Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Zhao X, Wei S. Intrathyroidal thymic carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/thyroidcastle.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- A malignant epithelial tumor with thymic differentiation occurring within the thyroid gland (WHO 5th edition)
- Intrathyroidal (ectopic) thymic carcinoma (ITC)
- CArcinoma Showing Thymus-Like differentiation (CASTLE)
- Terminology first used in 1991 (Hum Pathol 1991;22:349)
- Terminology not recommended by WHO 5th edition
- Entity first described in 1985 (World J Surg 1985;9:128)
Essential features
- Invasive intrathyroidal (ectopic) thymic carcinoma located at the lower pole of thyroid
Terminology
- Acceptable: thymic carcinoma
- Not recommended: CD5 positive thyroid carcinoma; lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of the thyroid; intrathyroidal epithelial thymoma; primary thyroid thymoma; thyroid carcinoma showing thymus-like differentiation; intrathyroidal carcinoma showing thymus-like elements (CASTLE)
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8589/3 - carcinoma showing thymus-like element
Epidemiology
- Rare; < 0.15% of all thyroid malignancies (World J Surg 2018;42:1754)
- M:F = 1:1.3; mean age of 48.5 years (Case Rep Med 2016;2016:7962385)
Sites
- Commonly involves the lower pole of thyroid lobes or attached to the thyroid (WHO 5th edition)
Etiology
- Thought to arise in intra or perithyroidal thymic tissue, vestiges of thymopharngeal duct or branchial pouch remnants (including solid cell nests) (Endocrinol Metab (Seoul) 2020;35:696, Thyroid 2013;23:511)
- Higher prevalence in Asian countries suggests that genetic, ethnic or environmental factors may contribute to tumorigenesis (Oncol Lett 2016;11:1321)
Clinical features
- Presents with a slow growing neck mass with hard consistency and poor mobility
- Some may present with hoarseness due to recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis (Am J Clin Pathol 2007;127:230)
Diagnosis
- Clinical suspicion of thyroid mass followed by a fine needle aspiration may not reach a definitive diagnosis; a diagnosis can be rendered based on histologic examination on resected specimen
Radiology description
- Cold nodule on scintigraphy
- Ultrasound: solid, heterogenous and hypoechoic mass
- CT: well defined soft tissue density without calcification
- MRI: isointensity on T1 weighted images and hyperintensity on T2 weighted images
- Nodular masses located in the lower neck between the inferior pole of the thyroid and the upper mediastinum (Br J Radiol 2016;89:20150726)
Prognostic factors
