Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Clinical images | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Bychkov A. Calcification. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/thyroidcalcification.html. Accessed December 20th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Deposition of calcium salts in thyroid gland
- More important to radiologists than pathologists
Epidemiology
- Prevalence in thyroidectomy specimens is 15% (Head Neck 2002;24:651)
- Found by ultrasound in 8% of benign (multinodular goiter) and 26% of malignant nodules (Head Neck 2002;24:651)
- Increases with advancing age
Sites
- Retrosternal thyroid / goiter tends to be calcified more heavily
Pathophysiology
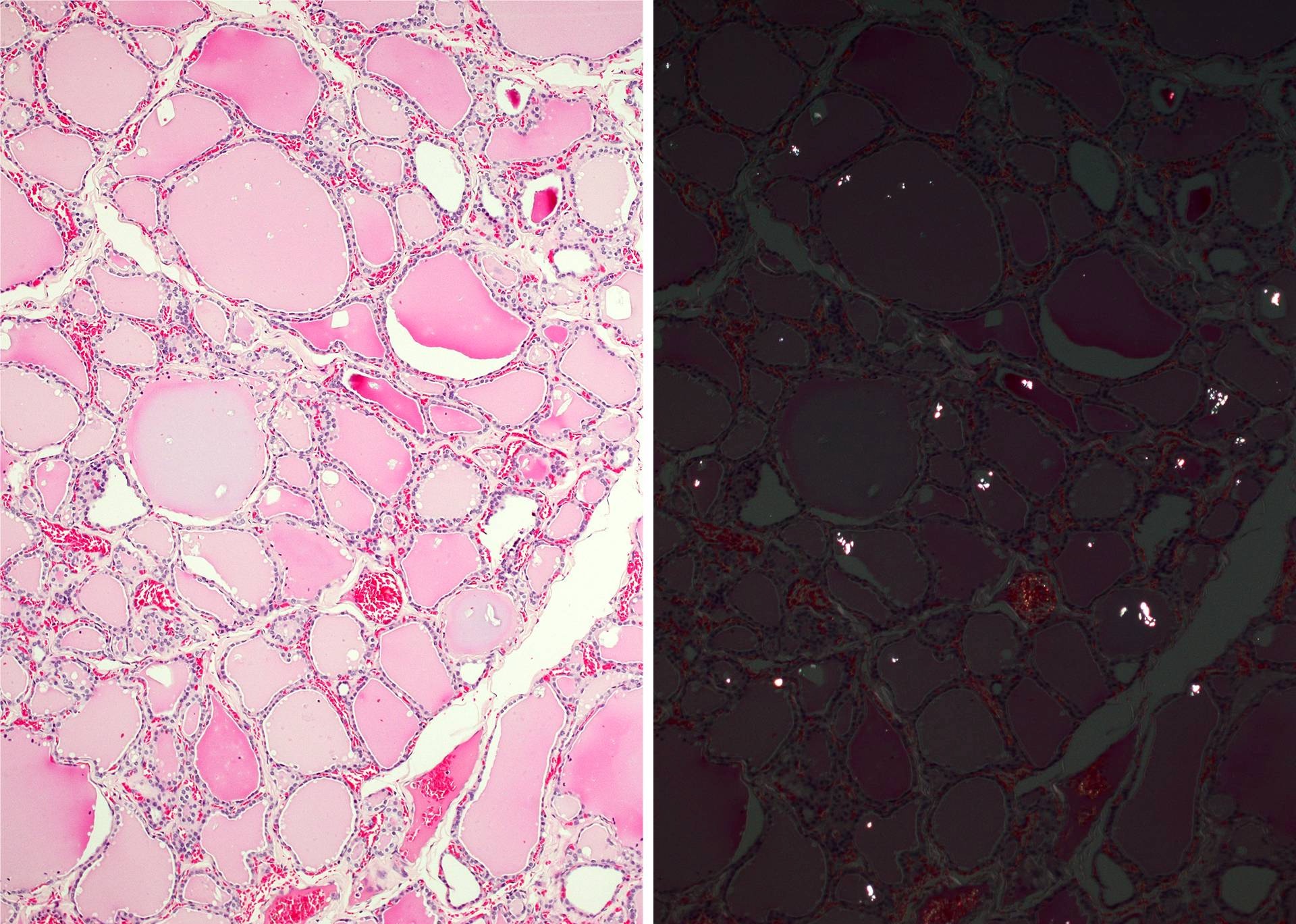
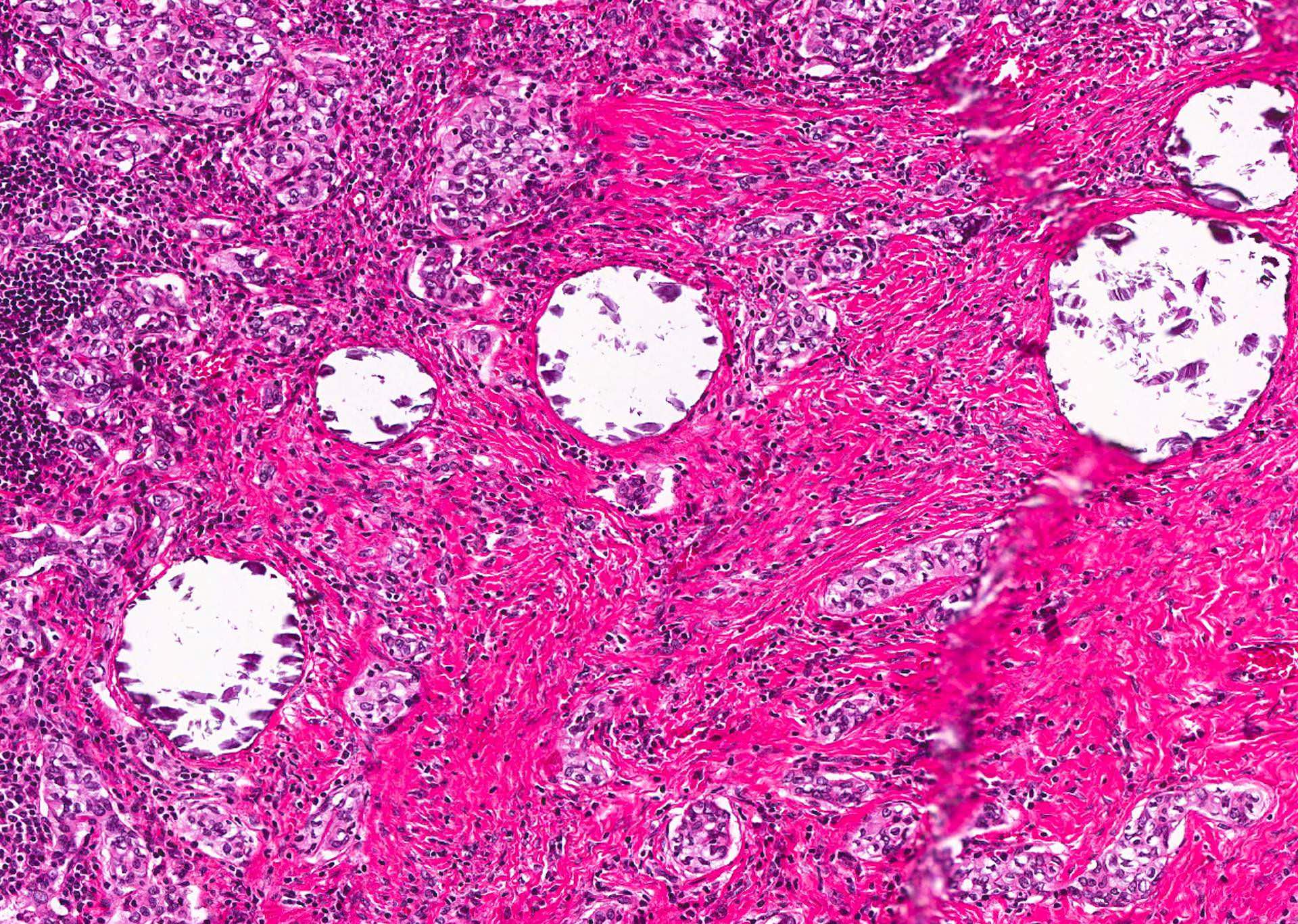
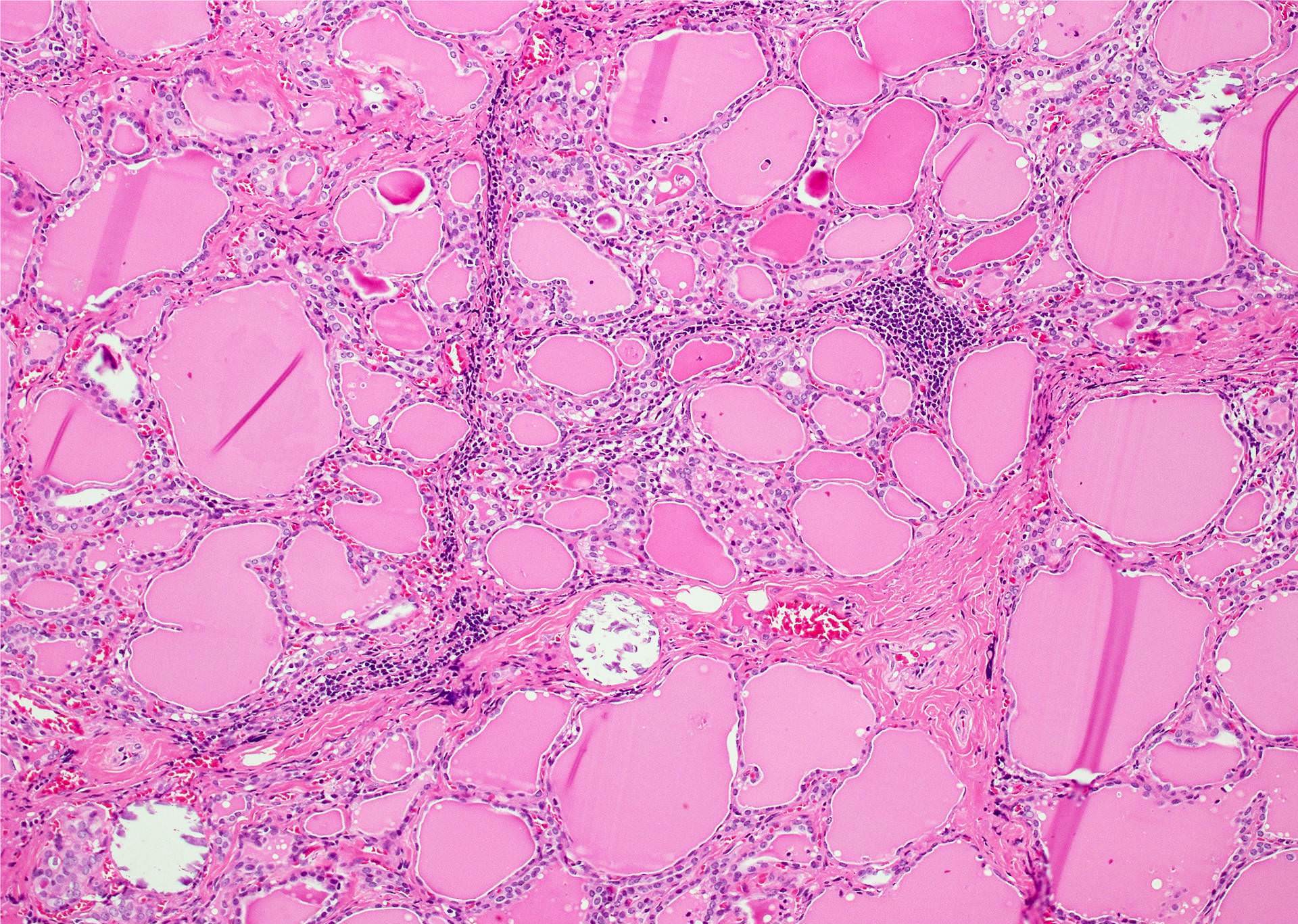
