Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Chapel DB, Bennet J. Angiomyofibroblastoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/vulvaangiomyofibroblastoma.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Angiomyofibroblastoma is a benign, site specific, soft tissue tumor of the lower genital tract with alternating hypo and hypercellular zones, bland spindle to epithelioid cells and abundant vessels
Essential features
- Benign lower genital tract tumor, seen predominantly in women
- Alternating hypo and hypercellular zones, comprised of bland plump spindle to epithelioid cells clustered around abundant small, thin walled vessels
- No specific immunophenotypic or molecular features reported
- Local excision curative; recurrences exceptionally rare
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- F > M
- In women, age range 21 - 71 years (median, fifth decade) (Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:373, Mod Pathol 1996;9:284, Hum Pathol 1997;28:1046, Hum Pathol 2014;45:1647)
- May occur in pregnancy (J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2011;37:1162)
- Rare examples in men (Am J Clin Pathol 1997;107:36)
Sites
- Labia majora most common site; rarely involves vagina or perineum (Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:373, Mod Pathol 1996;9:284, Hum Pathol 1997;28:1046, J Clin Pathol 2000;53:803, Hum Pathol 2014;45:1647)
Pathophysiology
- Histogenesis uncertain; may arise from subepithelial stroma or a perivascular stem cell (Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:373, J Clin Pathol 2000;53:803, Hum Pathol 1997;28:1046)
Clinical features
- Painless vulvar mass
- Present for weeks to years before diagnosis (Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:373)
- Rare cases multifocal
- Clinically resembles a Bartholin cyst or lipoma (Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:373, Hum Pathol 2014;45:1647)
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis typically follows complete local excision of a clinically benign appearing mass
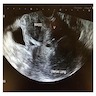
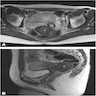
Radiology description
- Ultrasound: well circumscribed mass (Case Rep Obstet Gynecol 2018;2018:8579026, J Med Case Rep 2015;9:248)
- MRI: well circumscribed mass with homogeneous or heterogeneous signal; hypointense on T2 weighted images (Case Rep Obstet Gynecol 2018;2018:8579026, J Med Case Rep 2015;9:248, Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11:5509)
Prognostic factors
- Benign tumor
- Local recurrence exceptionally rare, even with positive margins (Hum Pathol 2014;45:1647, Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:373, Mod Pathol 1996;9:284, Hum Pathol 1997;28:1046)
- Single reported case with frank sarcomatous transformation, which recurred locally (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:1104)
