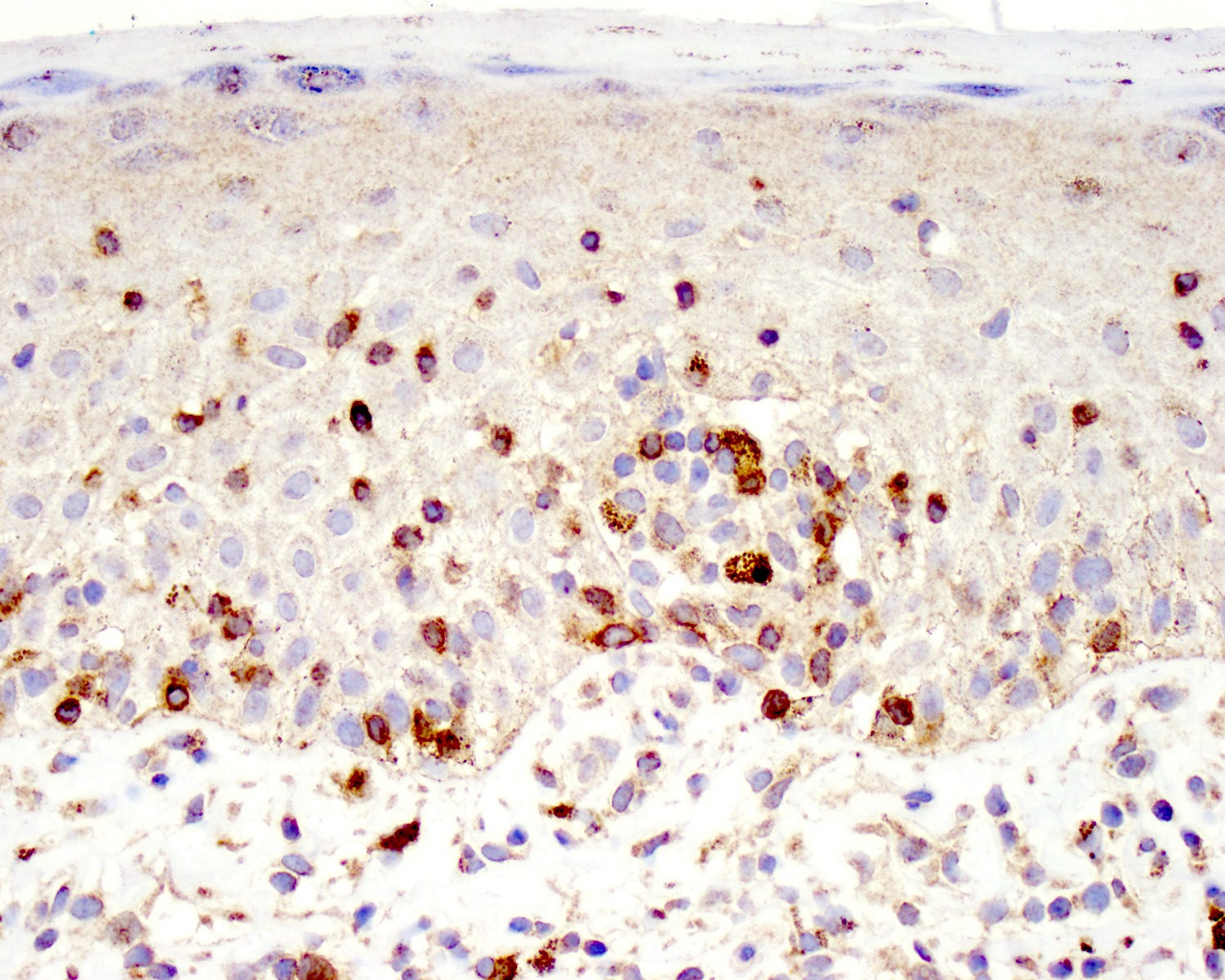
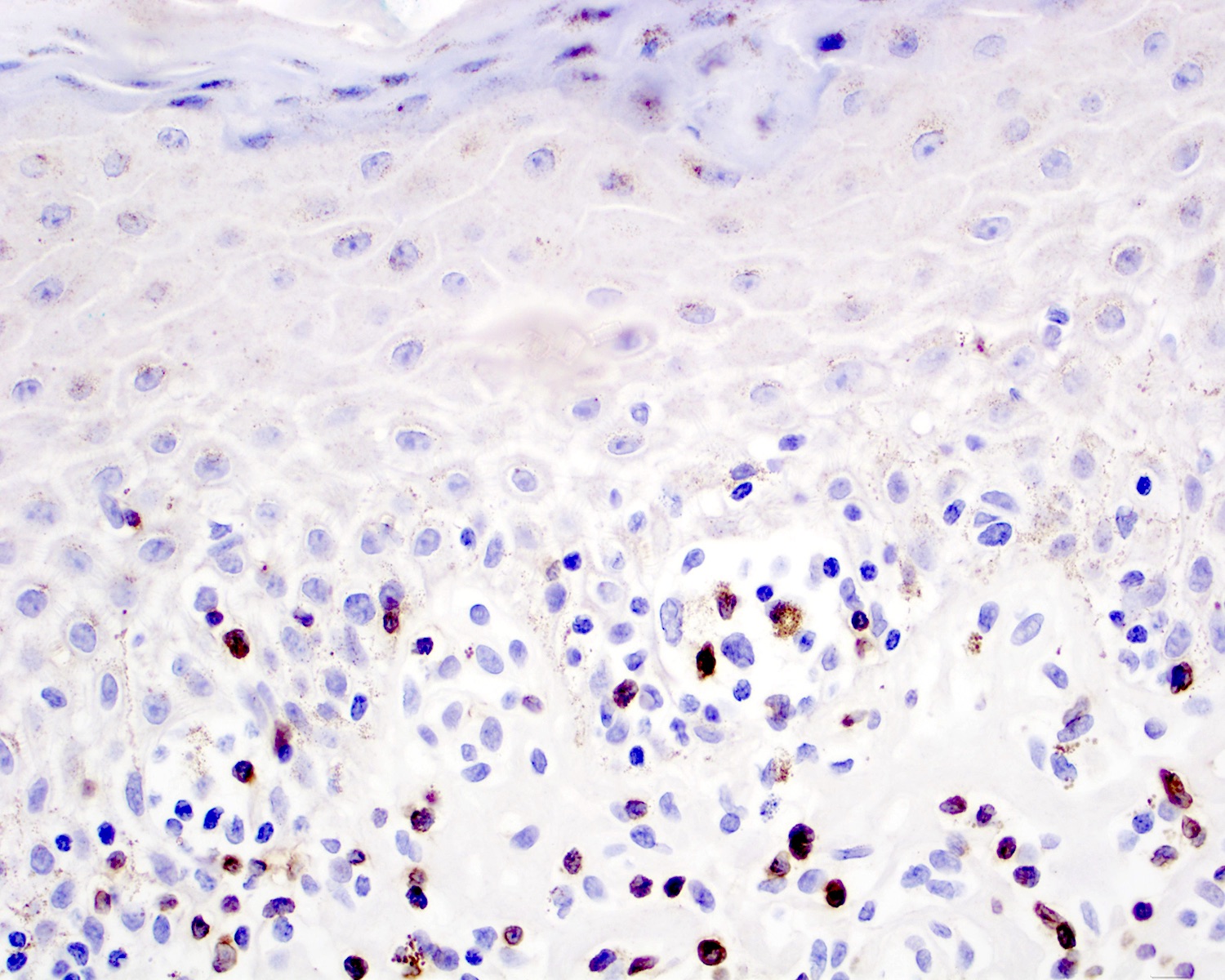
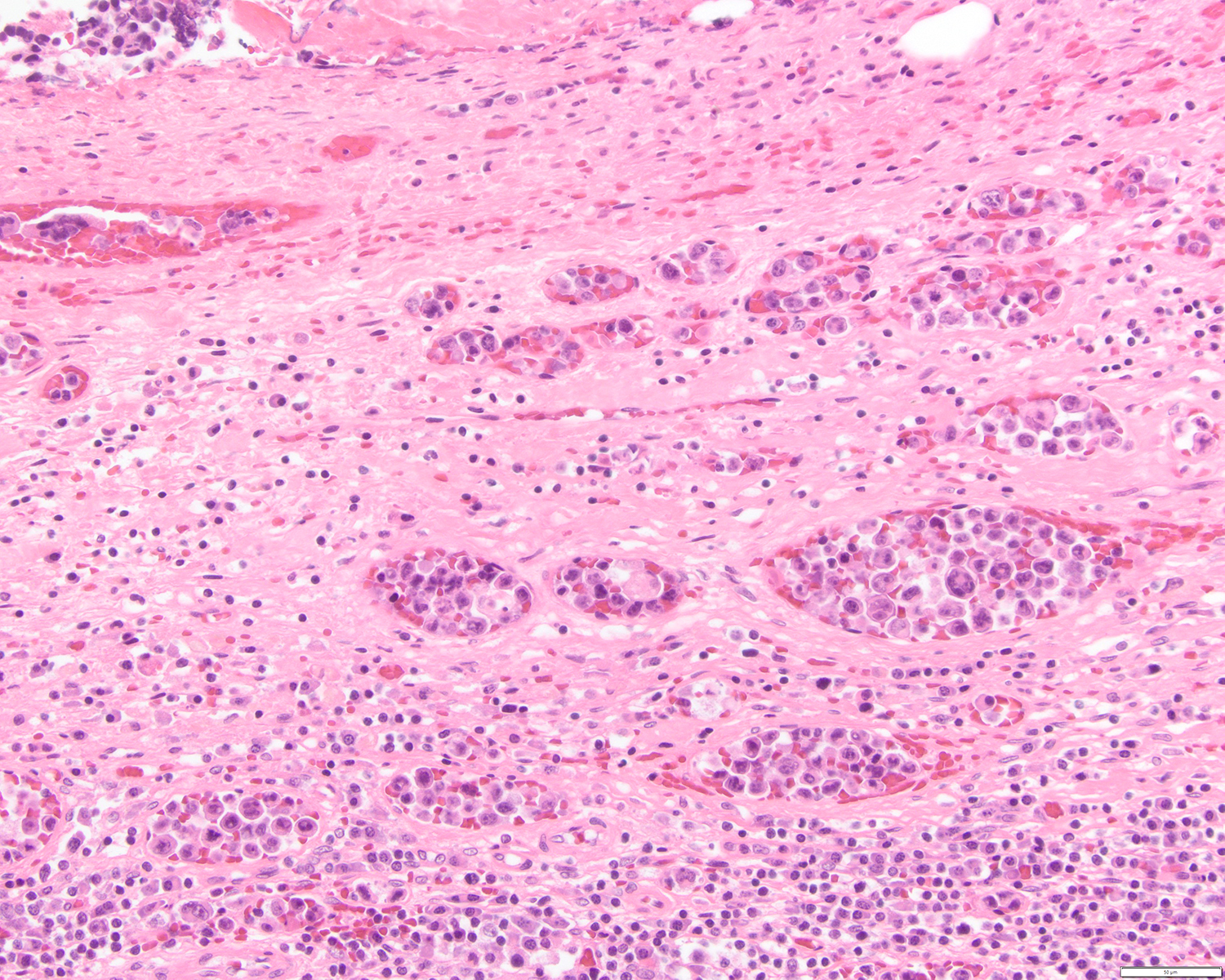
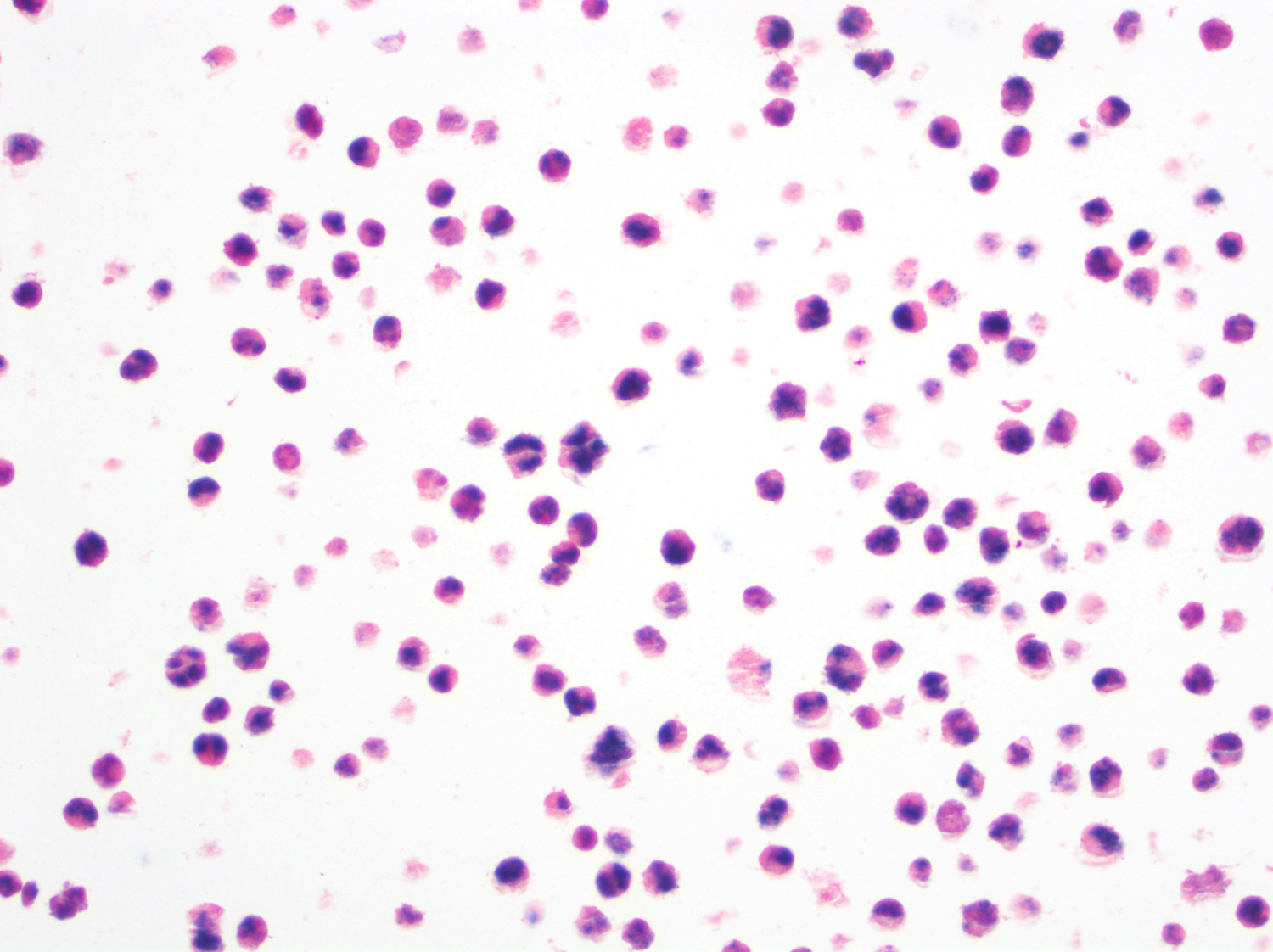
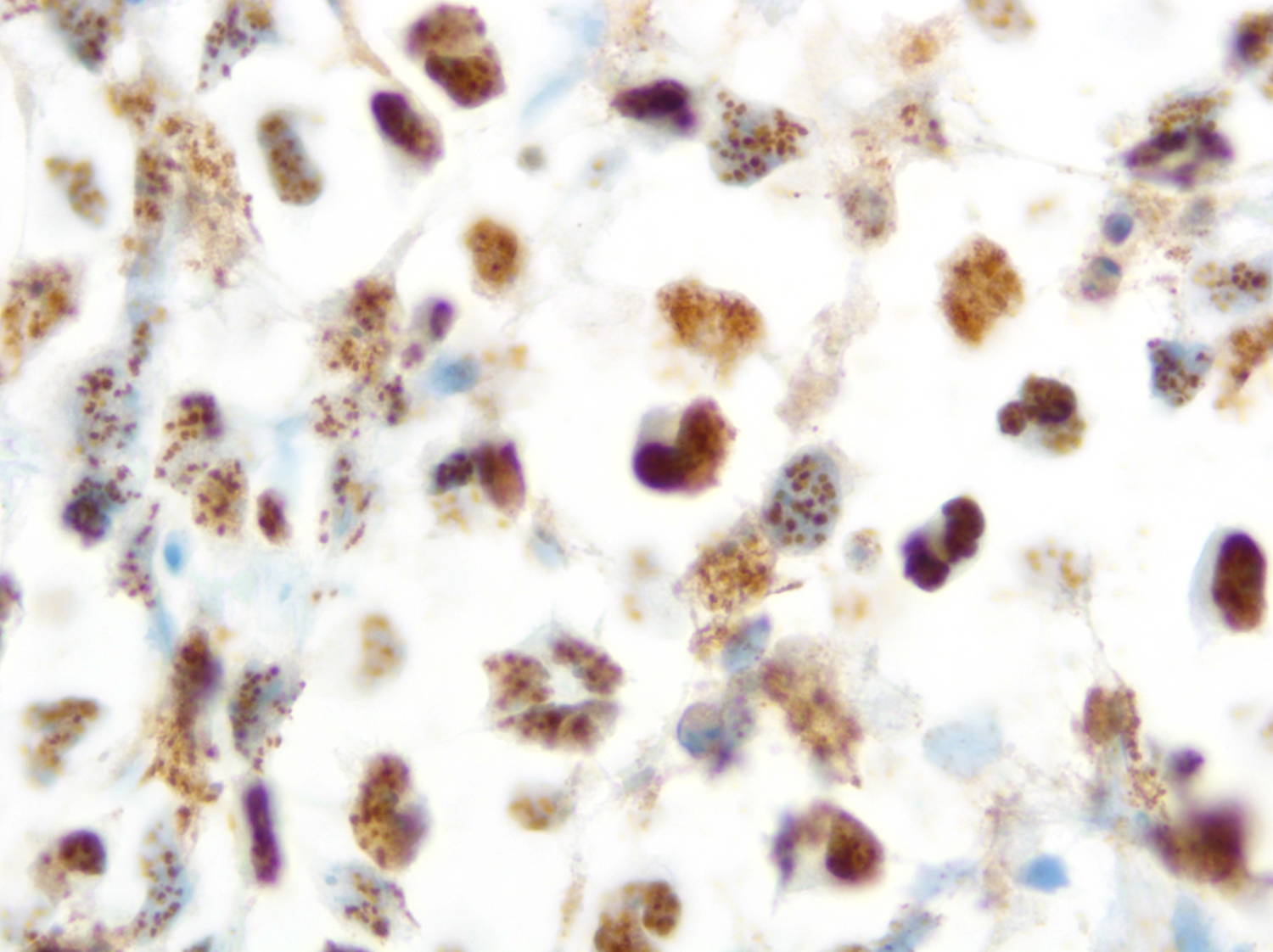
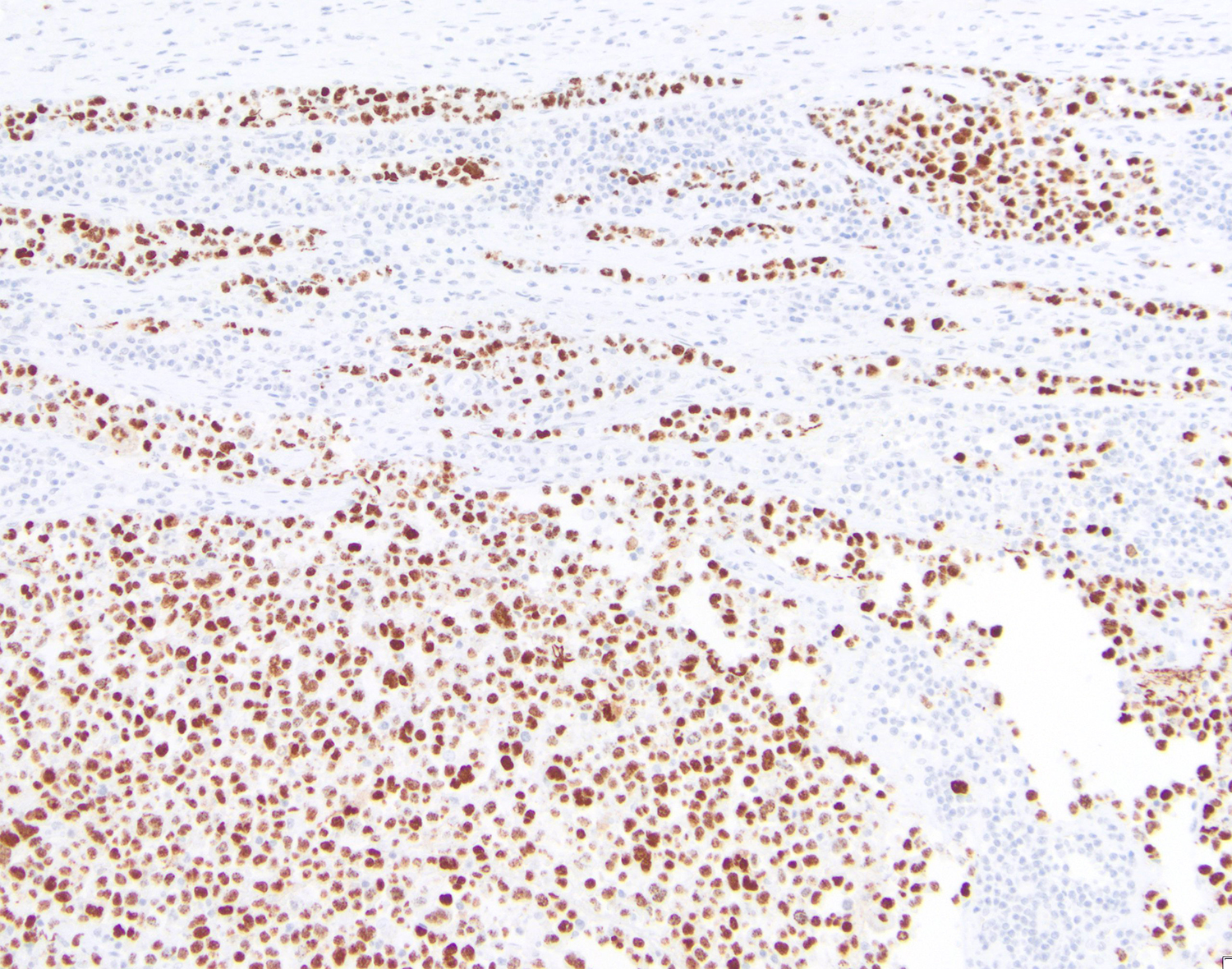
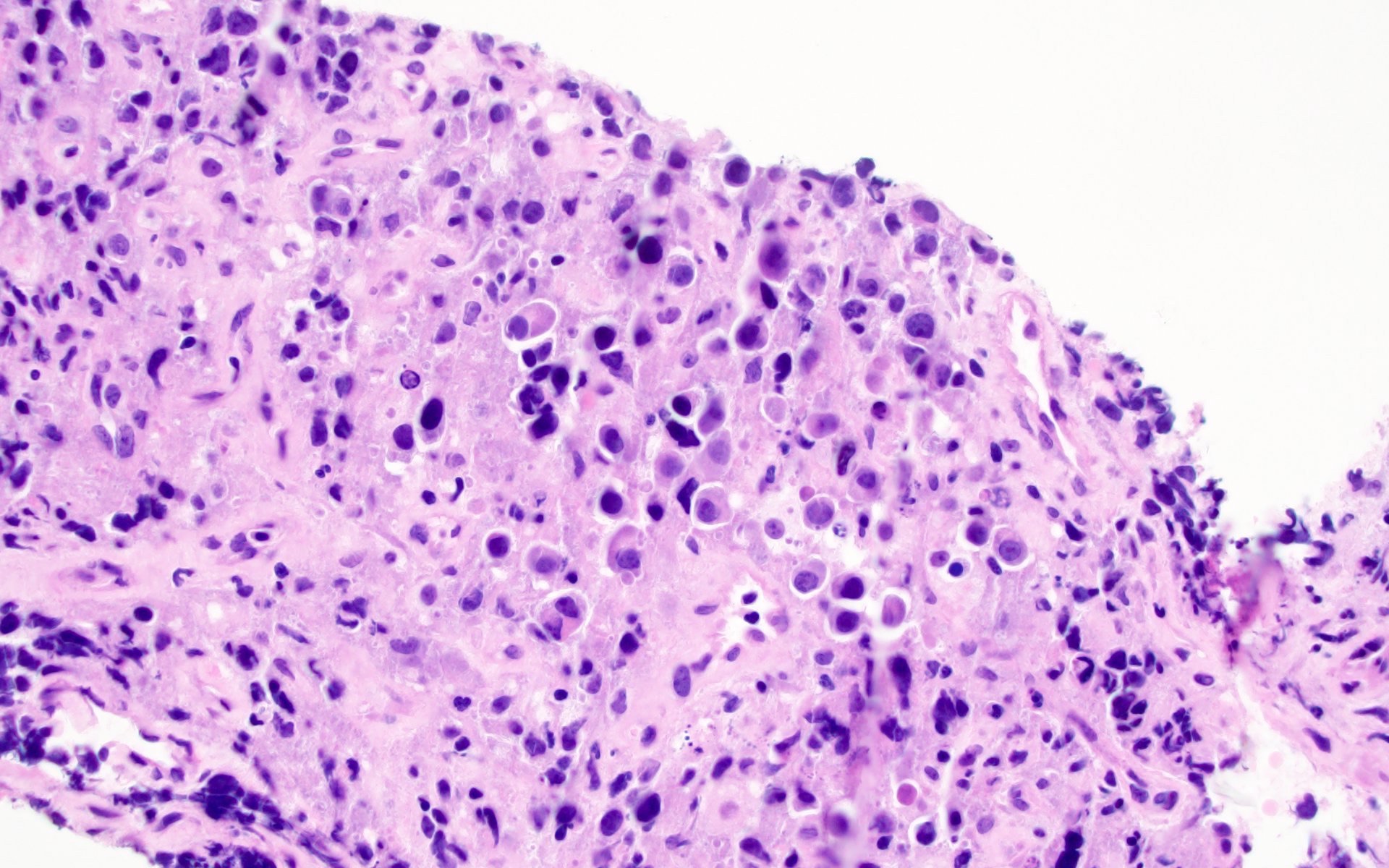
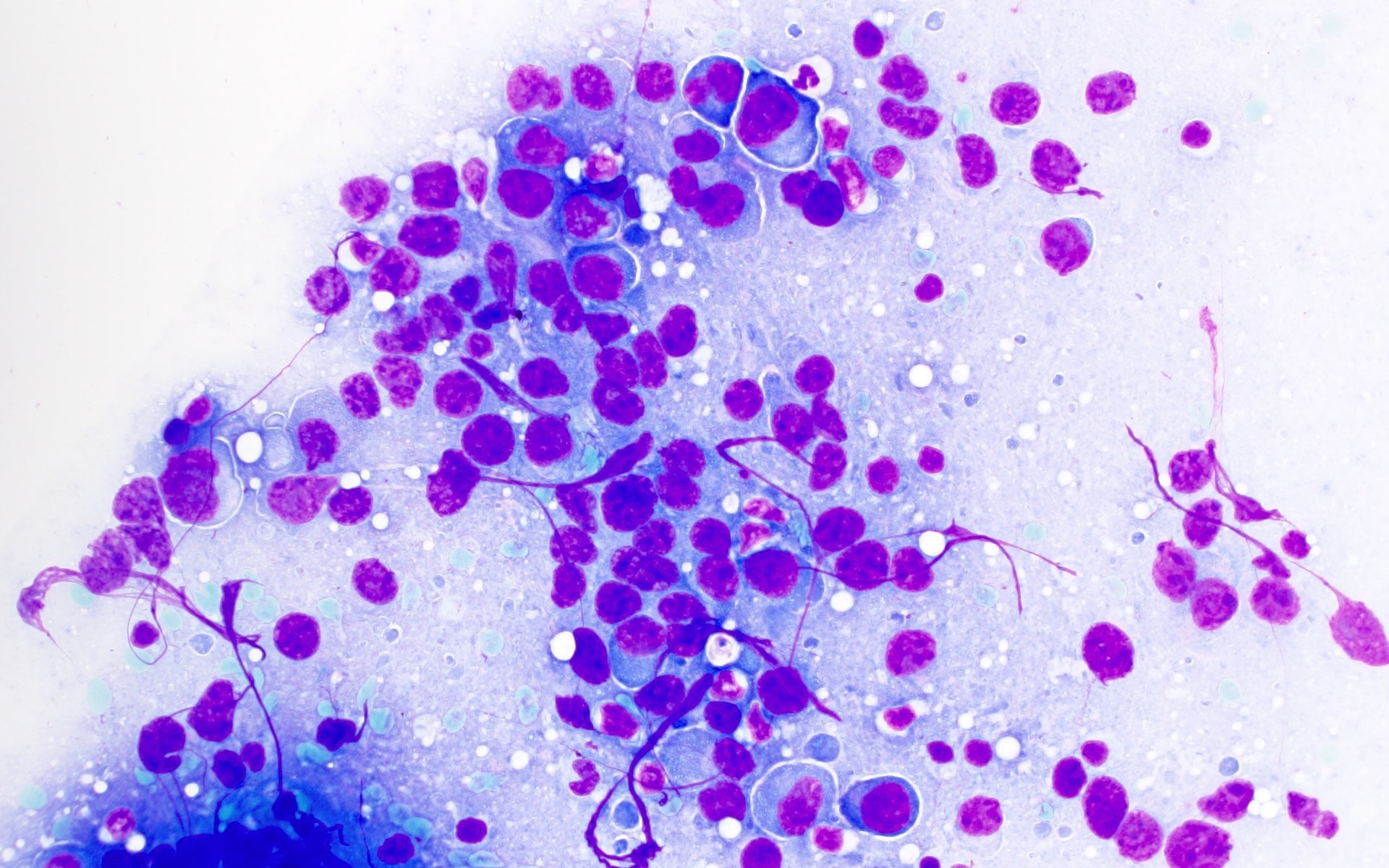
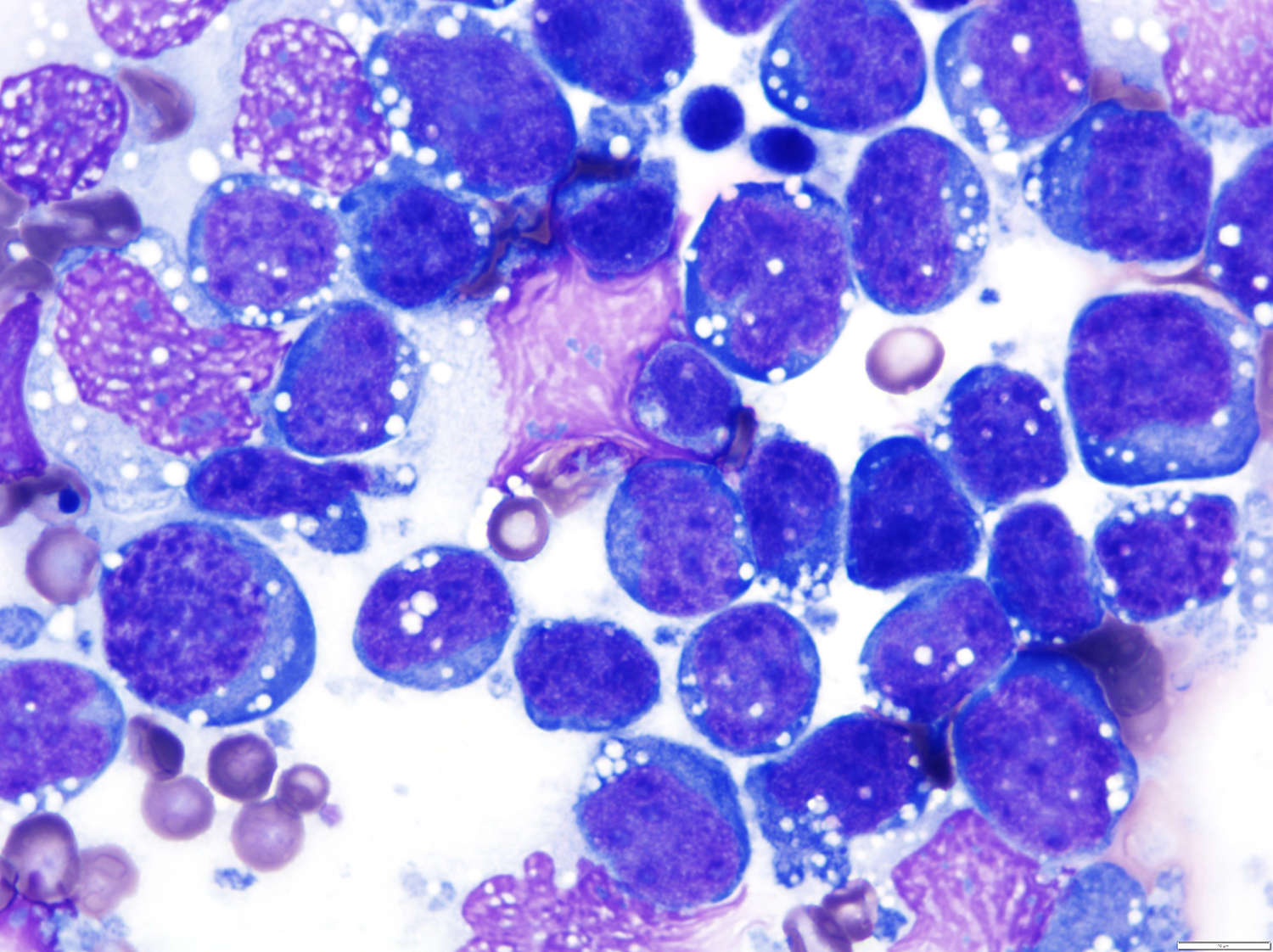
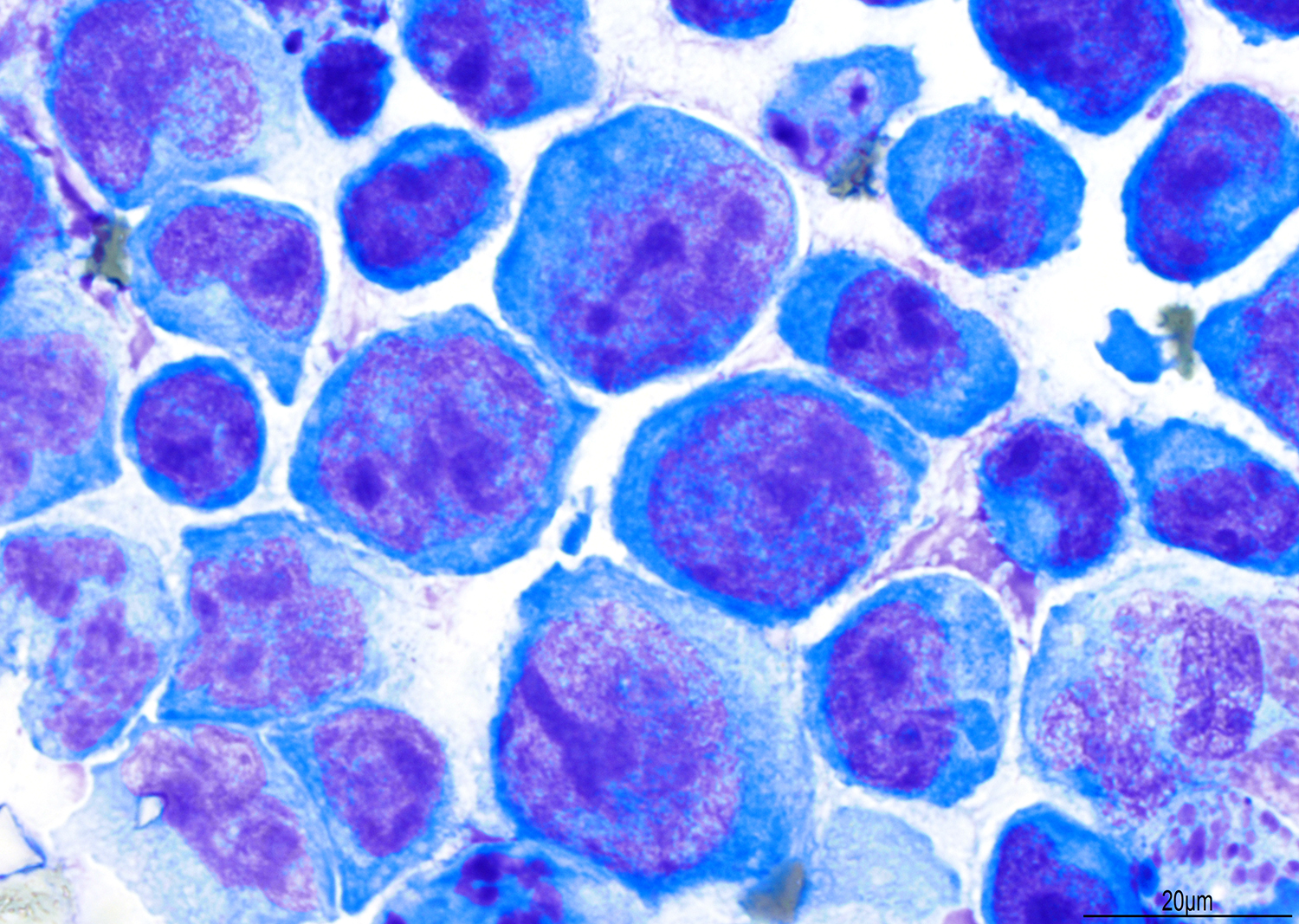
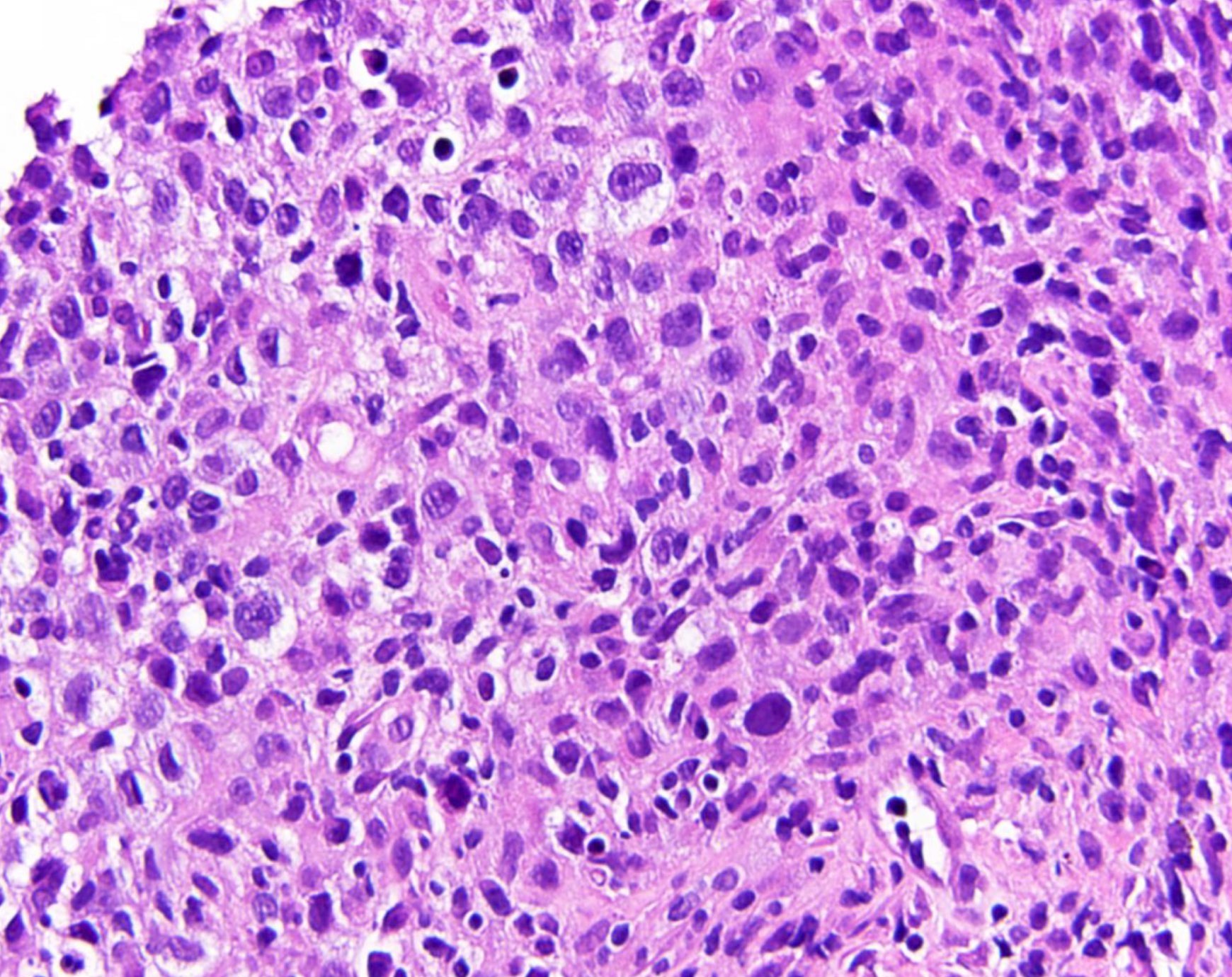
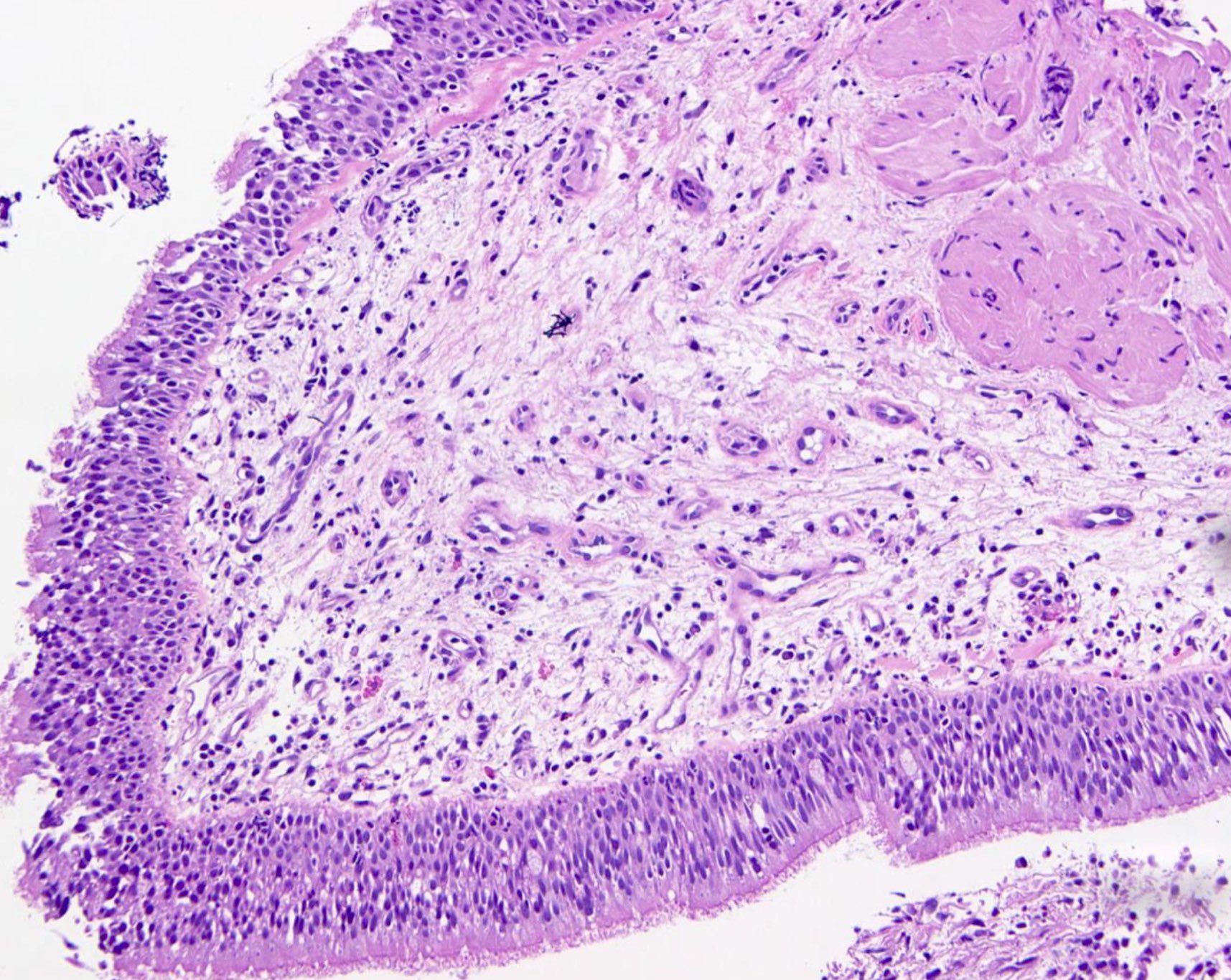
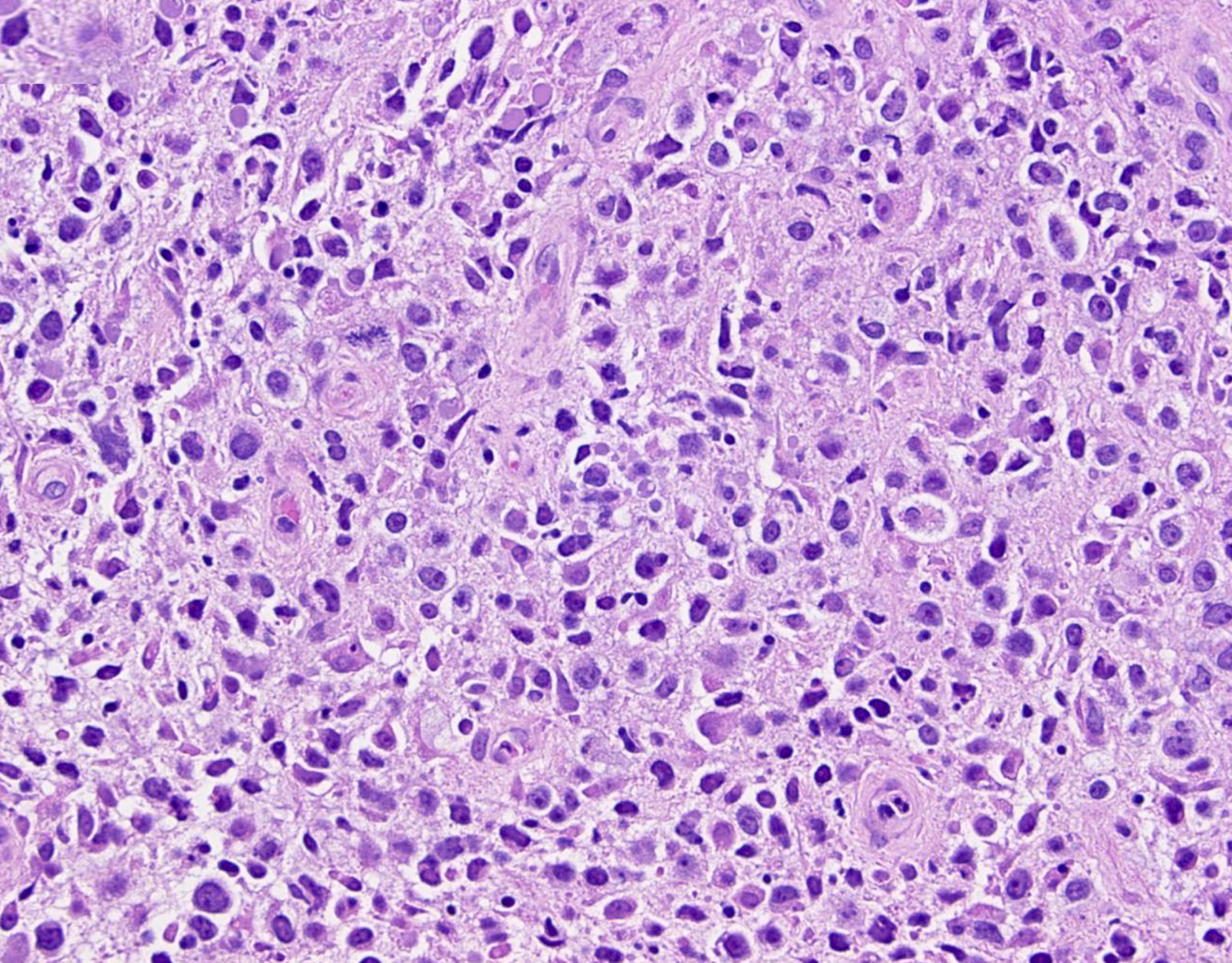
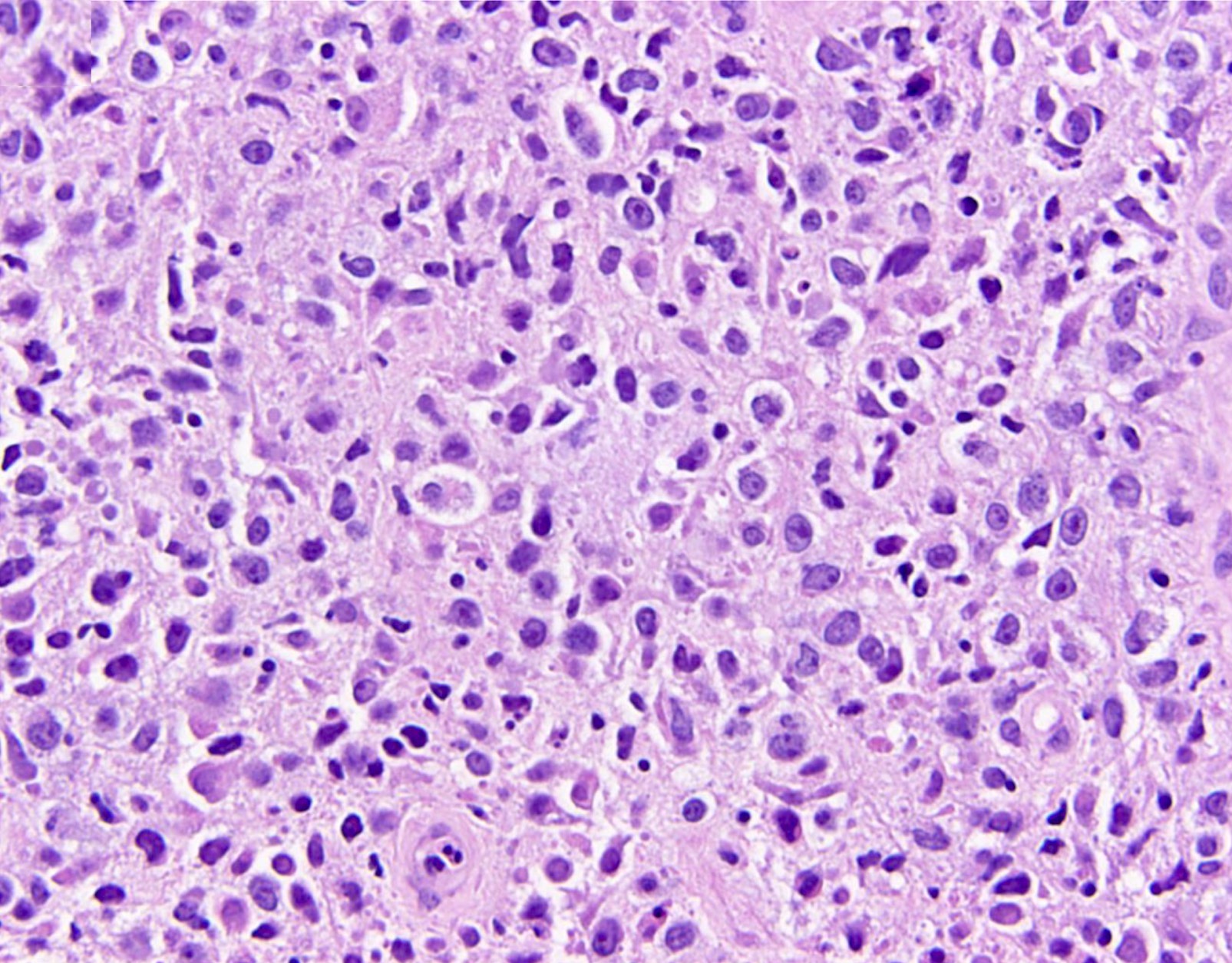
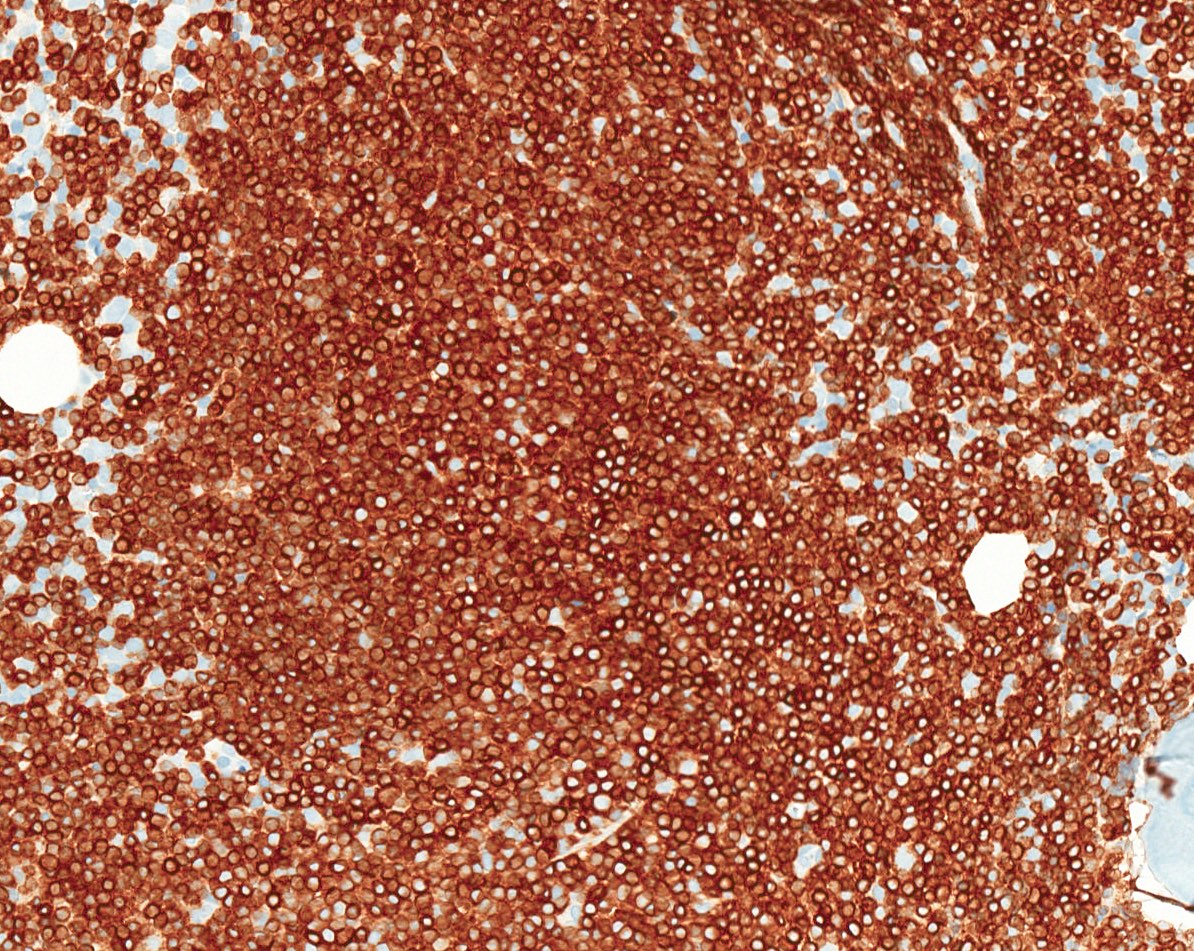
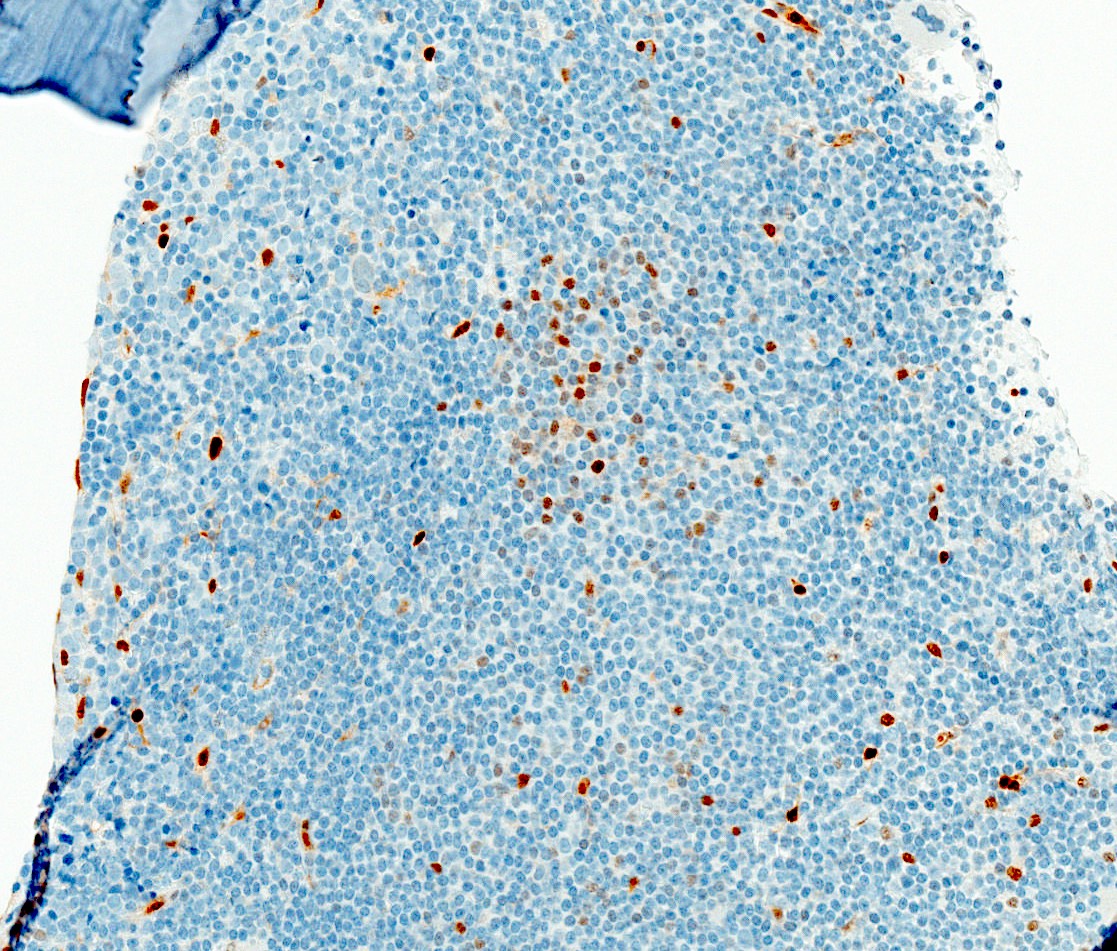
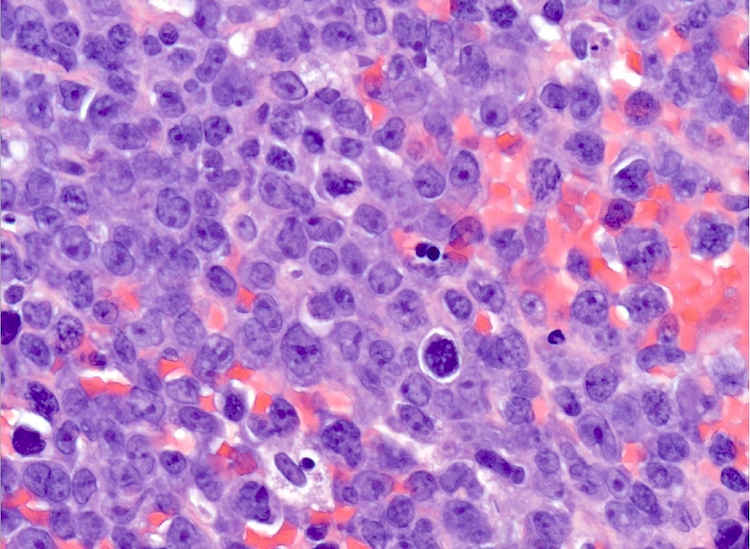
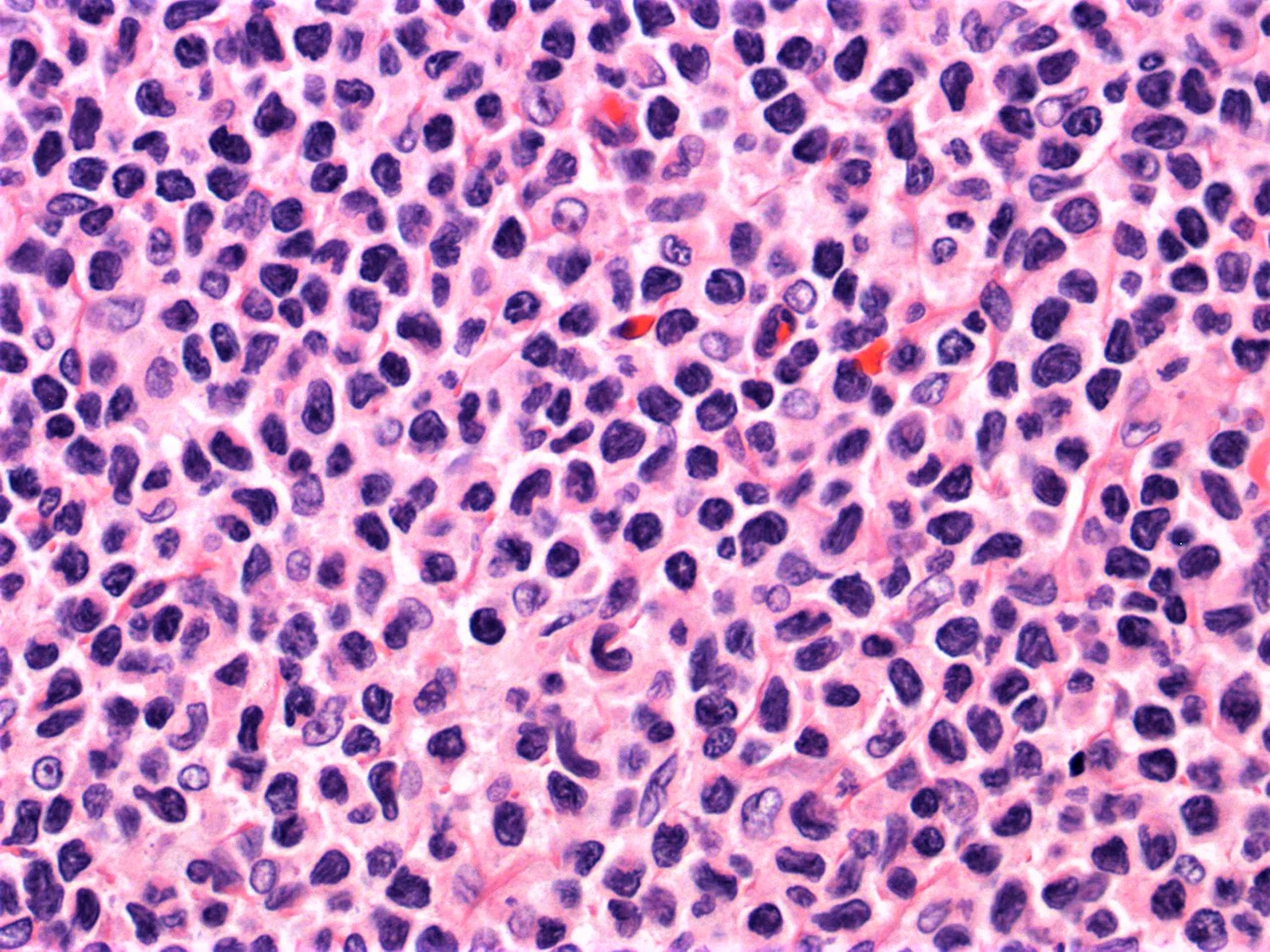
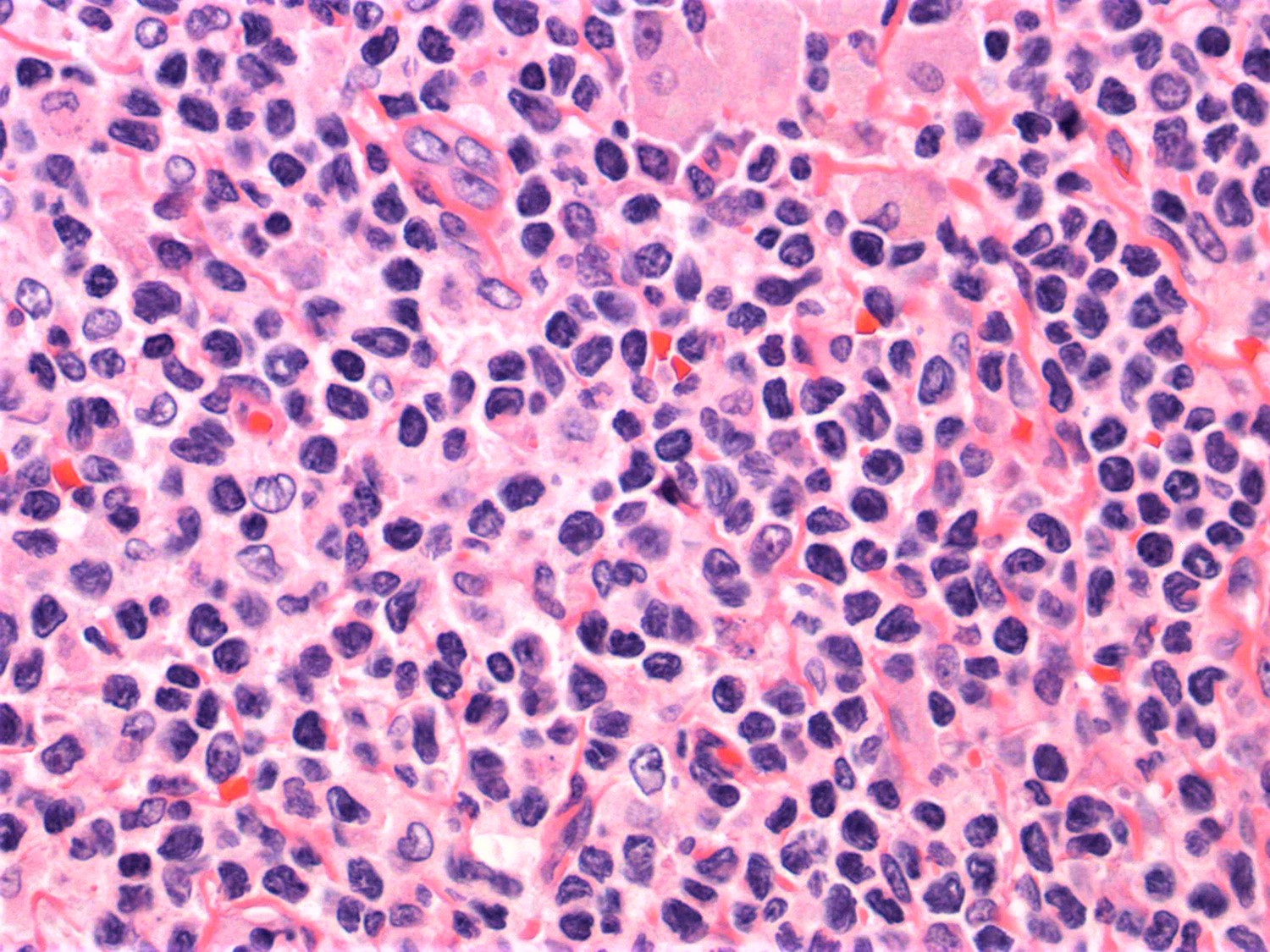
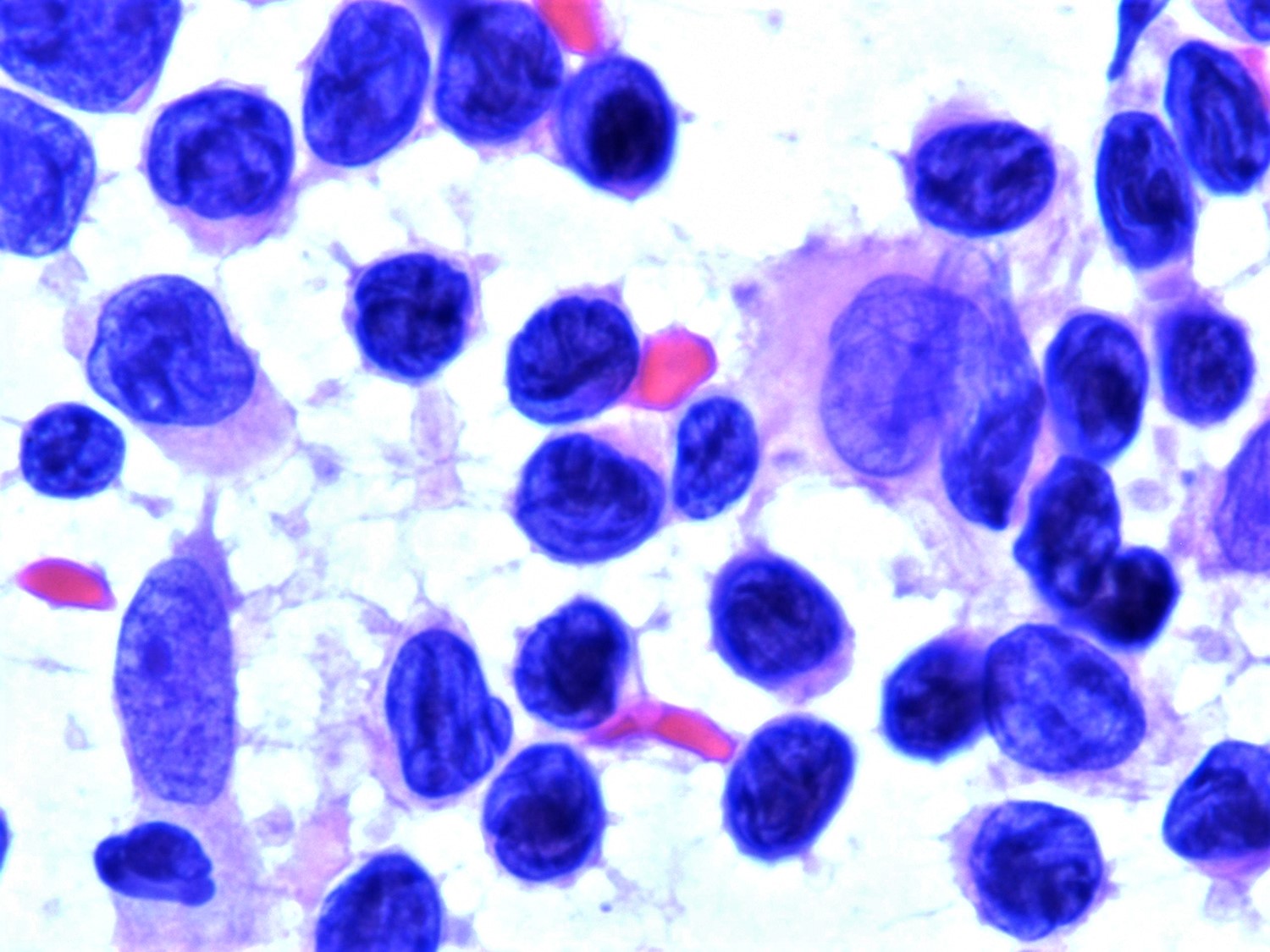
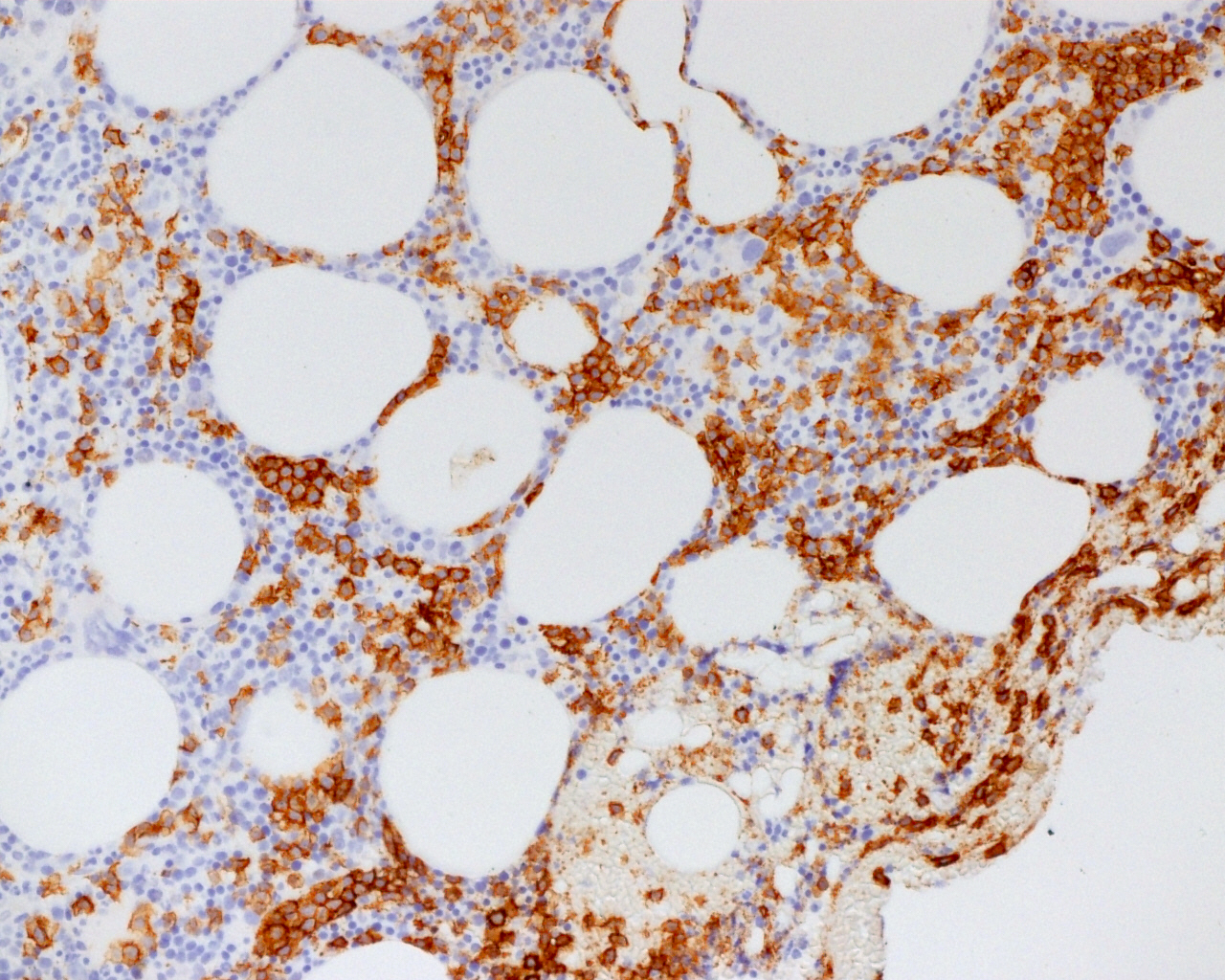
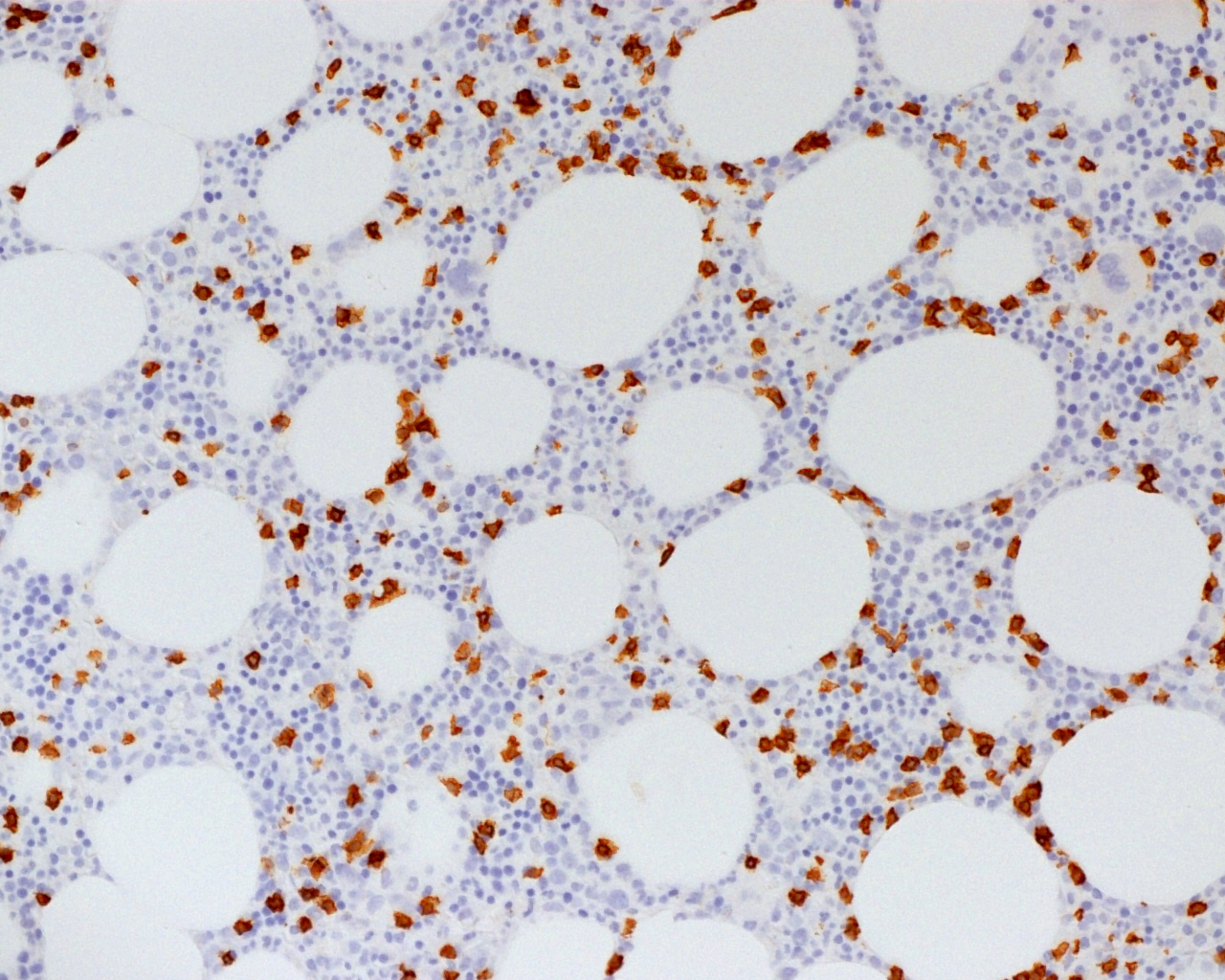
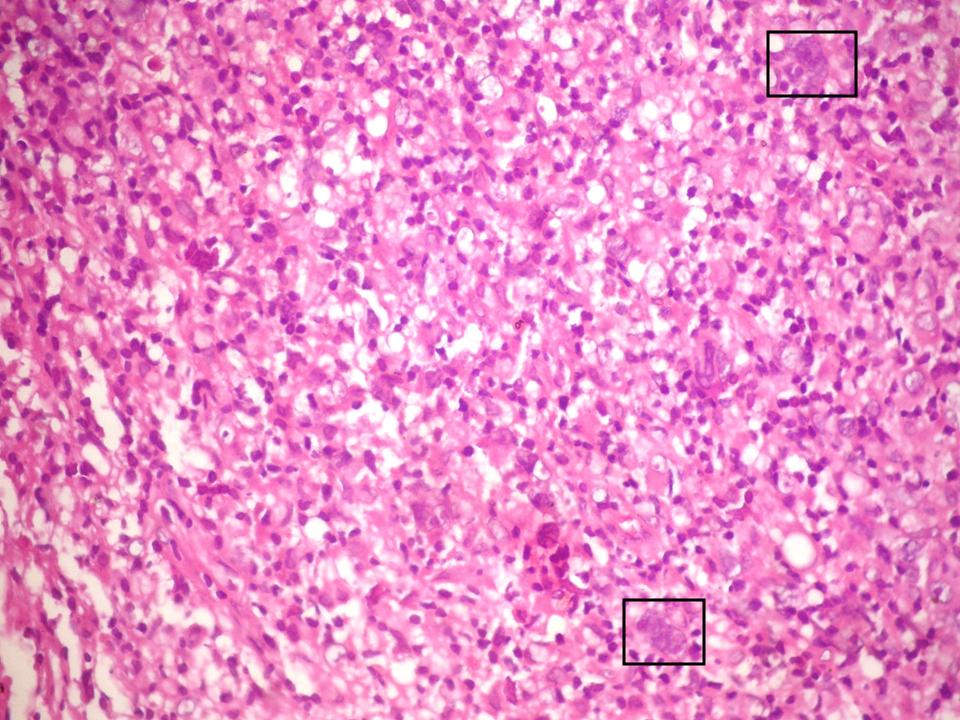
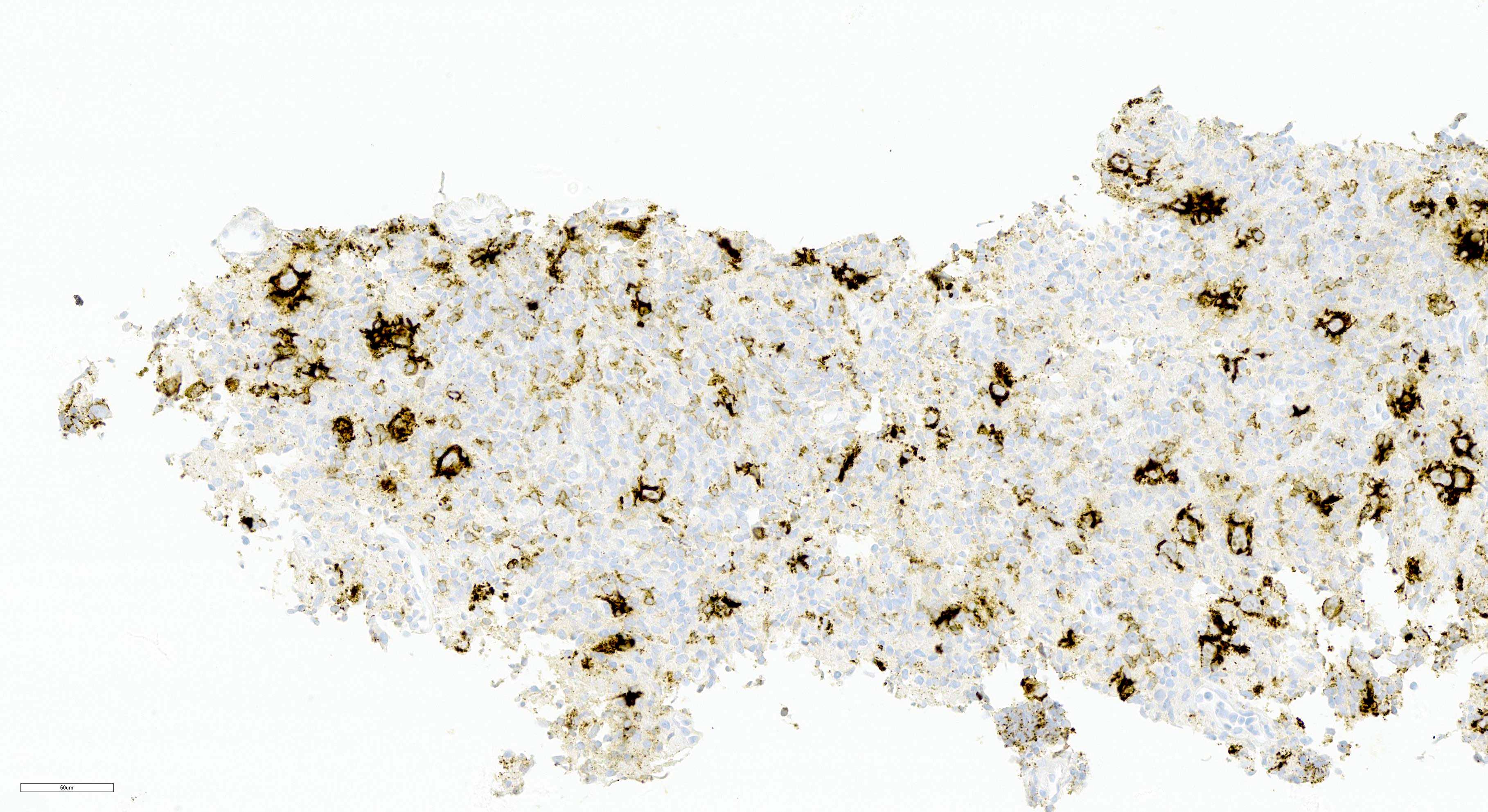
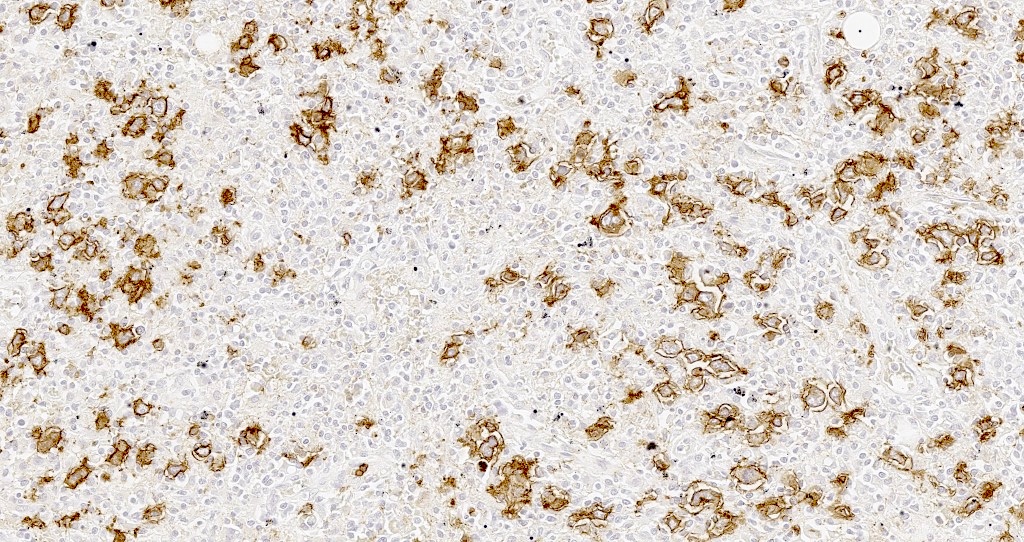
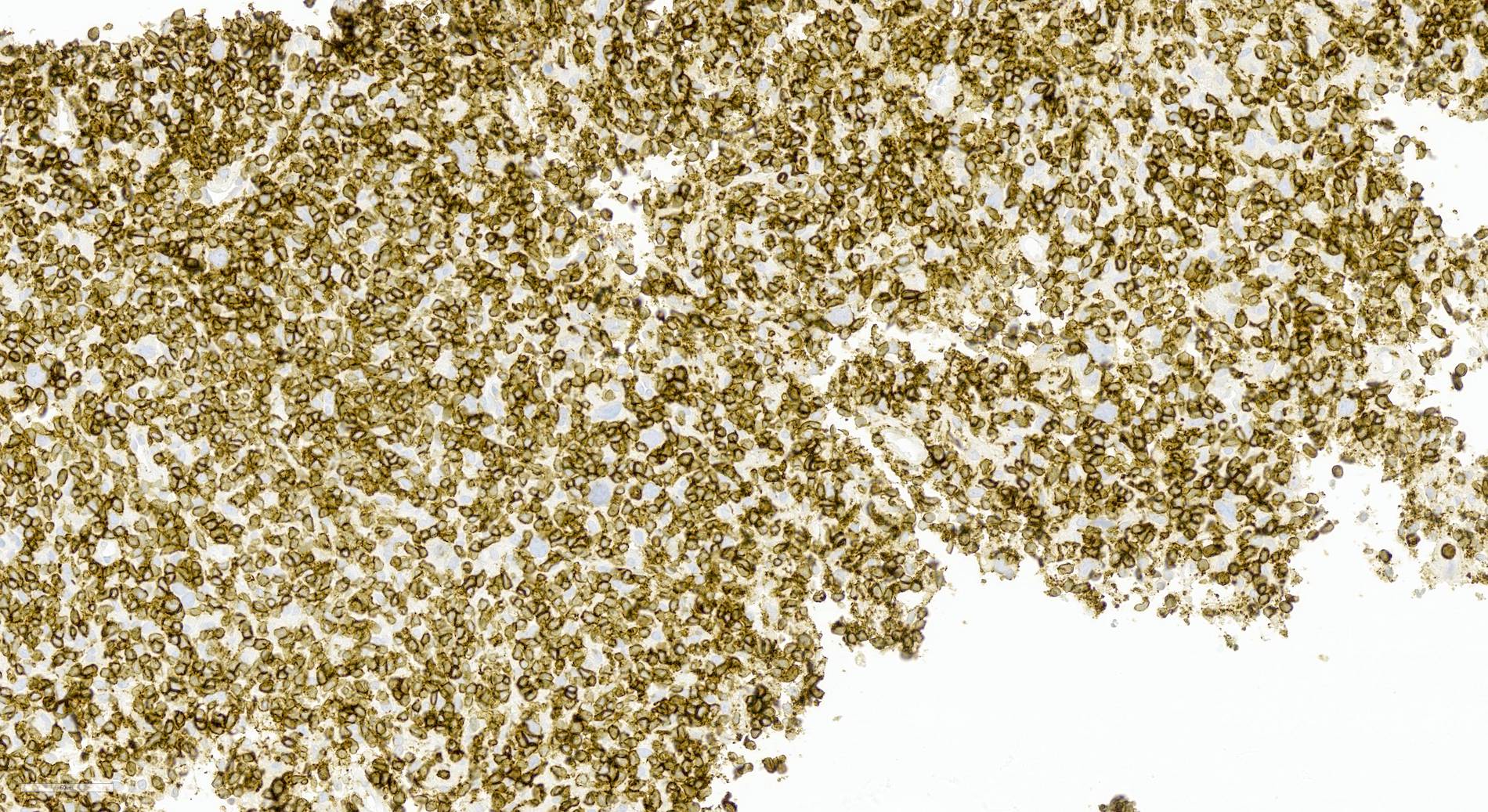
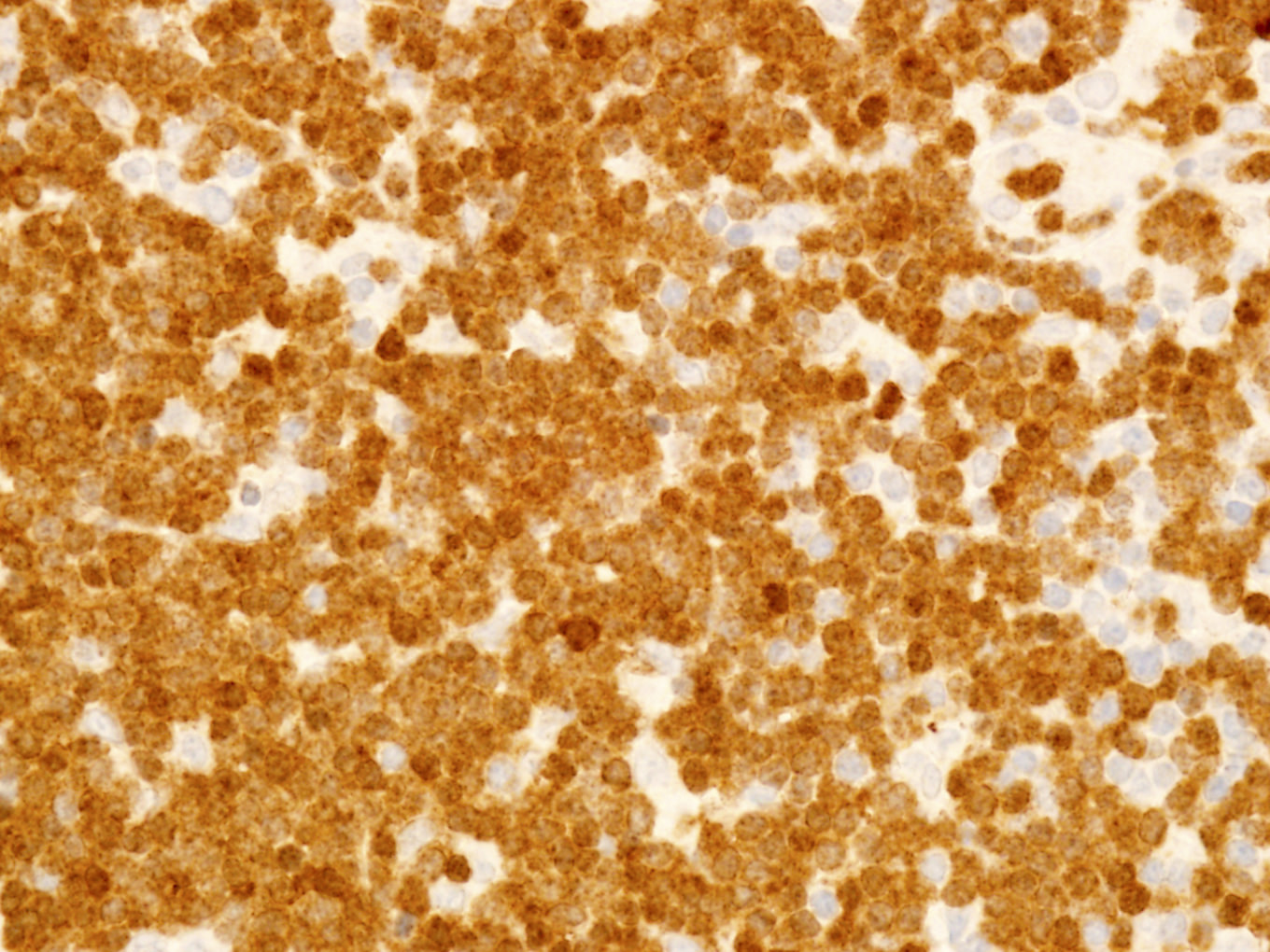
ALK+ LBCL
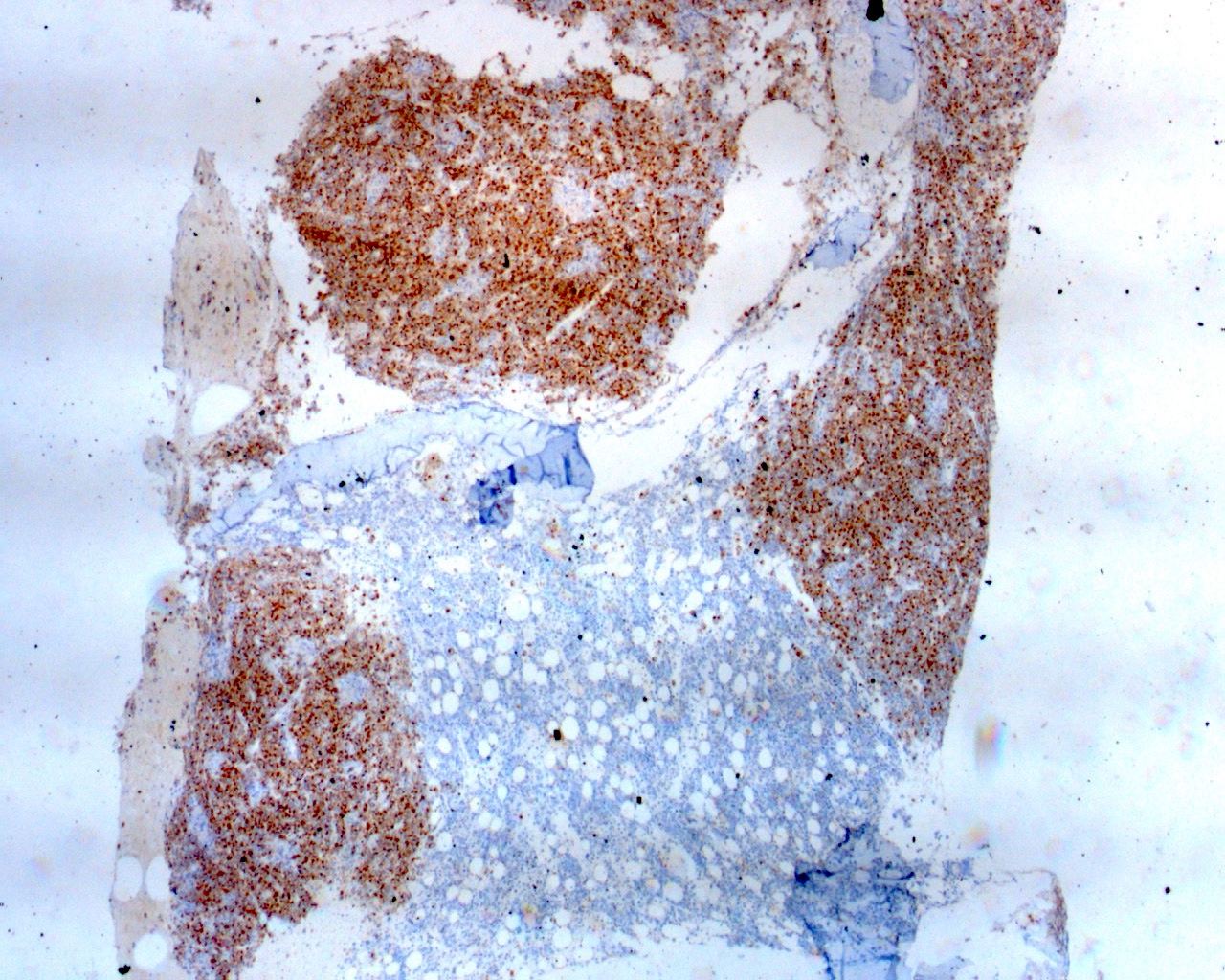
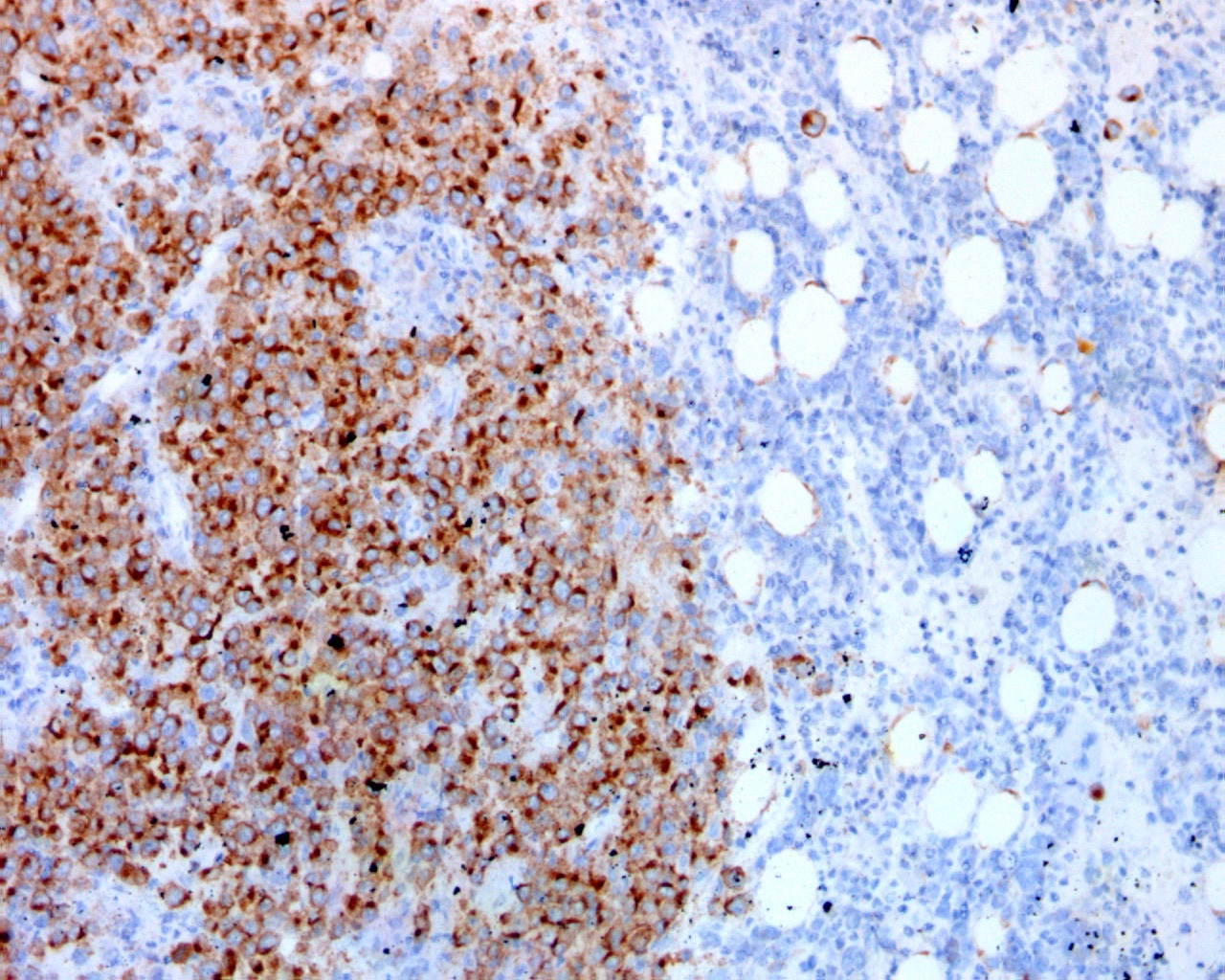
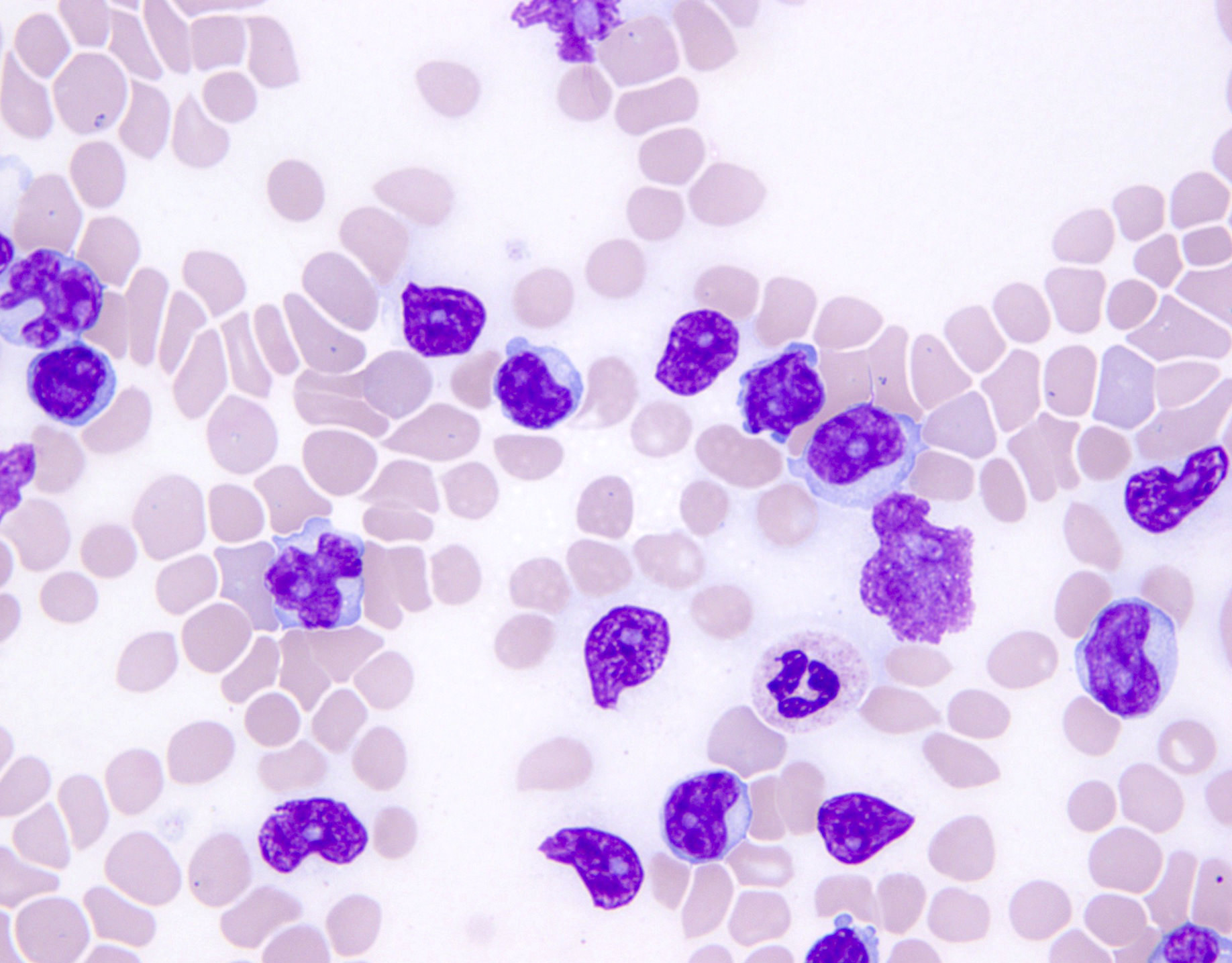
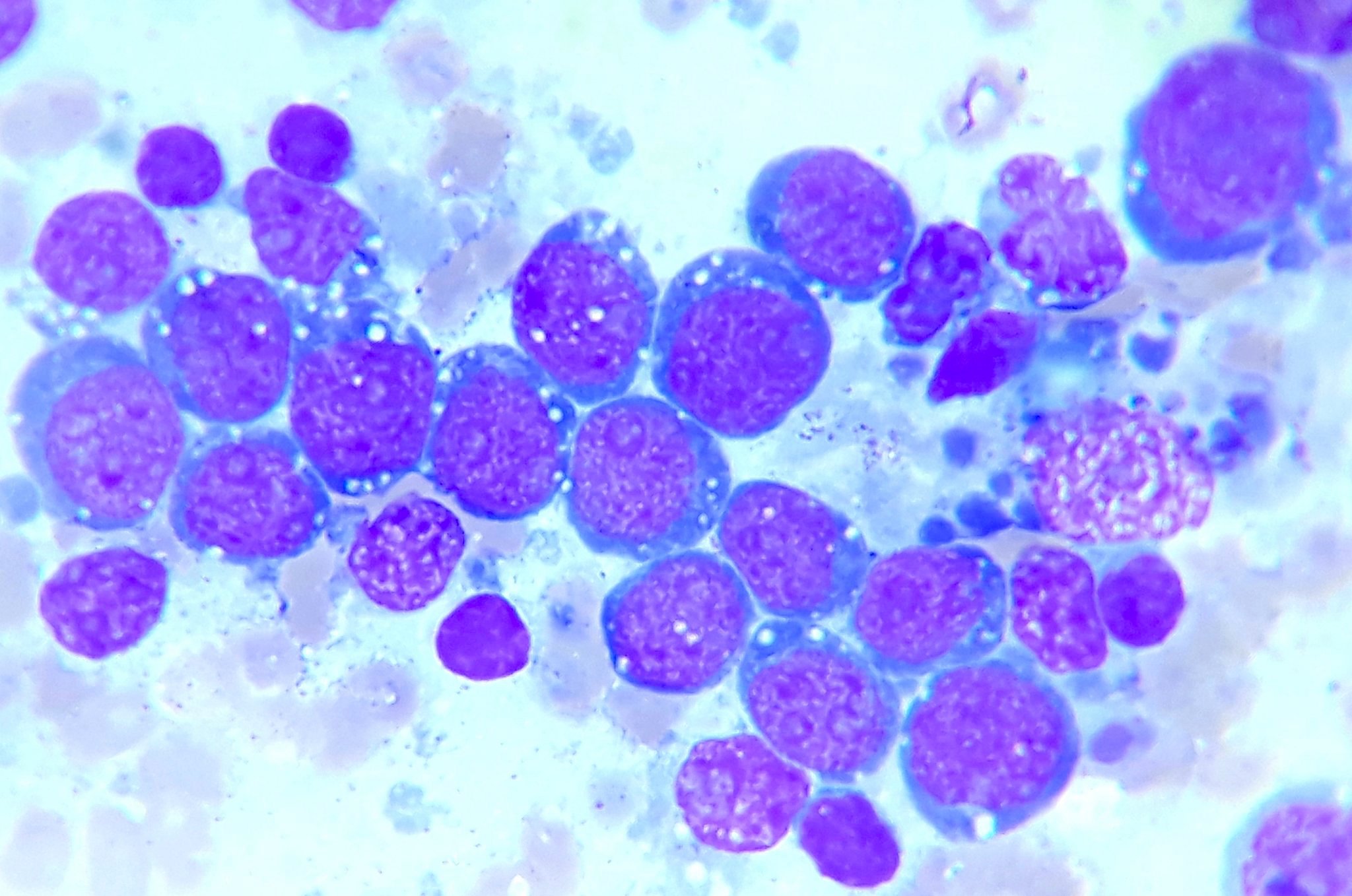
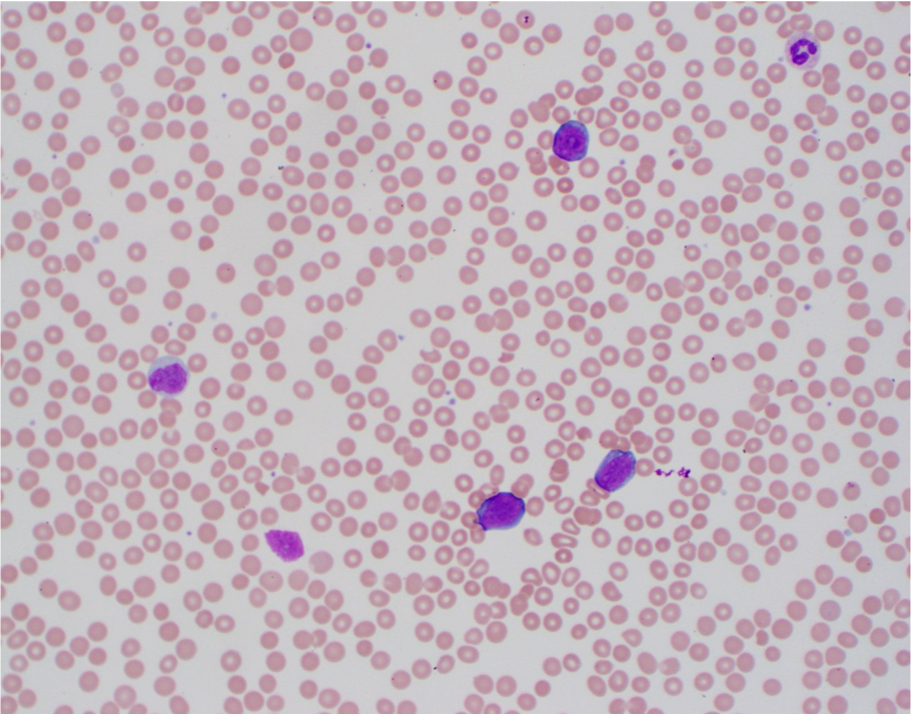
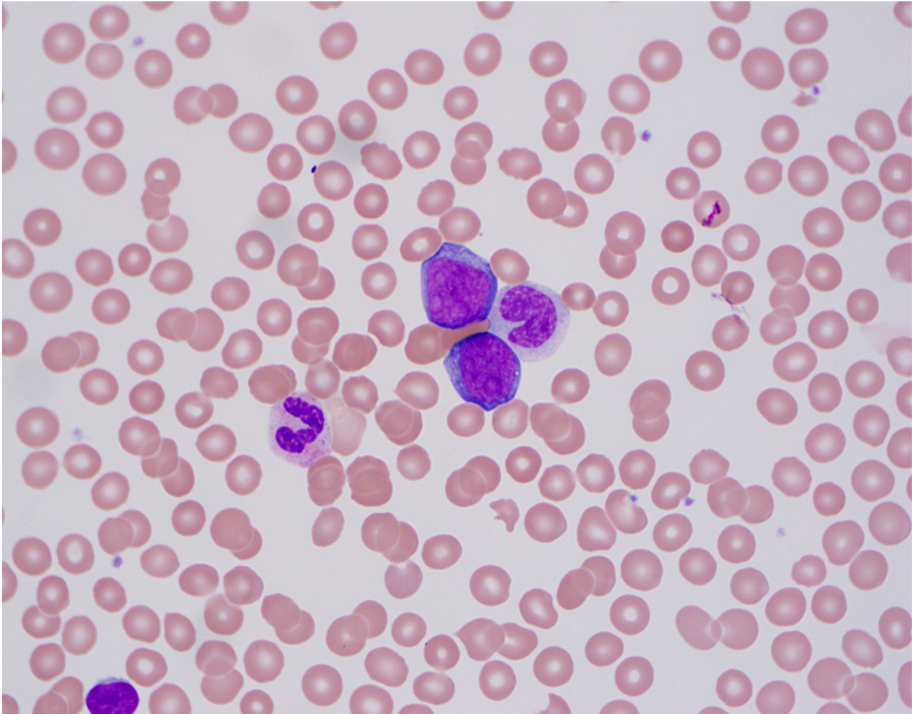
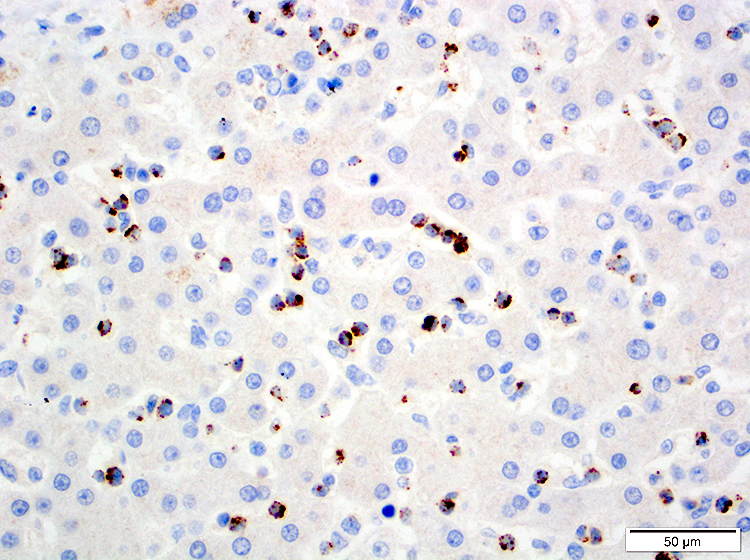
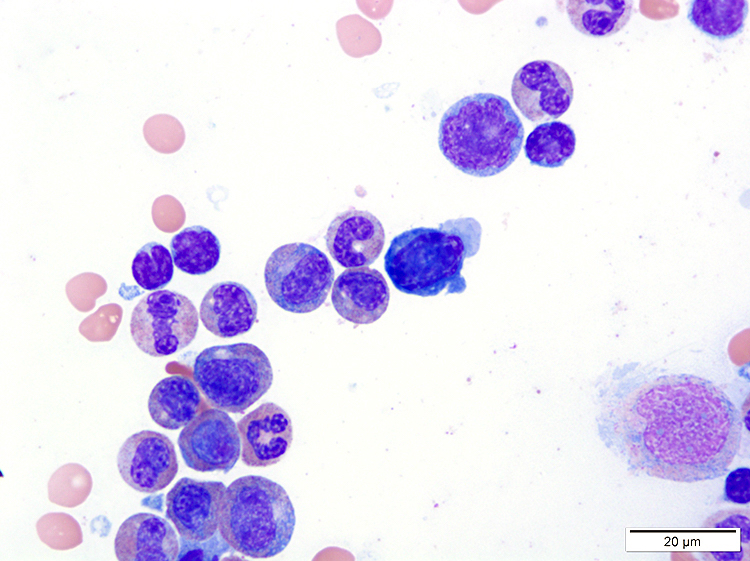
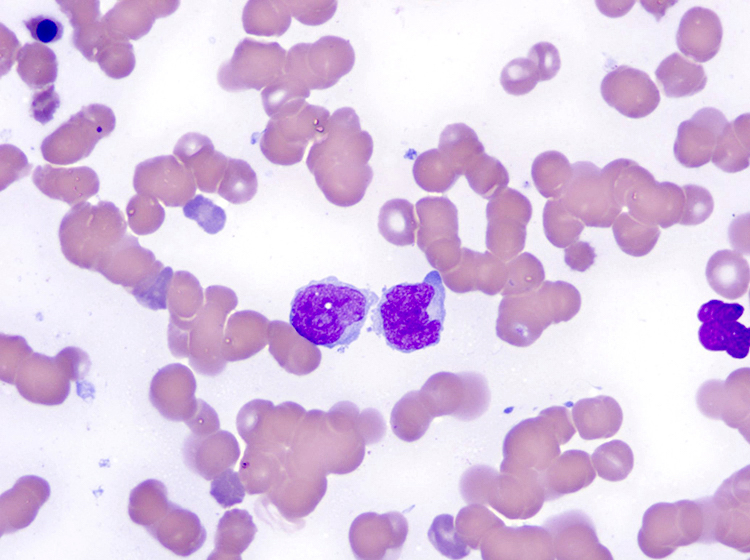
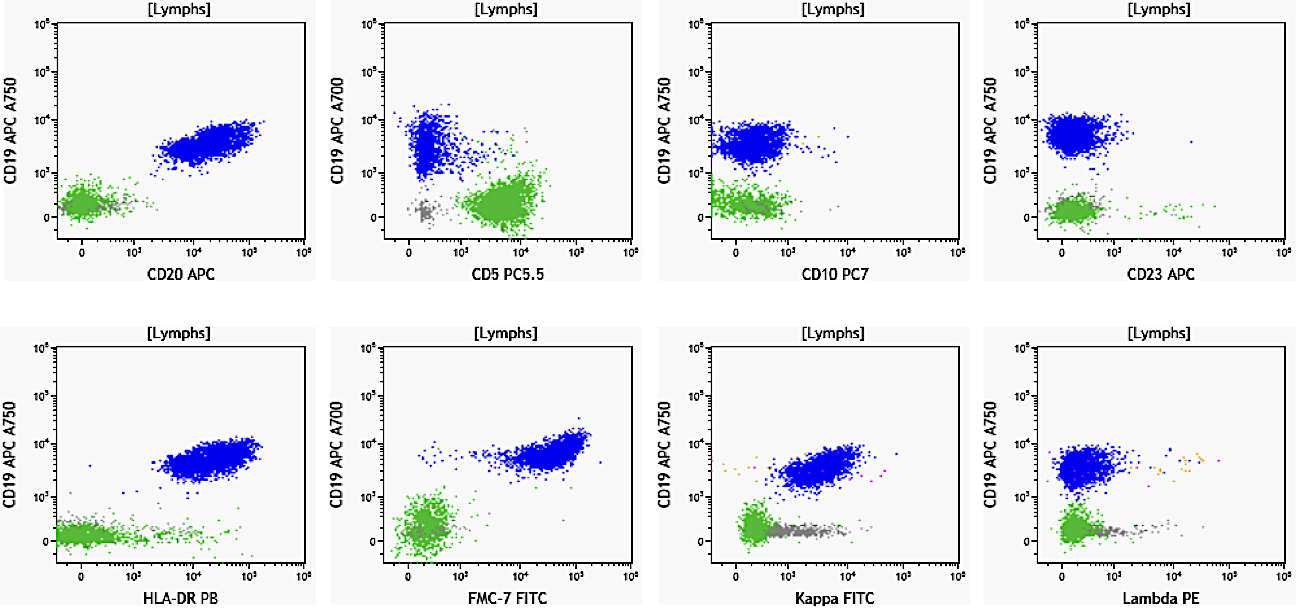
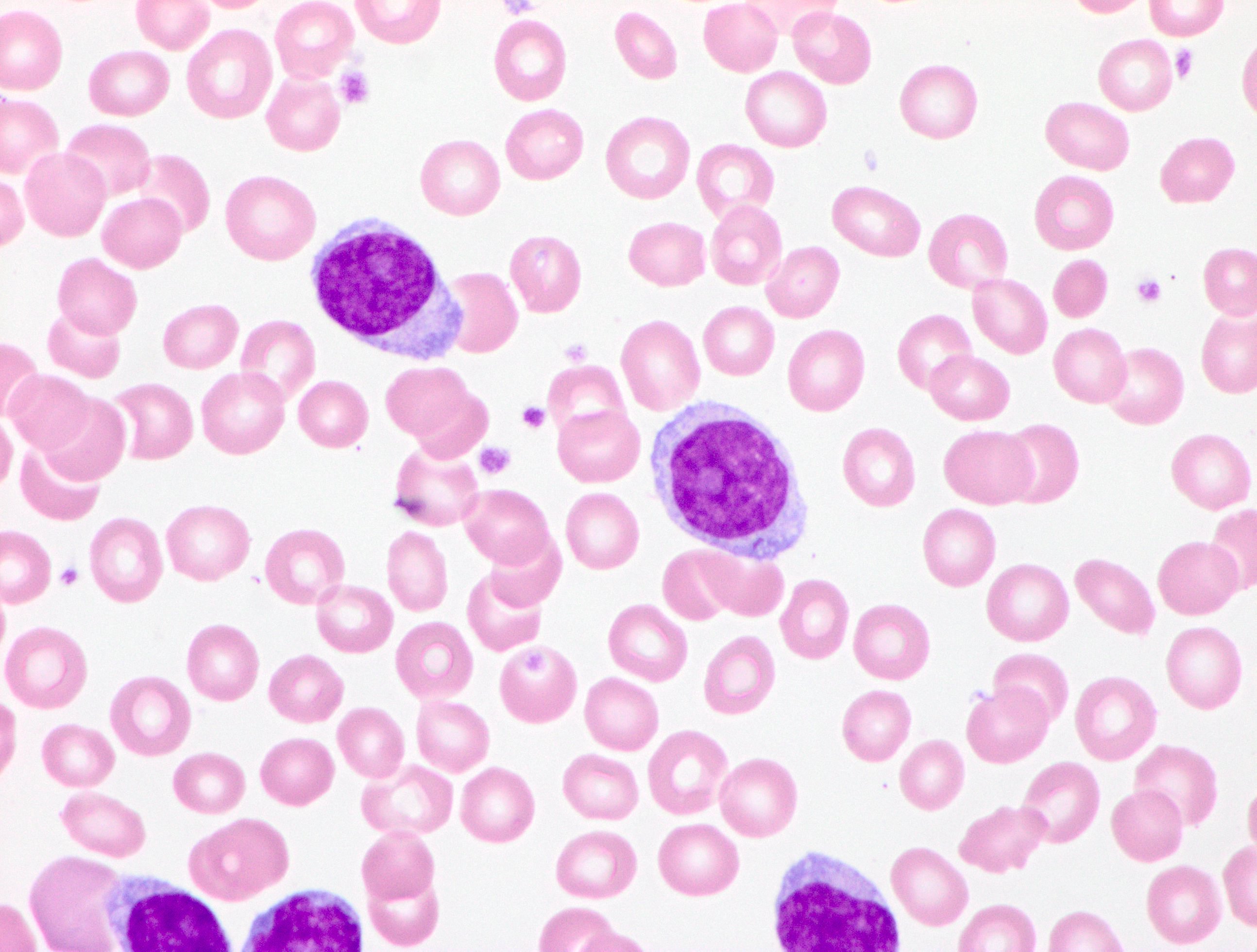
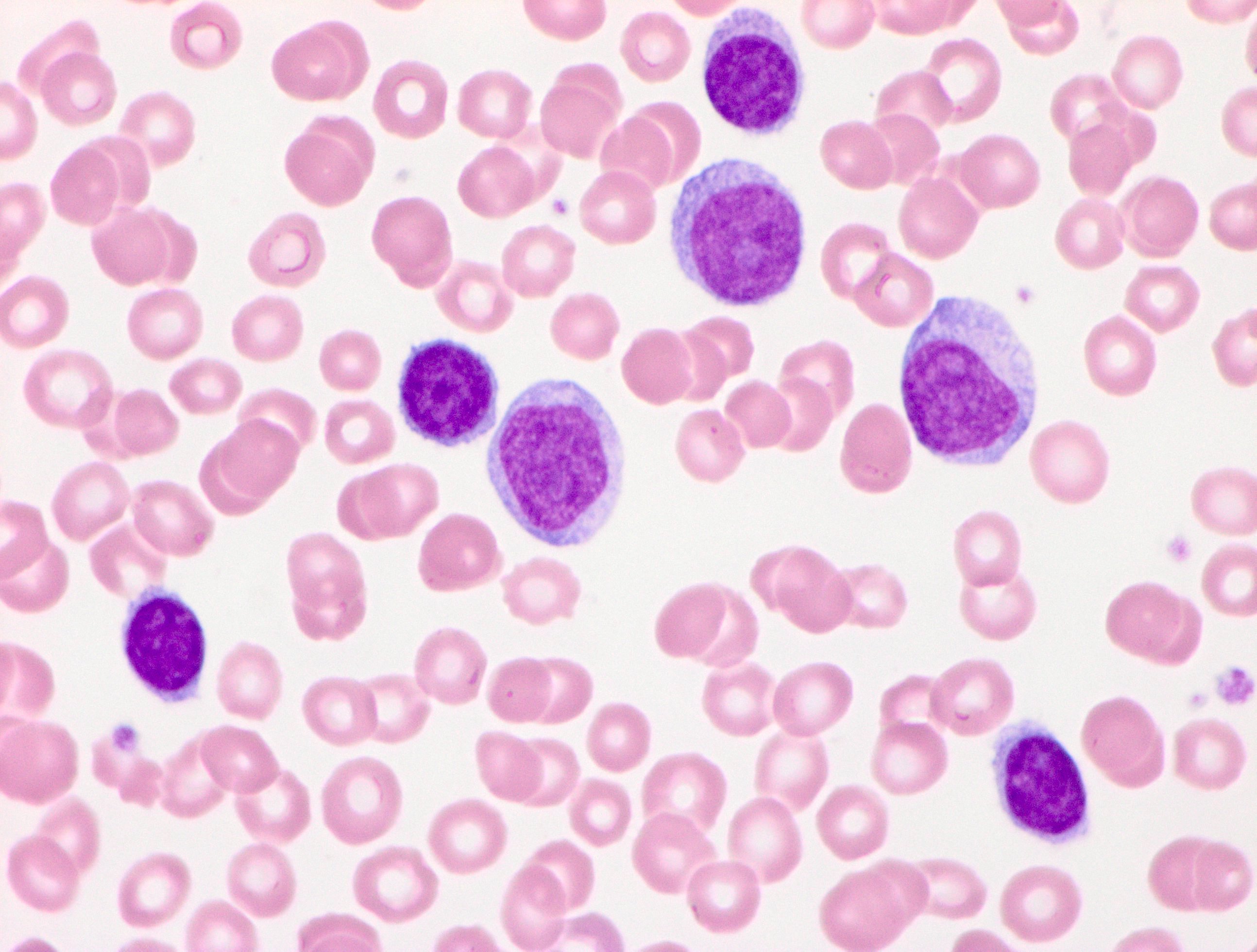
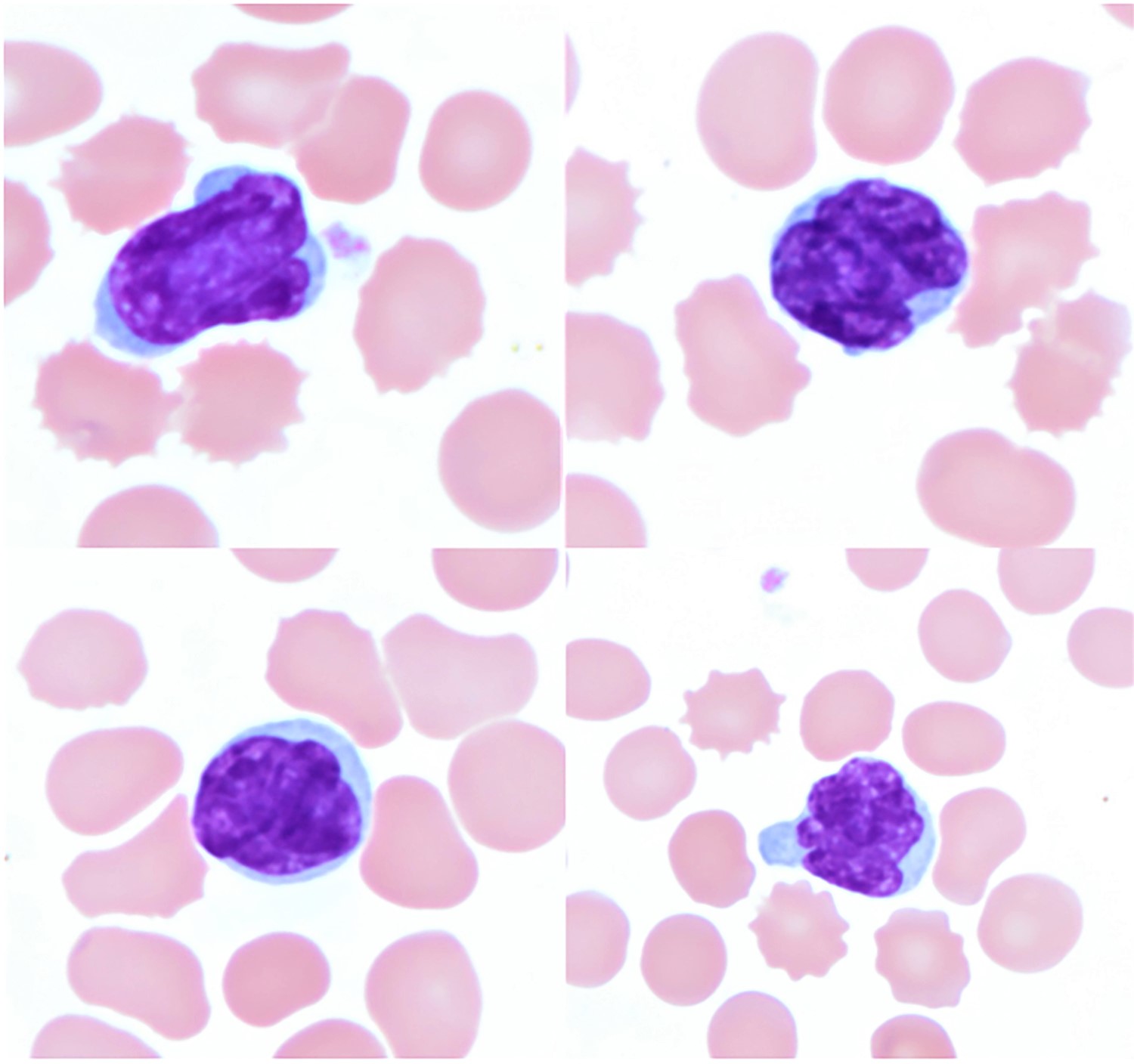
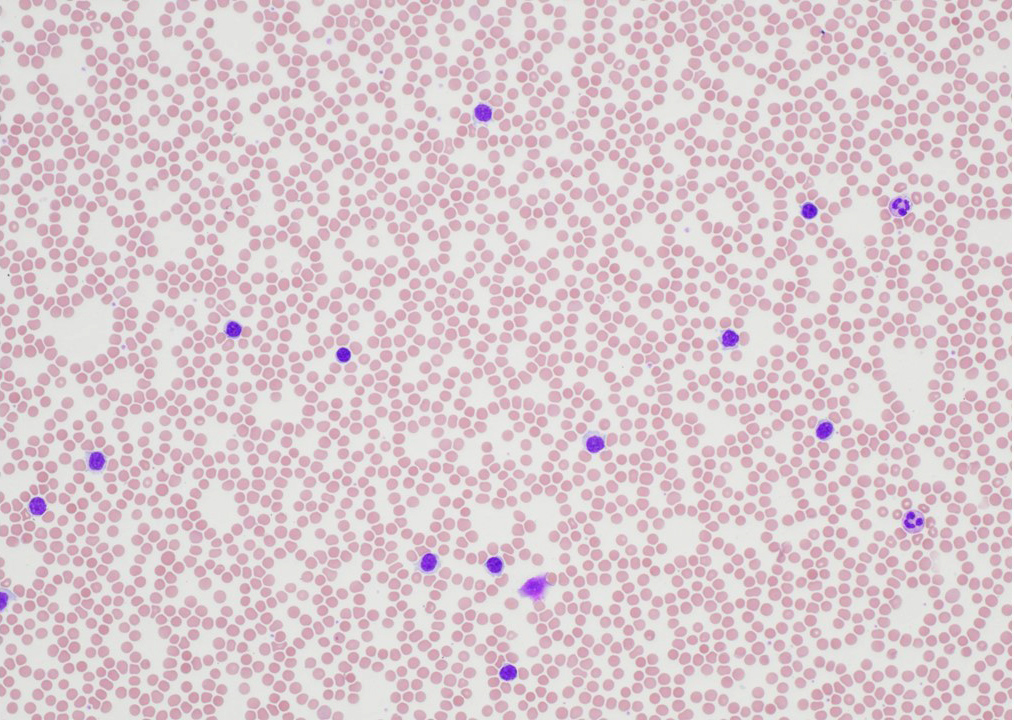
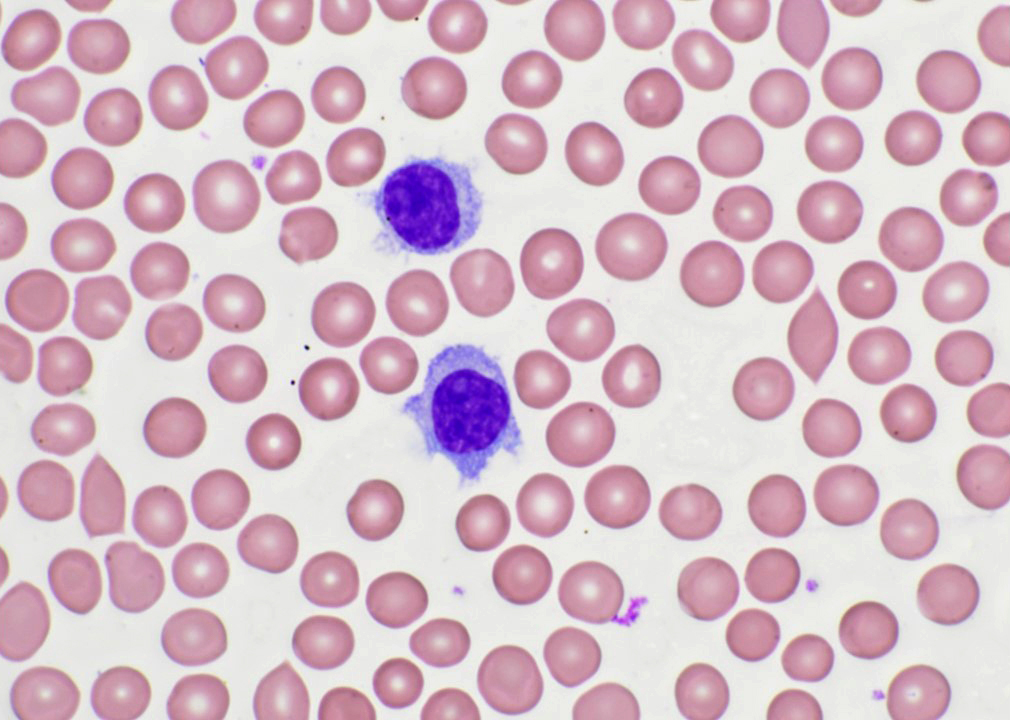
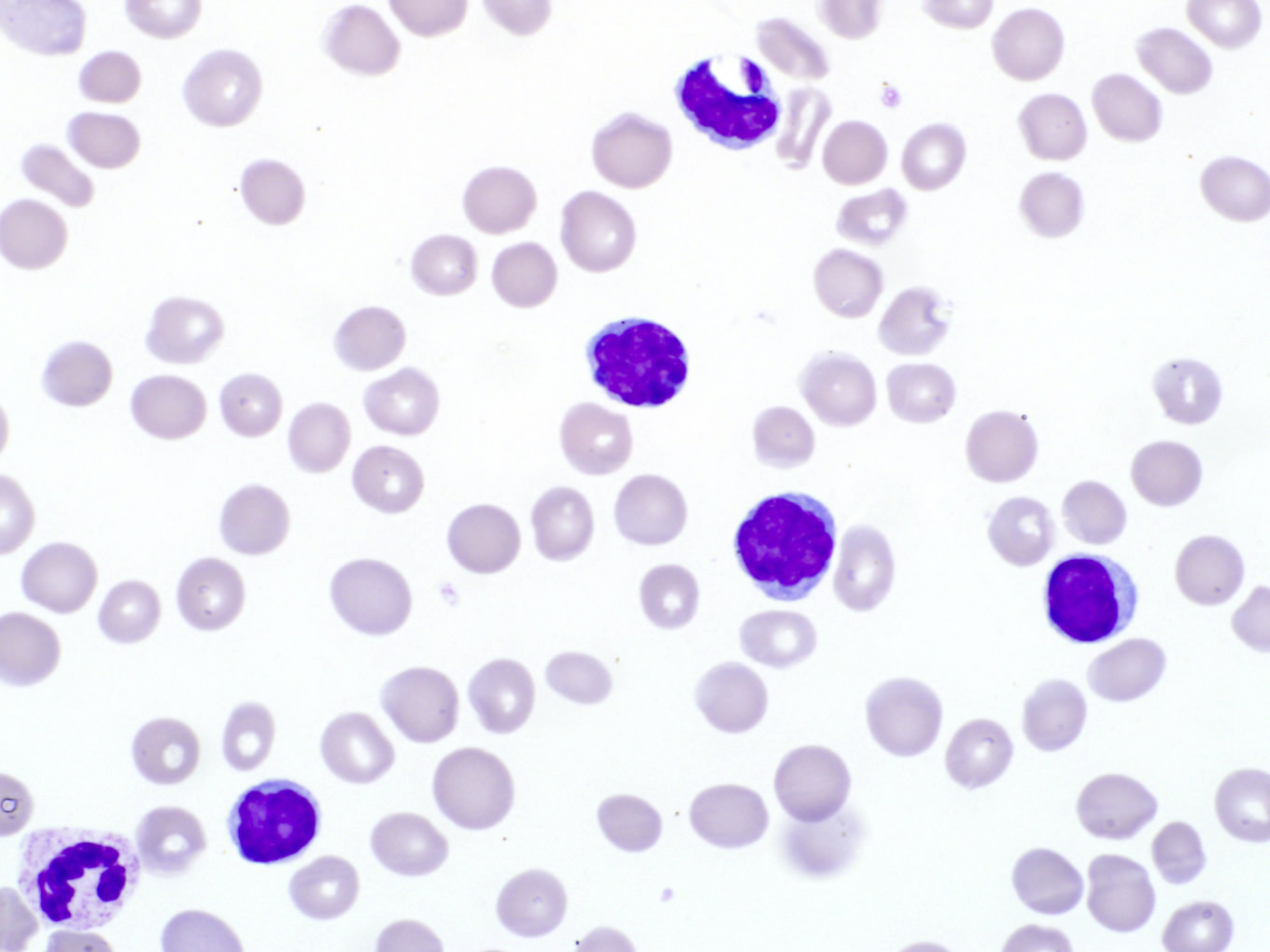
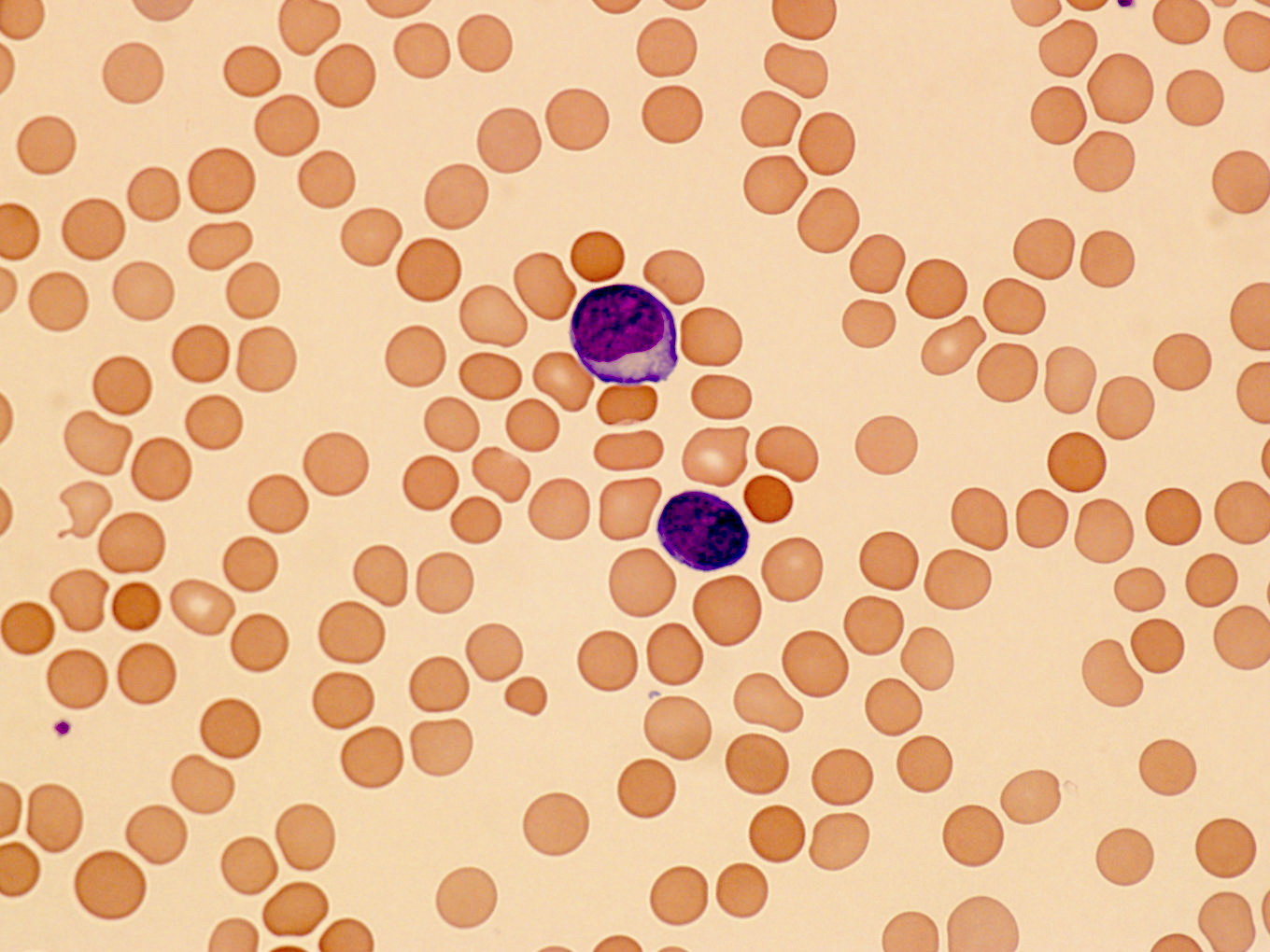
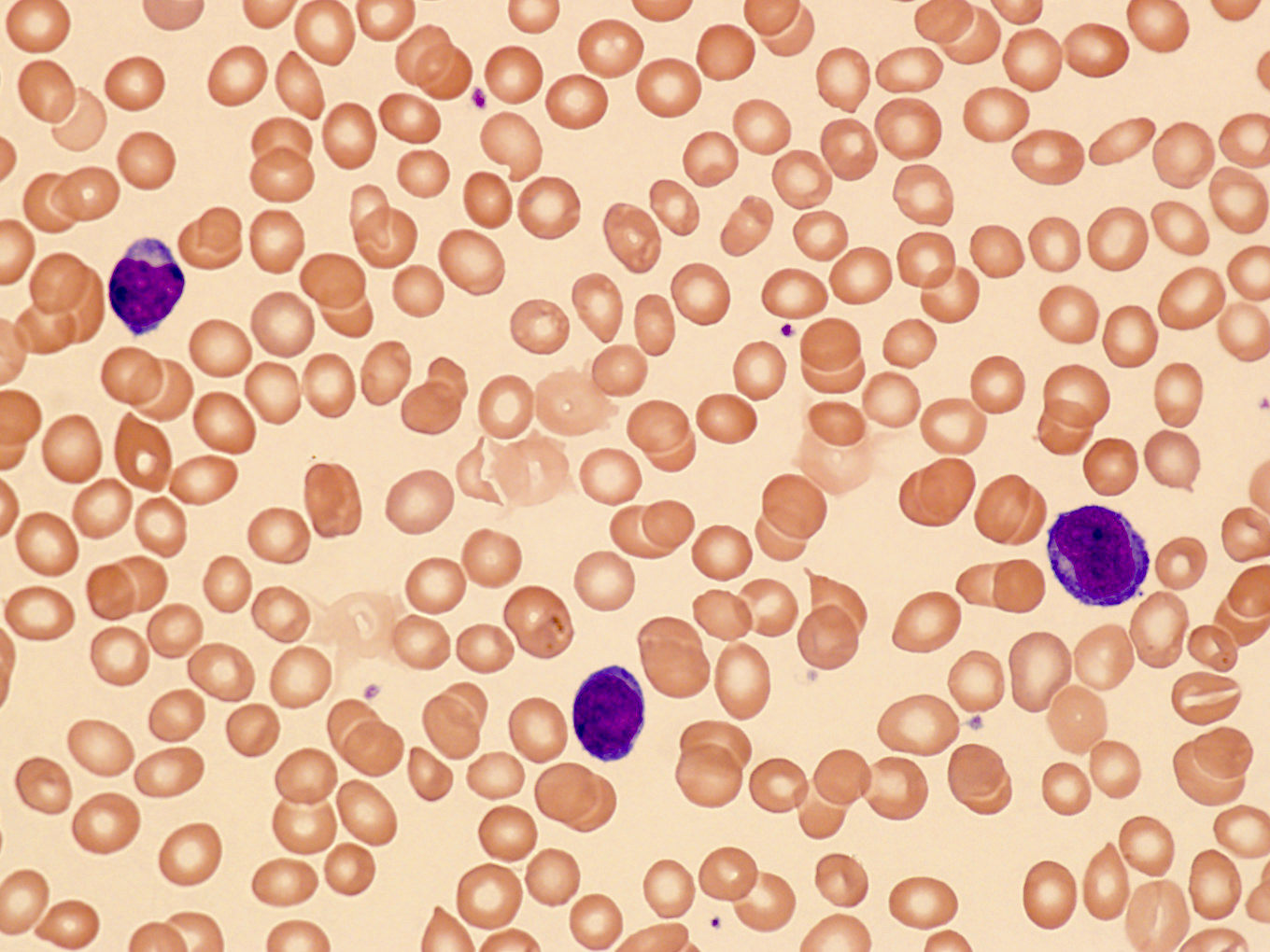
ATLL
Aggressive NK cell leukemia
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, ALK negative
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, ALK positive
Burkitt lymphoma
CHL lymphocyte depleted
CHL lymphocyte rich
CHL mixed cellularity
CLL / SLL
Classic Hodgkin lymphoma
Composite lymphoma
DLBCL / high grade B cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 rearrangements
DLBCL, NOS
DLBCL-primary testicular