- Good prognosis, with 5 year and 10 year survival of 90% and 82%; poorer prognosis if venus invasion, laryngeal nerve invasion, high proliferation index, extrathyroidal extension (Am J Clin Pathol 2007;127:230, Malays J Pathol 2020;42:259, Front Oncol 2018;8:477, Case Rep Med 2016;2016:7962385)
- Rare aggressive cases can occur; brain, liver and lungs are common metastatic sites (Hum Pathol 1991;22:349)
- Lymph node metastases are found at initial surgery in 40 - 50% of cases (Am J Clin Pathol 2007;127:230, Surg Today 2013;43:1261)
Case reports
- 38 year old woman with lenvatinib as salvage therapy in widely metastatic disease (Front Oncol 2022;12:923683)
- 58 year old woman with lung metastasis and carotid artery invasion (Ear Nose Throat J 2019;98:557)
- 60 year old woman status post thyroidectomy with recurrence after 5 years (Thyroid Res 2021;14:20)
- 66 year old man with complete remission after radiotherapy without resection (Strahlenther Onkol 2021;197:847)
Treatment
- Total thyroidectomy with selected neck dissection
- Adjuvant intensity modulated radiotherapy may improve locoregional control and survival (Endocr Relat Cancer 2021;28:593, Oncotarget 2016;7:81899)
- May respond to PDL1 inhibitor if high PDL1 expression in tumor cells (Front Oncol 2019;9:734)
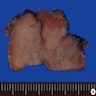
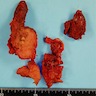
Gross description
