Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Agarwal S. Warthin-like. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/thyroidwarthin.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare histological variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC), having favorable prognosis
- Characterized by papillae lined by large oncocytic cells with nuclear features of PTC and prominent lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate within the papillary cores
- Proposed by Apel et al. in 1995 (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:810)
Essential features
- Histopathologically mimics Warthin tumor of salivary glands, i.e. the lining oncocytic epithelial cells and the abundant lymphoid stroma
- Commonly associated with lymphocytic / Hashimoto thyroiditis
Terminology
- Papillary carcinoma, Warthin-like variant
- Microscopically resembles Warthin tumor of salivary glands, hence the name
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Rare, 0.06 - 1.9% of all PTC (Med Ultrason 2019;21:152, Endocr J 2016;63:329)
- Age: 18 - 77 years (Int J Endocrinol 2015;2015:456027)
- Female preponderance, similar to other PTC (Int J Endocrinol 2015;2015:456027, ANZ J Surg 2016;86:492)
Sites
- Either lobe or isthmus of thyroid gland
Clinical features
- Usually asymptomatic / palpable neck mass (Med Ultrason 2019;21:152)
- May also manifest with cervical nodal metastasis
Diagnosis
- Diagnostic workup is similar to any thyroid mass / nodule
- Ultrasound with fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC)
- CT scan may be useful to evaluate extrathyroidal extension and lymph node metastases
- Final diagnosis is rendered on histopathological examination of resected tumor
- Accurate diagnosis of Warthin-like variant may not be possible on FNAC; however, preoperative recognition of Warthin-like PTC does not influence treatment decisions
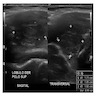
Radiology description
- Sonography:
- Solid, wider than tall and hypoechoic nodules (Med Ultrason 2019;21:152, Endocr J 2016;63:329)
- Margins: smooth / irregular / microlobulated
- Less commonly, punctate echogenic foci; taller than wide shape; cystic component
- American College of Radiology (ACR) Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TI-RADS) category 4 or 5 (Med Ultrason 2019;21:152)
- Occasionally misdiagnosed as benign (Endocr J 2016;63:329)
- Color Doppler ultrasound: little or no internal vascularity
- Thyroid parenchyma: heterogeneous echogenicity, indicative of diffuse thyroiditis
Prognostic factors
- Prognosis similar to classic PTC of similar size and stage or a more favorable prognosis (ANZ J Surg 2016;86:492, Int J Endocrinol 2015;2015:456027, Endocr J 2016;63:329, Med Ultrason 2019;21:152)