- Dystrophic calcification of thyroid results from degenerative changes (calcified colloid and degenerated epithelium, psammoma bodies, old hemorrhage, vessel wall, etc.)
- Metastatic calcification is caused by elevated blood calcium / phosphate
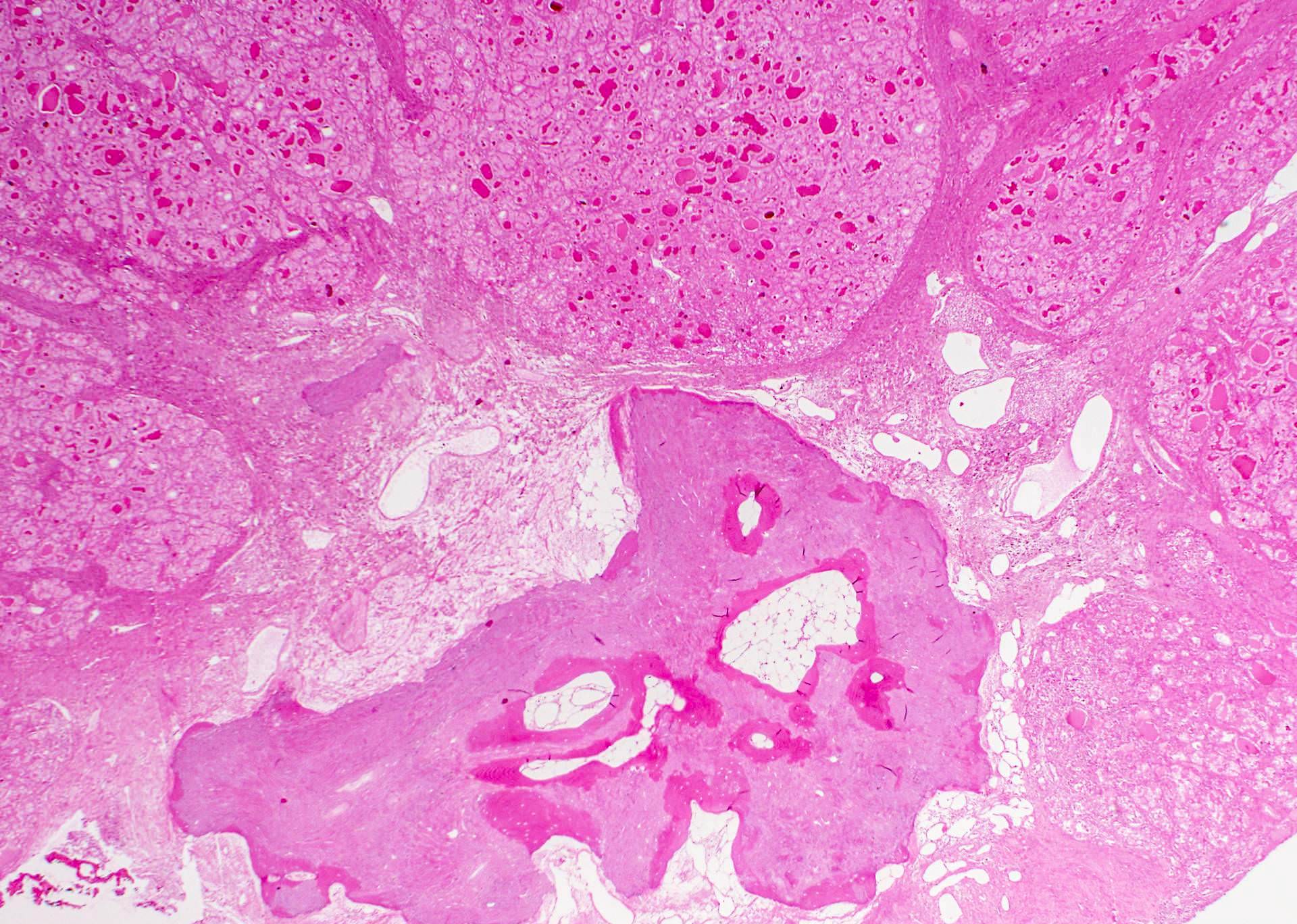
- Stromal calcification may progress to bone formation (Mod Pathol 2009;22:887)
Diagnosis
- Core needle biopsy is superior to FNA for thyroid nodules with macrocalcification (Thyroid 2015;25:657)