- Well defined, solid, lobulated pink-white mass with hard texture, fibrous septa; usually lacking calcifications or cysts on cut surfaces
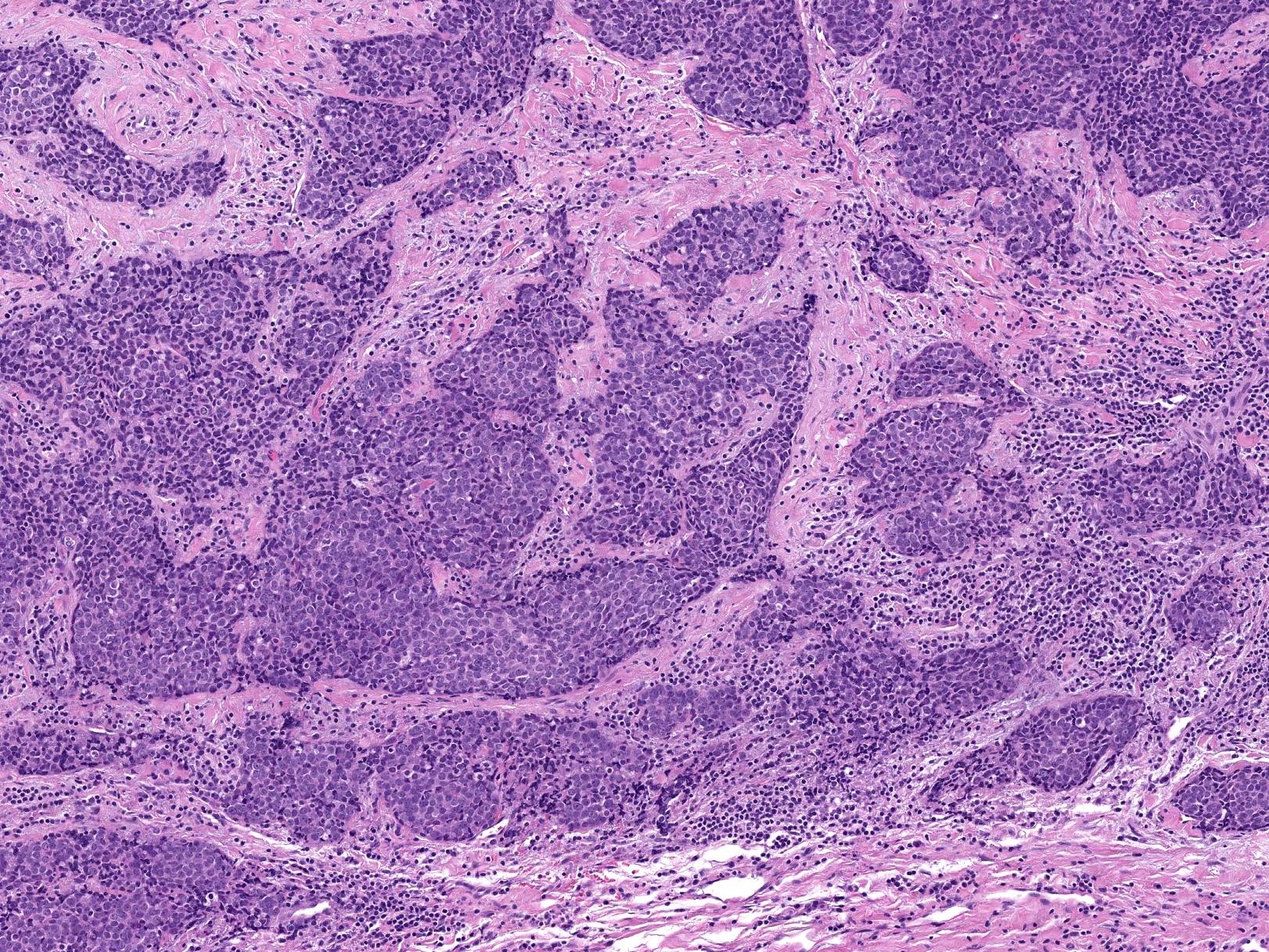
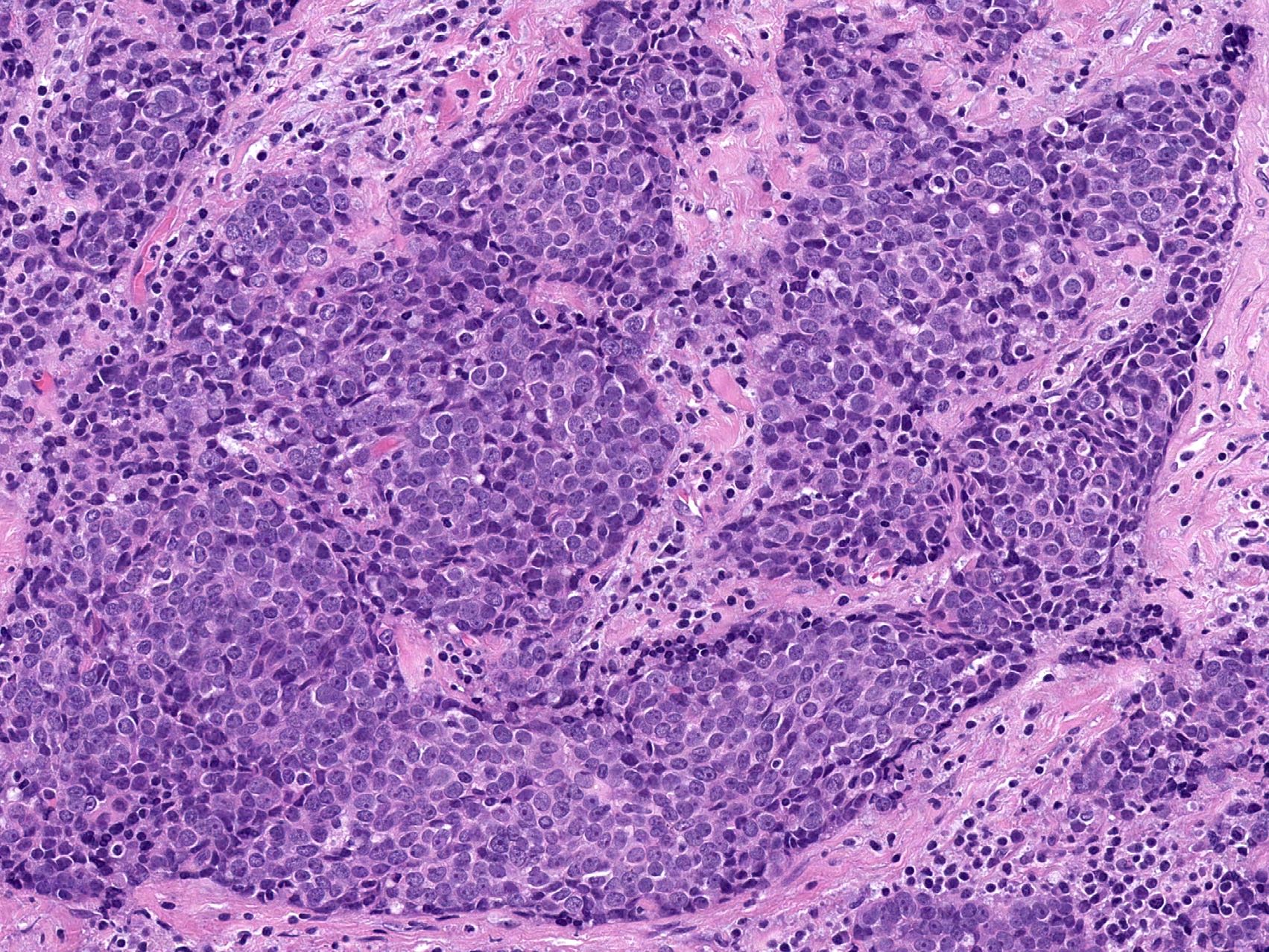
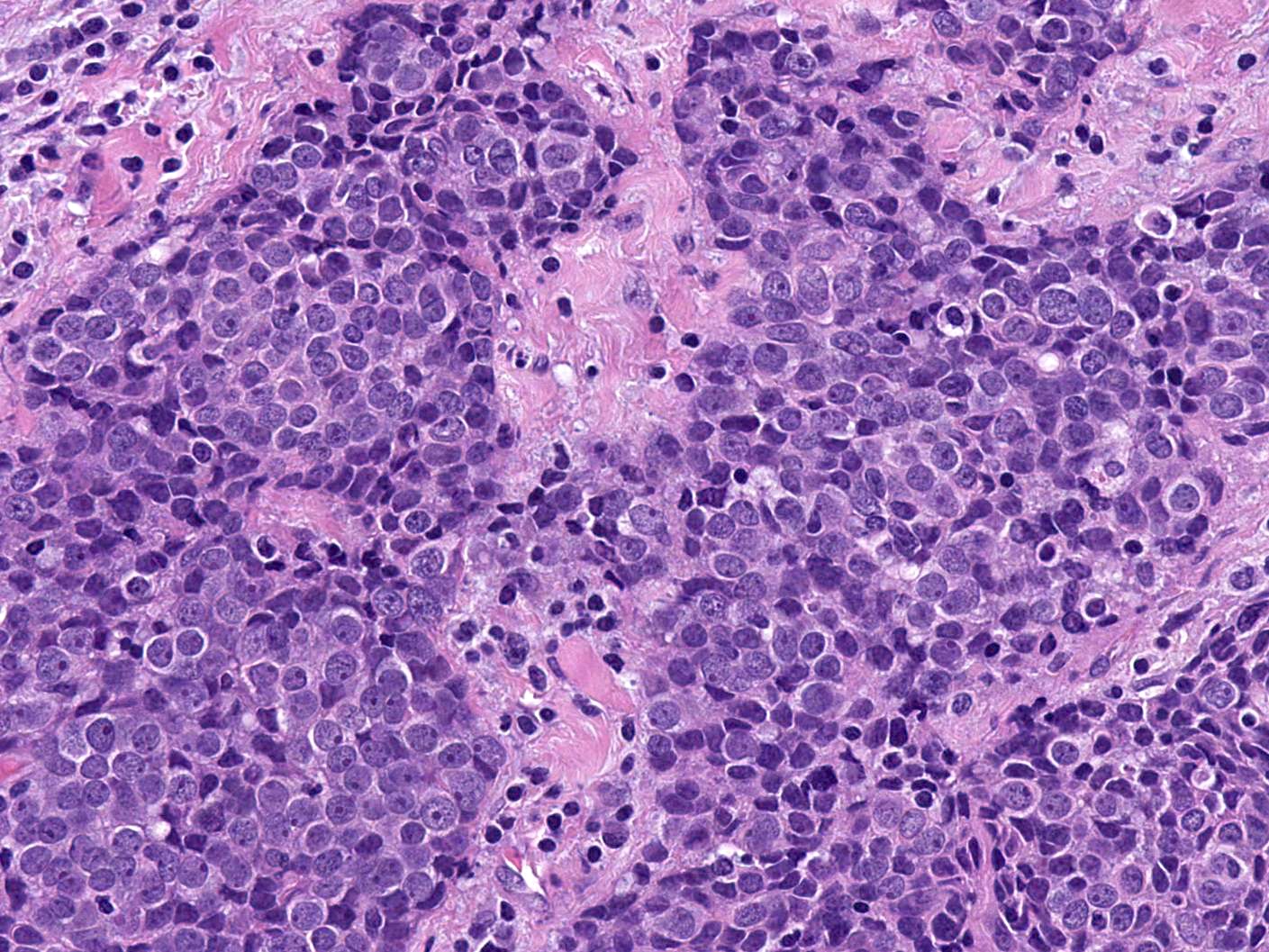
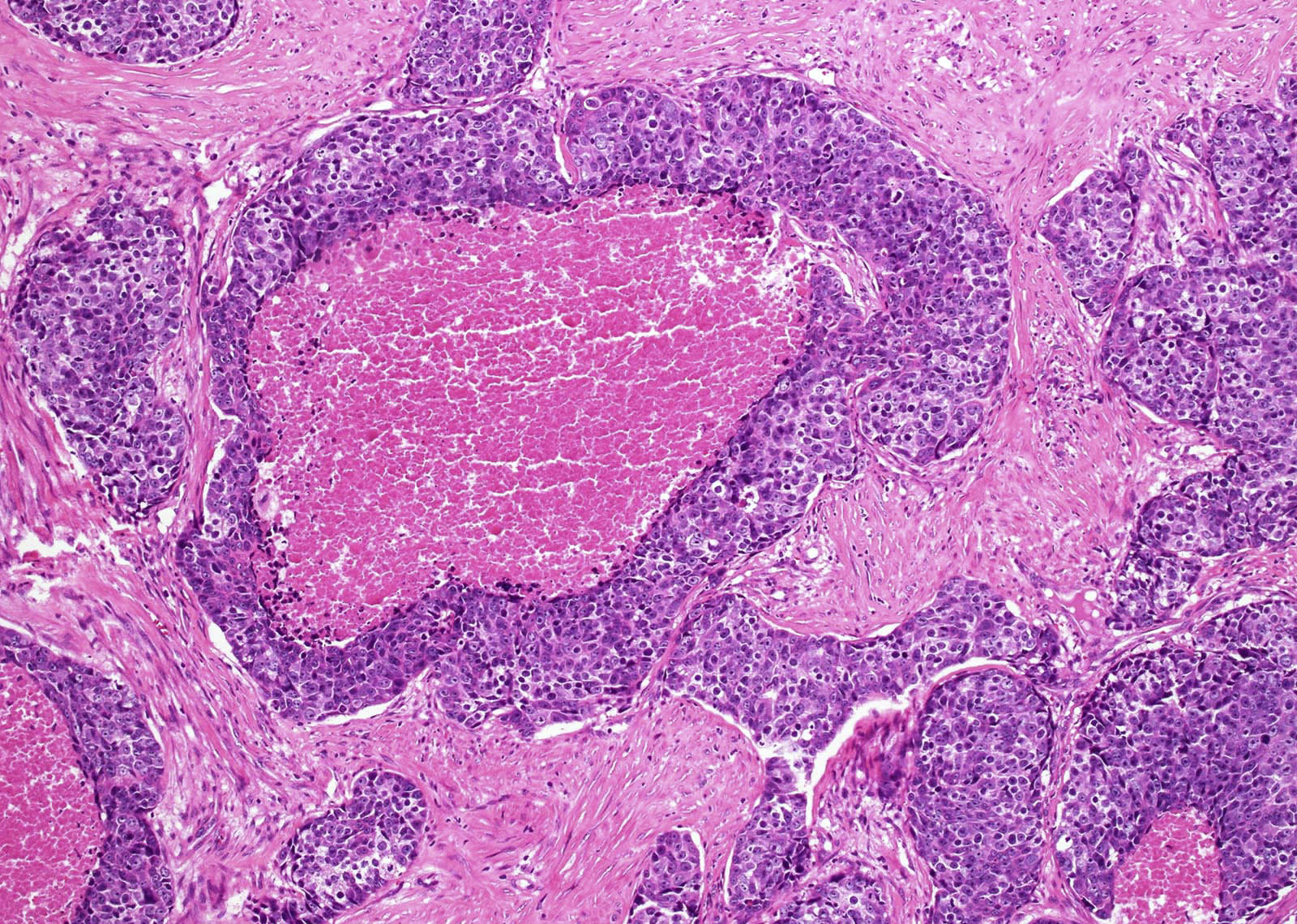
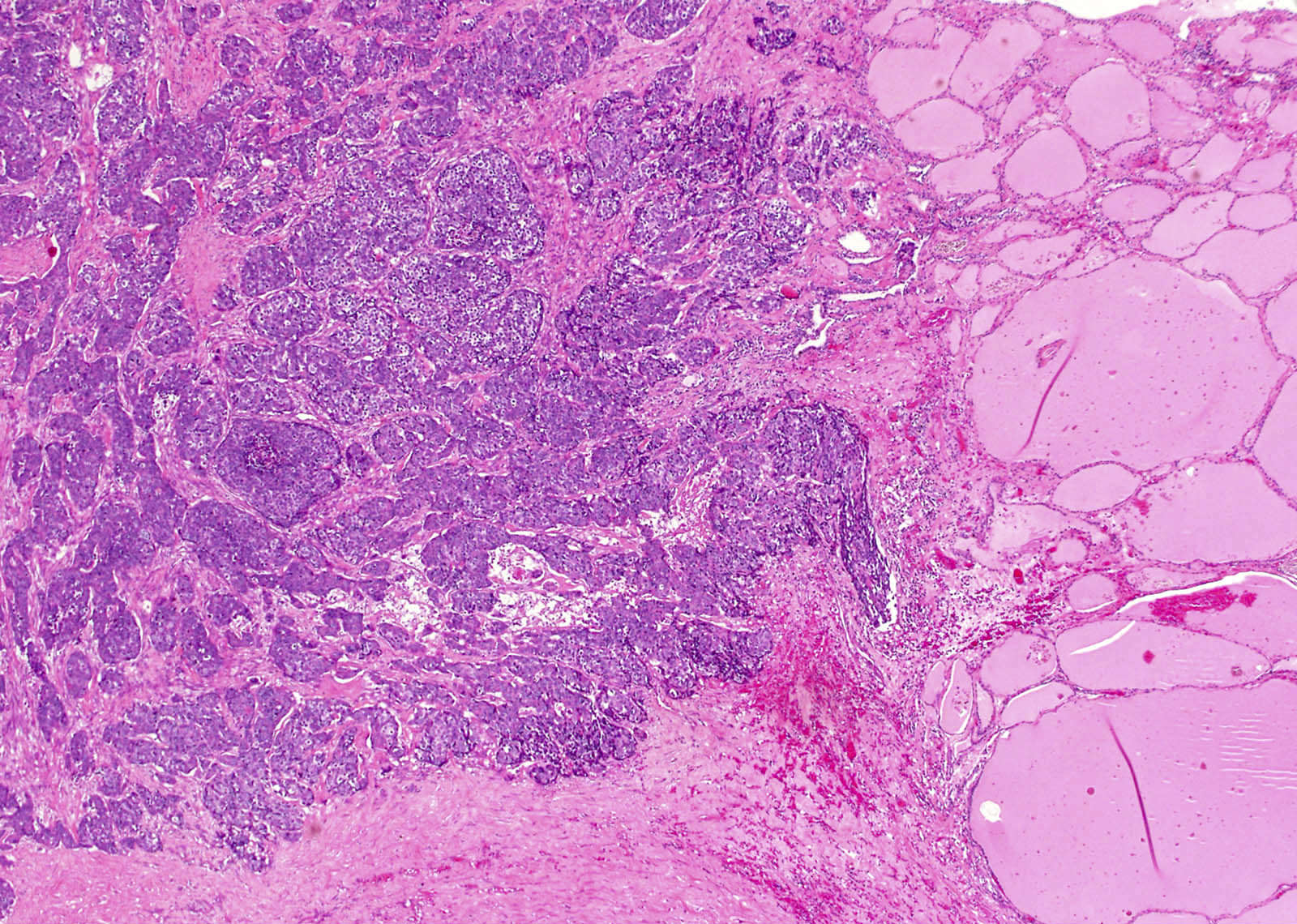
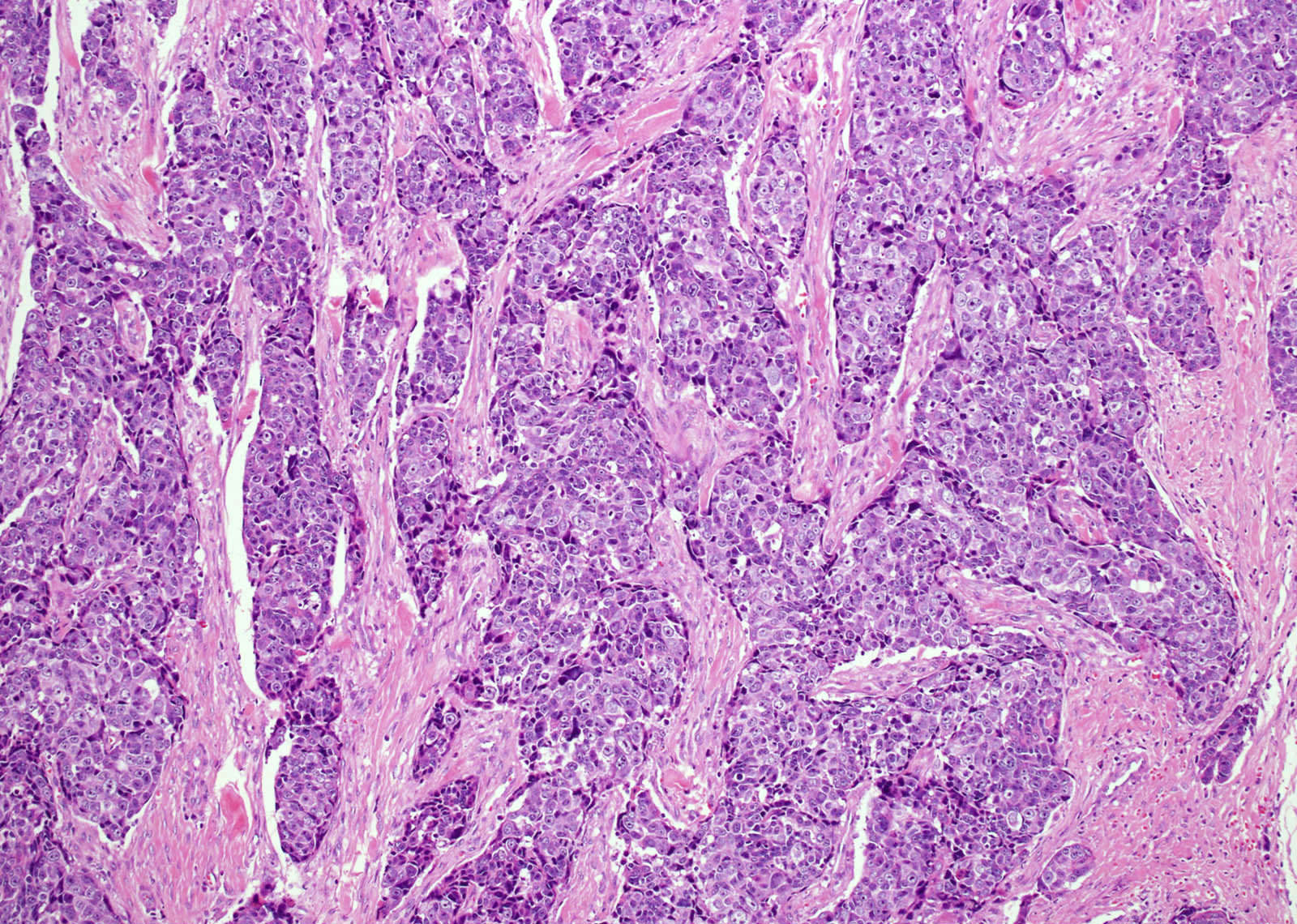
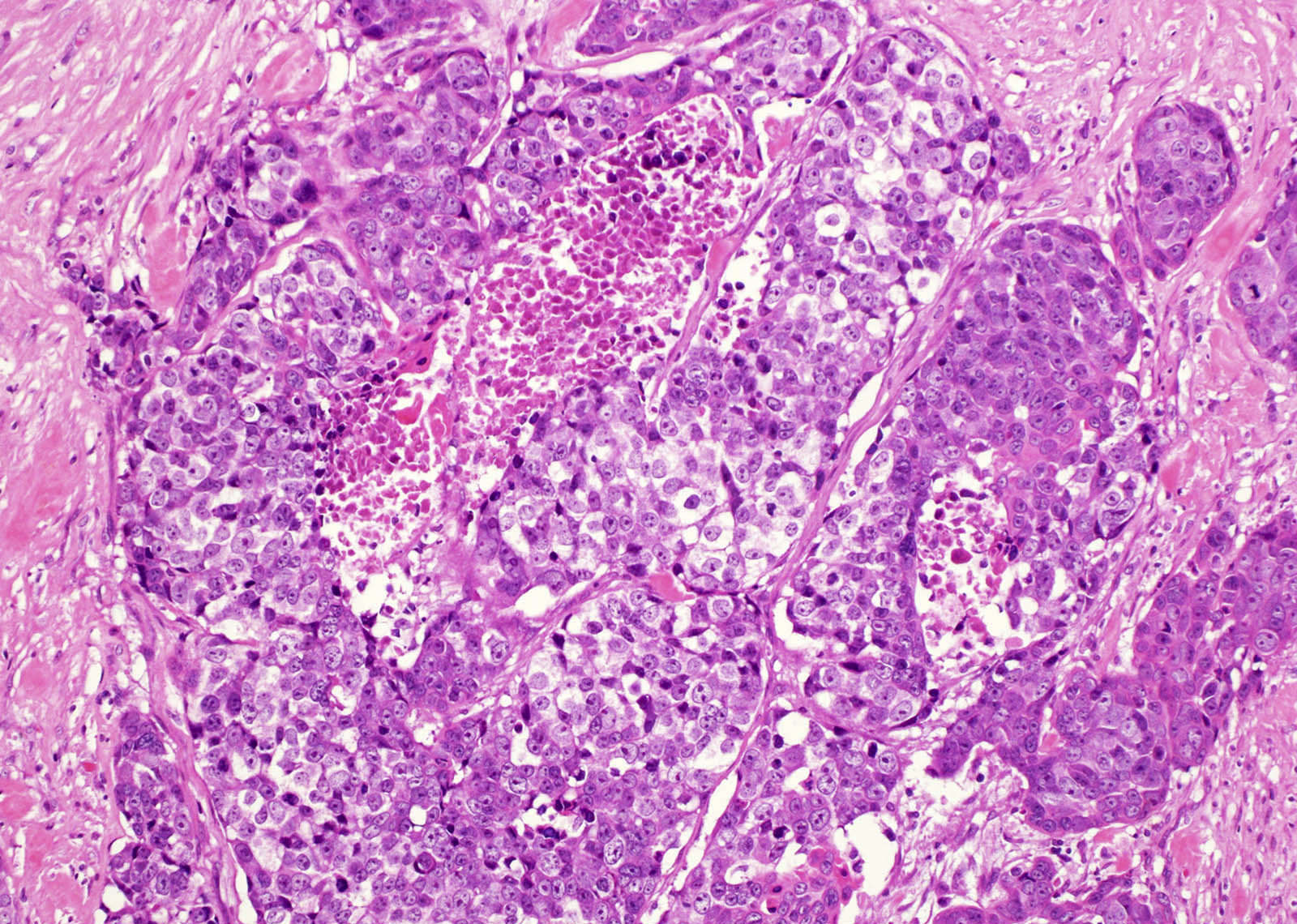
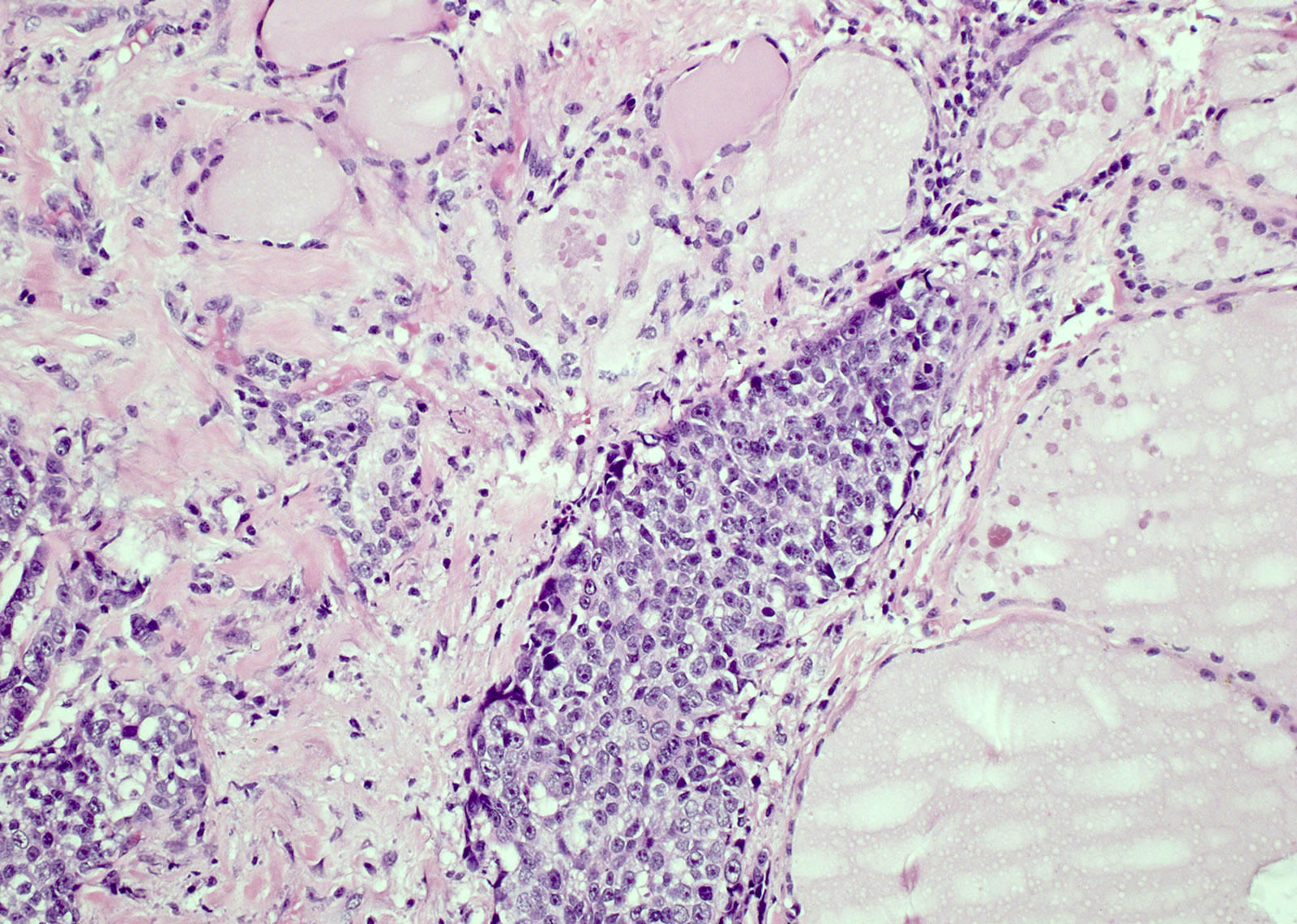
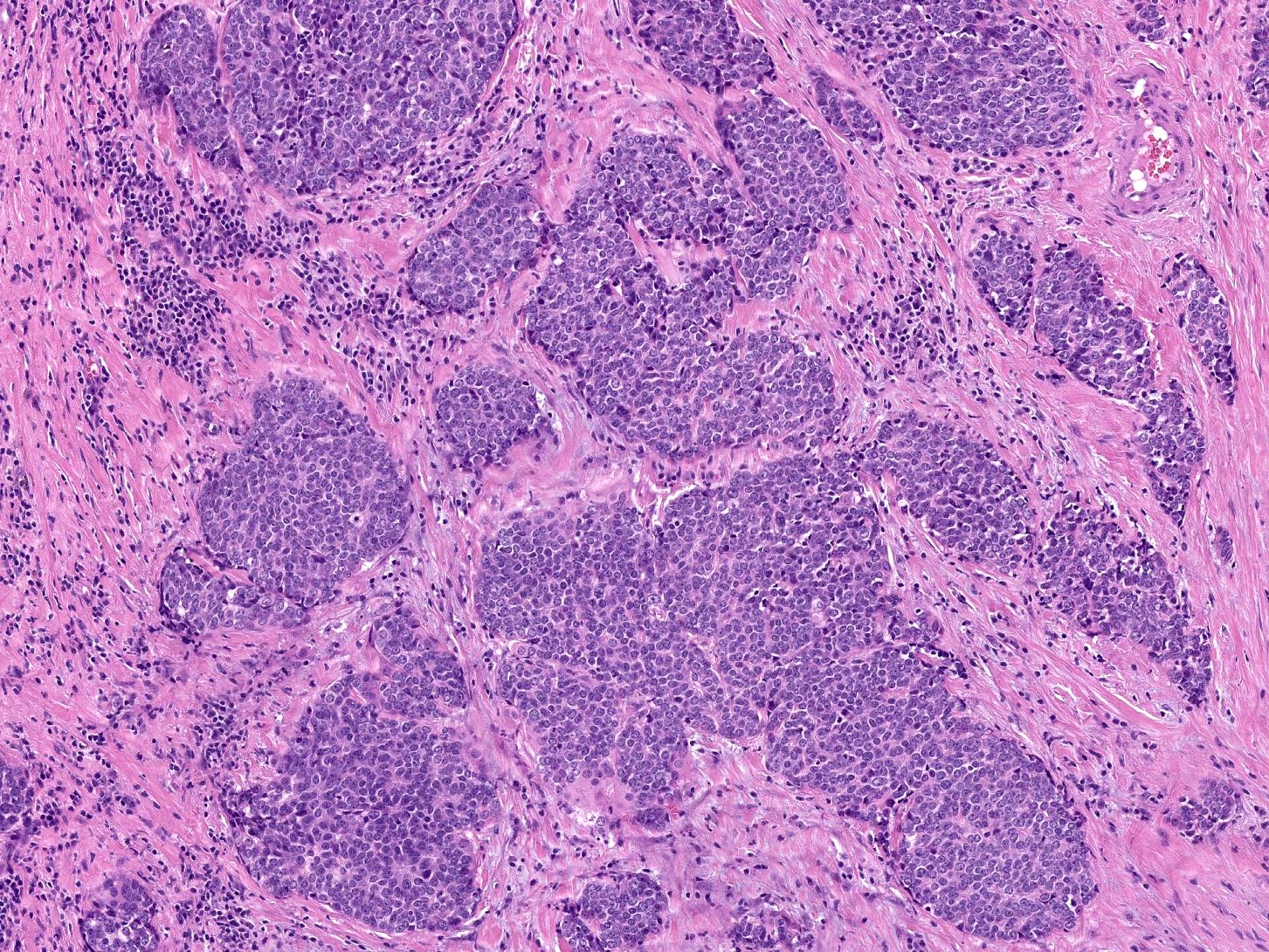
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Identical to those of thymic carcinoma of mediastinum (World J Surg 1985;9:128, Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:994, Hum Pathol 1991;22:349)
- Mostly similar to squamous cell carcinoma with lymphocyte rich stroma (Hum Pathol 1991;22:349)
- Fibrous bands separating variably sized solid islands / nests of squamoid or syncytial appearing tumor cells, with occasional single cell keratinization
- Variable lymphocytes (mixed mature T and B cells versus immature T cells in thymoma) and plasma cell infiltration
- Low mitotic count, Ki67 index of 10 - 30% (Surg Today 2013;43:1261)
Microscopic (histologic) images
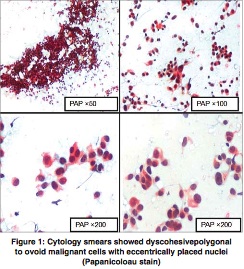
Cytology description