- Rare reports of aggressive behavior in case of dedifferentiation (Case Rep Med 2010;2010:495281, Endocr Pathol 2005;16:83)
- Risk stratification as per American Thyroid Association 2015 (Thyroid 2016;26:1)
Case reports
- 21 year old woman with Graves disease and a solitary thyroid nodule (J Cancer Res Ther 2015;11:652)
- 22 year old woman with a hypoechoic thyroid nodule (Case Rep Oncol Med 2012;2012:689291)
- 30 year old woman (Diagn Cytopathol 2017;45:837)
- 31 year old woman with a hypoechoic solid nodule (Korean J Pathol 2014;48:170)
- 36 year old woman with right neck tumor (Case Rep Endocrinol 2015;2015:251898)
- 47 year old woman with neck swelling (Cytopathology 2012;23:408)
- 50 year old woman with left lobe thyroid mass (Acta Cytol 1998;42:1437)
- 51 year old woman with simultaneous MALT lymphoma in a background of Hashimoto thyroiditis (J Clin Pathol 2010;63:662)
- 74 year old woman with anaplastic changes (Endocr Pathol 2005;16:83)
- 79 year old woman with a dedifferentiated component (Case Rep Med 2010;2010:495281)
Treatment
- Based on American Thyroid Association guidelines (Thyroid 2016;26:1)
- Also based on National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines (J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2018;16:1429)
- Usually surgical excision, such as lobectomy or total thyroidectomy with or without neck dissection
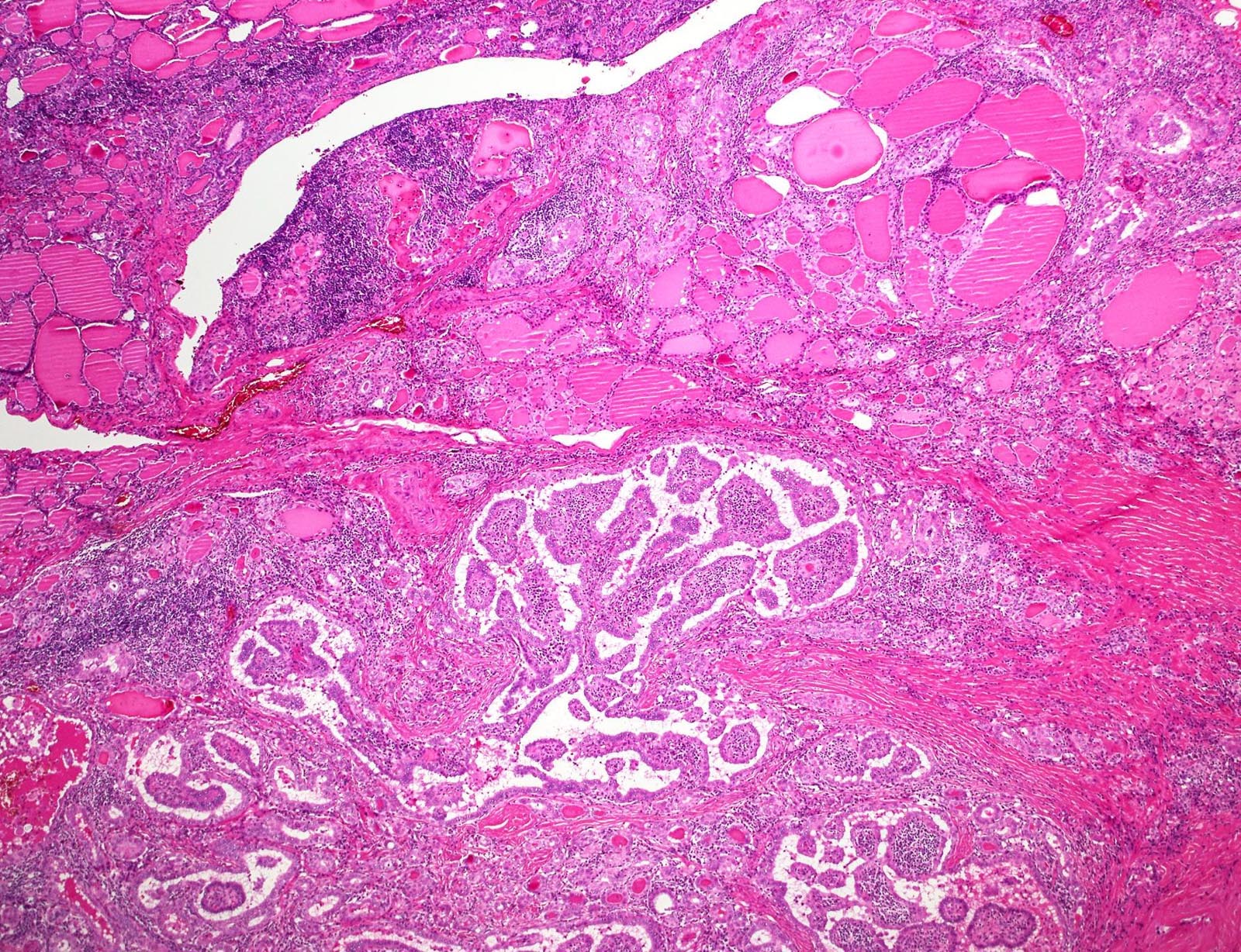
