Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Chapel DB, Bennett J. Cellular angiofibroma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/vulvacellularangiofibroma.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Cellular angiofibroma is a benign, site specific soft tissue tumor of the lower genital tract
Essential features
- Benign lower genital tract tumor, occurring equally in women and men
- Bland spindle cell fascicles, abundant medium sized hyalinized vessels and wispy stromal collagen
- Characterized by deletion of RB1 / FOXO1 locus on chr 13q
- Local excision curative; recurrences exceptionally rare
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- F ~ M
- In women, age range 22 - 77 years (median ~ 47 years) (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1426, J Cutan Pathol 2003;30:405)
- Men typically older (32 - 88 years; median ~ 65 years) (Mod Pathol 2011;24:82, Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:6)
Sites
- In women, labium majus most common, followed by vagina and perineum (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1426, Mod Pathol 2011;24:82, Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:636)
- In men, scrotum and groin most common (Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:6)
- Rare limb, chest wall and retroperitoneal cases (Diagn Pathol 2015;10:114)
Pathophysiology
- Histogenesis unknown
Clinical features
- Painless, slowly growing mass
- Present for weeks to years before diagnosis (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:636, Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1426)
- Clinically mimics Bartholin cyst, lipoma or leiomyoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1426)
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis typically follows complete local excision of a clinically benign appearing mass
Prognostic factors
- Local recurrence exceptionally rare, even with positive margins (Mod Pathol 2011;24:82, J Clin Pathol 2002;55:477)
- So called sarcomatous transformation does not increase risk of recurrence (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:707)
- No reports of distant metastasis
Case reports
- 37 year old woman with a painless vulvar mass (BMC Clin Pathol 2016;16:8)
- 49 year old woman with a recurrent vulvar cellular angiofibroma (J Clin Pathol 2002;55:477)
- 77 year old man with a left inguinal mass (IJU Case Rep 2020;3:69)
- 79 year old man with a scrotal mass (Diagn Pathol 2017;12:17)
Treatment
- Simple excision considered curative (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:636, Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1426)
- Re-excision for positive margins not mandatory
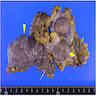
Gross description
- Well circumscribed, nodular or multilobulated, rubbery mass
- Cut surface white-tan to grey
- Gross hemorrhage and necrosis in < 5% (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1426)
- In women, size 0.6 - 12 cm (mean ~ 3 cm) (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1426, Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:636, Mod Pathol 2011;24:82)
- In men, size 0.6 - 25 cm (mean ~ 7 cm) (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1426, Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:6)