EBV related lymphoid proliferations
EBV+ DLBCL
EBV+ mucocutaneous ulcer
EBV+ nodal T and NK cell lymphoma
Enteropathy associated T cell lymphoma
Extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma
Fibrin associated large B cell lymphoma
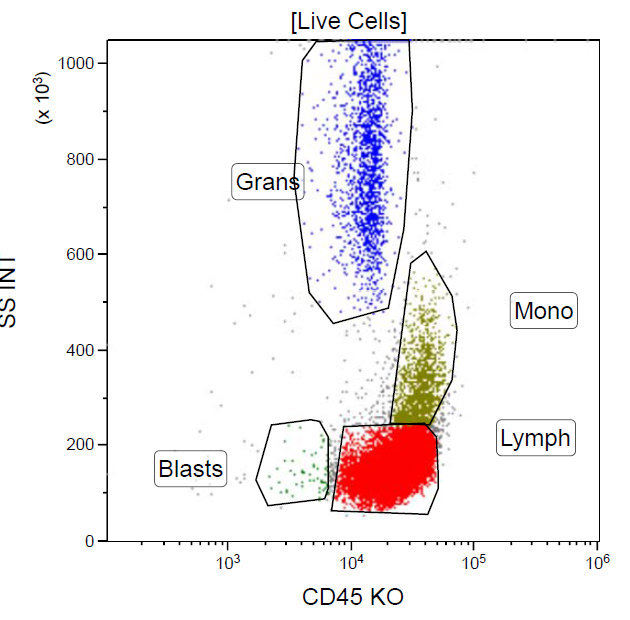
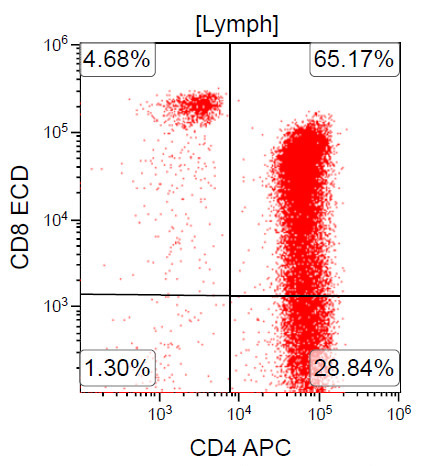
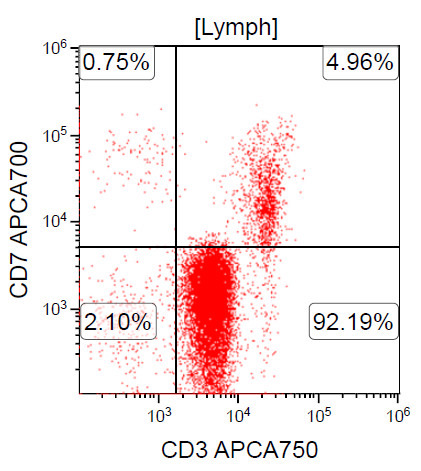
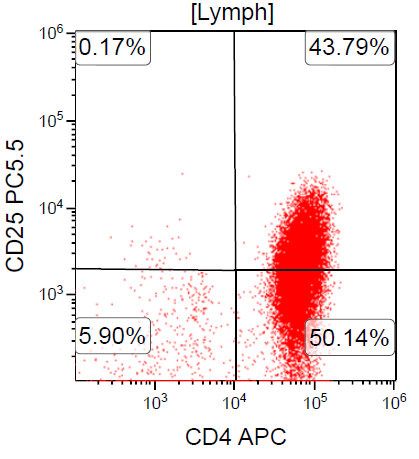
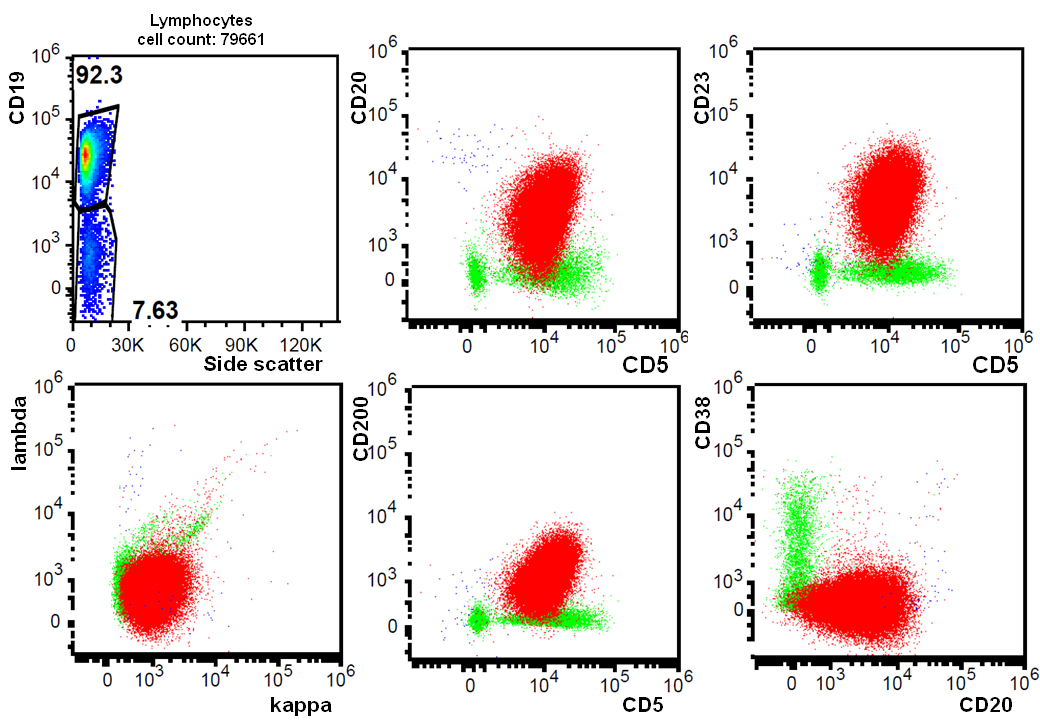
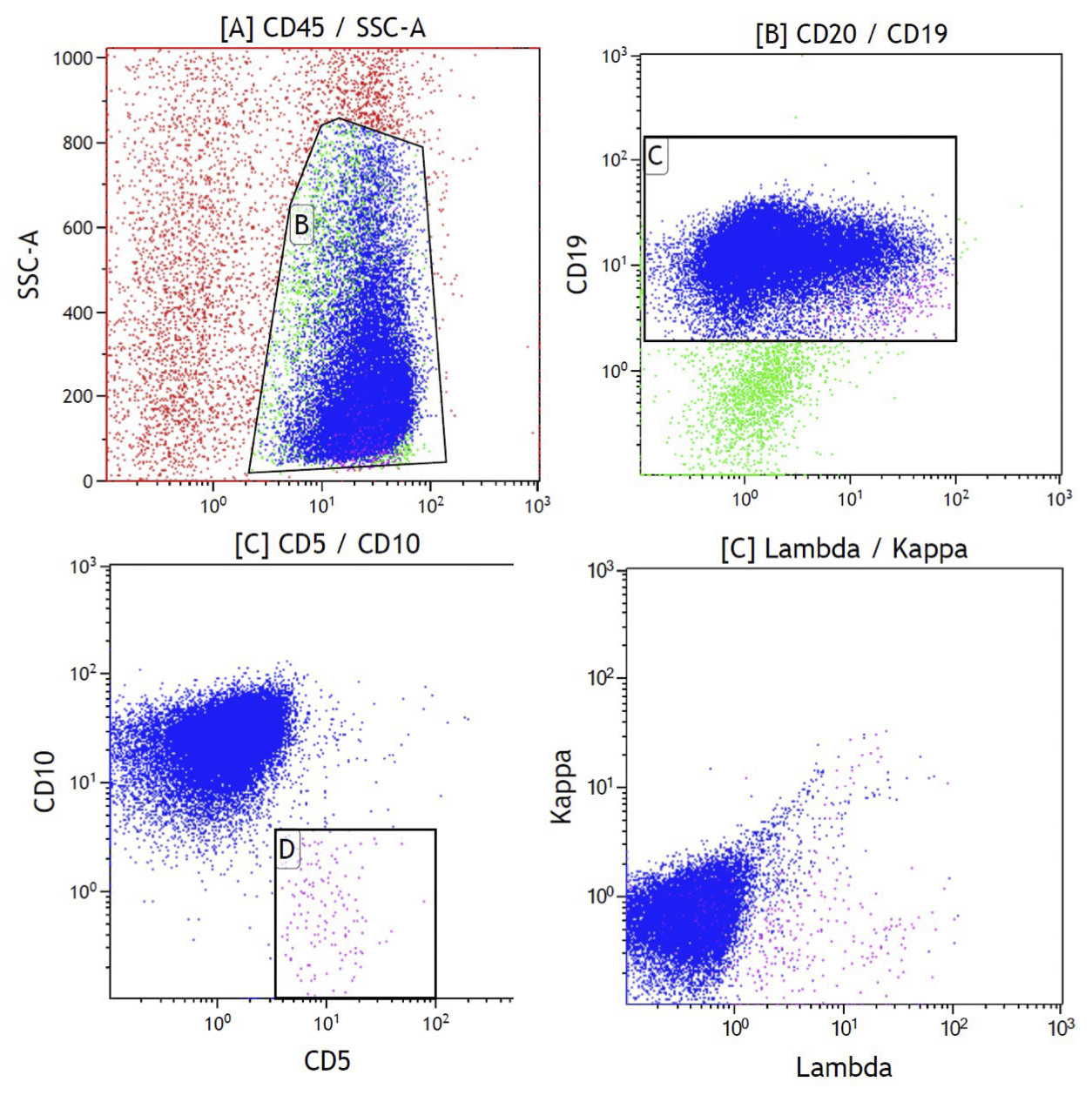
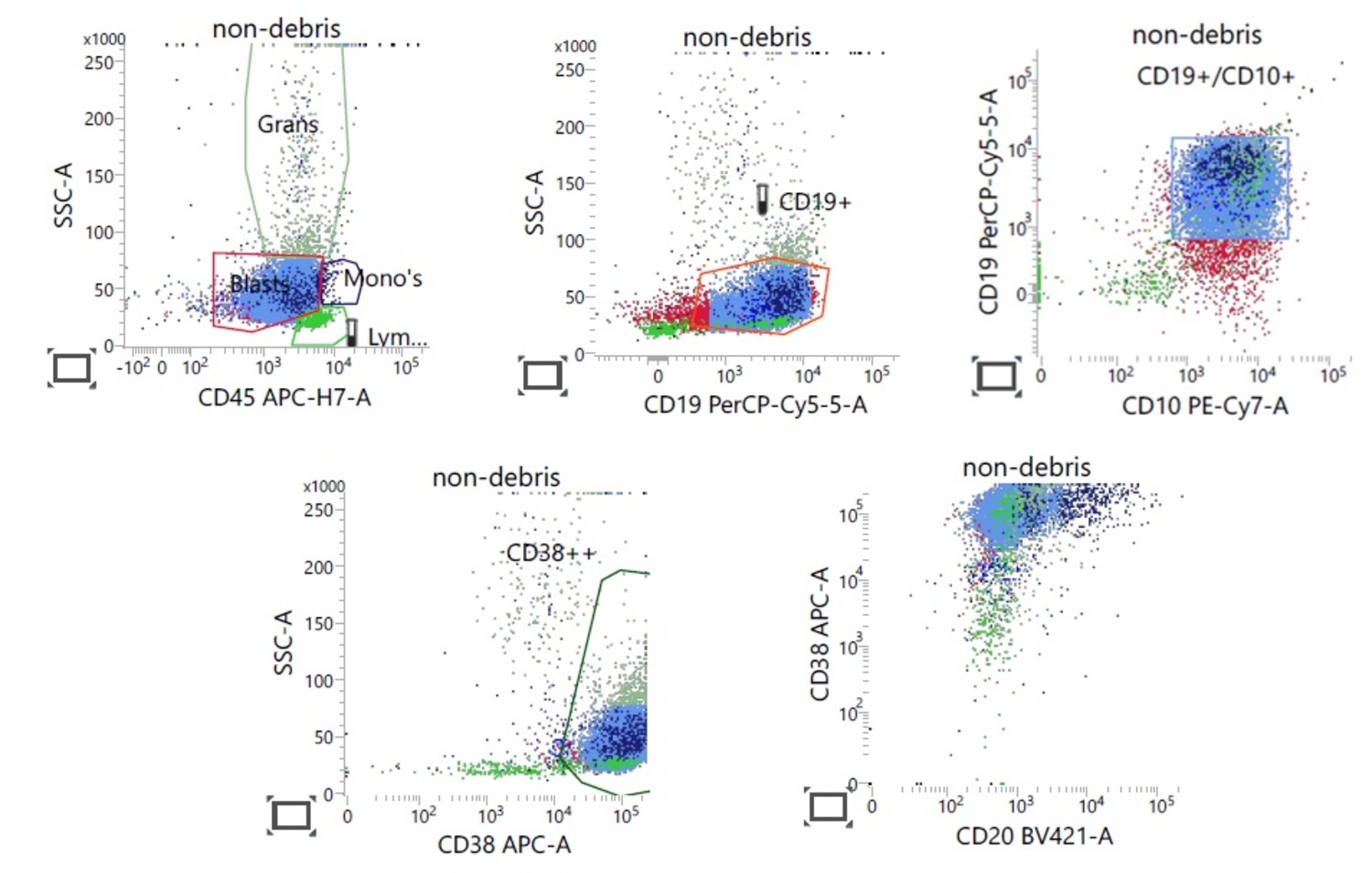
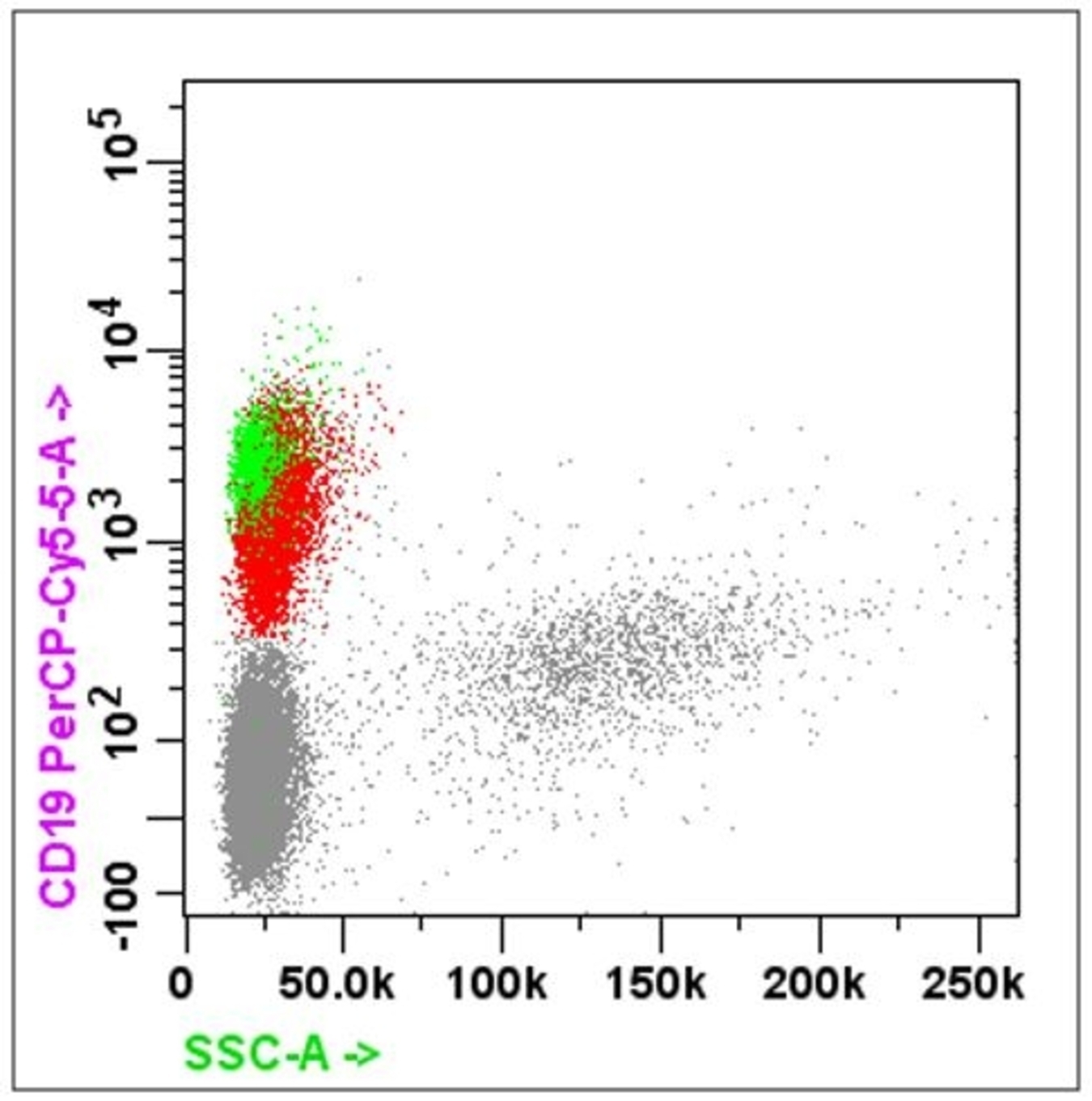
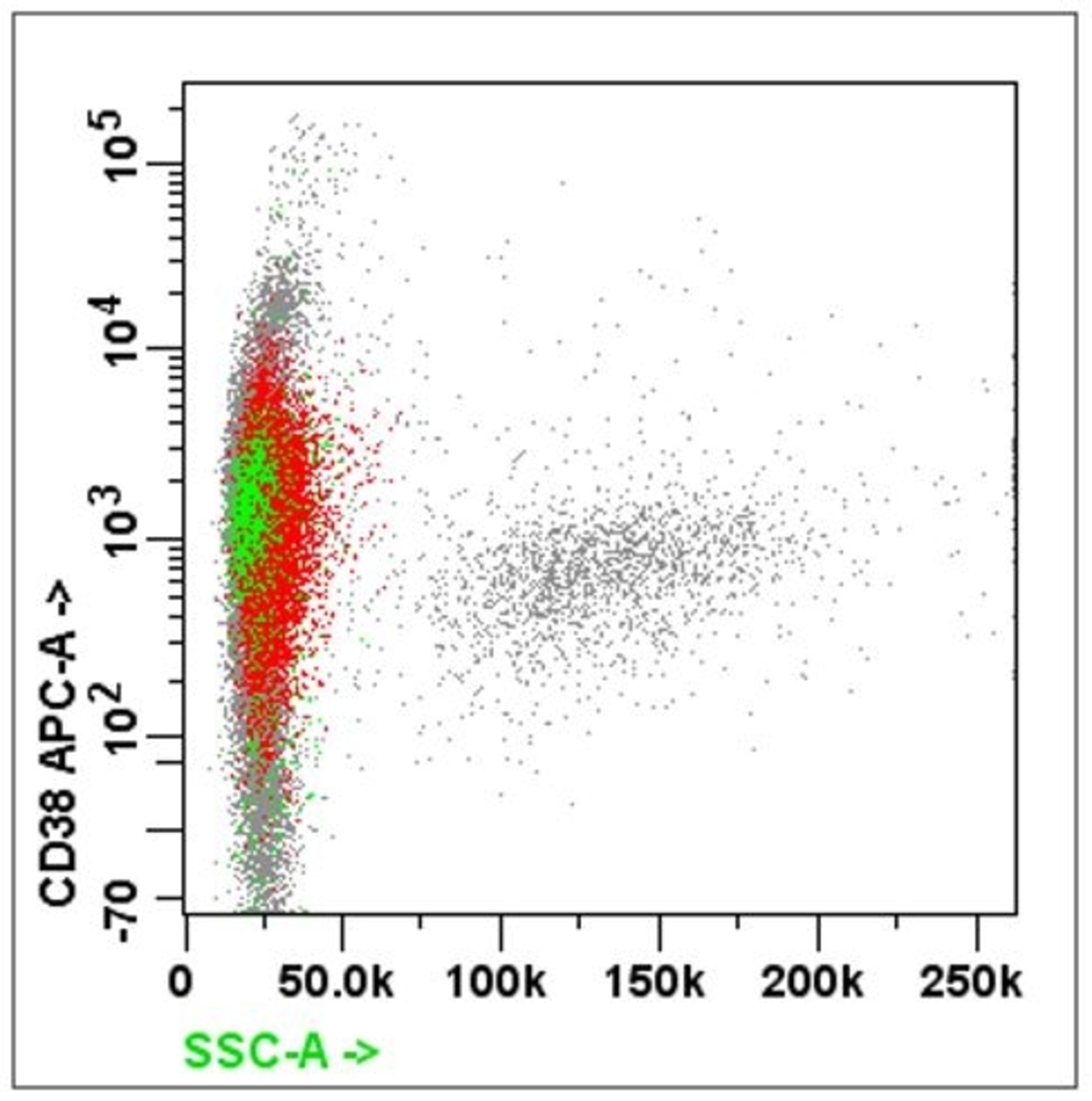
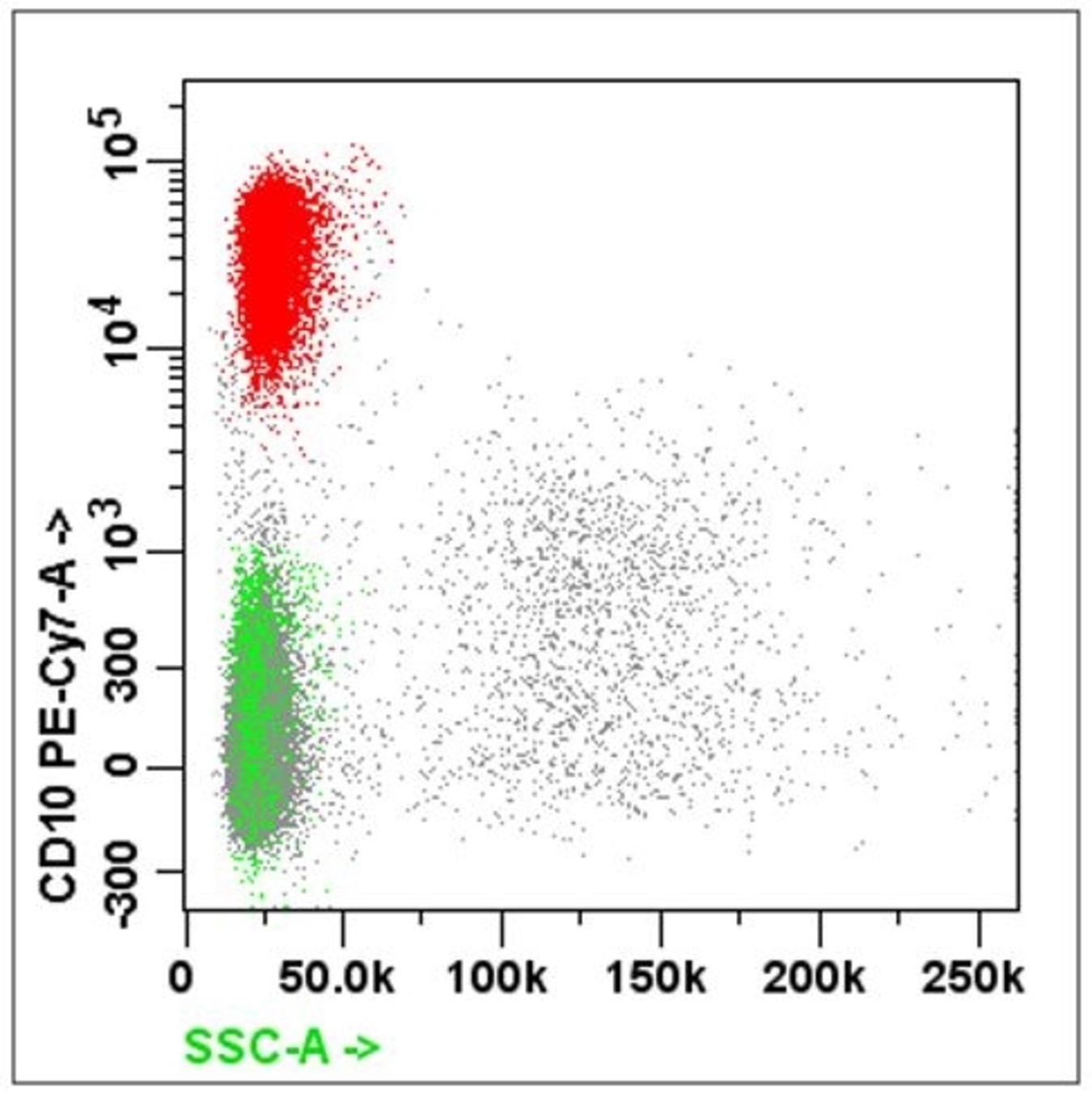
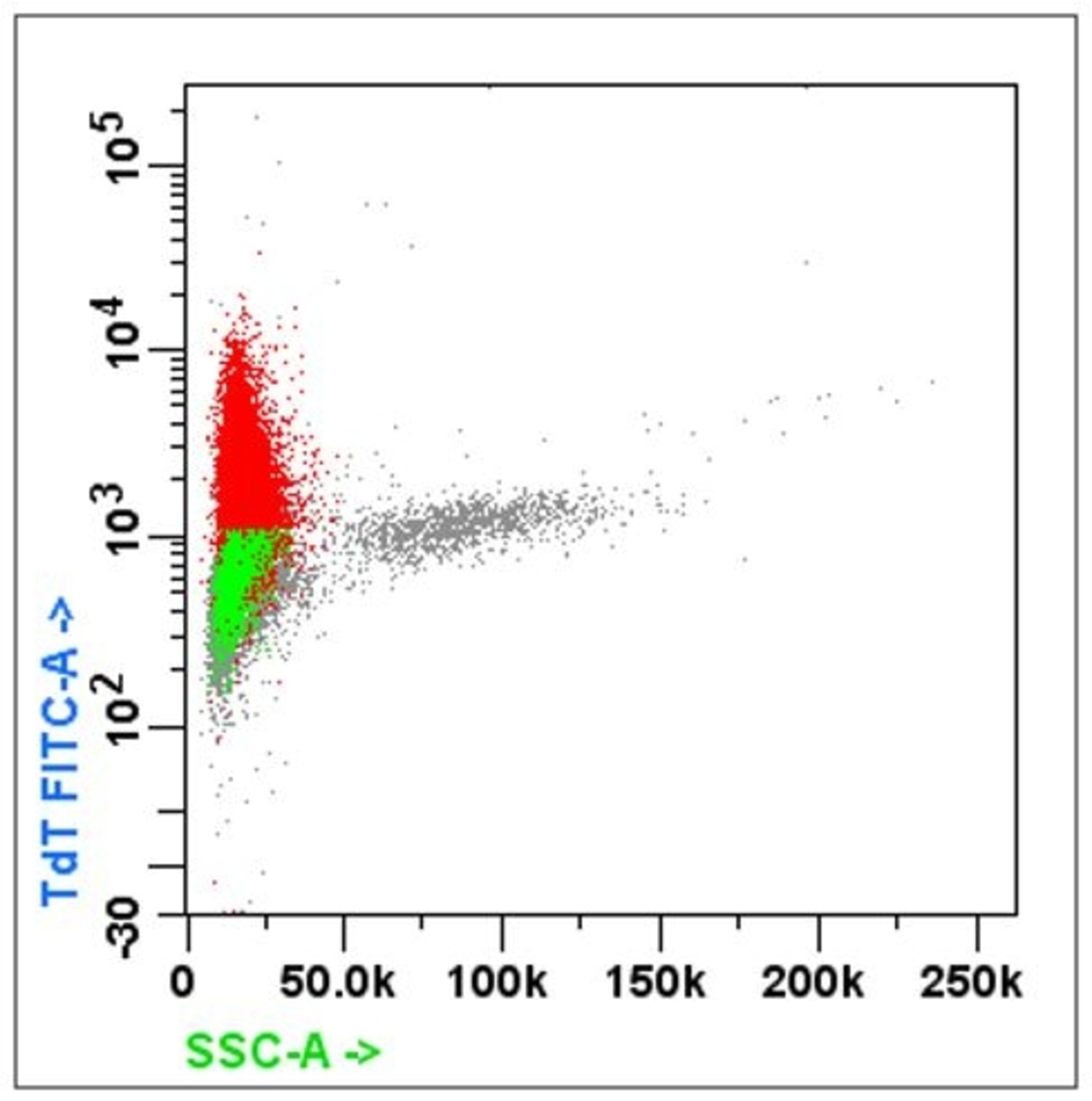
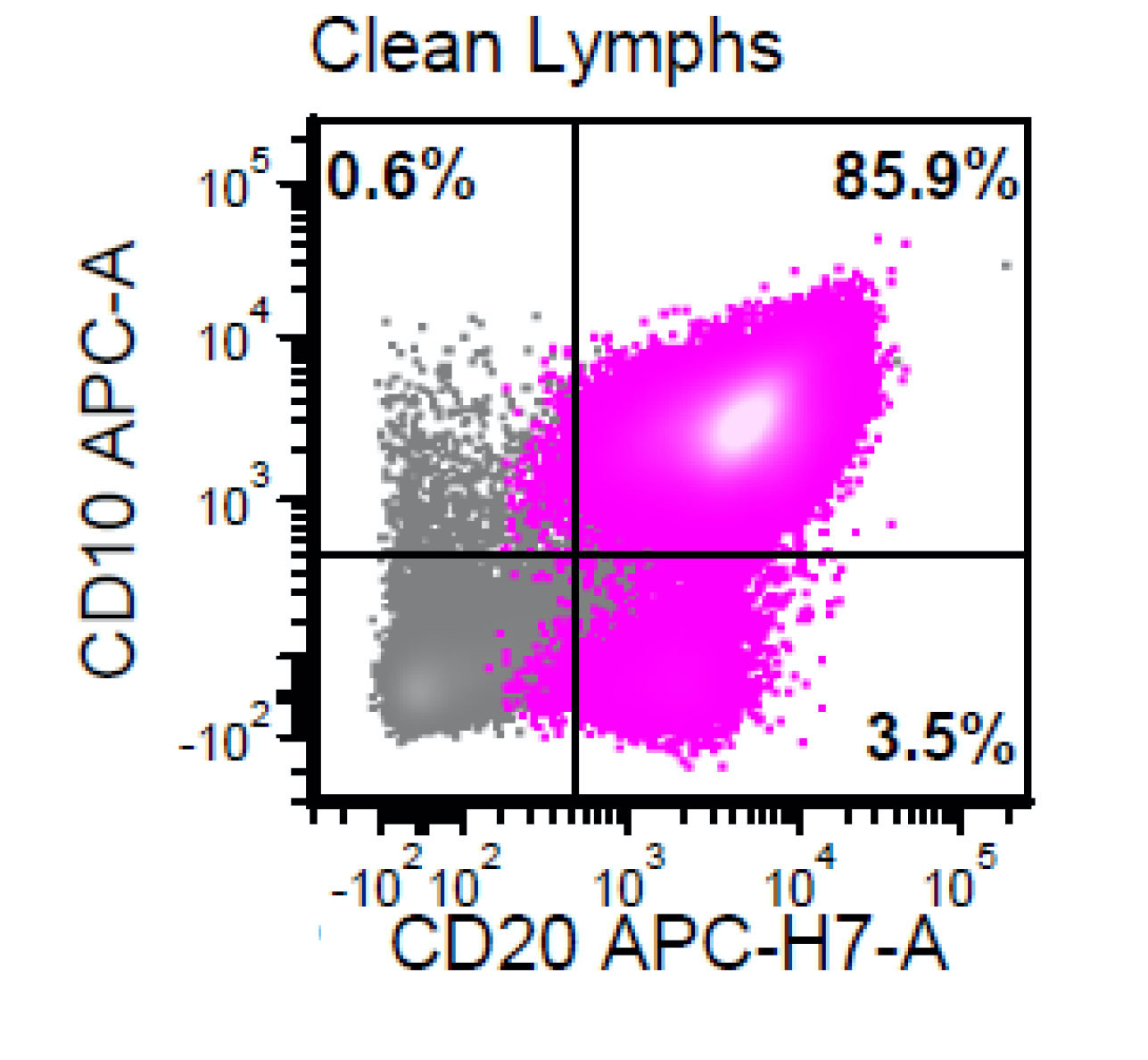
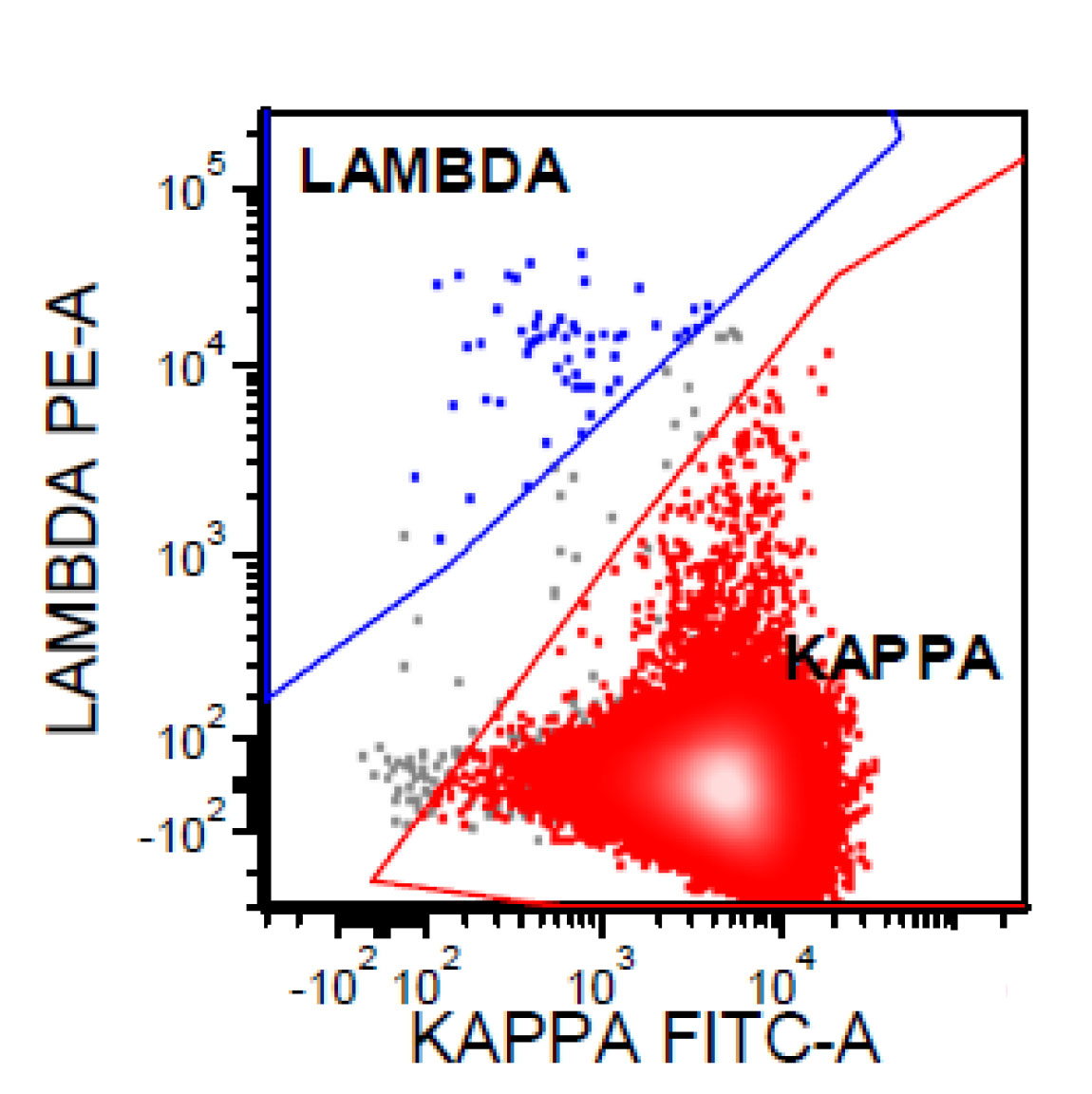
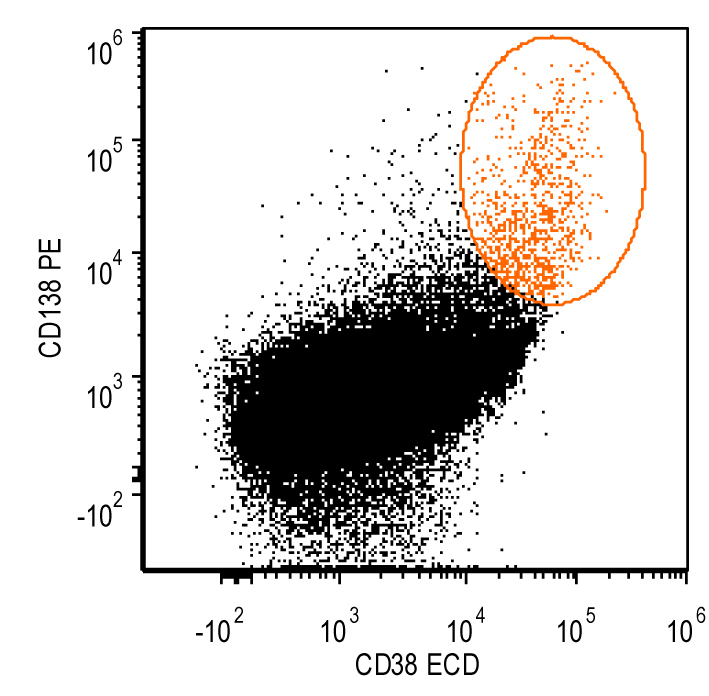
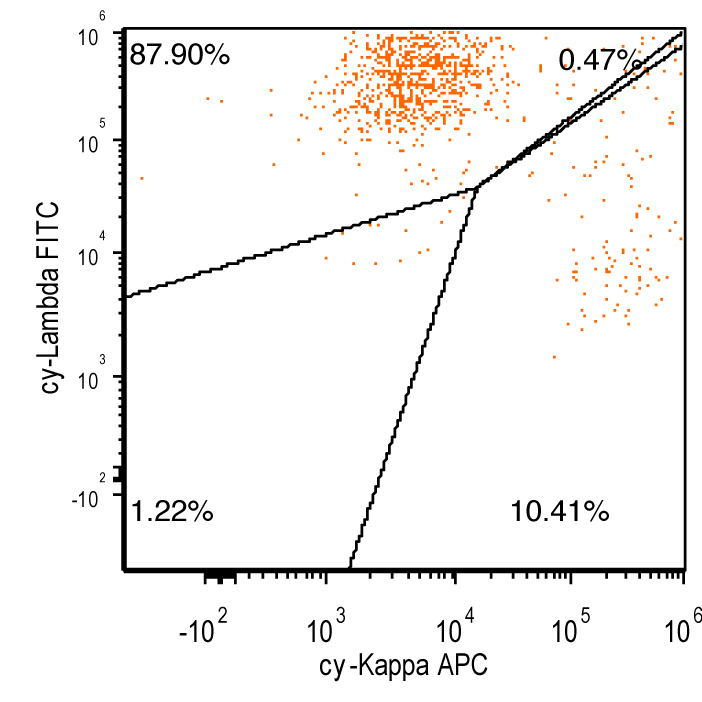
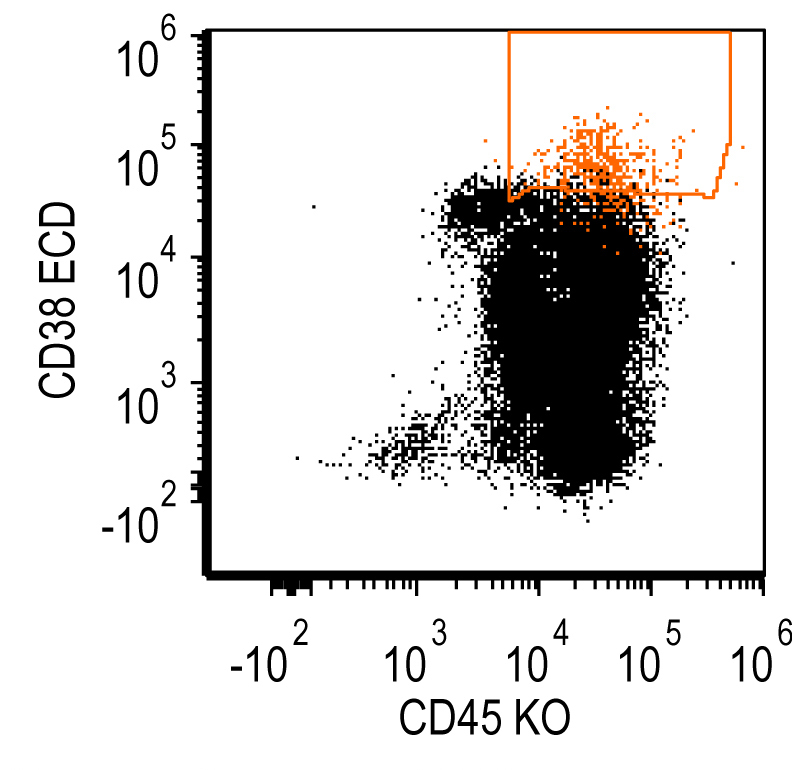
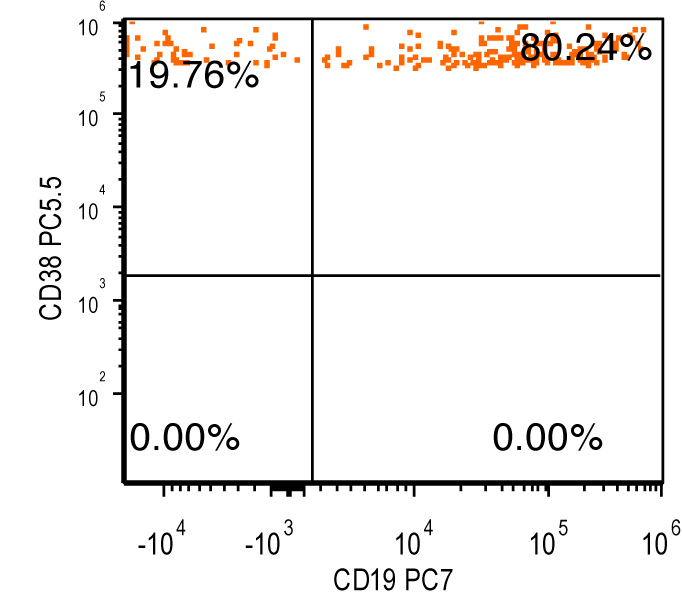
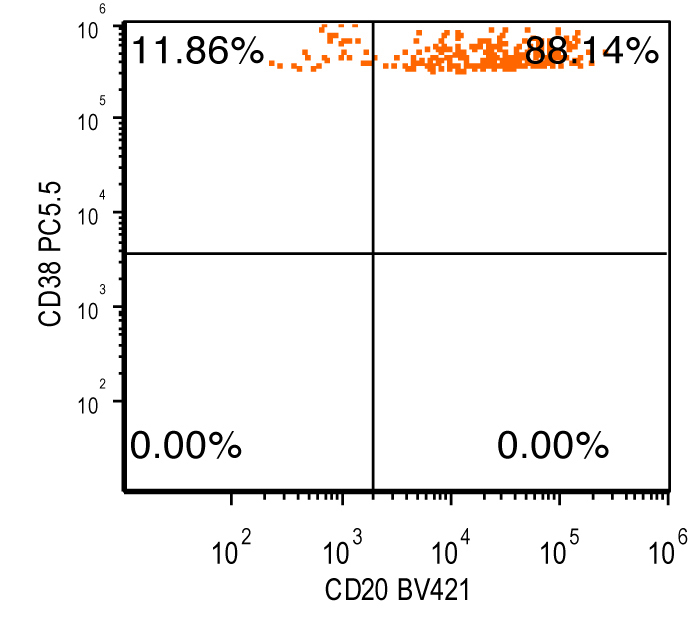
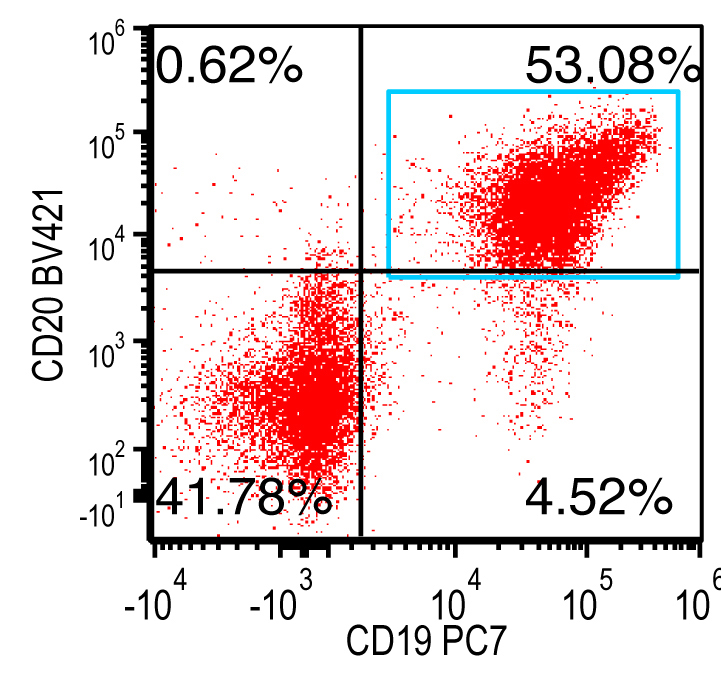
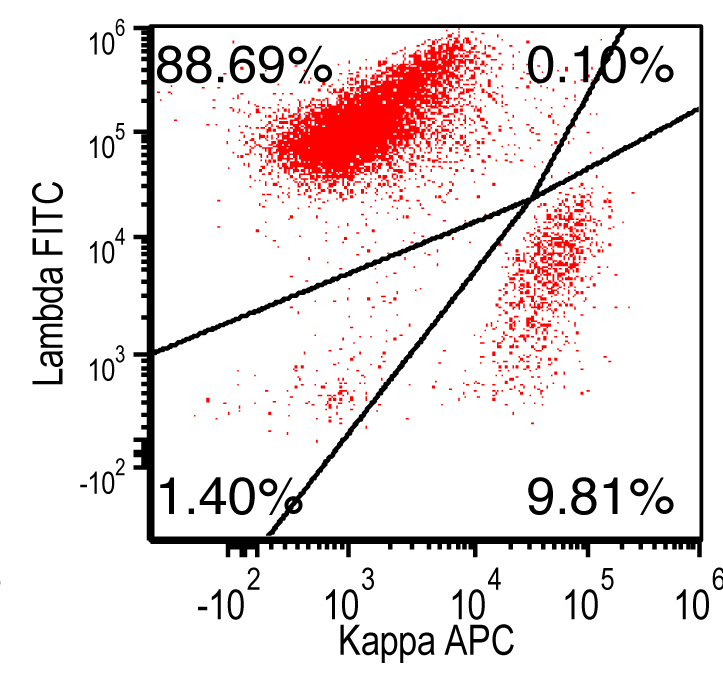
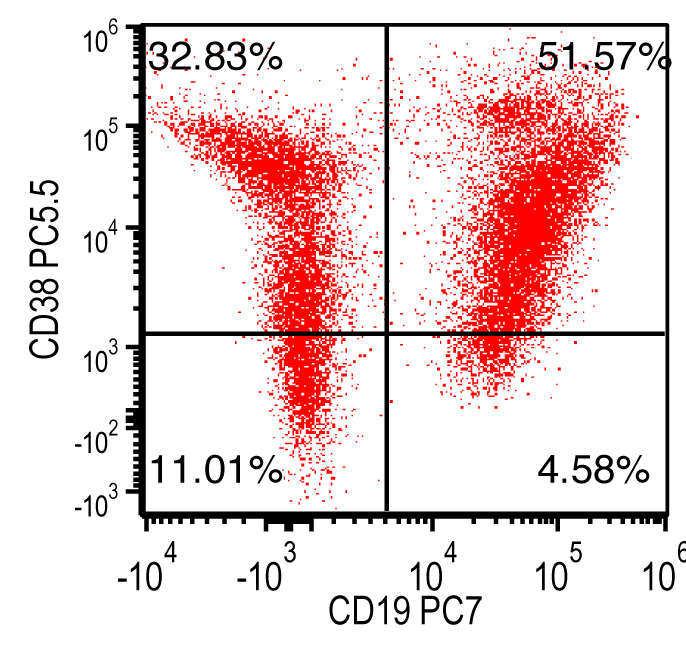
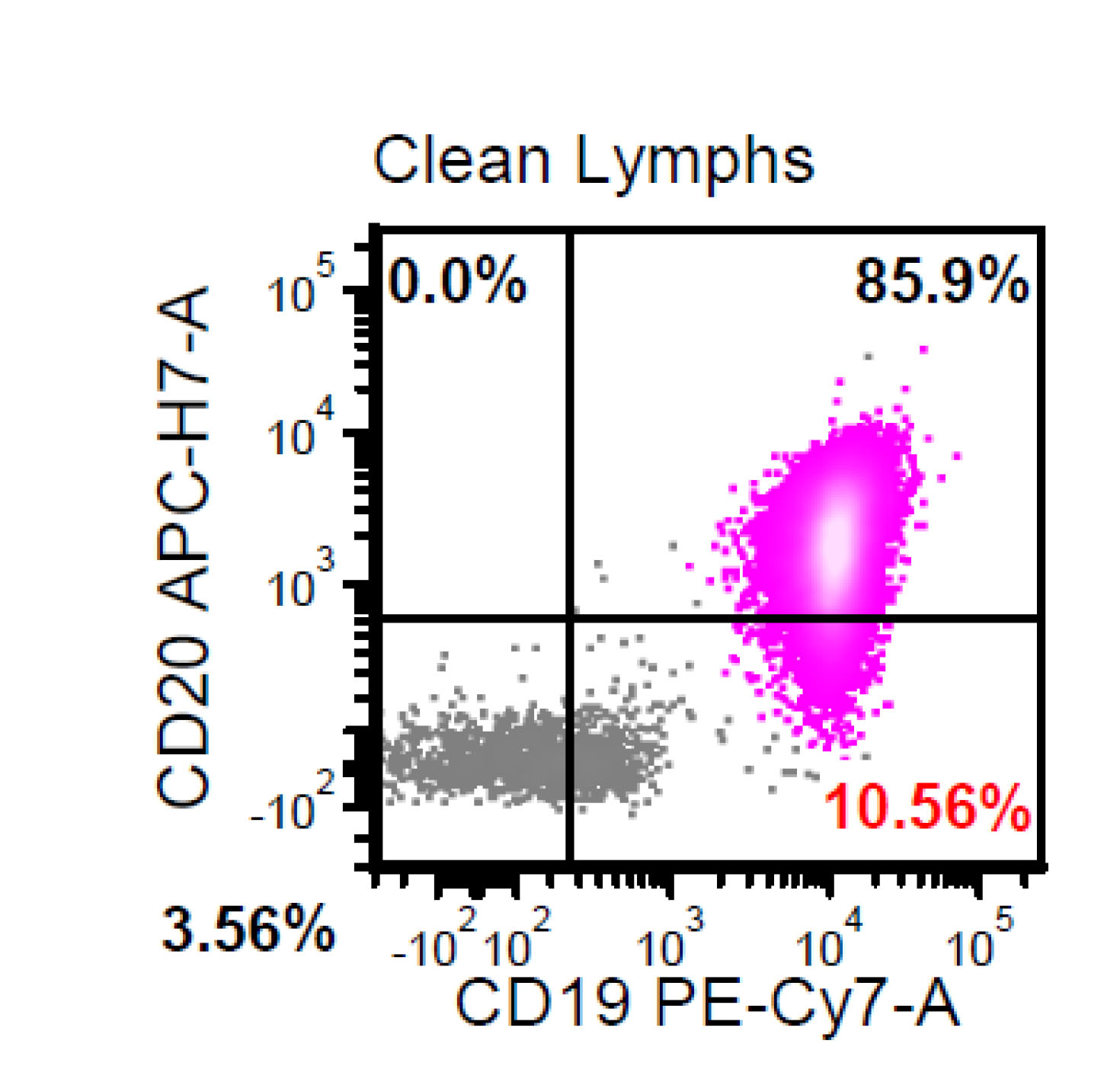
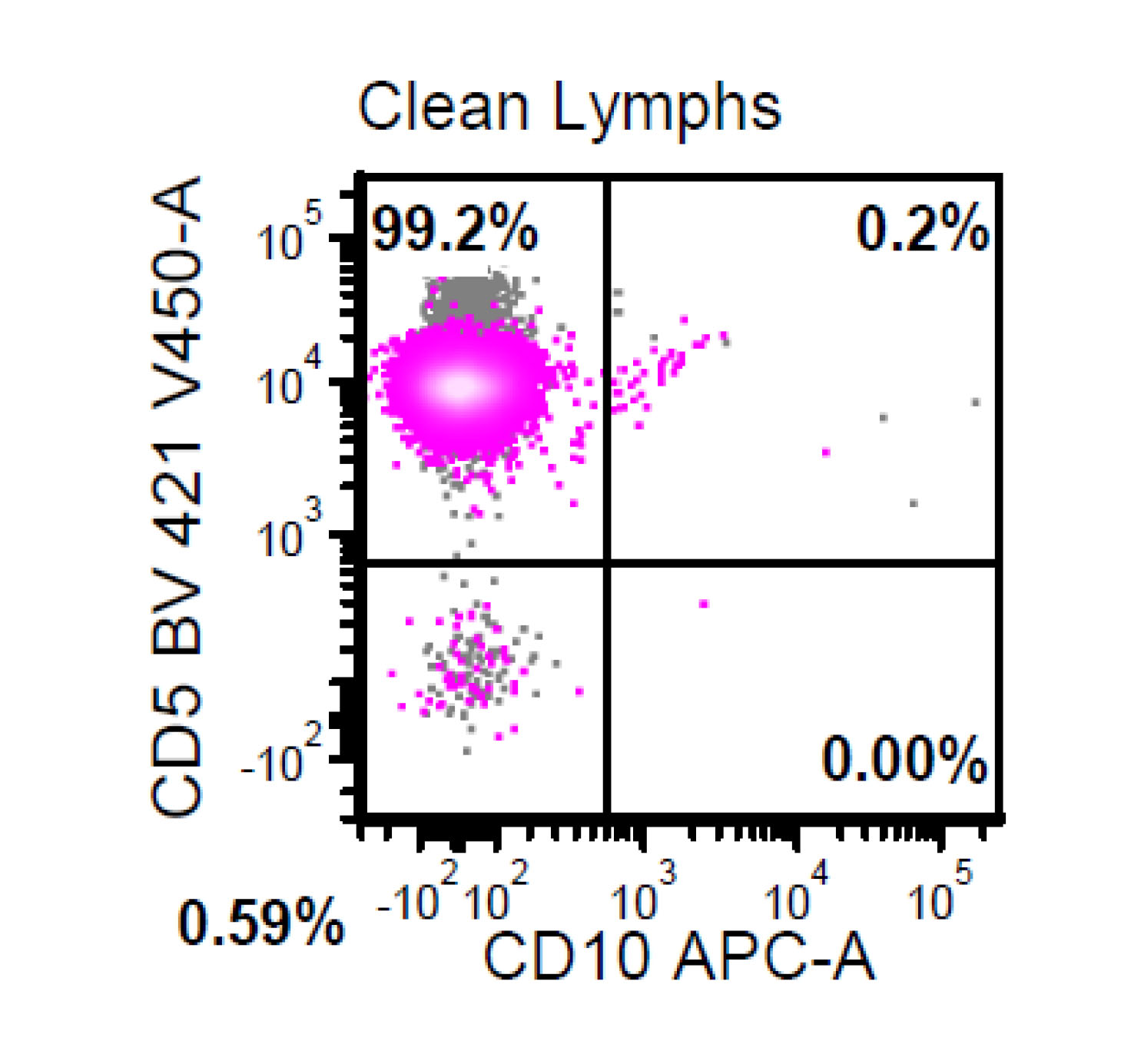
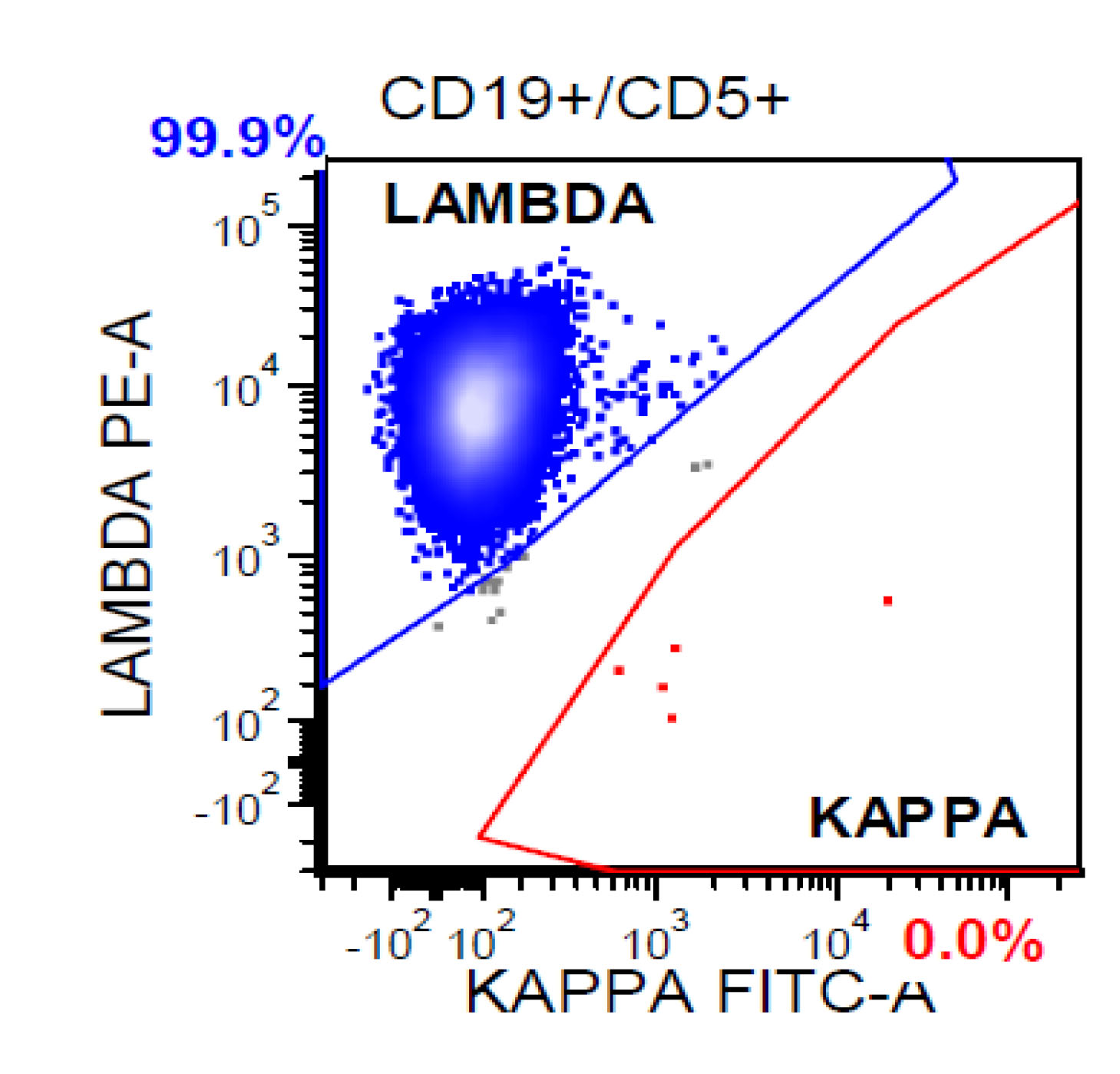
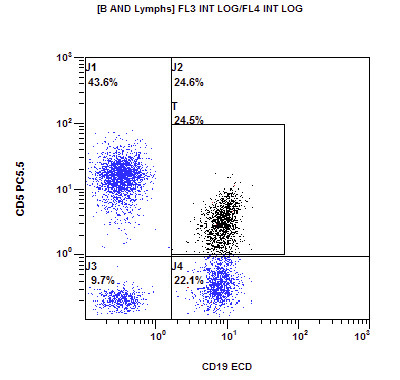
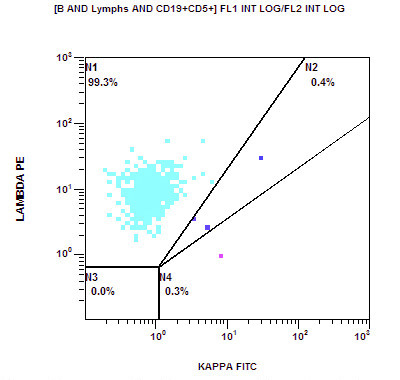
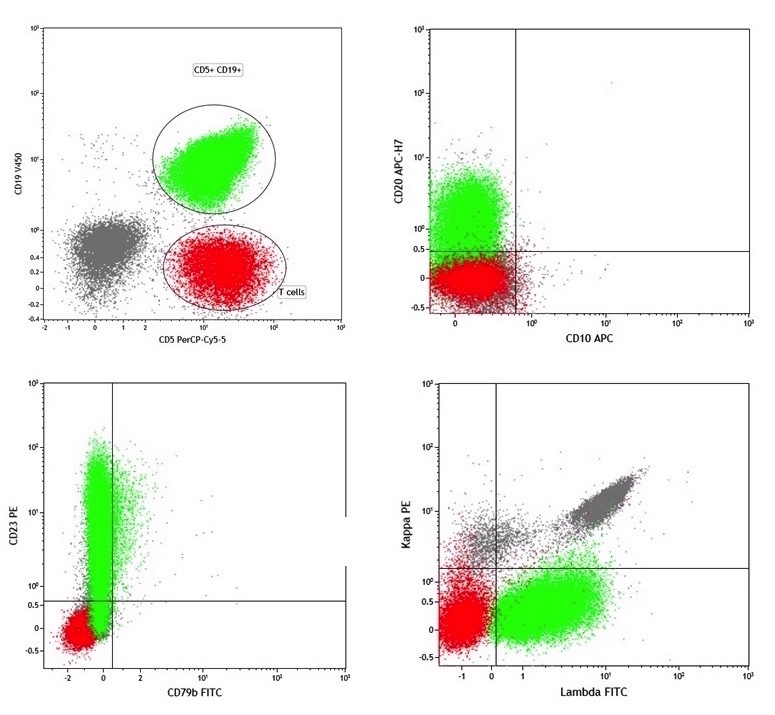
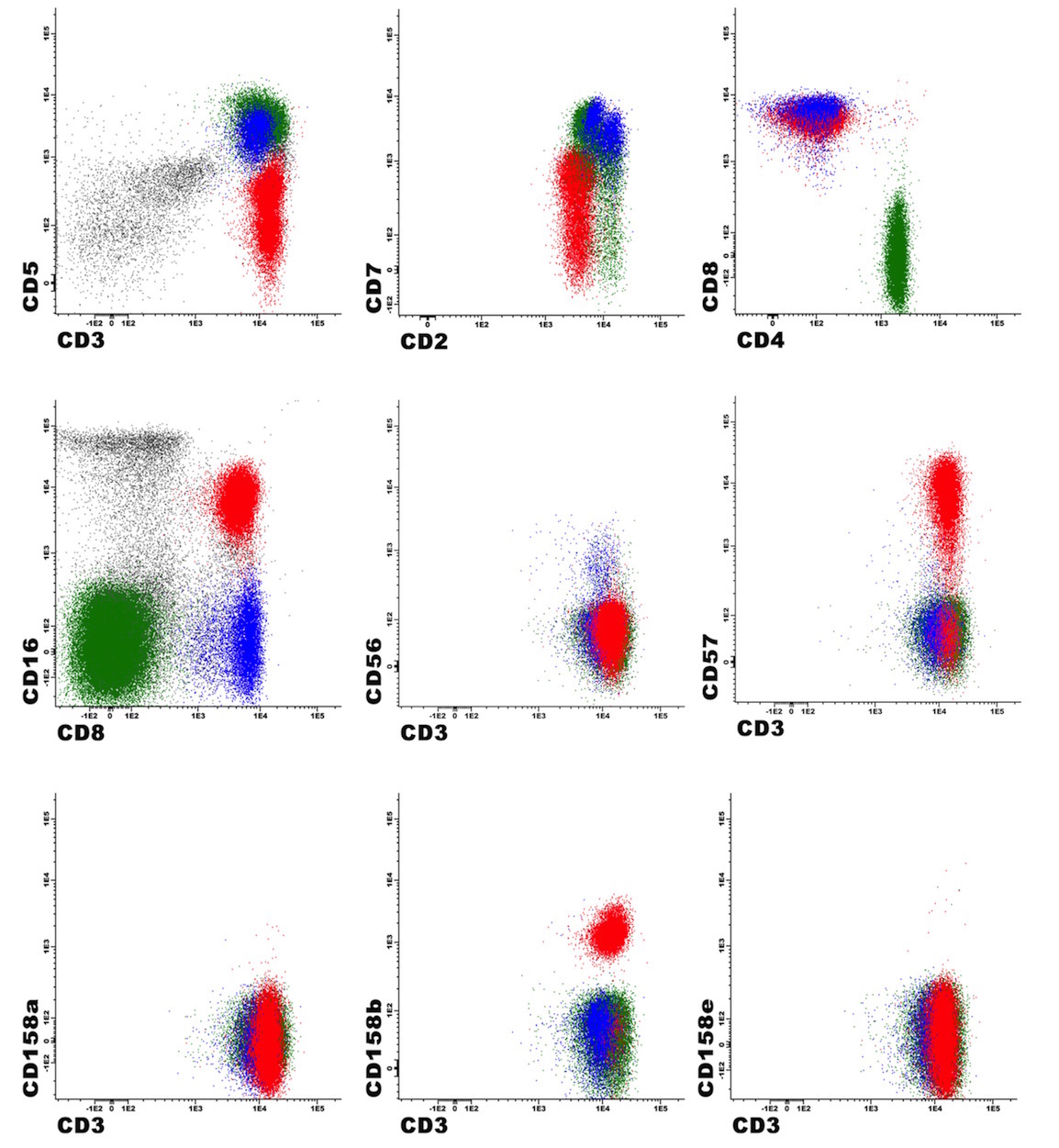
Flow cytometry
Fluid overload associated LBCL
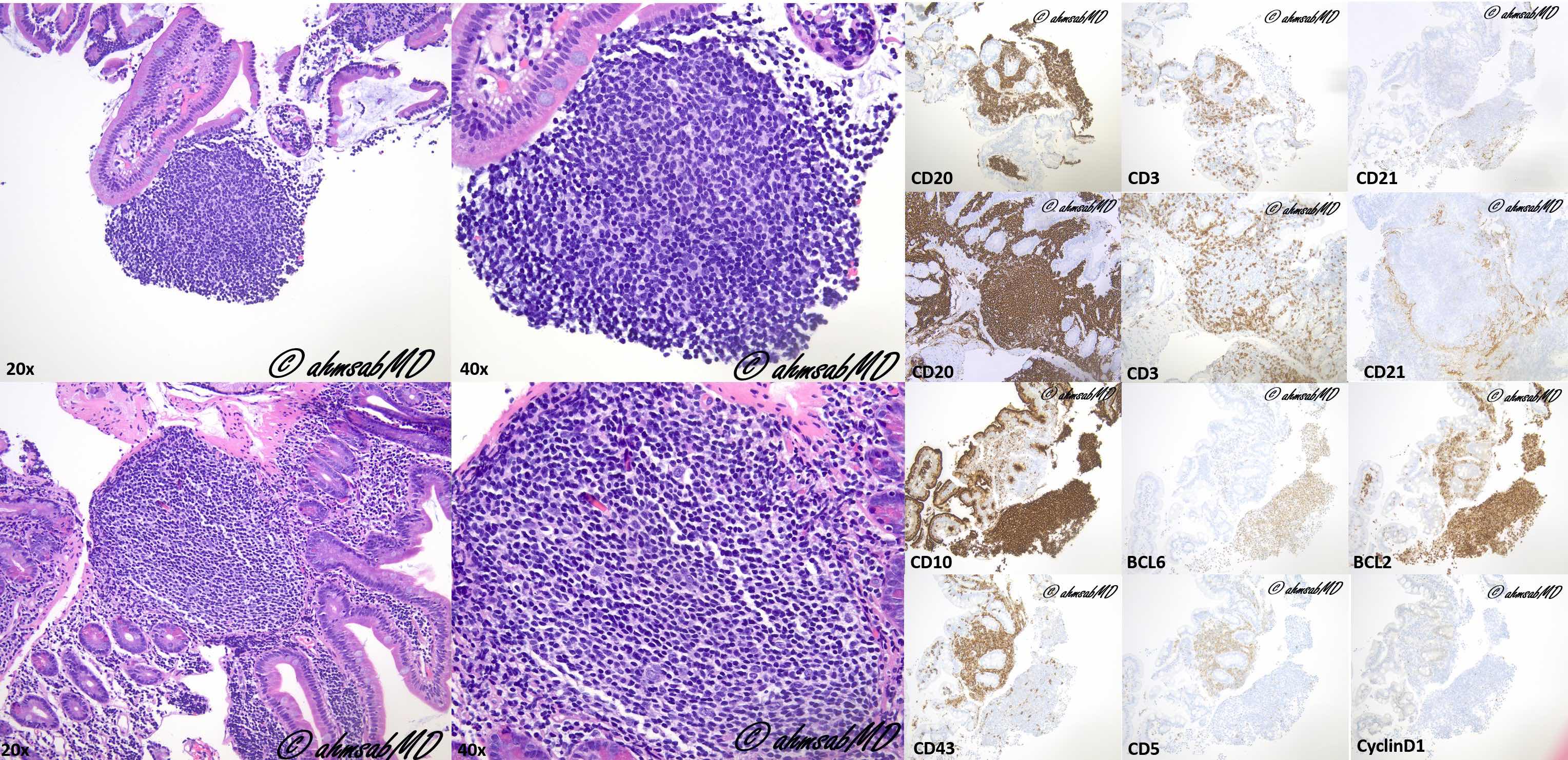
Follicular lymphoma-duodenal type
Follicular-usual
HHV8 positive DLBCL, NOS
HHV8 positive germinotropic lymphoproliferative disorder
Hairy cell leukemia
Hepatosplenic T cell lymphoma
High grade B cell lymphoma with 11q aberrations
High grade B cell lymphoma, NOS
In situ follicular B cell neoplasm
In situ mantle cell neoplasm
Inborn error of immunity-associated lymphoid proliferations and lymphomas
Indolent NK cell lymphoproliferative disease of the GI tract
Indolent T cell lymphoma of the GI tract
Intestinal T cell lymphoma, NOS
Intravascular LBCL
LBCL with IRF4 rearrangement
Lymphomas arising in immune deficiency / dysregulation
Lymphomatoid granulomatosis
Lymphomatoid papulosis
Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma
MALT-marginal zone
MCL-aggressive variants
MCL-classic