Gross description
- Usually solitary nodule, well circumscribed, unencapsulated and limited to the thyroid gland
- Solid, red-brown to tan or gray-white, 3 - 50 mm (Case Rep Oncol Med 2012;2012:689291)
- Variable cystic change, hemorrhagic areas, calcification
- Background thyroid parenchyma: pale yellow to tan, variable nodularity (consistent with Hashimoto thyroiditis)
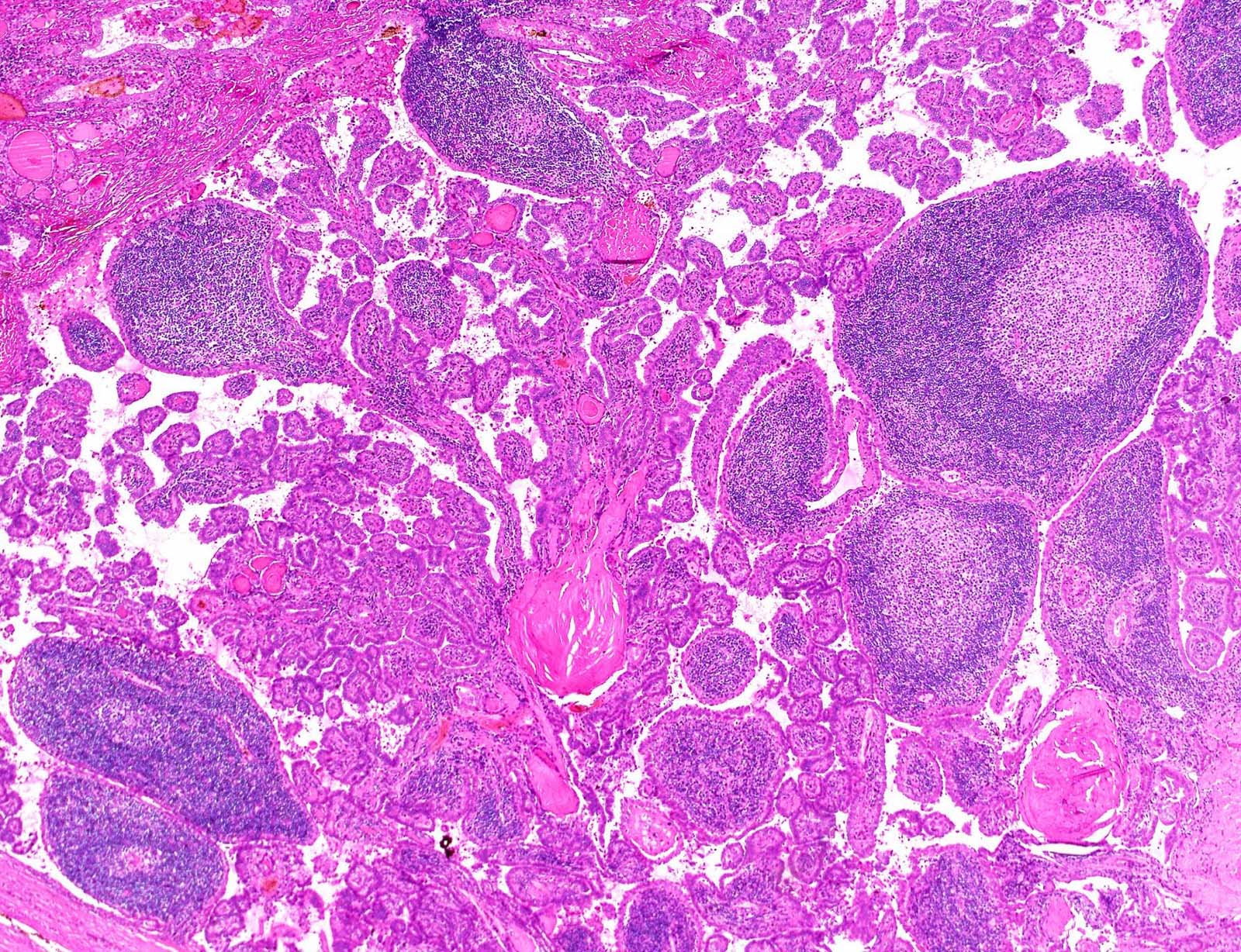
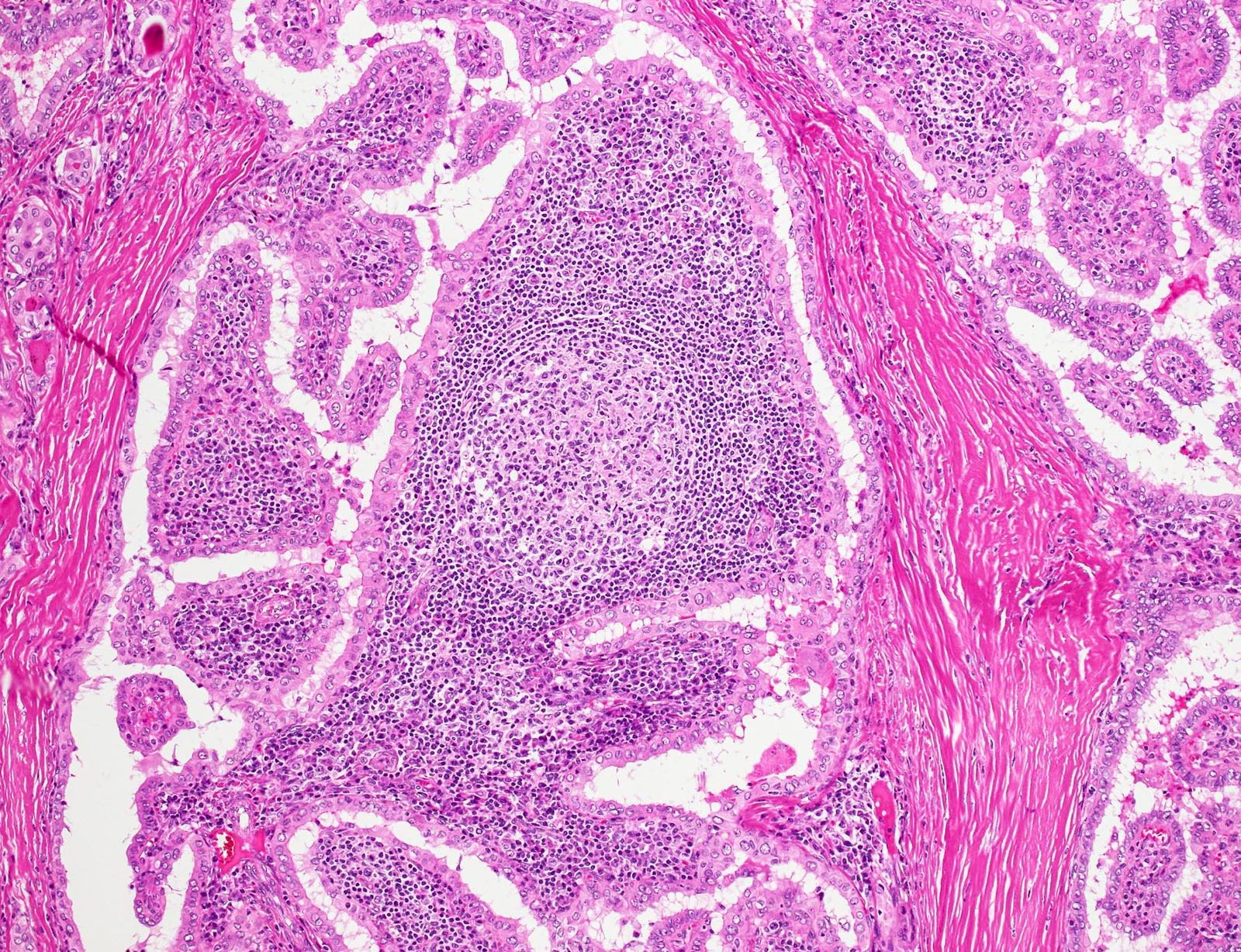
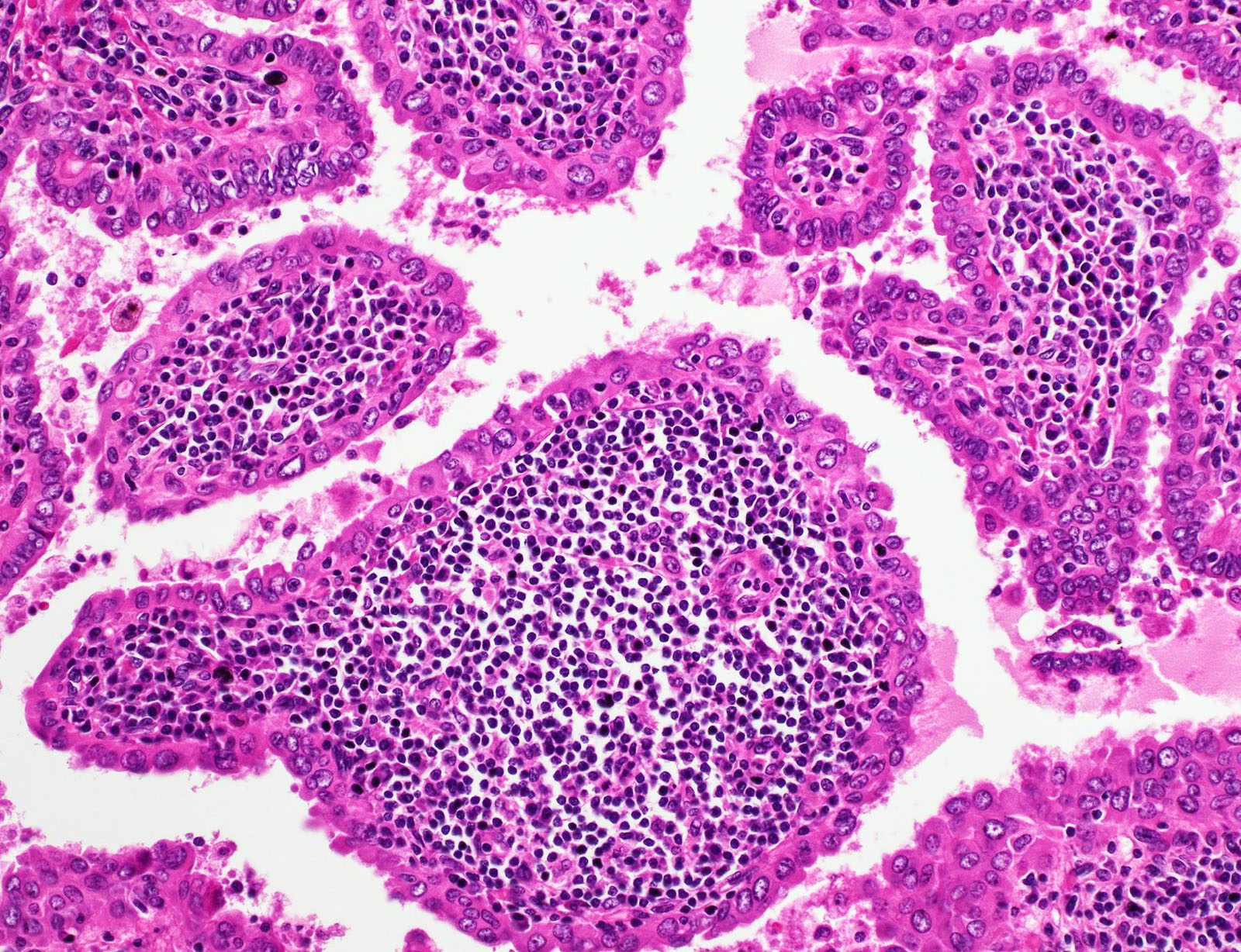
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Papillary architecture (Int J Endocrinol 2015;2015:456027)
- Heavy lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate in fibrovascular cores of papillae
- Lining cells
- Oncocytic
- Large, polygonal
- Abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm
- Nuclear features
- Prominent nuclear features of PTC
- Nuclear enlargement, grooves, chromatin clearing, intranuclear pseudoinclusions
- Inconspicuous nucleoli
- Associated thyroiditis in 53 - 93% (J Pathol Transl Med 2018;52:105, ANZ J Surg 2016;86:492, Int J Endocrinol 2015;2015:456027)
- Proportion of Warthin-like pattern to classify tumor as Warthin-like variant of PTC is not defined; supposed to be predominant
- Variable psammoma bodies (J Cytol 2017;34:183)
Microscopic (histologic) images
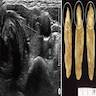
