Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Prognostic factors | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Islam S. Thyroid cancer-general. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/thyroidthyroidca.html. Accessed January 21st, 2025.
Definition / general
- 1% of all cancer in U.S., 0.2% of all cancer deaths
- Estimated 56,000 new cases and 1800 deaths in U.S. in 2012 (SEER)
- Increasing incidence due to new diagnostic practices which detect smaller tumors (Cancer Causes Control 2008;19:585, BMC Cancer 2006;6:284, BMC Cancer 2006 Apr 24;6:102), although increase may be abating (Eur J Endocrinol 2009;160:71)
Epidemiology
- Often estrogen receptor positive, which may explain female predominance of tumors in reproductive years (for other ages, incidence in males and females is similar, Mod Pathol 2003;16:437, Arch Pathol Lab Med 1991;115:1203)
- More common in U.S. whites than blacks, for unknown reasons (Ann Surg Oncol 2008;15:1169)
- Increased risk for children exposed to ionizing radiation (Cancer Causes Control 2009;20:75), particularly under age 1 year (Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008;22:1061), women atomic bomb survivors in Japan (Epidemiology 2009;20:181)
Prognostic factors
- 20 year survival is 90%, because most are indolent papillary carcinomas
- Good prognostic factors:
- Men under age 40 years or women under age 50 / 60
- Favorable histologic types
- Poor prognostic factors:
- Men age 41+ or women 51+
- Large tumor size, nuclear pleomorphism, tumor necrosis, vascular invasion, increased mitotic activity, higher stage, unfavorable subtypes (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:1007)
- Death usually from undifferentiated, poorly differentiated, Hürthle cell or medullary carcinoma, due to distant metastases
- Poor survival in those with bone metastases (5 year: 29%, 10 year: 13%, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2000;124:1440)
Treatment
- See also subtypes - either lobectomy, subtotal thyroidectomy or total thyroidectomy; also postoperative radioiodine therapy, TSH suppressive therapy, new molecular therapies (Ther Clin Risk Manag 2008;4:935)
- Can assess for recurrence with serum thyroglobulin levels (different assays show good agreement between themselves, Clin Biochem 2009;42:416), calcitonin (medullary carcinoma)
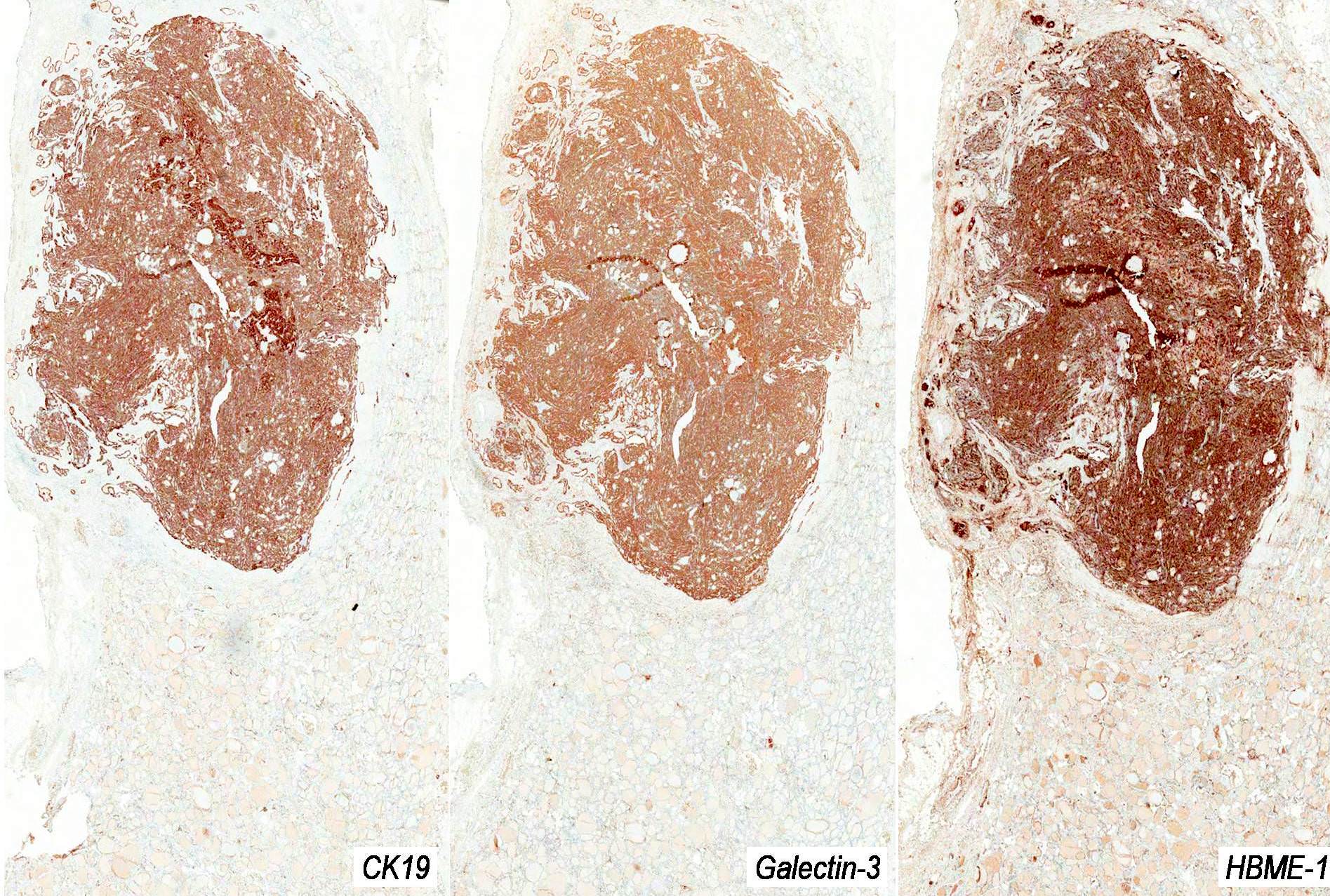
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Thyroglobulin (even if tumor is necrotic, Hum Pathol 1999;30:1373), TTF1
Negative stains
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Rearrangements of RET-PTC in 40% of papillary carcinomas, rearrangements of PAX8-PPARy in 40% of follicular carcinomas, BRAF mutations in 40 - 60% of papillary carcinomas (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2008;132:164)
Videos
Thyroid carcinoma
Advanced thyroid carcinoma
Differential diagnosis
- Post iodine 131 treatment for hyperthyroidism: see Radiation thyroiditis
Additional references