Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Transmission | Laboratory | Case reports | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Adkins BD, Booth GS. P1PK GLOB system. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/transfusionmedicineP1PKGLOB.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Antibodies to P and PP1Pk are clinically significant
- Typically, cold reacting antibodies
Essential features
- Antibodies to P and PP1Pk are clinically significant
- Autoanti-P antibodies seen in paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria and are associated with infection
- P acts as a receptor for parvovirus B19
Terminology
- P, GLOB (globoside) system antigen
- P1, first P1PK antigen described
- Pk, high prevalence P1PK antigen
- Anti-PP1Pk (arachaic Tja), antibody formed by p individuals
- Reference: Fung: Technical Manual, 19th Edition, 2017
Pathophysiology
- P1, Pk and NOR are synthesized by enzymatic modification of glycolipids
- P is derived from enzymatic modification of Pk by β1,3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase
- Individuals lacking these antigens due to recessive phenotypes can produce naturally occurring P1PK and GLOB system antibodies such as anti-PP1Pk in p (null) phenotype individuals
- Reference: Fung: Technical Manual, 19th Edition, 2017
Clinical features
- P acts as a receptor for parvovirus B19
- Individuals can develop autoanti-P with syphilis or upper respiratory infection
- Antibodies are IgG, bind at cold temperatures and cause complement mediated hemolysis upon warming
- Anti-PP1Pk is occasionally associated with hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn but can lead to early abortion as P1PK and GLOB system antigens are expressed at high levels on placental surfaces
- Antigens (type: carbohydrate) (Fung: Technical Manual, 19th Edition, 2017)
- Most high prevalence with expression on several tissue types
- P1 predominately expressed on red cells
Incidence among Caucasians
Adapted from Reid: The Blood Group Antigen FactsBook, 3rd Edition, 2012Antigen Incidence (%) P 99.9 P1 79 Pk High prevalence
- Antibodies:
- Antibodies to P and PP1Pk are clinically significant
- Anti-P autoantibodies associated with paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria
- Disease associations (Immunohematology 2020;36:99):
- P1PK antigens may be bound by Shiga toxins
- Some cancers such as breast and ovarian may express P1PK and GLOB system antigens
- P acts as a receptor for parvovirus B19
- Pk may bind HIV enabling entry
- P1 motif antigens are produced in hydatid (echinococcal) cyst fluid leading to antibodies, likewise, hydatid cyst fluid can be used as a neutralizing substance for anti-P1
Transmission
- Antibodies are generally naturally forming in null individuals but sensitization can occur due to pregnancy or transfusion
- P1 antibodies can occur in pigeon fanciers
- Reference: Clin Allergy 1980;10:643
Laboratory
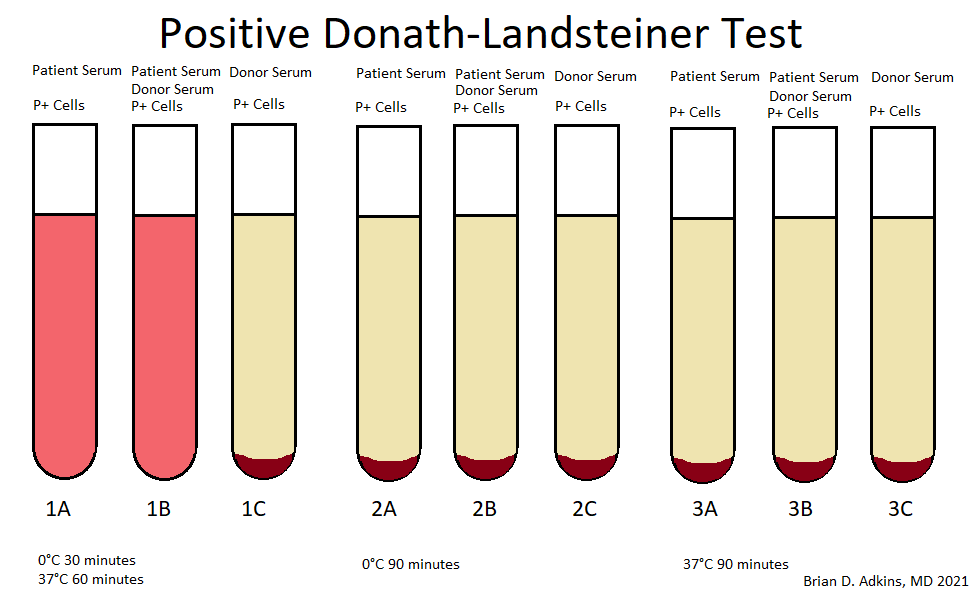
- Autoanti-P antibodies are characterized with the Donath Landsteiner test (Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed 2021 Aug 25 [Epub ahead of print])
- Hemolysis with incubation at 0 °C followed by incubation at 37 °C in tubes with patient serum and patient serum / donor serum and P+ cells (see below)
Contributed by Brian D. Adkins, M.D.
- Anti-P1 antibodies can be neutralized with pigeon egg whites or echinococcal cyst fluid
- The P1 phenotype is the most common phenotype (~80% of white individuals), with P2 representing the second most common phenotype (~20% of white individuals); variable phenotypes are seen amongst differing races and serum reactivity is reviewed below:
Reactivity with reagent anti-sera
| Reactions with reagent serum | |||||
| Anti-P1 | | Anti-Pk | Anti-PP1Pk (Tja) | Antibodies in patient serum | Patient RBC phenotype |
| + | + | 0 / + | + | None | P1 |
| 0 | + | 0 / + | + | Anti-P1 (occasionally) | P2 |
| 0 | 0 (occasional weak positivity due to crossreactivity) | 0 | 0 | Anti-PP1Pk (Tja) | p (rare) |
| + | 0 | + | + | Anti-P,-PX2 | P1k (rare) |
| 0 | 0 | + | + | Anti-P,-P1, -PX2 | P2k (rare) |
Case reports
- 4 year old girl with hemolytic transfusion reaction with anti-PP1Pk (Transfus Med Hemother 2021;48:240)
- 5 year old boy with recurrent paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (Transfusion 2017;57:1401)
- Case series of anti-PP1Pk in pregnant patients (Vox Sang 2021;116:591)
- 2 sisters with Pk phenotype presenting with recurrent miscarriage (Transfus Med 2019;29:202)
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A patient is found to have a P1 antibody. He works as a pigeon fancier and is preparing for an outpatient arthroscopic surgery. What substance may be used to neutralize and confirm this antibody?
- Breast milk
- Echinococcal cyst fluid
- Guinea pig urine
- Saliva
Board review style answer #1
B. Echinococcal cyst fluid and pigeon egg white can be used to neutralize P1 antibodies, which commonly occur in individuals caring for pigeons.
Comment Here
Reference: P1PK GLOB
Comment Here
Reference: P1PK GLOB
Board review style question #2
P red cell antigen of the GLOB system acts as a receptor for which microorganism?
- Babesia microti
- Francisella tularensis
- Parvovirus B19
- Plasmodium vivax
Board review style answer #2