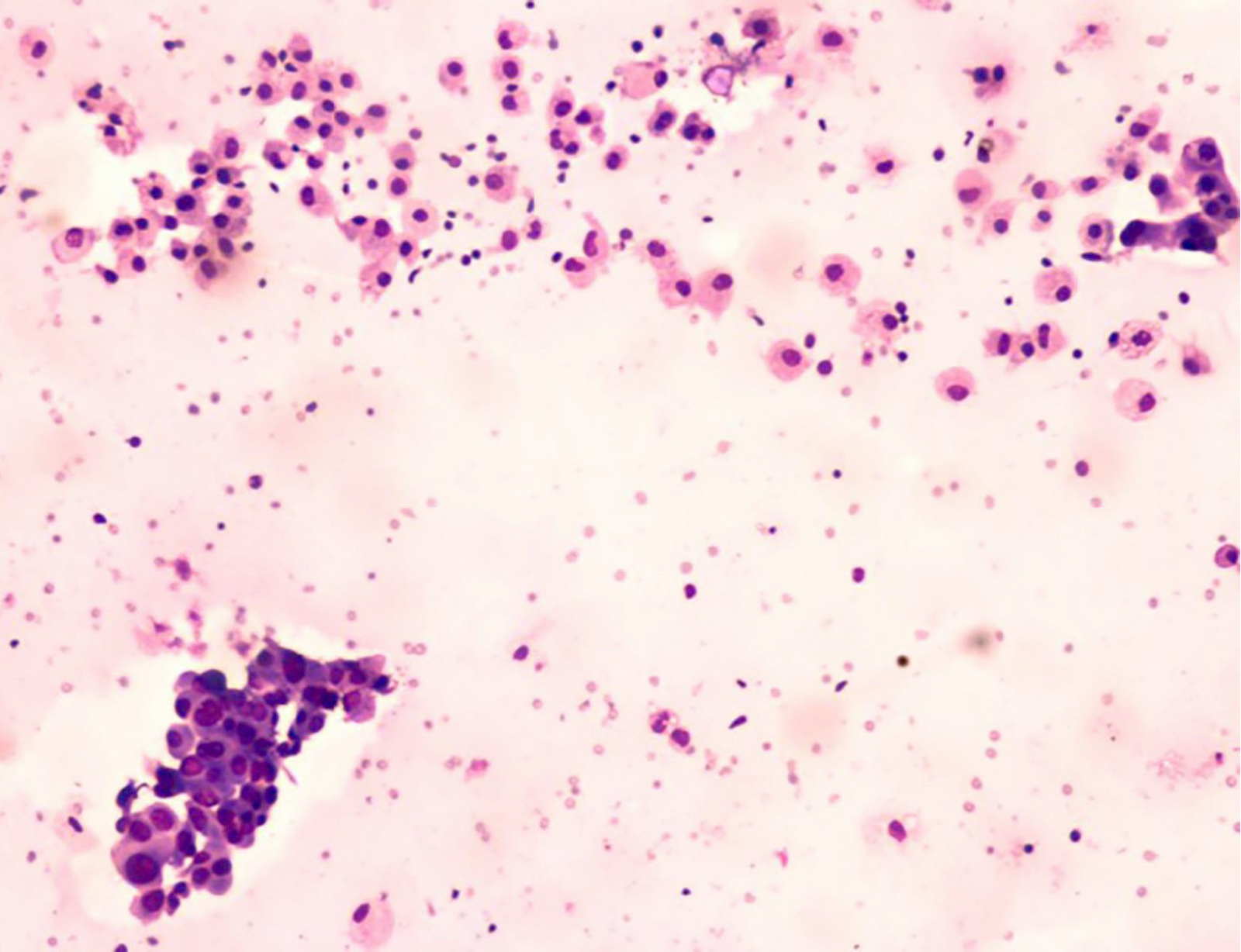
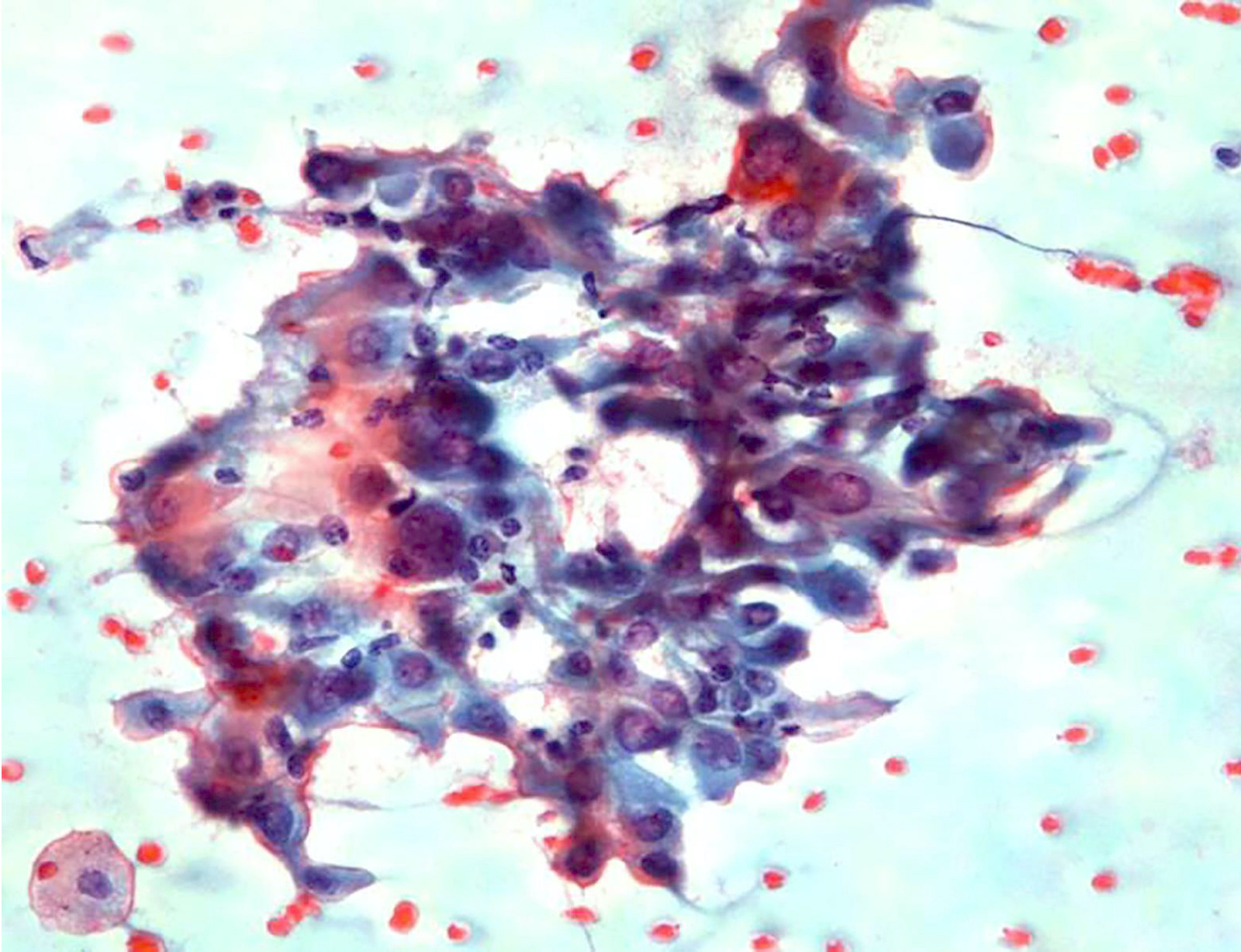
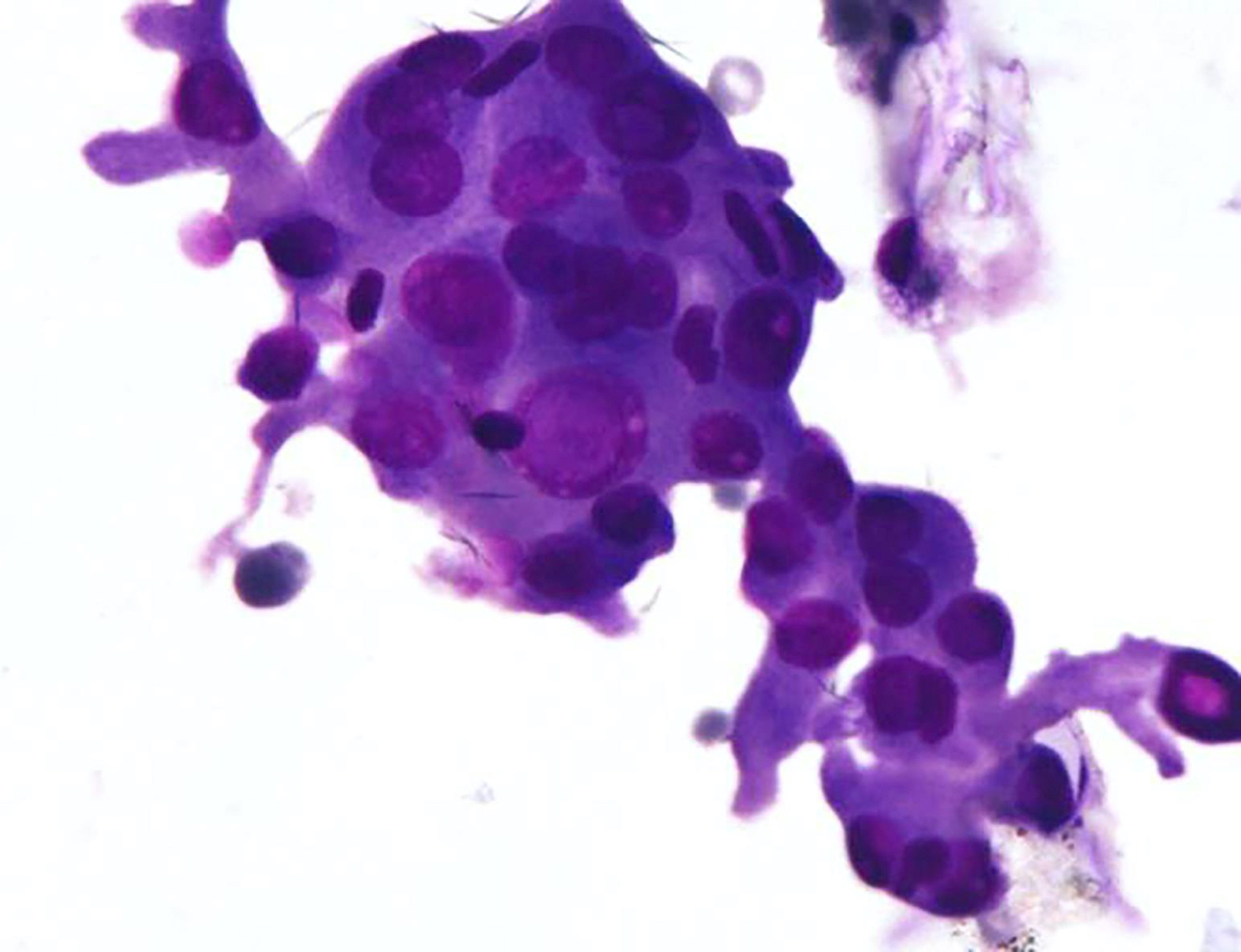
Cytology description
- Cellular aspirate with absent or scant colloid (Diagn Cytopathol 2019;47:1293)
- Patterns (J Pathol Transl Med 2018;52:105, Acta Cytol 2019 Oct 21 [Epub ahead of print], Diagn Cytopathol 2019;47:1293)
- Papillary fragments
- Monolayered macrofollicular sheets
- Lymphocytes within the tumor cell clusters and in papillary stalks
- Tumor cells
- Polygonal oncocytic cells
- Abundant dense cytoplasm, well defined cell margins
- Eccentric or centrally placed nuclei
- Well developed nuclear features of PTC
- Inconspicuous nucleoli
- Background
- Lymphocytes, plasma cells, histiocytes
- Multinucleated giant cells
- Usually Bethesda VI or V (Int J Endocrinol 2015;2015:456027, J Pathol Transl Med 2018;52:105, Diagn Cytopathol 2017;45:837)
- Rarely misdiagnosed as thyroiditis (Diagn Cytopathol 2017;45:837)
- Liquid based cytology (Korean J Pathol 2014;48:170)
- Easily visualized tumor cells
- Minimal / absent lymphocytic background
Cytology images
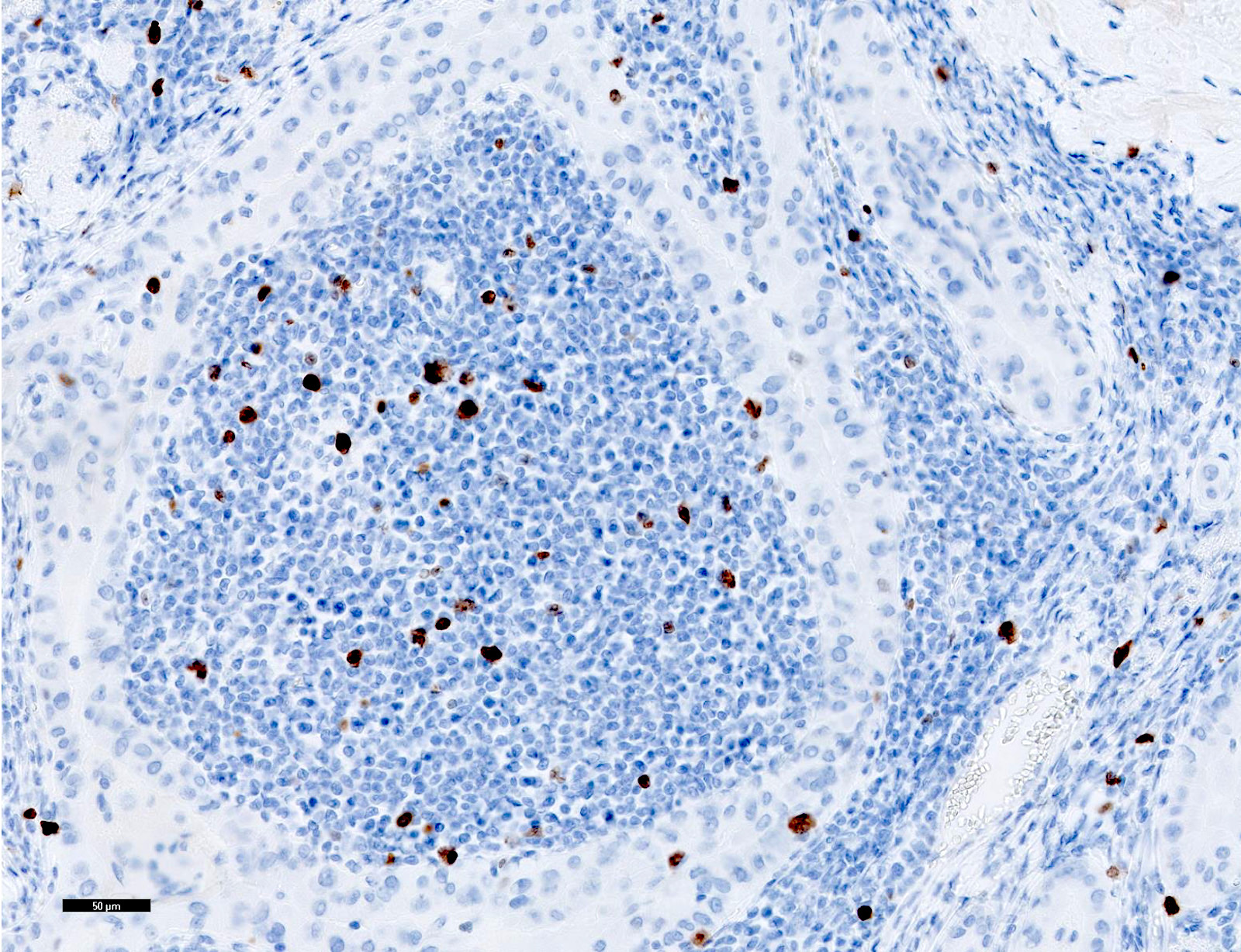
Positive stains
- Usually not needed; diagnosis is made on histology
- Thyroid specific: TTF1, PAX8, thyroglobulin
- Cytokeratins: AE1 / AE3, CK7, CK19
- Galectin3 (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2002;126:710)
- HBME1 (Pathol Oncol Res 2015;21:735)