MCL-leukemic nonnodal
Marginal zone-nodal
Mediastinal gray zone lymphoma
Monoclonal B cell lymphocytosis
Monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal
Mycosis fungoides subtypes
NK large granular lymphocytic leukemia
Nodal T follicular helper cell lymphoma, NOS
Nodal T follicular helper cell lymphoma, follicular type
Nodal T follicular helper lymphoma, angioimmunoblastic type
Nodular lymphocyte predominant B cell lymphoma / nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma
Nodular lymphocyte predominant B cell lymphoma / nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma
PTLD-classic Hodgkin
PTLD-polymorphic
Pediatric nodal marginal zone lymphoma
Pediatric type follicular lymphoma
Peripheral T cell lymphoma, NOS
Plasmablastic lymphoma
Polymorphic lymphoproliferative disorders arising in immune deficiency / dysregulation
Primary CNS lymphoma
Primary cutaneous CD4+ small or medium T cell lymphoproliferative disorder
Primary cutaneous CD8+ aggressive epidermotropic cytotoxic T cell lymphoma
Primary cutaneous PTCL, NOS
Primary cutaneous acral CD8+ lymphoproliferative disorder
Primary cutaneous gamma delta
Primary effusion lymphoma
Primary follicular lymphoma-testis
Primary mediastinal
Prolymphocytic leukemia
Richter syndrome
Sézary syndrome
Severe mosquito bite allergy
Splenic B cell leukemia / lymphoma
Splenic B cell lymphoma / leukemia with prominent nucleoli
Splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma
Splenic marginal zone lymphoma
Staging-primary cutaneous
Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma
Systemic EBV+ T cell lymphoma of childhood
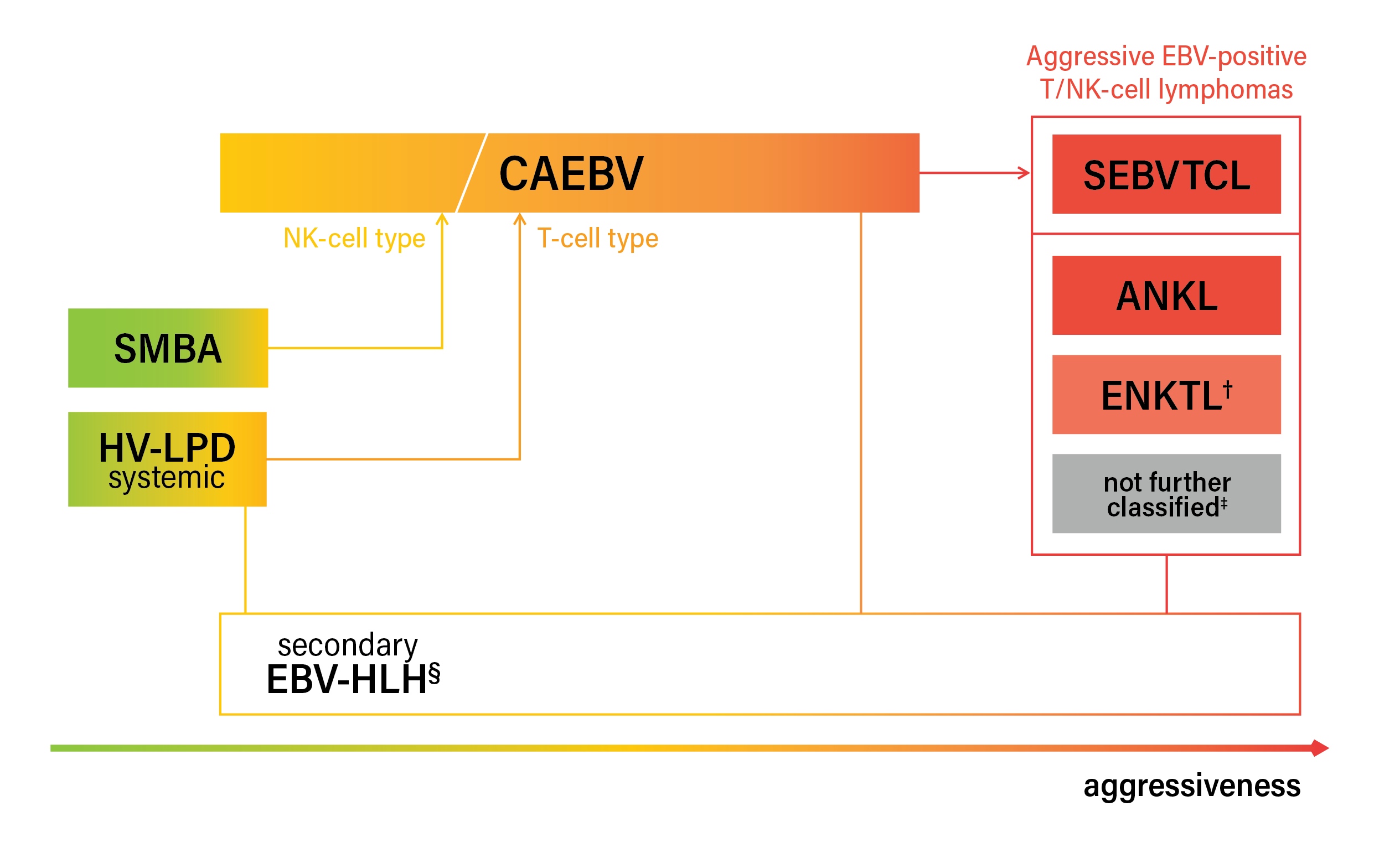
Systemic chronic active EBV disease
T cell / histiocyte rich LBCL
T cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia
T prolymphocytic leukemia
Unusual morphologic patterns of follicular lymphoma
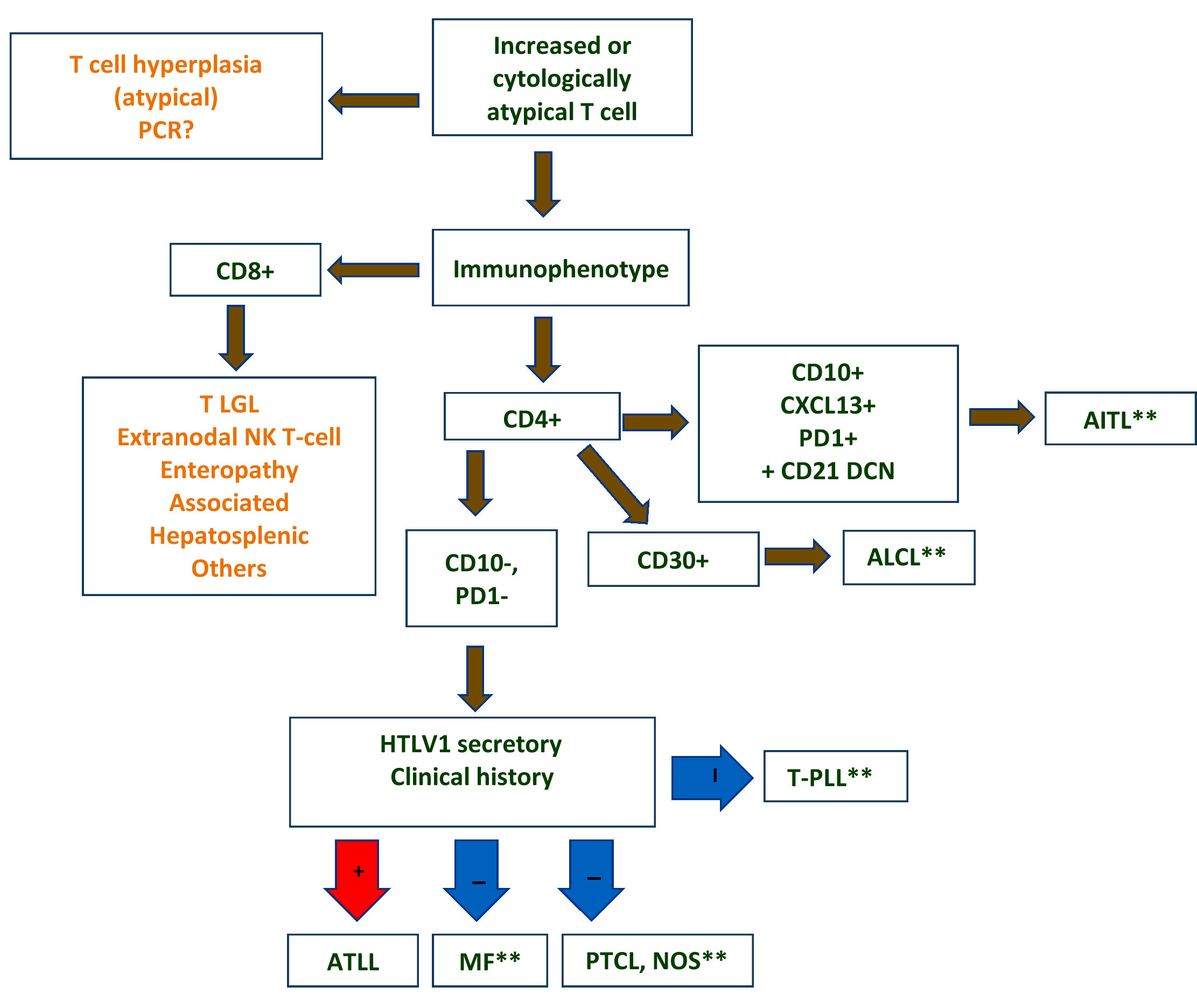
WHO 2016 T/NK cell
WHO 2022 & ICC-B cell
WHO 2022 & ICC-T / NK cellALK+ LBCL
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Marie Therese Manipadam, M.B.B.S., M.D.
ATLL
Diagrams / tables
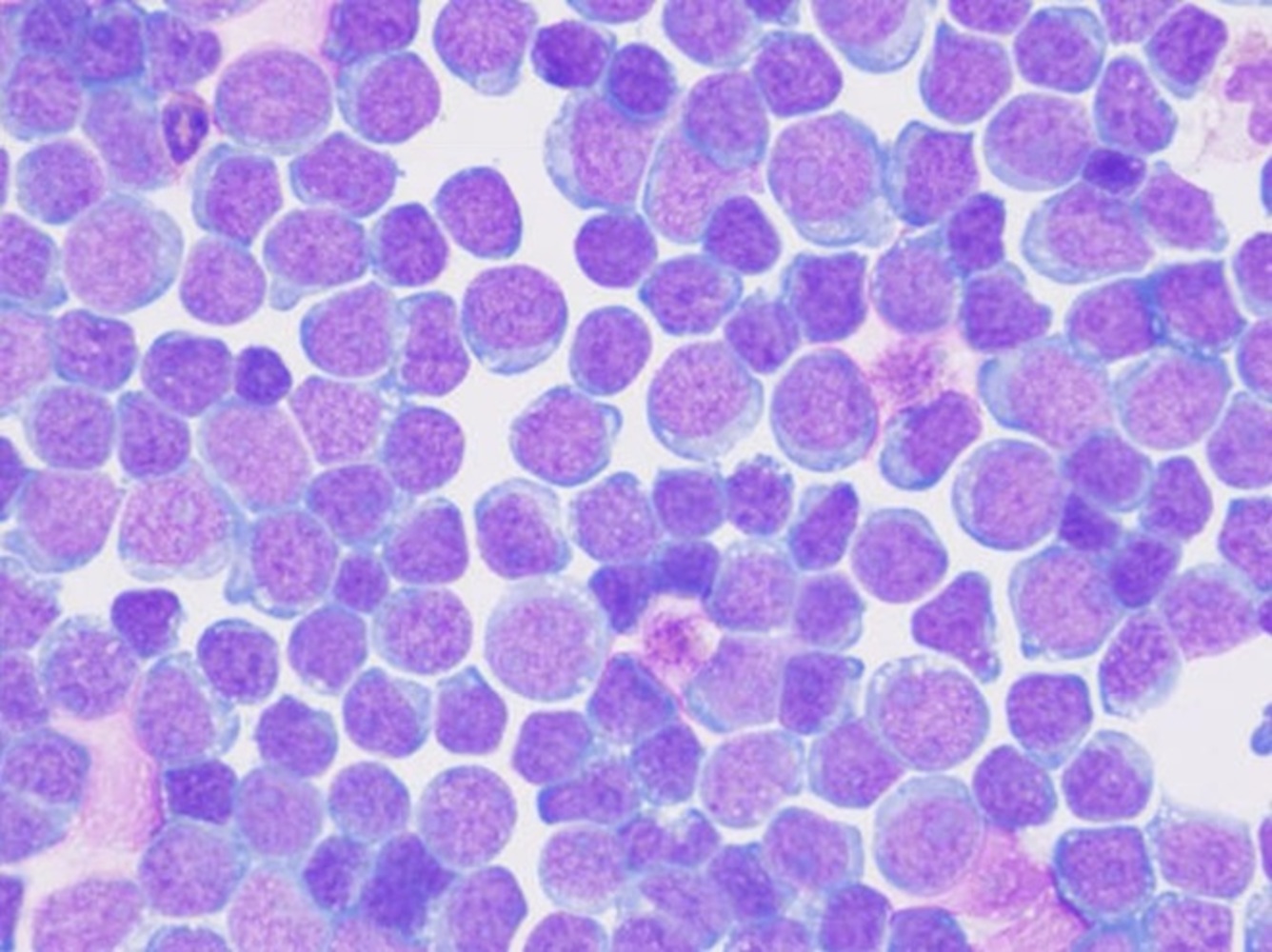
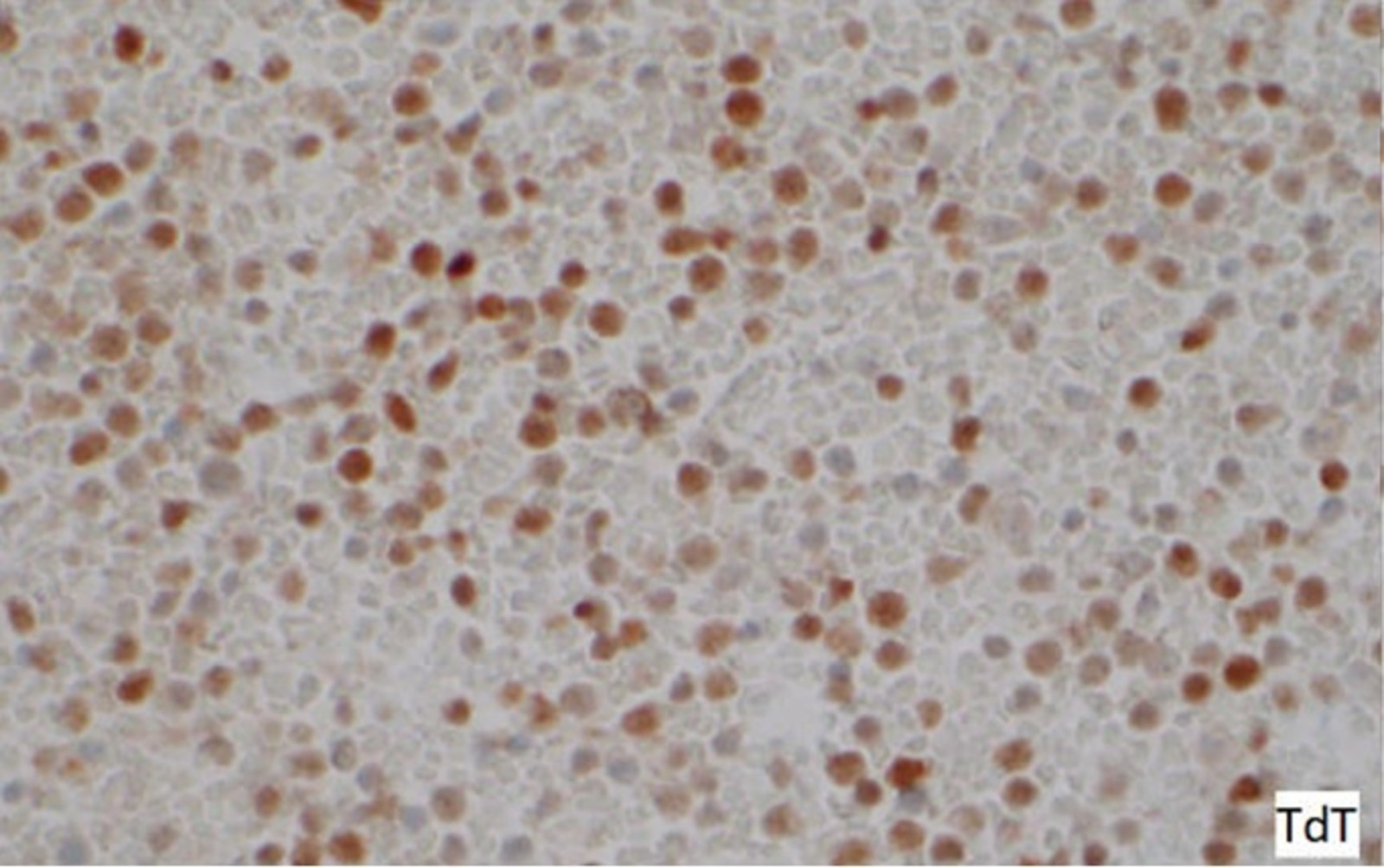
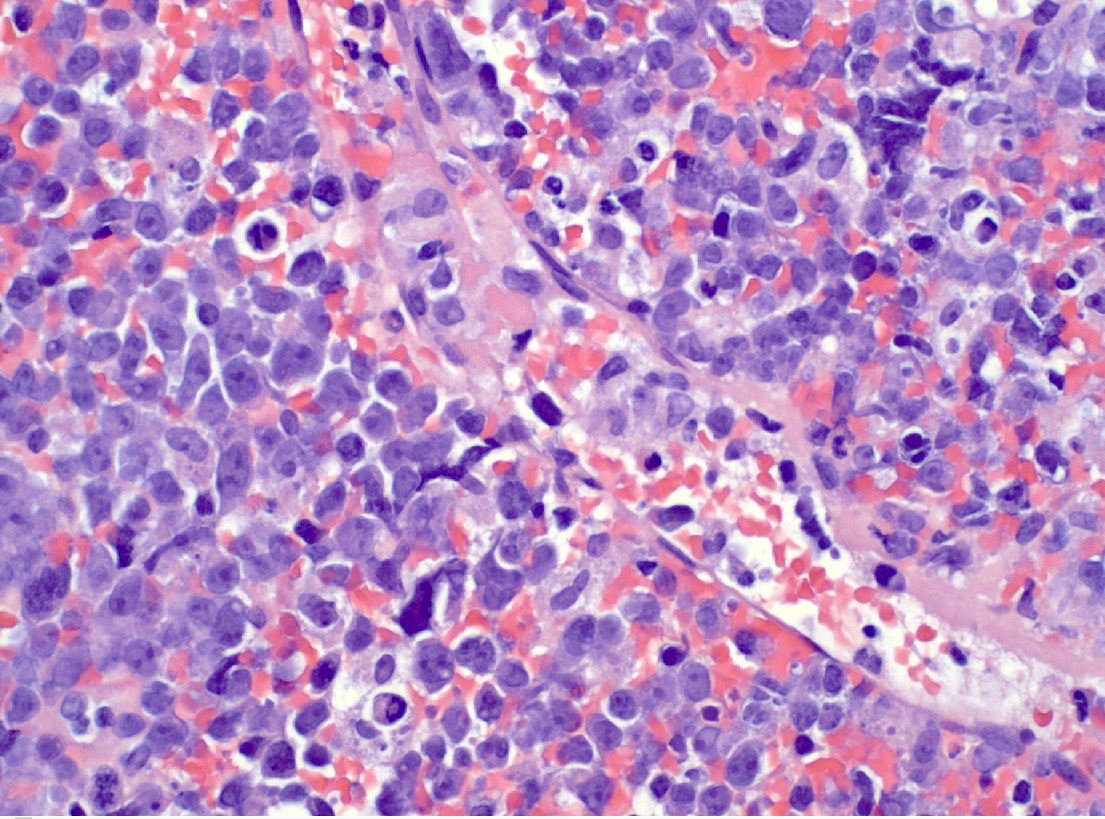
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Jennifer Chapman, M.D.