Laboratory
- Hypercalcemia due to hyperparathyroidism, in rare cases of metastatic calcification
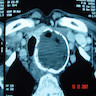
Radiology description
- Microcalcifications (< 2 mm and without acoustic shadow by ultrasound) in thyroid nodules are usually psammoma bodies
- Macrocalcifications (≥ 2 mm and with acoustic shadow) are secondary to tumor necrosis and can be seen in both benign and malignant nodules
- Peripheral (eggshell) calcifications surrounding the nodule are secondary to chronic degenerative changes
- Various patterns of calcification may be observed on Xray: nodular, flat, curvilinear, cloudy and a mixed type (Clin Radiol 1981;32:571)
Prognostic factors
- Microcalcification due to psammoma bodies is a strong predictor of thyroid carcinoma (Head Neck 2002;24:651, J Int Med Res 2012;40:350), but the association of macrocalcifications with malignancy is controversial (Thyroid 2013;23:1106)
Case reports
- 41, 49 and 72 year old women with osseous metaplasia and mature bone formation (Oncol Lett 2013;6:977)
- 49 year old woman with long standing goiter (Minerva Endocrinol 2000;25:81)
- 67 year old man with eggshell calcification (Cases J 2008;1:11)
- 74 year old man with metastatic calcification (J Nucl Med 1986;27:373)