- Nonspecific; features favoring ITC include syncytial or 3 dimensional tissue fragments of round or spindly tumor cells with large nuclei, vesicular chromatin and prominent nucleoli in a background of lymphocytes (Acta Cytol 2016;60:421)
- Resembles nasopharyngeal carcinoma (Diagn Cytopathol 1996;15:224)
Cytology images
Positive stains
- Similar to thymic carcinoma: high molecular weight keratin, p63, p40, CK19, CD5, CD117, MCL1, CEA, GLUT1, polyclonal PAX8 (Am J Clin Pathol 2015;143:223)
- BCL2, calretinin, CEA and p53 (APMIS 2013;121:523)
- CD5 and CD117 staining of epithelial cells is highly suggestive
- Stromal lymphocytes: CD3, CD5 and CD20 (variable)
- Scattered cells can be positive for chromogranin or synaptophysin (APMIS 2013;121:523, Pathol Res Pract 2013;209:662)
Negative stains
- EBV, thyroglobulin, TTF1, calcitonin, amyloid, monoclonal PAX8 (World J Surg 2011;35:1840, Oncol Lett 2016;11:1321, Endocr J 2018;65:1171)
- Stromal lymphocytes: TdT, CD1a
Electron microscopy description
- Substantial tonofibril with abundant and well developed intercellular desmosomes, indicative of squamous differentiation (Histol Histopathol 2013;28:543)
- Neuroendocrine granules in some cases (Am J Clin Pathol 2015;143:223)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Similar to thymomas and thymic carcinomas, gains on chromosomal arm 1q and losses on 6p, 6q and 16q are frequent chromosomal imbalances (Virchows Arch 2011;459:221)