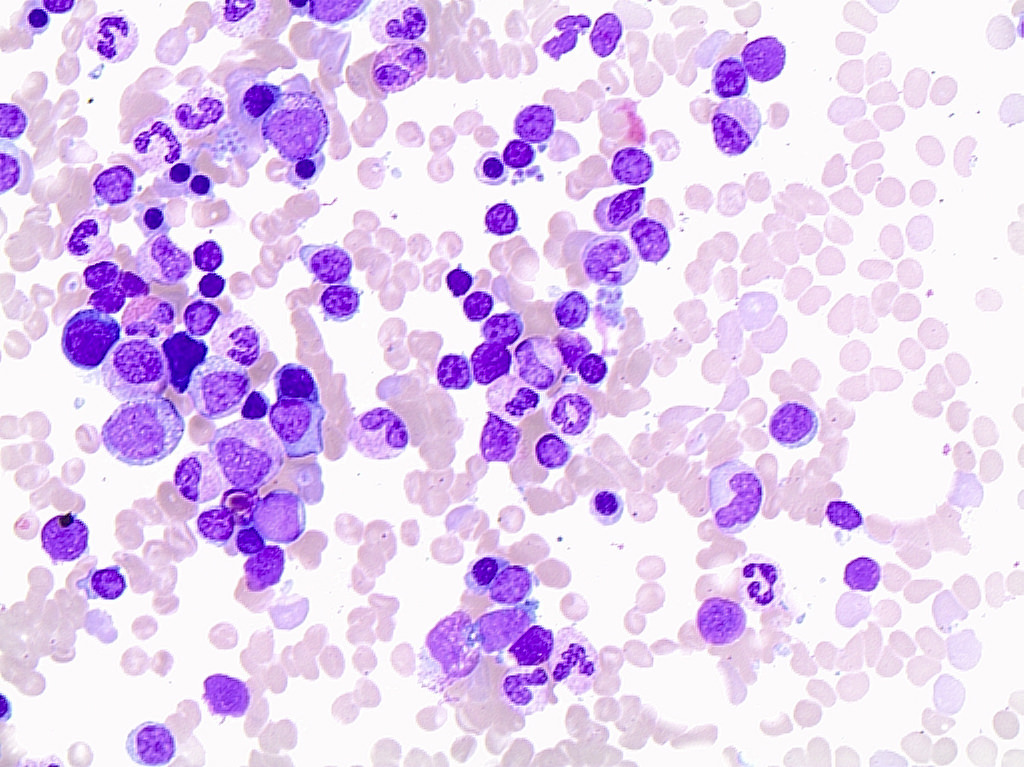
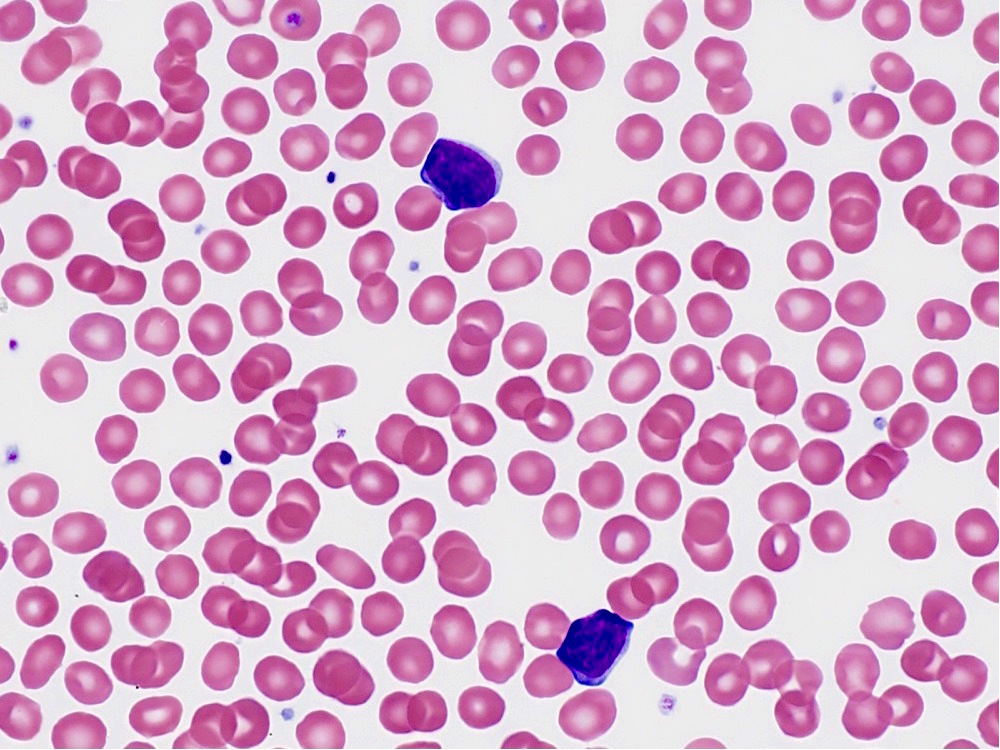
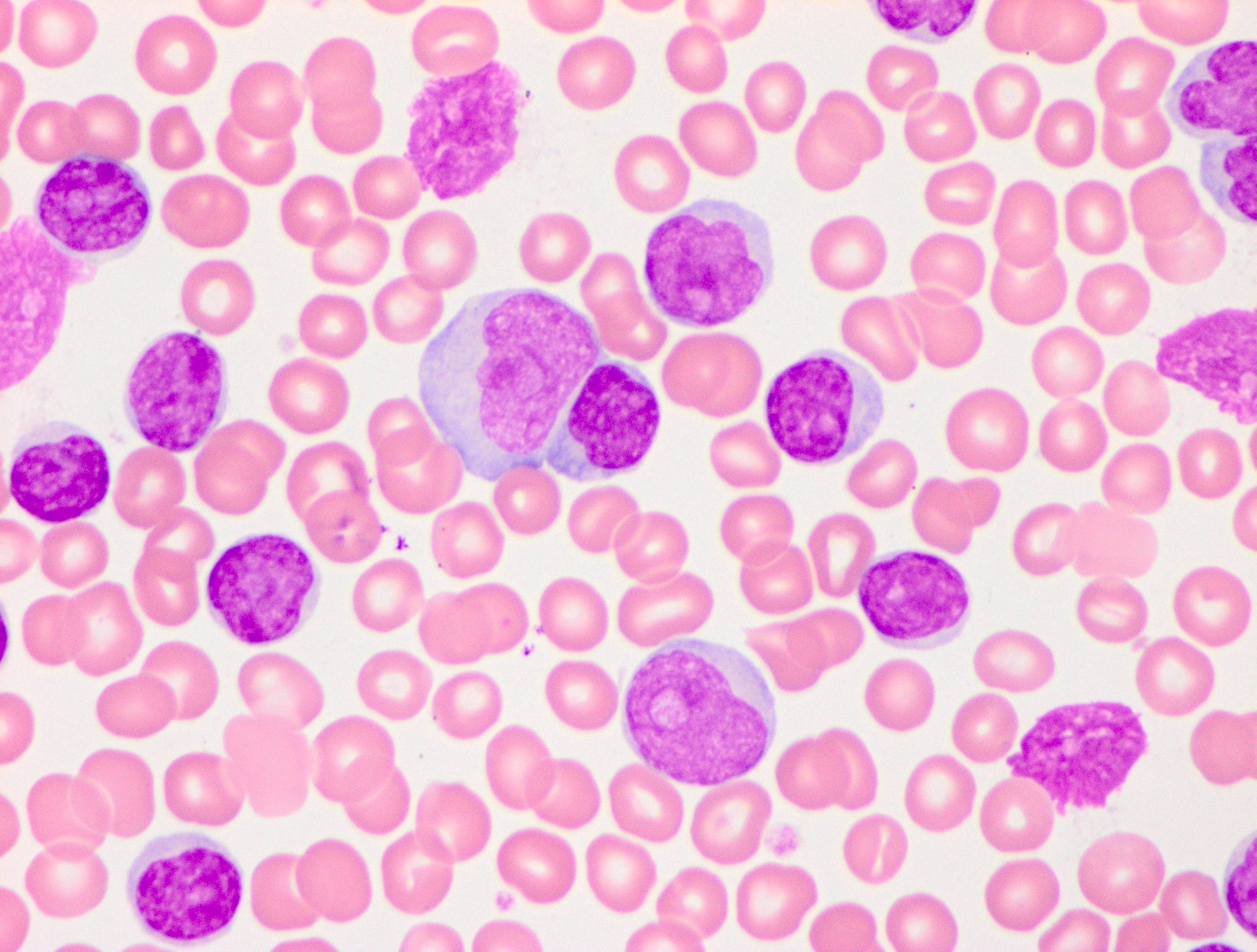
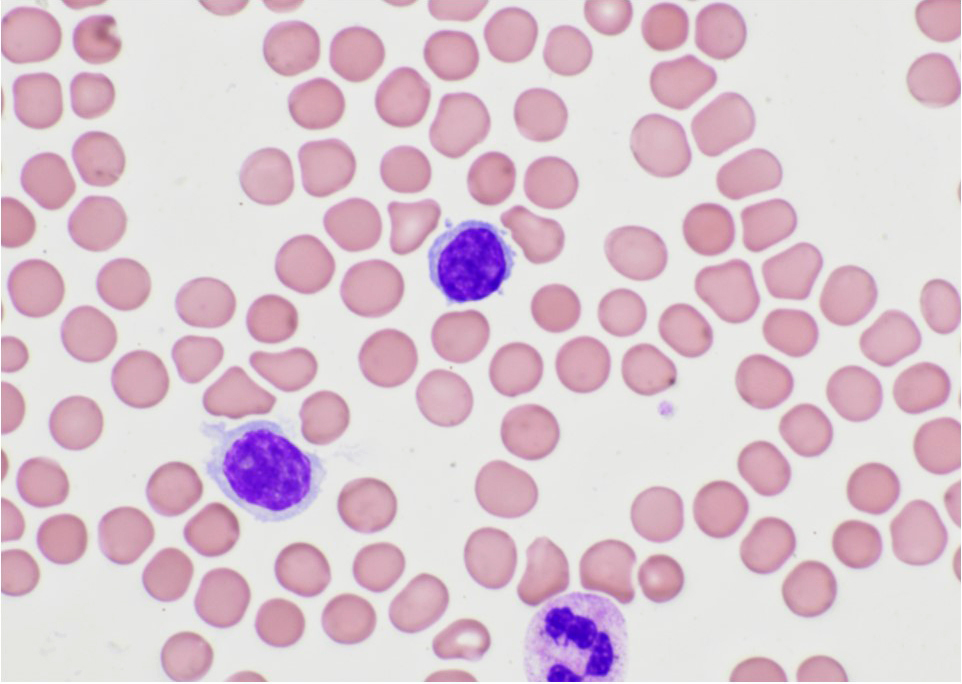
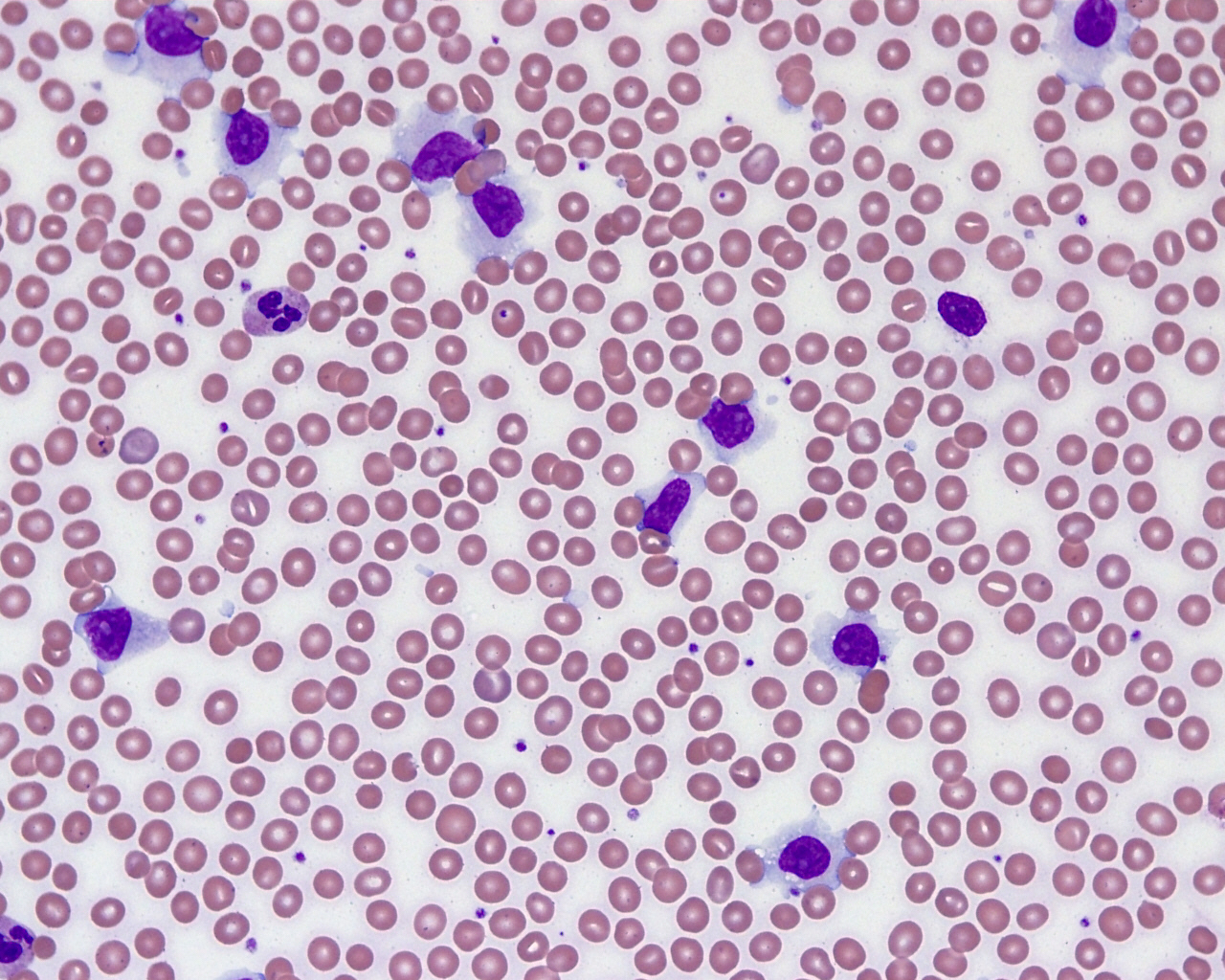
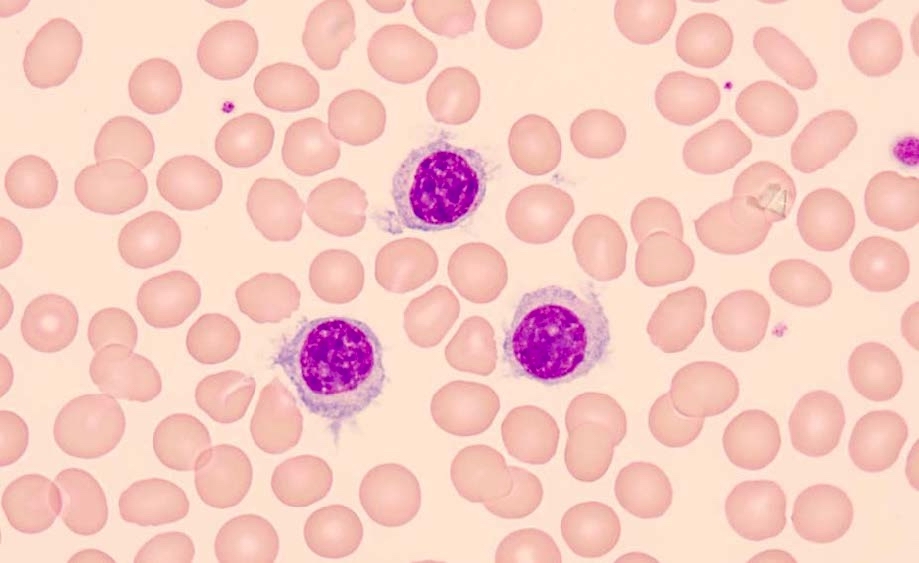
Peripheral smear images
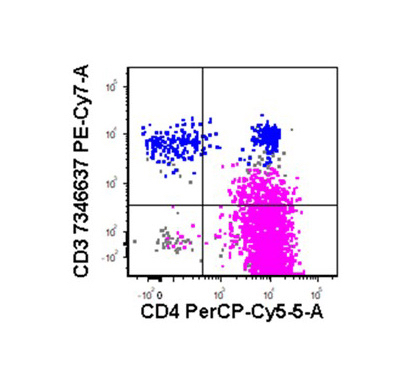
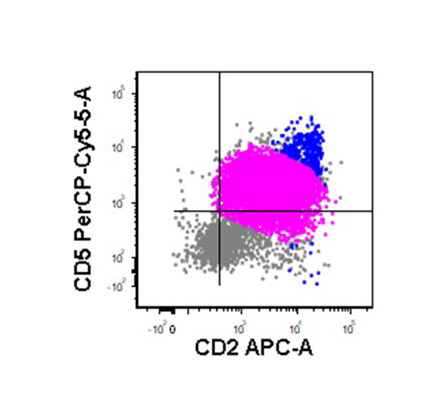
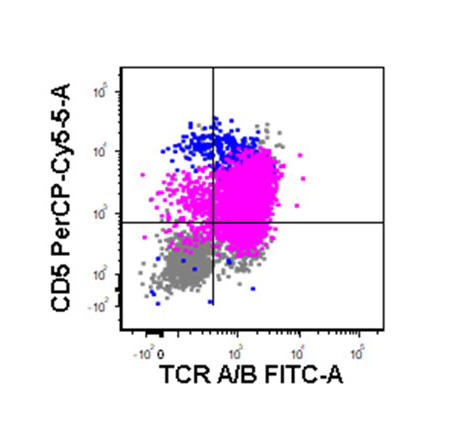
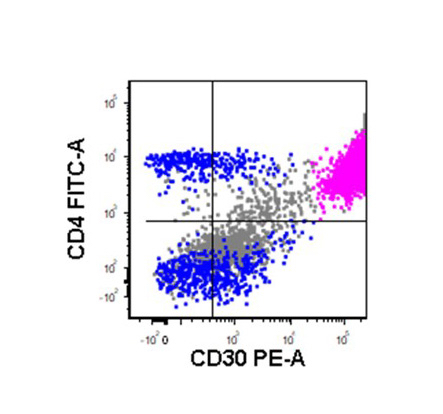
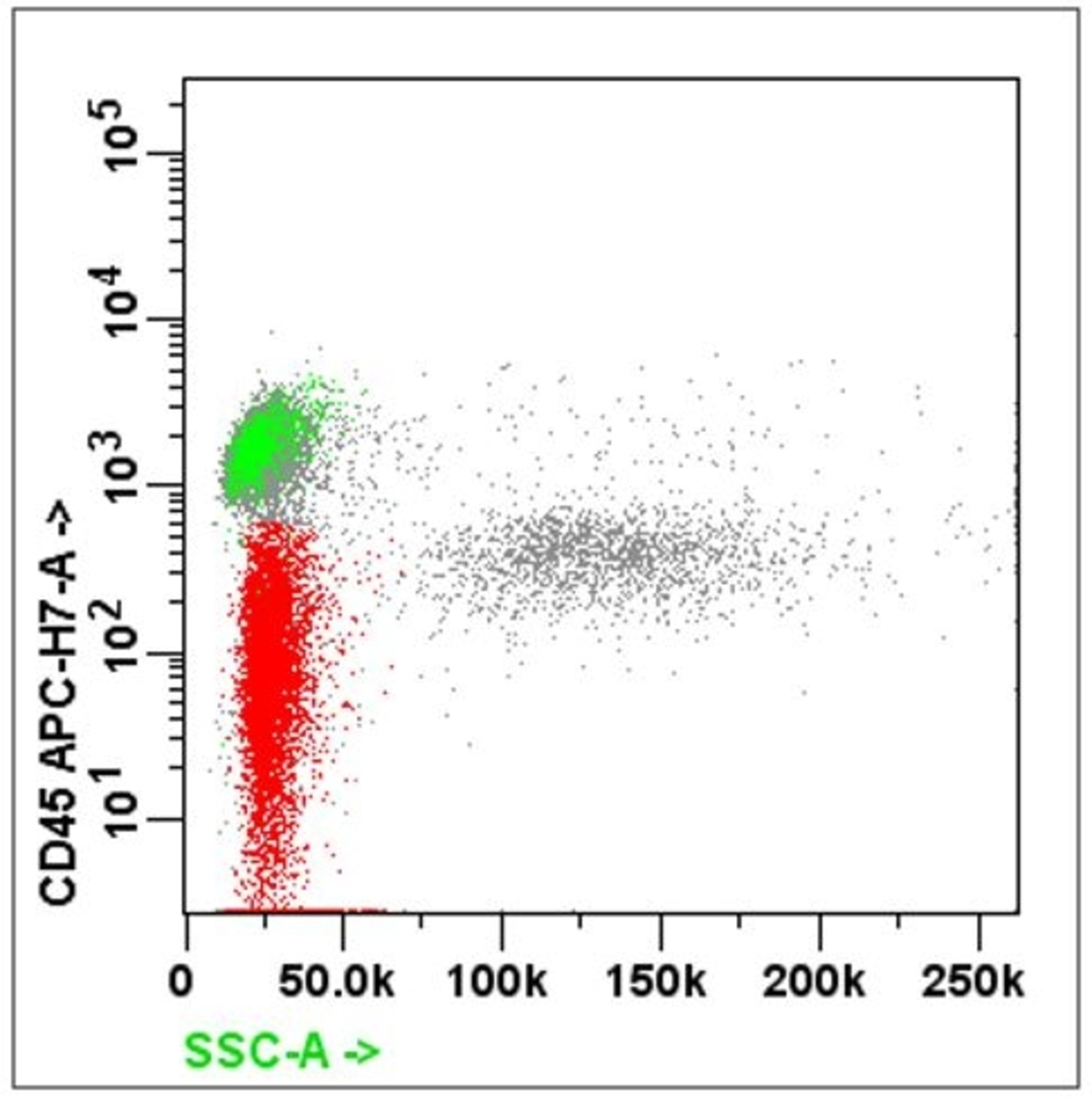
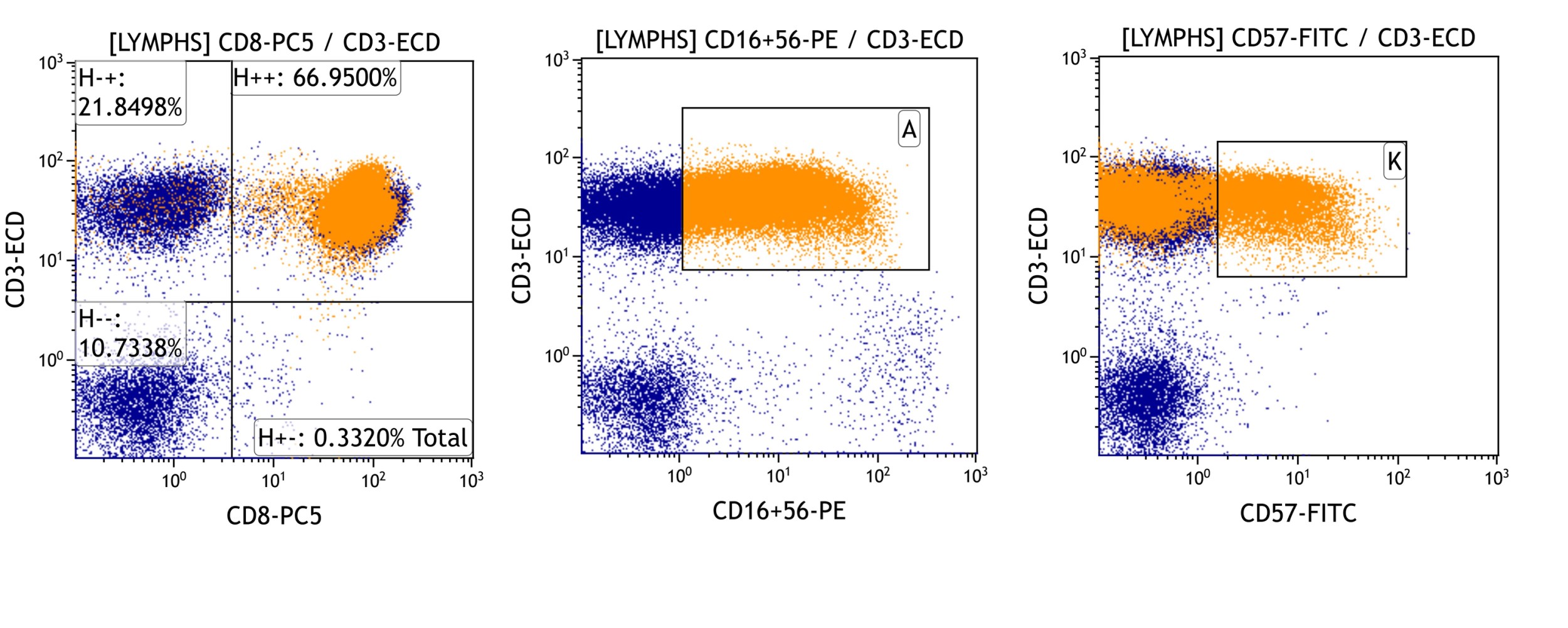
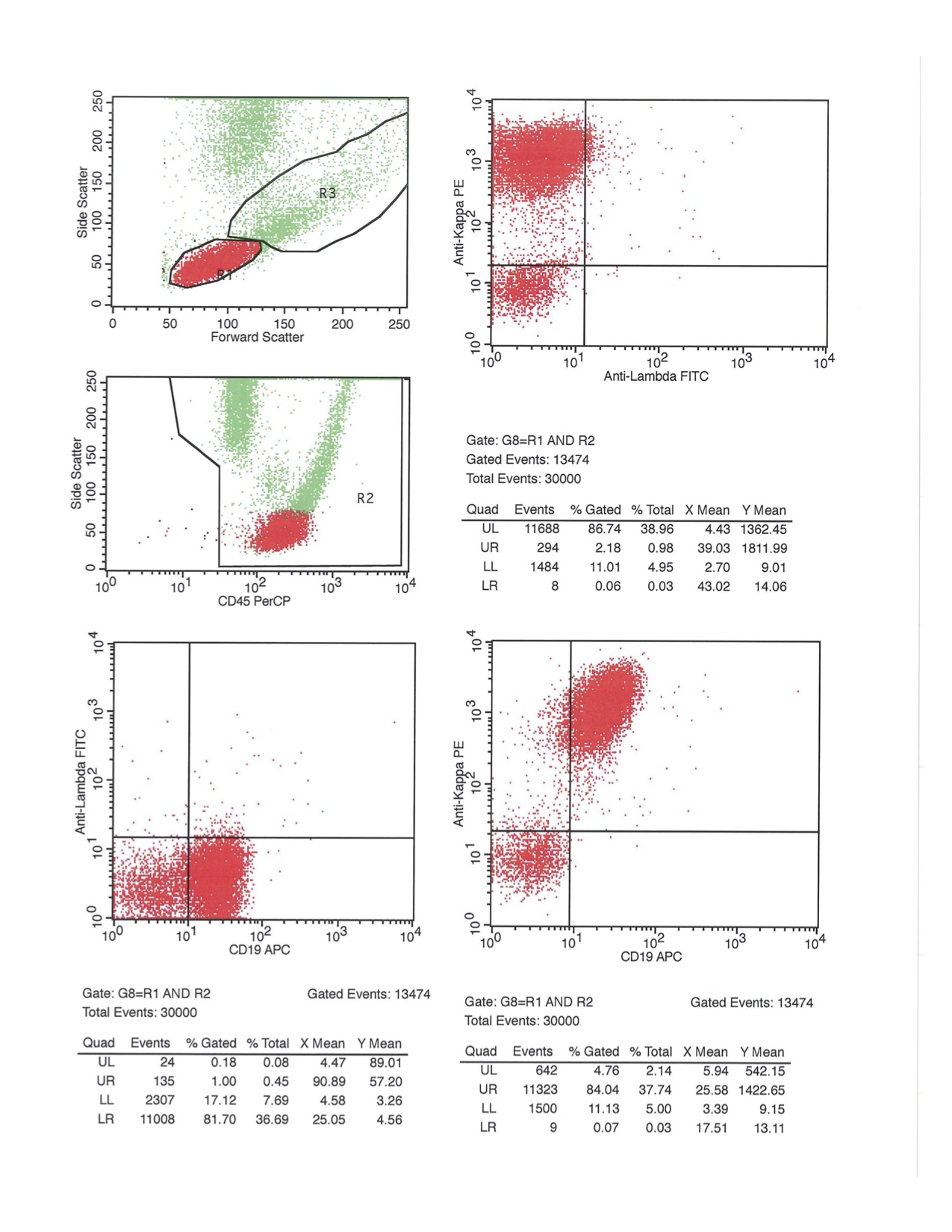
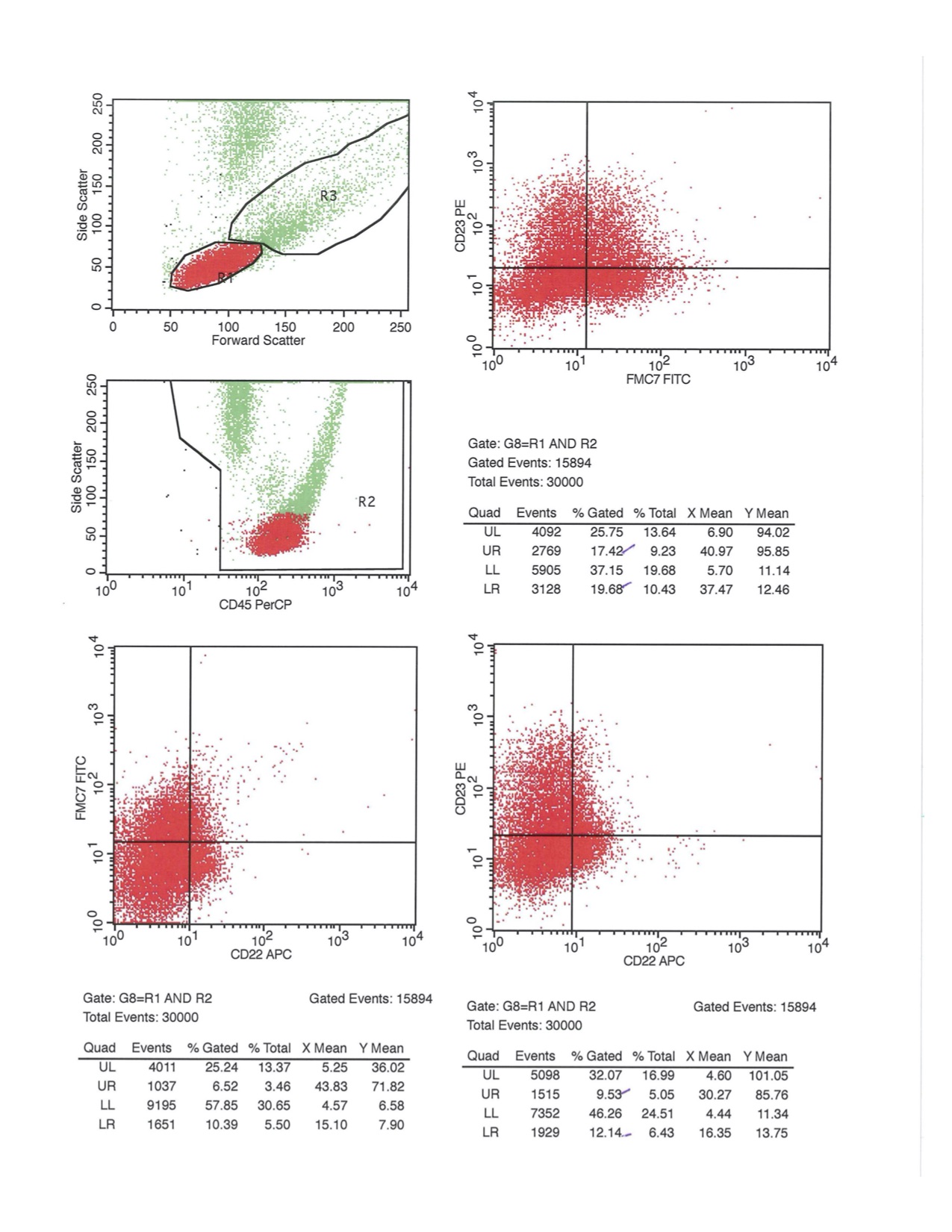
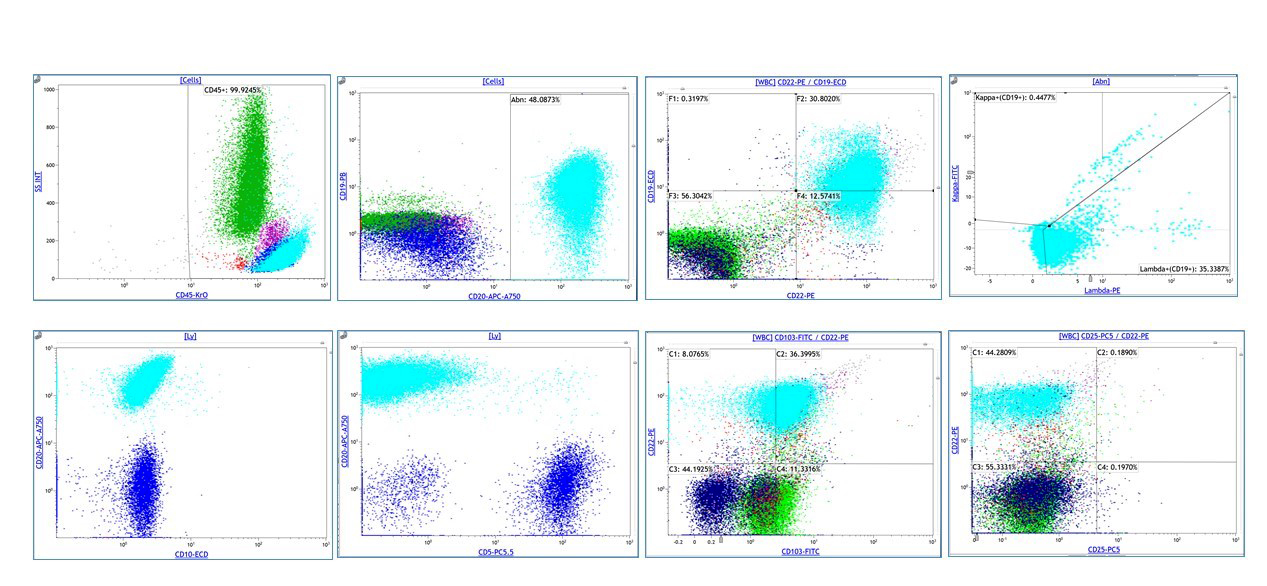
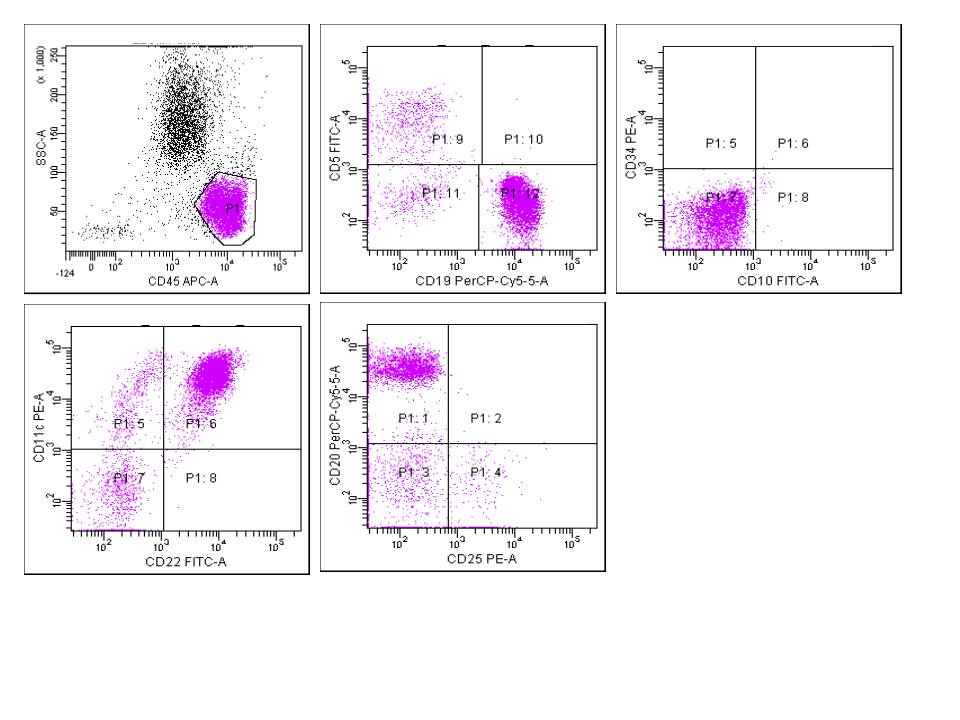
Flow cytometry images
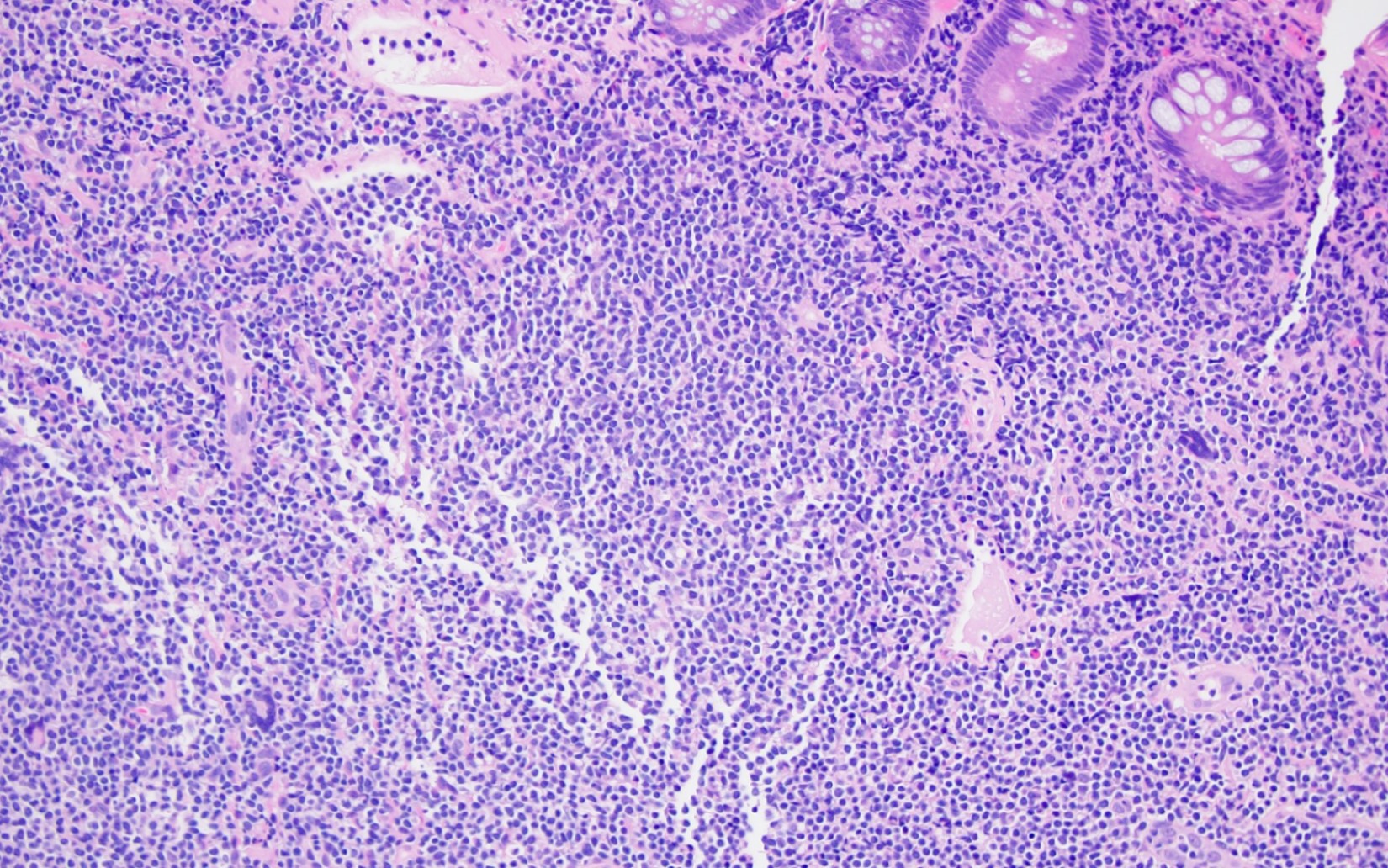
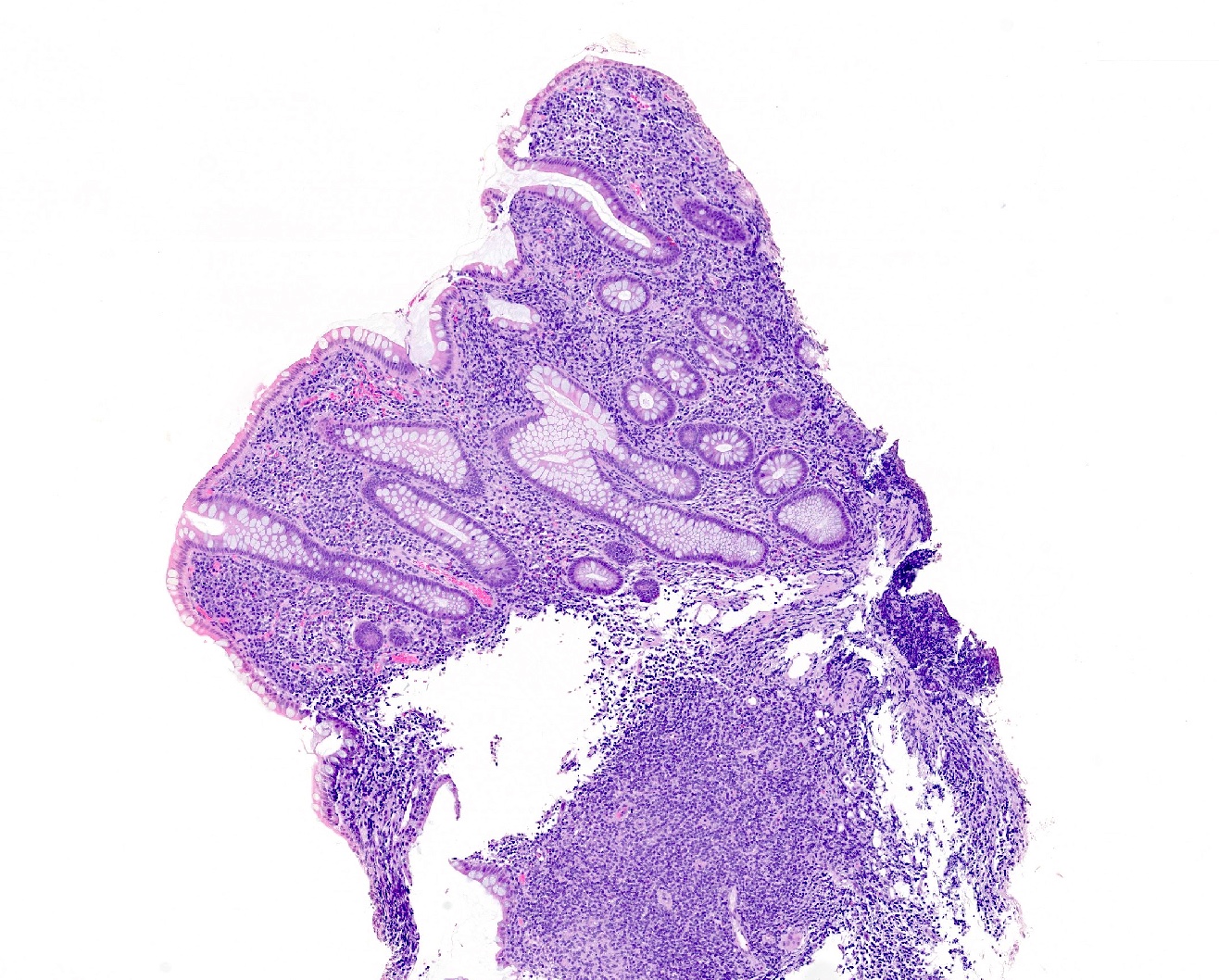
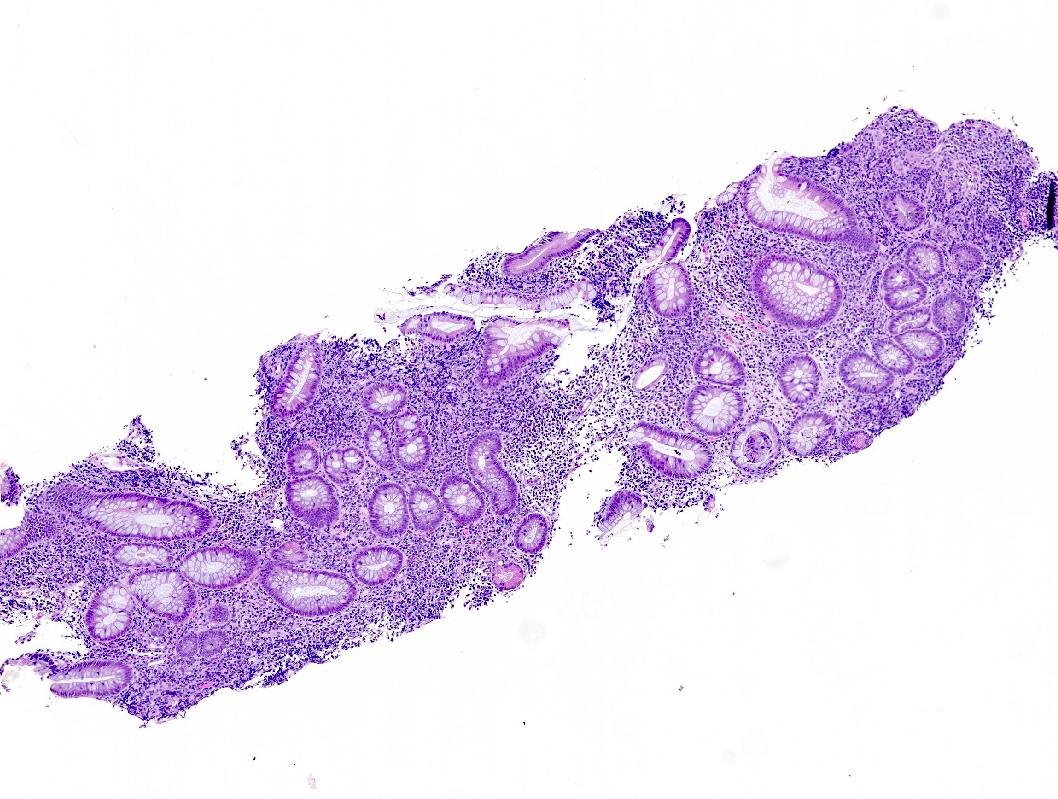
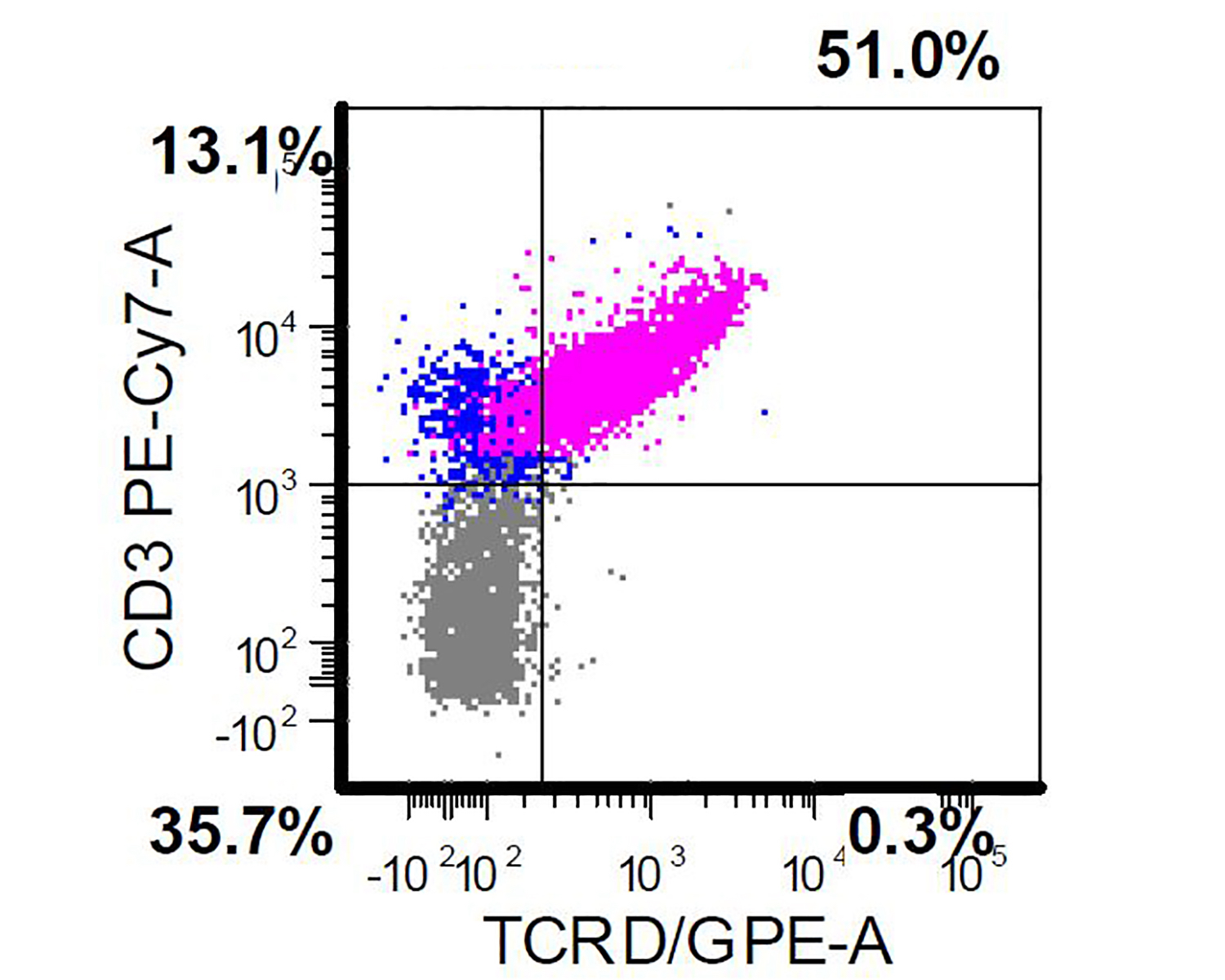
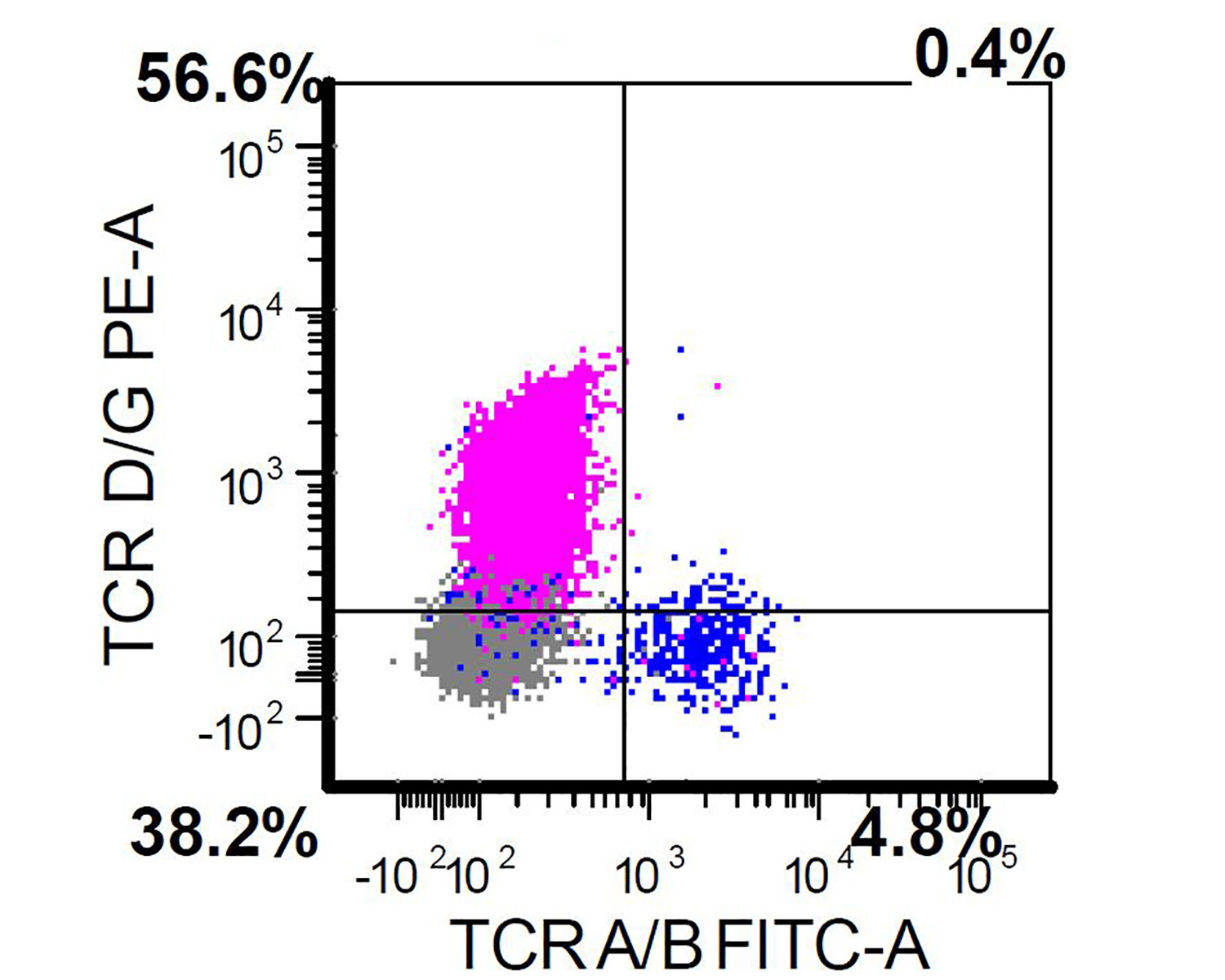
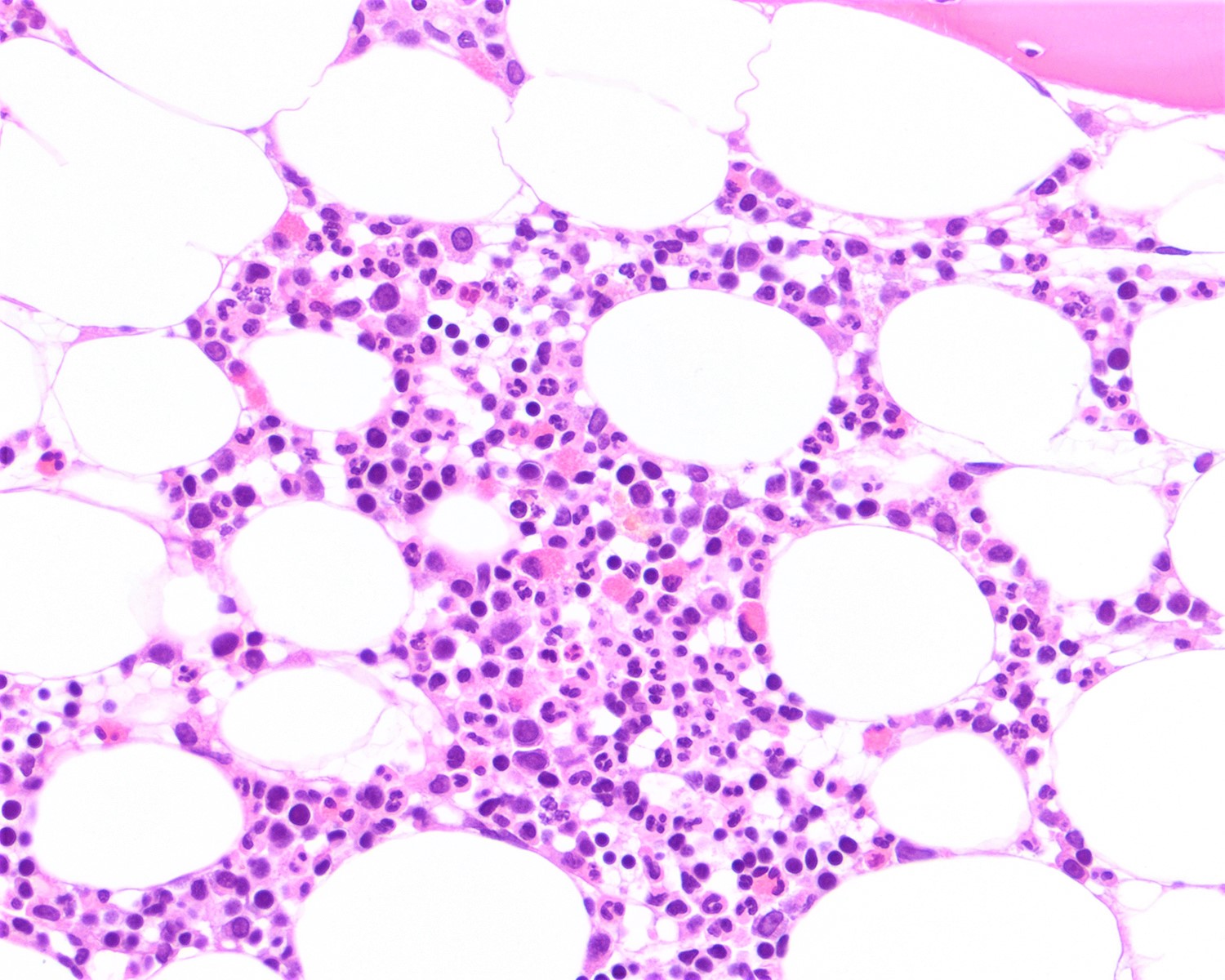
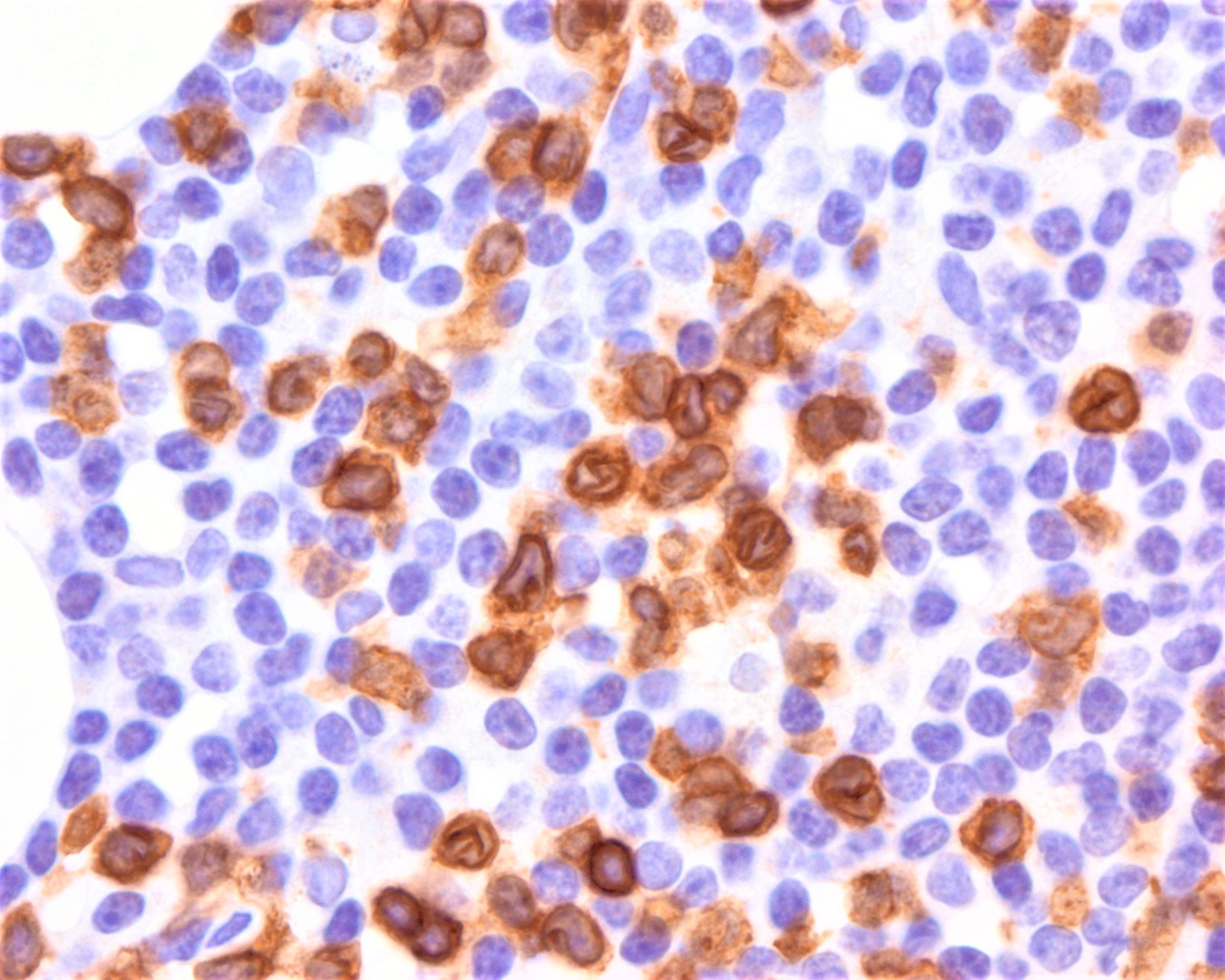
Aggressive NK cell leukemia
Microscopic (histologic) images
Flow cytometry images
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, ALK negative
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Jayalakshmi Balakrishna, M.D. and Elaine S. Jaffe, M.D.
Contributed by Doan Minh Khuy, M.D.
Flow cytometry images
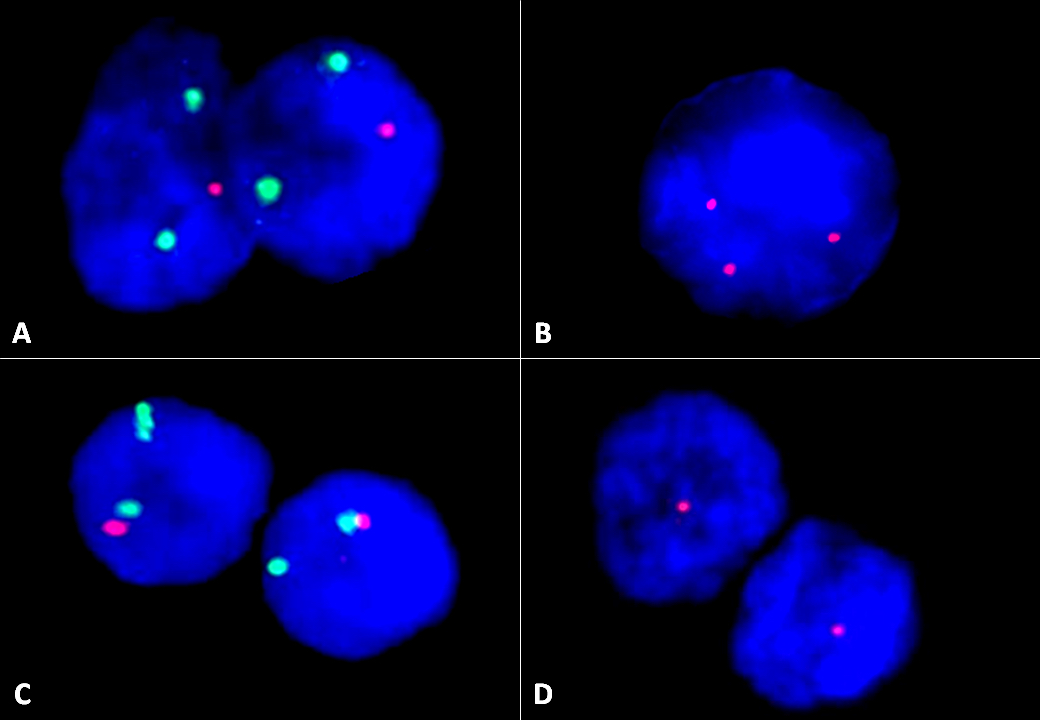
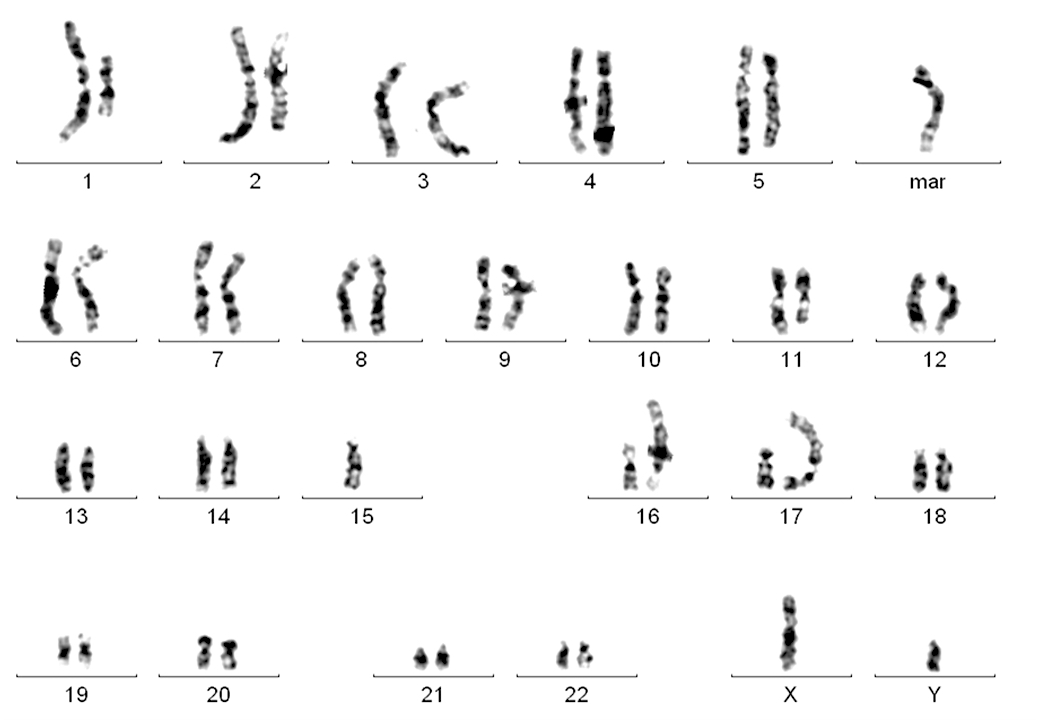
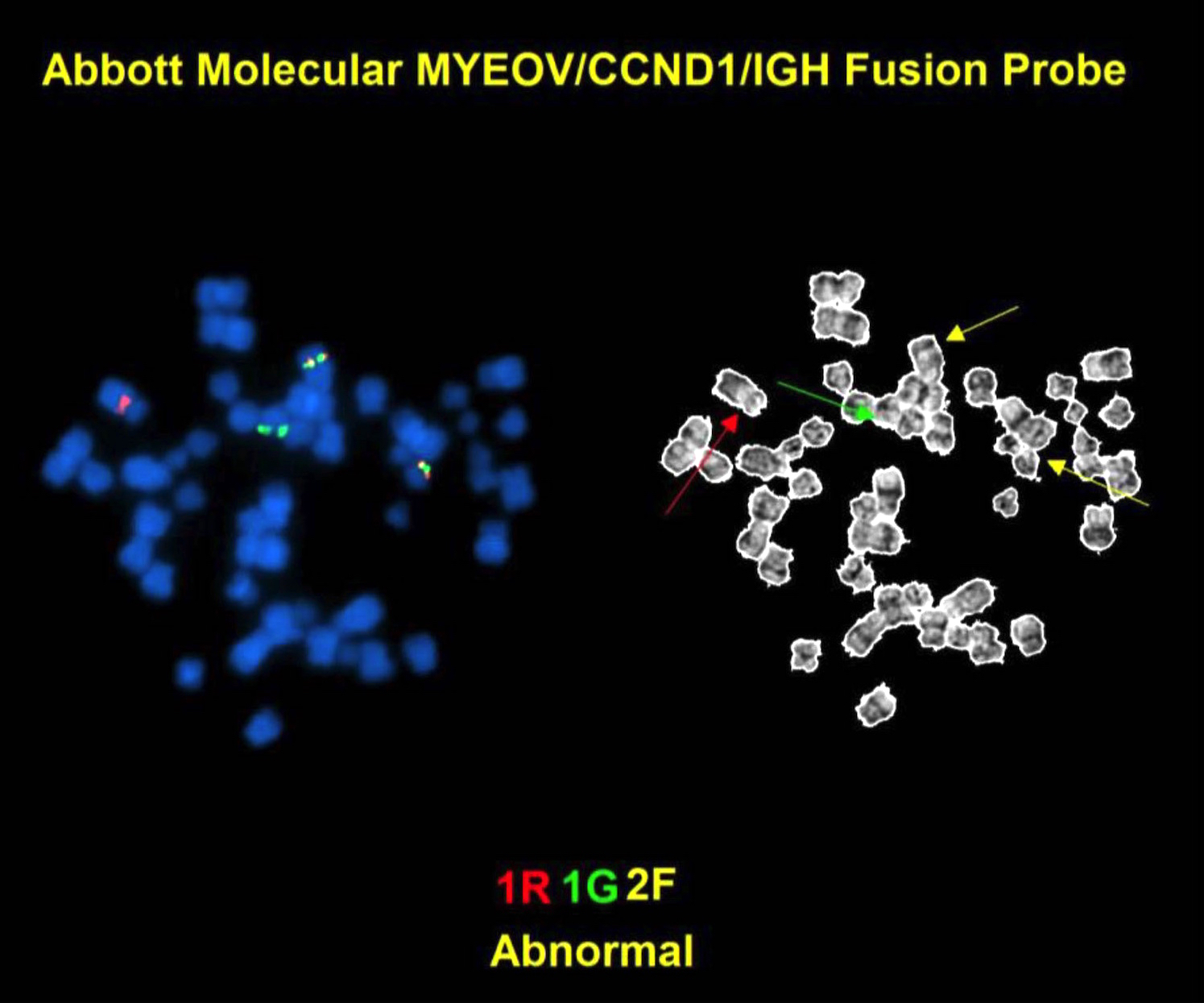
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, ALK positive
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Jayalakshmi Balakrishna, M.D., Elaine S. Jaffe, M.D.
Cytology images
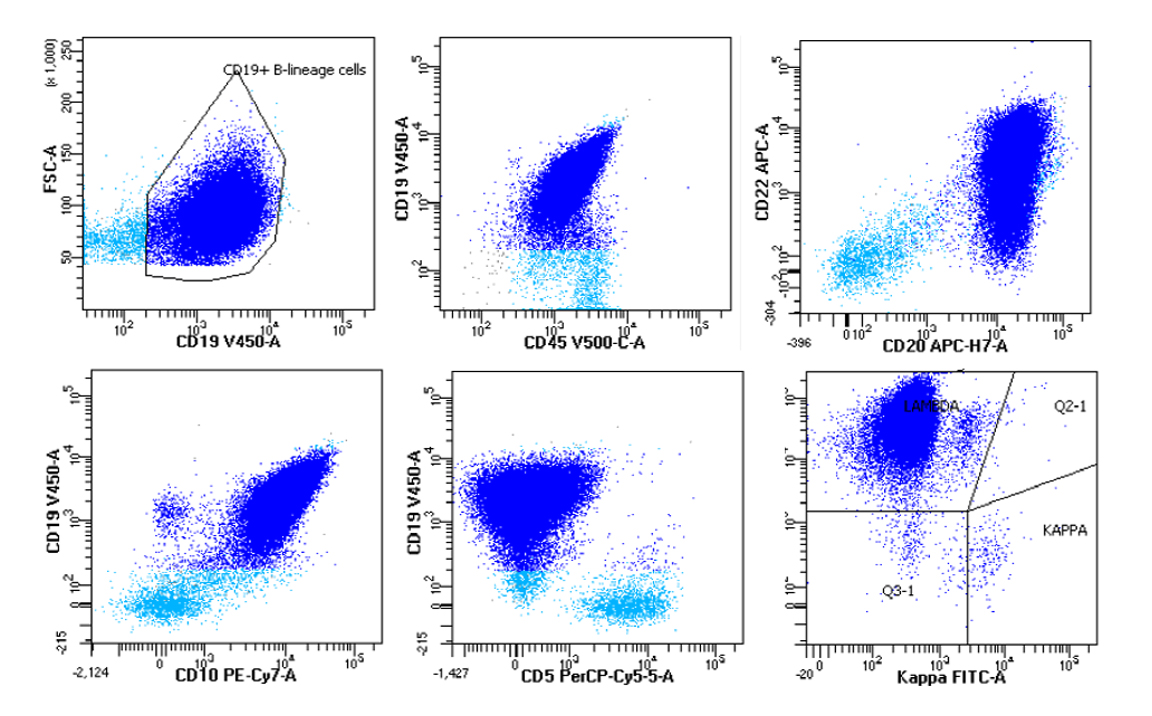
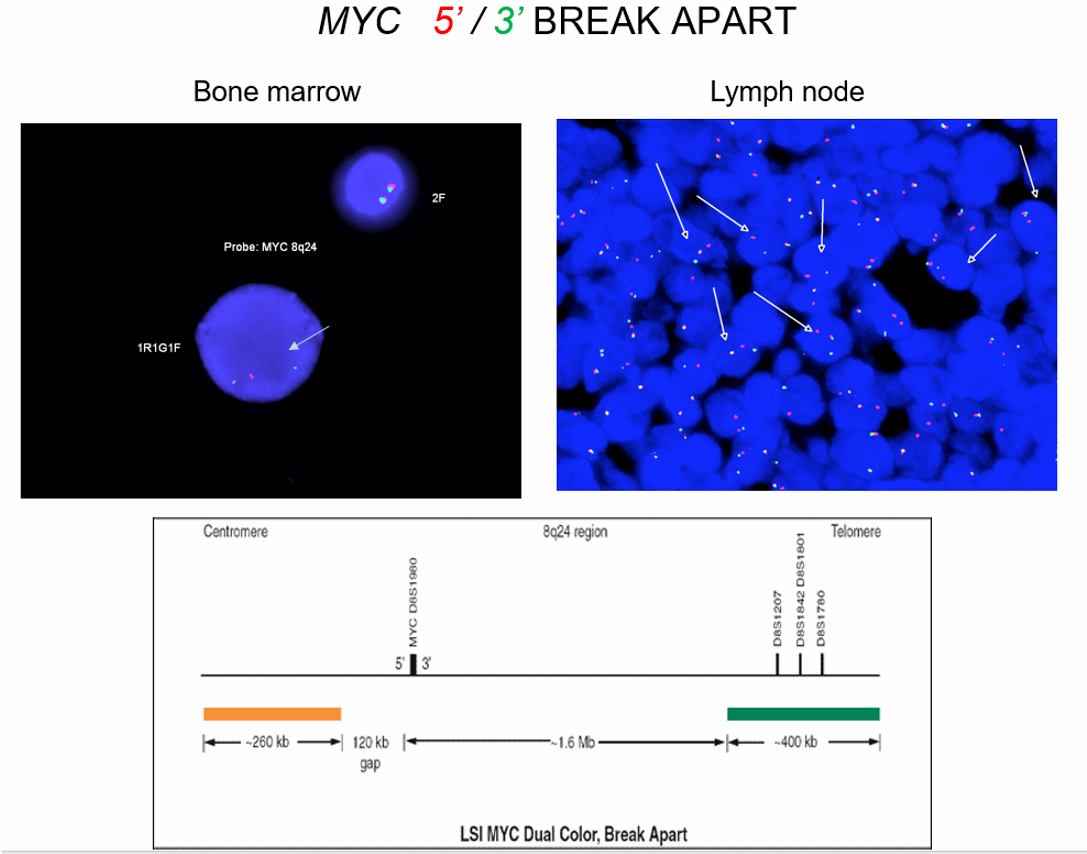
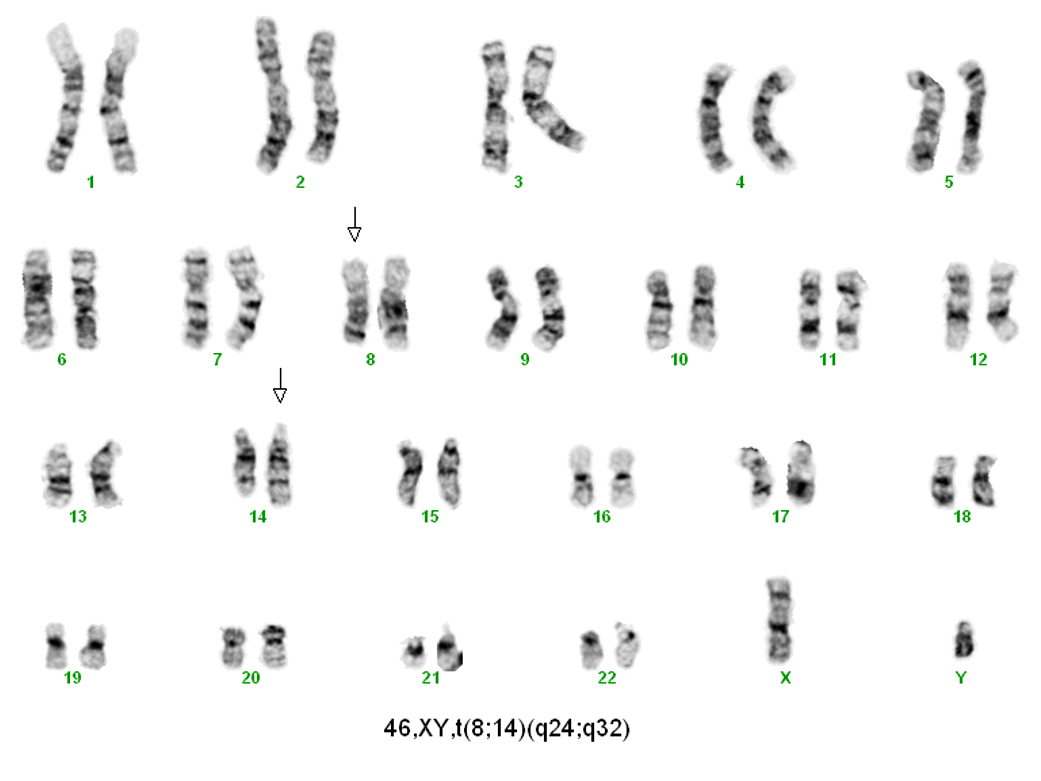
Burkitt lymphoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology images
Molecular / cytogenetics images
CHL lymphocyte depleted
Electron microscopy images
CHL lymphocyte rich
Microscopic (histologic) images
CHL mixed cellularity
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Laurence de Leval, M.D., Ph.D. and Carmen Bárcena, M.D.