Gross images
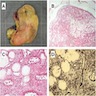
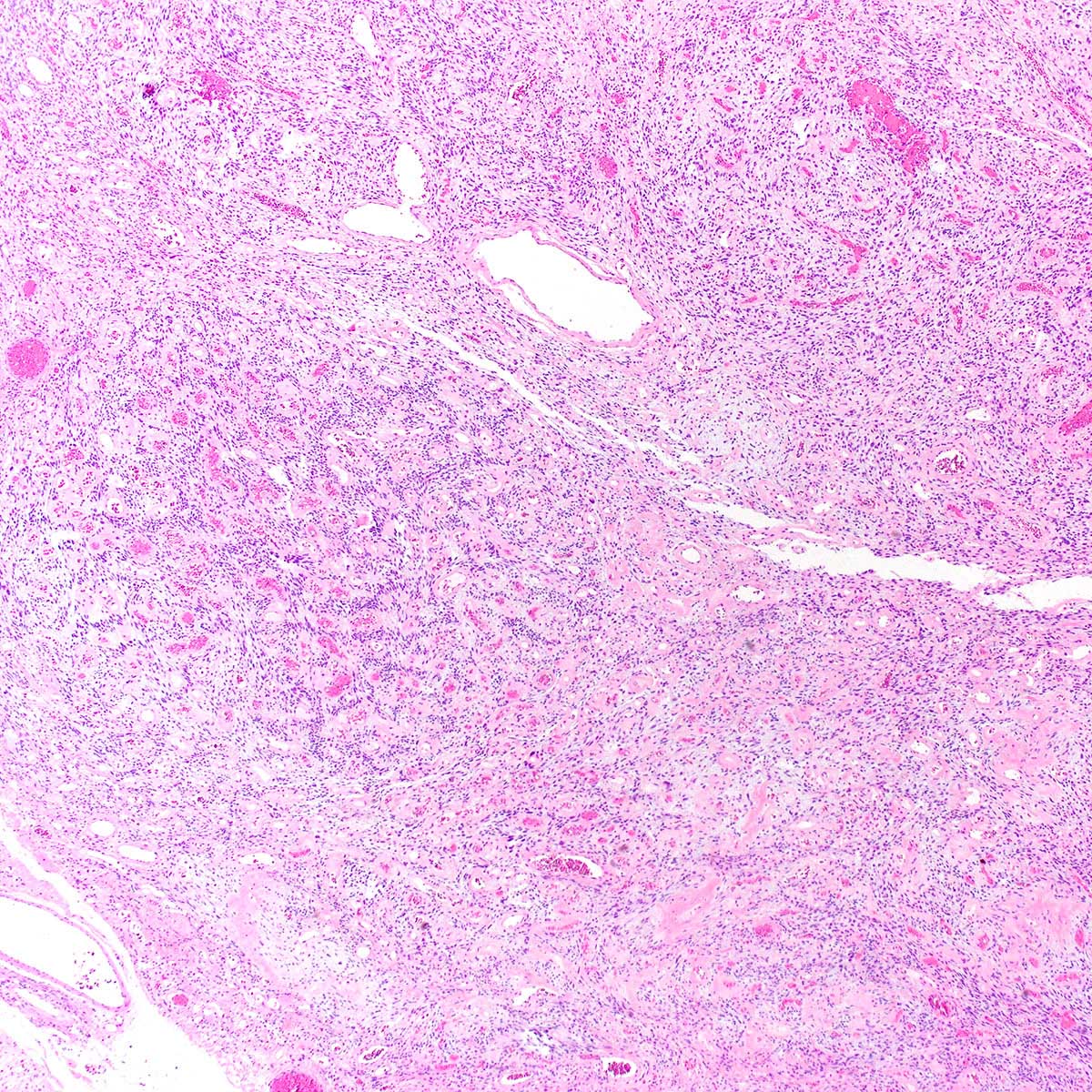
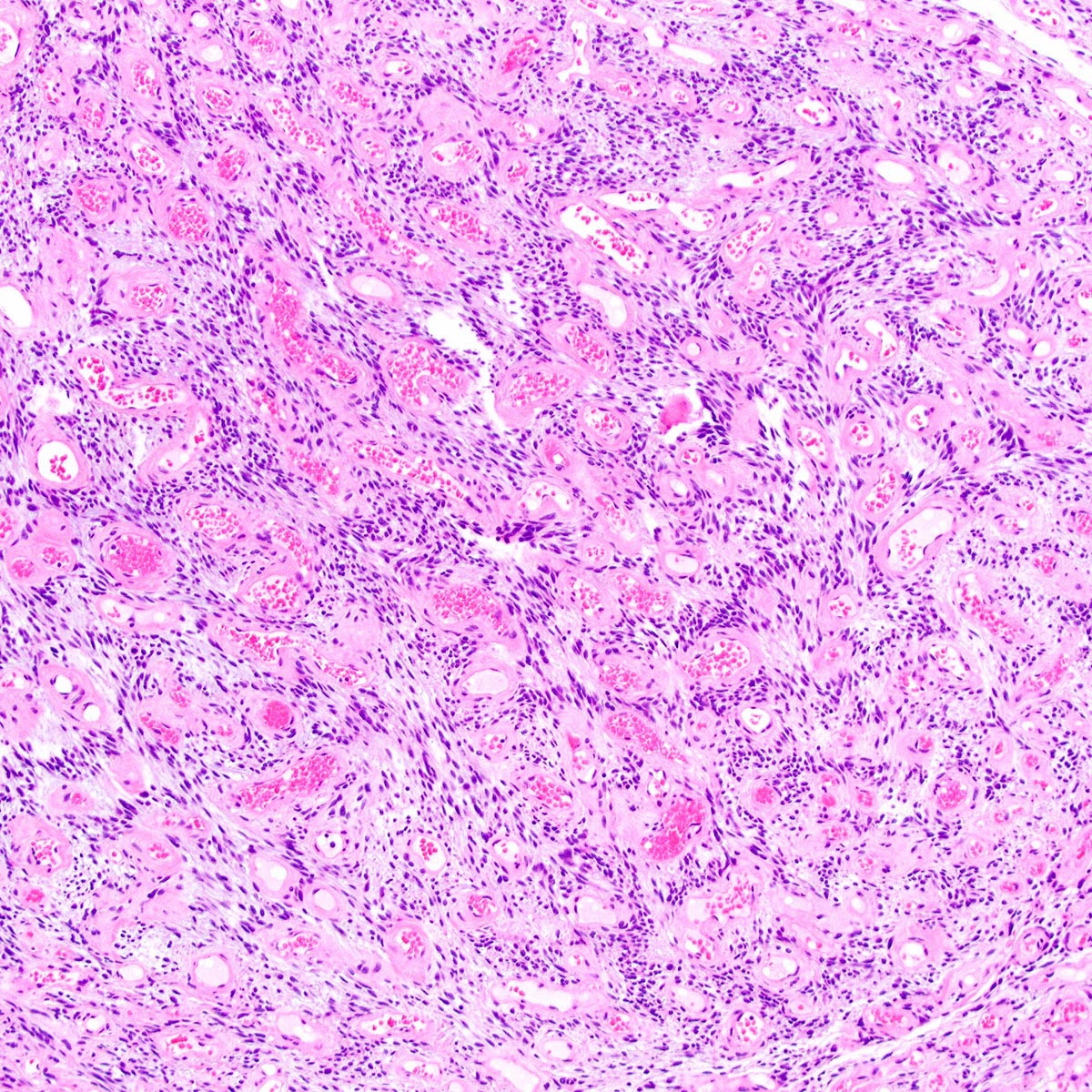
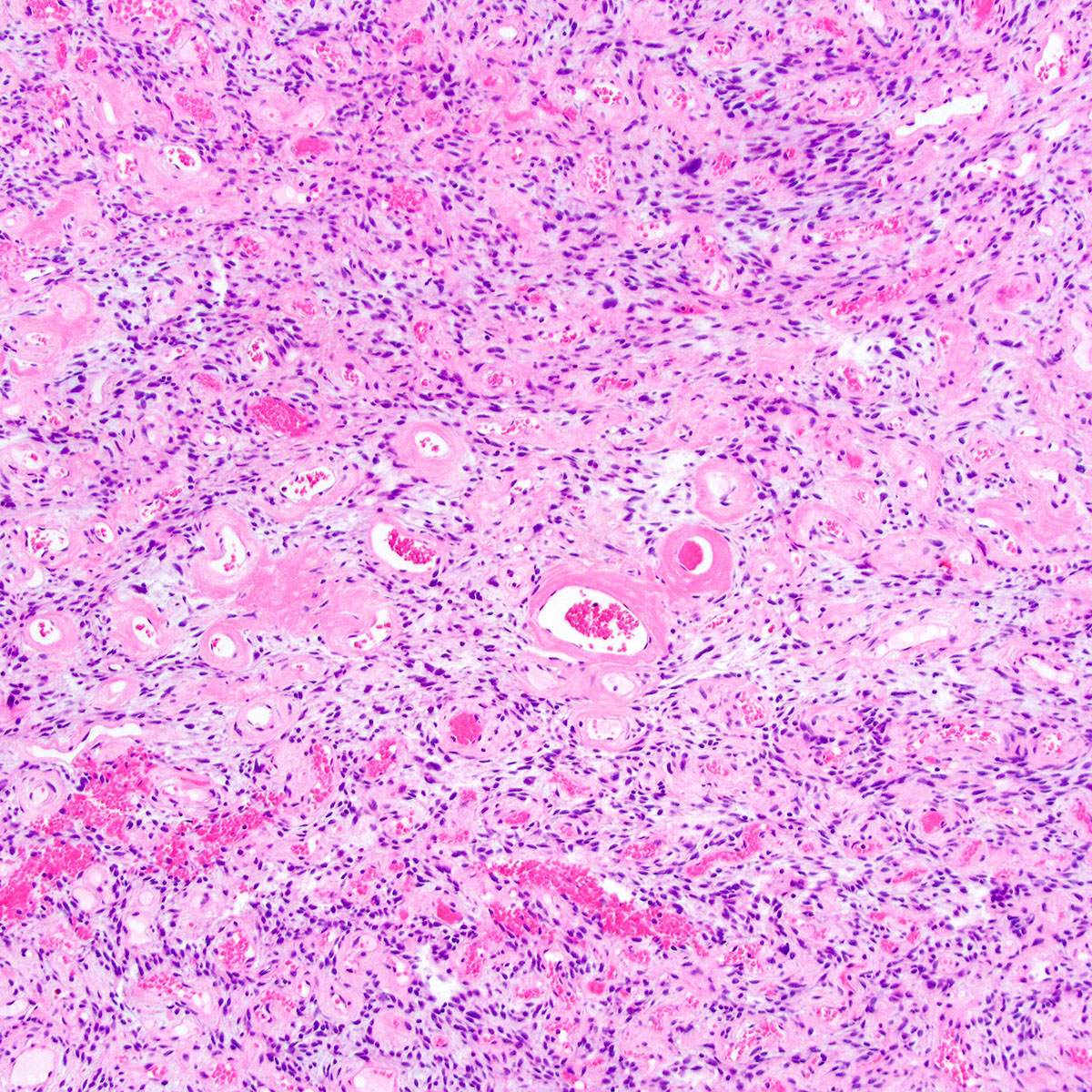
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Predominantly based in subcutis; rarely in dermis (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1426)
- Usually well circumscribed; rare cases infiltrative (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:636, Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1426)
- Fibrous pseudocapsule in a subset (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:636, Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1426)
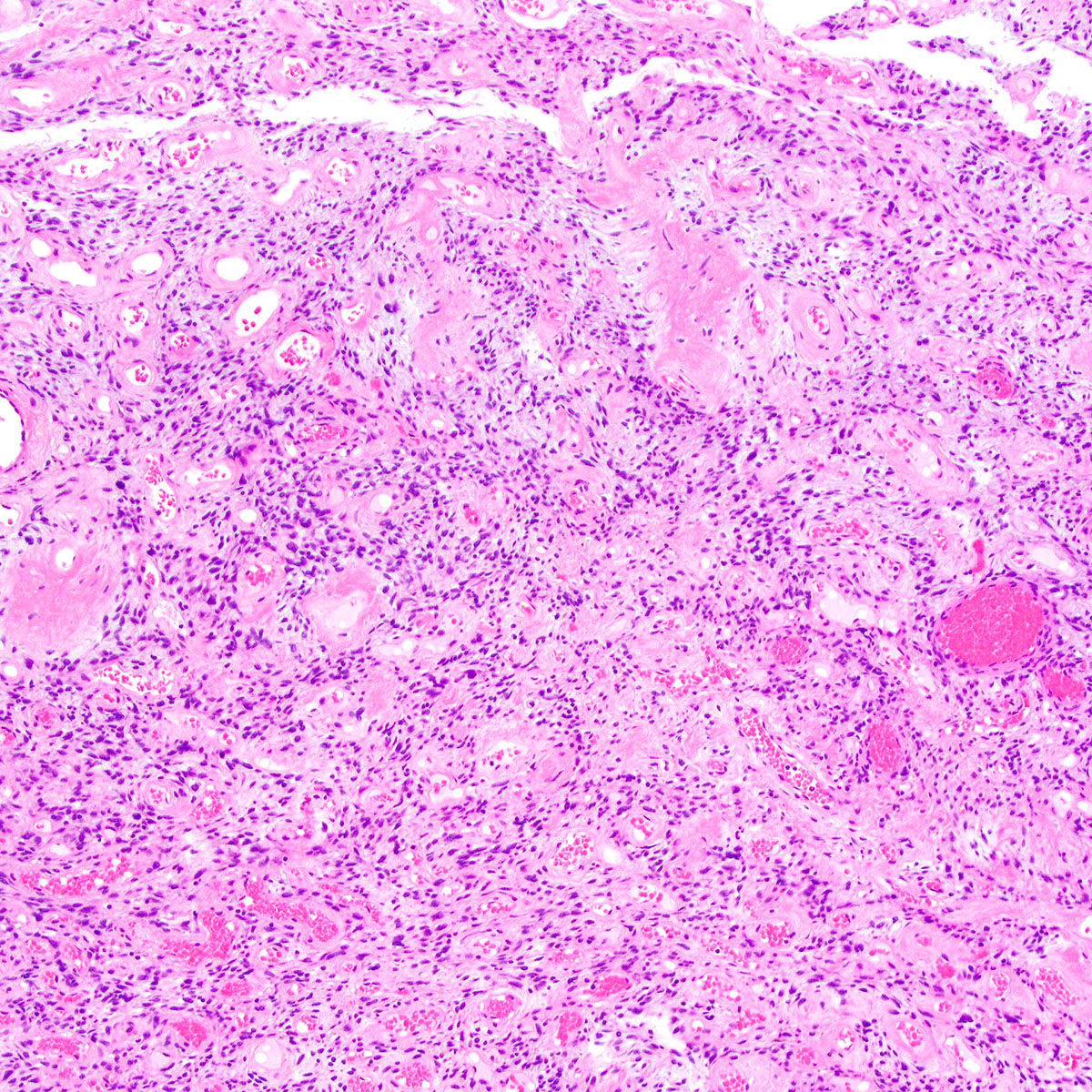
- Tumor cells:
- Small, monotonous spindle cells with bland, ovoid to fusiform nuclei
- Arranged in short intersecting fascicles
- Bland multinucleated cells common (Histopathology 2004;45:360)
- Mitoses typically rare (< 1 per 10 hpf) but occasionally brisk (> 10 per 10 hpf) (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:636, Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1426)
- Rare cases show focal or diffuse atypia or discrete areas of sarcomatous transformation (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:707)
- Sarcomatous transformation may resemble well differentiated liposarcoma, pleomorphic liposarcoma or undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma
- Tumor stroma and vasculature:
- Myxoid, edematous, fibrous or hyalinized stroma (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1426)
- Abundant medium sized, thick walled, hyalinized vessels
