Table of Contents
Definition / general | Laboratory | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Islam S. Hashimoto-fibrous. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/thyroidhashimotosthyroiditisfibrosing.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- 10 - 12% of all cases
- Large symptomatic goiter, marked hypothyroidism
- Fibrous atrophy variant:
- Similar to fibrous variant but thyroid gland is much smaller (1 - 6 g)
- Elderly patients with marked hypothyroidism and high titers of antithyroid antibodies
Laboratory
- Hypothyroidism with increased TSH
- Markedly elevated antithyroglobulin antibody
Treatment
- Surgery to relieve dysphagia or dyspnea
Gross description
- Large goiter does not adhere to surrounding structures
- May not be recognizable as thyroid tissue
Microscopic (histologic) description
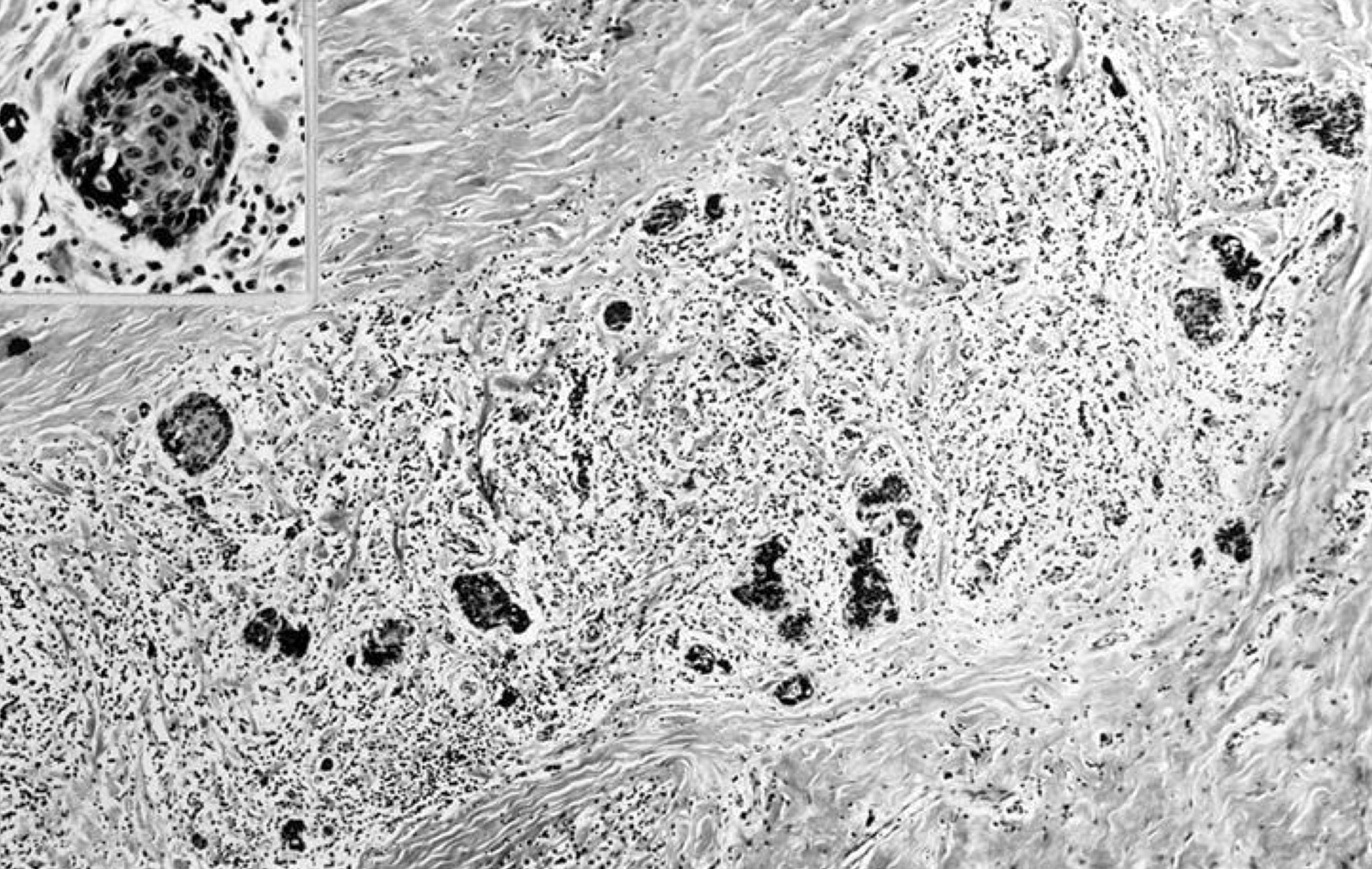
- Extensive dense (keloid-like) hyaline fibrosis within thyroid capsule
- Often extensive squamous metaplasia
- Marked follicular atrophy, although lobular architecture of gland is maintained
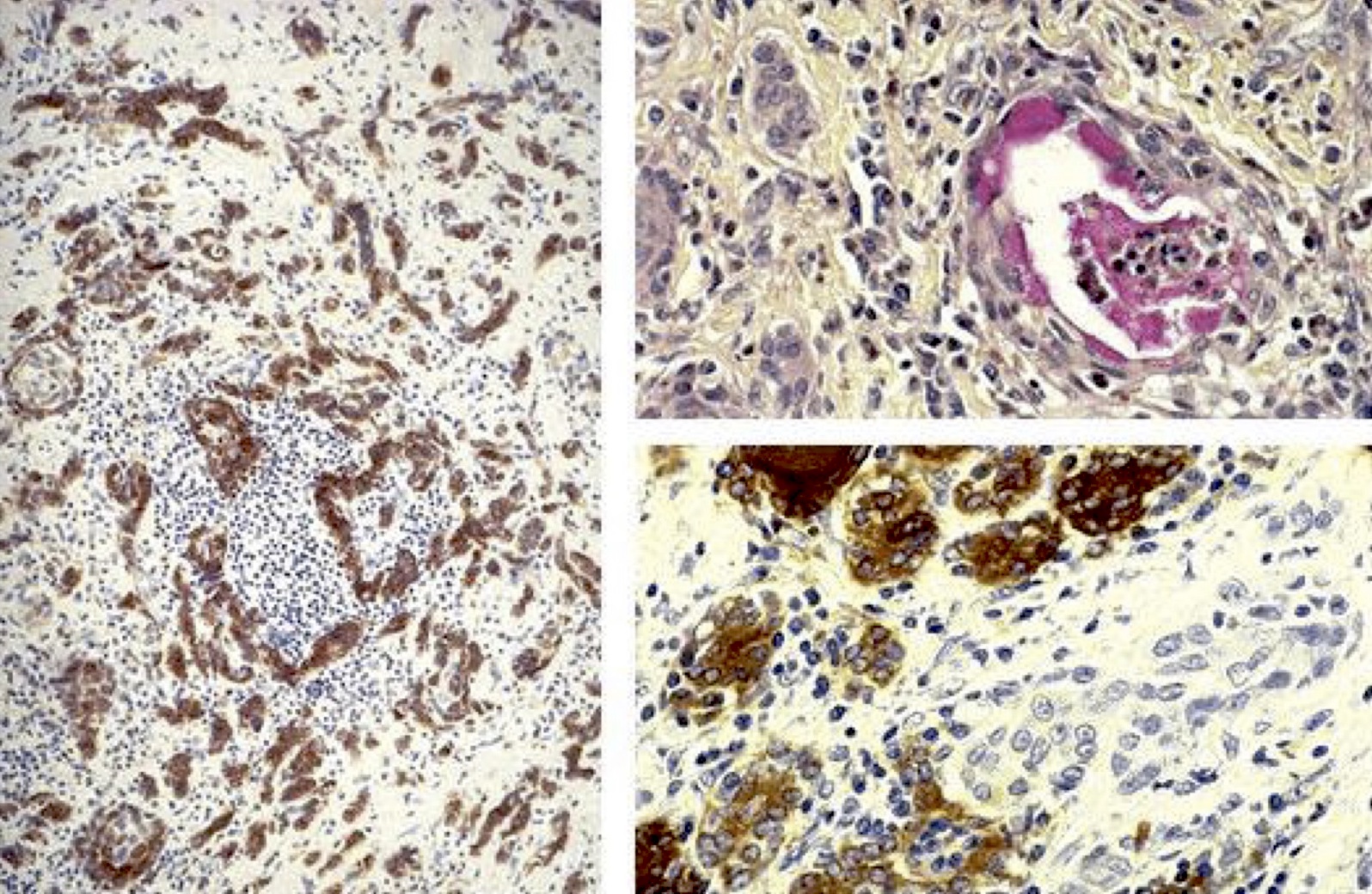
Microscopic (histologic) images
Differential diagnosis
- Carcinoma
- MALT lymphoma: (Pathol Oncol Res 2009;15:285)
- Riedel’s thyroiditis: adherence to adjacent structures with infiltration into nerve, fat, muscle and parathyroid glands; vasculitis; fibrous tissue is active proliferative type, residual thyroid tissue is relatively normal, phlebitis present (J Endocrinol Invest 2003;26:444, Histopathology 1983;7:739)