Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Jug R, Jiang X. Invasive EFVPTC. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/thyroidinvasiveEFVPTC.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Prognostically distinct entity from counterpart NIFTP (noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features)
Essential features
- Same nuclear features and follicular architecture as NIFTP but with vascular or tumor capsule invasion present
Terminology
- Encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma with invasion
ICD coding
- ICD-10: C73 - malignant neoplasm of thyroid gland
Epidemiology
- Women are affected more than men (F:M = 3.6:1)
- Mean age of patients 44 years (Diagn Histopathol 2016;22:171)
Sites
- Thyroid
Pathophysiology
- Thyroid parenchymal follicular cells follow well defined tumor progression model (Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 2015;13:3)
Etiology
- Exposure to radiation implicated in etiology of thyroid cancer (Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 2015;13:3)
Clinical features
- May be found incidentally on imaging or present as a visible or palpable tumor in the thyroid
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis made on histology of surgical specimens following submission and examination of entire tumor capsule (Am J Clin Pathol 2002;117:143)
Laboratory
- Follicular variants of papillary thyroid carcinoma may be associated with elevated serum thyroglobulin (Thyroid 2016;26:872)
Radiology description
- Ultrasound features include solid composition, smooth margins, parallel orientation, round to oval shape and presence of a halo (hypoechoic rim surrounding thyroid nodule) (Thyroid 2017;27:1177)
Prognostic factors
- Good prognosis
- Based on an international, multidisciplinary, retrospective study in which 101 participants