- Short wispy collagen bundles
- Minor adipocytic component in ~ 50%; rare cases show prominent adipocytic differentiation (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1426)
- Mast cells may be conspicuous
- Necrosis and hemorrhage absent
Microscopic (histologic) images
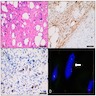
Positive stains
- Vimentin (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:636, Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1426, J Cutan Pathol 2003;30:405, Histopathology 2004;45:360, Mod Pathol 2011;24:82)
- ER (most), PR (most)
- CD34 (~50%)
- Tumors with sarcomatous transformation typically show p16 overexpression and rarely mutant p53 (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:707)
Negative stains
- Rb (i.e., expression lost) (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1119)
- Myogenic markers: SMA (rarely positive), desmin, caldesmon
- EMA (rarely positive)
- S100 (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:636, J Cutan Pathol 2003;30:405, Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1426, Histopathology 2004;45:360)
- Cytokeratin (AE1 / AE3, CAM5.2)
- CD117
- MDM2 and CDK4 in those with sarcomatous transformation (Diagnostics (Basel) 2020;10:35)
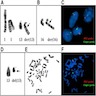
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Monoallelic RB1 / FOXO1 deletion (chr 13q12-22) in all tested cases (Mod Pathol 2011;24:82, Histopathology 2007;51:410, Diagn Pathol 2017;12:17)
- TP53 mutations present in a subset of cases with sarcomatous transformation (Diagnostics (Basel) 2020;10:35)
Sample pathology report
- Vulva, mass, excision:
- Cellular angiofibroma (3.2 cm) (see comment)
- Comment: Margins are negative for tumor.
Differential diagnosis
- Angiomyofibroblastoma:
- Alternating hypo and hypercellular foci
- Spindled to epithelioid to plasmacytoid cells, clustering around vessels
- Vascular hyalinization not prominent
- Spindle cell lipoma:
- Typically affects head and neck region in men
- Thick ropy collagen bands
- Hyalinized vessels not prominent
- Mammary type myofibroblastoma:
- Solitary fibrous tumor:
- Characteristic staghorn / hemangiopericytoma-like vessels
- More marked variation in cellularity
- Thick bands of hyalinized collagen
- STAT6 positive
- Leiomyoma:
- Perineurioma:
- Lacks vascular hyalinization
- EMA positive
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 48 year old woman presented with a painless 3.5 cm vulvar mass, which had been slowly growing for 18 months. She underwent complete local excision of a rubbery, well circumscribed mass. A representative photomicrograph is shown. Which of the following is true about this lesion?
- Complete local excision is considered curative
- Immunohistochemistry for estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor is typically negative
- Nuclear pleomorphism is associated with an increased risk of distant metastasis
- Rb protein is typically overexpressed
- This lesion occurs exclusively in women
Board review style answer #1
A. Complete local excision is considered curative. This is a cellular angiofibroma.
Comment Here
Reference: Cellular angiofibroma
Comment Here
Reference: Cellular angiofibroma
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2