Case reports
- 35 year old woman with a 5 cm vaginal angiomyofibroblastoma (J Med Case Rep 2015;9:248)
- 36 year old woman with a 5 cm prolapsing vaginal angiomyofibroblastoma (Case Rep Obstet Gynecol 2018;2018:8579026)
- 42 year old woman with a 4 cm right labial angiomyofibroblastoma (J Midlife Health 2019;10:105)
- 46 year old woman with a 14 cm pedunculated vulvar angiomyofibroblastoma (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11:5509)
Treatment
- Conservative local excision considered curative (Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:373, Hum Pathol 1997;28:1046)
- Positive margins do not necessitate re-excision
- Sole case with sarcomatous transformation managed with radical vulvectomy and adjuvant radiation (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:1104)
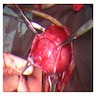
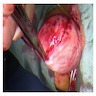
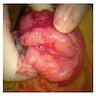
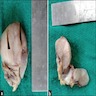
Gross description
- Size range: 0.5 - 12 cm (average ~ 3 - 5 cm) (Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:373, Mod Pathol 1996;9:284, Pathol Int 1995;45:487, Hum Pathol 1997;28:1046)
- Well circumscribed, nodular
- Cut surface homogeneous, white-tan; no necrosis or hemorrhage (Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:373, Hum Pathol 2014;45:1647)
