Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Chang R, Chen H. Disordered proliferative. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/uterusdisorderedproliferative.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Abnormal proliferative endometrium with architectural changes due to persistent unopposed estrogen stimulation
- Generally taken as benign, not precancerous (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2008;27:318, Int J Gynecol Pathol 2007;26:103)
Essential features
- Continuum of the spectrum of changes seen with persistent, unopposed estrogen stimulation, which can lead to hyperplasia without atypia
- Presence of irregularly shaped or cystic dilated glands with relatively normal gland to stroma ratio
Epidemiology
- Common in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), obesity and perimenopausal women
- Associated with anovulation (J Clin Pathol 2006;59:801)
Sites
- Endometrium
Pathophysiology
- Unopposed estrogen → disordered proliferative endometrium (early phase) → hyperplasia without atypia (later phase) (Mod Pathol 2000;13:309)
Etiology
- Unopposed estrogen stimulation (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2007;26:103)
Clinical features
- Asymptomatic or abnormal uterine bleeding
Diagnosis
- Endometrial biopsy or curettage
Radiology description
- Ultrasound may show irregularly thickened endometrium
Treatment
- Observation
- Progesterone, if symptomatic (abnormal uterine bleeding) (J Clin Pathol 2006;59:801, J Am Board Fam Med 2006;19:590)
- Elimination of the cause of estrogen excess (e.g. weight loss in obesity)
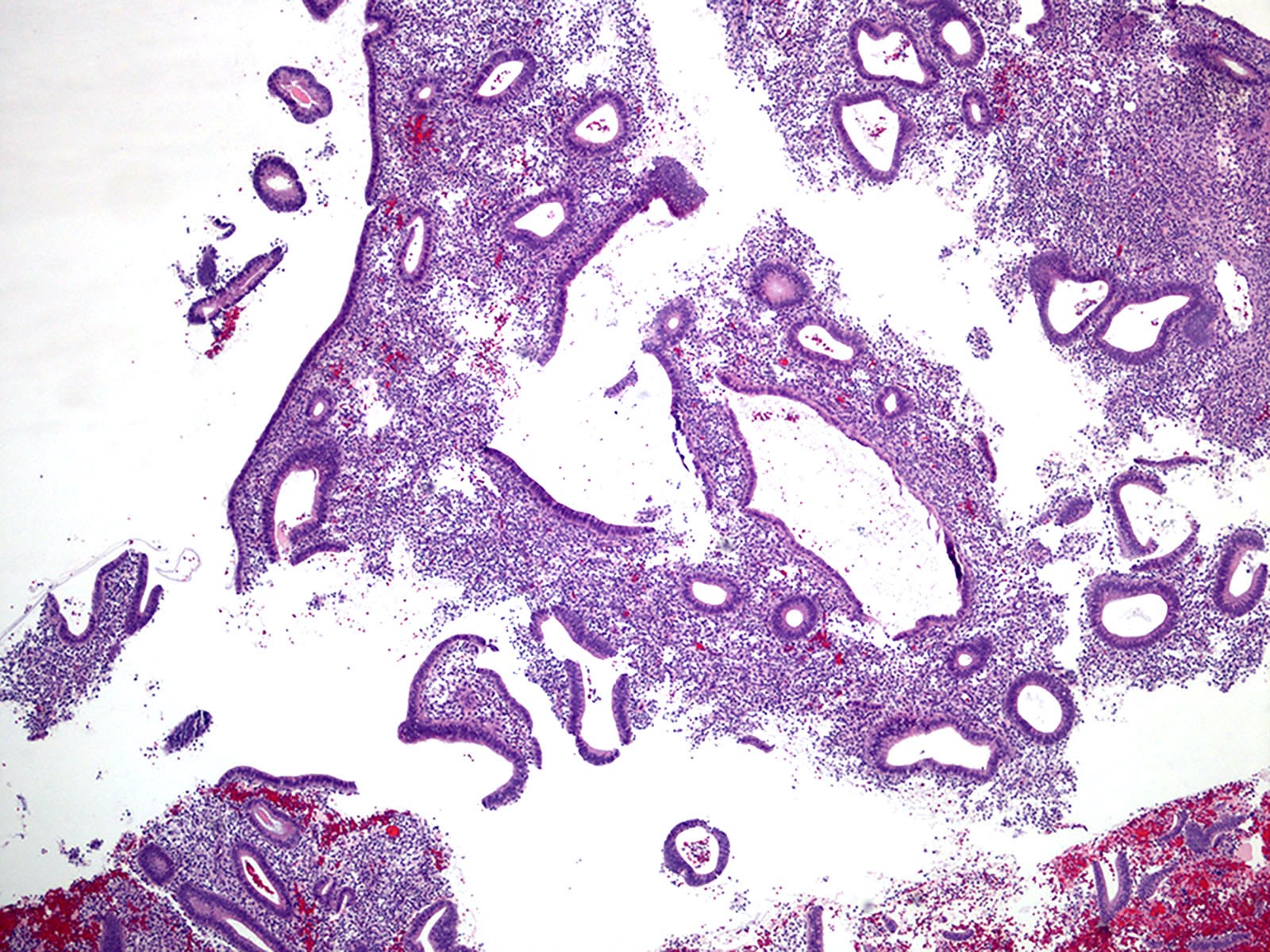
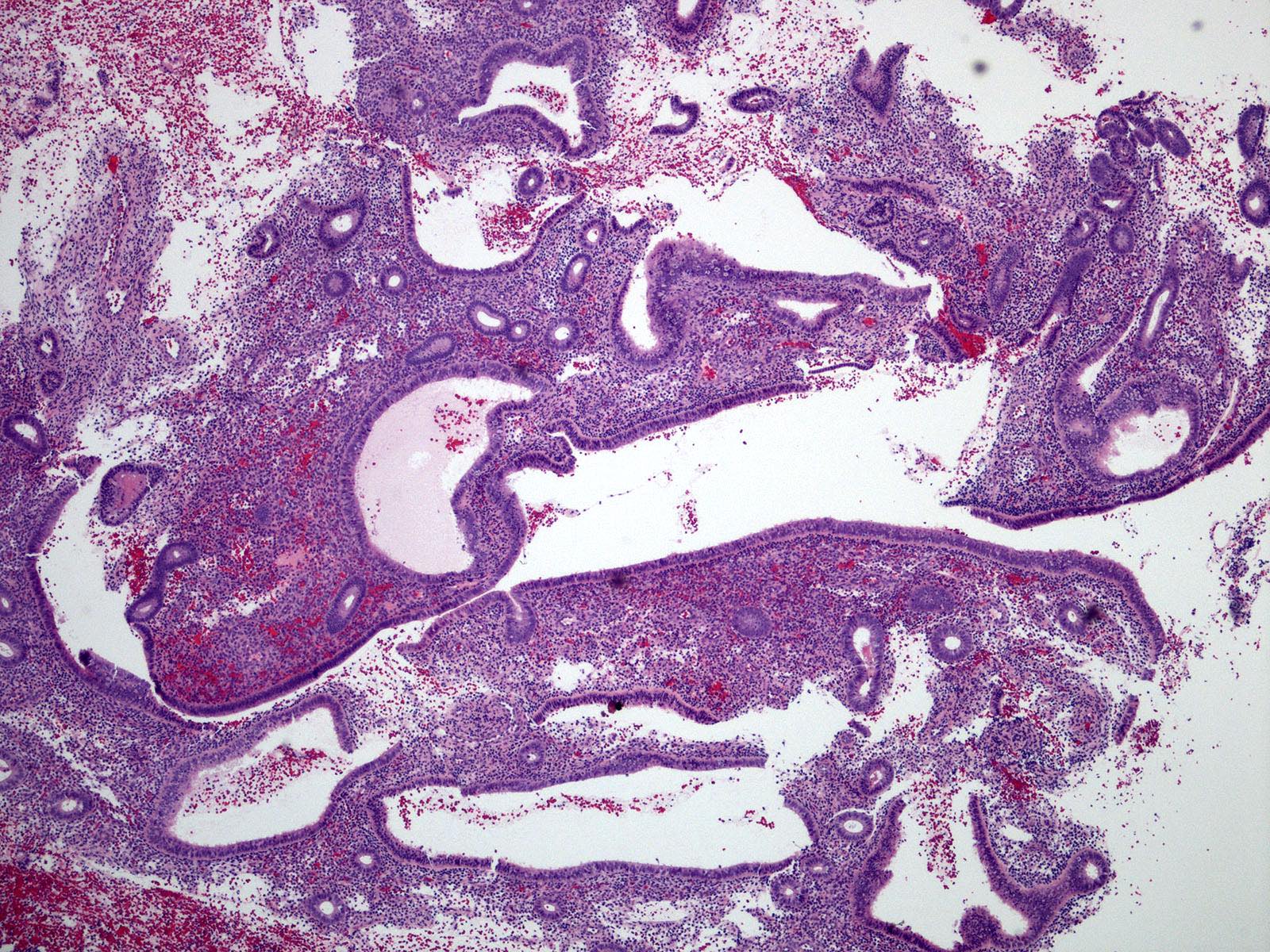
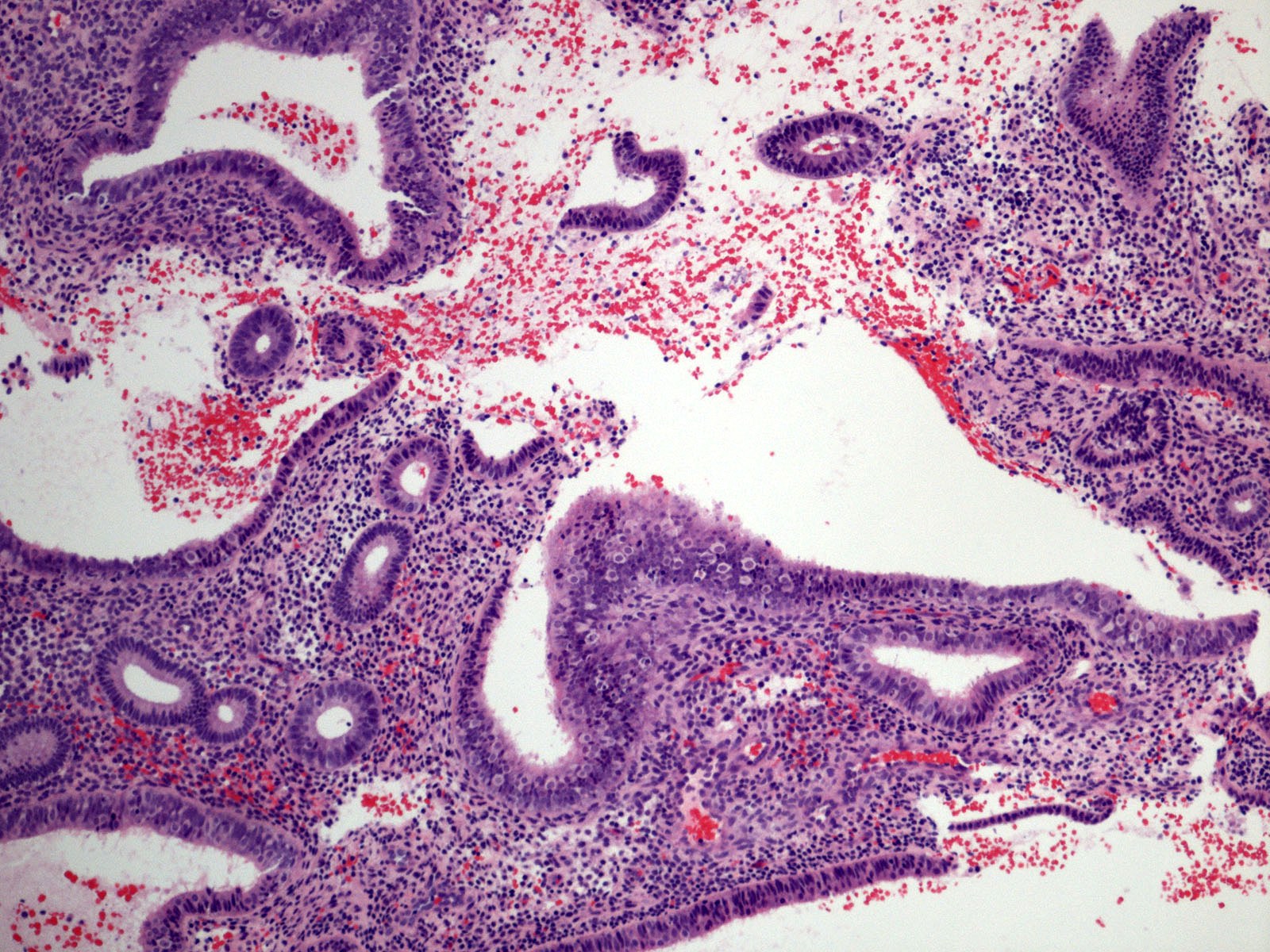
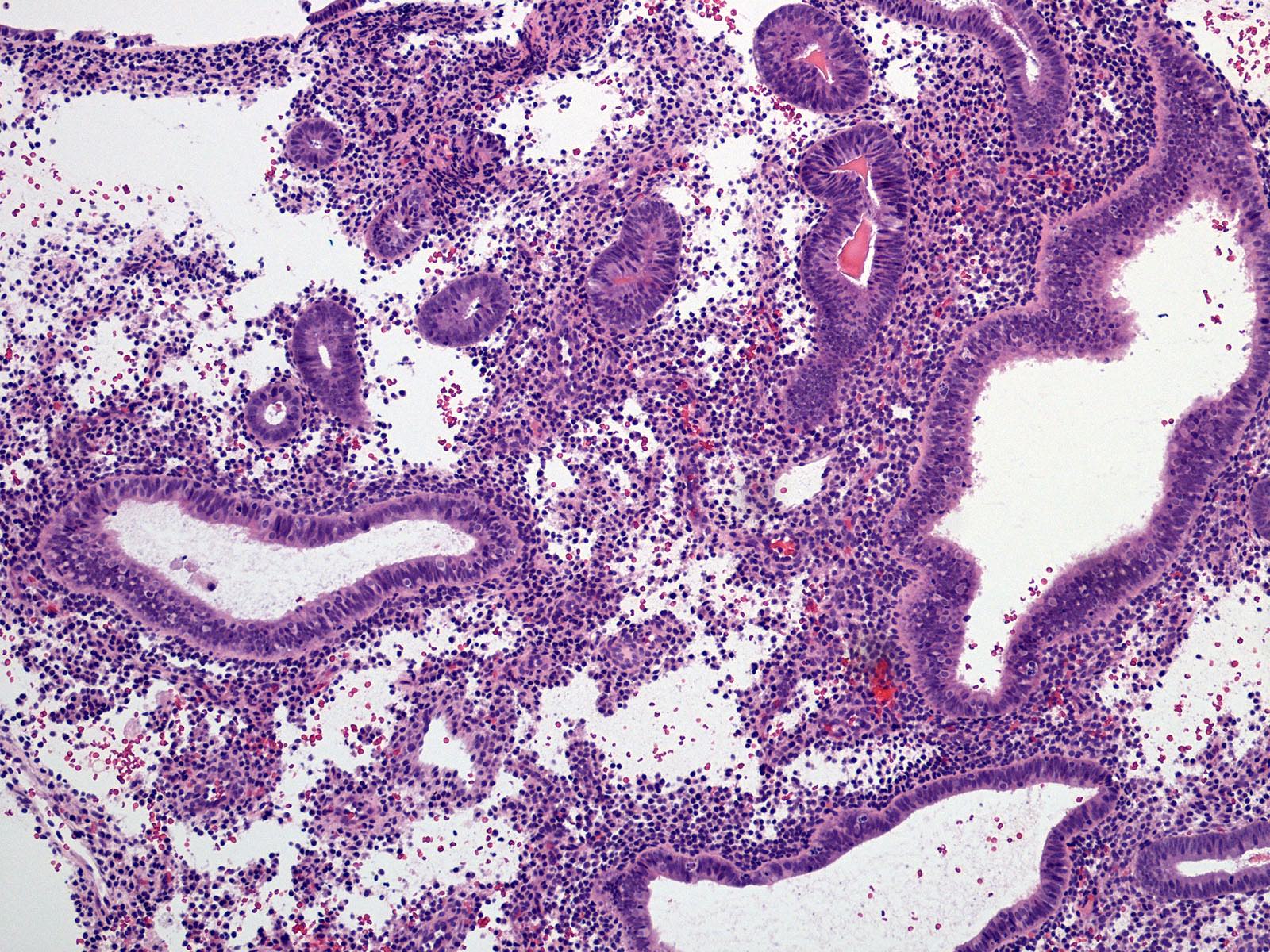
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Cystically dilated glands (> 2x normal size) randomly interspersed among proliferative endometrial glands
- Dilated glands usually with irregular shape (branched, convoluted, scalloped outer contours)