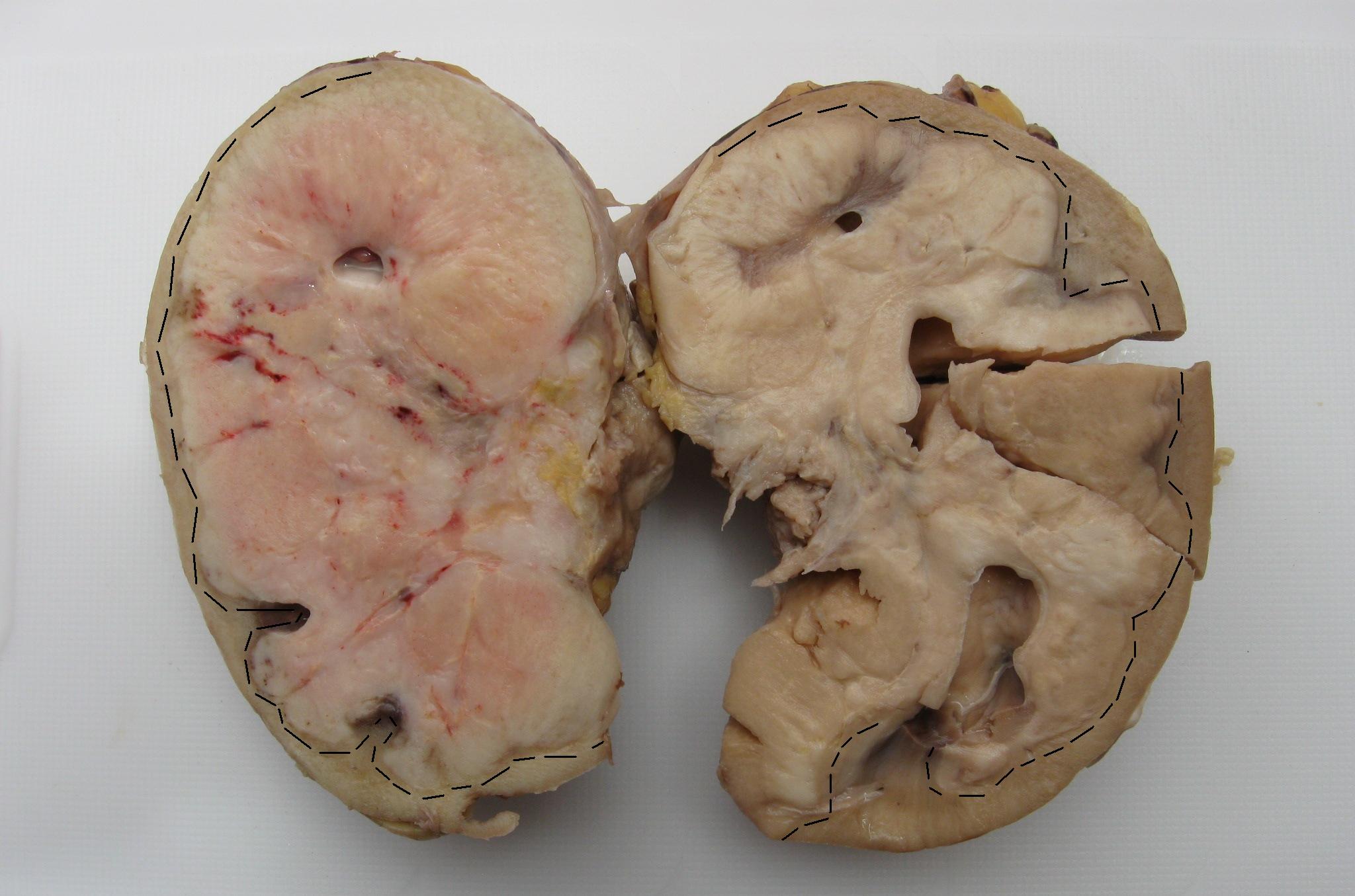
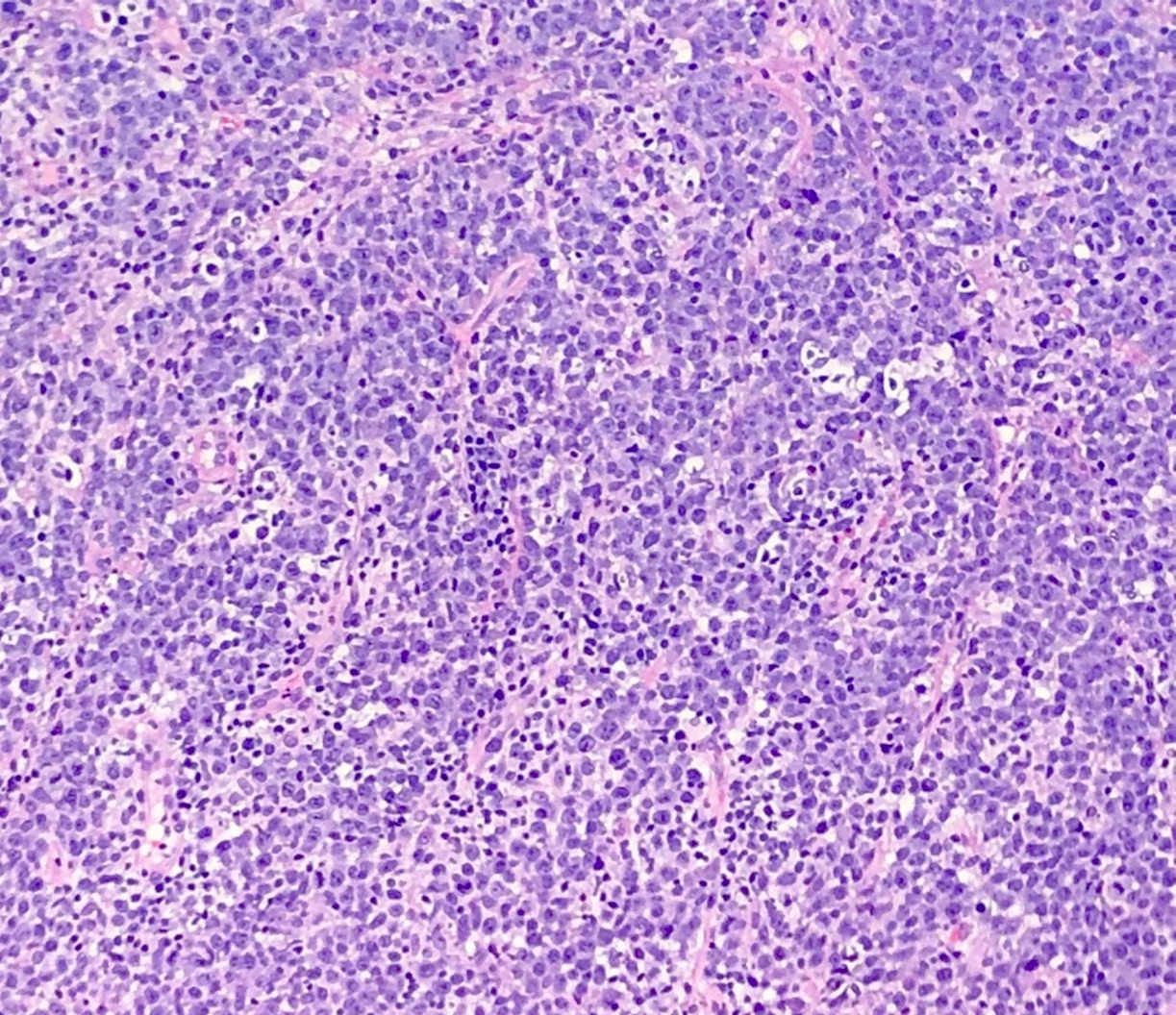
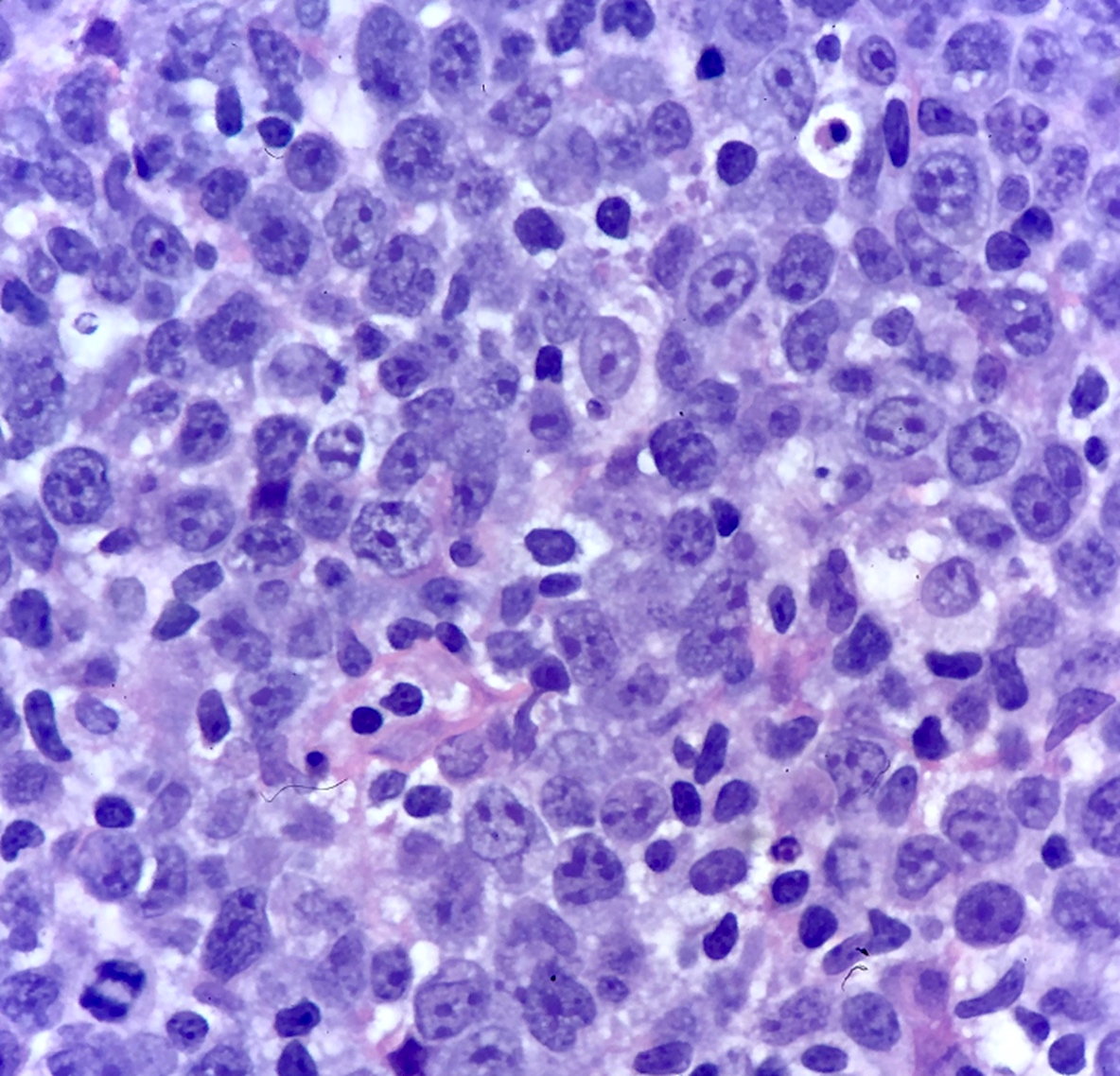
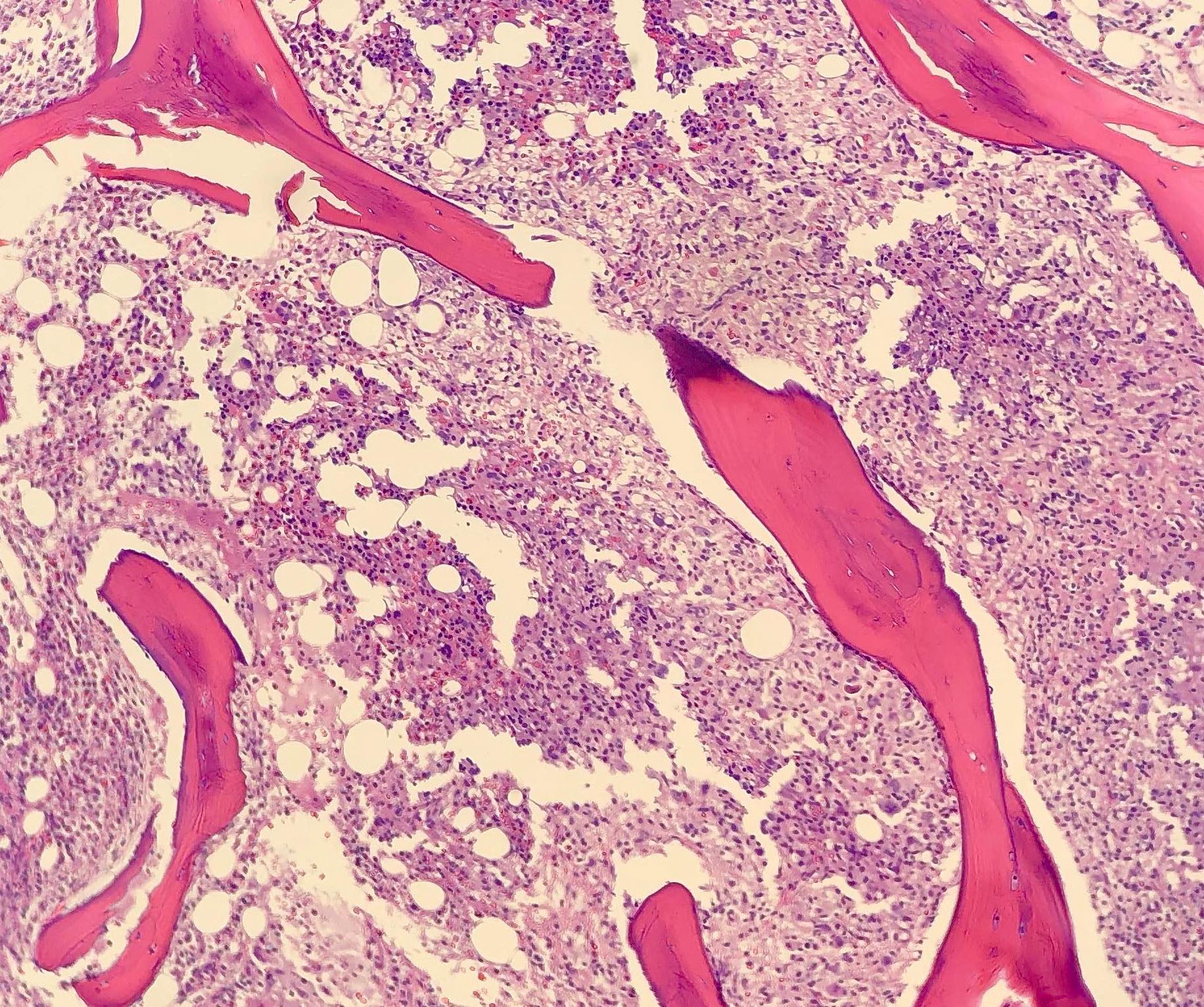
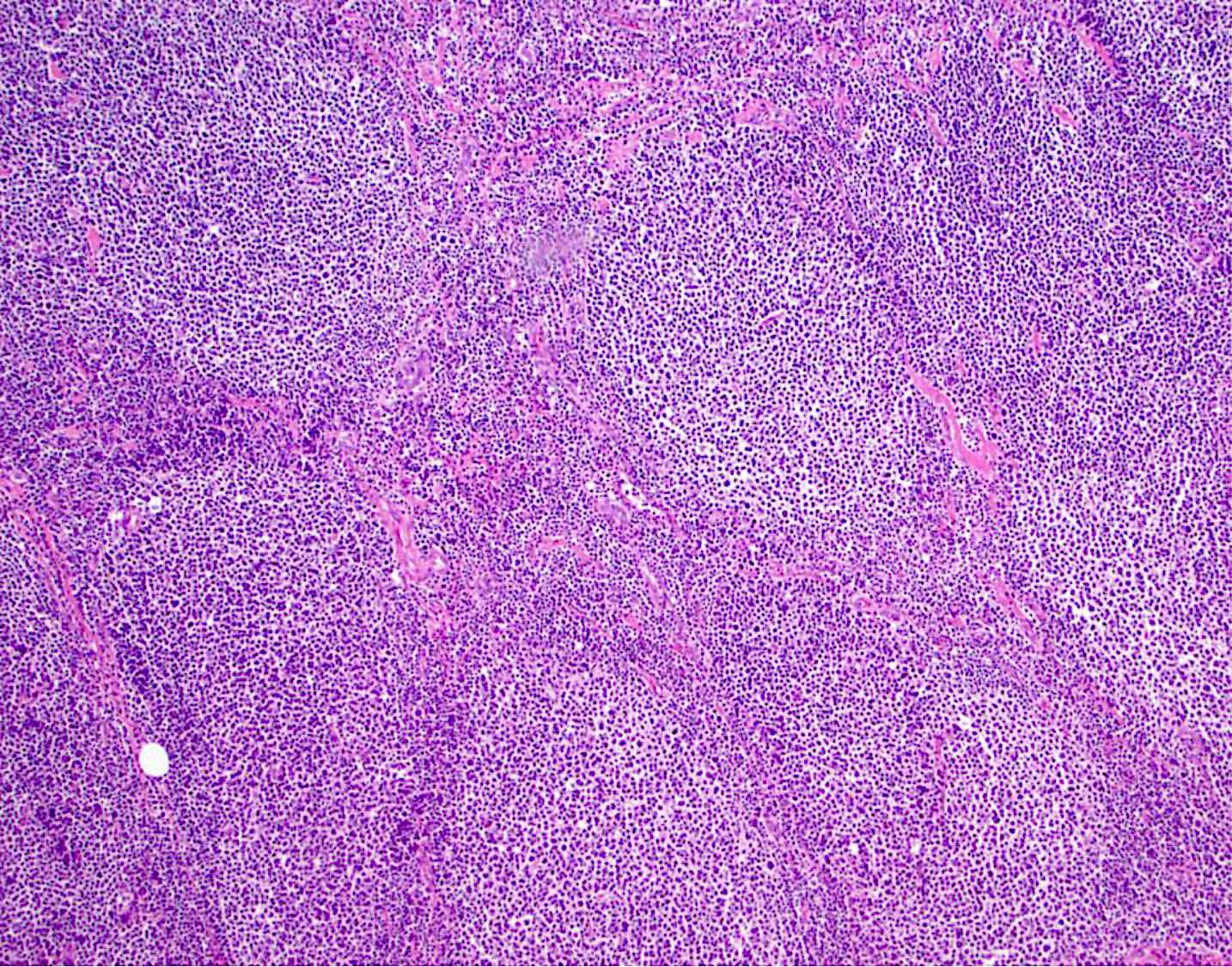
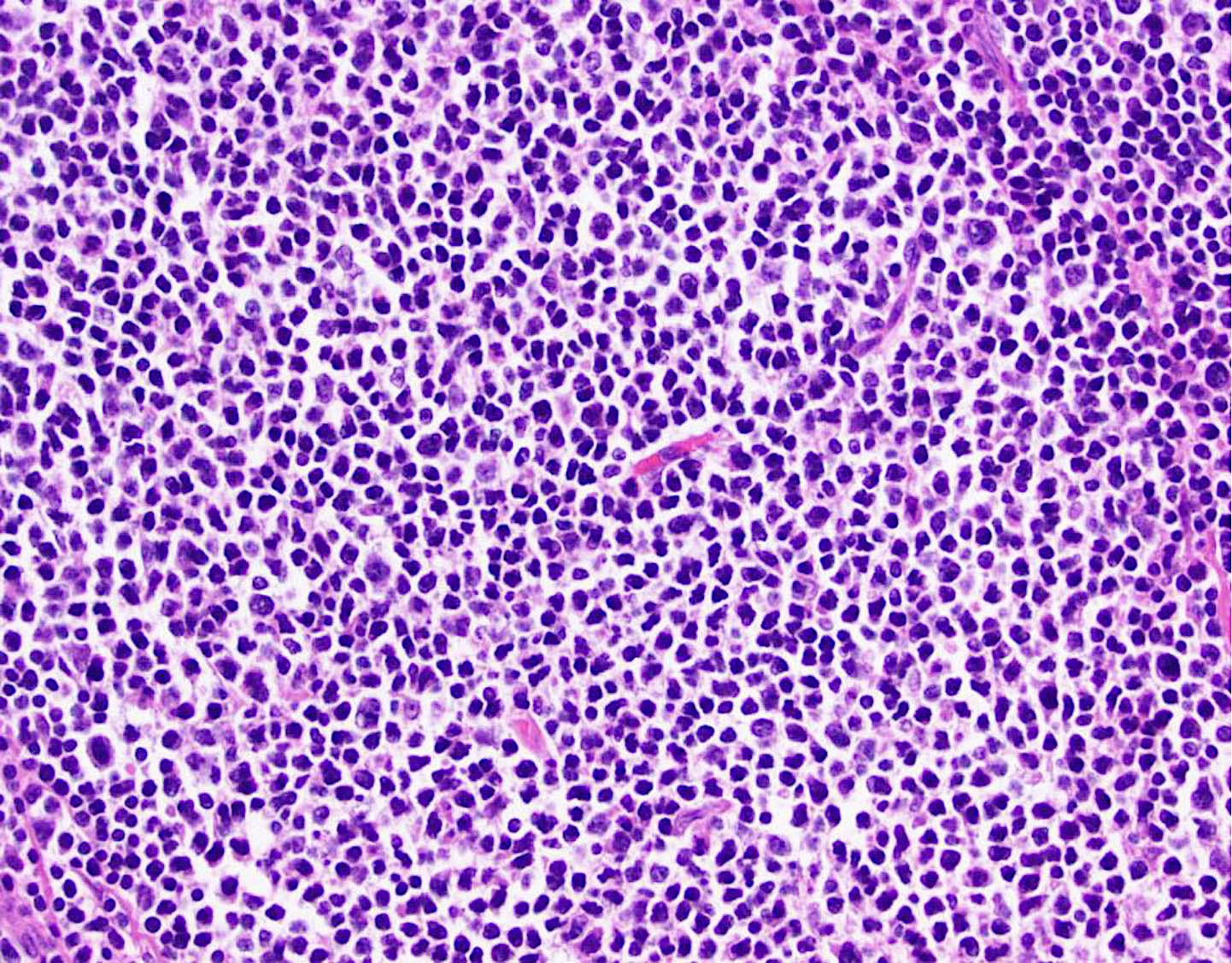
CLL / SLL
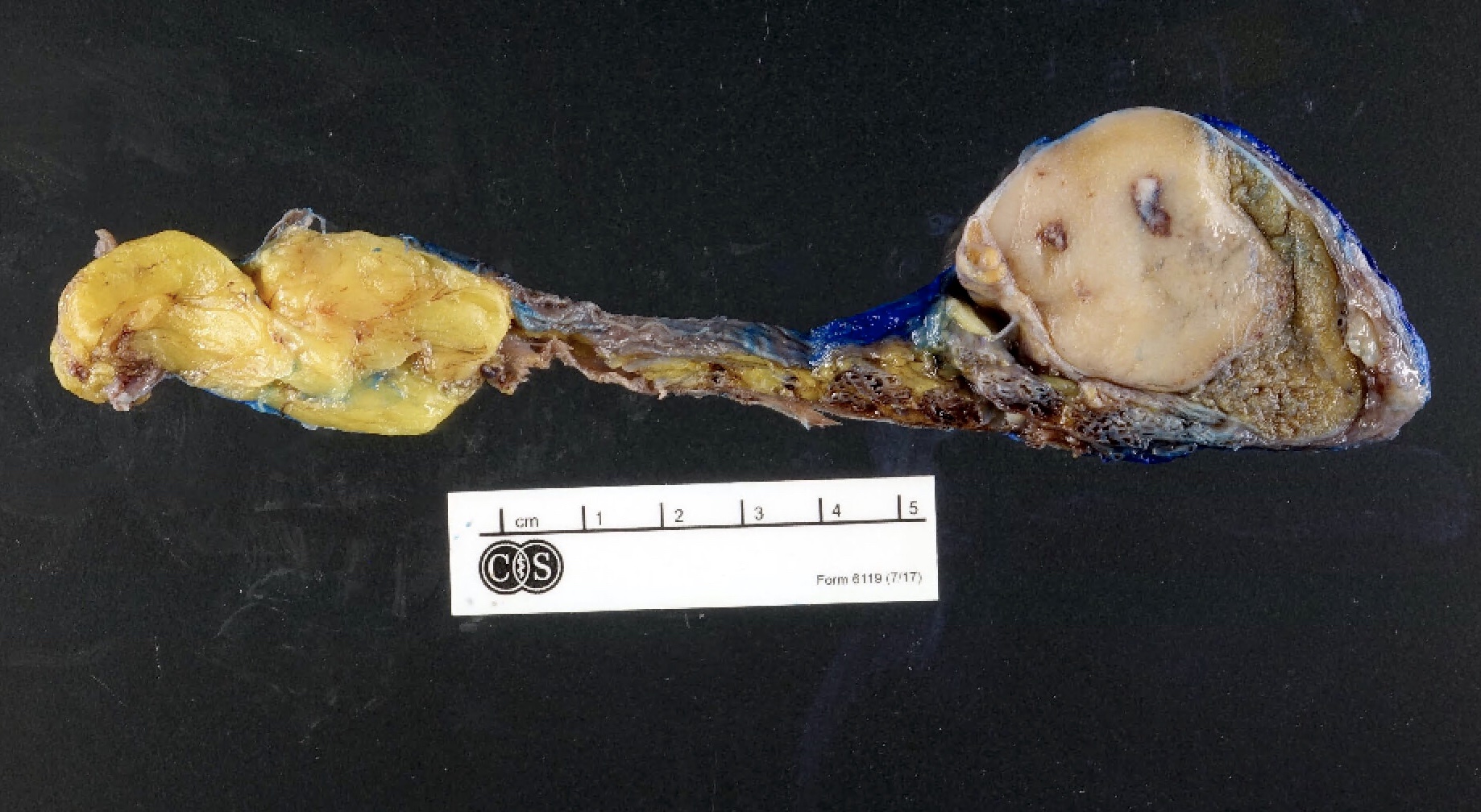
Gross images
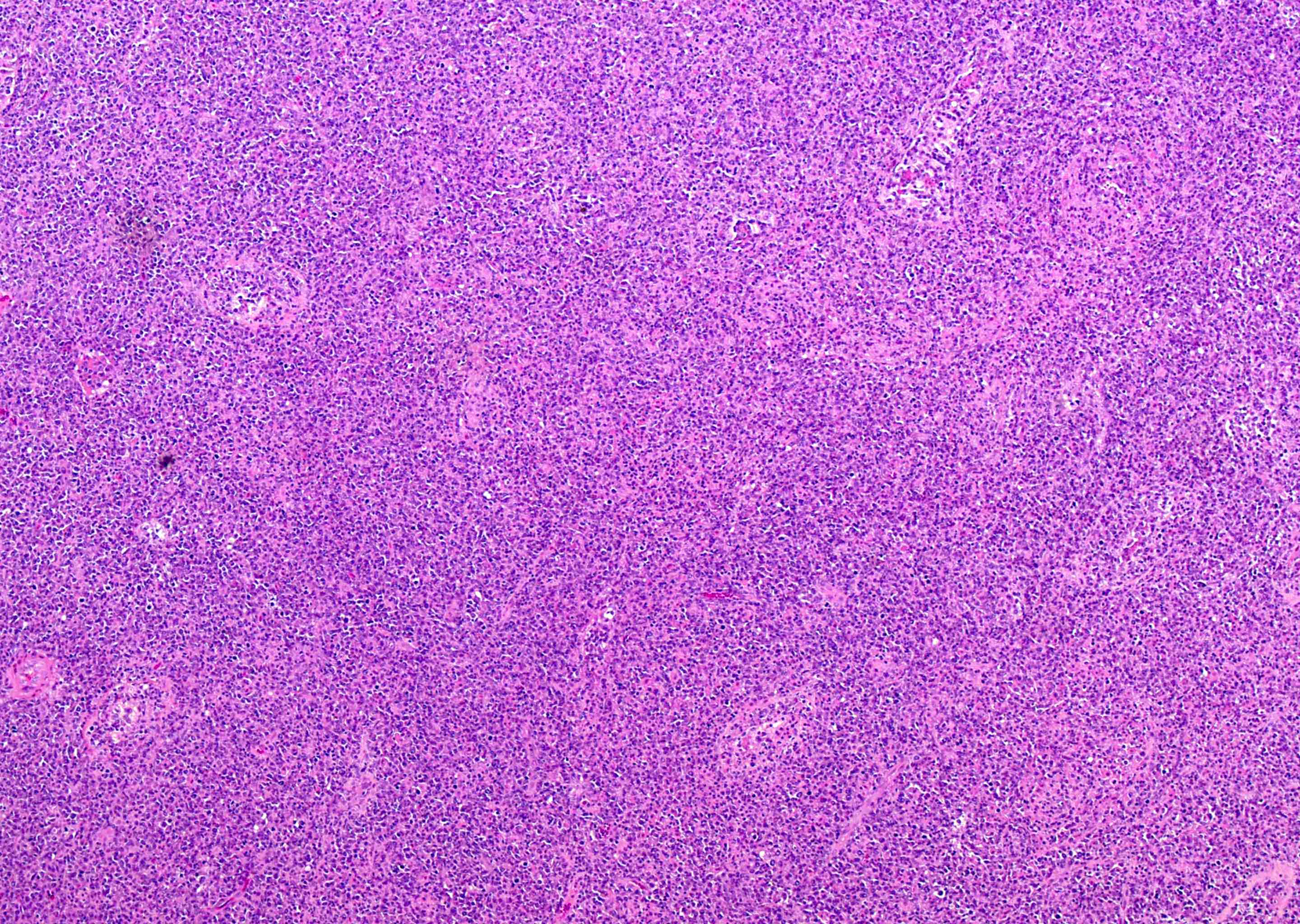
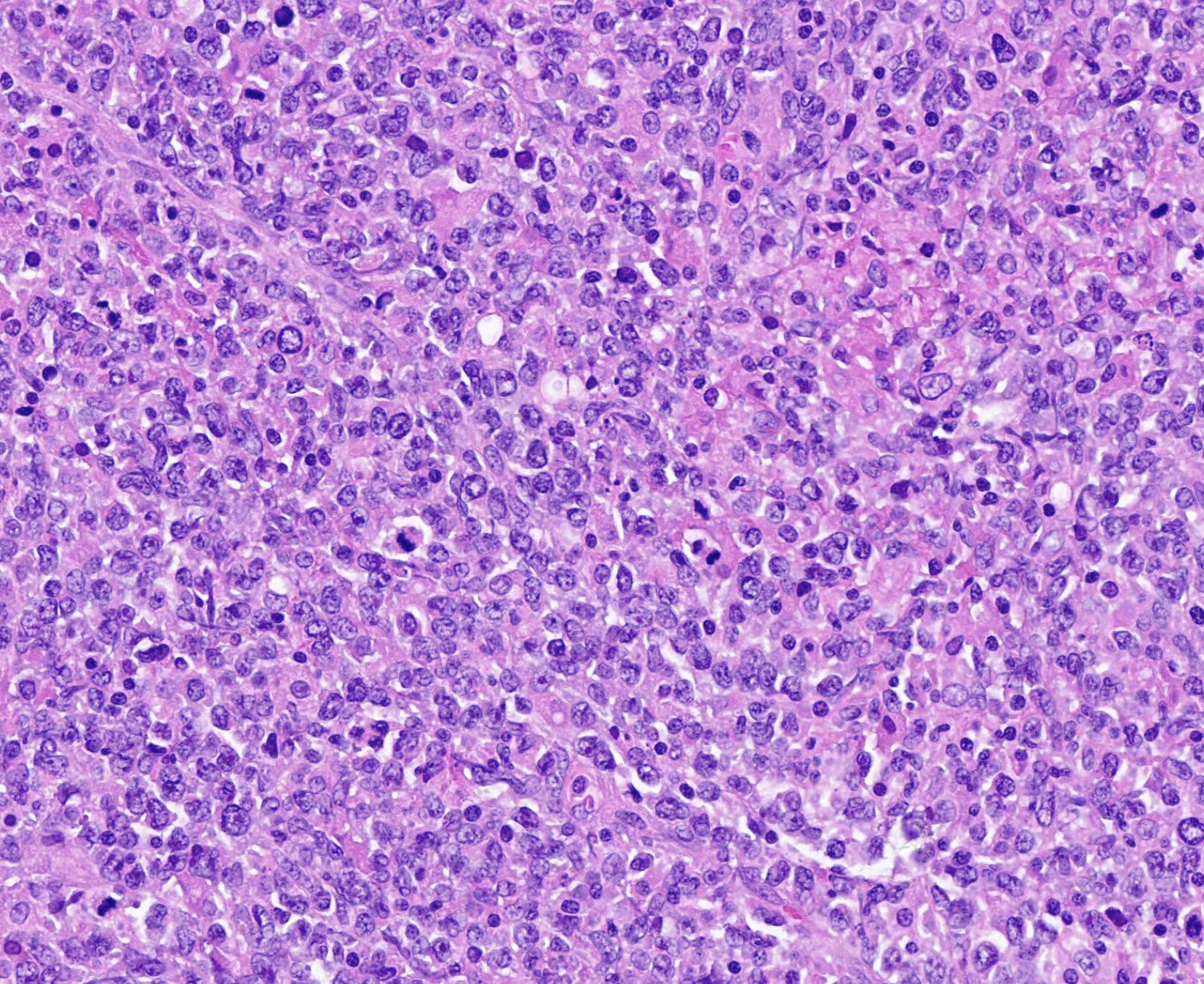
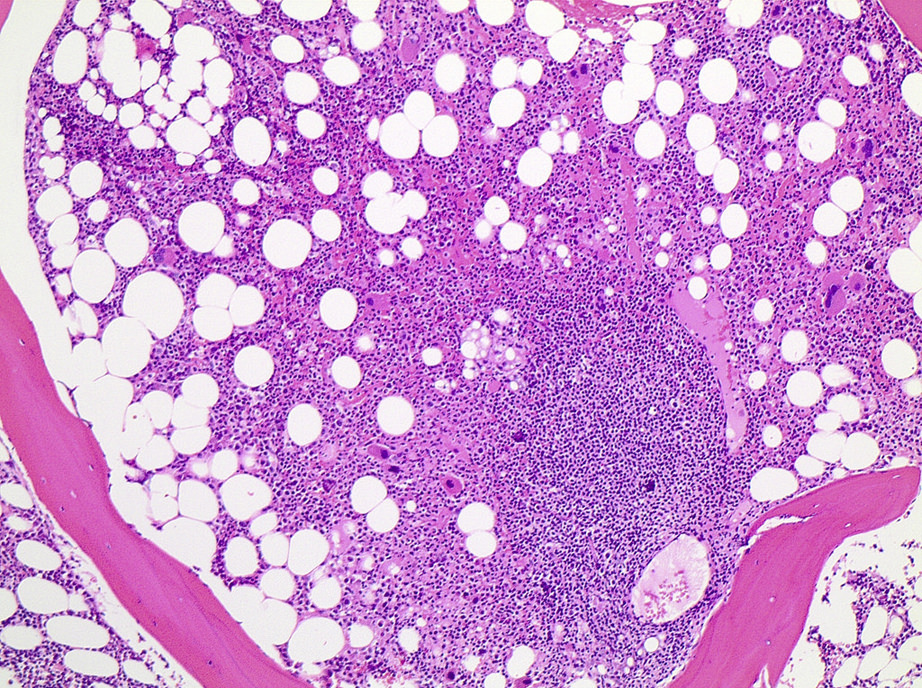
Microscopic (histologic) images
Classic Hodgkin lymphoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Emily Mason, M.D., Ph.D.
Composite lymphoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
DLBCL / high grade B cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 rearrangements
Microscopic (histologic) images
DLBCL, NOS
Microscopic (histologic) images
Videos
Overview of histologic features
DLBCL-primary testicular
Microscopic (histologic) images
EBV related lymphoid proliferations
Diagrams / tables
Table 1: EBV viral gene expression patterns during different types of latency
| Genes | Latency III | Latency II | Latency I | Latency 0 |
| Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1) | + | + | + | - |
| Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA2) | + | - | - | - |
| Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 3 (EBNA3) | + | - | - | - |
| Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen (EBNA) LP | + | - | - | - |
| Latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) | + | + | - | - |
| Latent membrane protein 2 (LMP2) | + | + | - | - |
| Epstein-Barr encoded RNAs (EBERs) | + | + | + | + |
| BHRF1 micro RNAs (miRNAs) | + | - | - | - |
| BamHI A rightward transcript (BART) micro RNAs (miRNAs) | + | + | + | + |
Table 2: Main Epstein-Barr virus serological profiles
| Anti-viral capsid antigen (VCA) IgG | Anti-viral capsid antigen (VCA) IgM | Anti-Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen (EBNA) IgG | Interpretation |
| - | - | - | Seronegative individual |
| Variable | + | - | Primary infection |
| + | - | + | Past infection |
| + | - | - | Past infection (adults) or primary infection (children) |
| + | + | + | Past infection or end of primary infection |
| - | - | + | Indeterminate |
Table 3: Viral latency type in EBV associated lymphoproliferative disorders and lymphomas
| Disease | Percentage of EBV related cases | Latency pattern | Viral proteins expressed | EBER expression pattern | ||||
| EBNA1 | EBNA2 | LMP1 | LMP2 | EBER | ||||
| B cell lymphoproliferative disorders | ||||||||
| Infectious mononucleosis | 100 | III | + | + | + | + | + | Many small and large cells are EBV+ (mainly B cells and rare positive T and NK cells); most of the EBV+ cells are present in the paracortical area |
| EBV positive mucocutaneous ulcer | 100 | I or II | + | - | + | + | + | EBV expression is variable with most cases showing scattered EBV+ cells |
| Lymphoproliferative disorders associated with immune deficiency and dysregulation | > 90 | III or II | + | + | + | + | + |
|
| T / NK lymphoproliferative disorders of childhood | ||||||||
| Hydroa vacciniforme lymphoproliferative disorder | 100 | II | + | - | + | + | + | EBV expression in around 50% of lesional cells |
| Severe mosquito bite allergy | 100 | II | + | - | - | - | + | EBV is positive in few of the lesional NK cells; a much higher density of EBV+ cells should raise suspicion of NK cell lymphoma |
| Chronic active EBV disease (CAEBVD) | 100 | II | + | - | + | + | + | EBV is uniformly expressed in many cytotoxic T cells in most cases |
| B cell lymphomas | ||||||||
| EBV positive diffuse large B cell lymphoma, NOS | 100 | II or III | + | + | + | + | + | Most of the large atypical lymphoma cells are EBV+, a cutoff of 80% has been proposed |
| Diffuse large B cell lymphoma with chronic inflammation | 100 | II or III | + | + | + | + | + | Most of the lymphoma cells are diffusely positive for EBER |
| Fibrin associated large B cell lymphoma | 100 | II or III | + | + | + | + | + | Most of the lymphoma cells are diffusely positive for EBER |
| Primary effusion lymphoma | Most of the lymphoma cells are positive for EBER in the EBV positive cases | |||||||
| HIV associated | 100 | I | + | - | - | - | + | |
| HIV unrelated | 70 - 90 | I | + | - | - | - | + | |
| Lymphomatoid granulomatosis | 100 | III | + | + | + | + | + | The large neoplastic B cells are EBV positive; the number of EBV+ cells determines the grade |
| Plasmablastic lymphoma | 60 - 75 | I | + | - | - | - | + | Most of the lymphoma cells are diffusely EBV positive |
| Burkitt lymphoma | Most lymphoma cells are positive for EBER in EBV positive cases | |||||||
| Endemic | > 95 | I | + | - | - | - | + | |
| Sporadic | 20 - 80 | I | + | - | - | - | + | |
| AIDS related DLBCL | The pattern of EBV expression coincides with the histological subtype of lymphoma occurring in the immunocompetent state | |||||||
| Immunoblastic | 70 - 100 | III | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Nonimmunoblastic | 10 - 30 | III | + | + | + | + | + | |
| CNS lymphomas | 80 - 100 | III | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Hodgkin lymphoma |
| |||||||
| EBV unrelated | 20 - 90 | II | + | - | + | + | + | |
| EBV associated | 100 | II | + | - | + | + | + | |
| EBV positive T and NK cell lymphomas | ||||||||
| Extranodal, NK / T cell lymphoma | 100 | I or II | + | - | Variable | Variable | + | Virtually all lymphoma cells are positive for EBER |
| Aggressive NK cell leukemia | 90 | II | + | - | + | + | + | Most lymphoma cells are EBV positive |
| Primary nodal EBV positive T / NK cell lymphoma | 100 | II | + | - | + | + | + | Most lymphoma cells are EBV positive |
| Systemic EBV positive T cell lymphoma of childhood | 100 | II | + | - | + | + | + | Most lymphoma cells are EBV positive |
Table 4: Differential diagnosis of EBV positive B cell lymphoproliferative disorders and lymphomas
| Features | Infectious mononucleosis | EBV+ mucocutaneous ulcer | EBV+ classic Hodgkin lymphoma | EBV+ diffuse large B cell lymphoma |
| Clinical | ||||
| Age | Young, elderly | Elderly | Young and elderly | Elderly |
| Lymphadenopathy | Present | Absent | Present, nodal or mediastinal | Present, high stage |
| LDH elevation | Present, mild to moderate | Absent | Present | Present |
| Extranodal disease | Absent | Present | Extremely rare as primary disease | Can be present, late stages |
| Clinical course | Self limited in majority of cases | Waxing and wanning | Progressive | Aggressive, poor outcome |
| Morphology | ||||
| Architecture | Paracortical | Ulcer | Effacement | Effacement |
| Circumscription | Absent | Present, lymphocytic rim at base | Absent | Absent, diffuse involvement |
| Large cells | Reed-Sternberg-like cells | Reed-Sternberg-like cells | Reed-Sternberg cells | Sheets of large neoplastic cells, some RS-like cells |
| EBV latency type | III | II / III | II | III / II |
| Immunohistochemistry | ||||
| CD45 | Positive in most cells | Positive in most cells | Negative in HRS cells | Positive in neoplastic cells |
| CD20 | Positive in large cells | Positive in large cells | Mostly negative in HRS cells, faint reactivity in HRS cells in ~20% of cases | Positive in large cells |
| PAX5 | Positive, strong | Positive, strong | Positive, weak | Positive, strong |
| BOB.1 | Positive, strong | Positive, strong | Negative, can be weak | Positive, strong |
| MUM1 | Positive | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| BCL6 | Negative | Negative | Negative | Can be positive |
| CD10 | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| CD30 | Positive in HRS-like cells, usually dim | Positive in HRS-like cells, usually dim | Positive in HRS cells, strong | Positive |
| CD15 | Positive in up to 50% of cases | Positive in up to 50% of cases | Positive, variable | Positive in up to 50% of cases |
| PDL1 | Negative | Negative | Positive in > 80% | Can be positive (40 - 60%, extranodal) |
| Diagnostic molecular testing | ||||
| B cell | Polyclonal | Clonal in 50% of the cases | Clonal | Monoclonal IGH gene rearrangements |
| T cell | Polyclonal | Oligoclonal and restricted TCR rearrangement patterns | Polyclonal, restricted pattern in elderly patients | Oligoclonal and restricted TCR rearrangement patterns |
| Genetic features | No immune evasion features | No immune evasion features | Immune evasion (host evasion) | Immune evasion (host evasion) |
Table 5: Differential diagnosis of EBV positive T and NK lymphomas
| Feature | Extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma | Aggressive NK cell leukemia | EBV positive nodal T and NK cell lymphoma | Systemic EBV+ T cell lymphoma of childhood |
| Clinical presentation | ||||
| Age | Adults | Young to middle aged adults | Older adults | Children, young adults |
| Site at presentation | Nasopharynx (70 - 80%), others (20 - 30%): skin, gastrointestinal (GI) | Bone marrow, spleen, peripheral blood, rarely lymph nodes (20%) | Lymph nodes, no nasal involvement by definition | Systemic proliferation: bone marrow, liver or spleen, CNS |
| Behavior | Localized disease, frequent dissemination | Fatal | Aggressive | Fulminant |
| Median survival | 26 - 76 months | Weeks | 4 months | Days to weeks |
| Hemophagocytic syndrome | Generally absent | Present | Uncommon | Always present |
| Morphology | ||||
| Cytology of neoplastic cells | Variable atypia, spectrum from small to large cells | Large granular atypical lymphocytes, distinct nucleoli and clear cytoplasm (smears) | Pleomorphic medium sized cells, with centroblastic, anaplastic or plasmacytoid features | Small to intermediate sized with subtle to absent atypia (most common) or large atypical cells |
| Necrosis | Common | Frequently present | Variable | Absent |
| Angiocentricity and angiodestruction | Present | Frequently present | Uncommon | Absent |
| Apoptosis | Present | Frequently present | Variable | Absent |
| Ancillary testing | ||||
| CD2 | Positive | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| CD3 | Often negative; subset is positive | Negative | Positive | Positive |
| CD3ε | Positive | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| CD4 | Negative | Negative | Negative | Usually negative |
| CD8 | Positive | Usually negative | Positive (> 80%) | Usually positive |
| CD56 | Positive | Positive | Mostly negative (positive < 20%) | Negative |
| Cytotoxic granules | Positive | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| EBER | All neoplastic cells | All neoplastic cells, a subset is negative (< 15%) | All neoplastic cells | Majority of neoplastic cells |
Table 6: Differential diagnosis of EBV+ B cell lymphoproliferations with Hodgkin-like features
| Disease | Clinical features | Morphology | Immunophenotype | Lineage, clonality and molecular features |
| EBV+ mucocutaneous ulcer |
|
|
|
|
| EBV+ diffuse large B cell lymphoma, NOS |
|
|
|
|
| EBV+ classic Hodgkin lymphoma |
|
|
|
|
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Roberto N. Miranda, M.D. and Roman Segura-Rivera, M.D.
EBV+ DLBCL
Microscopic (histologic) images
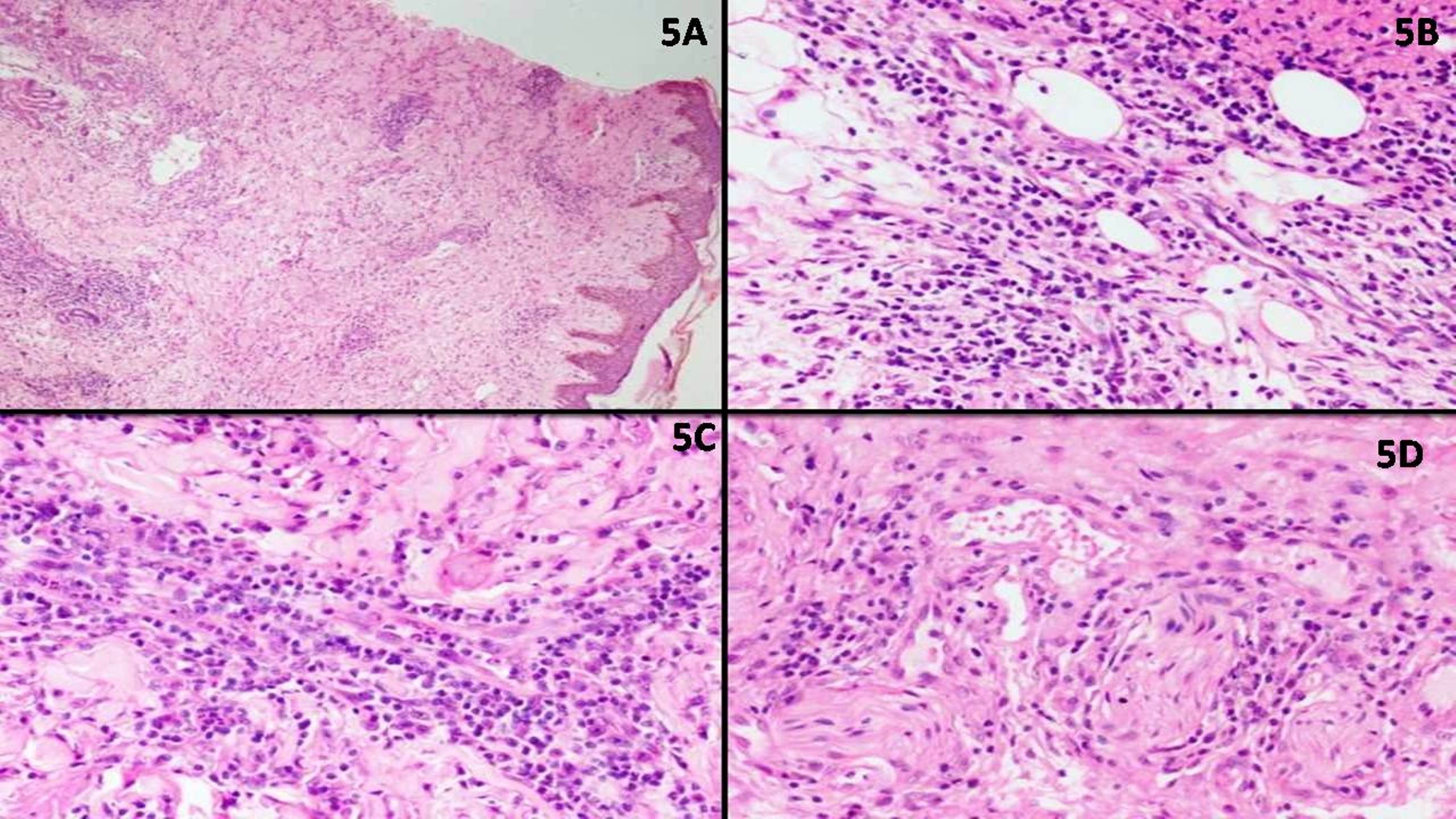
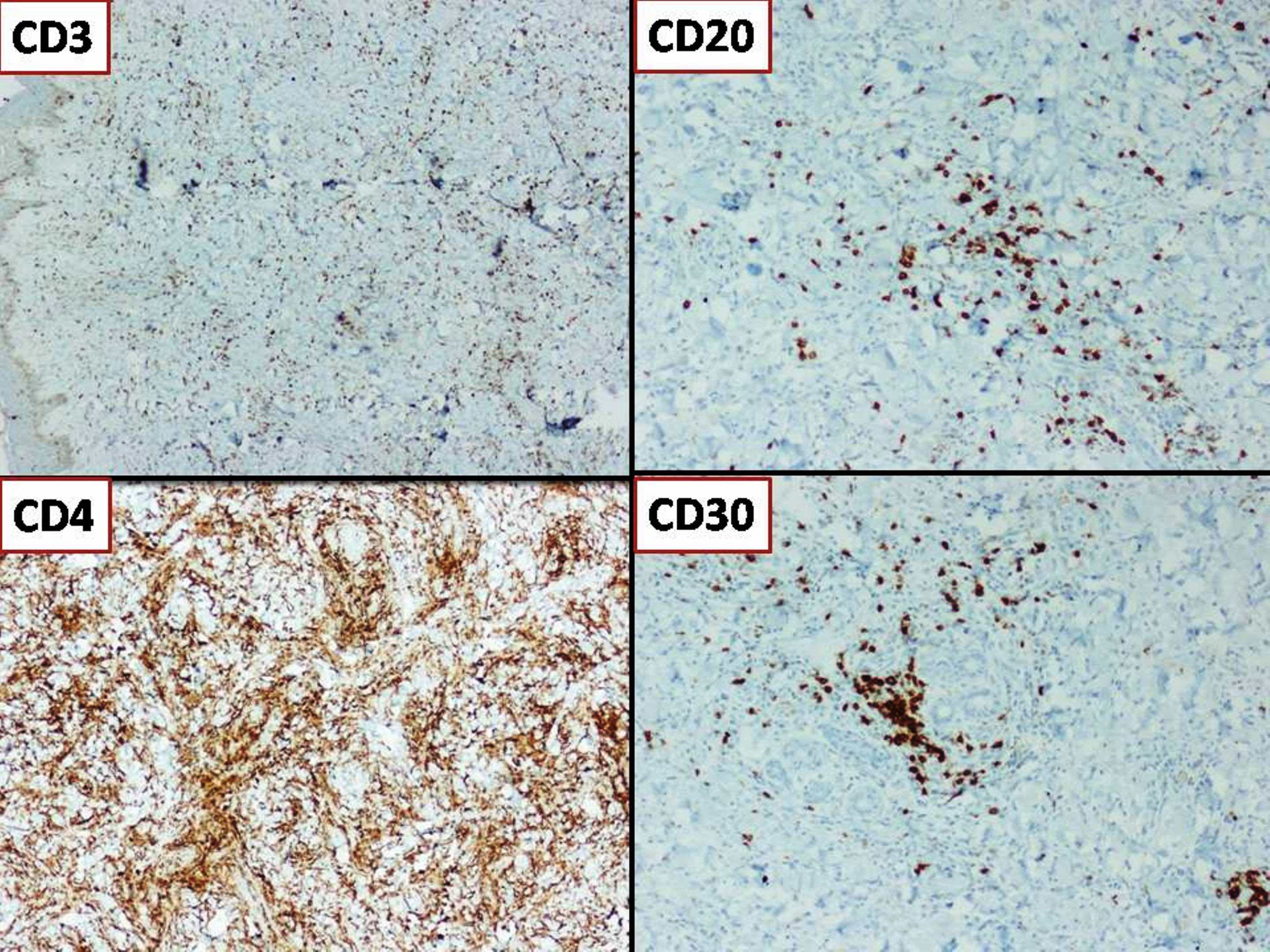
EBV+ mucocutaneous ulcer
Diagrams / tables
Microscopic (histologic) images
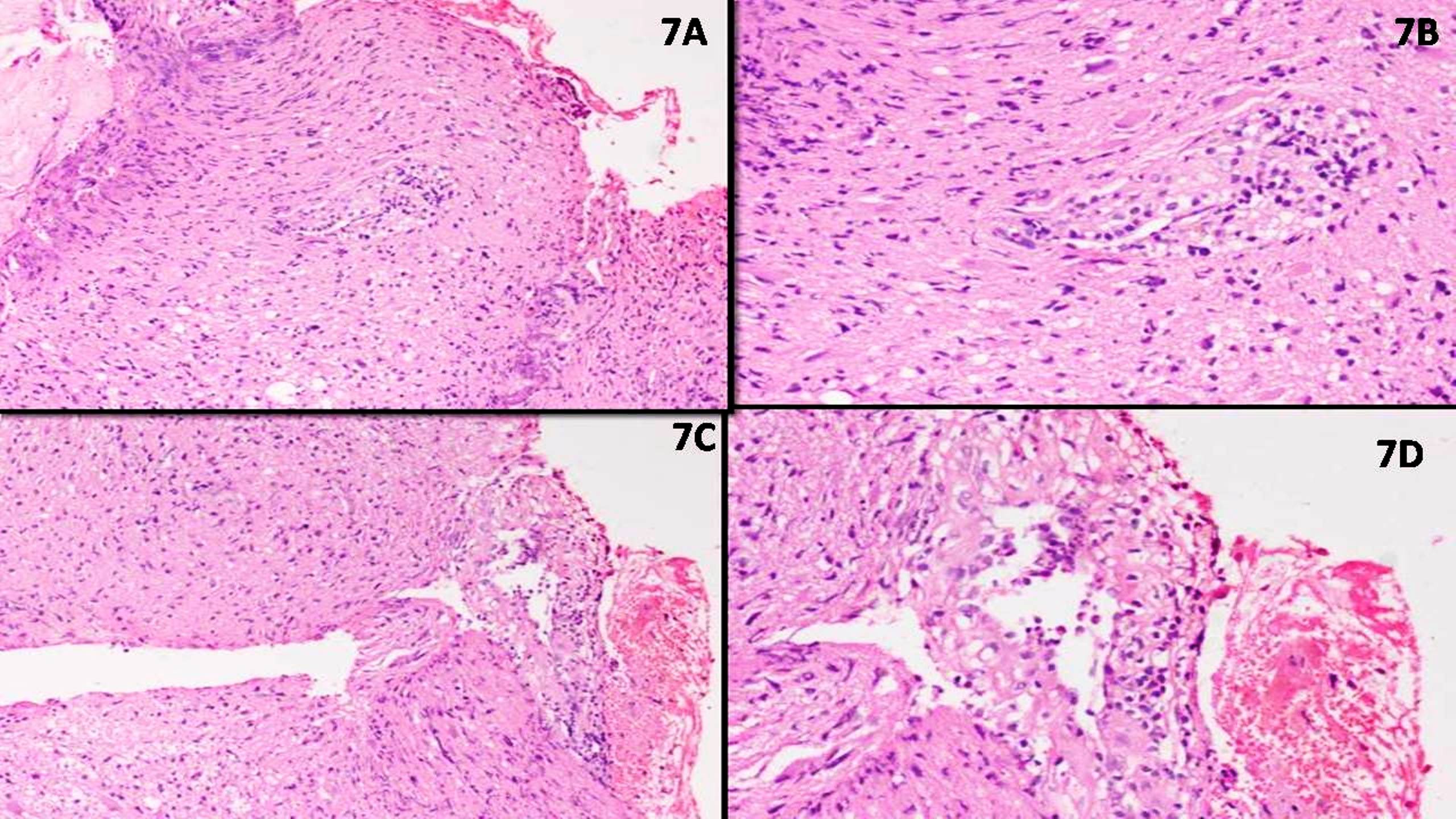
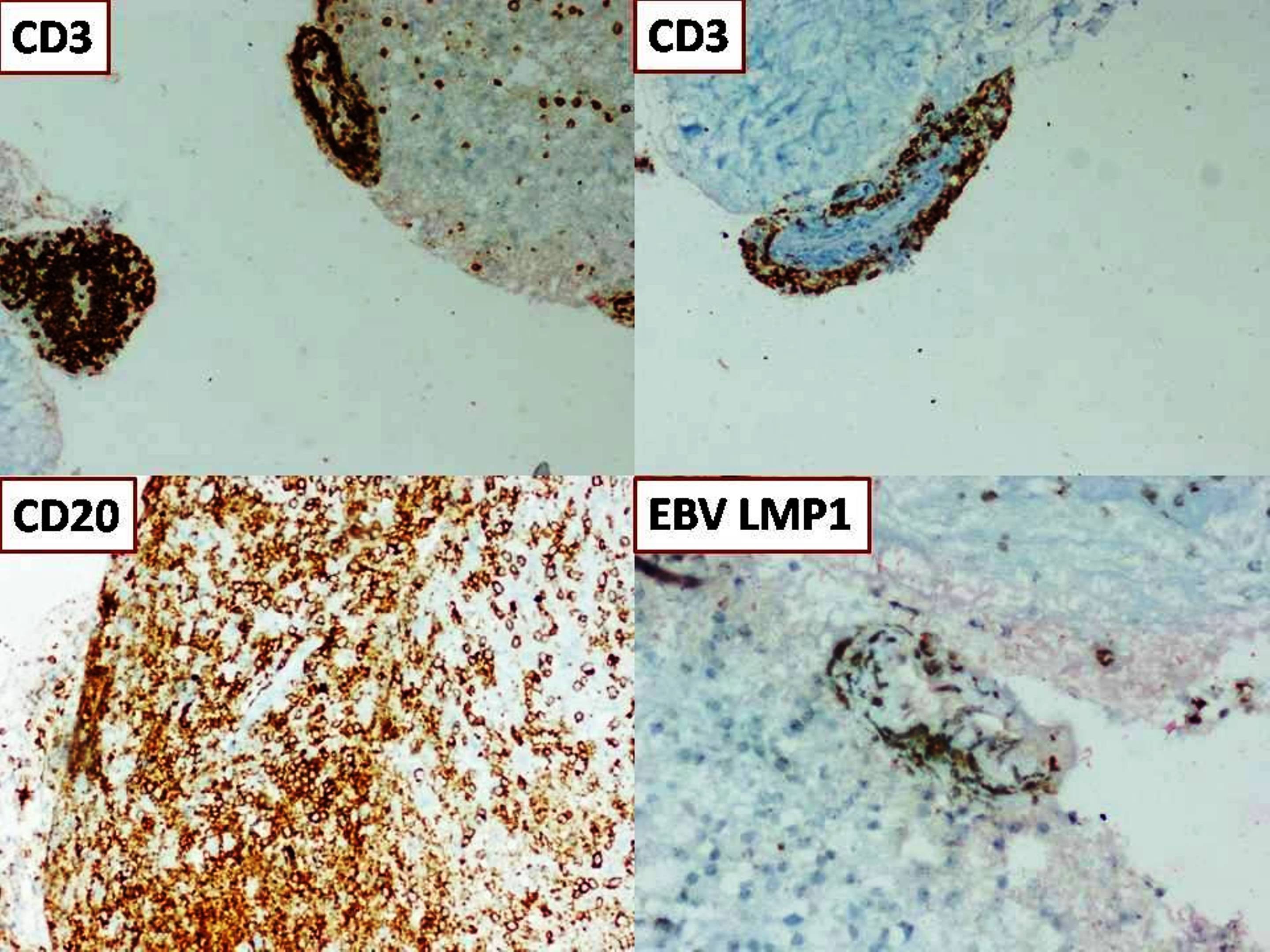
EBV+ nodal T and NK cell lymphoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Enteropathy associated T cell lymphoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Roberto N. Miranda, M.D.
Extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Roberto N. Miranda, M.D. and Carlos A. Torres-Cabala, M.D.