- Unusual calcification in mixed papillary and follicular carcinoma (Radiology 1976;119:554)
- Association with hypothyroidism (Clin Radiol 1992;45:209)
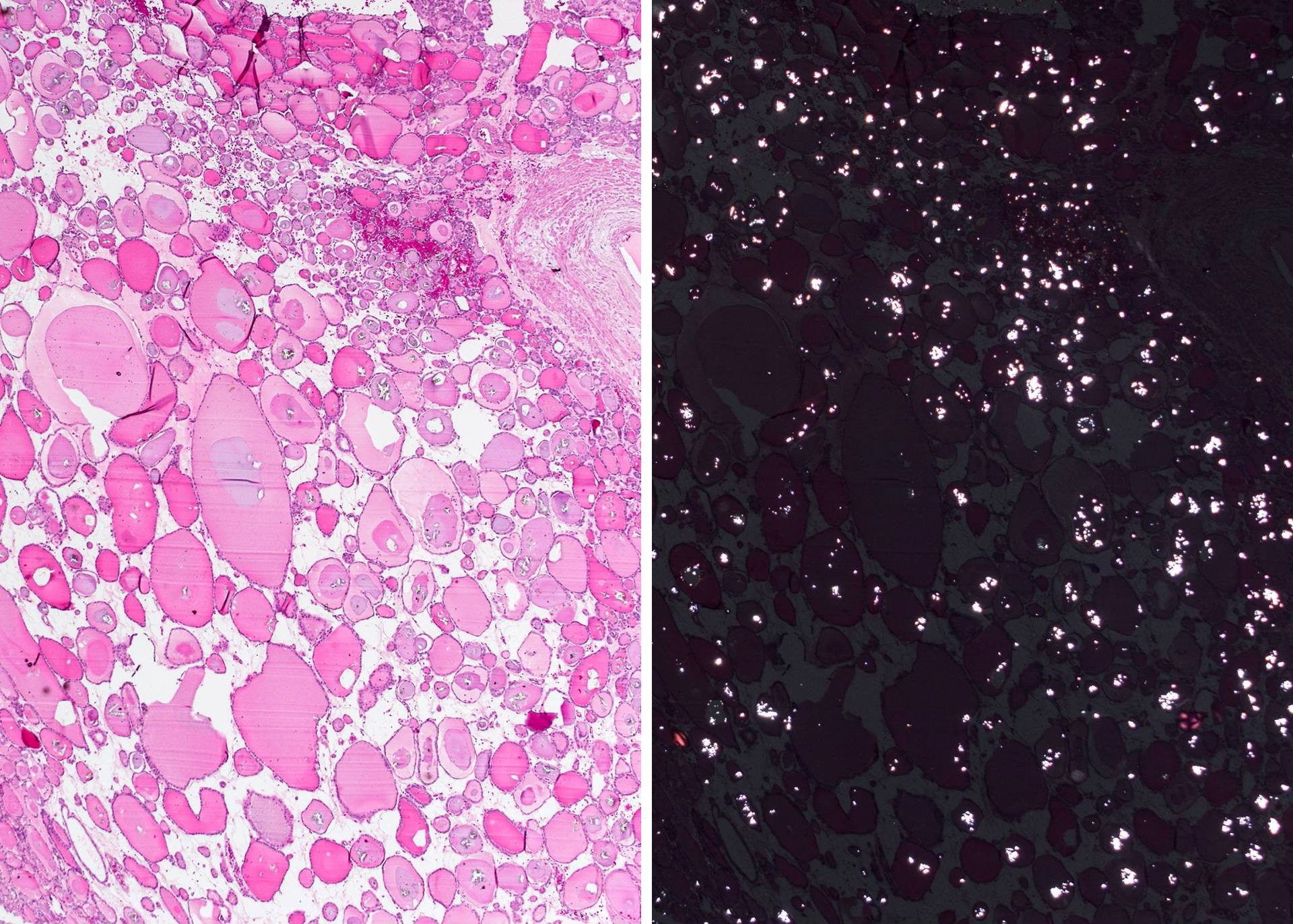
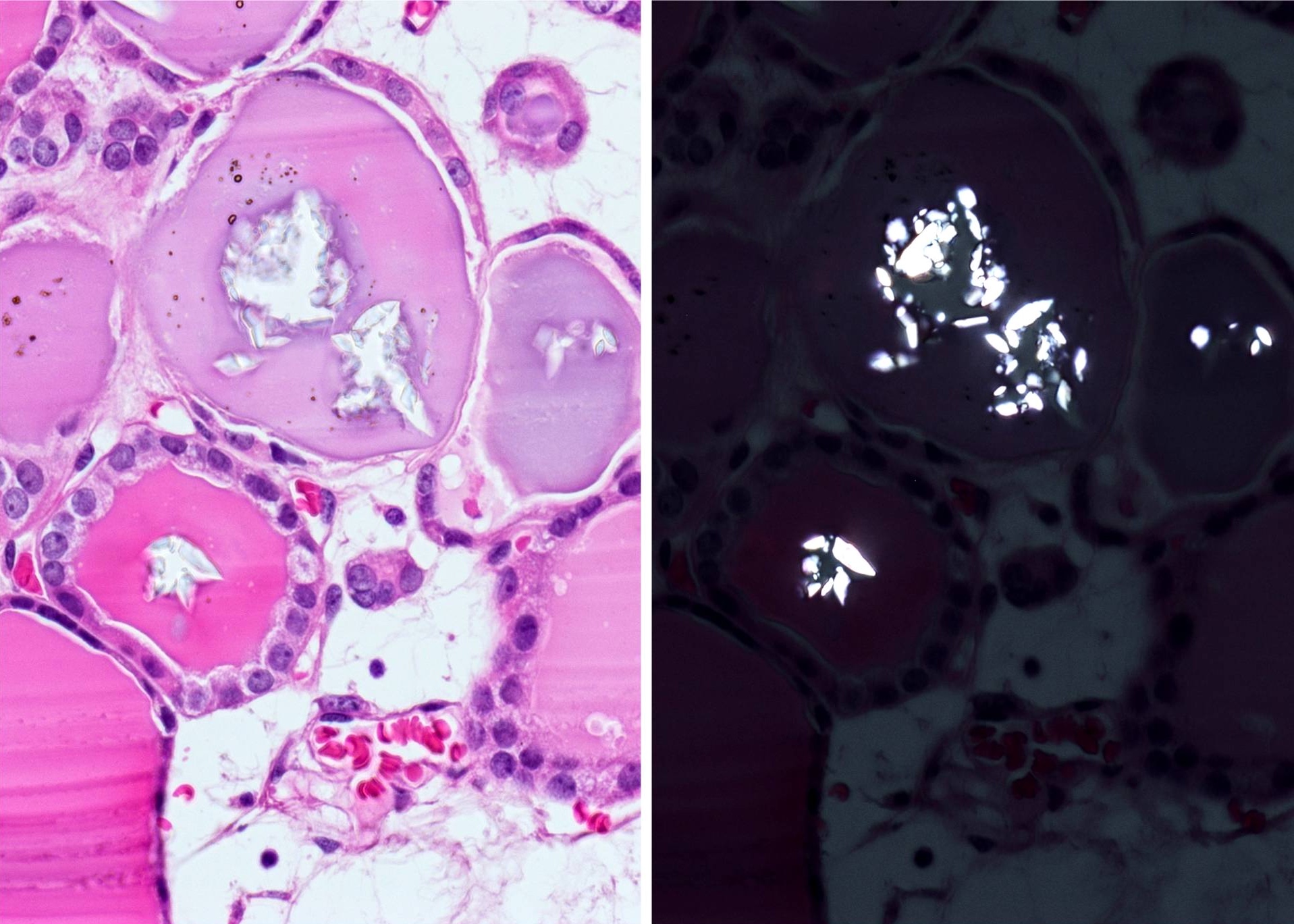
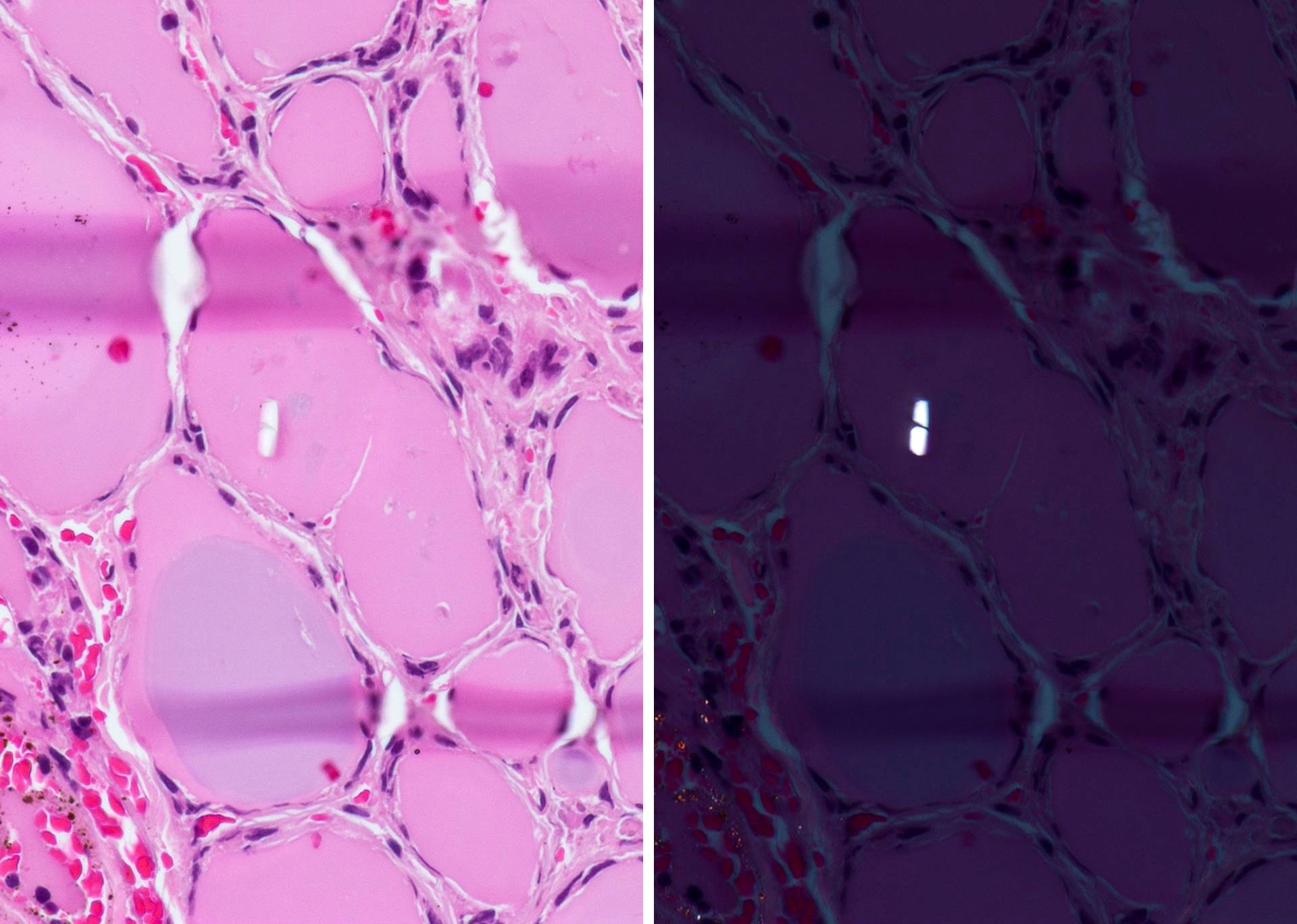
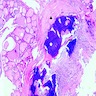
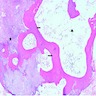
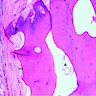
Microscopic (histologic) images
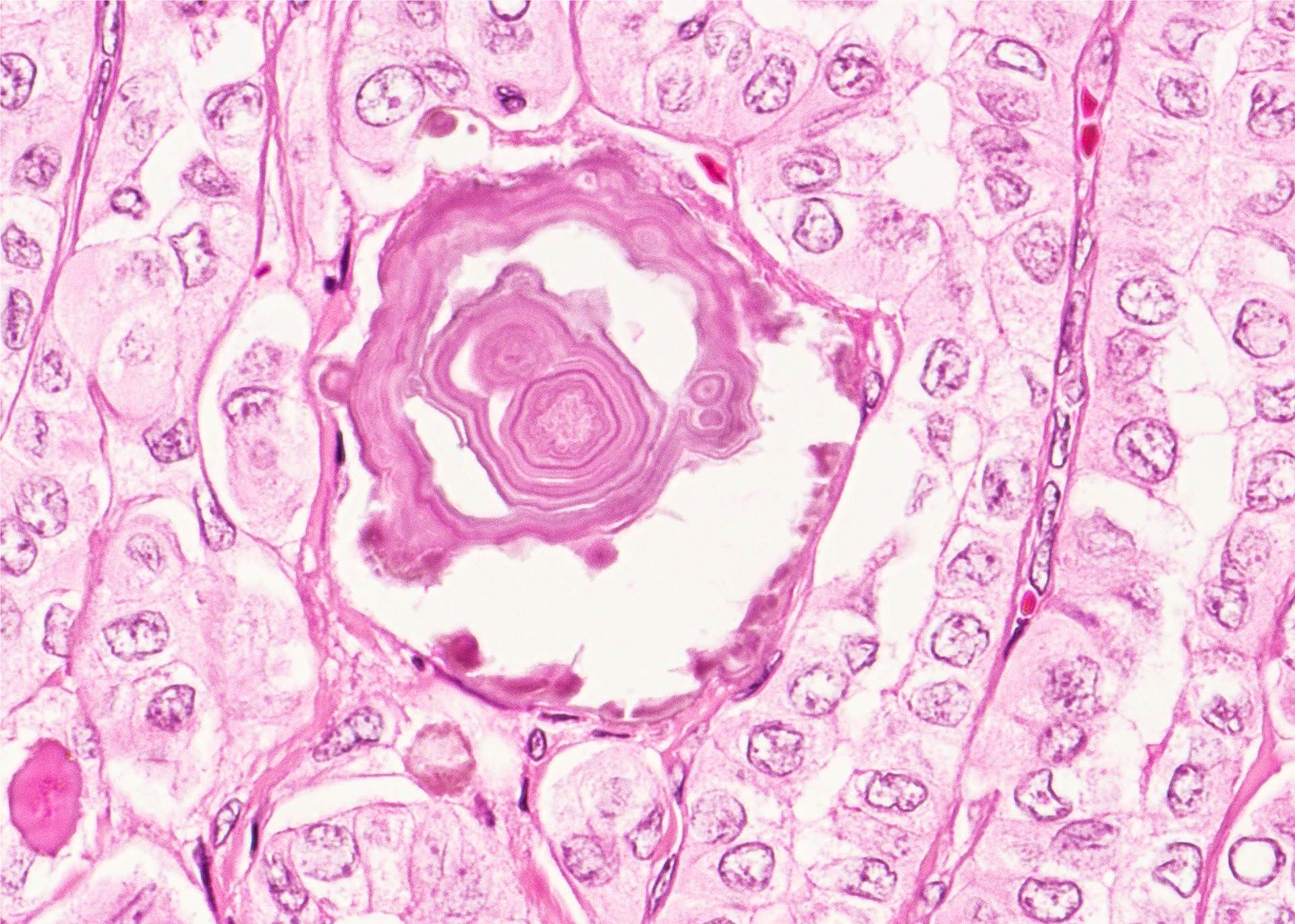