- > 10% of overall glands
- Relatively normal gland to stroma ratio (glands occupy < 50% of the surface area)
- Metaplastic changes common, including tubal metaplasia, eosinophilic syncytial metaplasia, etc.
- Stromal hemorrhage and breakdown common
- Lack of cytologic atypia
Microscopic (histologic) images
Sample pathology report
- Endometrium, biopsy:
- Disordered proliferative endometrium
- Anovulatory type endometrium
Differential diagnosis
- Proliferative endometrium:
- Irregular glands may be present but only focal (< 10%) and small and only mildly dilated
- Vast majority of glands: round donut or straight tubular shape, lined with tall pseudostratified columnar epithelium; mitotic figures commonly seen
- Endometrial hyperplasia without atypia:
- Continuum with disordered proliferative endometrium
- Irregular dilated glands, more diffusely distributed
- Gland to stroma ratio > 1 (glands occupy ≥ 50% of the surface area)
- Endometrial polyp:
- Often with dilated glands and metaplasia
- Polypoid
- Dense fibrotic stroma
- Thick walled vessels
- Endometrioid intraepithelial neoplasm (EIN) / atypical hyperplasia (AH):
- Chronic endometritis:
- Can result in glandular crowding, abnormal gland shapes and variable degrees of cytologic atypia
- Presence of stromal plasma cells
- Presence of stromal spindling and edema
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is true about disordered proliferative endometrium?
- Associated with a significantly elevated risk of malignancy
- May contain foci of atypia
- Most common with women in their 20s
- Treatment is with exogenous estrogens
- Typically seen in patients with factors leading to unopposed estrogen stimulation (obesity, anovulation)
Board review style answer #1
E. Typically seen in patients with factors leading to unopposed estrogen stimulation (obesity, anovulation)
Comment Here
Reference: Disordered proliferative
Comment Here
Reference: Disordered proliferative