- Sole case with sarcomatous transformation was large (13 cm) with gross hemorrhage and necrosis (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:1104)
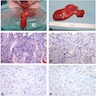
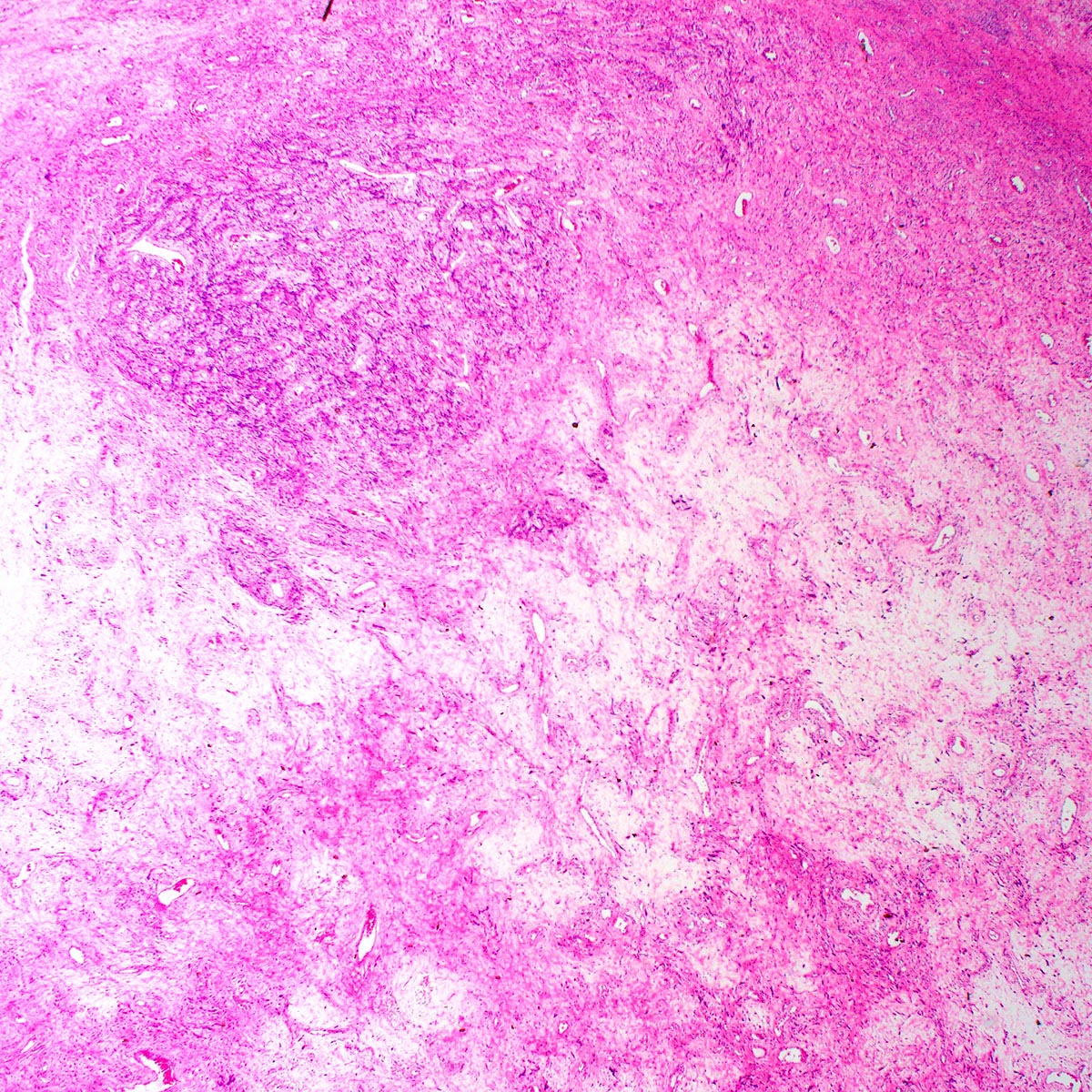
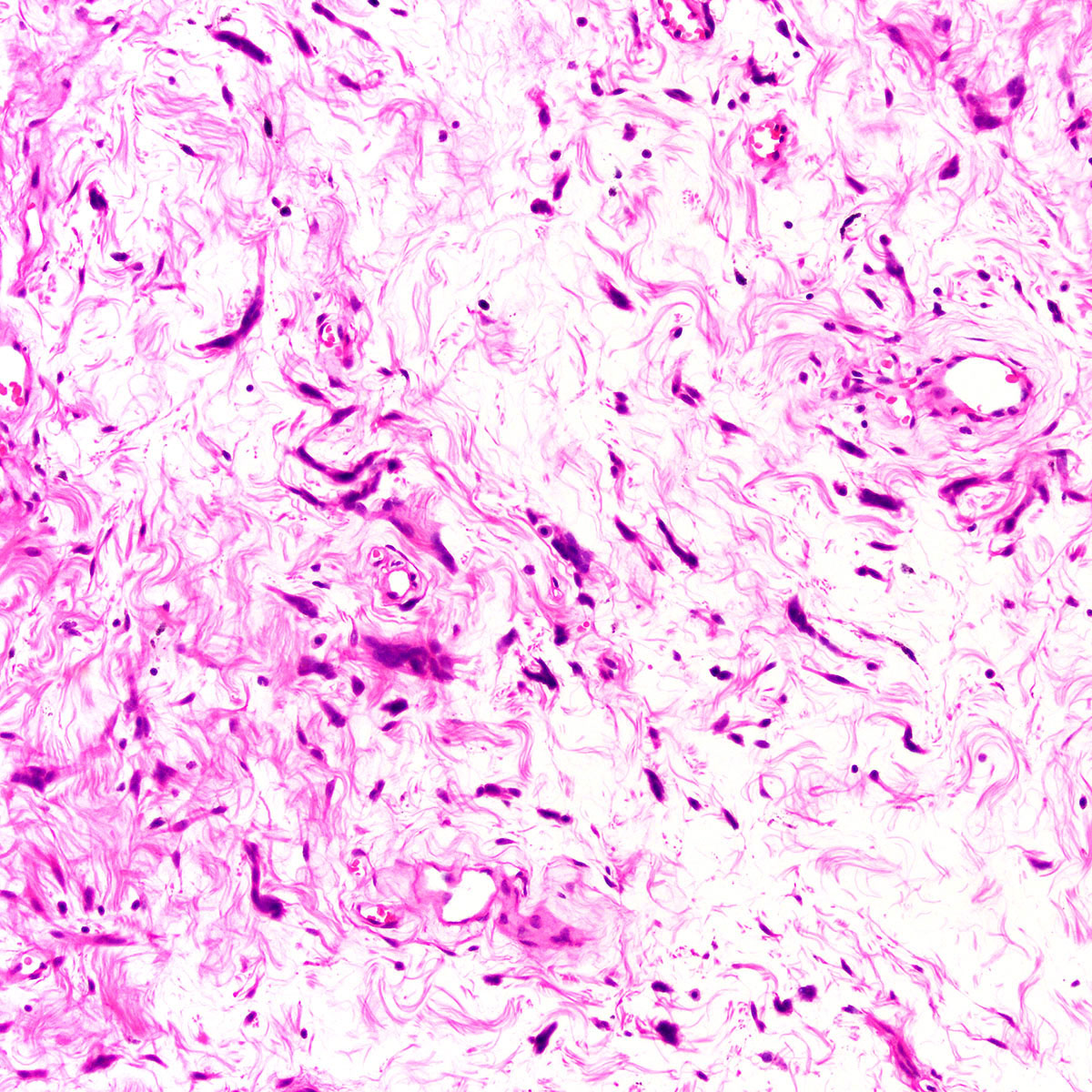
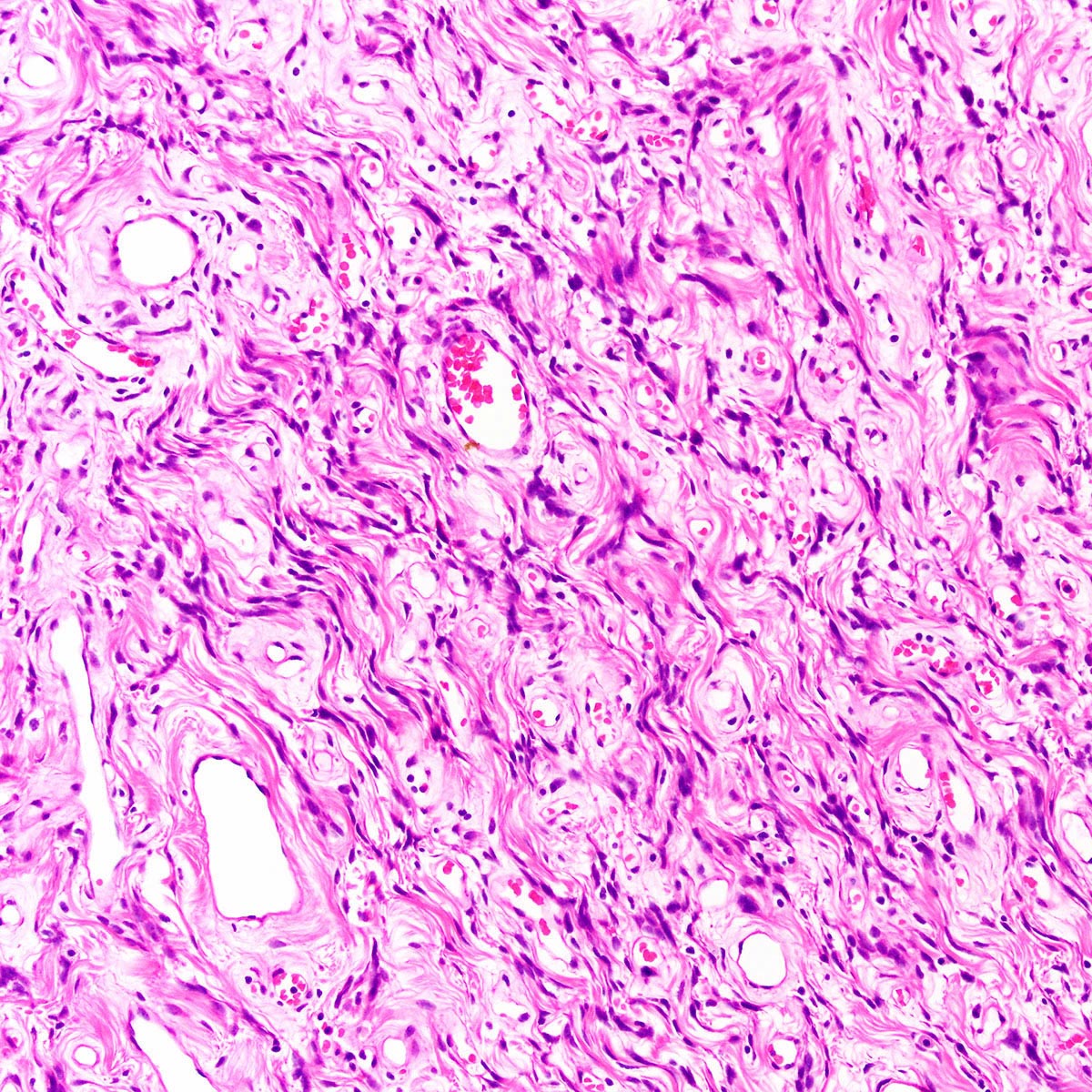
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Well circumscribed, noninfiltrative
- Fibrous pseudocapsule in a subset (Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:373)
- Characteristic alternating hypo and hypercellular zones (Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:373)
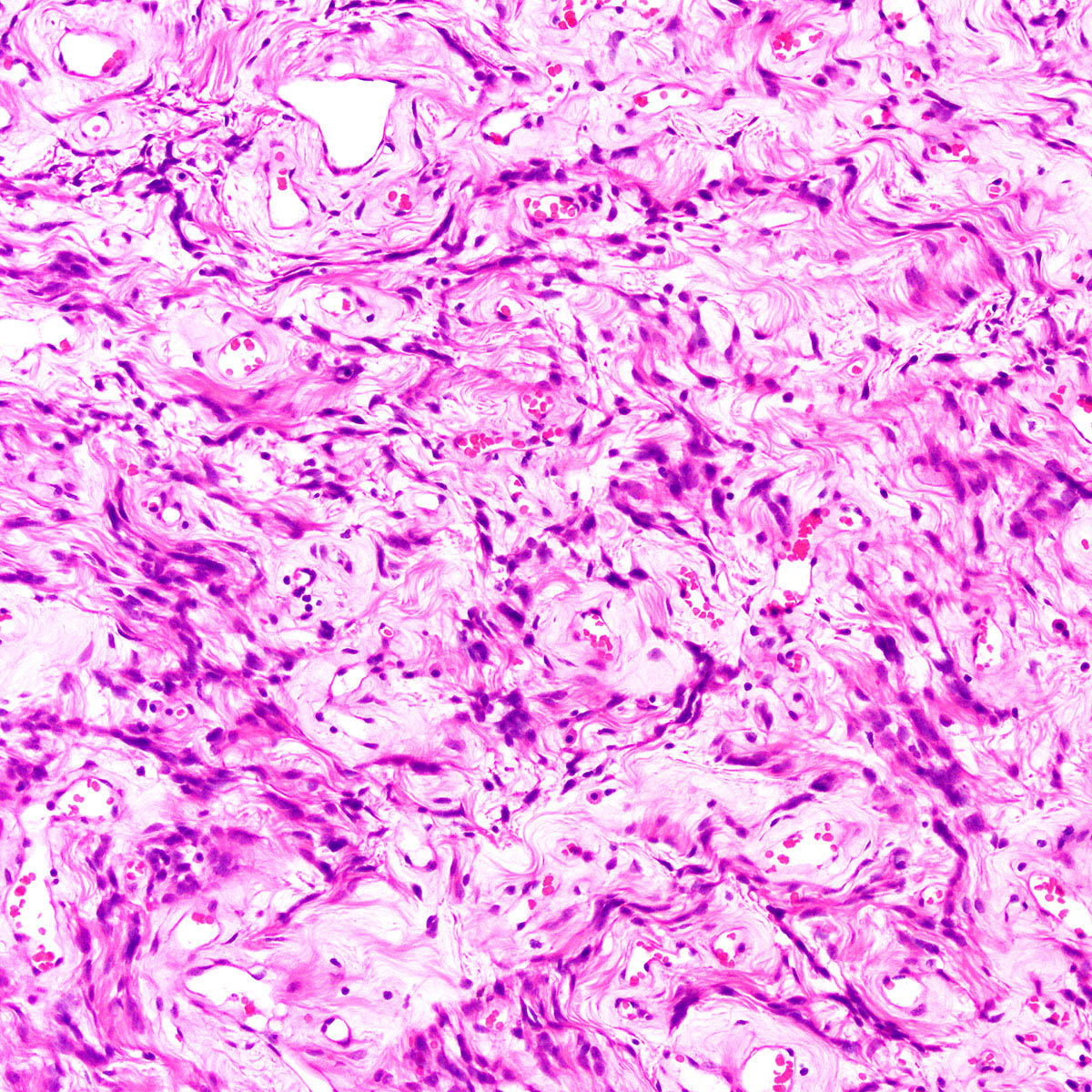
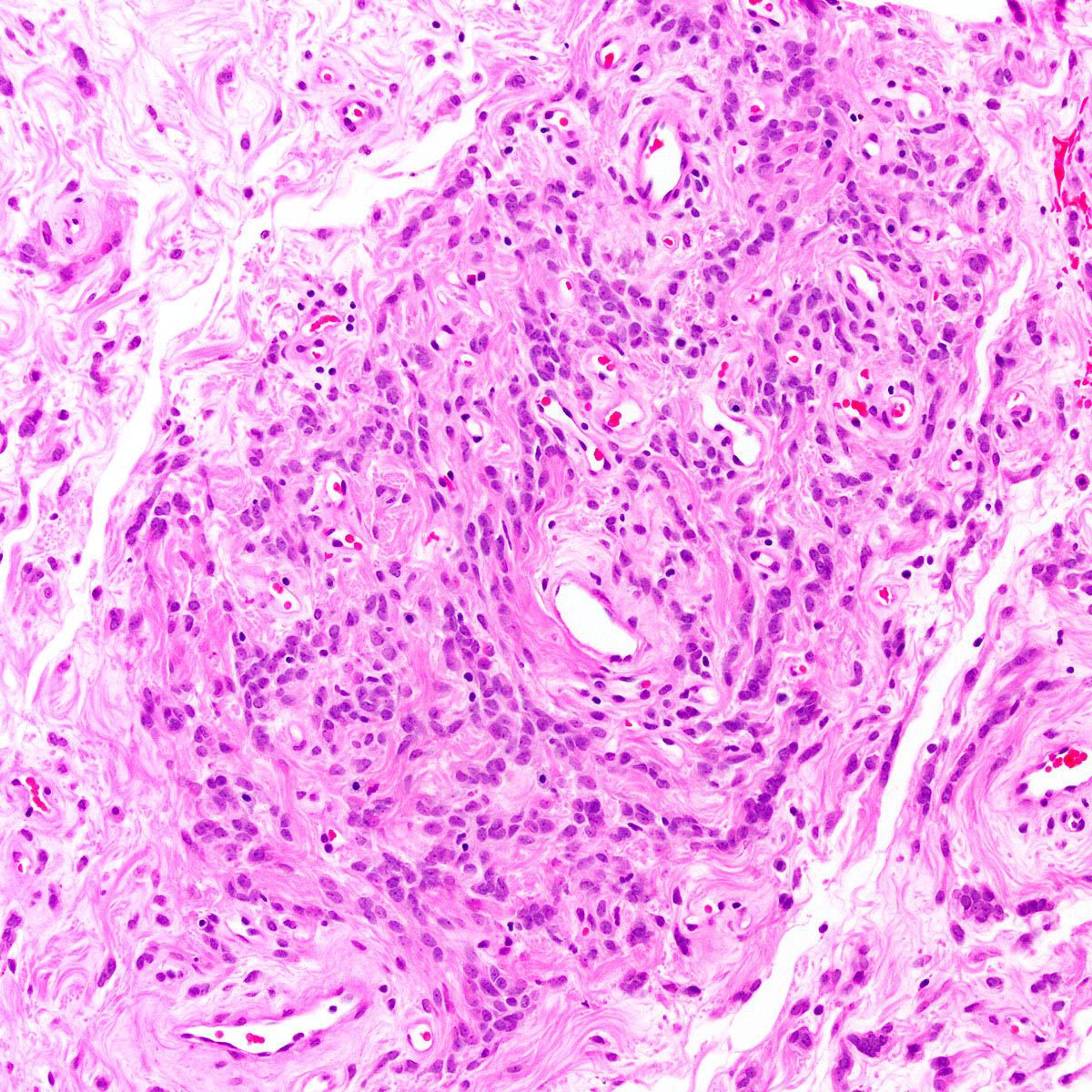
- Tumor cells:
- Spindle to epithelioid to plasmacytoid myofibroblastic cells
- Typically bland chromatin and inconspicuous nucleoli; scattered mildly atypical cells in a minority (Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:373)
- Bland multinucleated cells common (Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:373)
- Mitoses rare or absent; no atypical mitoses
- Tumor stroma and vasculature:
- Lacks prominent stromal mucin
- Hypocellular foci show edematous stroma with scattered fine to thick bands of stromal collagen
- In hypocellular foci, tumor cells appear randomly distributed
- In hypercellular foci, tumor cells congregate around small, irregularly distributed, thin walled vessels
- Occasional larger vessels interspersed