had invasive EFVPTC, 12 patients experienced an adverse event (including 5 patients developing distant metastases and 2 patients dying of the disease) by a median follow up time of 13 years (JAMA Oncol 2016;2:1023)
Case reports
- 35 year old man with invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma metastatic to lung at presentation (Mod Pathol 2010;23:1191)
- 43 year old patient with encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma showing capsular and vascular invasion on histology (ARS Medica Tomitana 2018;24:15)
- 3 cases of encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma with focal vascular invasion and bone metastases (Mod Pathol 2000;13:861)
Treatment
- Hemithyroidectomy with or without isthmusectomy, near total thyroidectomy or total thyroidectomy
- Depending on size and stage, may consider lymph node dissection and radioactive iodine ablation for subtotal thyroidectomies (Thyroid 2009;19:1167)
Gross description
- Well circumscribed encapsulated solid nodules (Head Neck Pathol 2011;5:51)
- Capsular invasion may or may not be grossly evident (Head Neck Pathol 2009;3:86)
Frozen section description
- Frozen sections generally not recommended on primary thyroid tumors, particularly ones with preoperative cytology diagnoses of follicular patterned lesions, as diagnosis of these requires evaluation of the entire capsule
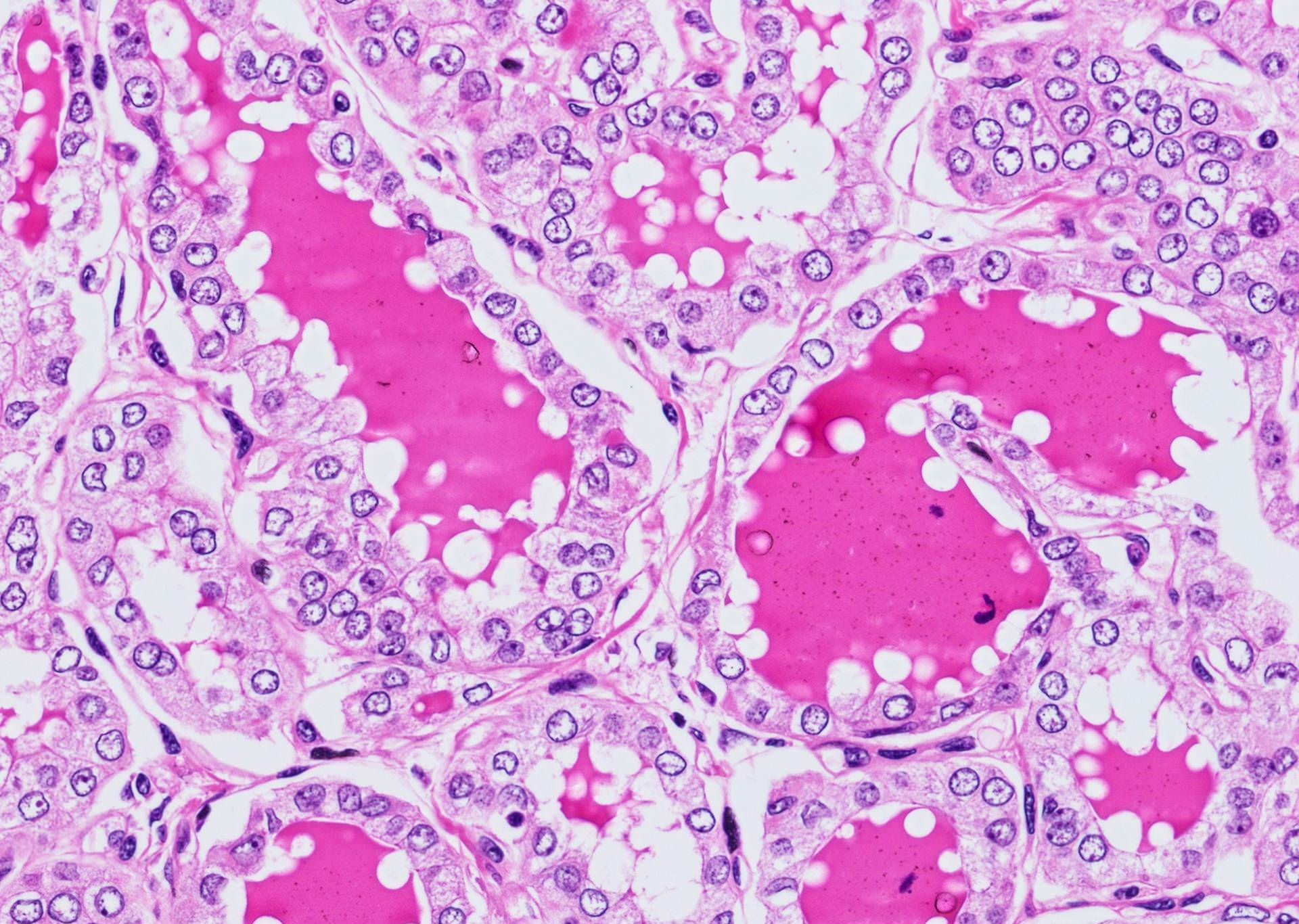
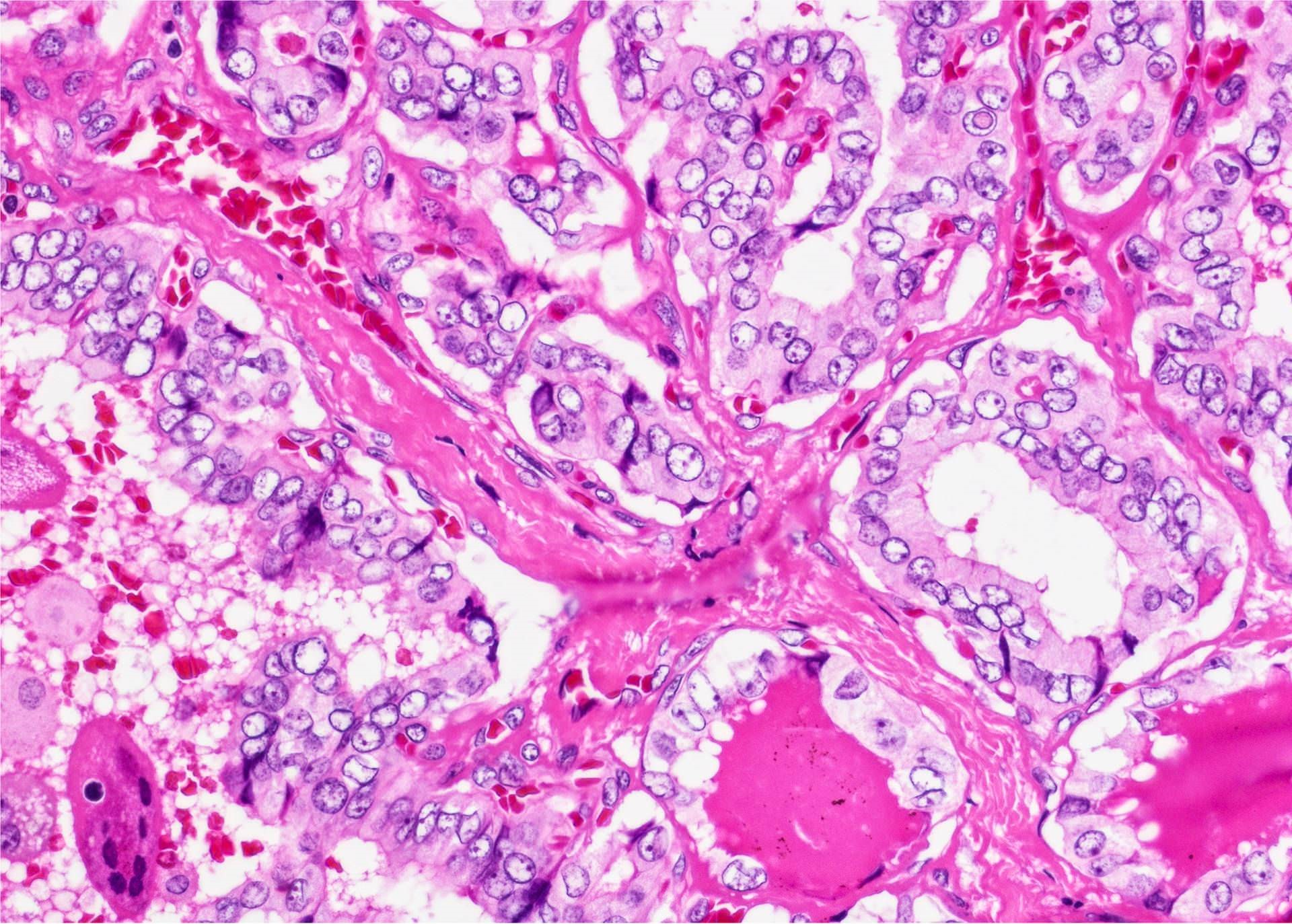
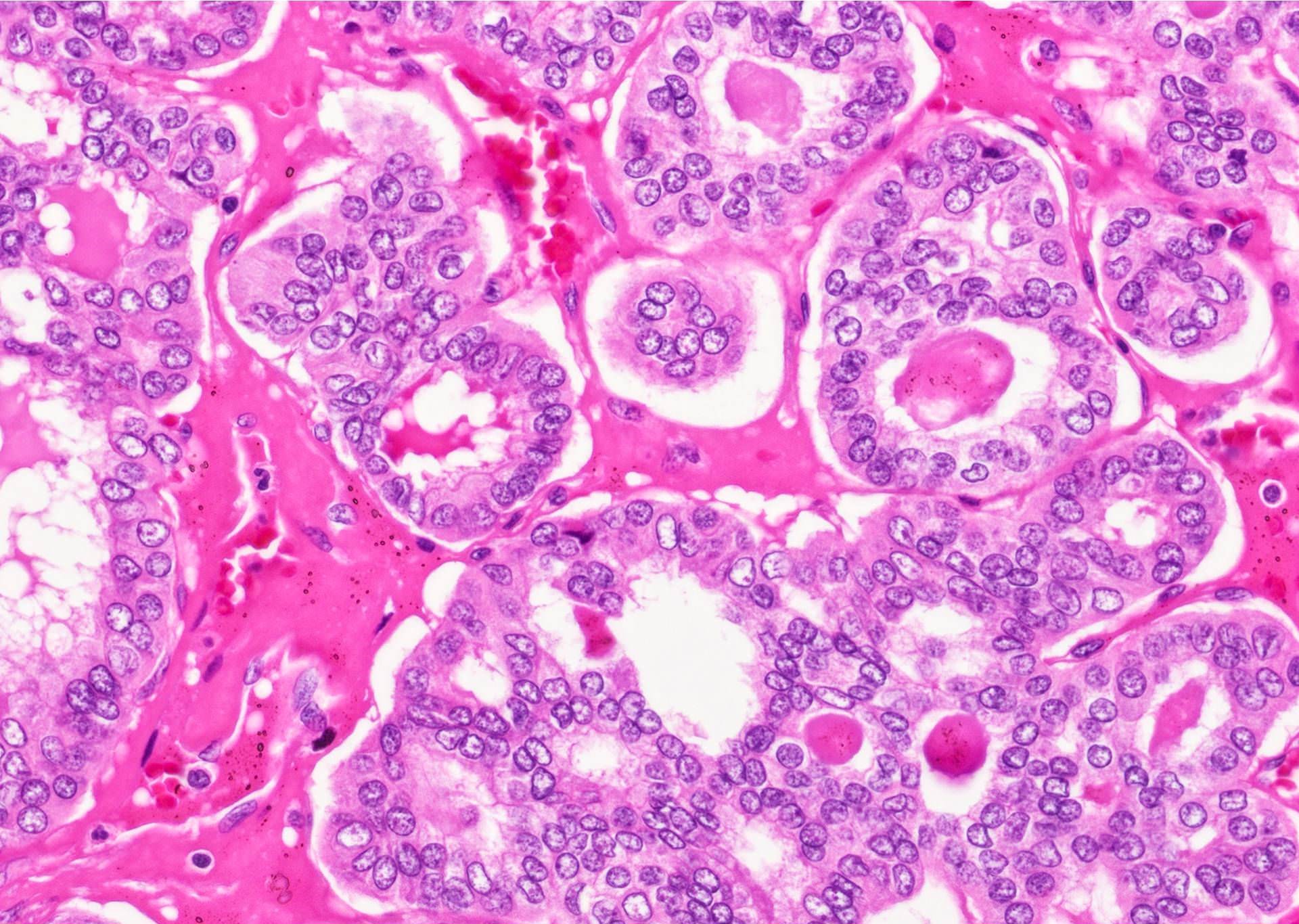
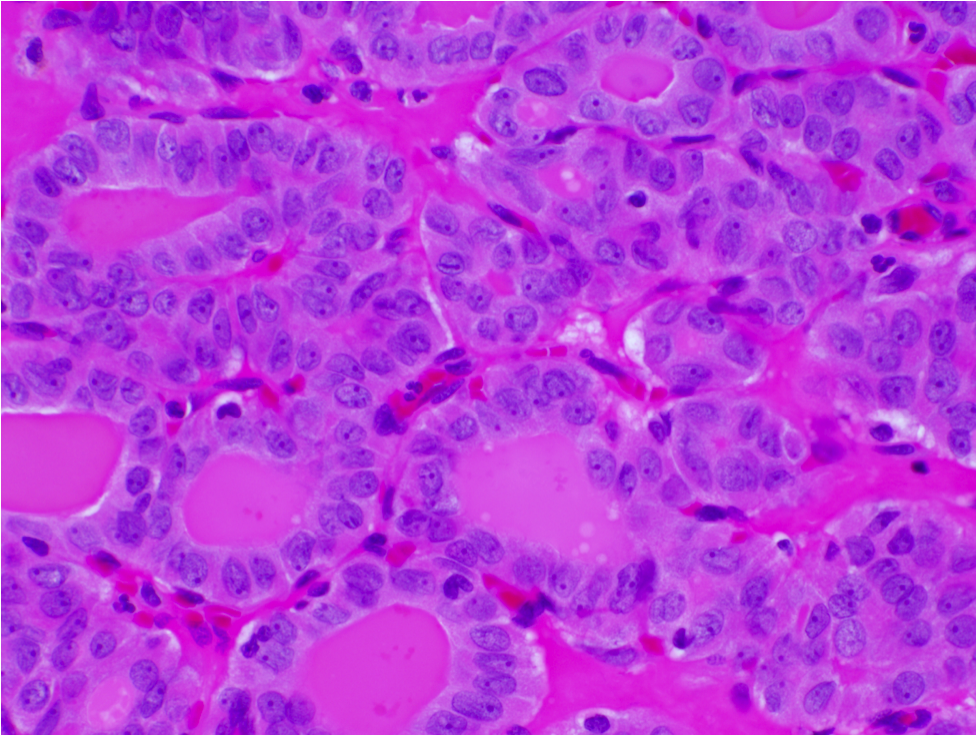
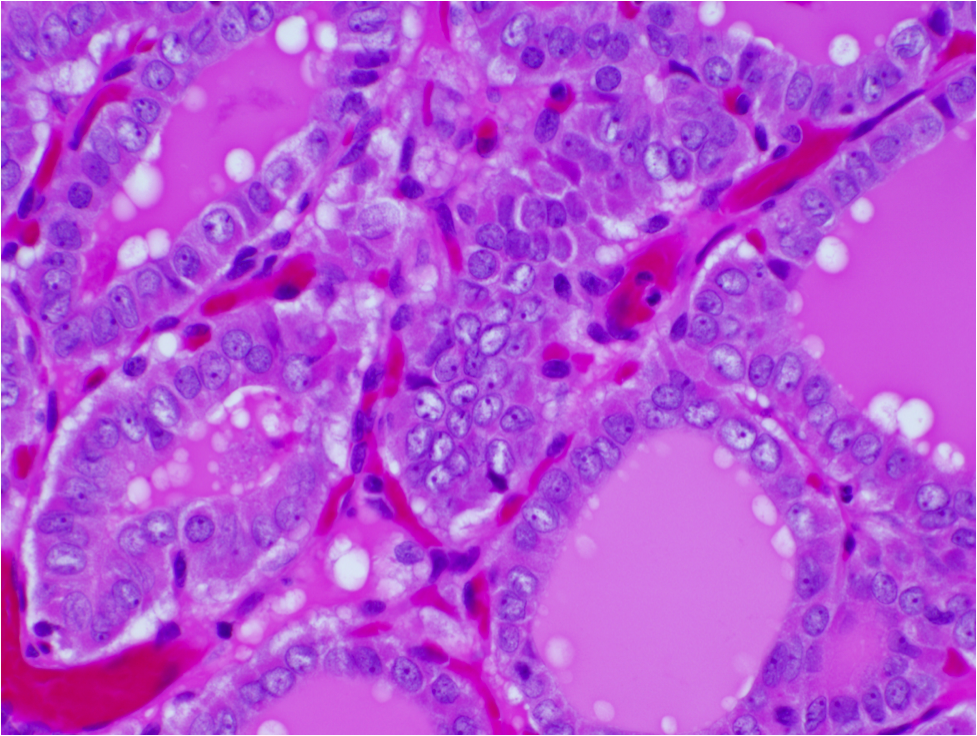
Microscopic (histologic) description
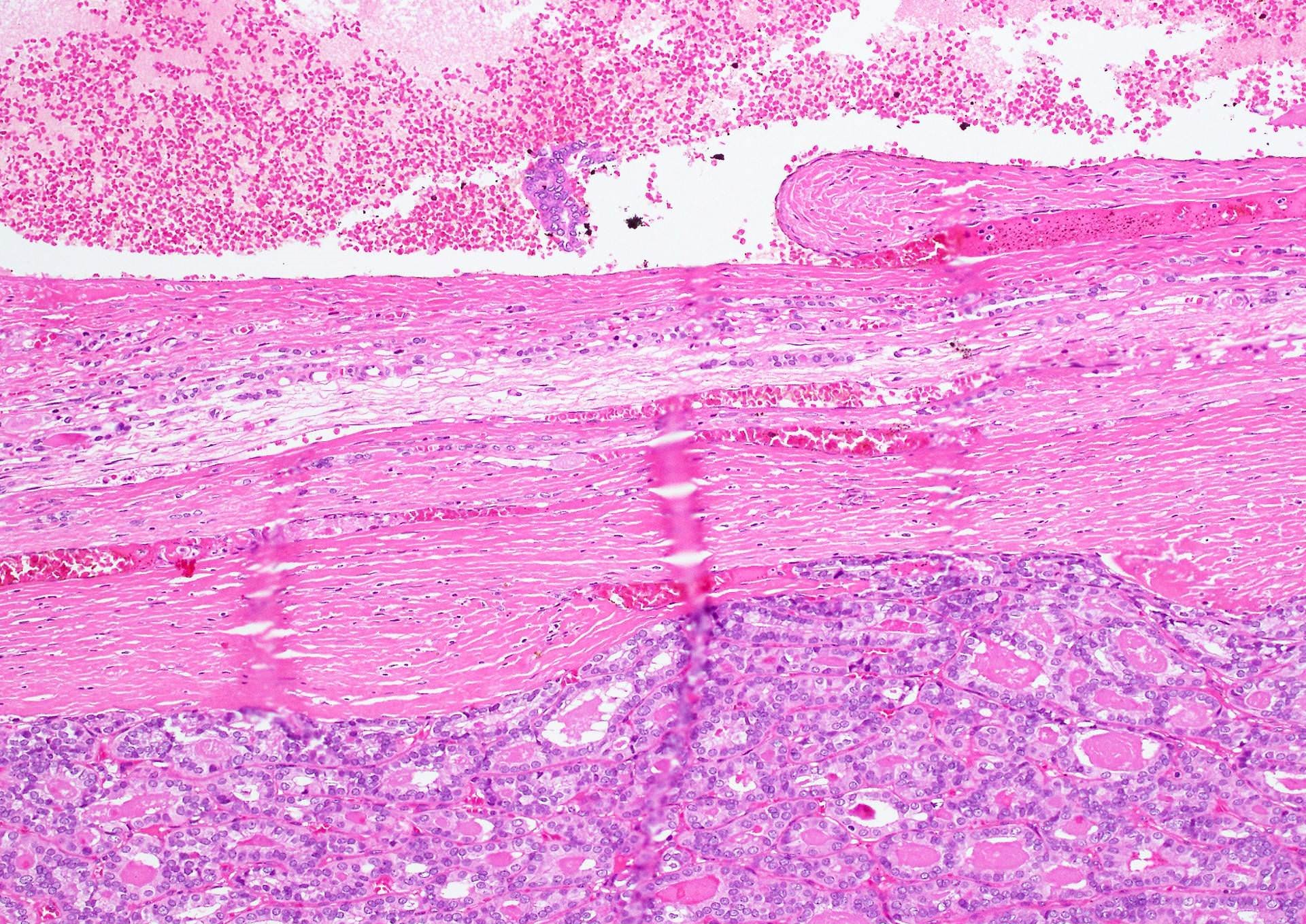
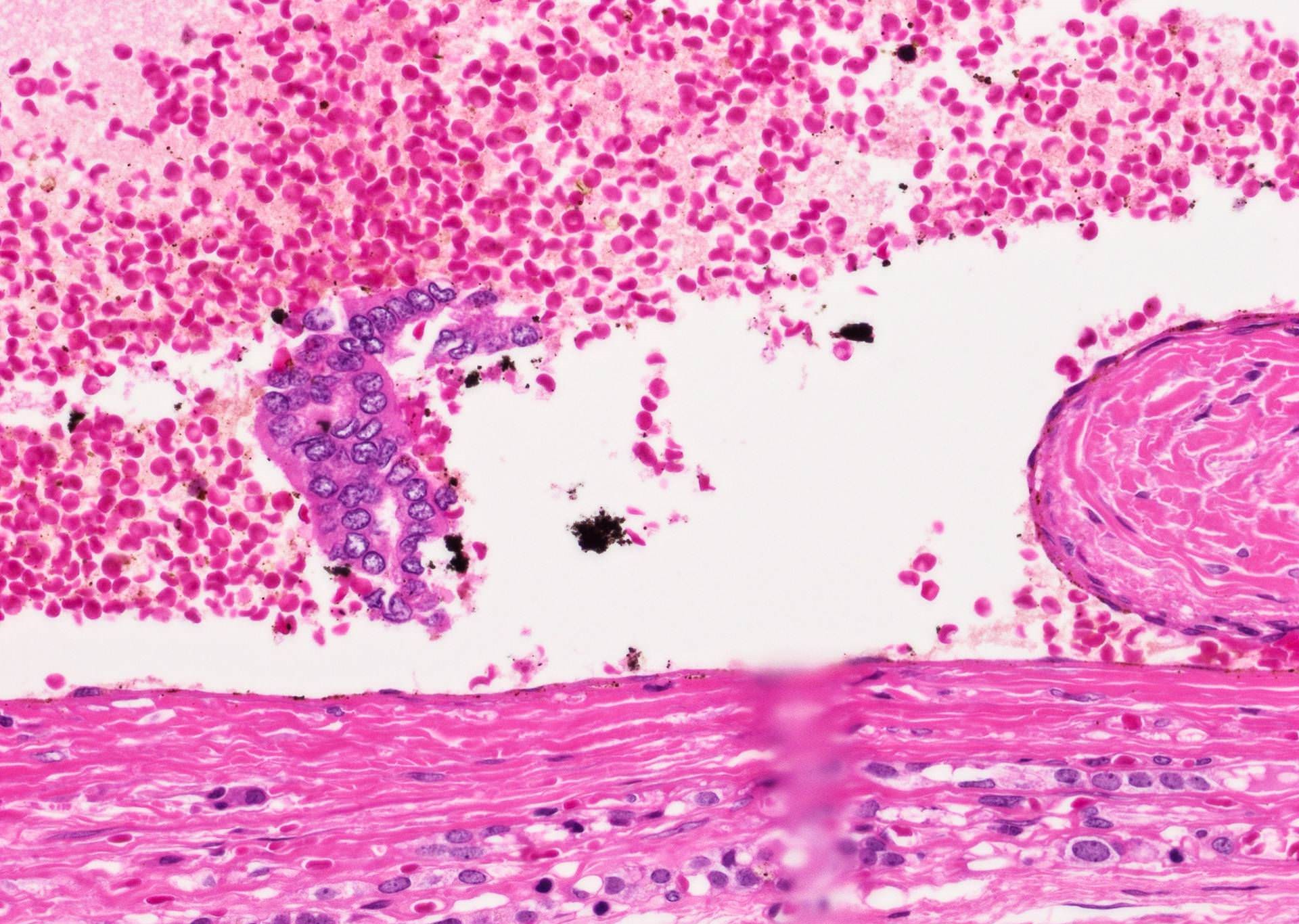
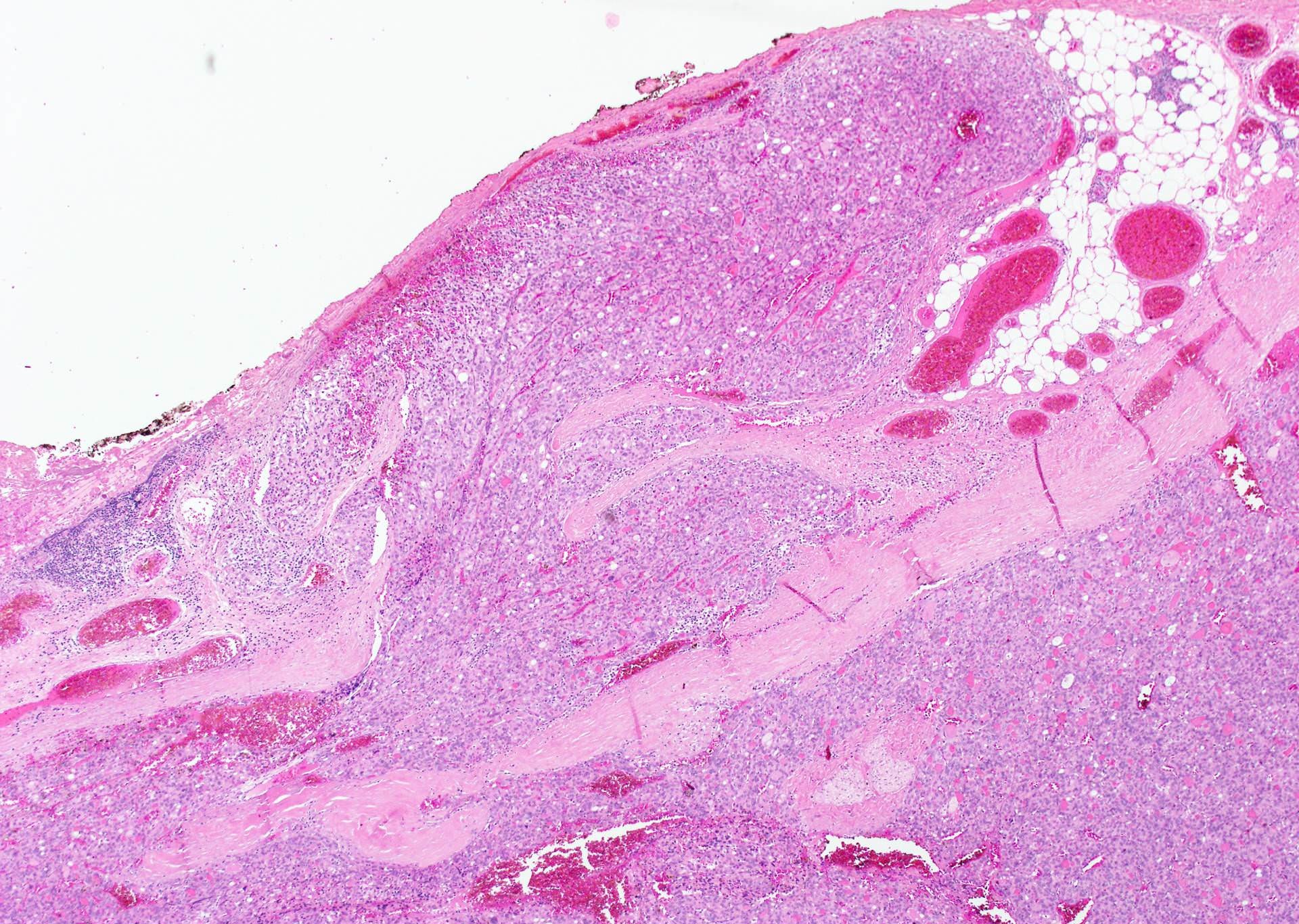
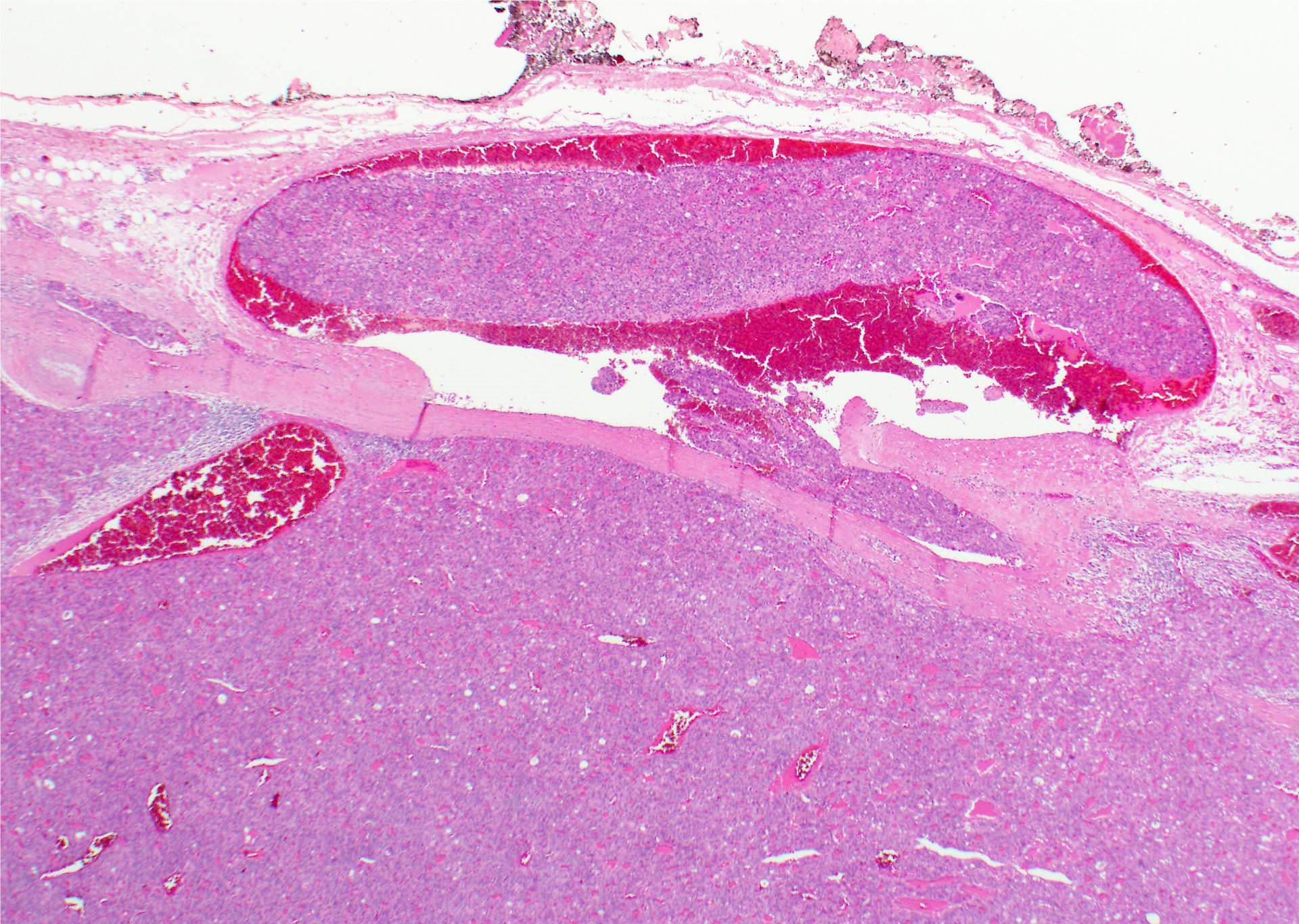
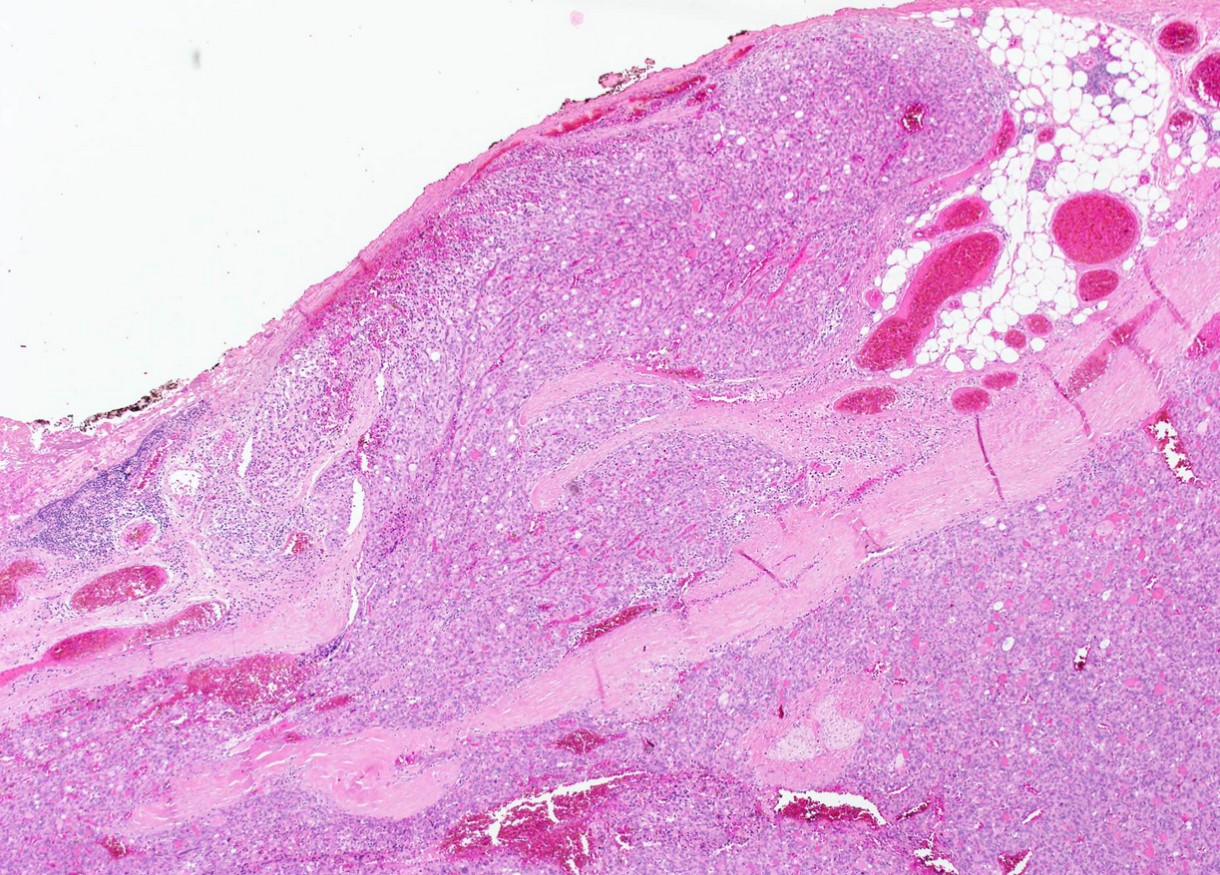