- MIB1 index 2 - 5% (Histopathology 2001;39:17)
- Papillary cores: CD45, CD20, CD3 in lymphocytes; S100 dendritic / Langerhans cells (Histopathology 2001;39:17)
Negative stains
- CK20
- Calcitonin and neuroendocrine markers (synaptophysin, chromogranin)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- BRAFV600E mutation in 65 - 75% (Int J Endocrinol 2015;2015:456027, Virchows Arch 2005;446:589)
- RET / PTC fusion based on limited evidence (Histopathology 2000;36:493)
Sample pathology report
- Thyroid, total thyroidectomy:
- Papillary thyroid carcinoma, Warthin-like variant, left lobe, 2.5 cm (see synoptic report)
Differential diagnosis
- Oncocytic variant of PTC:
- Lacks lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate in the papillary stalks
- Tall cell variant of PTC:
- Tumor cells have a height 2 to 3 times their width and constitute at least 30% of all tumor cells
- Papillary stalks lack the lymphocyte rich stroma
- Classic type PTC with focal oncocytic change:
- Absent lymphoid stroma
- Only focal oncocytic change
- Classic type PTC associated with lymphocytic / Hashimoto thyroiditis:
- Tumor cells lack oncocytic change
- Absent lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate in papillary cores
- May contain small areas of Warthin-like architecture (papillary cores stuffed with lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate), which is not sufficient to qualify the whole tumor as Warthin-like variant