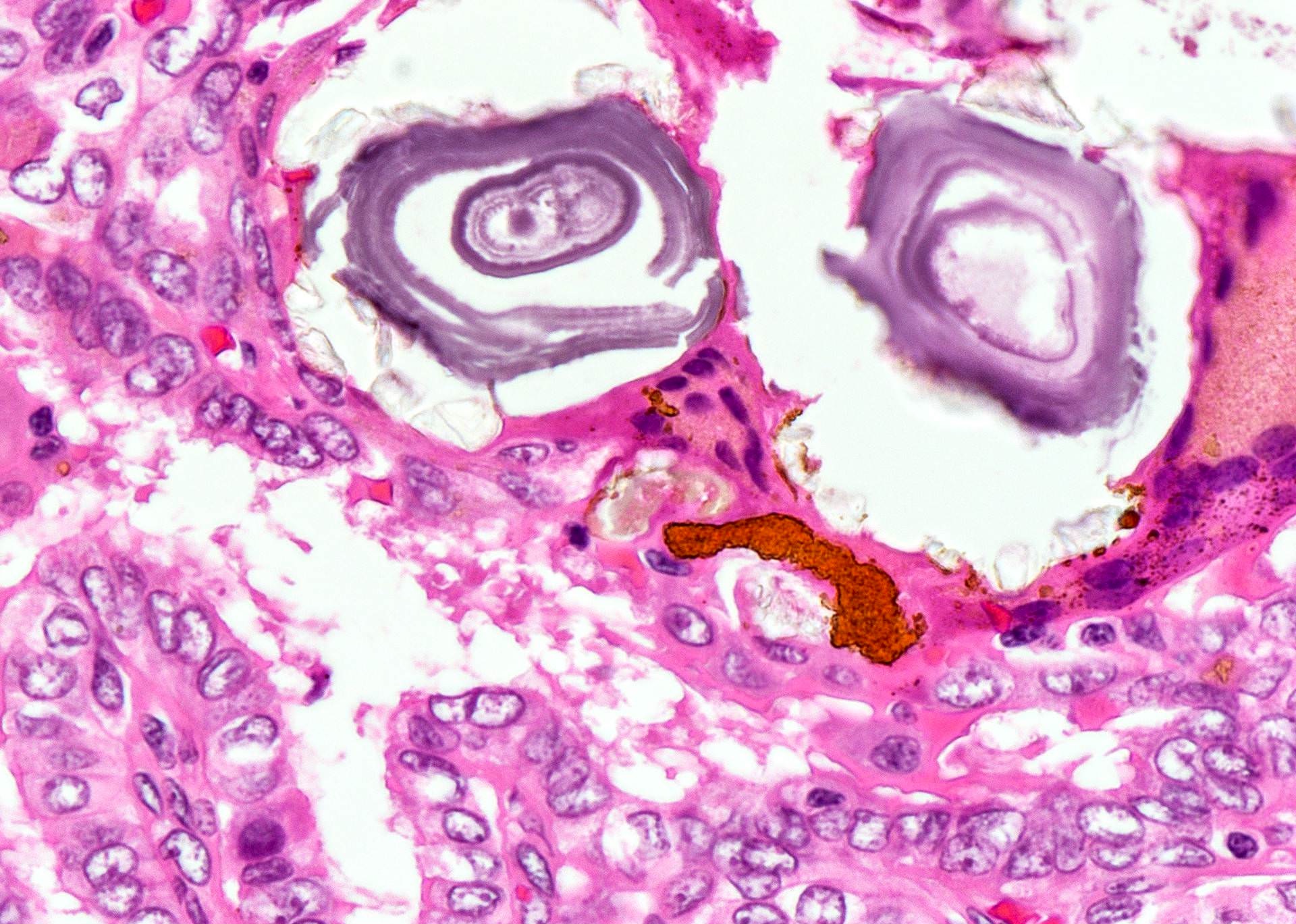
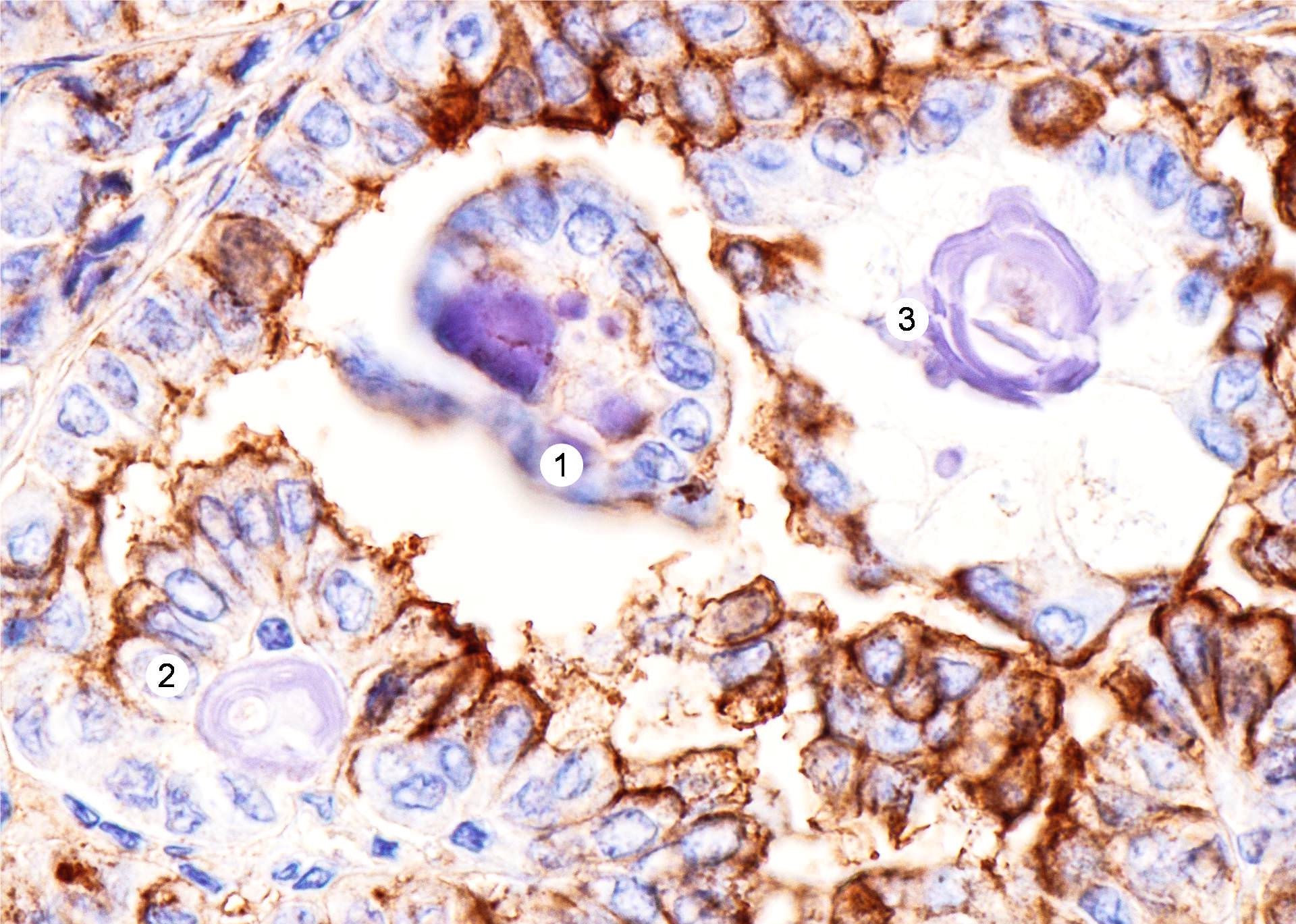
Contributed by Andrey Bychkov, M.D., Ph.D.
Images hosted on other servers:
Positive stains
Differential diagnosis
- Psammoma bodies are highly specific for papillary thyroid carcinoma, but should be differentiated from dystrophic stromal calcifications and inspissated colloid, both of which lack concentric laminations
- Thyroid calcium oxalate crystals