- Tumor invades capsule or extends into adjacent thyroid tissue or has evidence of lymphovascular invasion
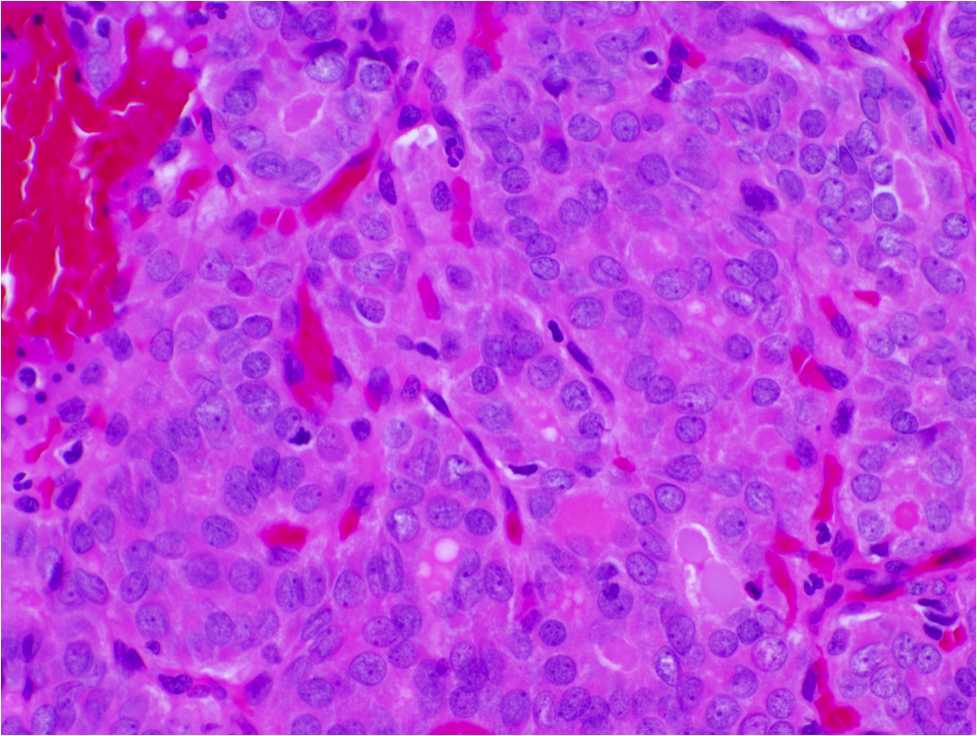
- Nuclear features of papillary thyroid carcinoma:
- Size and shape: nuclear enlargement / overlapping / crowding, elongation
- Nuclear membrane irregularities: irregular contours, grooves, pseudoinclusions
- Chromatin characteristics: clearing with margination / glassy nuclei
- Follicular growth pattern may be microfollicular, normofollicular or macrofollicular with abundant colloid
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Andrey Bychkov, M.D., Ph.D. and Rachel Jug, M.B.B.Ch., B.A.O.