Fibrin associated large B cell lymphoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Jordan M. Hall, M.D., Hyunkyu Shin, M.D., Dr. Christian Schürch, M.D., Ph.D., Falko Fend, M.D. and Claudia Wickenhauser, M.D., Ph.D. (Case #529)
Flow cytometry
Diagrams / tables
Fluid overload associated LBCL
Cytology images
Follicular lymphoma-duodenal type
Diagrams / tables
| Nodal Follicular Lymphoma | Duodenal Follicular Lymphoma |
| Grade 1 - 2 or 3 | Grade 1 - 2 |
| Stage III or IV | Stage I or II |
| BCL2, CD10, BCL6: Positive | BCL2, CD10, BCL6: Positive |
| AID: Positive | AID: Negative |
| CD21 stain: Dense stain in the center of germinal center of follicles |
CD21 stain: Accentuated staining at the periphery of germinal center of follicles |
| BCL2 and BCL6 rearrangements: + | BCL2 and BCL6 rearrangements: + |
| CREBBP mutations present | CREBBP mutations present |
| KMT2D mutations present | Lower KMT2D mutations present |
Microscopic (histologic) images
Follicular-usual
Diagrams / tables
| World Health Organization grading of follicular lymphoma | |||
| Grade | Definition | Pattern | Immunohistochemistry and cytogenetics |
| 1 | 0 - 5 centroblasts/high power field | Follicular or diffuse |
IHC: CD10: + (95 - 100%) BCL2: + (85 - 90%) FISH: BCL2 translocation: + (80 - 90%) BCL6 rearrangement: + (3%) Ki67: < 20%* |
| 2 | 6 - 15 centroblasts/high power field | Follicular or diffuse | |
| 3A | > 15 centroblasts/high power field Centrocytes present | Follicular If diffuse component: Reported as diffuse large B cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma (% of each component is reported); correlate with clinical features and overall grade in cases with small areas of diffuse pattern |
IHC: CD10: + (80 - 95%) BCL2: + (50 - 75%) FISH: BCL2 translocation: + (60 - 70%) BCL6 rearrangement: + (30 - 40%) Ki67: > 20% |
| 3B | > 15 centroblasts/high power field Lack centrocytes | Follicular If diffuse component: Reported as diffuse large B cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma (% of each component is reported) |
IHC: CD10: + (40 - 85%) BCL2: + (45 - 75%) FISH: BCL2 translocation: + (15 - 30%) BCL6 rearrangement: + (40 - 50%) CD10-IRF4/MUM1+: common Ki67: > 50% |
Notes:
- IHC: immunohistochemistry
- FISH: fluorescence in situ hybridization
- High power field of 0.159 mm2 (40× objective)
- Follicular: > 75% (proportion follicular %)
- Diffuse: 0% (proportion follicular %)
- * ~20% of low grade follicular lymphomas have a high proliferation (Ki67) rate (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1490)
- References: Arch Pathol Lab Med 2018;142:1330, Haematologica 2018;103:1182, Swerdlow: WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th Edition, 2017
Microscopic (histologic) images
Flow cytometry images
HHV8 positive DLBCL, NOS
Microscopic (histologic) images
HHV8 positive germinotropic lymphoproliferative disorder
Microscopic (histologic) images
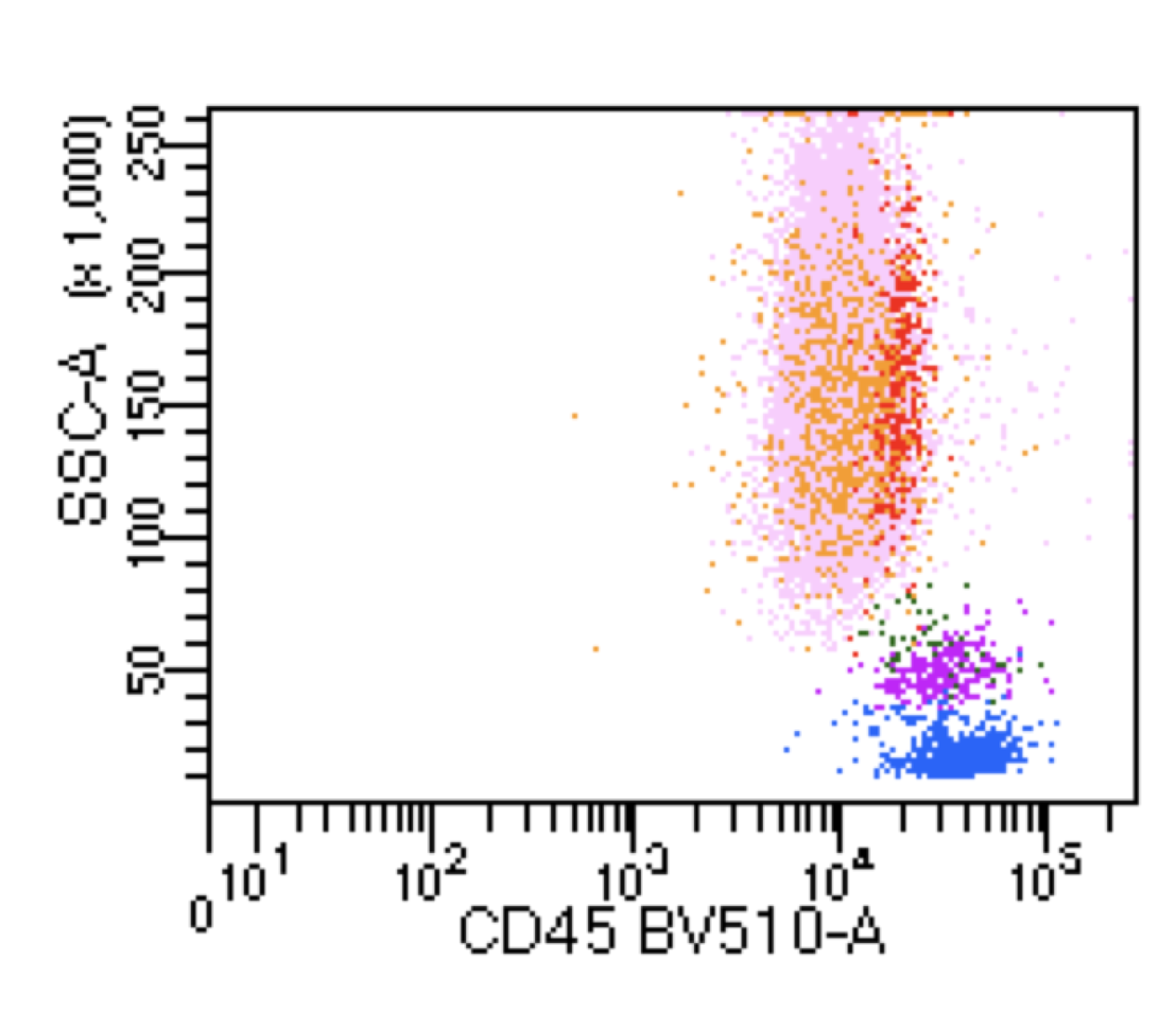
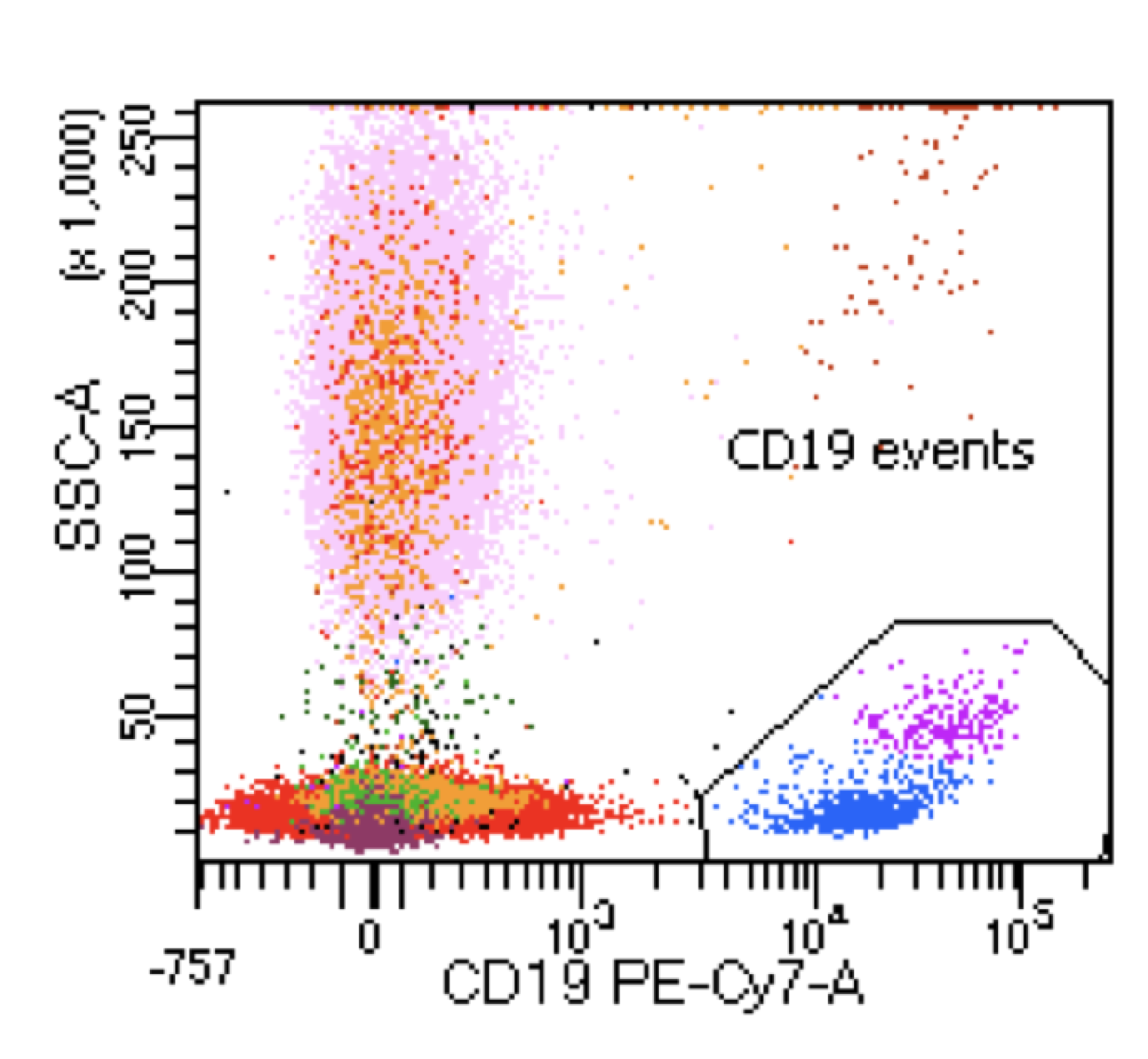
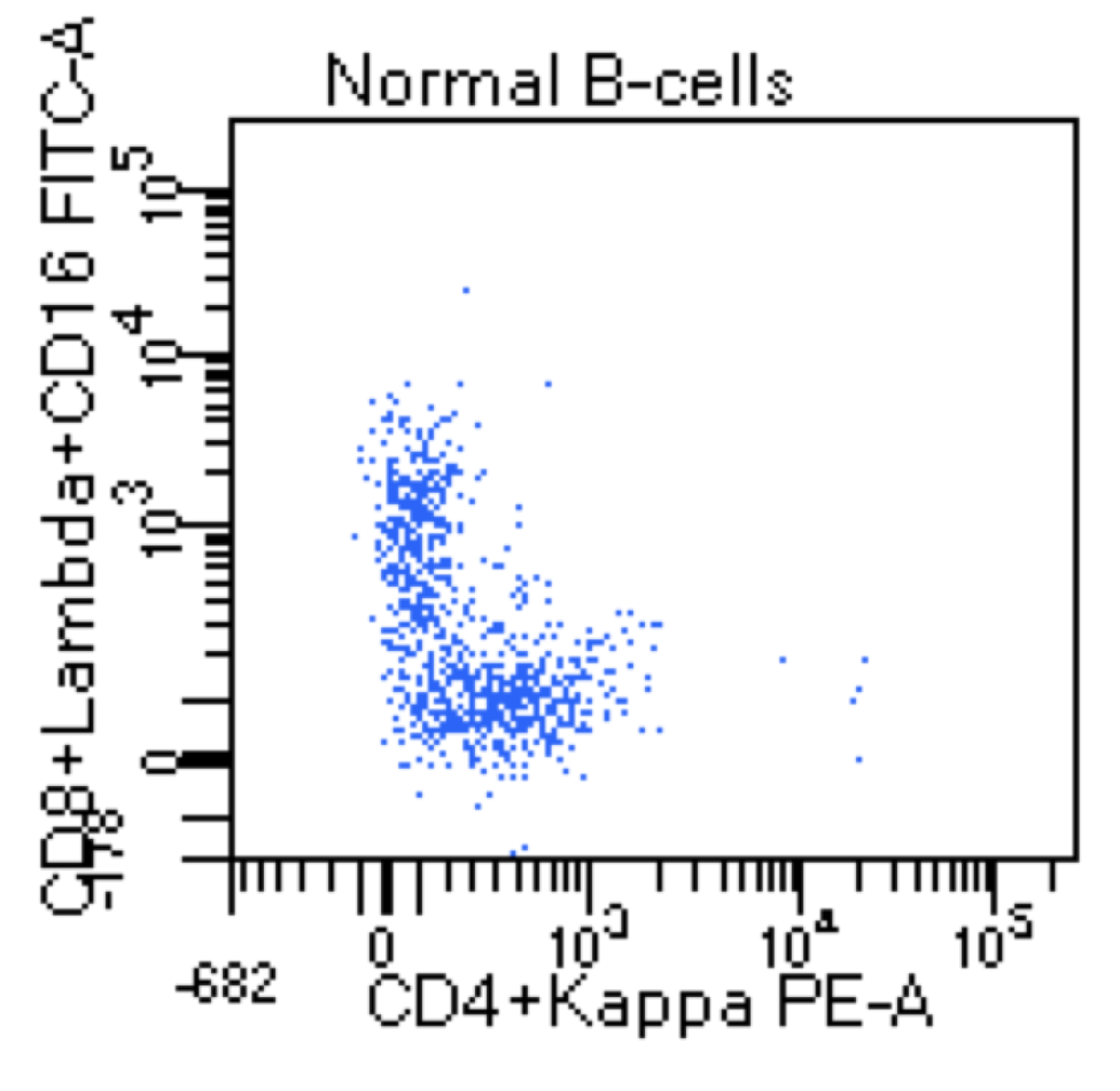
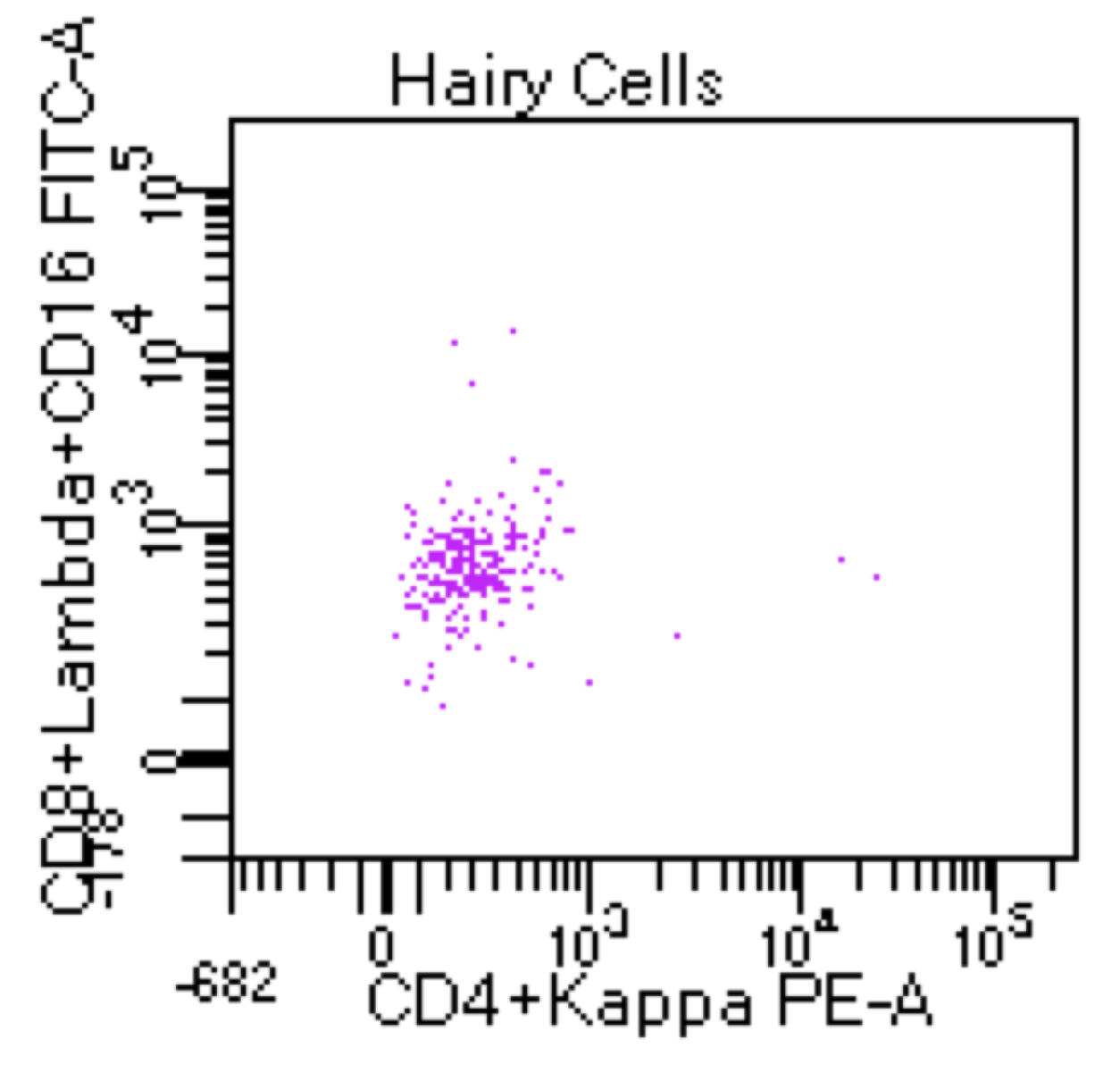
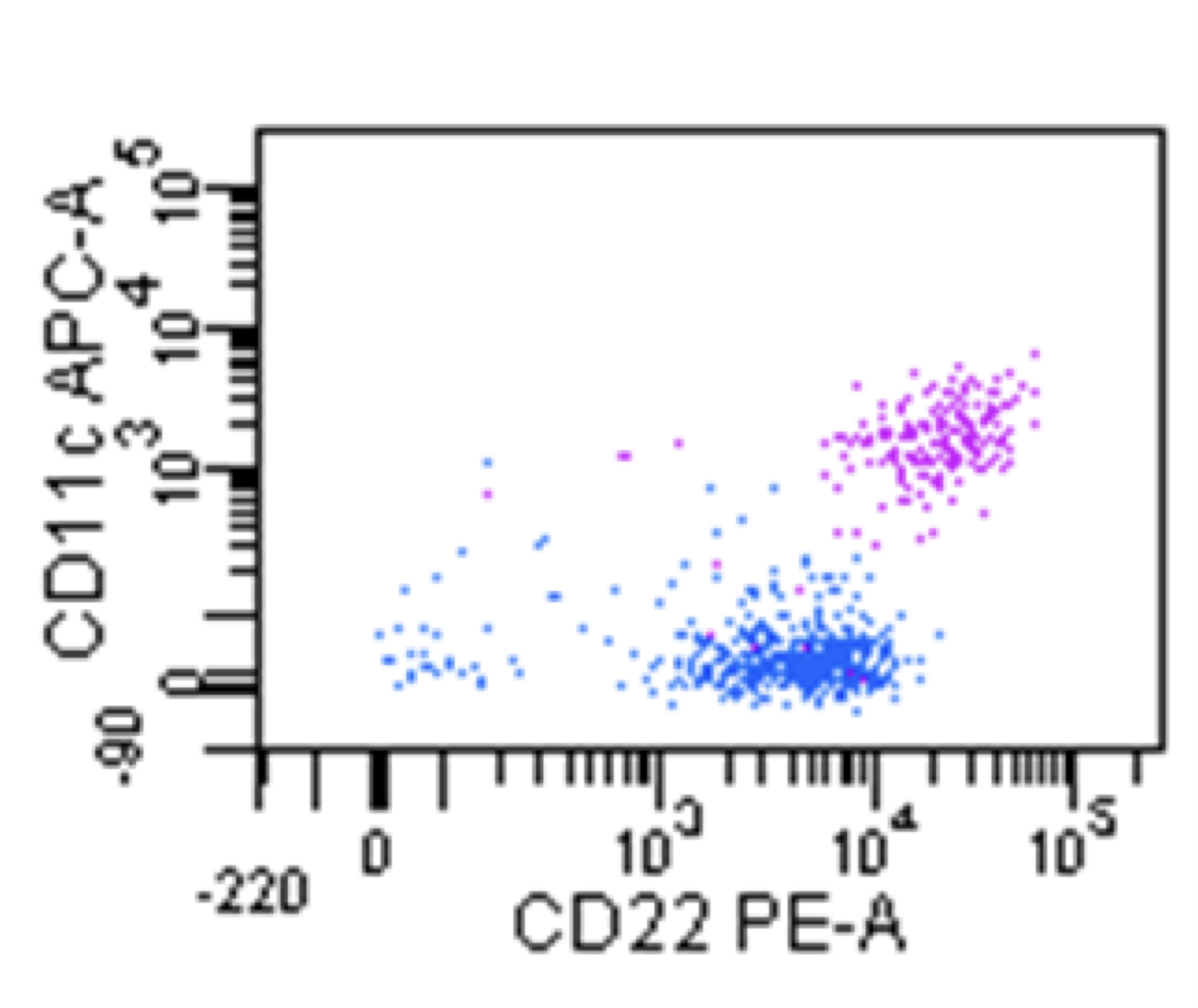
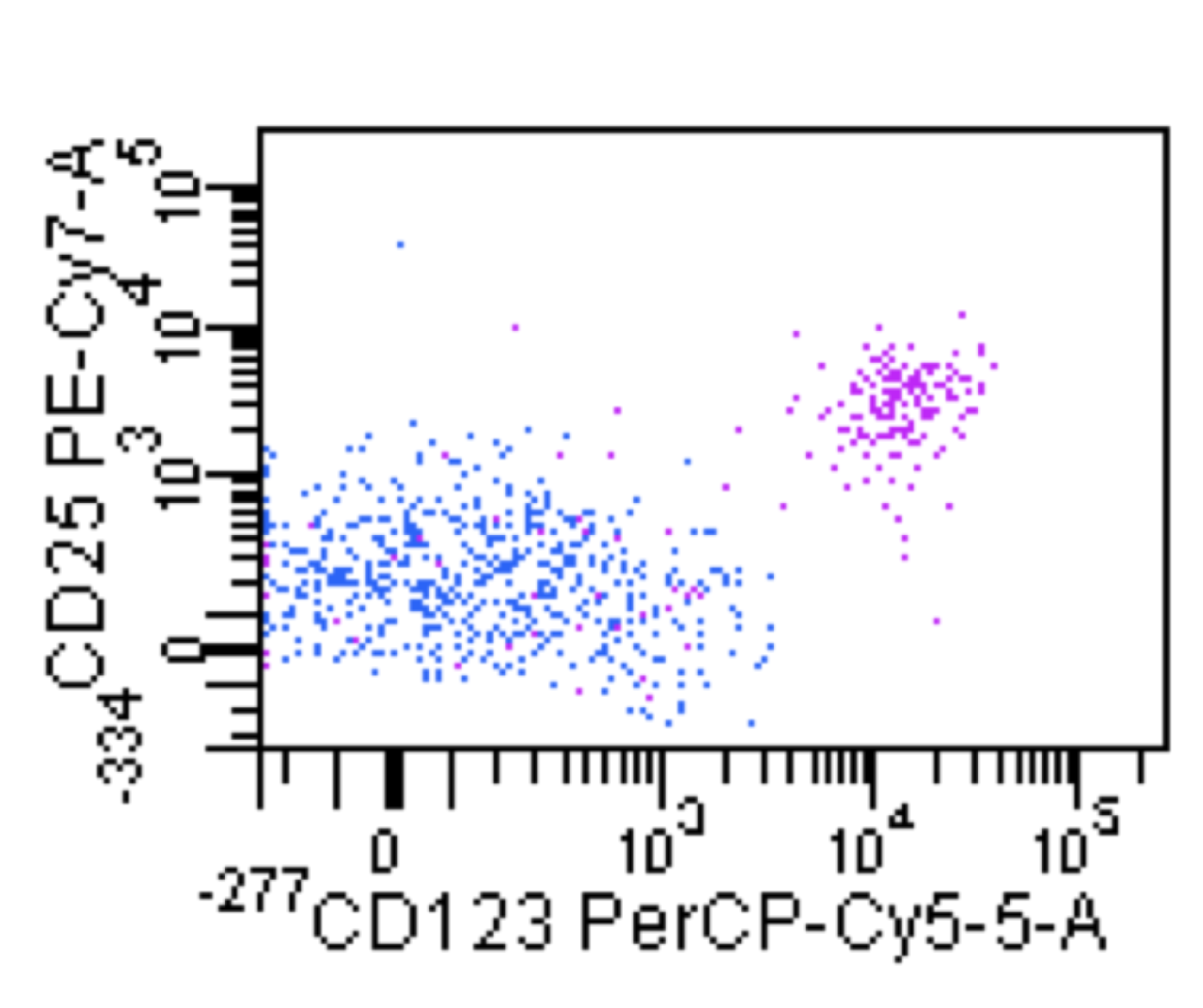
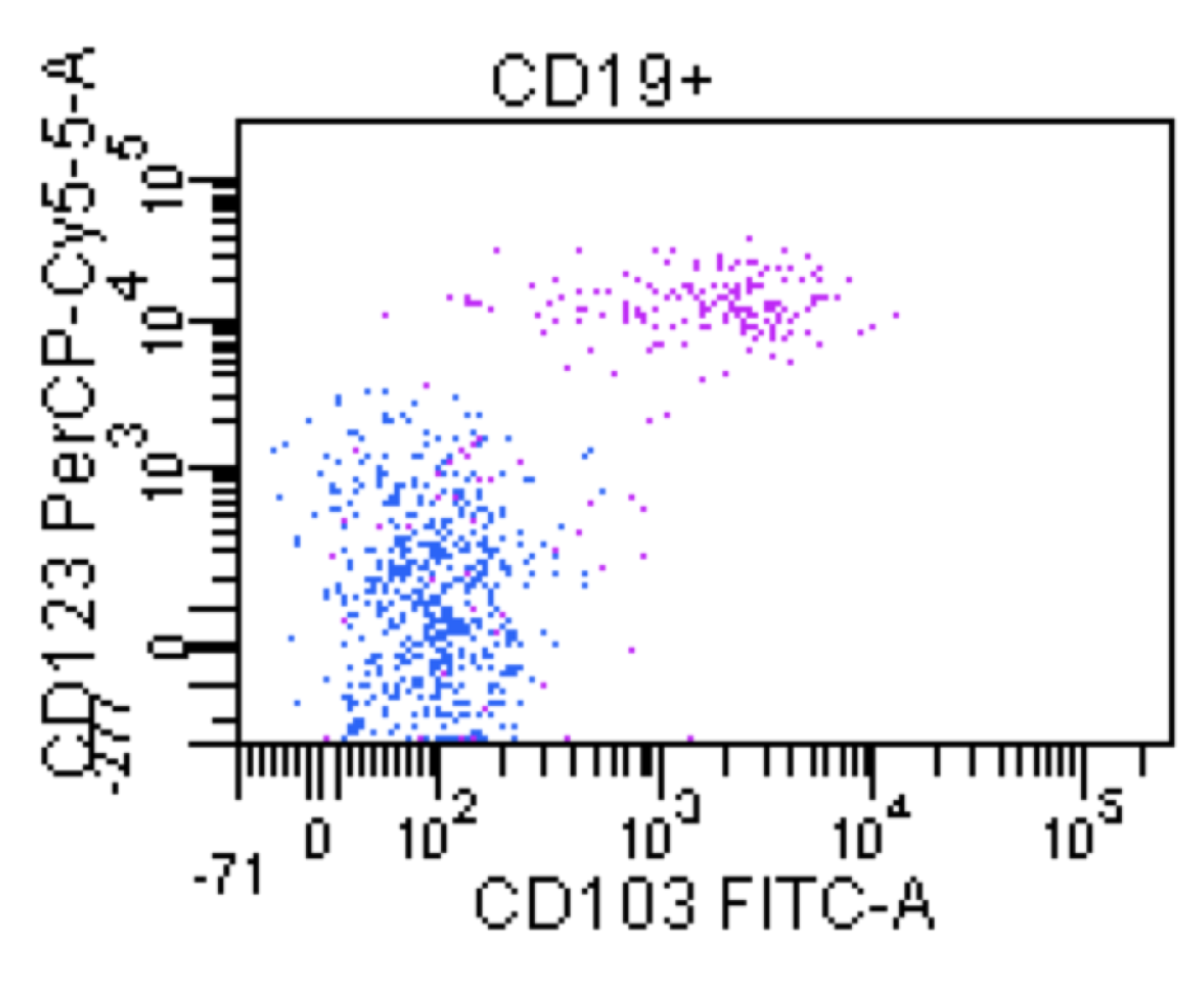
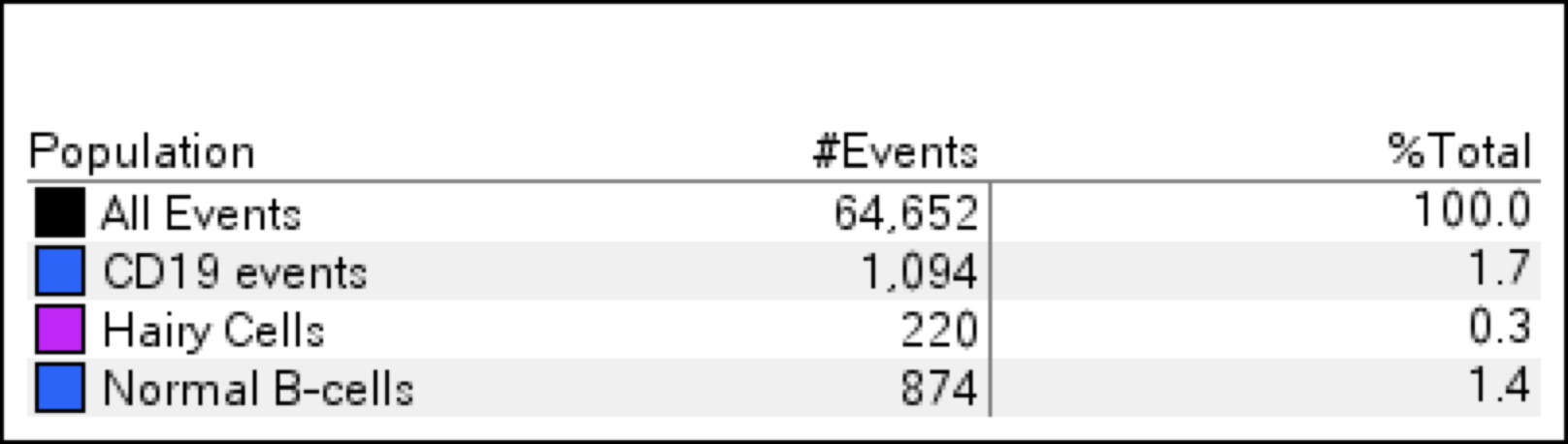
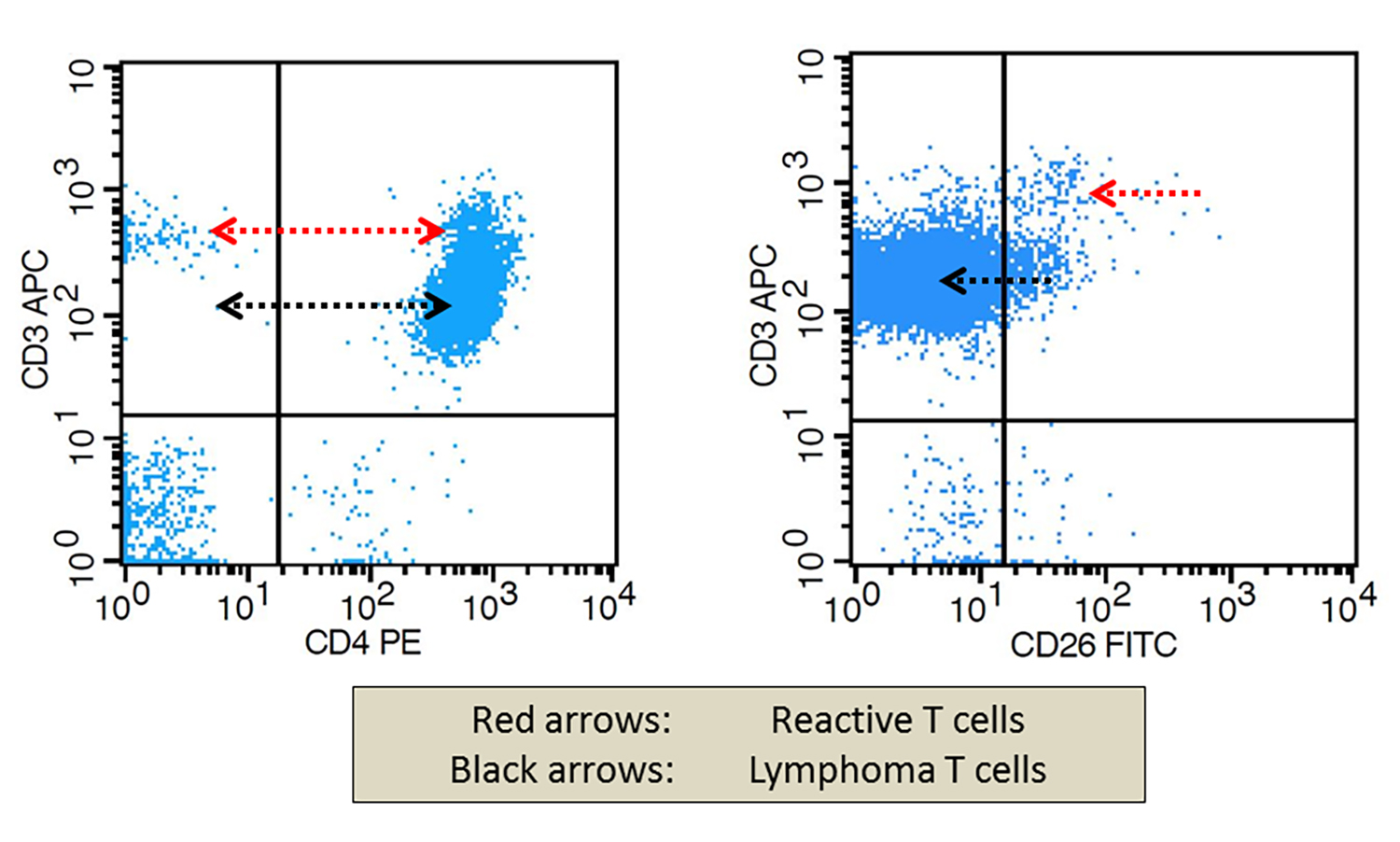
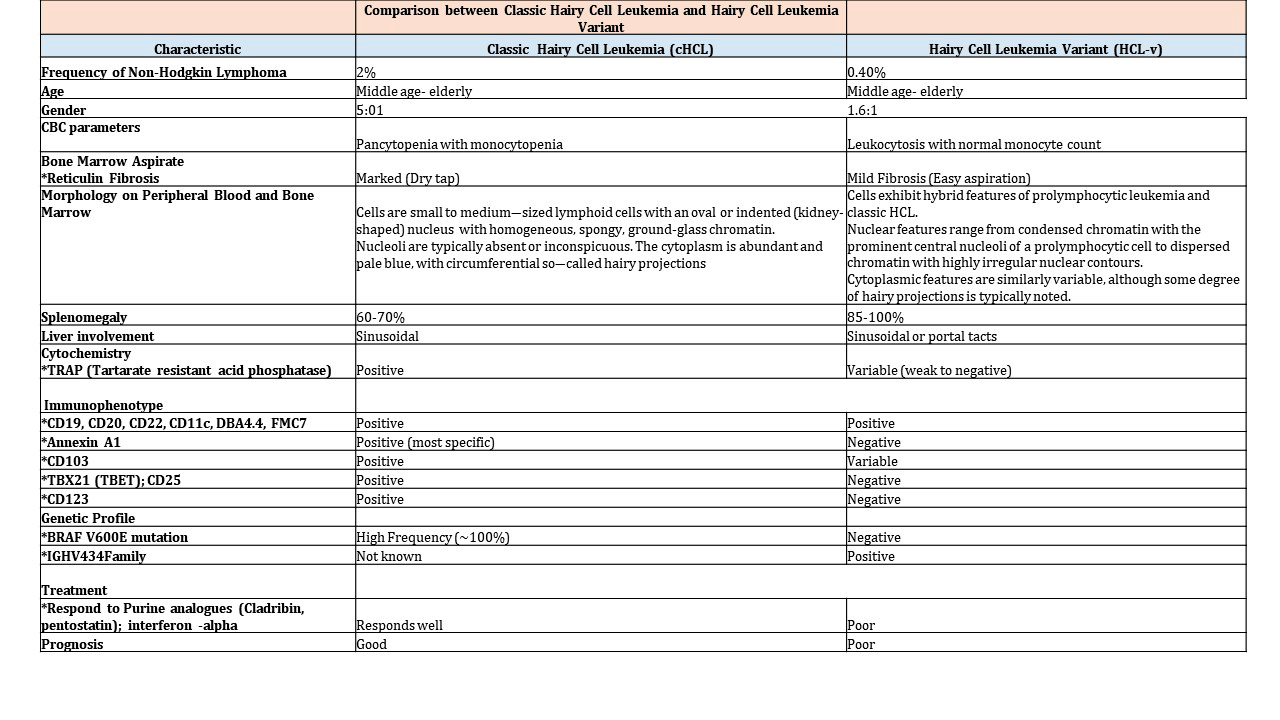
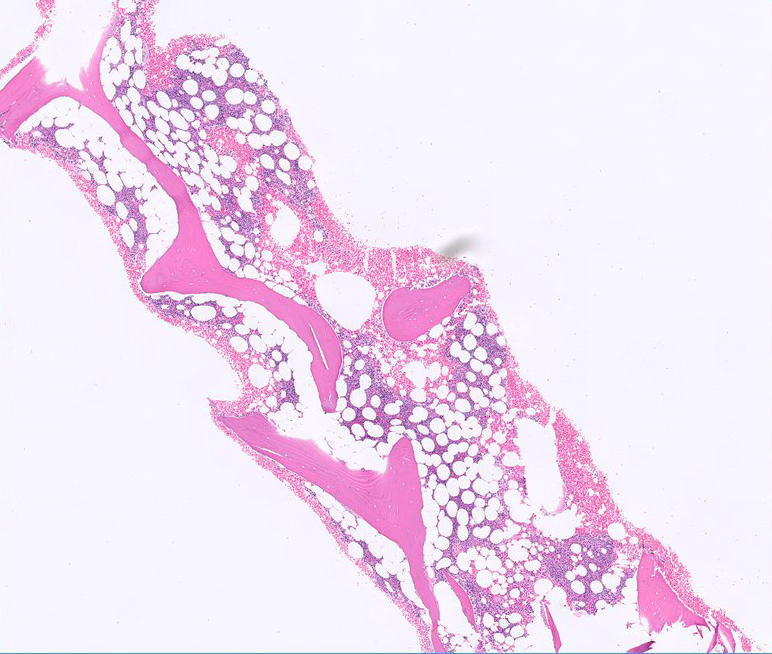
Hairy cell leukemia
Microscopic (histologic) images
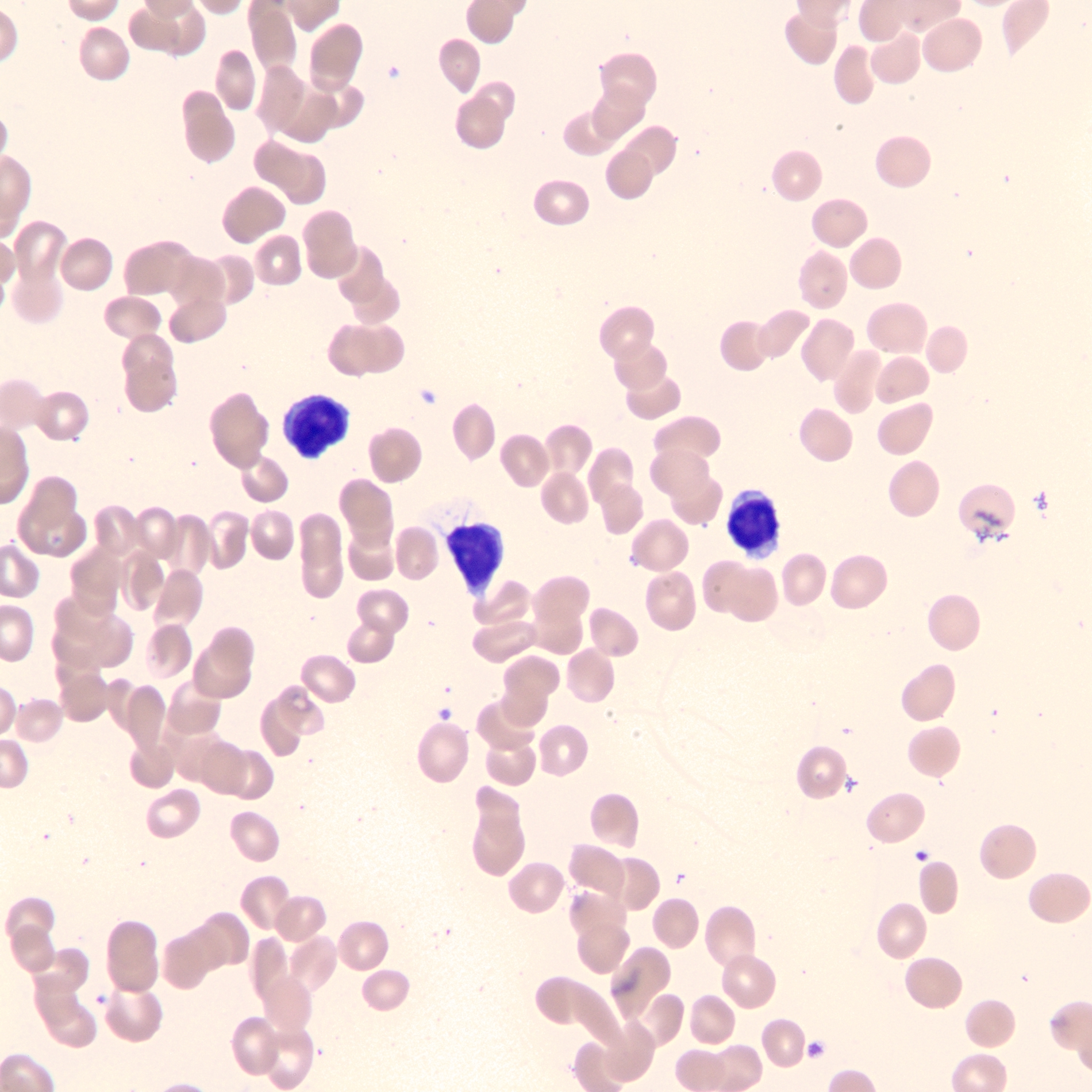
Peripheral smear images
Contributed by Buthaina Al-Maashari, M.D., Dietrich Werner, M.D. and @pleasingpathology on Instagram
Images hosted on other servers:
Flow cytometry images
Hepatosplenic T cell lymphoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Roberto N. Miranda, M.D.
High grade B cell lymphoma with 11q aberrations
Microscopic (histologic) images
High grade B cell lymphoma, NOS
Microscopic (histologic) images
In situ follicular B cell neoplasm
Microscopic (histologic) images
In situ mantle cell neoplasm
Microscopic (histologic) images
Inborn error of immunity-associated lymphoid proliferations and lymphomas
Microscopic (histologic) images
Indolent NK cell lymphoproliferative disease of the GI tract
Microscopic (histologic) images
Indolent T cell lymphoma of the GI tract
Microscopic (histologic) images
Intestinal T cell lymphoma, NOS
Microscopic (histologic) images
Intravascular LBCL
Microscopic (histologic) images
LBCL with IRF4 rearrangement
Microscopic (histologic) images
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Lymphomas arising in immune deficiency / dysregulation
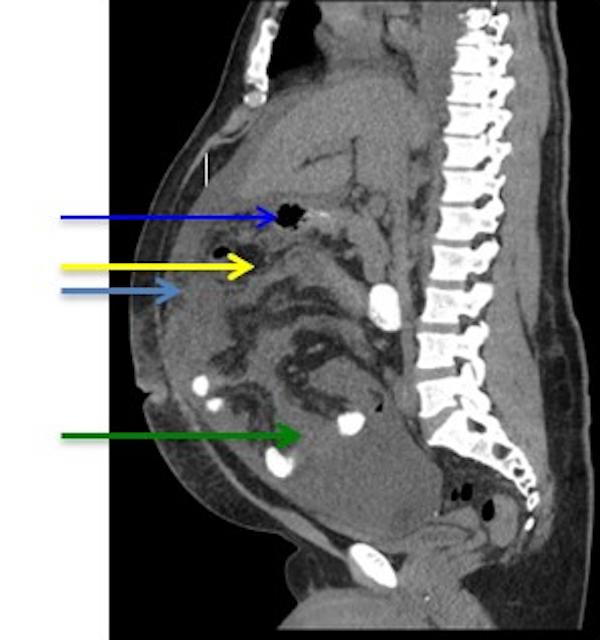
Radiology images
N/A
Clinical images
N/A
Gross images
N/A
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Roberto N. Miranda, M.D.
Cytology images
N/A
Peripheral smear images
N/A
Flow cytometry images
N/A
Electron microscopy images
N/A
Molecular / cytogenetics images
N/A
Videos
N/A
Lymphomatoid granulomatosis
Radiology images
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Nicholas Joseph Dcunha, M.B.B.S., M.D. and Elanthenral Sigamani, M.B.B.S., M.D.
Lymphomatoid papulosis
Clinical images
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Roberto N. Miranda, M.D.
Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Ling Zhang, M.D.
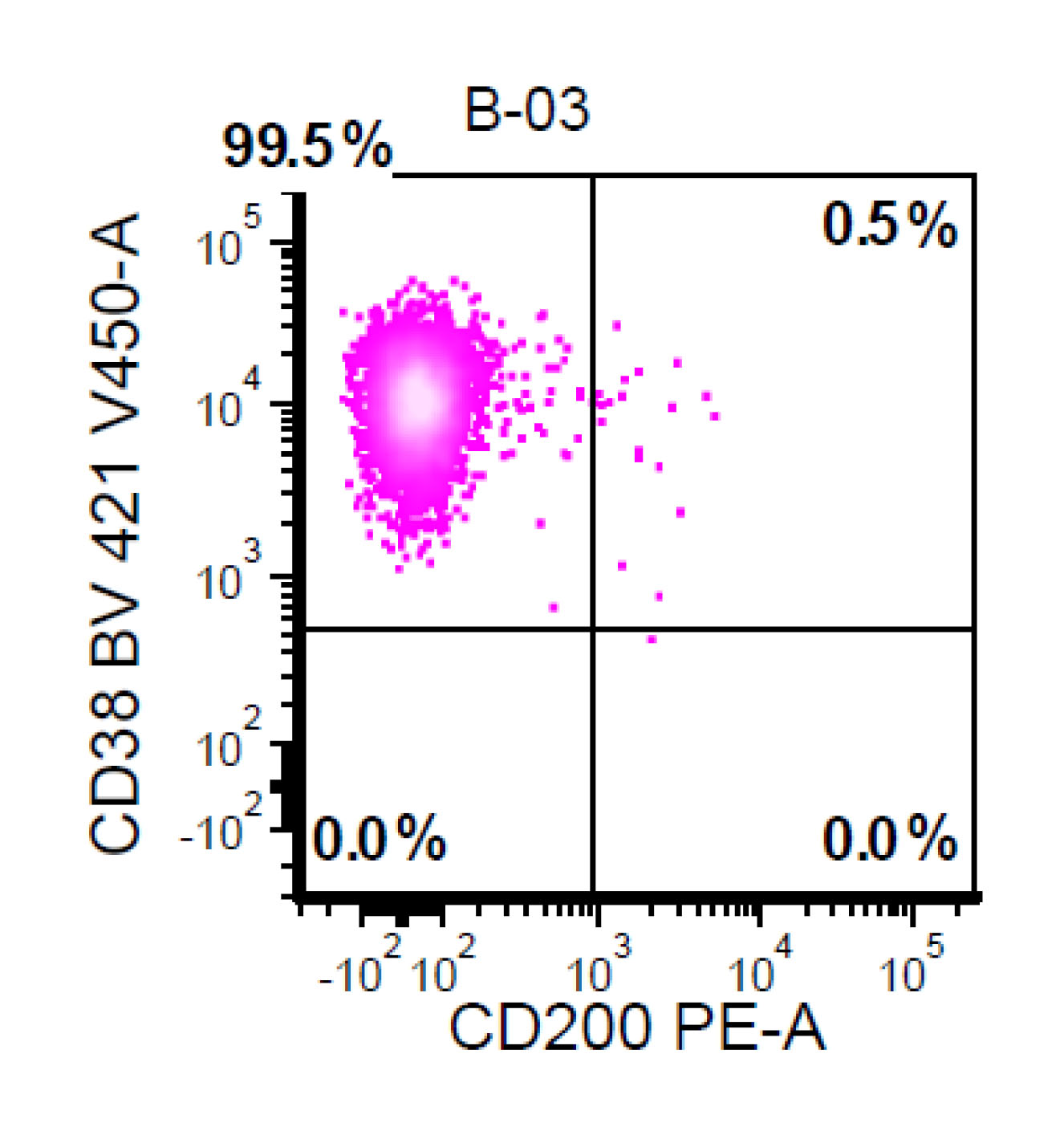
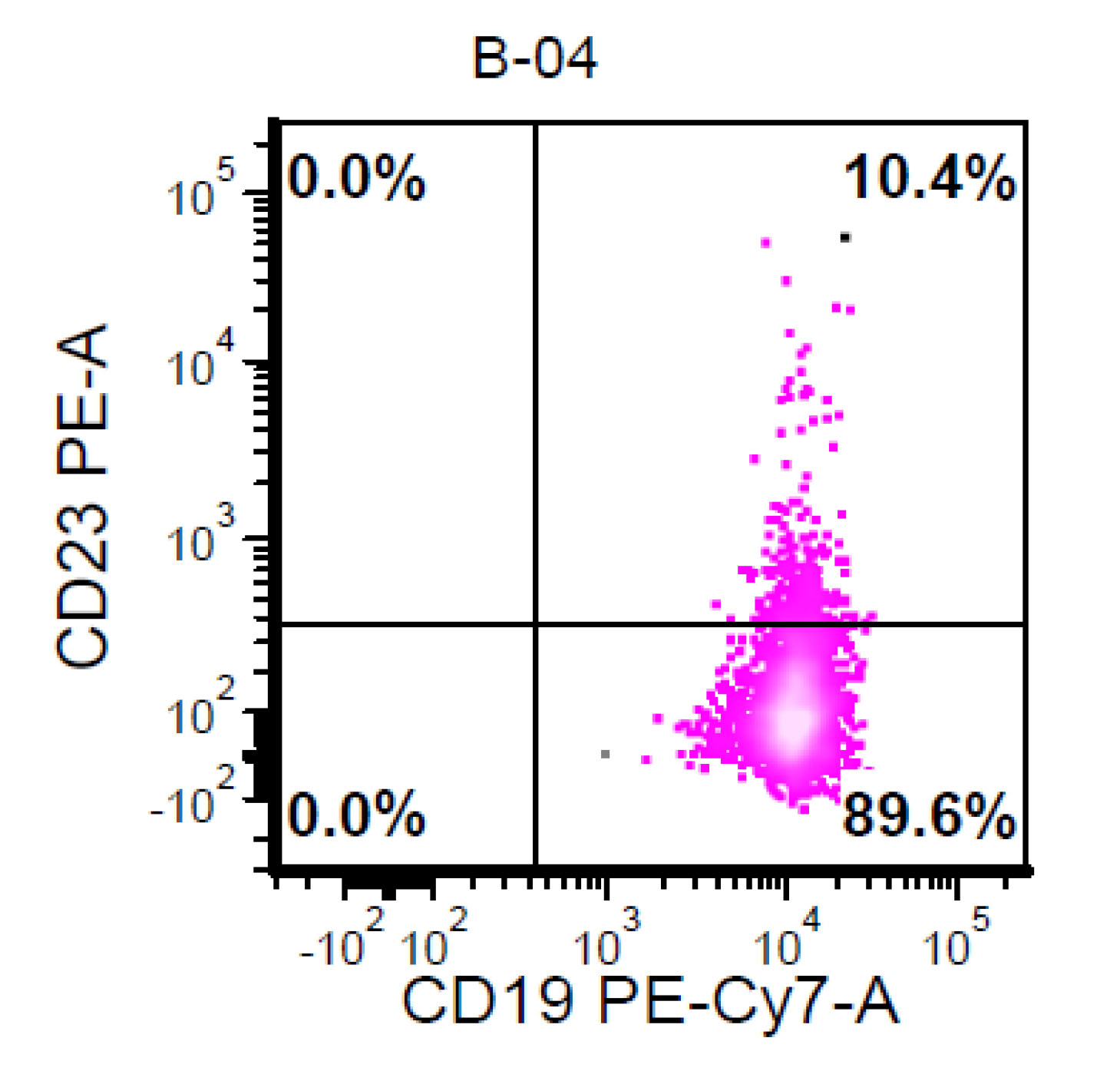
Flow cytometry images
Contributed by Ling Zhang, M.D. and Caroline An, M.D.
Molecular / cytogenetics images
MALT-marginal zone
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Roberto N. Miranda, M.D.
MCL-aggressive variants
Microscopic (histologic) images
Flow cytometry images
Molecular / cytogenetics images
MCL-classic
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Chi Young Ok, M.D.
Flow cytometry images
Molecular / cytogenetics images
MCL-leukemic nonnodal
Microscopic (histologic) images
Flow cytometry images
Marginal zone-nodal
Microscopic (histologic) images
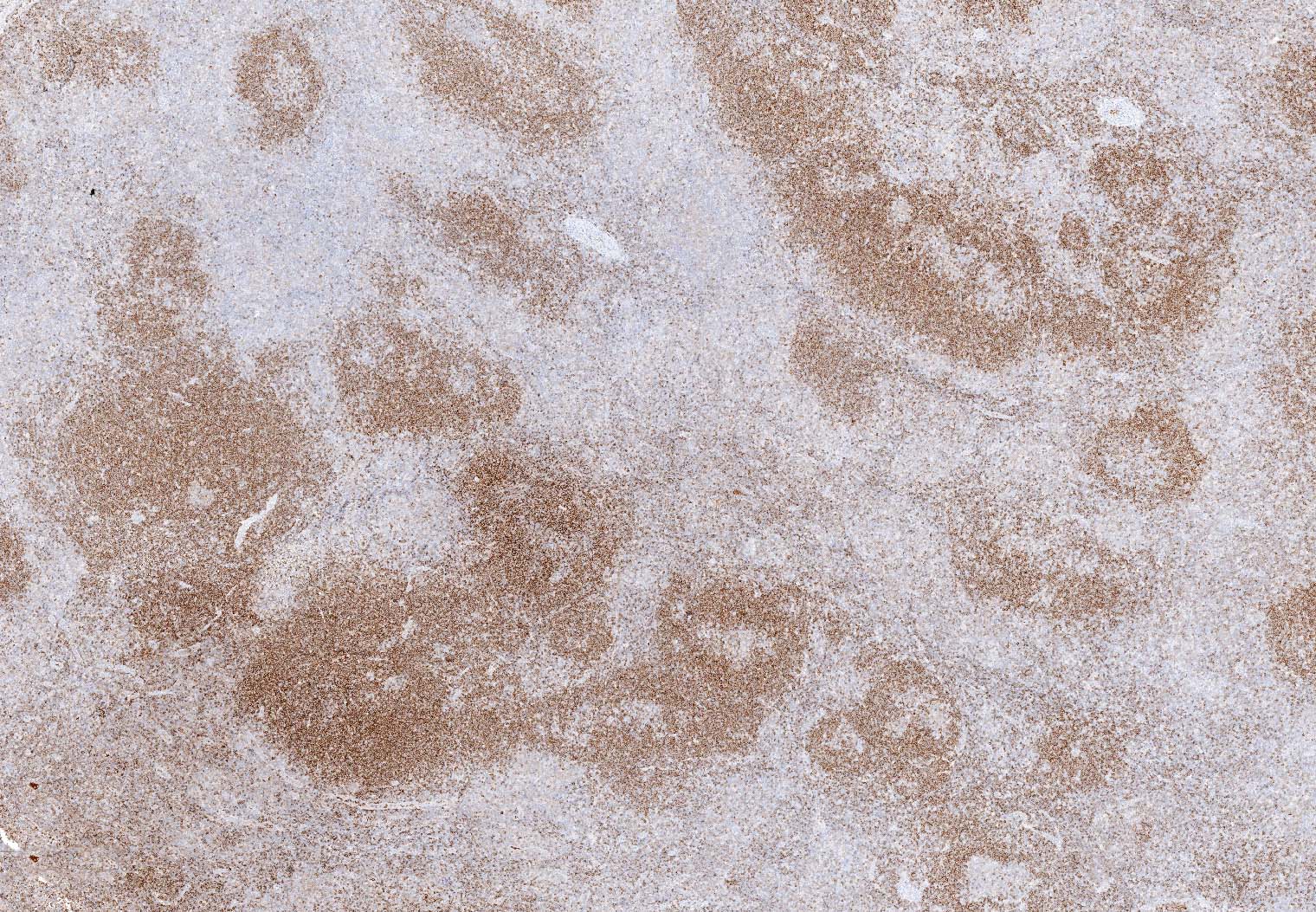
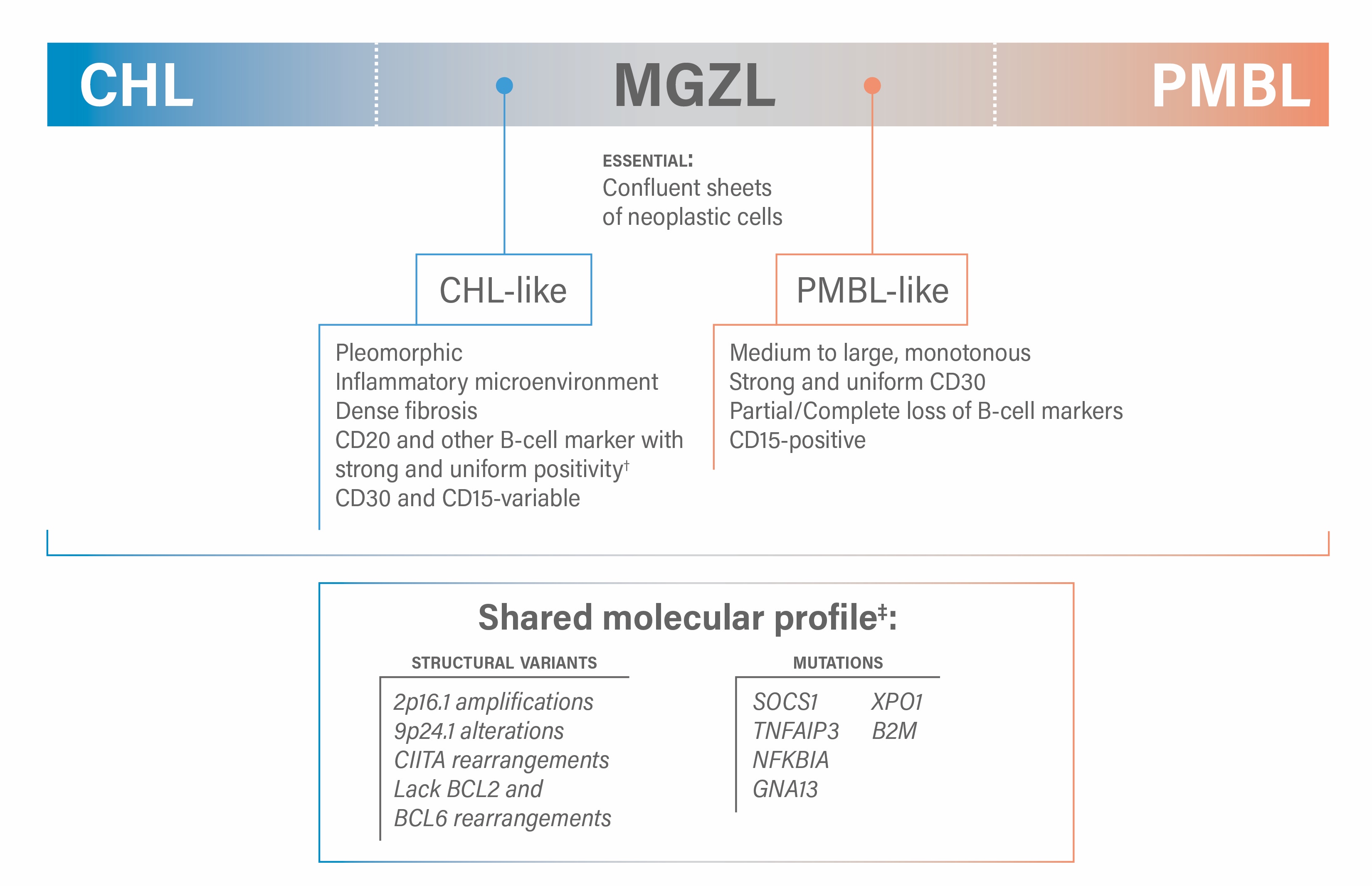
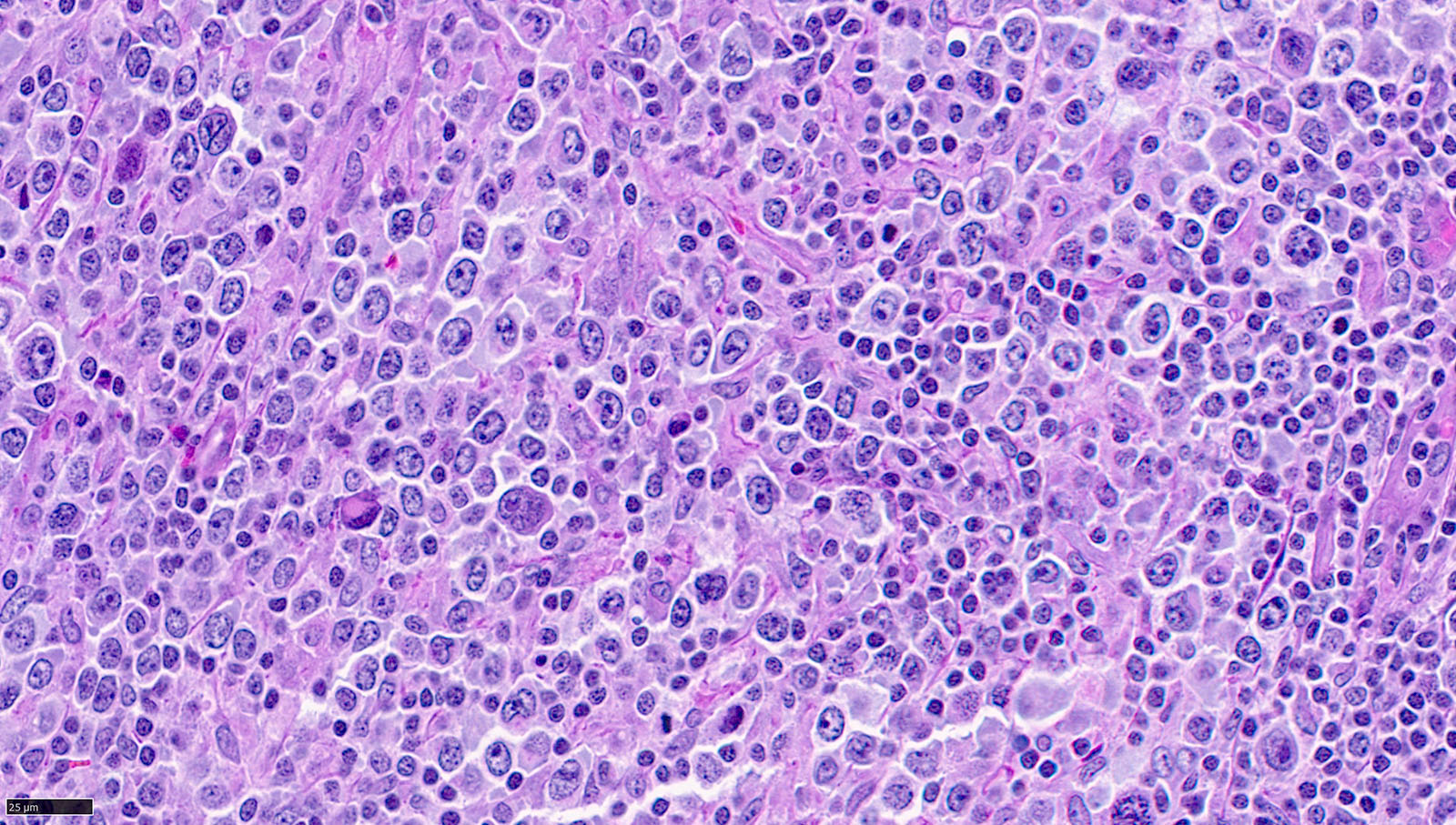
Mediastinal gray zone lymphoma
Diagrams / tables
Microscopic (histologic) images
Monoclonal B cell lymphocytosis
Peripheral smear images
Monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal
Radiology images
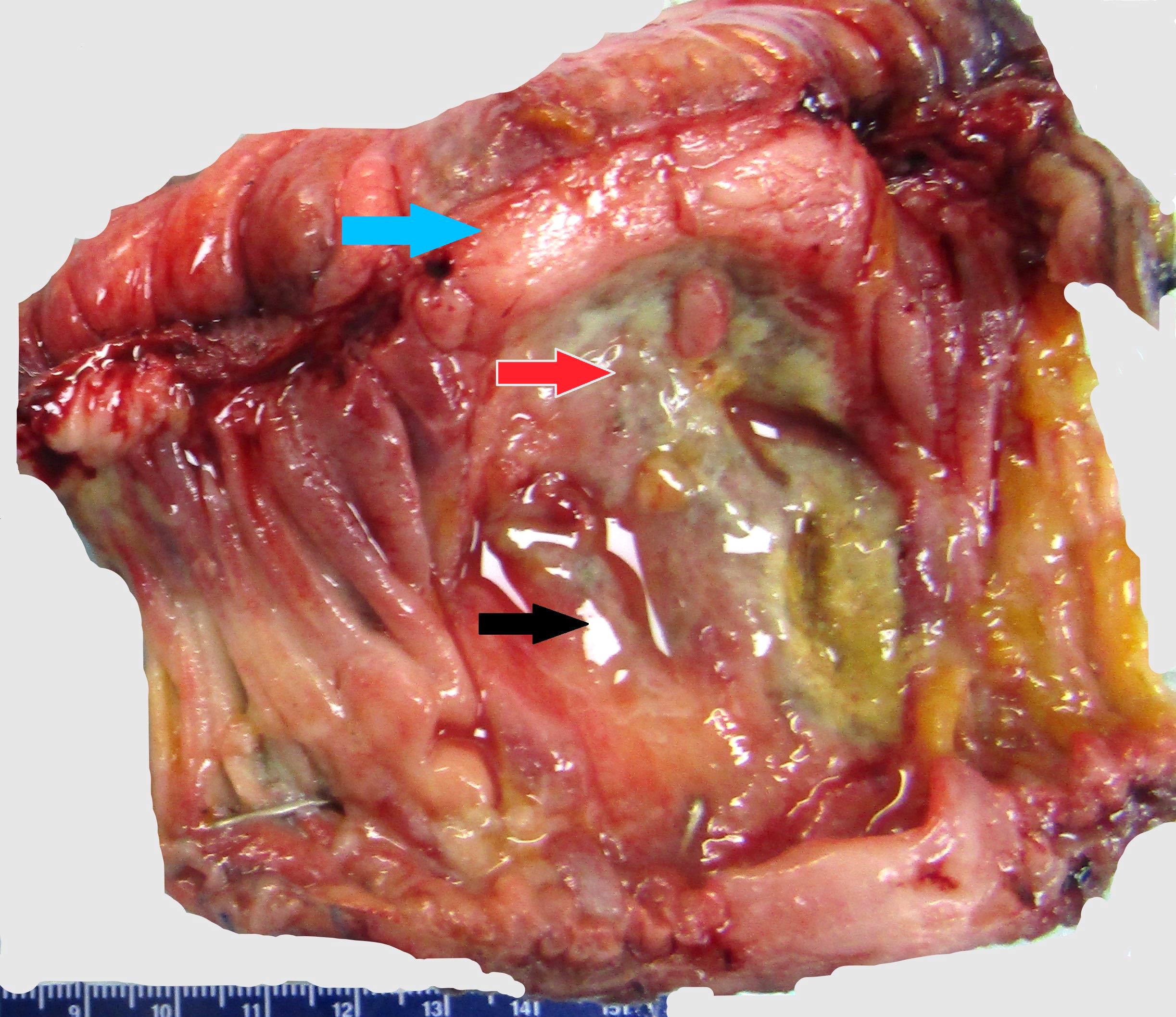
Gross images
Microscopic (histologic) images
Mycosis fungoides subtypes
Clinical images
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Roberto N. Miranda, M.D. and Carlos A. Torres-Cabala, M.D.
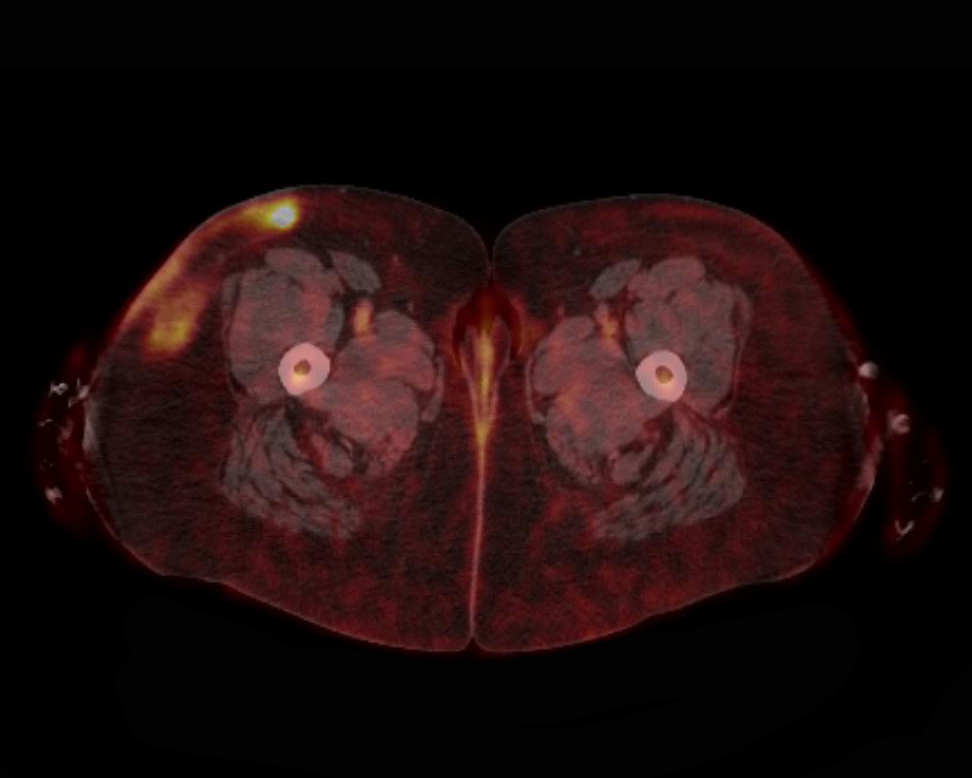
NK large granular lymphocytic leukemia
Microscopic (histologic) images
Peripheral smear images
Flow cytometry images
Nodal T follicular helper cell lymphoma, NOS
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Catalina Amador, M.D.
Nodal T follicular helper cell lymphoma, follicular type
Microscopic (histologic) images
Flow cytometry images
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Nodal T follicular helper lymphoma, angioimmunoblastic type
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Roberto N. Miranda, M.D.
Nodular lymphocyte predominant B cell lymphoma / nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Elaine S. Jaffe, M.D., Jayalakshmi Balakrishna, M.D. and Lauren B. Smith, M.D.
Nodular lymphocyte predominant B cell lymphoma / nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Elaine S. Jaffe, M.D., Jayalakshmi Balakrishna, M.D. and Lauren B. Smith, M.D.
PTLD-classic Hodgkin
Microscopic (histologic) images
PTLD-polymorphic
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Daniel Cassidy, M.D. and Jennifer Chapman, M.D.
Pediatric nodal marginal zone lymphoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Pediatric type follicular lymphoma
Diagrams / tables
Pediatric type follicular lymphoma versus follicular lymphoma usual type
| Pediatric type FL | Usual type FL | |
| Age | Young | Old age (sixth decade) |
| Stage | Low (I - II) | High (III - IV) in majority of cases |
| Location | Head and neck | Variable |
| Extranodal location | Absent | Present, variable |
| Histology | Grade 3 | Grade 1 - 3 |
| BCL2 (IHC) | Negative / dim | Usually positive |
| CD10 | Positive (~100%) | Positive (usually) |
| Ki67 | High | Low (except for high grade) |
| t(14;18) IGH-BCL2 | Absent | Present, up to 90% |
| Monotypic B cells by flow cytometry | Frequent | Frequent |
| Monoclonal IgH rearrangements | Frequent | Frequent |
| BCL6 or MYC rearrangements | Absent | Variably present |
| Genetic | 1p36 loss | Complex, variable |
| Mutations | TNFRSF14, MAP2K1, IRF8 (K66R) | CREBBP, EZH2, KMT2D |
| Prognosis | Favorable | Variable |
Microscopic (histologic) images
Peripheral T cell lymphoma, NOS
Diagrams / tables
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology images
Plasmablastic lymphoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Polymorphic lymphoproliferative disorders arising in immune deficiency / dysregulation
Diagrams / tables
Microscopic (histologic) images
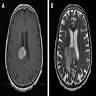
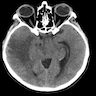
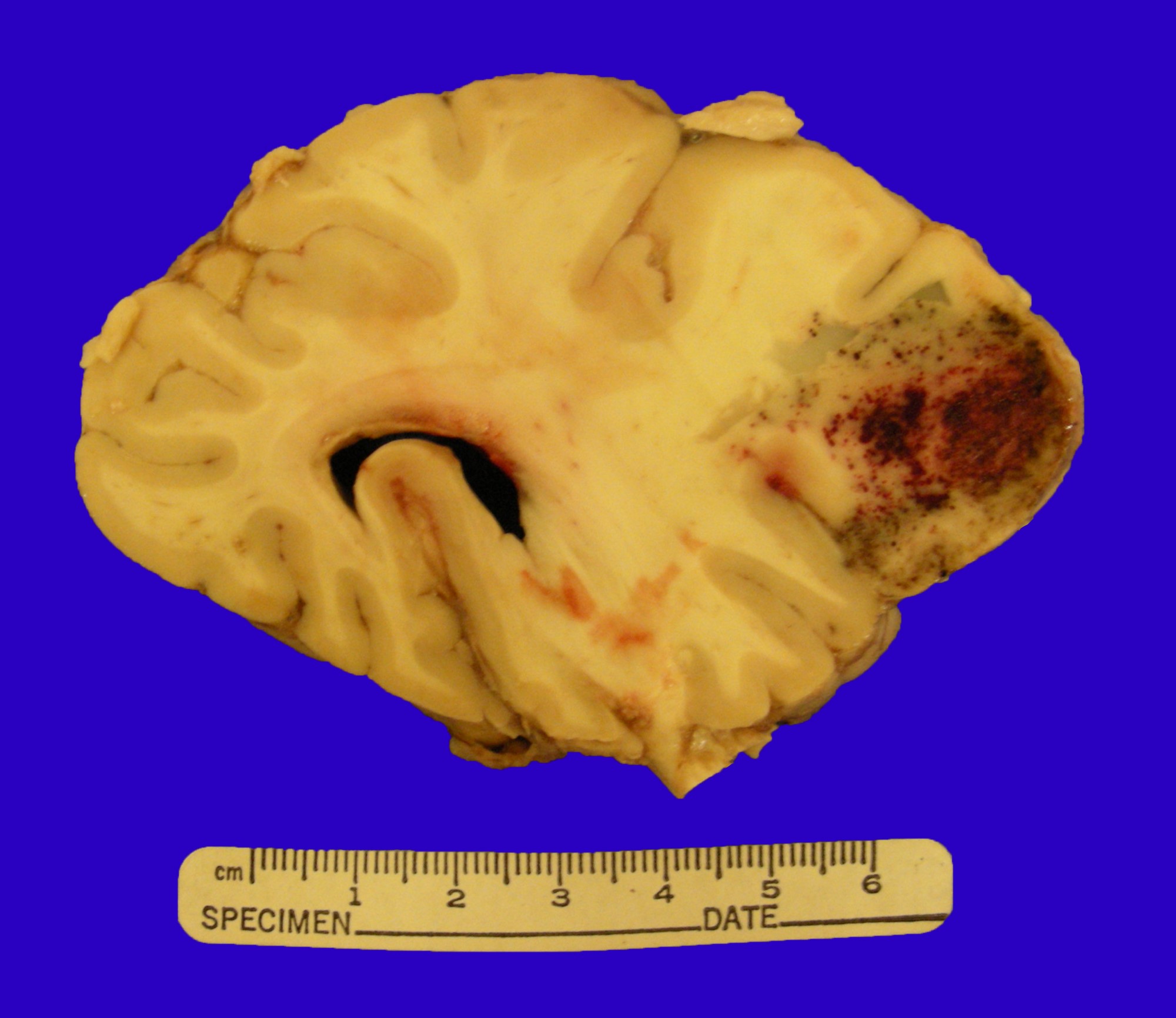
Primary CNS lymphoma
Radiology images
Images hosted on other servers:
Clinical images
Microscopic (histologic) images
Primary cutaneous CD4+ small or medium T cell lymphoproliferative disorder
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Jennifer Chapman, M.D.
Primary cutaneous CD8+ aggressive epidermotropic cytotoxic T cell lymphoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Roberto N. Miranda, M.D.
Primary cutaneous PTCL, NOS
Microscopic (histologic) images
Primary cutaneous acral CD8+ lymphoproliferative disorder
Microscopic (histologic) images
Primary cutaneous gamma delta
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Roberto N. Miranda, M.D.