- EGFR gene amplification and EGFR gene mutations in exon 20 (p.T790M) and exon 21 (p.R841K) were identified in some cases by FISH (Diagn Cytopathol 2018;46:413, Endocr Pathol 2020;31:274)
- No mutations in c-kit identified despite c-kit / CD117 immunohistochemistry positivity (Am J Clin Pathol 2015;143:223)
- TERT promoter mutation has been identified in some cases (Endocr Pathol 2020;31:274)
- Higher mutation rates for N4BP1 and many genetic alterations were related to the NFkB signaling pathway (Virchows Arch 2023;482:813)
Sample pathology report
- Thyroid, total thyroidectomy:
- Intrathyroidal thymic carcinoma, 1.2 cm, confined to the thyroid (see comment)
- No lymphovascular invasion
- Negative margins
- Comment: Immunohistochemistry performed on block 1A with adequate controls show that the tumor cells are positive for p63, CD5 and CD117 and negative for thyroglobulin and TTF1. The findings support the diagnosis above.
Differential diagnosis
- Anaplastic carcinoma with squamous component:
- Squamous cell carcinoma:
- Poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma:
- TTF1 and thyroglobulin usually positive; CD5, CD117 and squamoid markers usually negative
- Often a component of well differentiated thyroid carcinoma
- Adamantinoma-like Ewing sarcoma (Head Neck Pathol 2022;16:679):