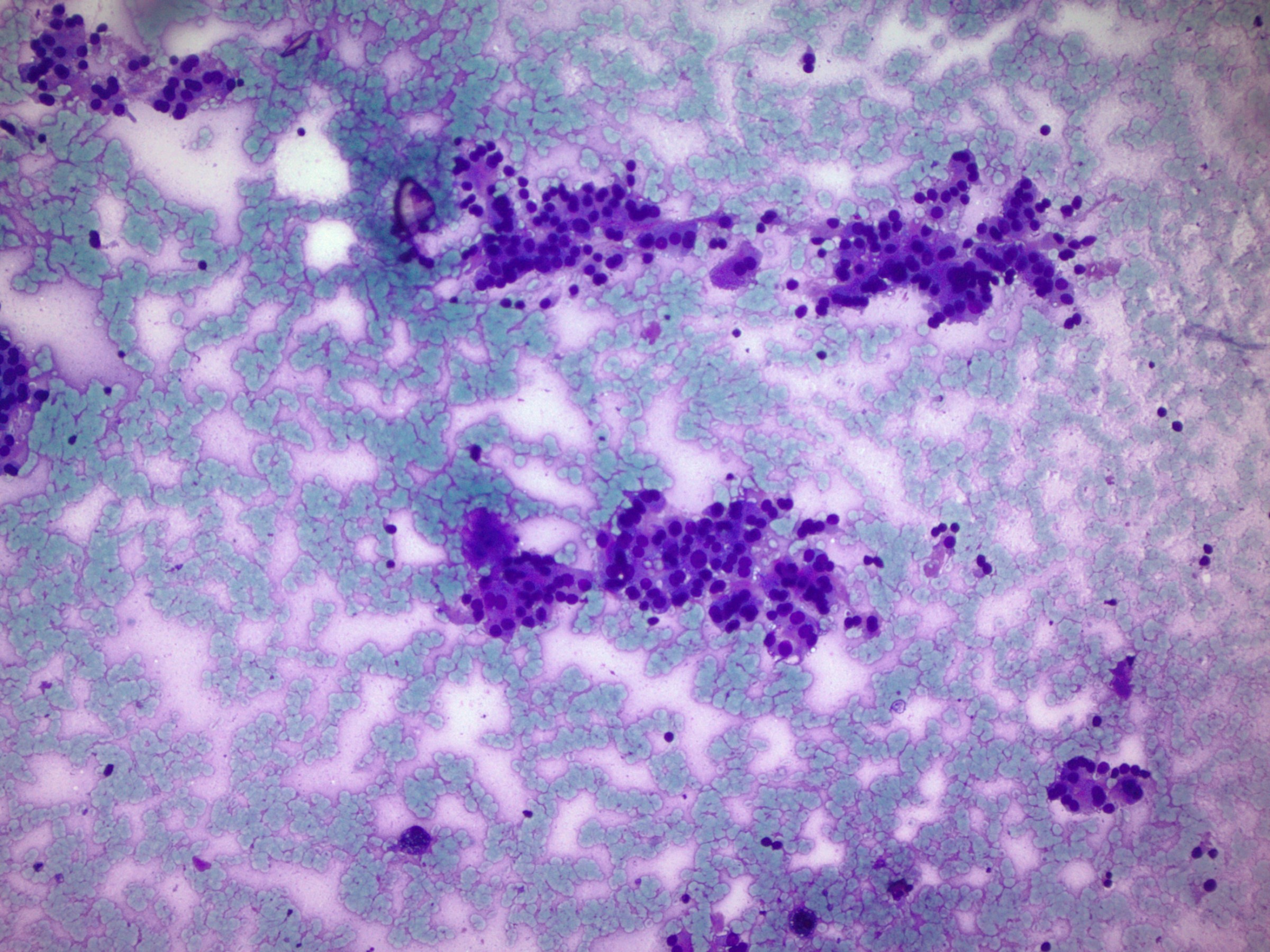
Cytology description
- FNA samples are usually hypercellular with neoplastic cells containing nuclear features of papillary thyroid carcinoma arranged in microfollicles
- Nuclear features are more subtle than conventional papillary thyroid carcinoma (Endocr Pathol 2014;25:257)
- Colloid may be present
- Cannot distinguish invasive EFVPTC from NIFTP on cytology, as cannot evaluate capsule on FNA
Positive stains
Negative stains
- Calcitonin, parathyroid hormone
- BRAF V600E not generally seen in EFVPTC (J Korean Med Sci 2018;33:e75)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Shares molecular features (RAS type mutations) with follicular adenoma, follicular carcinoma (Mod Pathol 2010;23:1191)
- Follicular variants of papillary thyroid carcinoma more commonly harbor RAS type mutations than classic variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma (more BRAF type mutations); however, invasive EFVPTC is associated with more BRAF type mutations than noninvasive EFVPTC (which is associated with more RAS type mutations) (Cell 2014;159:676, Mod Pathol 2010;23:1191)
Sample pathology report
- Right lobe, partial thyroidectomy:
- Invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma
Differential diagnosis
- Encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma:
- Tumor lacks evidence of capsular or lymphovascular invasion
- Noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features:
- Same nuclear features and follicular architecture but lacks vascular or tumor capsular invasion
- Follicular carcinoma:
- Thyroid carcinoma with capsular or lymphovascular invasion, similarly composed of follicles but lacks papillary nuclear features
- Follicular adenoma:
- Thyroid neoplasm without capsular or lymphovascular invasion, similarly composed of follicles but lacks papillary nuclear features
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which histological feature in the image above separates invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features?
- Capsular invasion
- Lymph node metastasis
- Microfollicular growth pattern
- Mitotic figures
- Nuclear enlargement
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Which of the following histologic descriptions meets the criteria for capsular invasion?
- Bosselation on inner aspect of capsule
- Follicles aligned parallel to capsule
- Follicles aligned perpendicular to capsule
- Tumor bud invading into but not through capsule
- Tumor transgresses through and beyond outer contour of capsule
Board review style answer #2
E. Tumor transgresses through and beyond outer contour of capsule
Comment Here
Reference: Invasive EFVPTC
Comment Here
Reference: Invasive EFVPTC