Flow cytometry images
Primary effusion lymphoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology images
Contributed by Barina Aqil, M.D., Mario L. Marques-Piubelli, M.D. and Roberto N. Miranda, M.D. (Case #519)
Primary follicular lymphoma-testis
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features:
| Nodal follicular lymphoma | Testicular follicular lymphoma | |
| Age (median) | Adults and elder (sixth decade) | Children and young adults |
| Gender (M:F) | Men and women | Men only |
| Affected sites | Lymph nodes with extranodal spread | Testicle and adnexa |
| Symptoms | Generalized lymphadenopathy | Painless mass |
| Stage (Ann Arbor) | High (III - IV) in most cases | IE |
Pathologic features:
| Nodal follicular lymphoma | Testicular follicular lymphoma | |
| Gross appearance | Discrete mass or complete effacement | Discrete mass or diffuse involvement |
| Histologic grade | Grades 1 - 3 | Grade 3 |
Immunophenotype:
| Nodal follicular lymphoma | Testicular follicular lymphoma | |
| CD10 | Variable | Variable |
| BCL2 | Usually positive | Negative |
Molecular features:
| Nodal follicular lymphoma | Testicular follicular lymphoma | |
| IGH-BCL2 | Present, up to 90% | Negative |
Microscopic (histologic) images
Primary mediastinal
Microscopic (histologic) images
Prolymphocytic leukemia
Microscopic (histologic) images
Peripheral smear images
Flow cytometry images
Richter syndrome
Microscopic (histologic) images
Sézary syndrome
Clinical images
Microscopic (histologic) images
Peripheral smear images
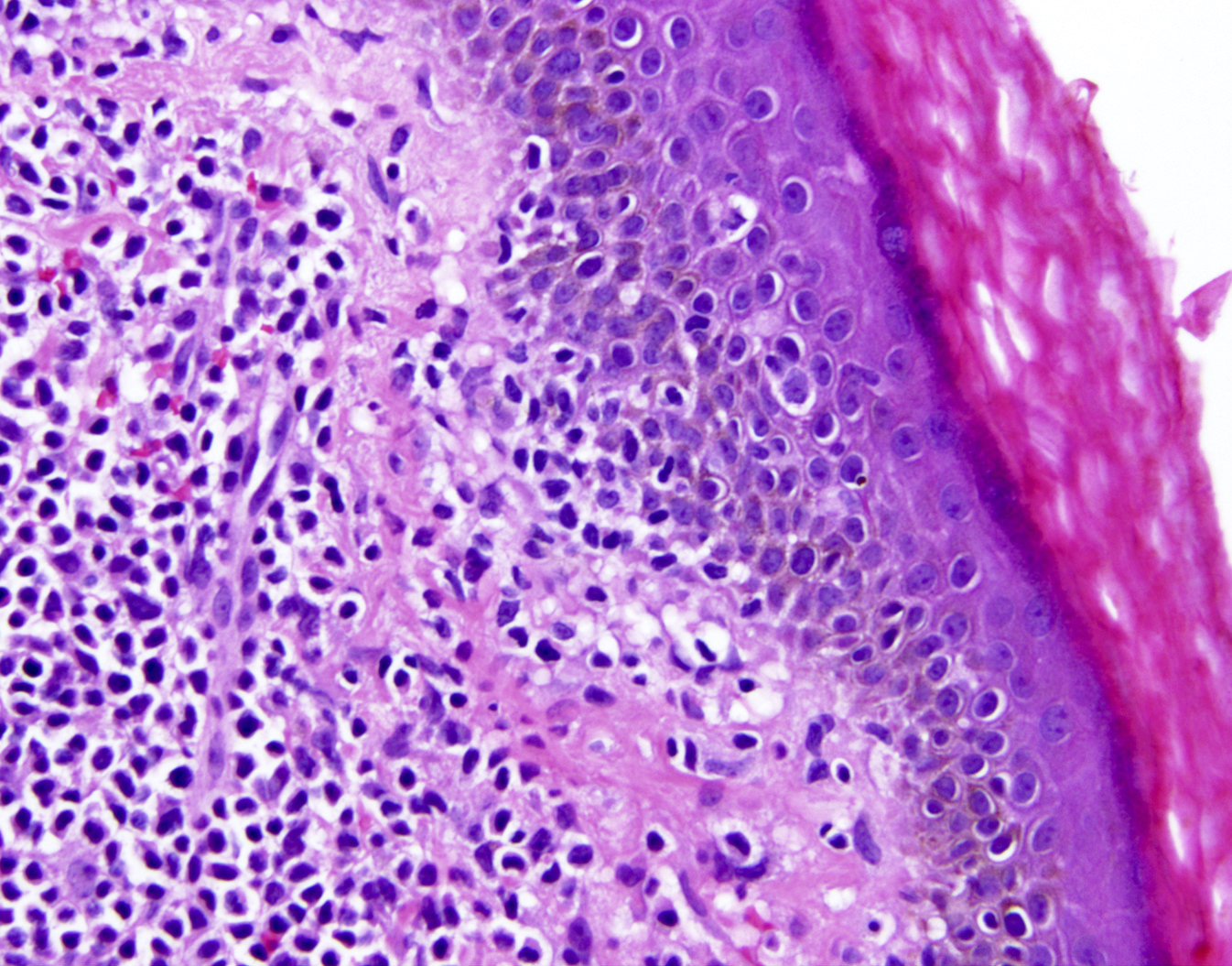
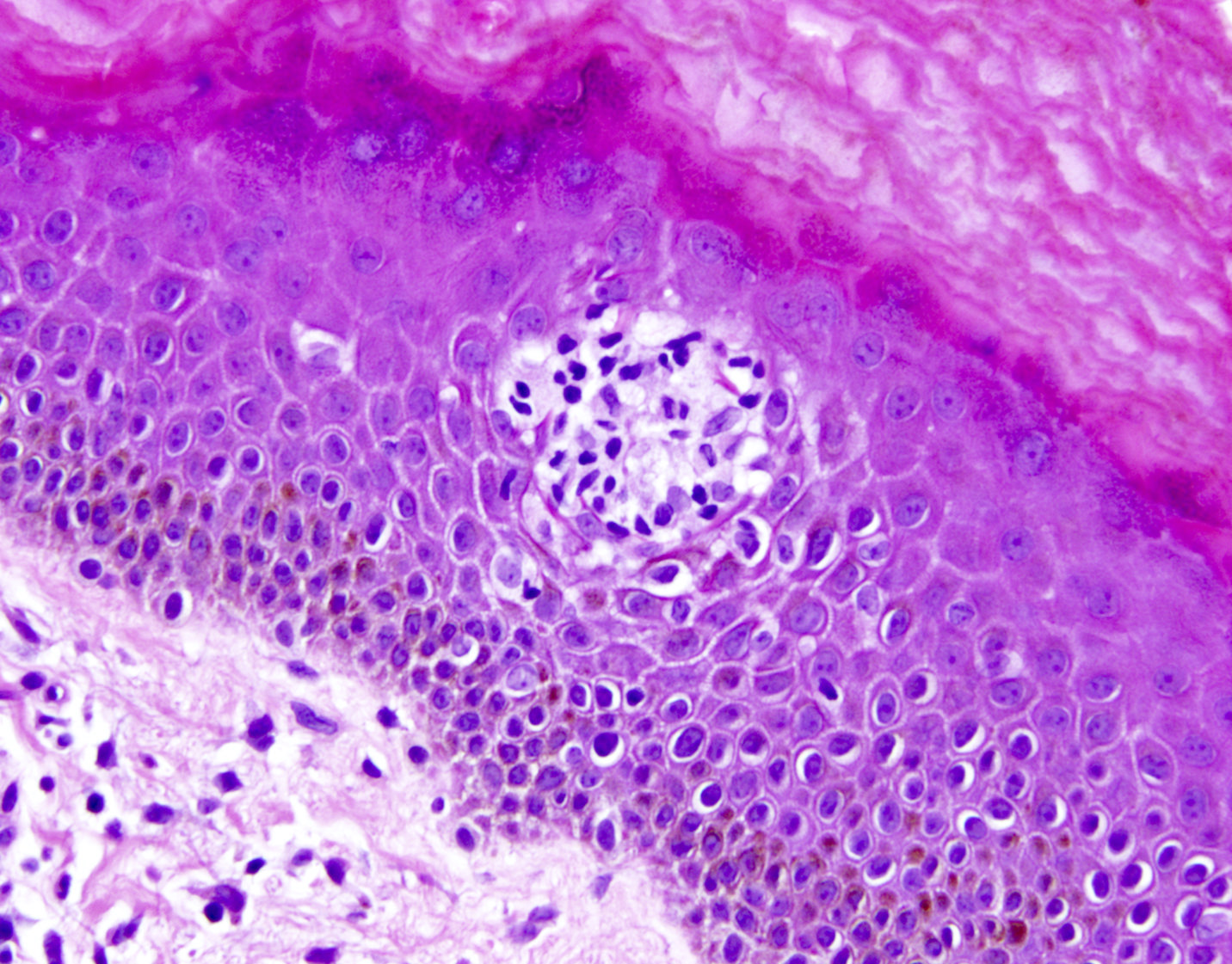
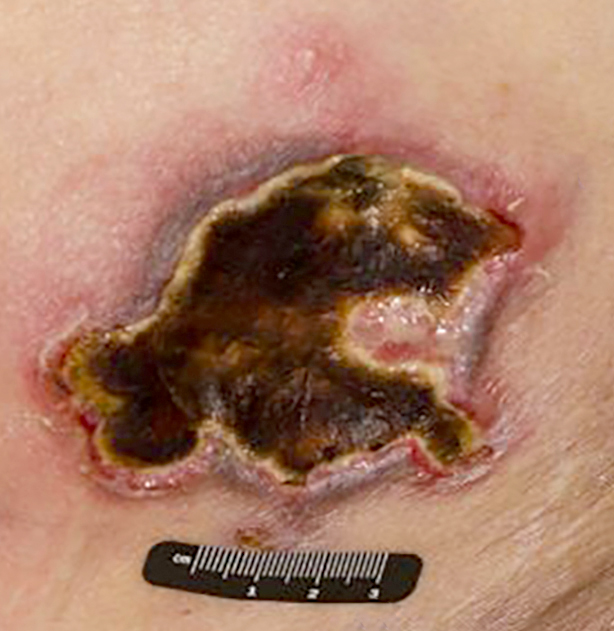
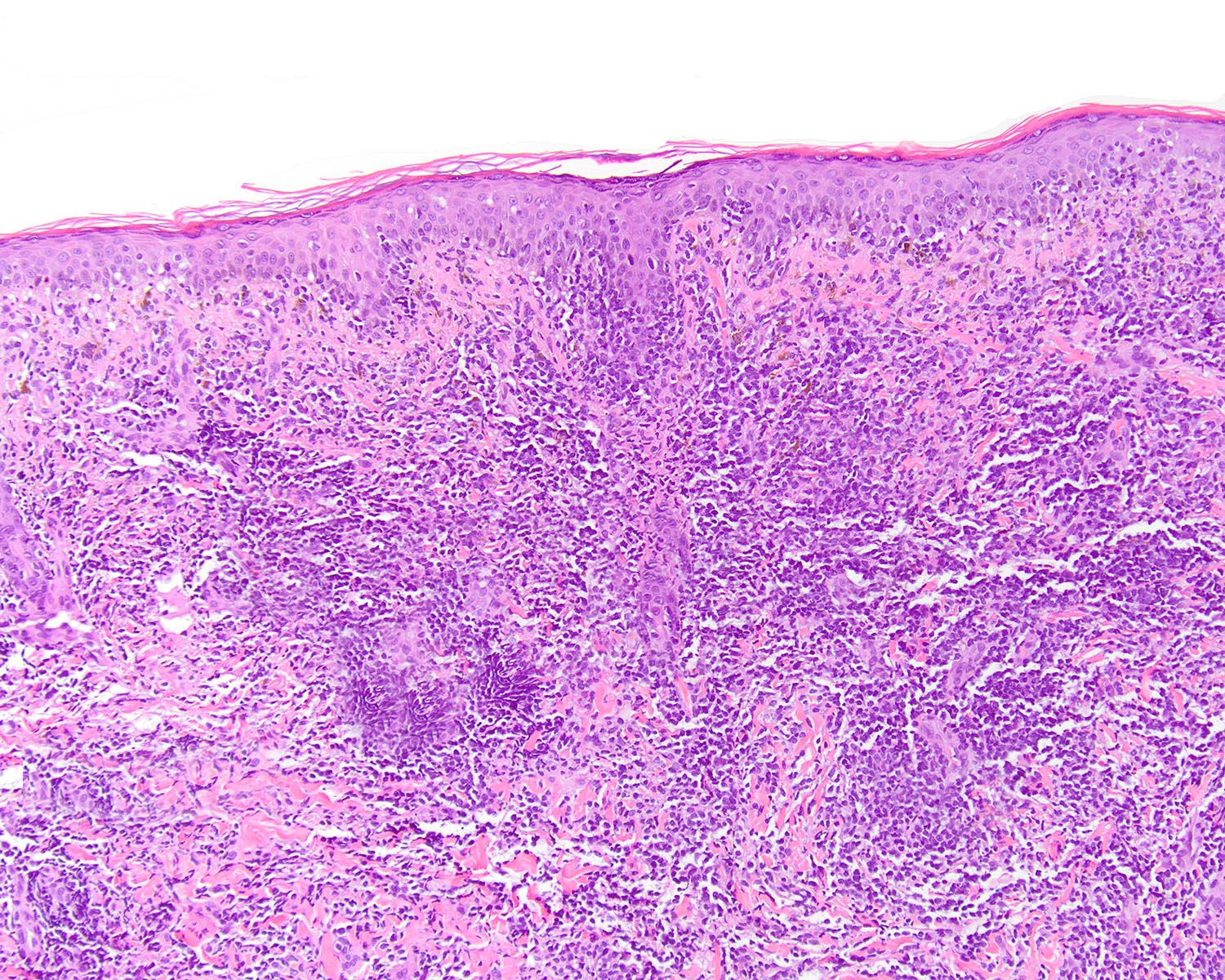
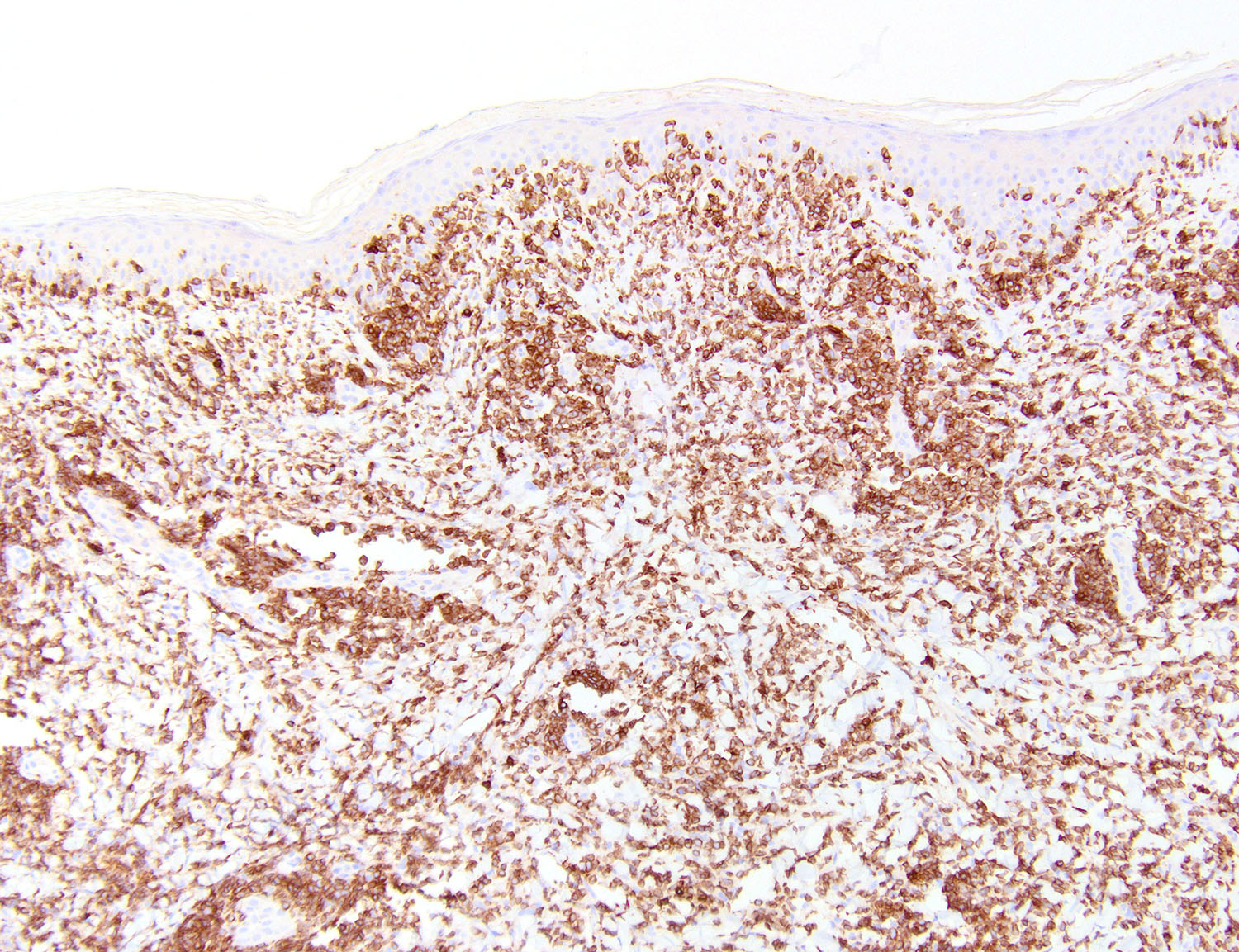
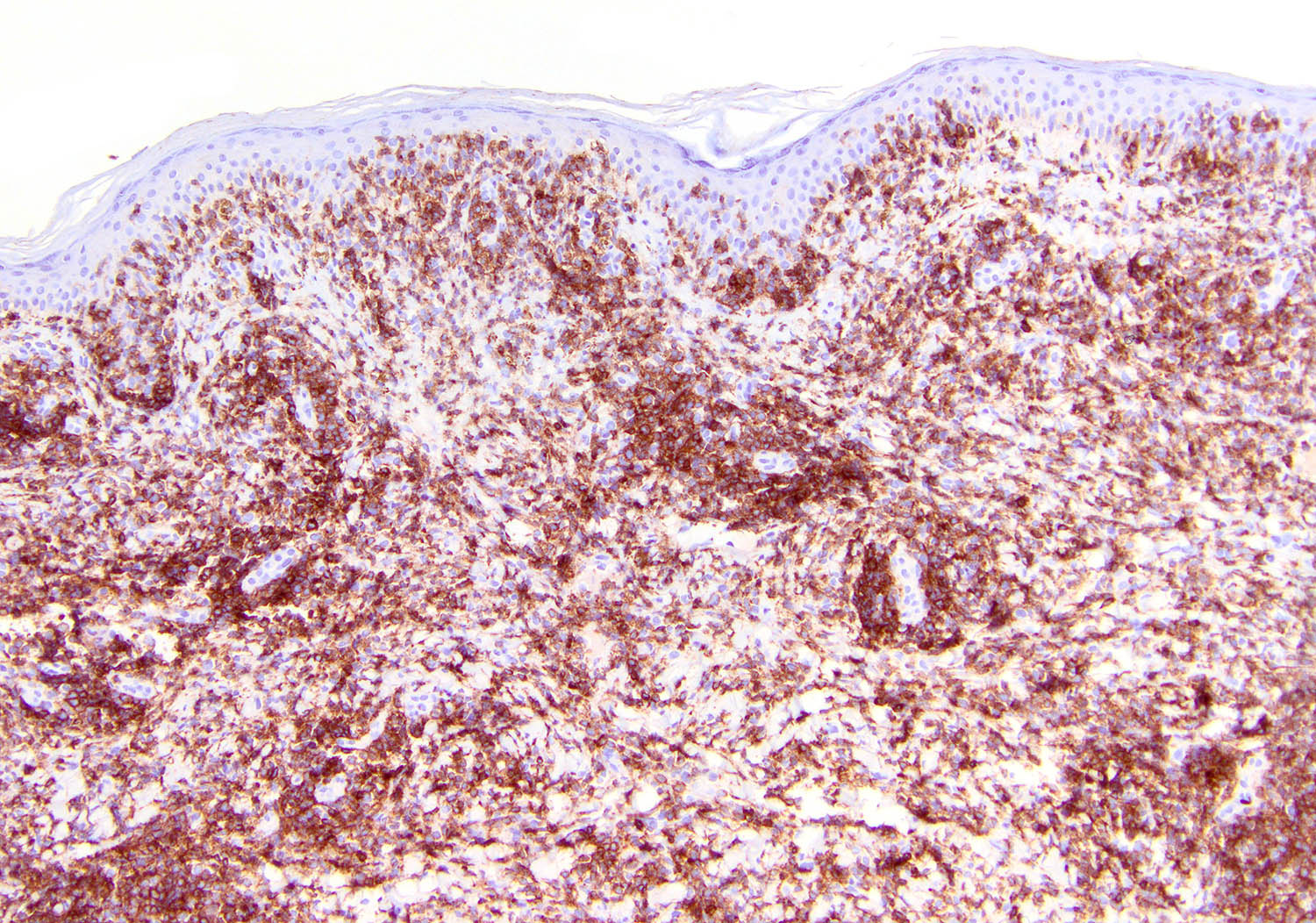
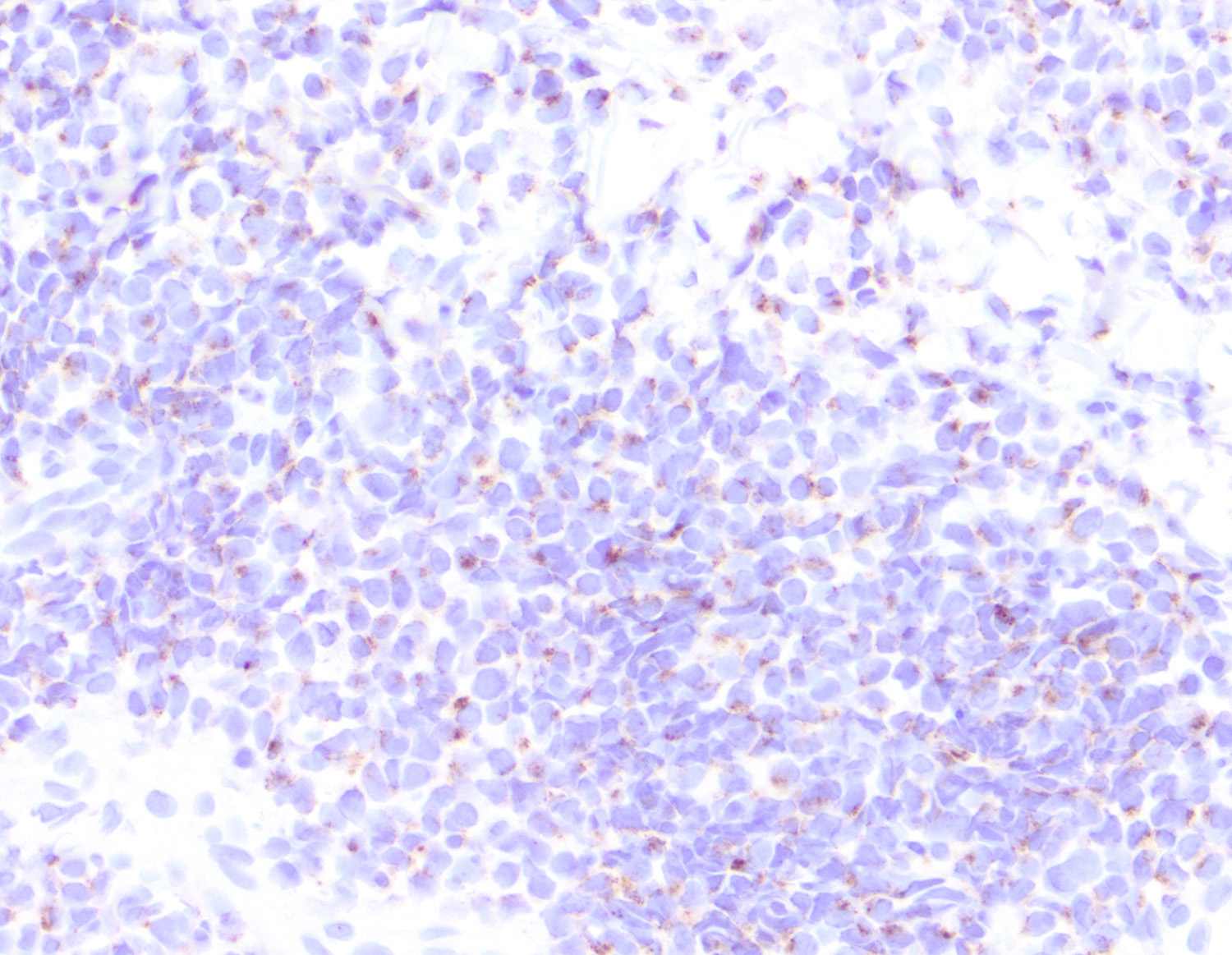
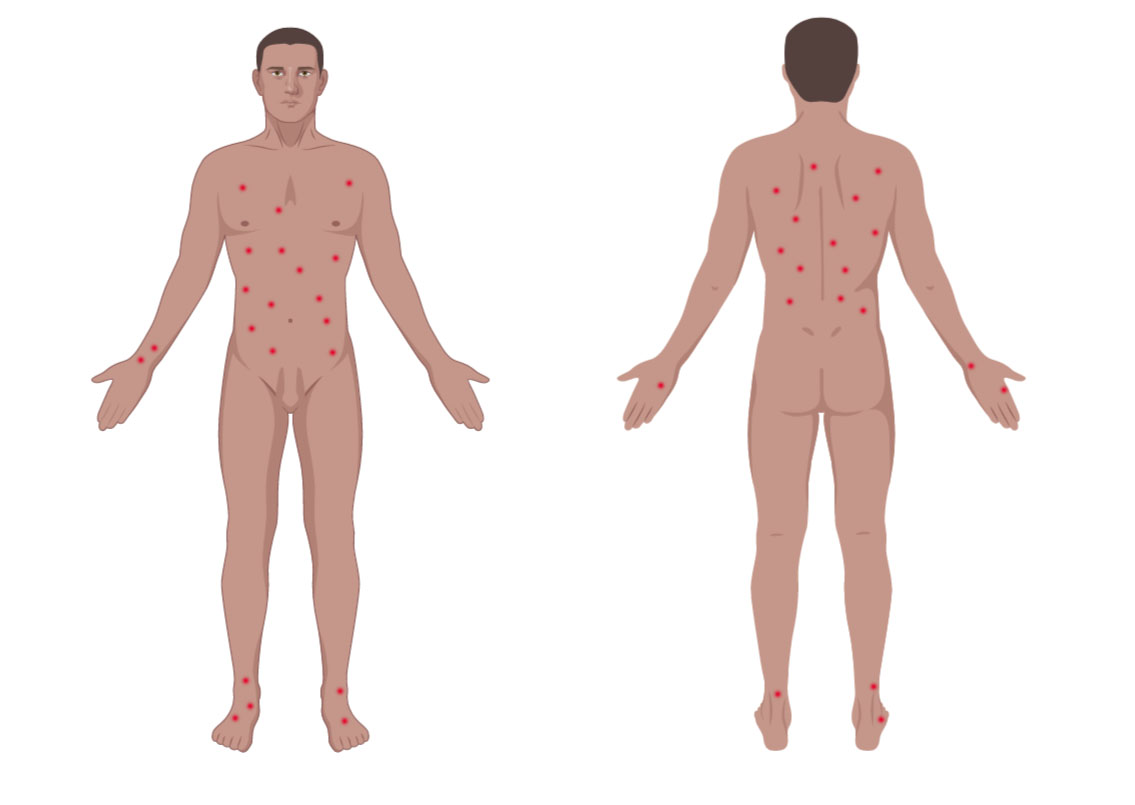
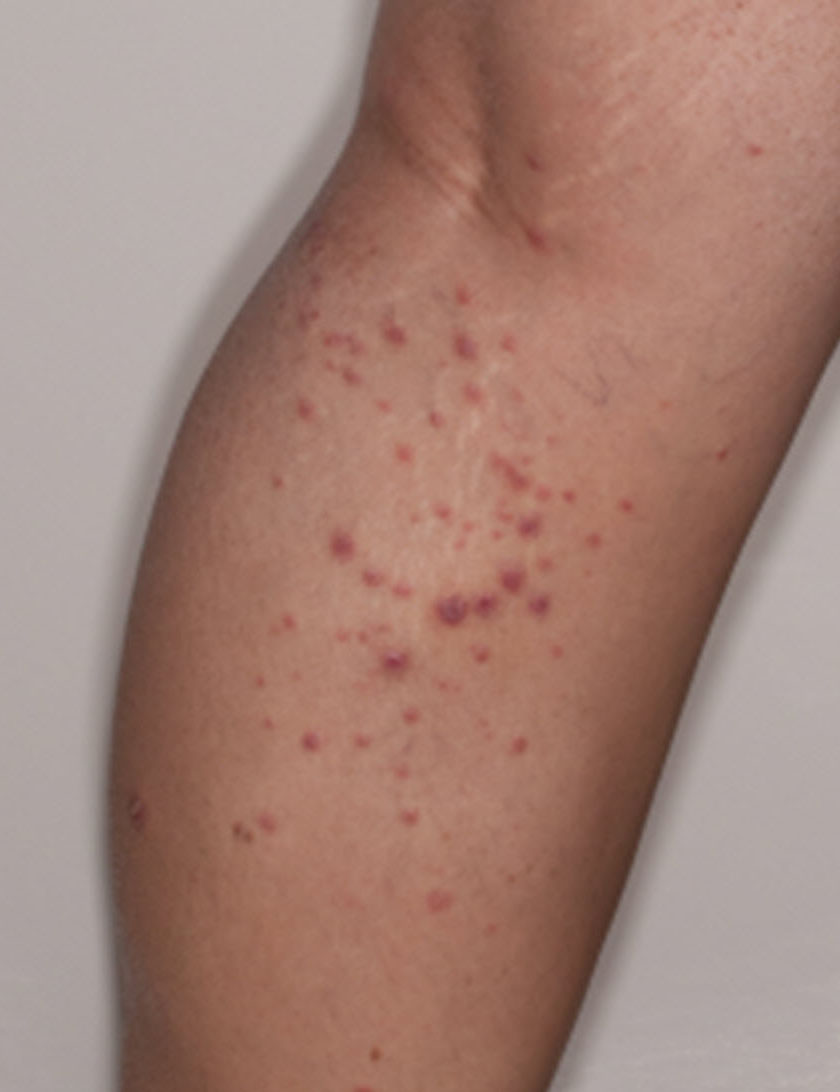
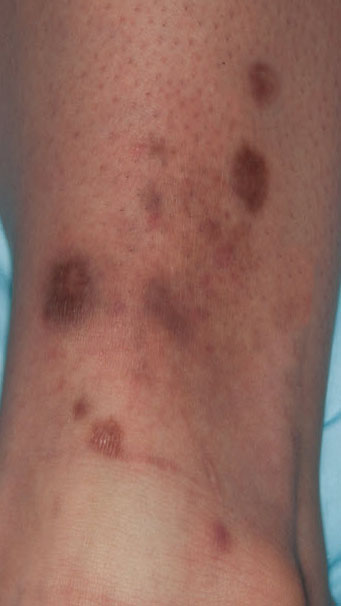
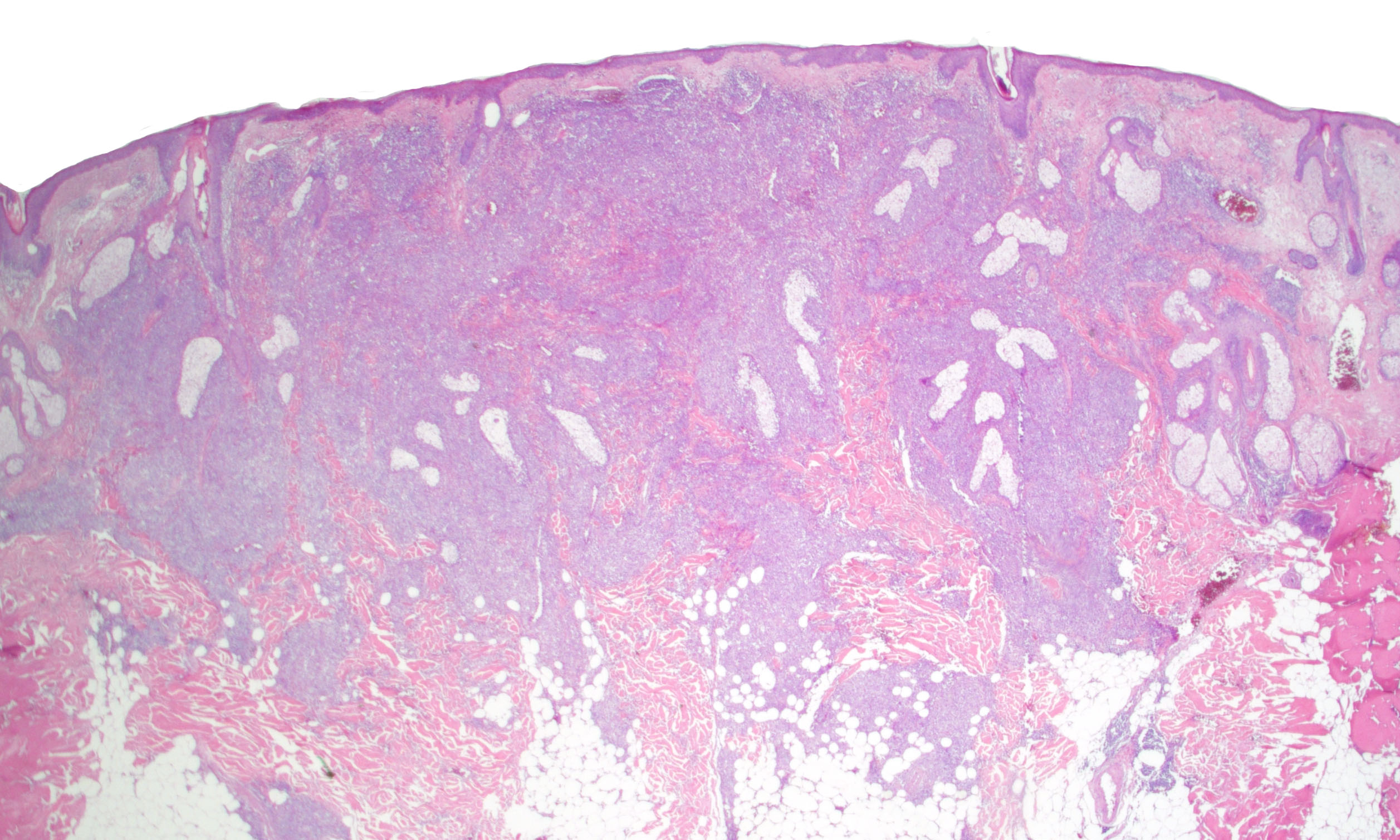
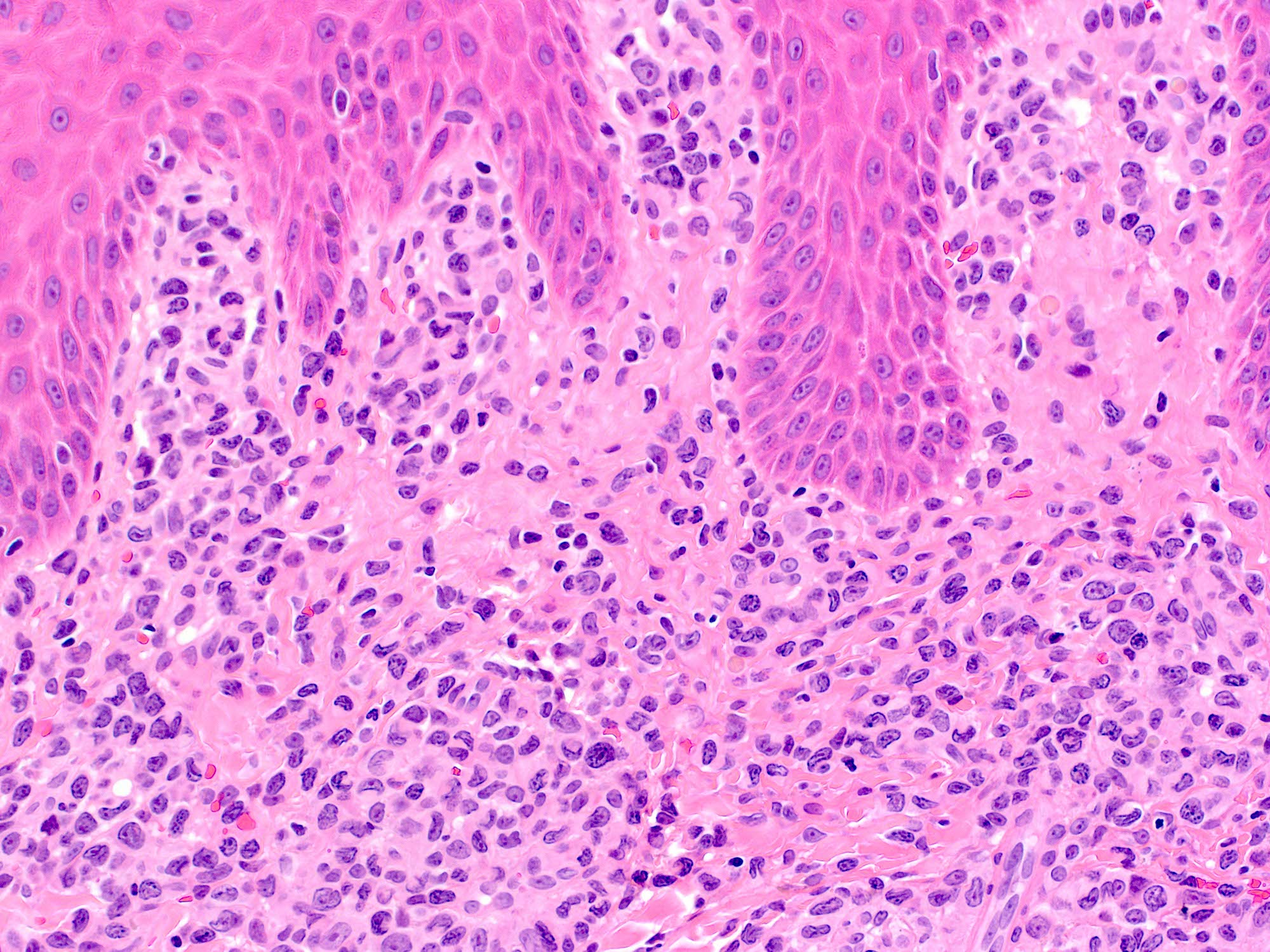
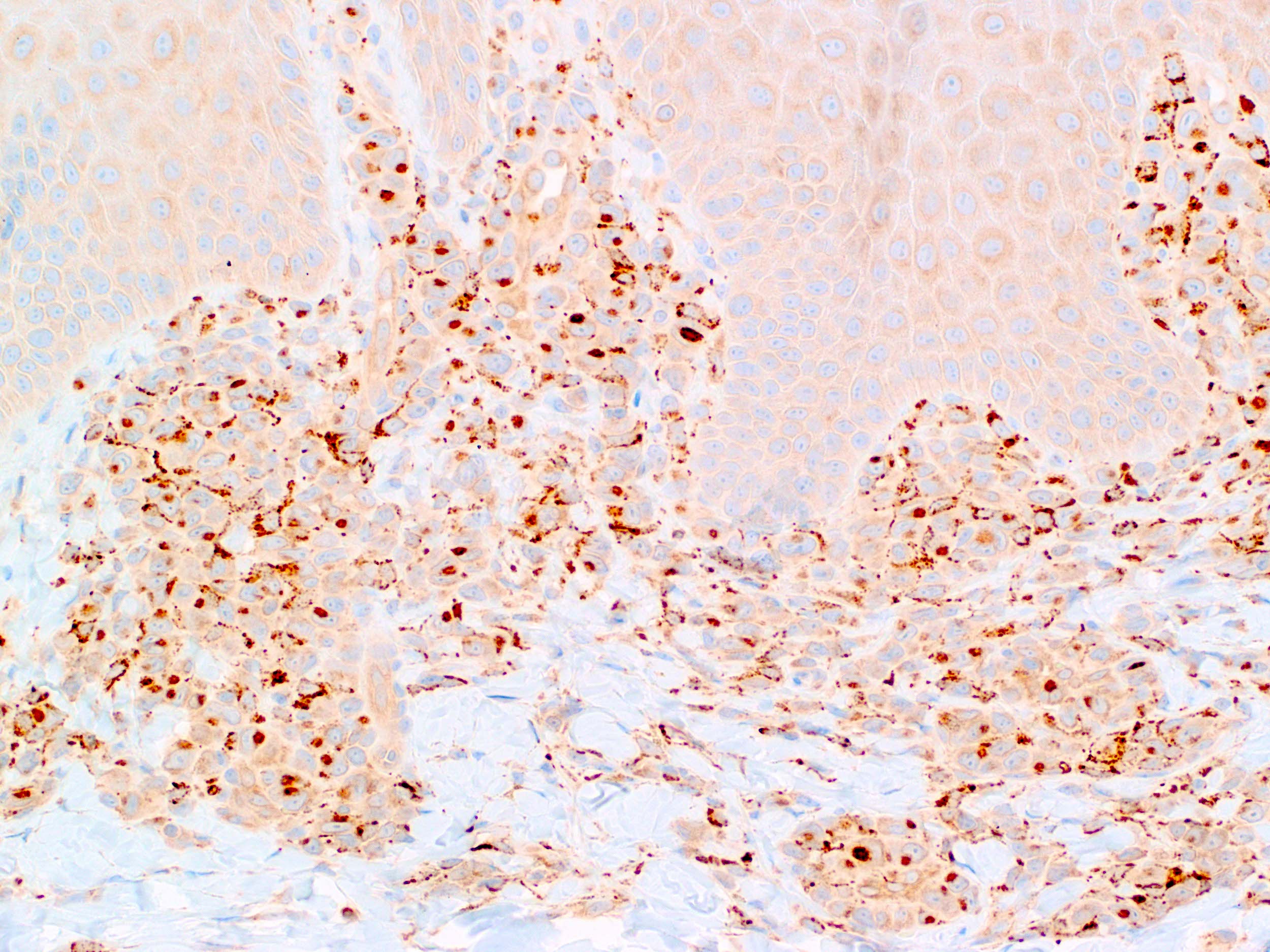
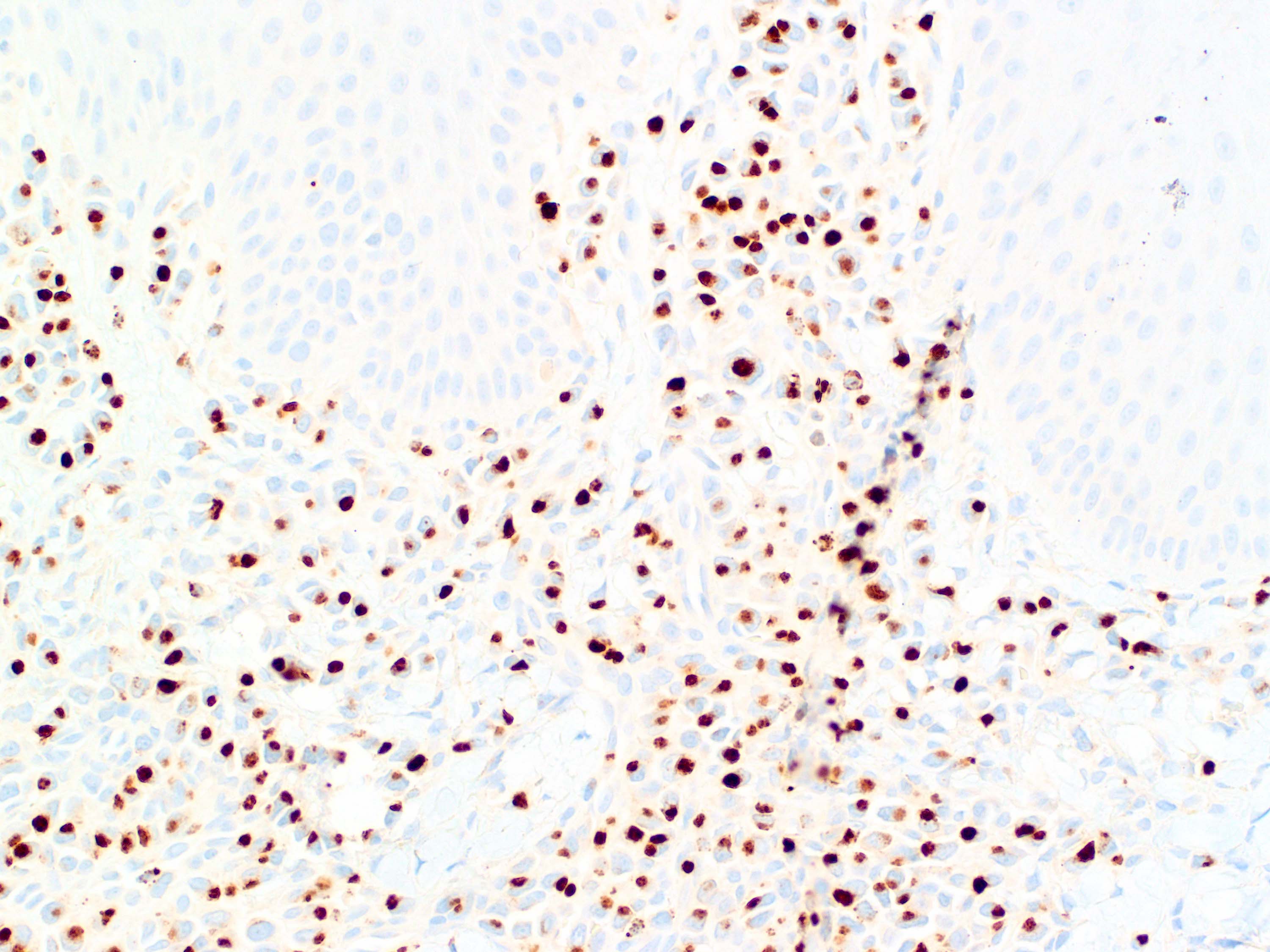
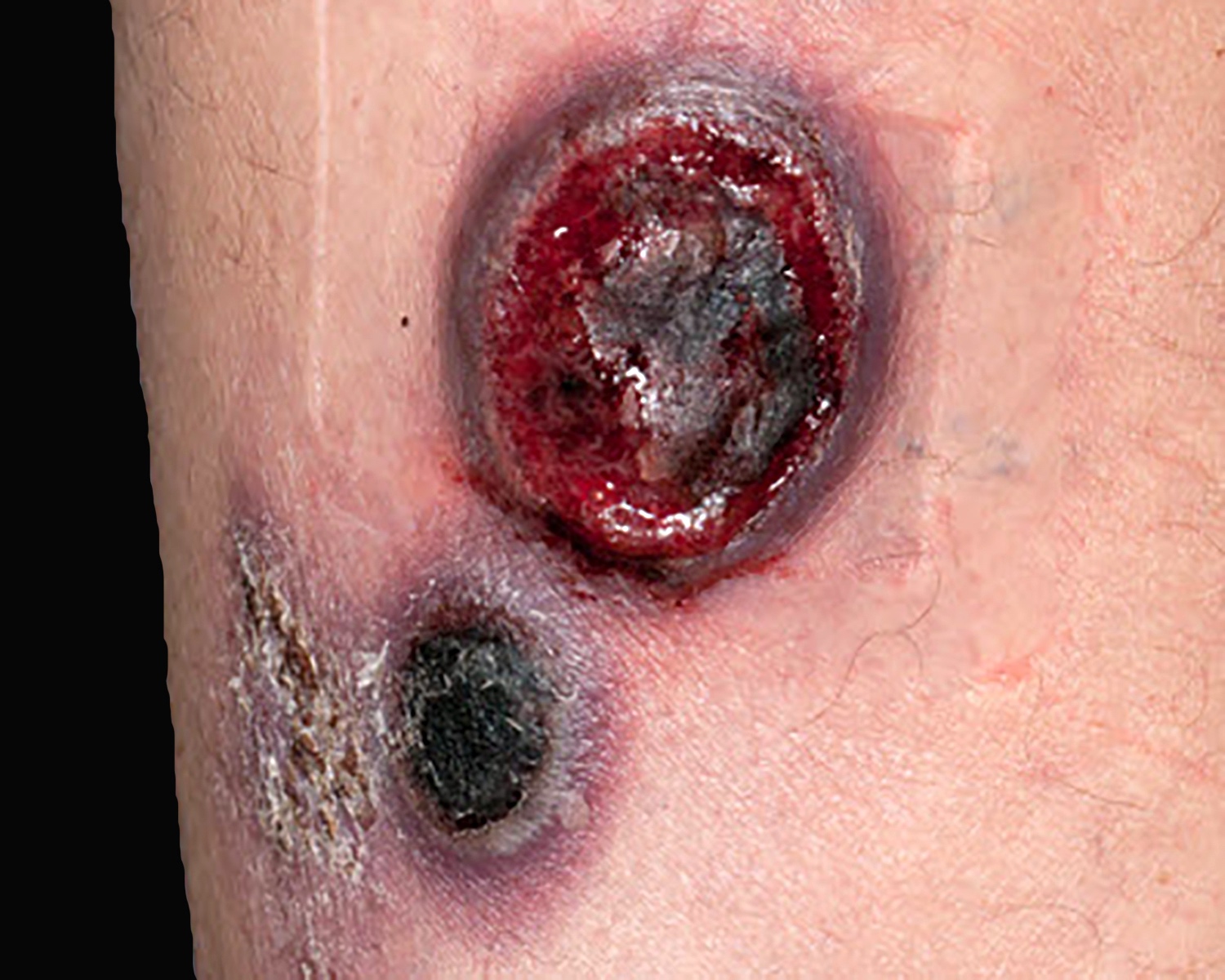
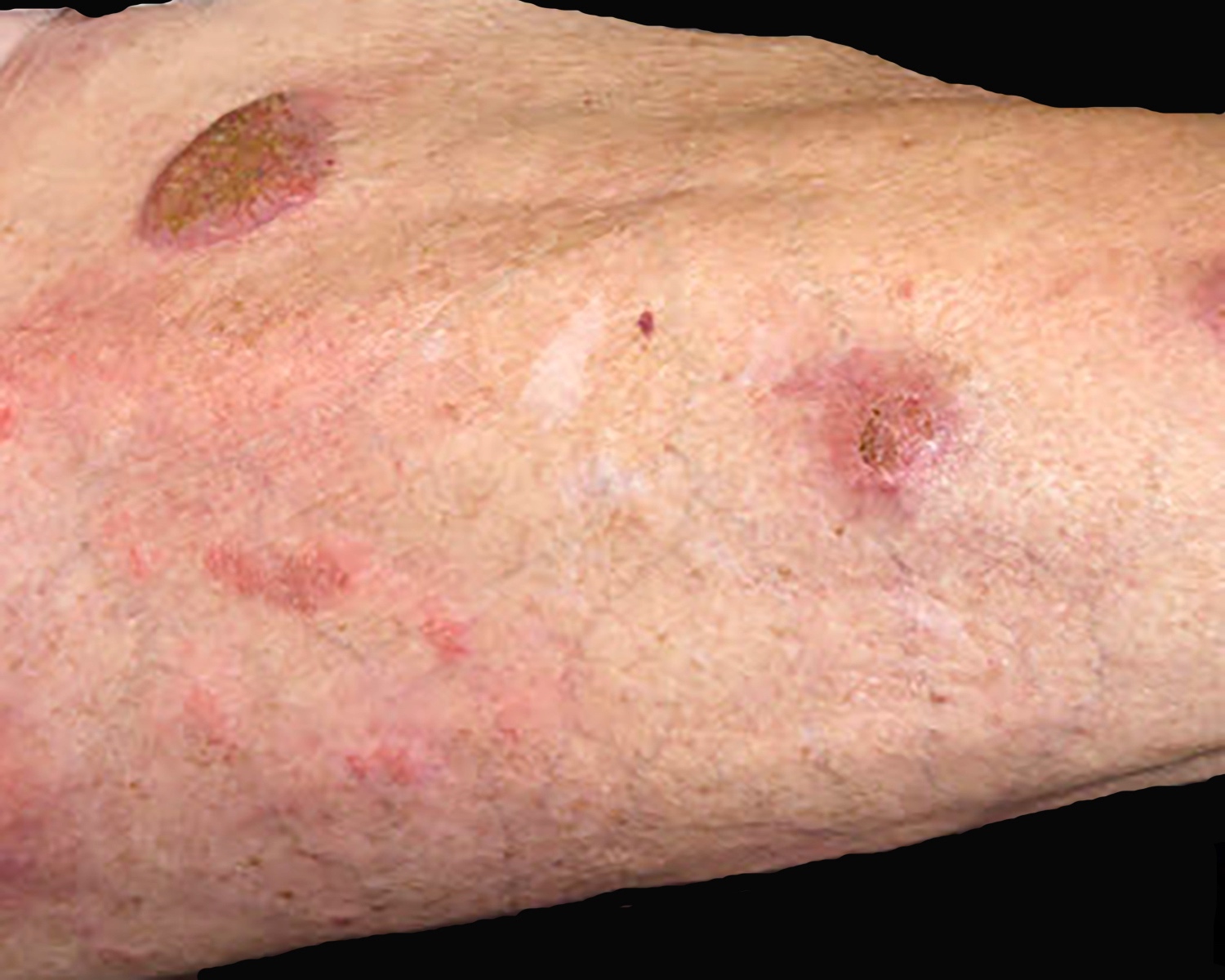
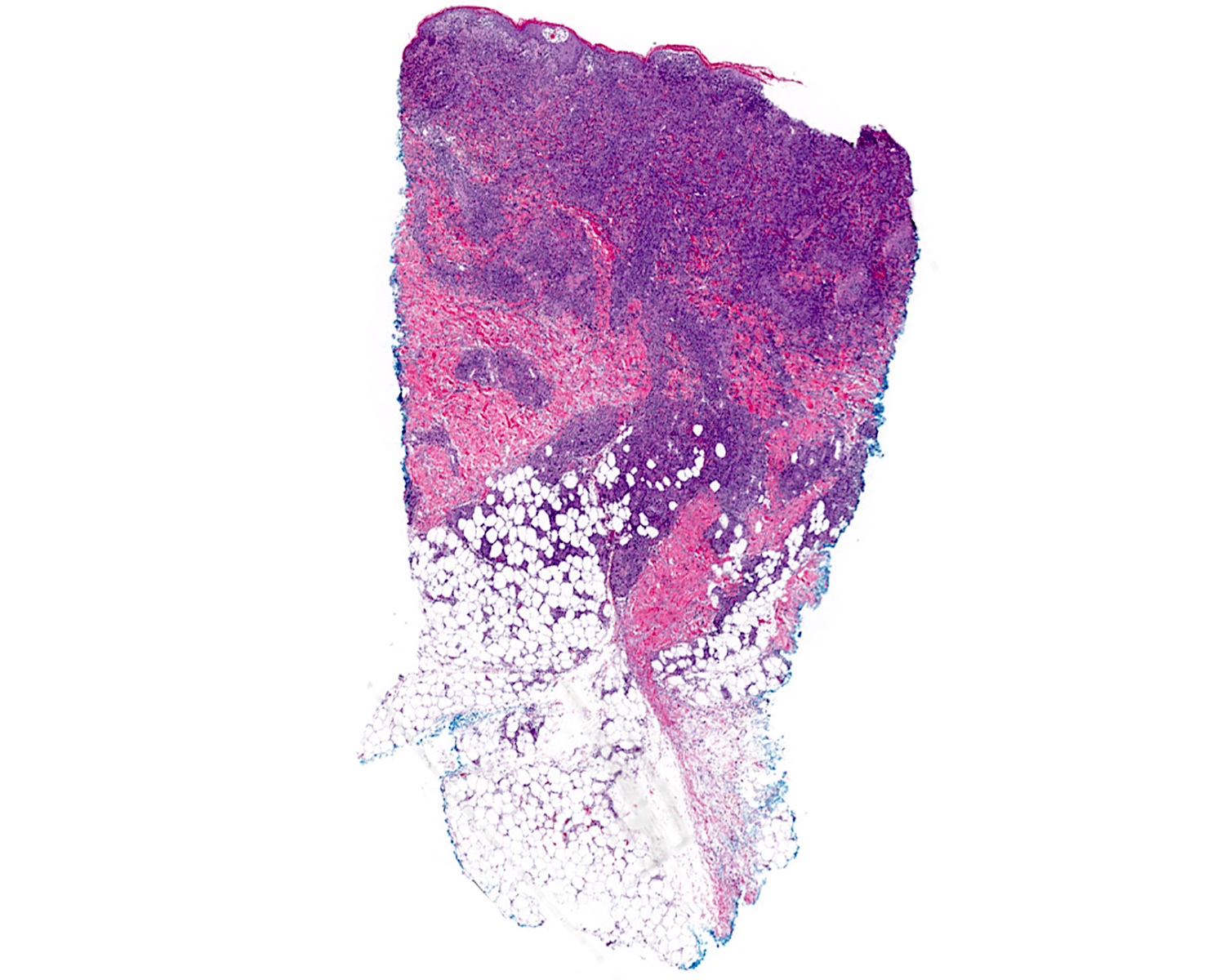
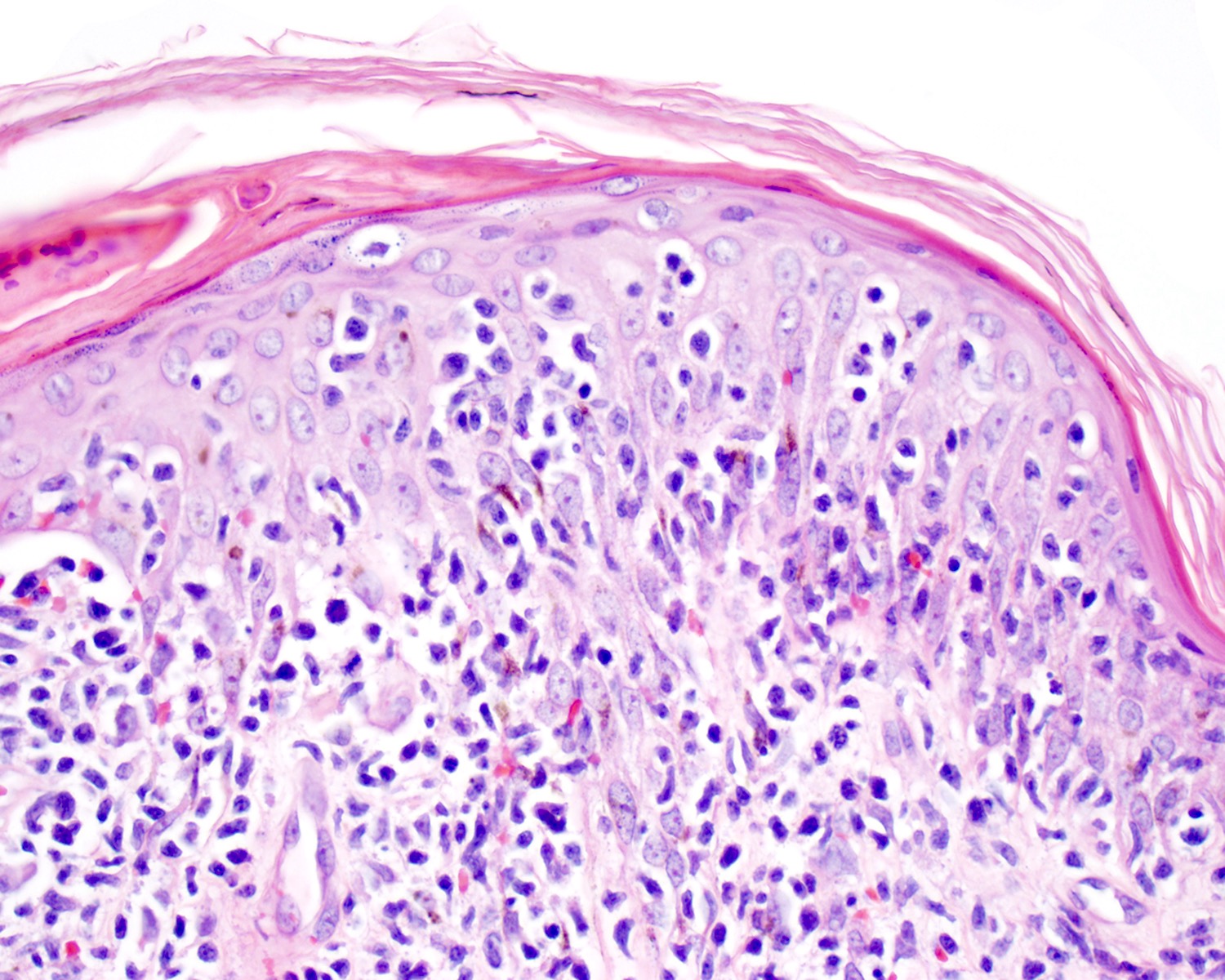
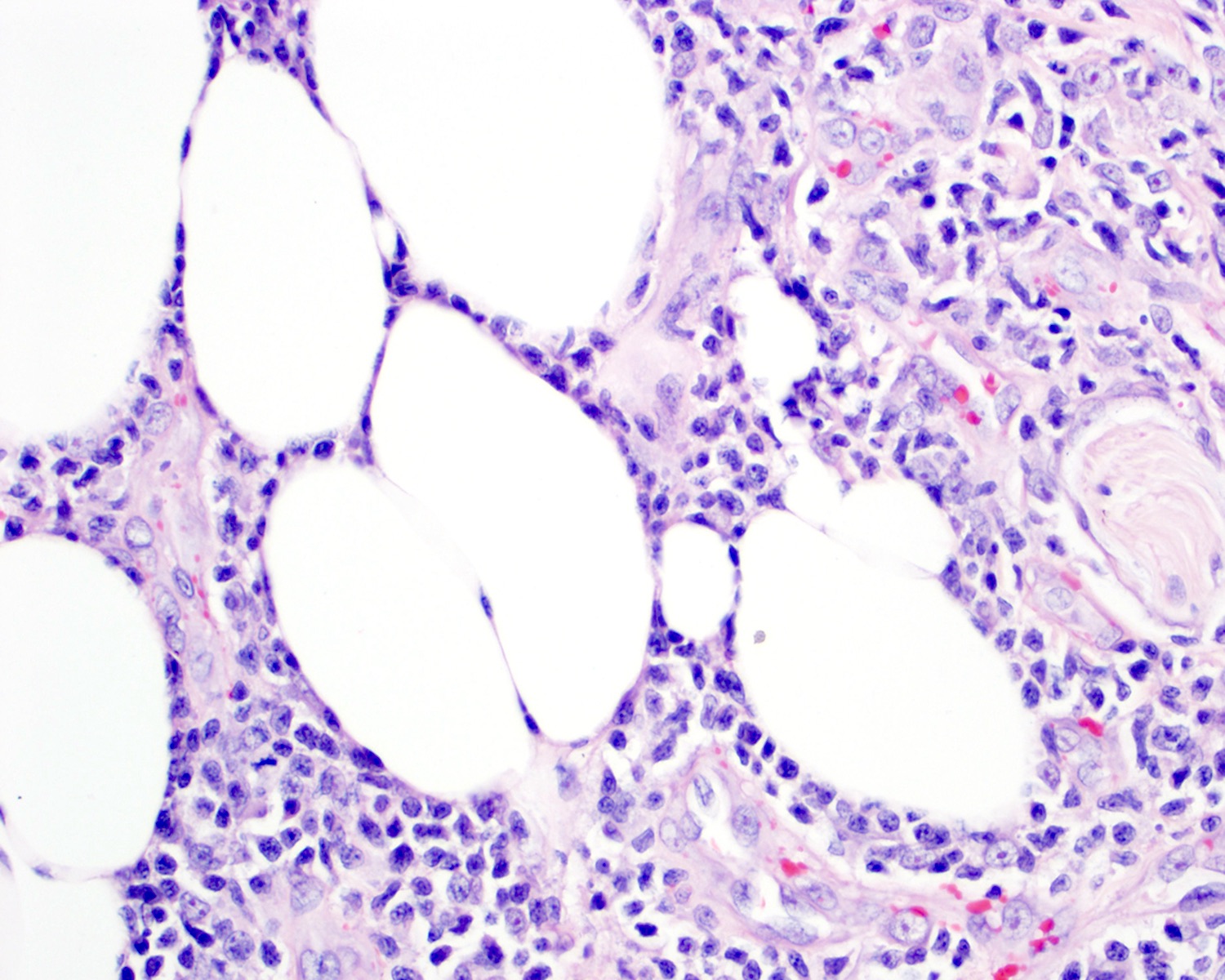
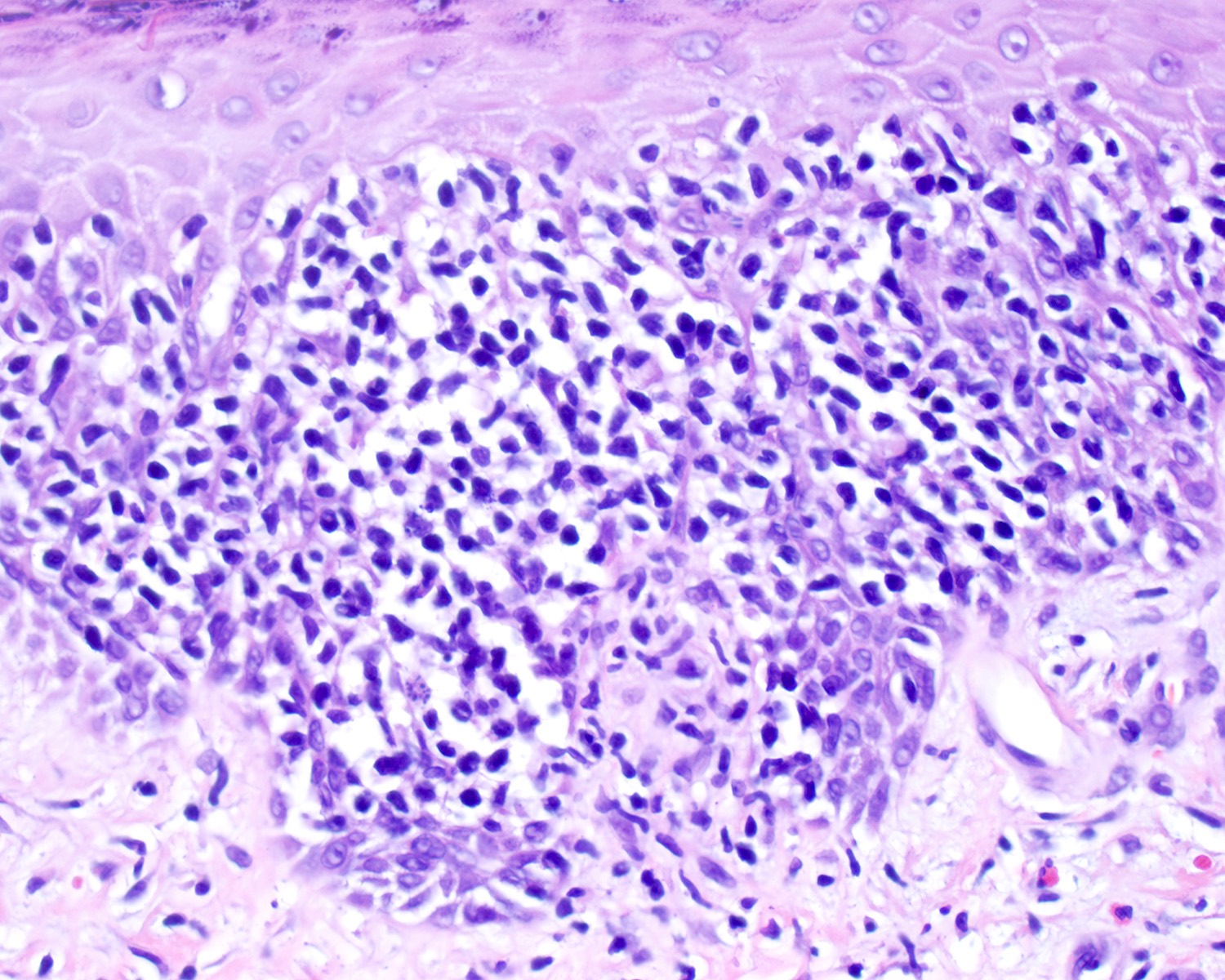
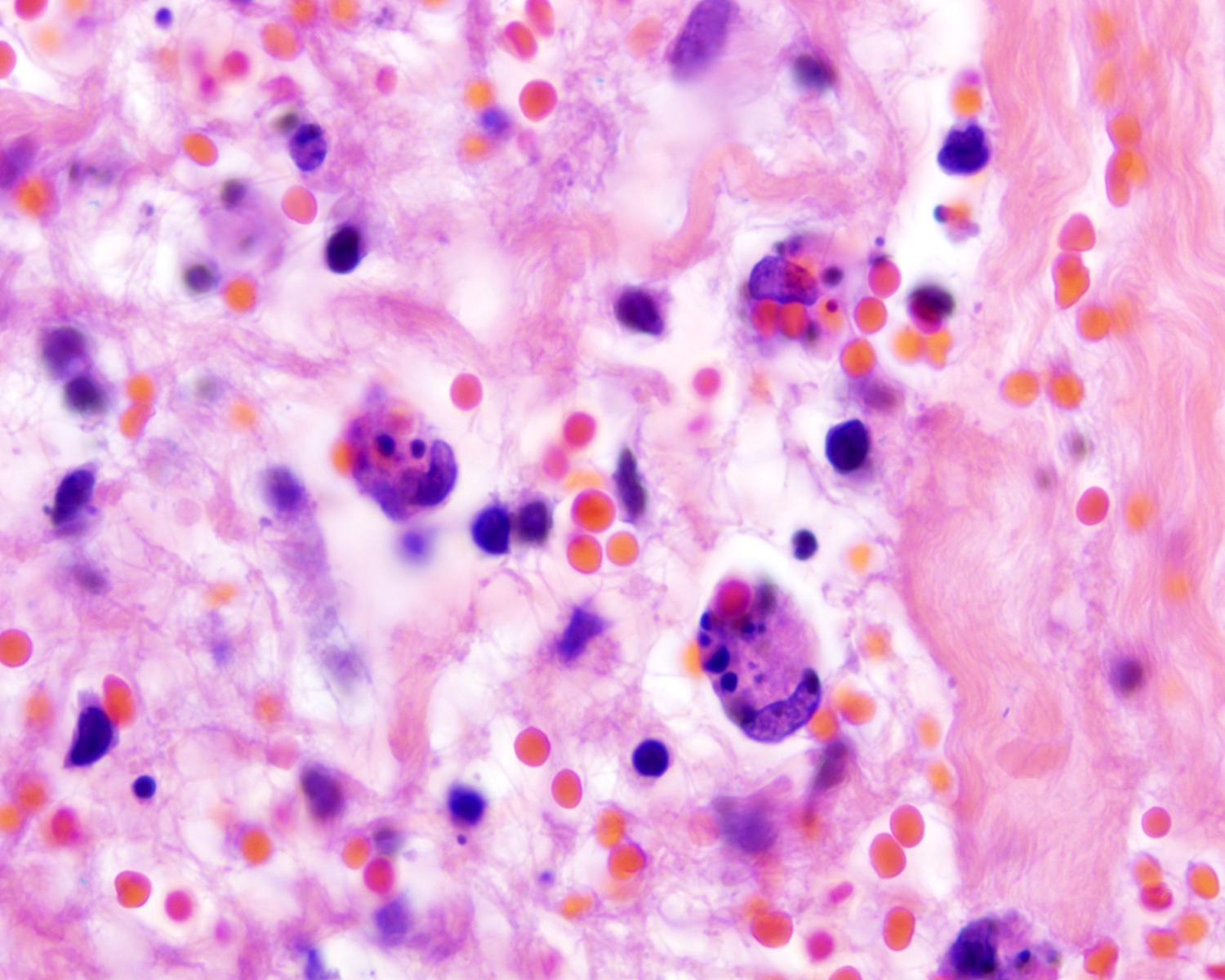
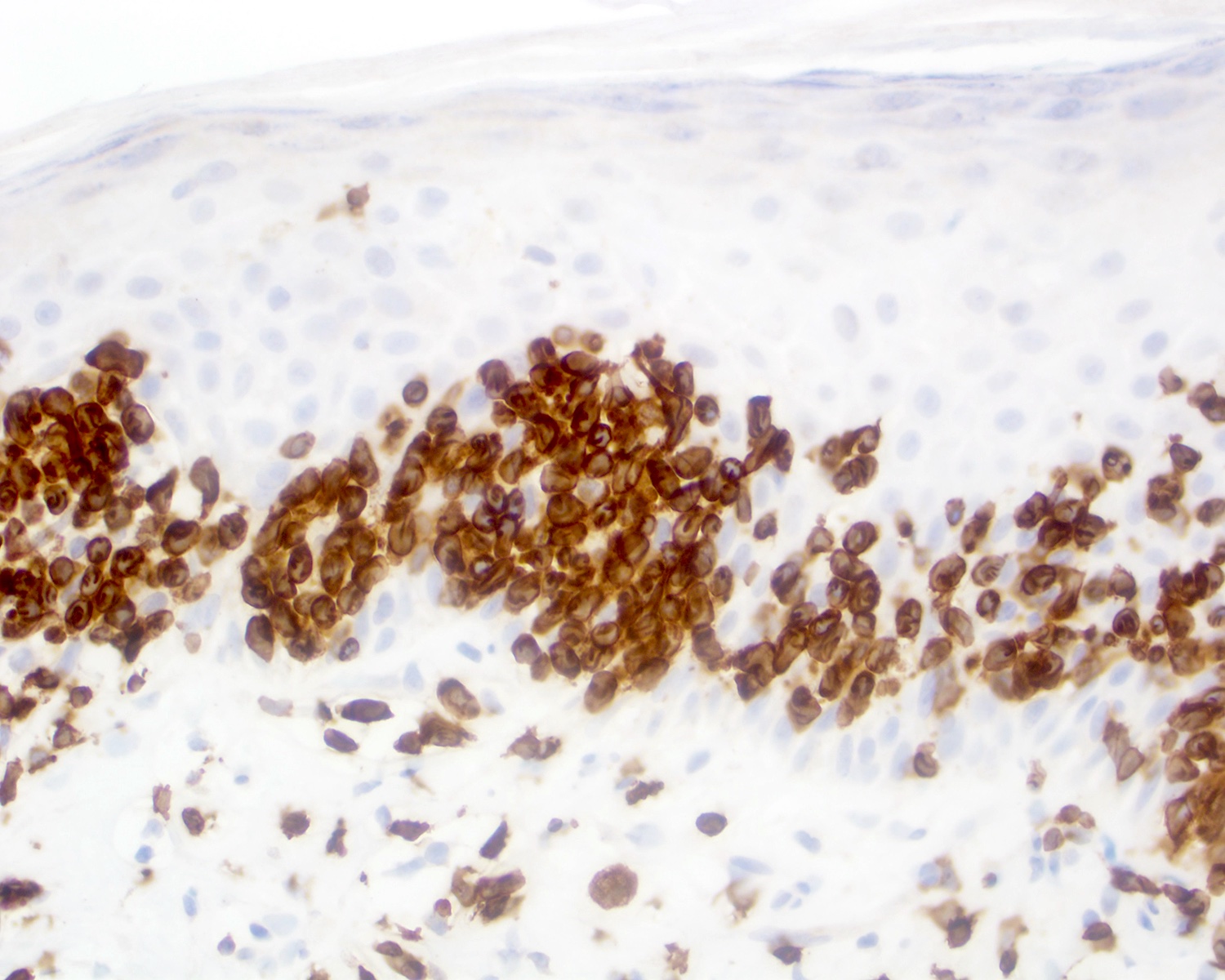
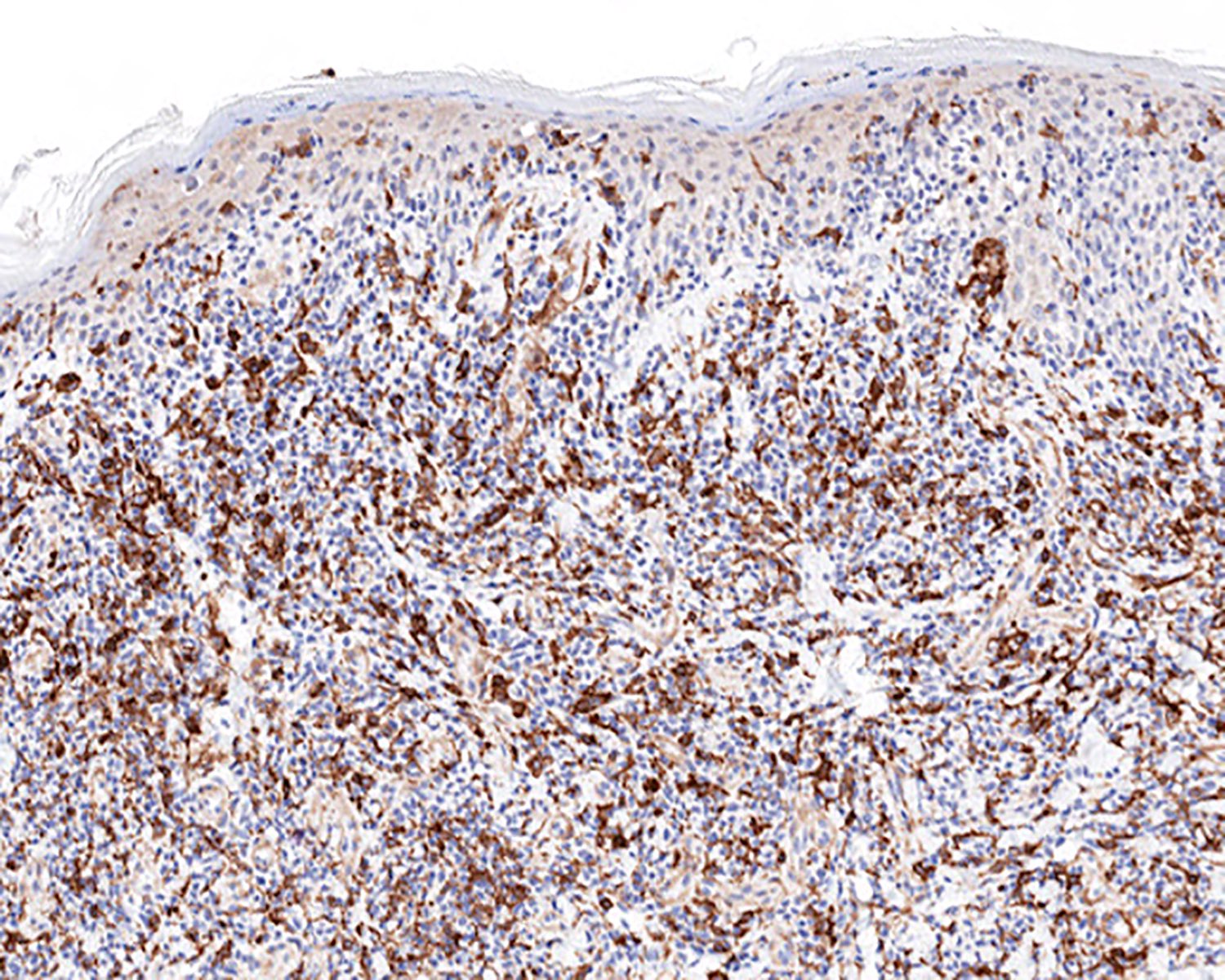
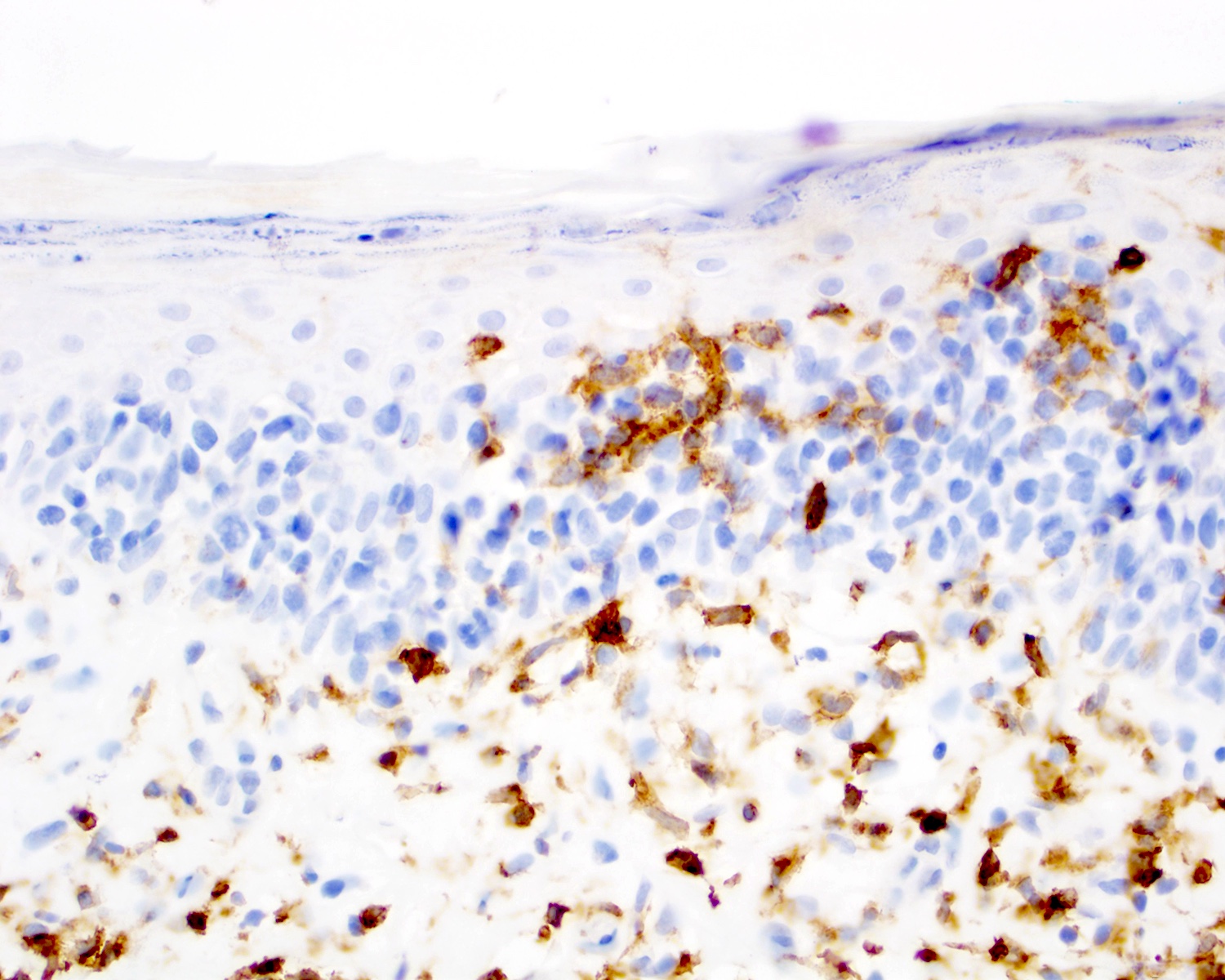
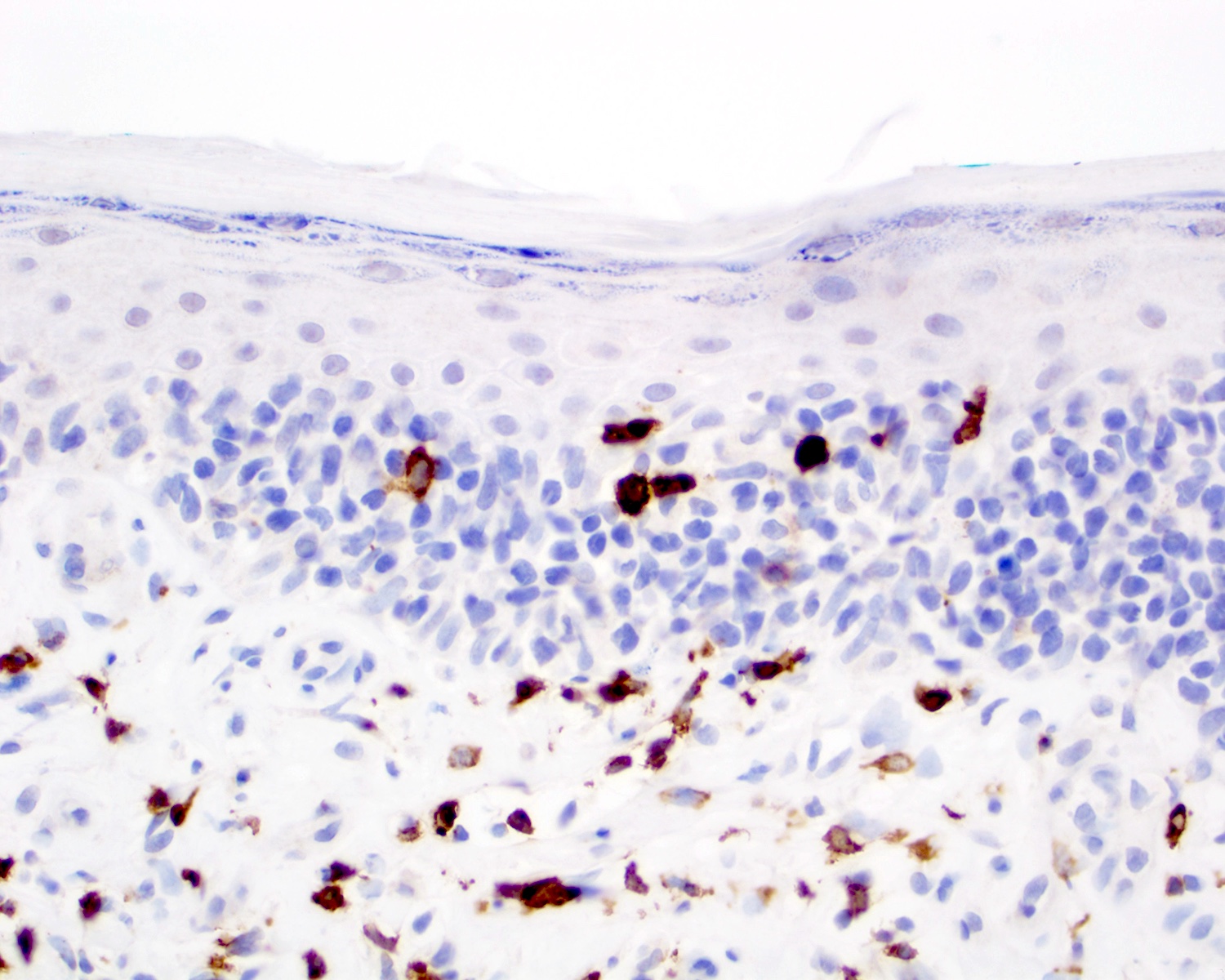
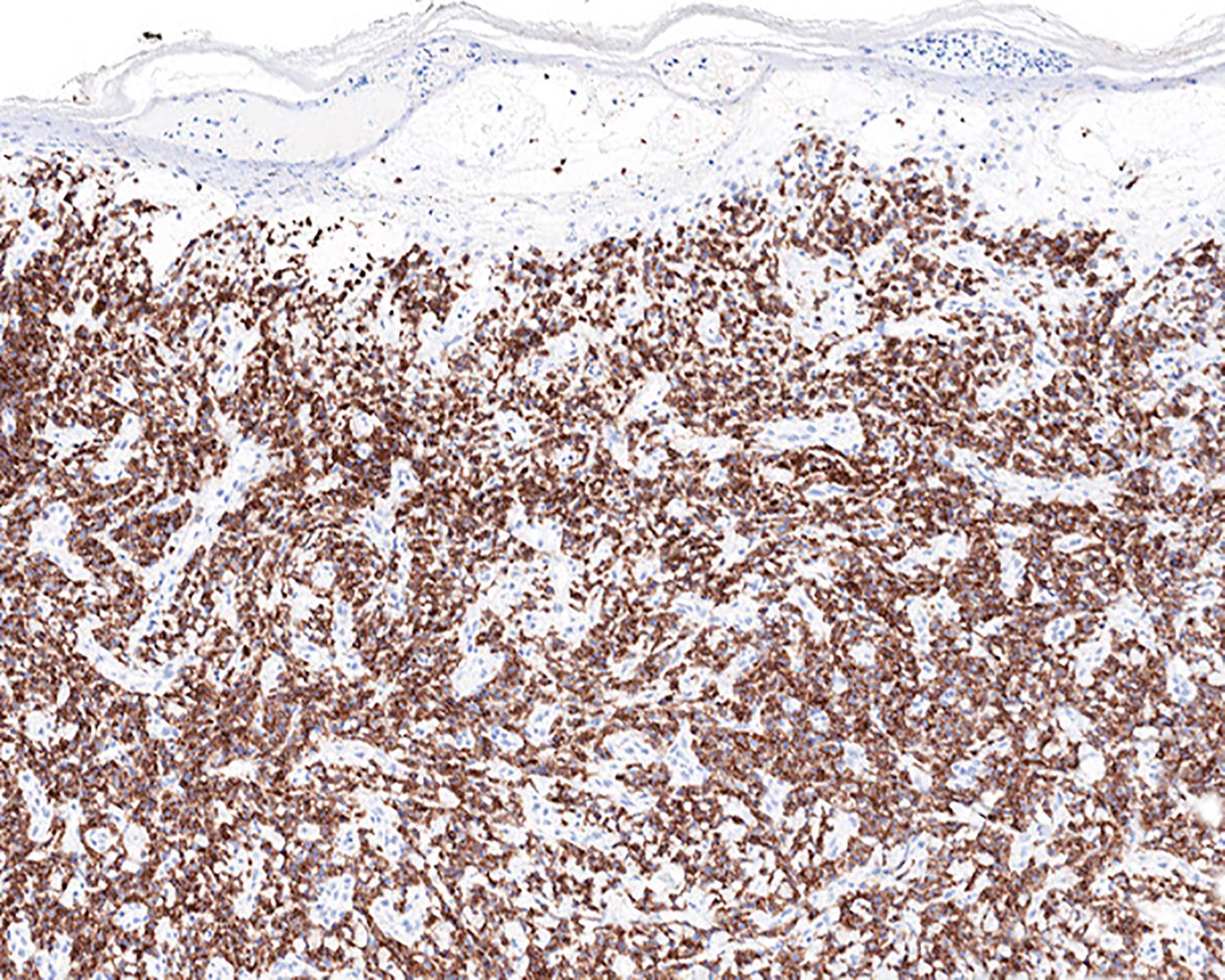
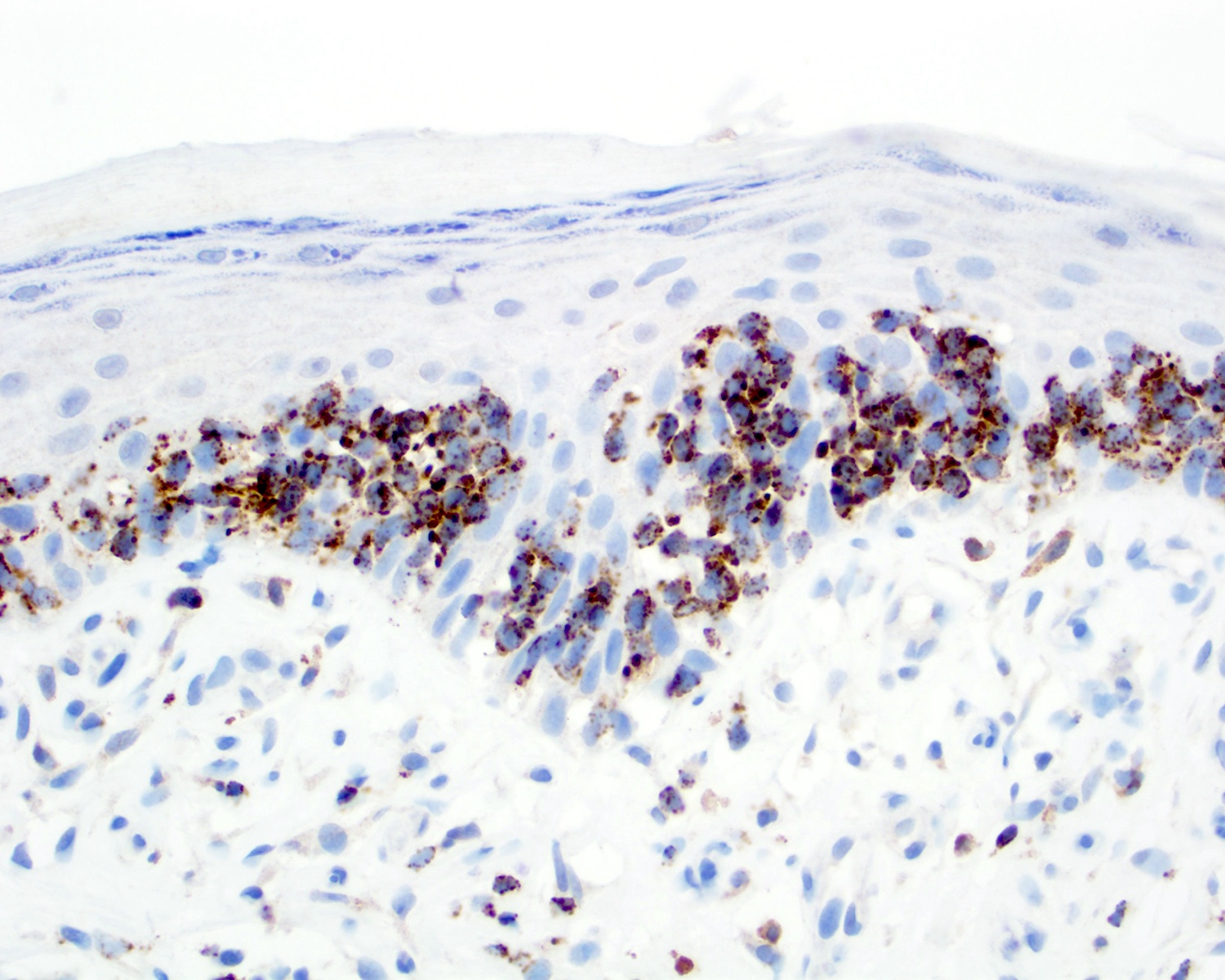
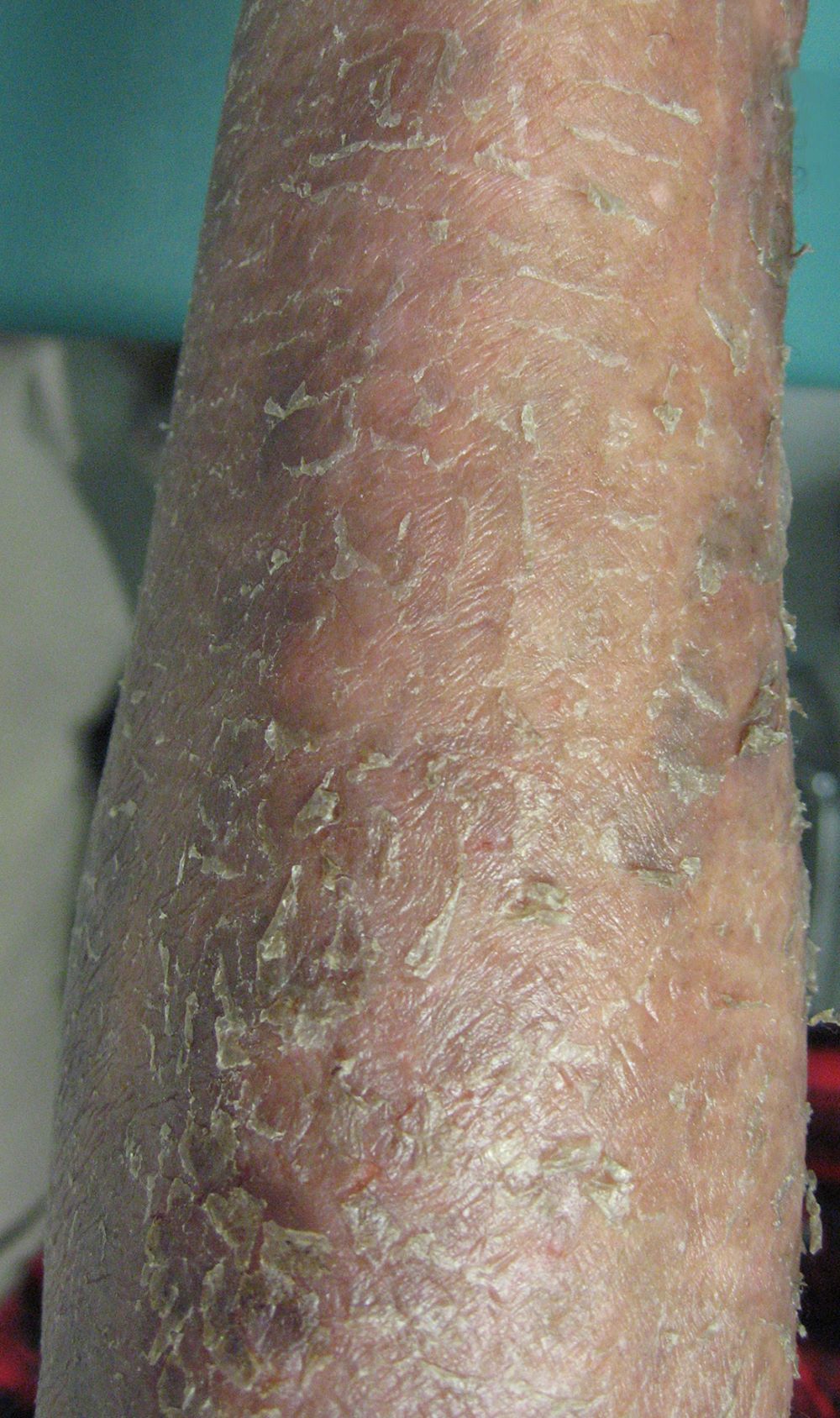
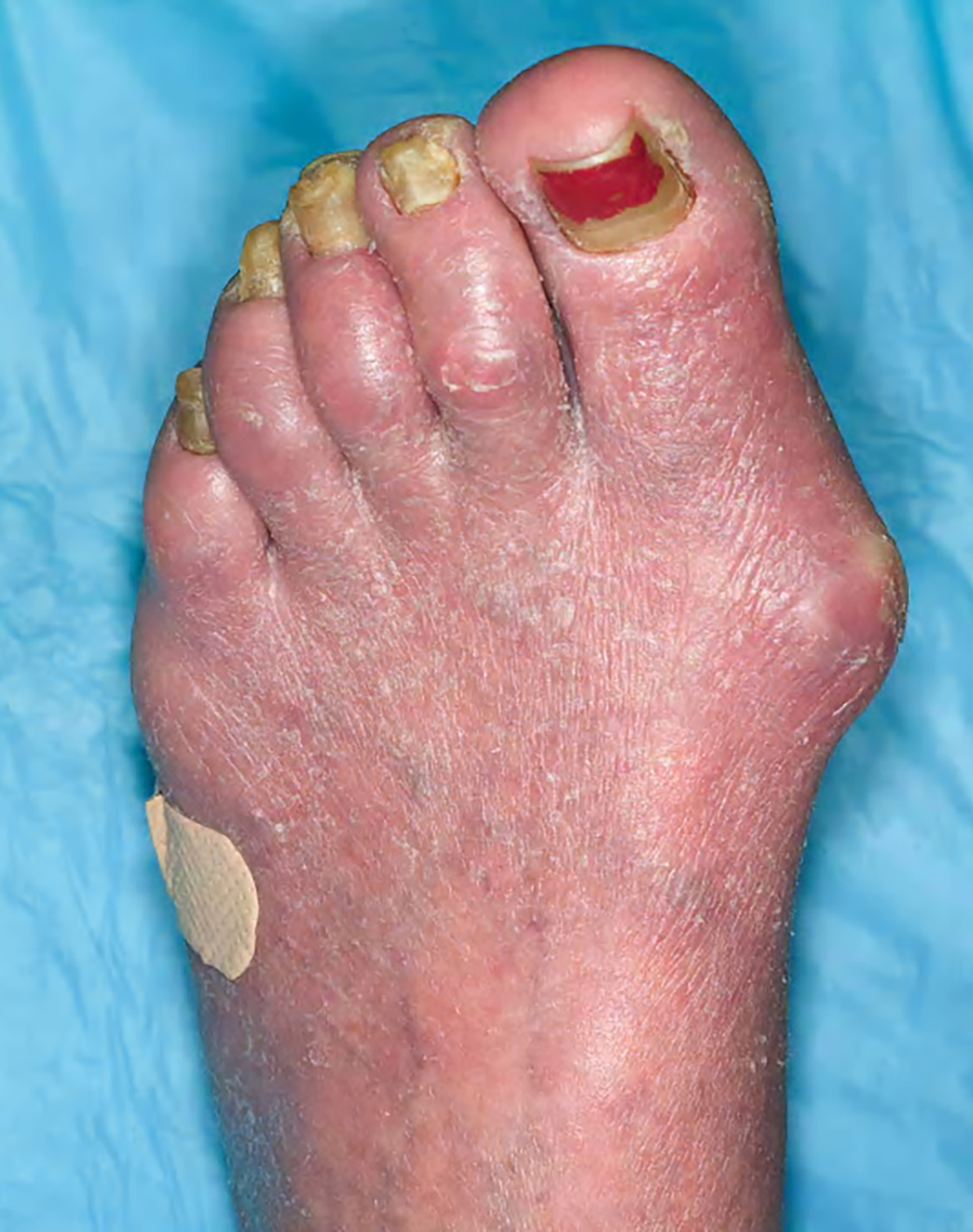
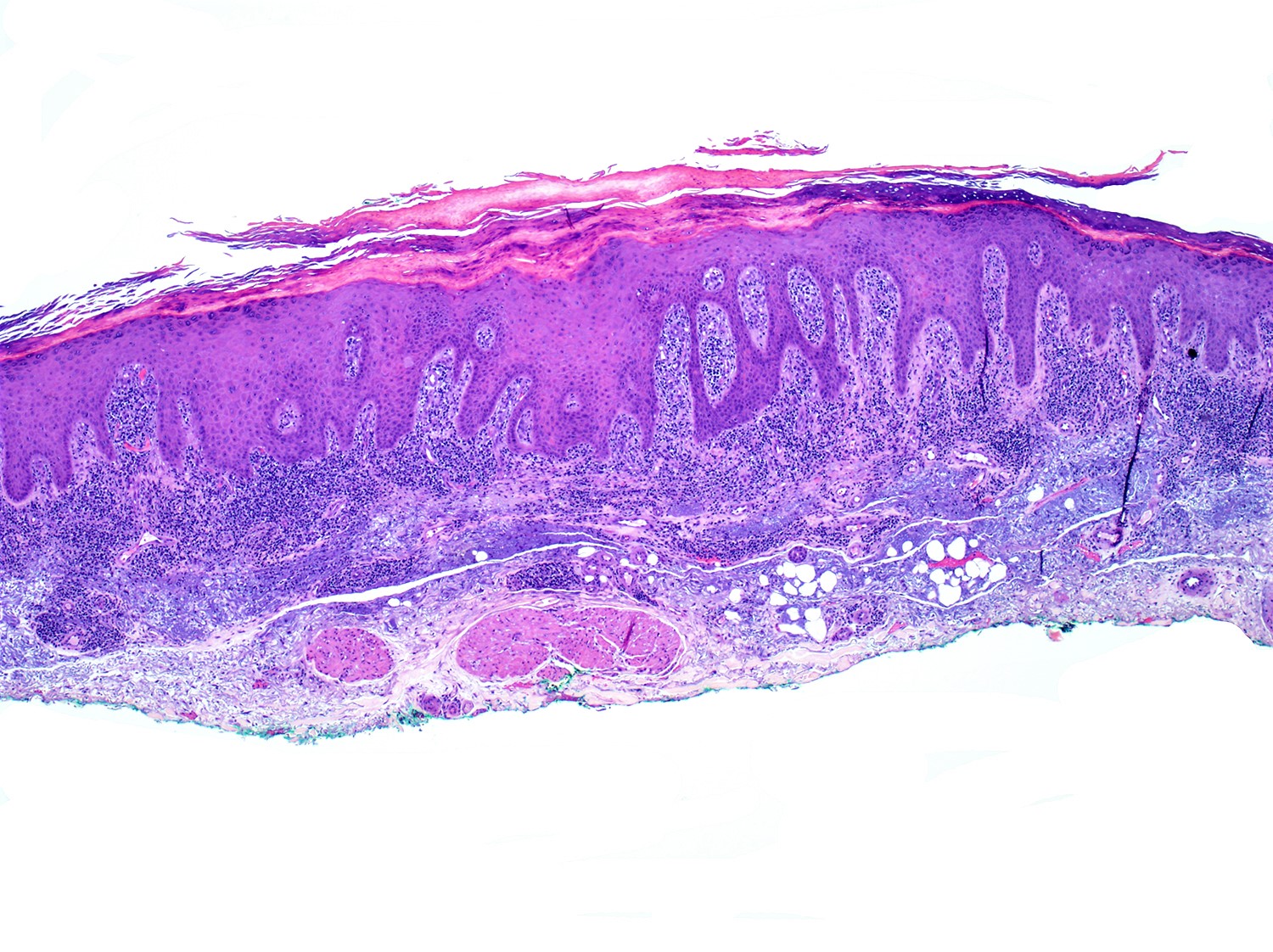
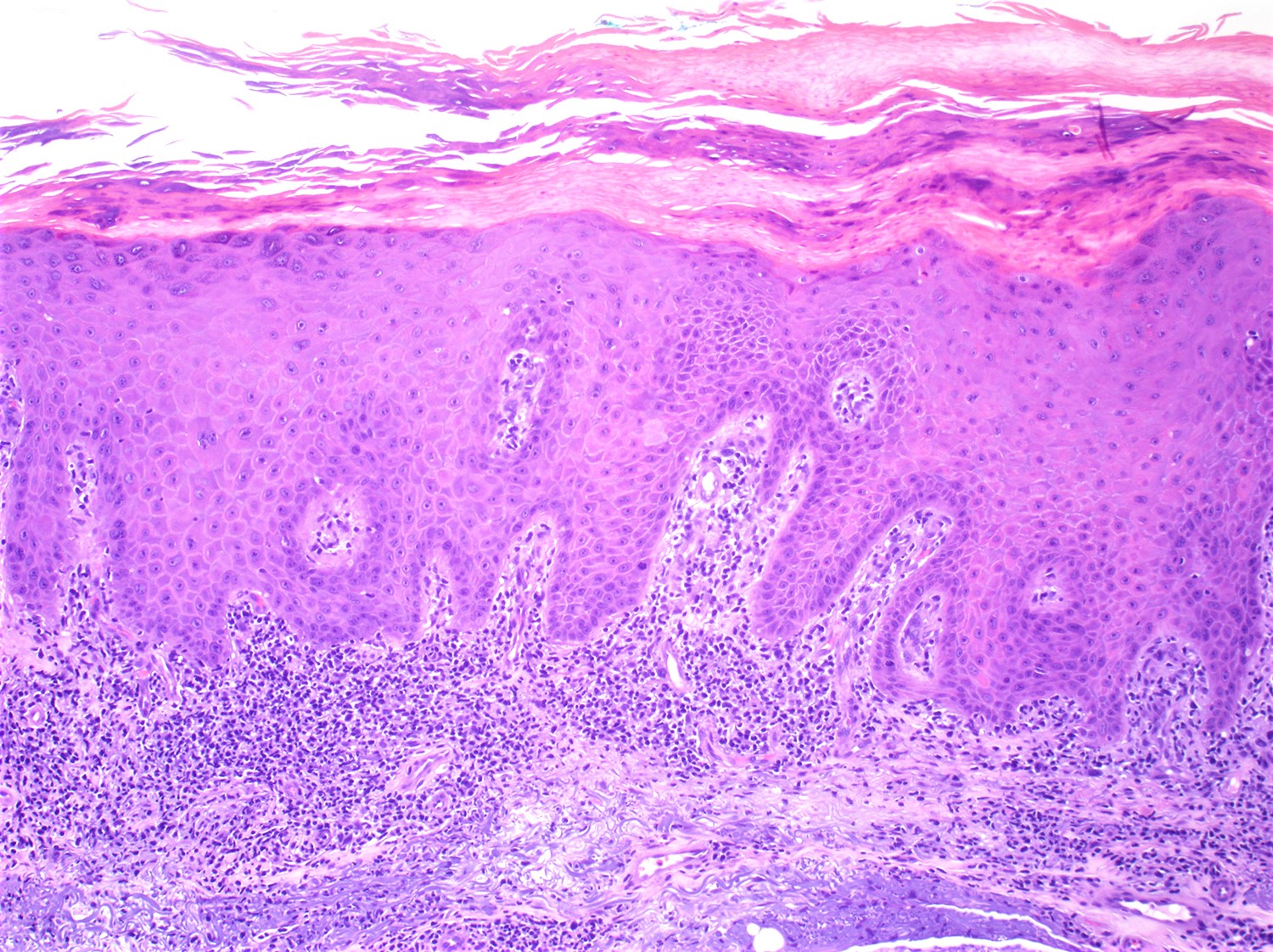
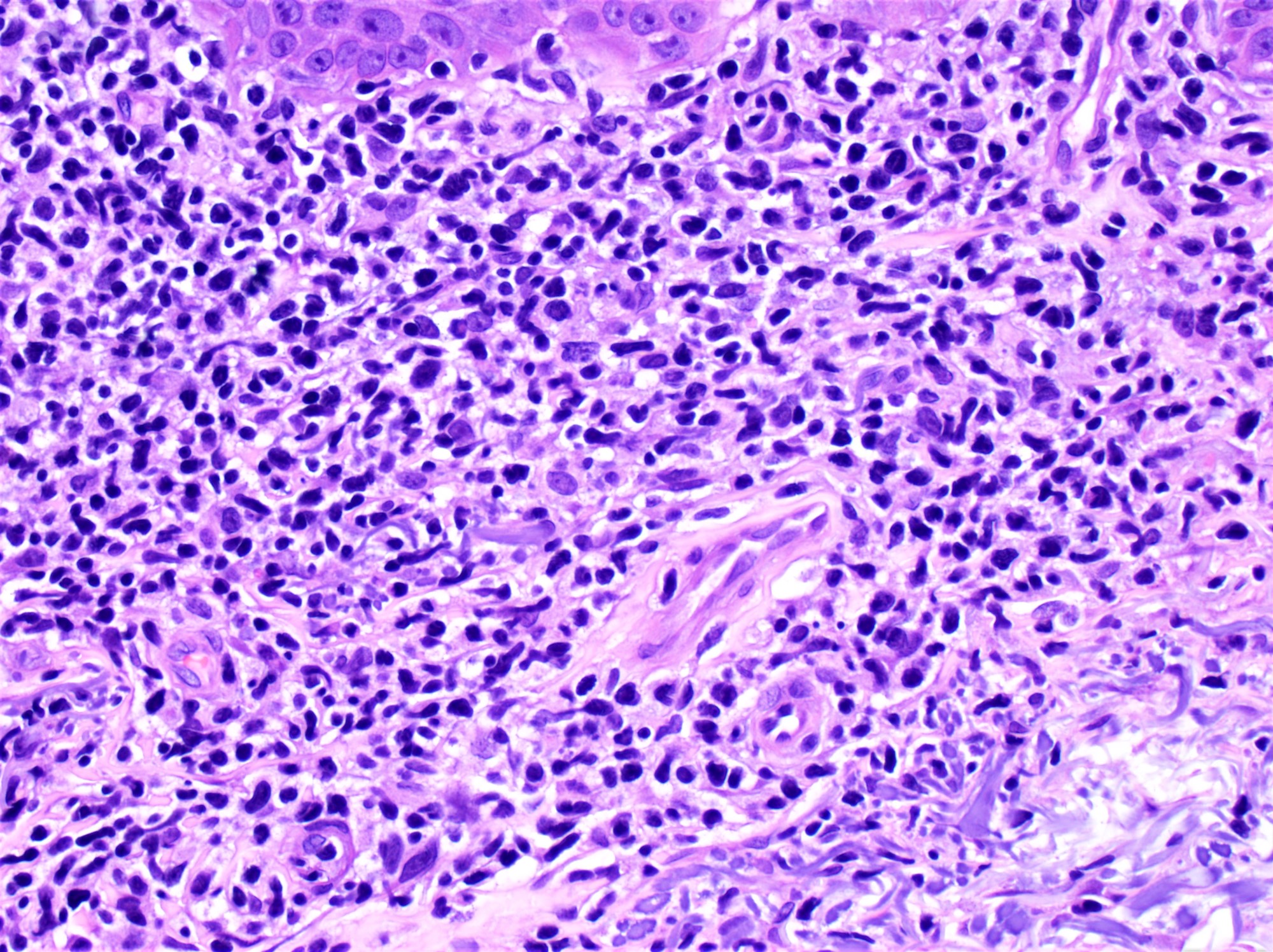
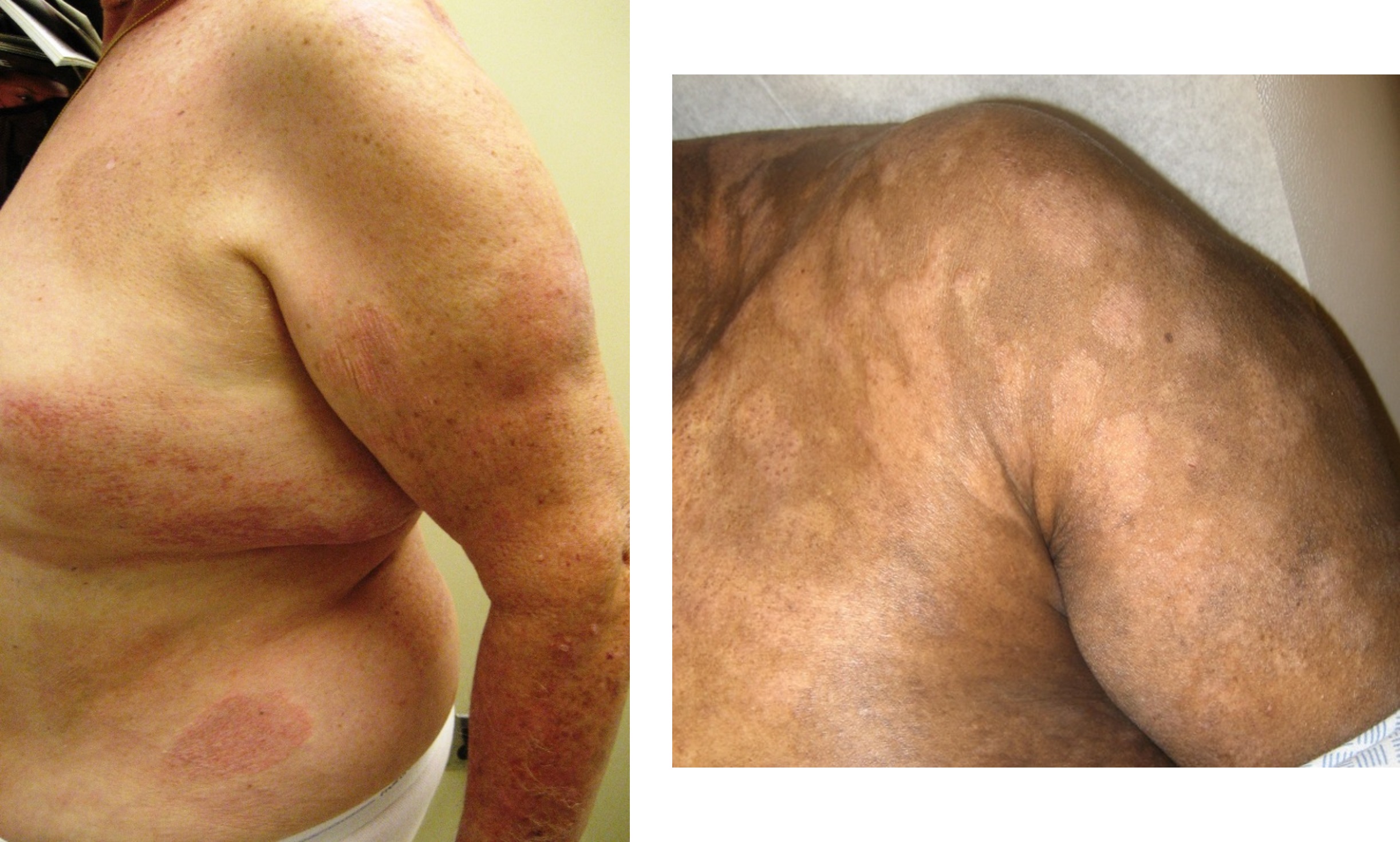
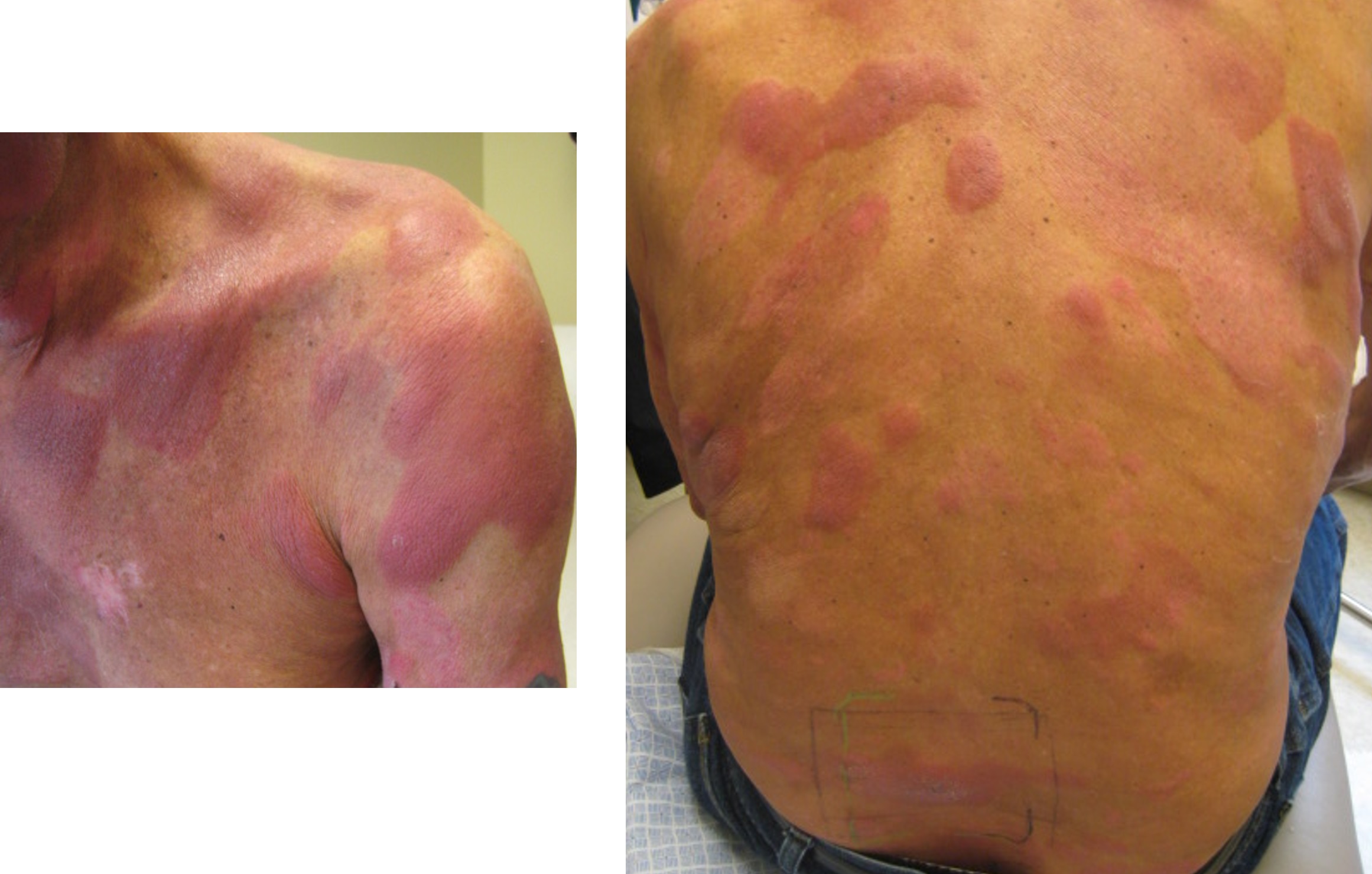
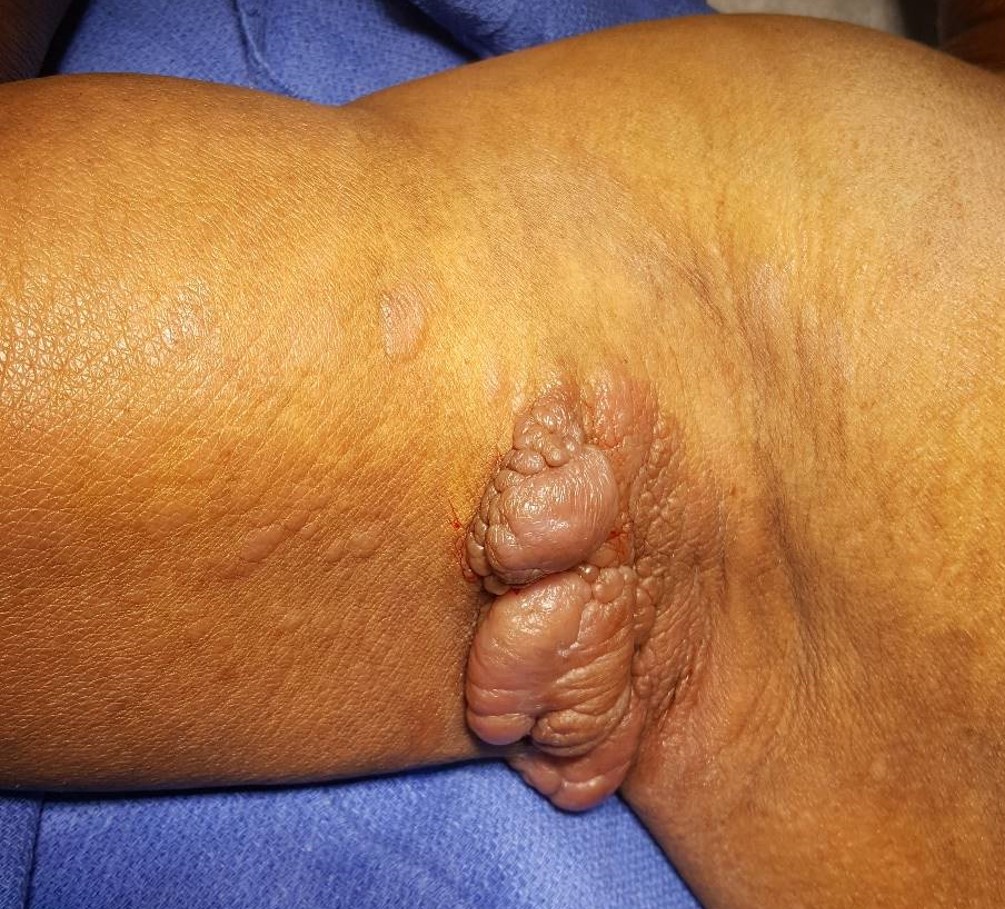
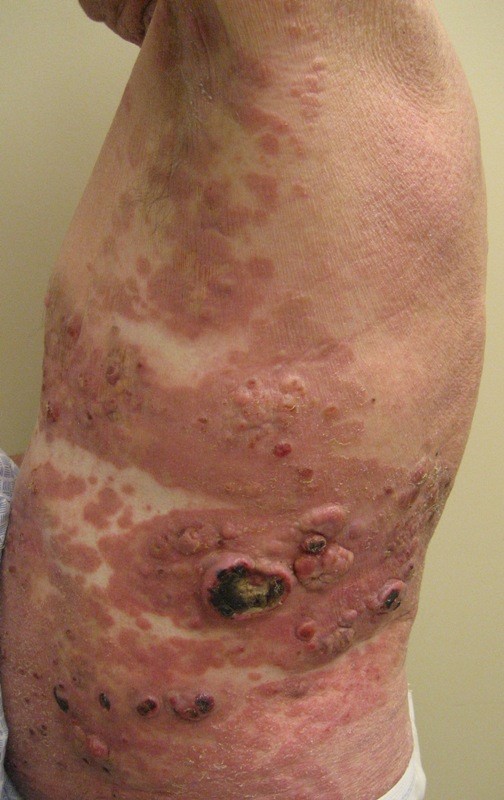
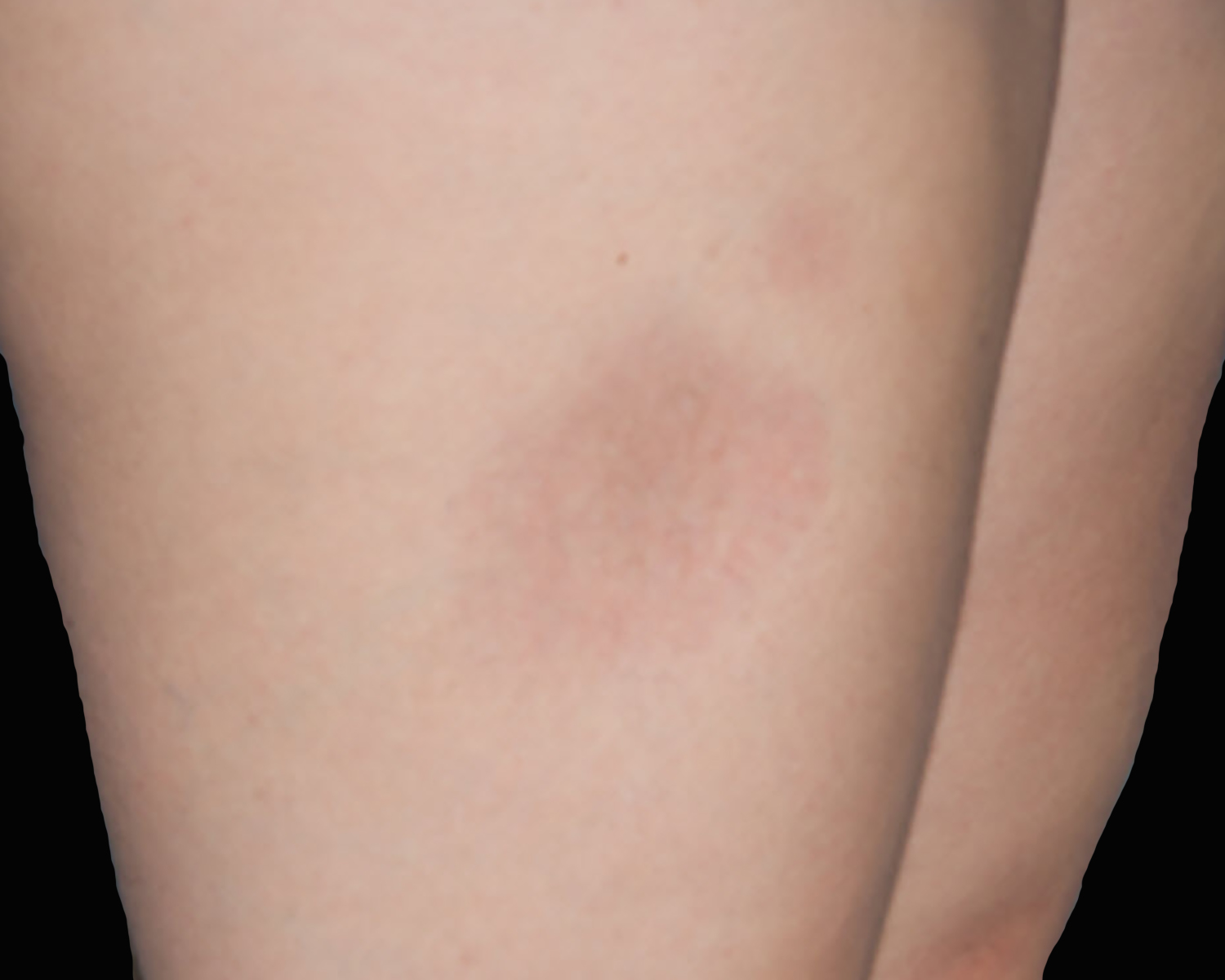
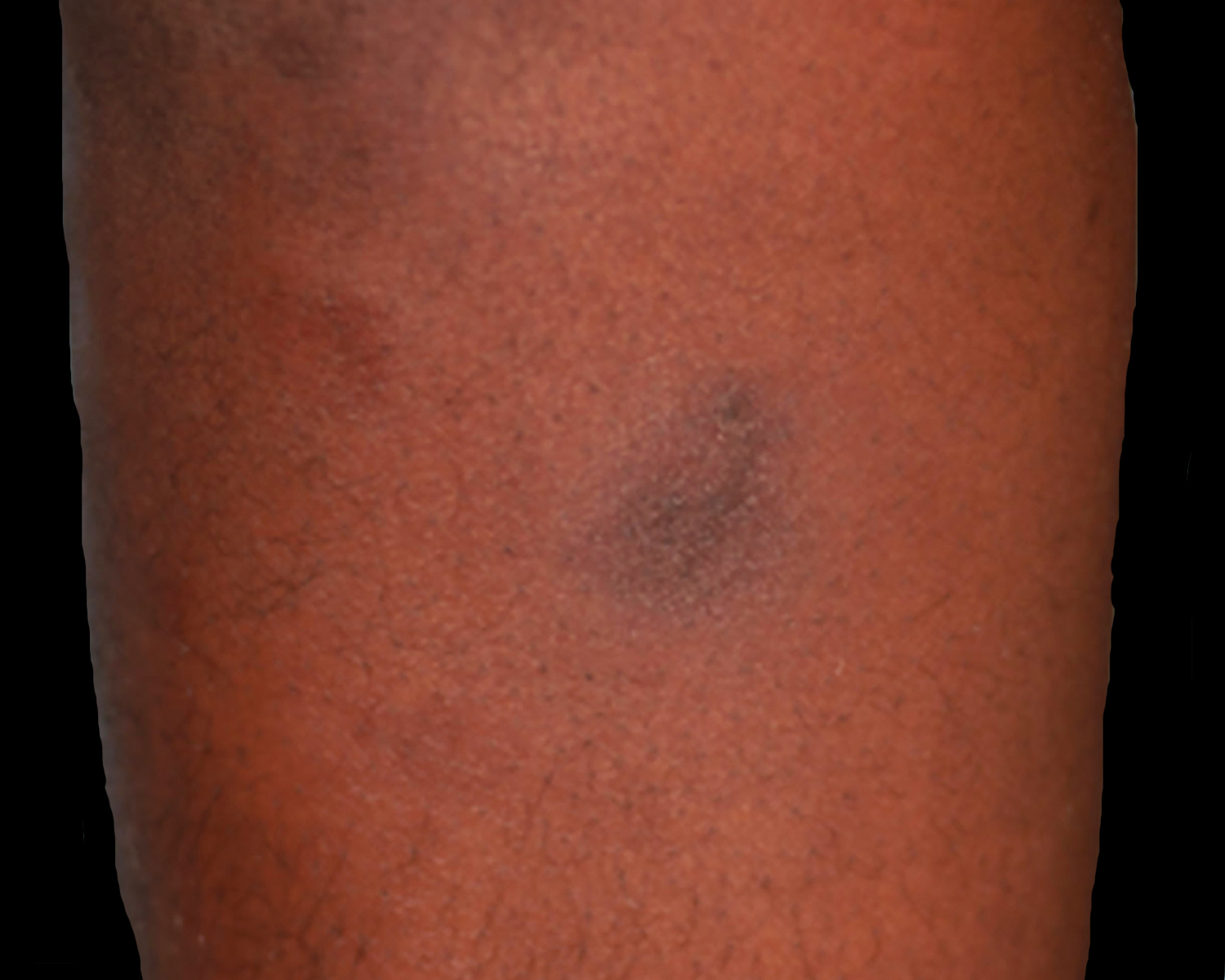
Severe mosquito bite allergy
Clinical images
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Carlos Barrionuevo-Cornejo, M.D., Ph.D.
Splenic B cell leukemia / lymphoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Flow cytometry images
Splenic B cell lymphoma / leukemia with prominent nucleoli
Diagrams / tables
Microscopic (histologic) images
Peripheral smear images
Flow cytometry images
Splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma
Radiology images
Microscopic (histologic) images
Peripheral smear images
Splenic marginal zone lymphoma
Staging-primary cutaneous
Diagrams / tables
Clinical images
Videos
Diagnosis and staging of cutaneous lymphoma
Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Systemic EBV+ T cell lymphoma of childhood
Microscopic (histologic) images
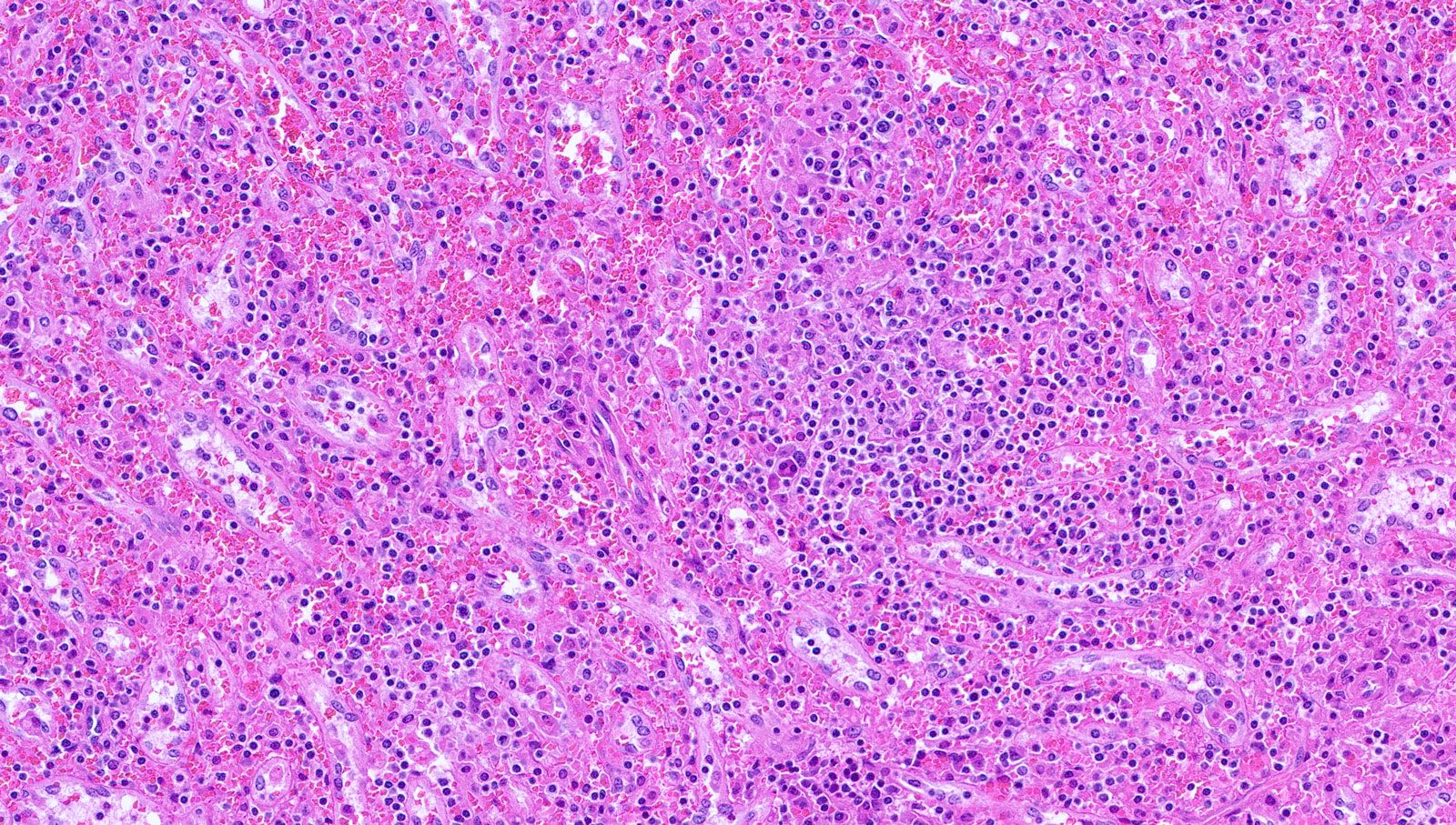
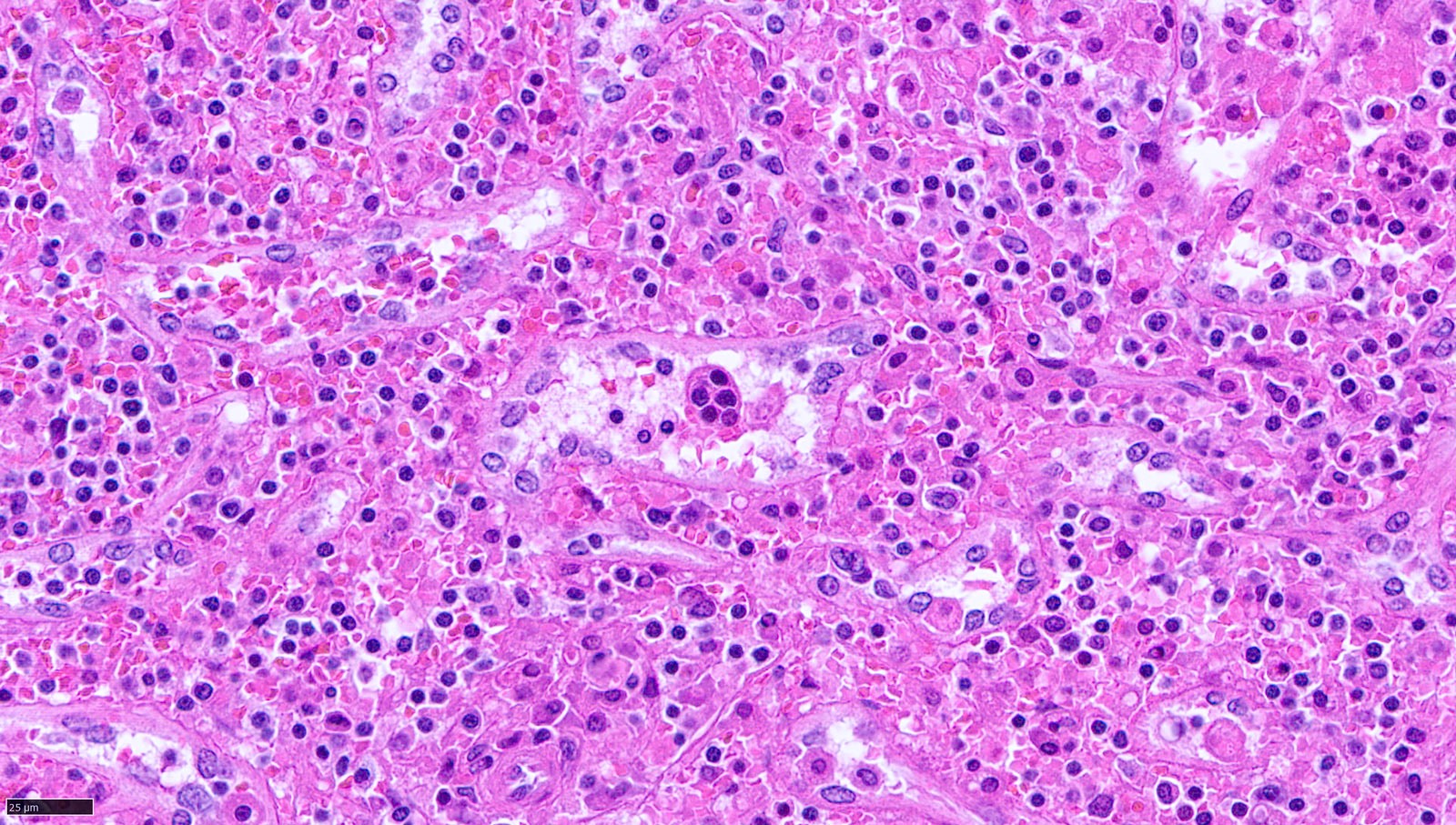
Systemic chronic active EBV disease
Diagrams / tables
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Elaine Jaffe, M.D. and João Víctor Alves de Castro, M.D.
Flow cytometry images
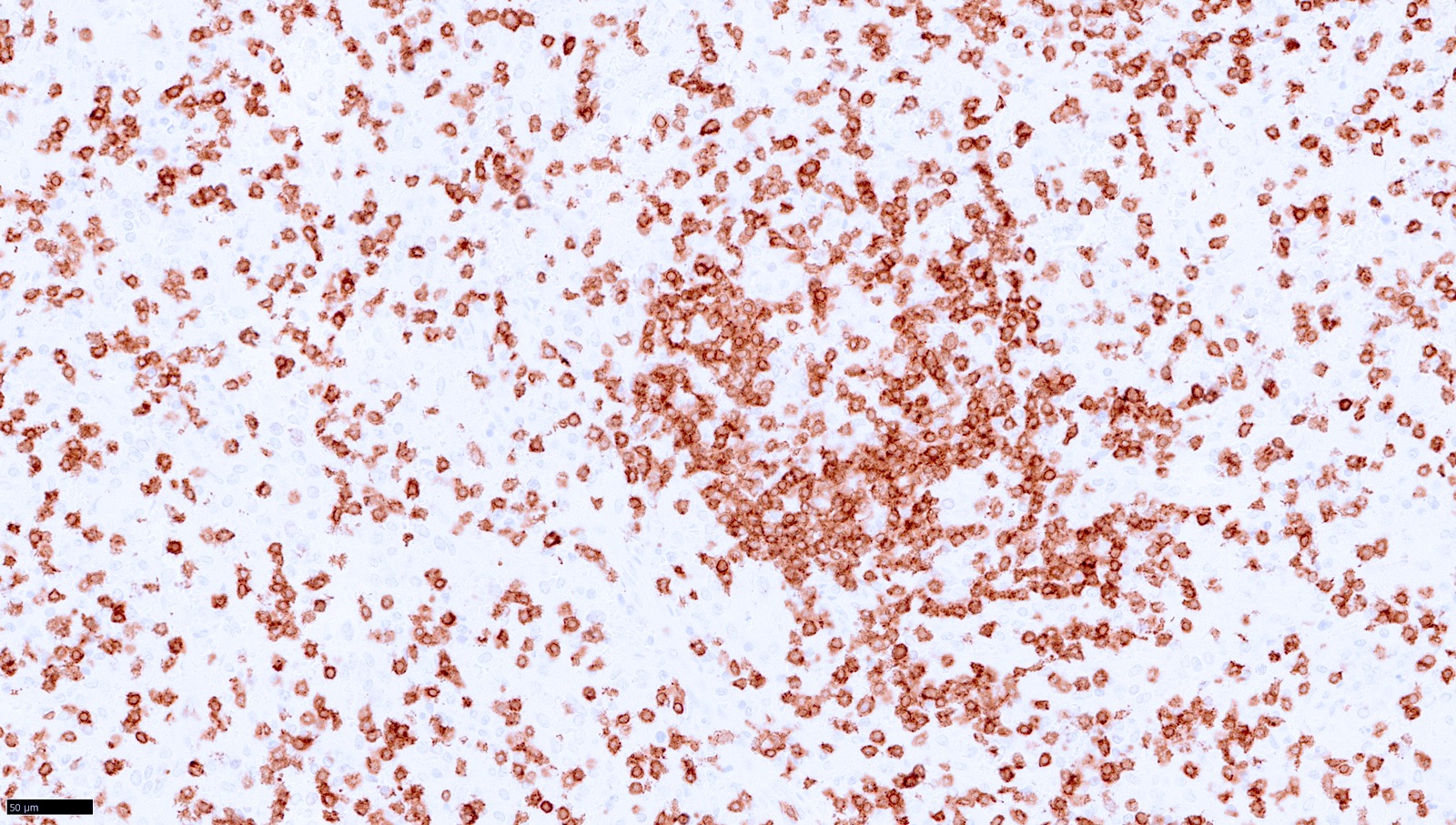
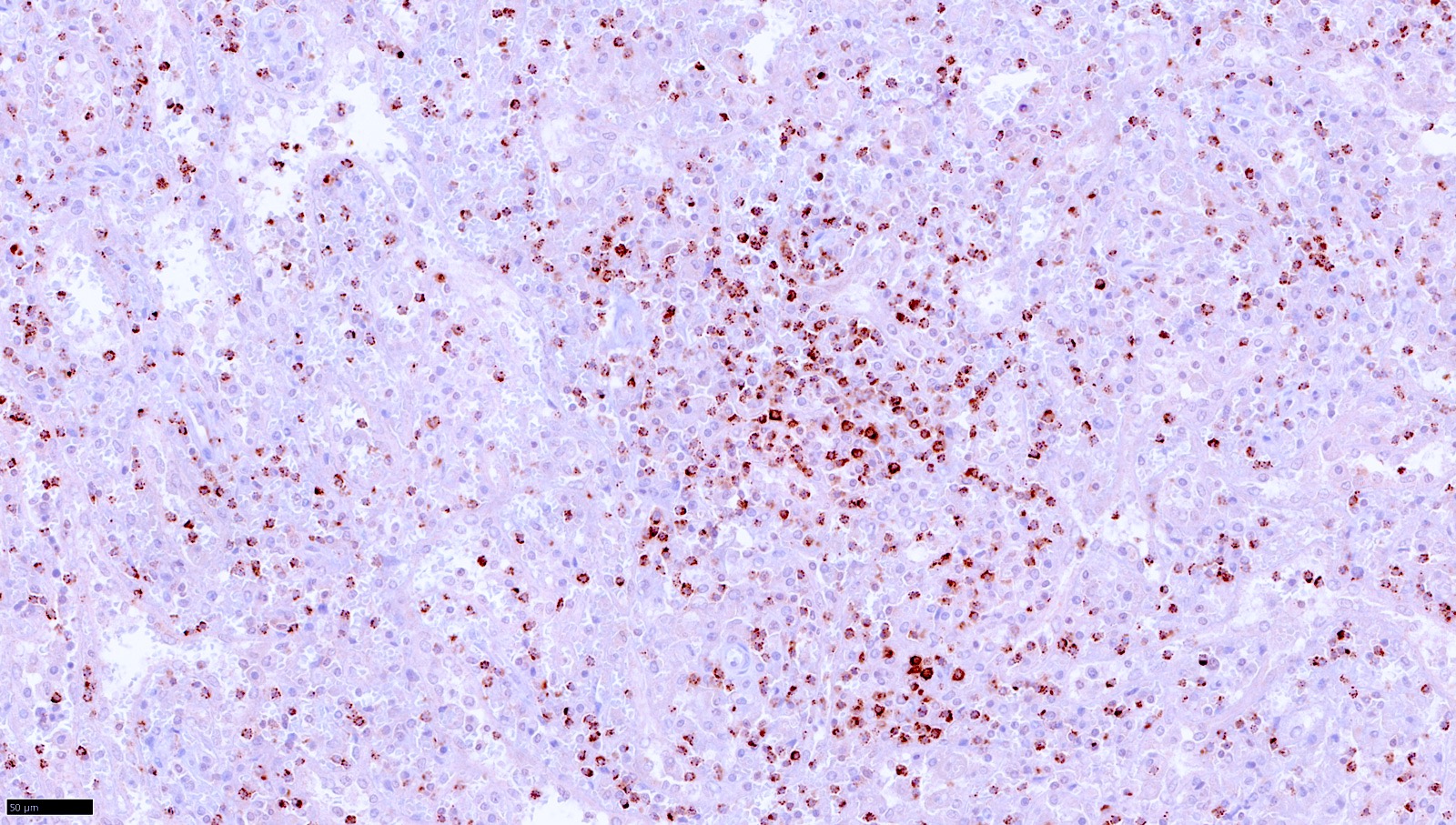
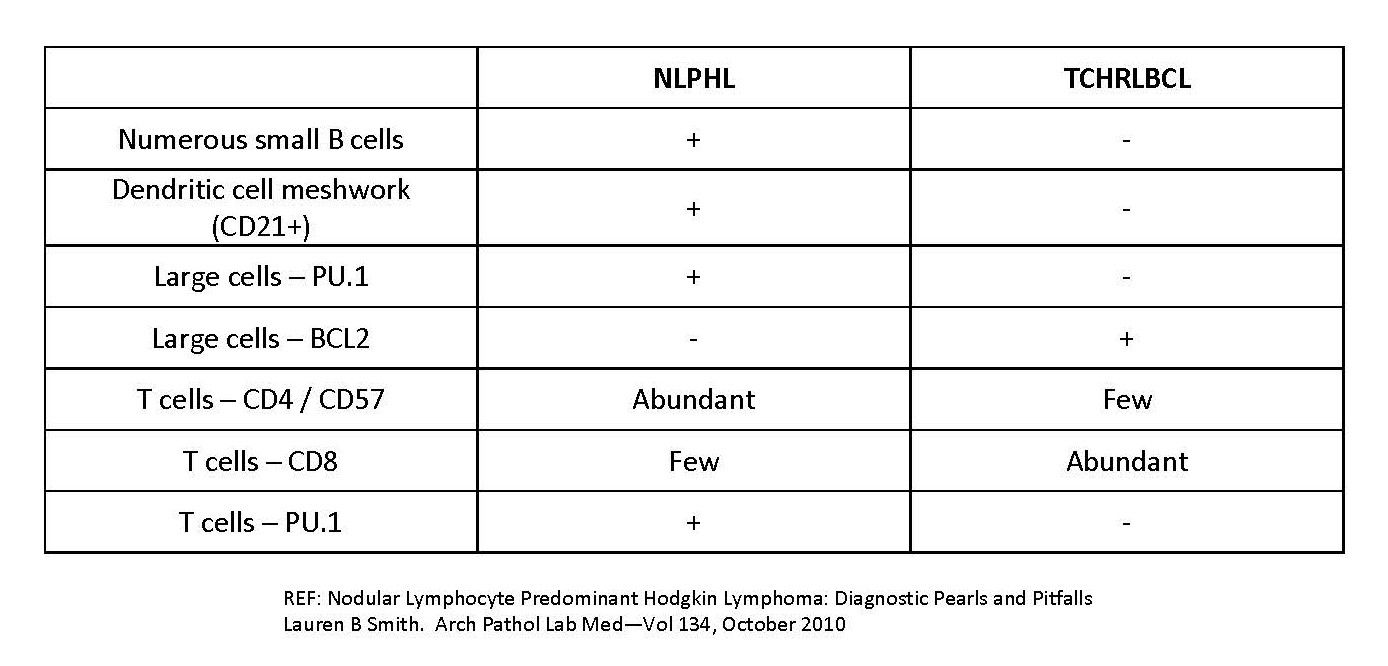
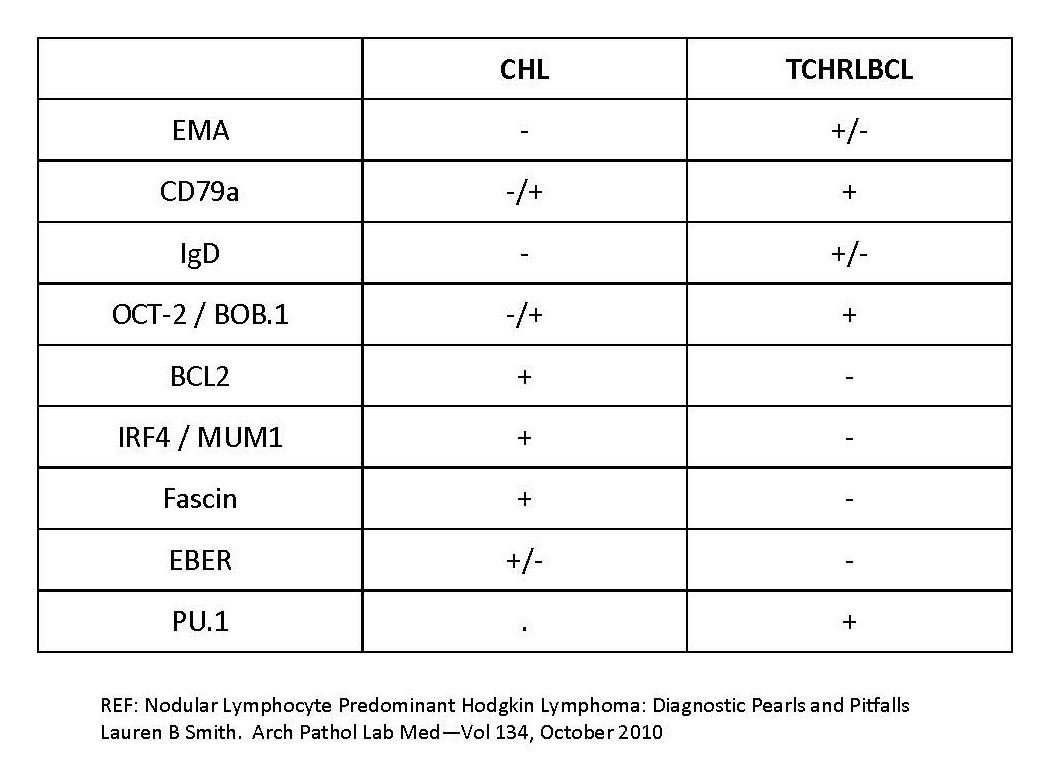
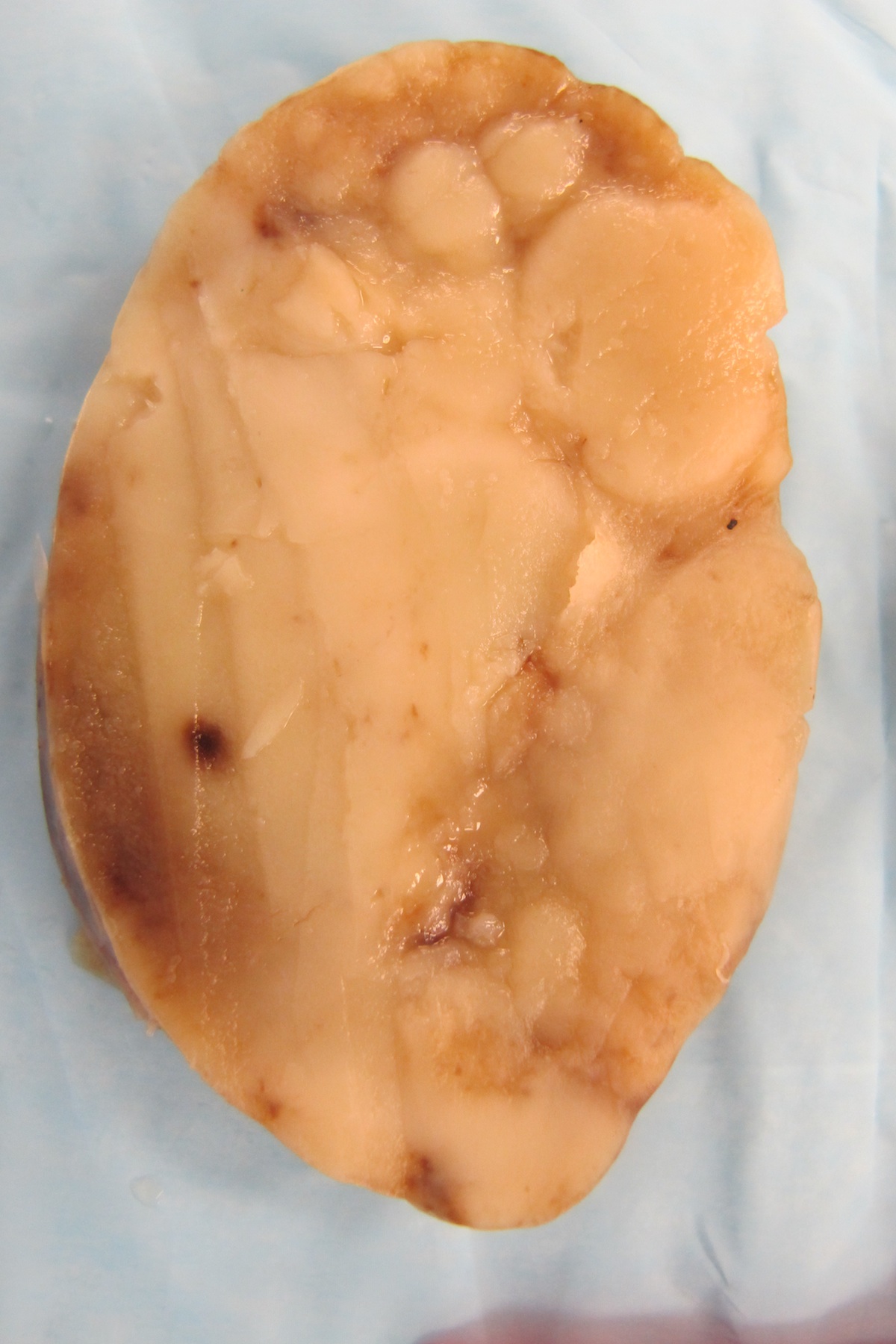
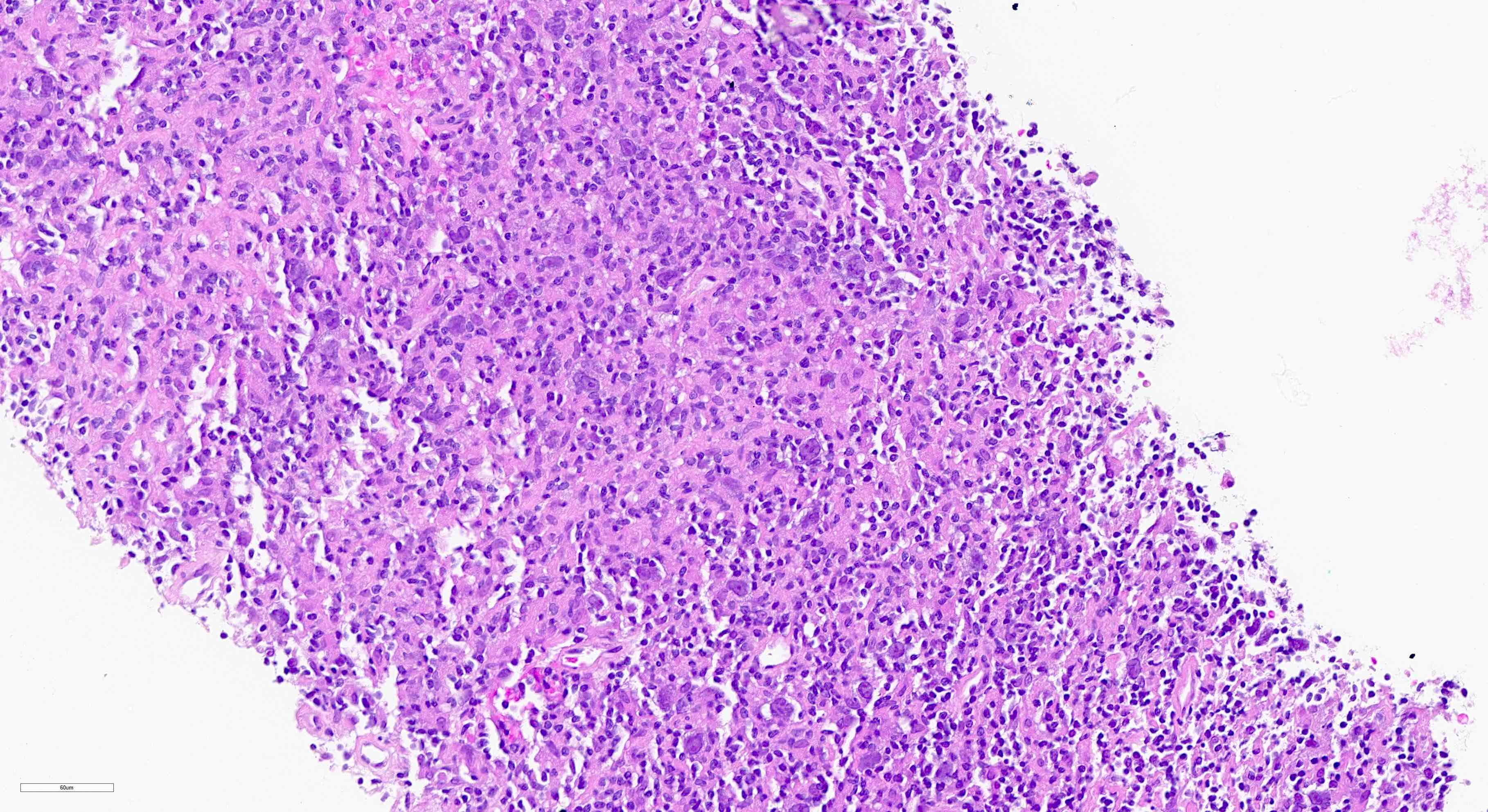
T cell / histiocyte rich LBCL
Gross images
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Aaron Auerbach, M.D., M.P.H., Asmaa Gaber Abdou, M.D. and Nancy Youssef Asaad, M.D.
Contributed by Contributed by Mingyi Chen, M.D., Ph.D. (Case #317)
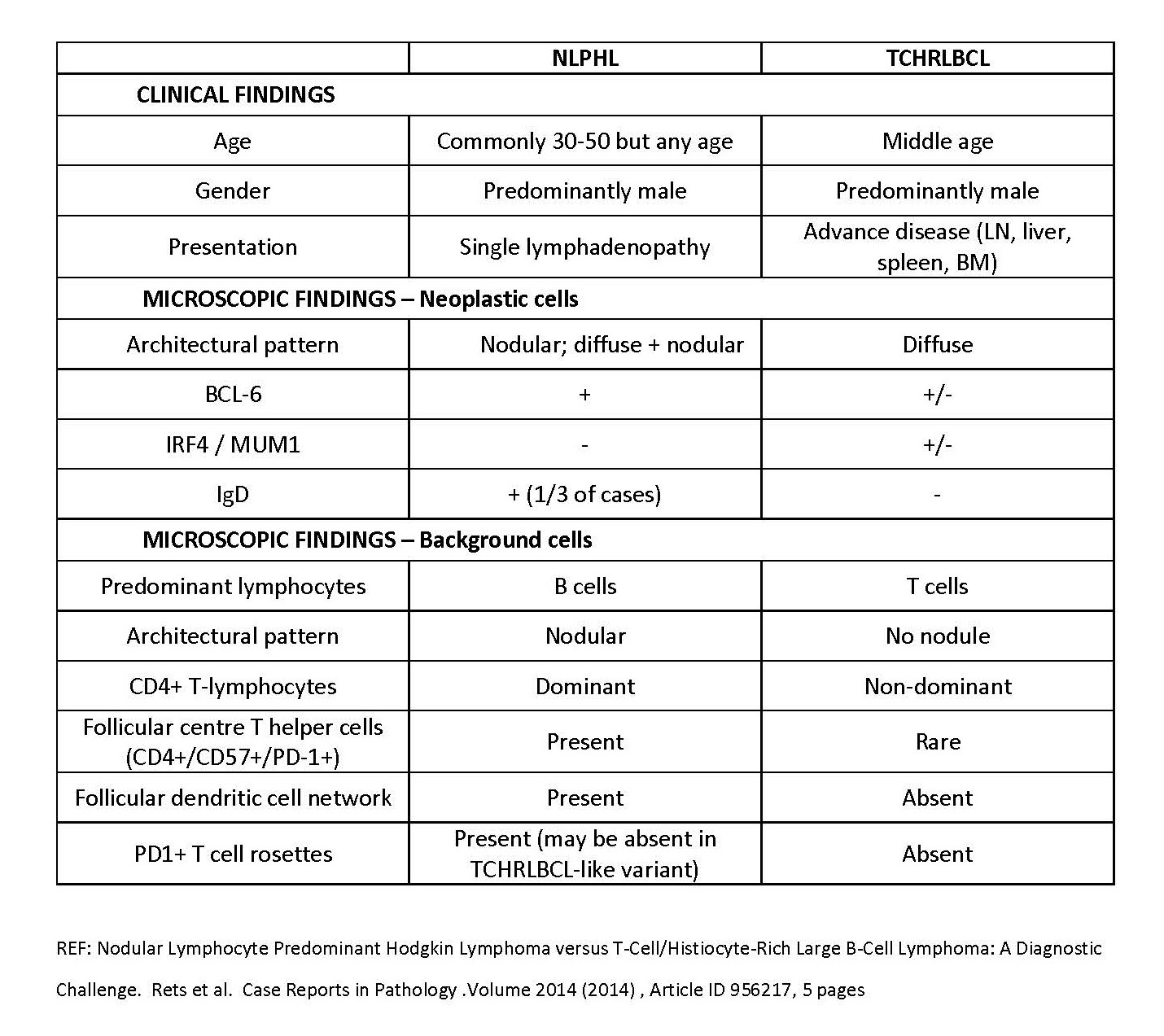
Videos
NLPHL versus THRLBCL
T cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Min Shi, M.D., Ph.D. and Dragan Jevremovic, M.D., Ph.D.
Peripheral smear images
Flow cytometry images
T prolymphocytic leukemia
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Min Shi, M.D., Ph.D. and Dragan Jevremovic, M.D., Ph.D.
Peripheral smear images
Flow cytometry images
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Unusual morphologic patterns of follicular lymphoma
Diagrams / tables
Table 1
| FL with Castleman-like changes |
| FL with plasmacytic differentiation with or without IgG4 positive plasma cells |
| FL with marginal zone differentiation, typically involving MALT sites |
| FL negative for CD10, positive for MUM1 with BCL6 abnormalities |
| EBV positive FL |
| Floral variant of FL |
Microscopic (histologic) images
WHO 2016 T/NK cell
WHO 2022 & ICC-B cell
Microscopic (histologic) images
WHO 2022 & ICC-T / NK cell
Diagrams / tables
Table 1: T / NK cell entities - comparison of WHO (2016), WHO (2022) and ICC (2022)
| WHO HAEM4R | WHO HAEM5 | ICC |
| Precursor T cell neoplasms | ||
| T lymphoblastic leukemia / lymphoma | T lymphoblastic leukemia / lymphoma, NOS | T lymphoblastic leukemia / lymphoma |
Early T cell precursor lymphoblastic leukemia / lymphoma | Early T cell precursor lymphoblastic leukemia | Early T cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia, NOS |
| Early T cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia, BCL11B activated | ||
| NK lymphoblastic leukemia / lymphoma* | [Entity removed] | NK cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia* |