- Neuroendocrine carcinomas, including Merkel cell carcinoma and medullary thyroid carcinoma:
- Positive for neuroendocrine markers; negative for squamoid markers
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 40 year old man presented with a mass in the left lower pole of the thyroid. The tumor is shown in the photomicrograph above. The tumor is positive for p63, CD5 and CD117 and negative for thyroglobulin and TTF1. Which of the following is most likely the correct diagnosis?
- Follicular carcinoma
- Intrathyroidal thymic carcinoma
- Medullary carcinoma
- Papillary carcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma
Board review style answer #1
B. Intrathyroidal thymic carcinoma. Intrathyroidal thymic carcinoma often involves the lower pole of thyroid lobes with nests of squamoid epithelial cells, scattered lymphocytes and fibrous bands, along with typical immunohistochemistry phenotype. Answers A, C and D are incorrect because the morphology and immunoprofile are not consistent with this diagnosis. Answer E is incorrect because the immunoprofile shows thymic differentiation.
Comment Here
Reference: Intrathyroidal thymic carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Intrathyroidal thymic carcinoma
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is true about intrathyroidal thymic carcinoma?
- CD5 in intrathyroidal thymic carcinoma only highlights the lymphocytes
- Most commonly located in upper pole of thyroid
- Most patients have a poor prognosis and die from this tumor
- Nests of squamoid cells with lymphocyte infiltrate is the key microscopic feature
- Polyclonal PAX8 can be used to distinguish from thyroid carcinoma
Board review style answer #2
D. Nests of squamoid cells with lymphocyte infiltrate is the key microscopic feature of intrathyroidal thymic carcinoma. Answer A is incorrect because CD5 also highlights the epithelial cells, which is a feature of thymic differentiation.
Answer B is incorrect because intrathyroidal thymic carcinoma commonly involves the lower pole of thyroid lobes or attached to the thyroid.
Answer C is incorrect because intrathyroidal thymic carcinoma has relatively good prognosis, with 5 year and 10 year survival of 90% and 82%.
Answer E is incorrect because intrathyroidal thymic carcinoma arising from the intrathyroidal ectopic thymus also exhibits moderate to strong nuclear reactivity for polyclonal PAX8; thus, this cannot be used to distinguish from thyroid carcinoma. Monoclonal PAX8 was reported to be negative in intrathyroidal thymic carcinoma (Endocr J 2018;65:1171).
Comment Here
Reference: Intrathyroidal thymic carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Intrathyroidal thymic carcinoma