- Mast cells typically conspicuous
- Adipocytic differentiation in ~ 25 - 50% (Mod Pathol 1996;9:284, Hum Pathol 1997;28:1046)
- Rare cases with predominant adipocytic differentiation = lipomatous variant of angiomyofibroblastoma (Hum Pathol 1997;28:1046, Hum Pathol 2014;45:1647, Int J Gynecol Pathol 2015;34:204)
- Rare tumors show mixed features of angiomyofibroblastoma and aggressive angiomyxoma; should be managed like aggressive angiomyxoma (Histopathology 1997;30:3)
- Sole case with sarcomatous transformation showed hypercellular foci with cytologic atypia, increased mitoses and lymphovascular invasion (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:1104)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
Negative stains
- SMA (rarely not negative)
- Muscle specific actin (rarely not negative)
- CD34 (rarely not negative) (Mod Pathol 1996;9:284, Hum Pathol 1997;28:1046, Hum Pathol 2014;45:1647)
- S100 (Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:373, Mod Pathol 1996;9:284, Pathol Int 1995;45:487, Hum Pathol 2014;45:1647)
- Cytokeratin (AE1 / AE3)
- EMA
- Factor XIIIa
- HMB45
- p63
Electron microscopy description
- Features consistent with myofibroblastic differentiation (Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:373)
- Stromal cells surrounded by incomplete basal lamina
- Well developed, rough endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus
- Abundant intermediate filaments and pinocytotic vessels
- Nucleus with delicate heterochromatin
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- No specific or recurrent molecular alterations reported
- No deletion of RB1 / FOXO1 (chr 13q14) (Hum Pathol 2014;45:1647)
- No HMGA2 rearrangement (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2007;46:981)
Sample pathology report
- Vulva, mass, local excision:
- Angiomyofibroblastoma (3.5 cm) (see comment)
- Comment: Margins are negative.
Differential diagnosis
- Aggressive angiomyxoma:
- Typically large (most > 10 cm)
- Infiltrative
- More uniformly hypocellular
- No perivascular congregation of cells
- Tumor cells more uniformly spindled (versus epithelioid)
- Perivascular myoid bundles characteristic
- Red blood cell extravasation common
- HMGA2 positive
- FISH shows HMGA2 rearrangement in a subset (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2007;46:981)
- Leiomyoma:
- Solitary fibrous tumor:
- Superficial angiomyxoma:
- More uniformly hypocellular
- No perivascular congregation of cells
- Prominent stromal mucin, often with acellular mucin clefts / pools
- Stromal neutrophils conspicuous
Additional references
Board review style question #1
On a routine exam, a 46 year old woman was found to have a 3 cm, painless mass on her labia majora. Her gynecologist suspected a Bartholin cyst and performed a conservative local excision. A representative photomicrograph from the lesion is shown. The lesion was grossly and microscopically well circumscribed but the surgical margin was focally positive. By immunohistochemistry, the tumor cells were positive for desmin, ER and PR. Which of the following statements about this lesion is true?
- Approximately 10% experience distant metastasis
- Conservative local excision is considered curative
- HMGA2 IHC is positive in ~ 90%
- If surgical margins are positive, local recurrence risk exceeds 50%
- Stromal neutrophils are found in virtually all such lesions
Board review style answer #1
B. Conservative local excision is considered curative. This is an angiomyofibroblastoma
Comment Here
Reference: Angiomyofibroblastoma
Comment Here
Reference: Angiomyofibroblastoma
Board review style question #2
Which of the following statements about angiomyofibroblastoma is true?
- Abundant, thick walled hyalinized vessels are characteristic
- At low magnification, alternating hypo and hypercellular zones are characteristic
- Men and women are affected in approximately equal numbers
- Rb IHC is negative, reflecting underlying RB1 / FOXO1 (chr 13q14) deletion
- The vagina is affected approximately 3 times as often as the vulva
Board review style answer #2
B. At low magnification, alternating hypo and hypercellular zones are characteristic
Comment Here
Reference: Angiomyofibroblastoma
Comment Here
Reference: Angiomyofibroblastoma