| Tumor-like lesions with T cell predominance | ||
| [Not included] | Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease | [Not included] |
| [Not included] | Indolent T lymphoblastic proliferation | [Not included] |
| [Not included] | Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome | [Not included] |
| Mature T / NK cell leukemias | ||
| T prolymphocytic leukemia | T prolymphocytic leukemia | T cell prolymphocytic leukemia |
| T cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia | T large granular lymphocytic leukemia | T cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia |
| Chronic lymphoproliferative disorder of NK cells* | NK large granular lymphocytic leukemia | Chronic lymphoproliferative disorder of NK cells* |
| Adult T cell leukemia / lymphoma | Adult T cell leukemia / lymphoma | Adult T cell leukemia / lymphoma |
| Sézary syndrome | Sézary syndrome | Sézary syndrome |
| Aggressive NK cell leukemia | Aggressive NK cell leukemia | Aggressive NK cell leukemia |
| Primary cutaneous T cell lymphomas | ||
| Primary cutaneous CD4 positive small or medium T cell LPD* | Primary cutaneous CD4 positive small or medium T cell LPD | Primary cutaneous small or medium CD4 positive T cell LPD |
| Primary cutaneous acral CD8 positive T cell lymphoma* | Primary cutaneous acral CD8 positive lymphoproliferative disorder | Primary cutaneous acral CD8 positive lymphoproliferative disorder |
| Mycosis fungoides | Mycosis fungoides | Mycosis fungoides |
| Primary cutaneous CD30 positive T cell LPD: lymphomatoid papulosis | Primary cutaneous CD30 positive T cell LPD: lymphomatoid papulosis | Primary cutaneous CD30 positive T cell LPD: lymphomatoid papulosis |
| Primary cutaneous CD30 positive T cell LPD: primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma | Primary cutaneous CD30 positive T cell LPD: primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma | Primary cutaneous CD30 positive T cell LPD: primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma |
| Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma | Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma | Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma |
| Primary cutaneous gamma / delta T cell lymphoma | Primary cutaneous gamma / delta T cell lymphoma | Primary cutaneous gamma / delta T cell lymphoma |
| Primary cutaneous CD8 positive aggressive epidermotropic cytotoxic T cell lymphoma* | Primary cutaneous CD8 positive aggressive epidermotropic cytotoxic T cell lymphoma | Primary cutaneous CD8 positive aggressive epidermotropic cytotoxic T cell lymphoma |
| [Not included] | Primary cutaneous peripheral T cell lymphoma, NOS | [Not included] |
| Intestinal T cell and NK cell lymphoid proliferations and lymphomas | ||
| Indolent T cell lymphoproliferative disorder of the gastrointestinal tract* | Indolent T cell lymphoma of the gastrointestinal tract | Indolent clonal T cell LPD of the gastrointestinal tract |
| [Not included] | Indolent NK cell LPD of the gastrointestinal tract | Indolent NK cell LPD of the gastrointestinal tract |
| Enteropathy associated T cell lymphoma | Enteropathy associated T cell lymphoma | Enteropathy associated T cell lymphoma |
| Type II refractory celiac disease | ||
| Monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T cell lymphoma | Monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T cell lymphoma | Monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T cell lymphoma |
| Intestinal T cell lymphoma, NOS | Intestinal T cell lymphoma, NOS | Intestinal T cell lymphoma, NOS |
| Hepatosplenic T cell lymphoma | ||
| Hepatosplenic T cell lymphoma | Hepatosplenic T cell lymphoma | Hepatosplenic T cell lymphoma |
| Anaplastic large cell lymphoma | ||
| Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, ALK positive | ALK positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma | Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, ALK positive |
| Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, ALK negative | ALK negative anaplastic large cell lymphoma | Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, ALK negative |
| Breast implant associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma* | Breast implant associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma | Breast implant associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma |
| Nodal T follicular helper (TFH) cell lymphoma | ||
| Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma | Nodal TFH cell lymphoma, angioimmunoblastic type | Follicular helper T cell lymphoma, angioimmunoblastic type |
| Follicular T cell lymphoma* | Nodal TFH cell lymphoma, follicular type | Follicular helper T cell lymphoma, follicular type |
| Nodal peripheral T cell lymphoma (PTCL) with TFH phenotype* | Nodal TFH cell lymphoma, NOS | Follicular helper T cell lymphoma, NOS |
| Other peripheral T cell lymphomas | ||
| Peripheral T cell lymphoma, NOS | Peripheral T cell lymphoma, NOS | Peripheral T cell lymphoma, NOS |
| EBV positive NK / T cell lymphomas | ||
| [Not included] [variant of PTCL, NOS] | EBV positive nodal T and NK cell lymphoma | Primary nodal Epstein-Barr virus positive T / NK cell lymphoma* |
| Extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma, nasal type | Extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma | Extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma, nasal type |
| EBV positive T and NK cell lymphoid proliferations and lymphomas of childhood | ||
| Severe mosquito bite allergy | Severe mosquito bite allergy | Severe mosquito bite allergy |
| Hydroa vacciniforme-like lymphoproliferative disorder | Hydroa vacciniforme lymphoproliferative disorder, classic or systemic | Hydroa vacciniforme lymphoproliferative disorder, classic or systemic |
| Chronic active EBV infection of T and NK cell type, systemic form | Systemic chronic active EBV disease | Chronic active EBV disease (T and NK cell phenotype) |
| Systemic EBV positive T cell lymphoma of childhood | Systemic EBV positive T cell lymphoma of childhood | Systemic EBV positive T cell lymphoma of childhood |
Microscopic (histologic) images
Recent Lymphoma & related disorders Pathology books
Find related Pathology books: hematopathology, dermatopathology, immunology / transplant, lab medicine, molecular, oncology