- Follicular neoplasm with oncocytic change:
- Lacks well developed nuclear features of PTC; round nuclei, prominent nucleoli and rare intranuclear inclusions
- Usually lacks papillae
- Absent stromal lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate in stalks of papillae
- Hashimoto thyroiditis:
- Lacks papillae
- Oncocytic cells of Hashimoto thyroiditis have round nuclei with a prominent single nucleolus and lack well developed nuclear features of PTC
- Cytology:
- Hürthle cell neoplasm:
- Lacks papillary fragments, nuclear features of PTC and a lymphocytic background, except if associated lymphocytic thyroiditis
- Oncocytic PTC:
- Usually lacks lymphocytic background, except if associated with lymphocytic thyroiditis
- Cannot be differentiated on liquid based cytology
- Classic type PTC:
- Lacks diffuse oncocytic change
- Usually lacks lymphocytic background except if associated with lymphocytic thyroiditis
- Tall cell variant of PTC:
- Tall columnar cells with cytoplasmic tails
- Hashimoto thyroiditis:
- Lacks well developed nuclear features of PTC and papillary fragments
- Hürthle cell neoplasm:
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
E. Warthin tumor. Warthin-like variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma is characterized on histomorphology by papillae lined by oncocytic cells and a dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate within the papillary cores, closely mimicking Warthin tumor of salivary gland. The latter shows oncocytic columnar cells with underlying basal cells, resting on a dense lymphoid stroma.
Comment Here
Reference: Warthin-like variant
Comment Here
Reference: Warthin-like variant
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is typically associated with Warthin-like variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma?
- Favorable clinical outcome
- Frequent dedifferentiation
- Mitochondrial DNA mutations
- Multiple (soap bubble-like) intranuclear inclusions
- Tumor cells have height 2 to 3 times the width
Board review style answer #2
A. Favorable clinical outcome. Warthin-like variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) has a favorable clinical outcome and dedifferentiation is unusual. It harbours BRAFV600E mutation in 65 - 75% cases. Mitochondrial DNA mutations are characteristic of oncocytic variant of PTC. Tumor cells having height 2 to 3 times the width is a diagnostic feature of tall cell variant of PTC. Multiple soap bubble-like intranuclear inclusions are typically described in tall cell variant of PTC but can be seen in other variants like hobnail variant also.
Comment Here
Reference: Warthin-like variant
Comment Here
Reference: Warthin-like variant