Table of Contents
Definition / general | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Cytology images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Shahid I. Acute / infectious thyroiditis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/thyroidinfectious.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Also called acute thyroiditis
- Via blood or direct seeding from upper respiratory infections, causes sudden onset of pain and glandular enlargement
- Risk factors: malnourished infant, debilitated elderly, immunosuppression, trauma
- Often Streptococcus haemolyticus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus; gram negative bacteria associated with trauma; also Pneumocystis jiroveci in HIV+ patients with low CD4 counts (Mycoses 2007;50:443)
Clinical features
- Rarely is suppurative (Pediatr Emerg Care 2008;24:764)
- May be associated with pyriform sinus fistula (Pediatr Surg Int 2007;23:779)
Diagnosis
- Usually based on serologic tests
Case reports
- 23 year old woodcutter with blastomycosis (Thyroid 2008;18:659)
- 31 year old woman with Aspergillus and end stage AIDS (Postgrad Med J 2001;77:336)
- With septic emboli from endocarditis (Postgrad Med J 2008;84:445)
- Renal transplant recipient with Salmonella infection complicated with suppurative thyroiditis and ruptured aortic mycotic aneurysm (Transplant Proc 2008;40:3759)
- Odontogenic origin (Minerva Stomatol 2007;56:461)
- Allescheria boydii thyroiditis in posttransplant patient (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1978;102:158)
Treatment
- Drainage, antibiotics, fistulectomy
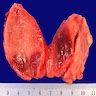
Gross description
- Normal or slightly enlarged thyroid gland
- May have suppurative areas
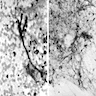
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Neutrophils, possibly microabscesses and tissue necrosis
- Fungi are associated with necrosis, acute inflammation and granulomas
Stains
- Gram stain or GMS / PAS may help identify bacteria or fungi; use ISH or IHC for viruses
Differential diagnosis
- Ischemic necrosis
- Subacute thyroiditis