Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Epidemiology | Clinical features | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Wei S. Squamous cell carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/thyroidSCC.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Considered a variant of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma in the 2022 WHO
- Very rare, highly lethal thyroid carcinoma with pure squamous component
- Clinically and pathologically shares features with anaplastic thyroid cancers; can be regarded as a variant of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma
- Must rule out:
- Metastasis or direct invasion of squamous cell carcinoma from oropharynx, larynx, trachea, lung, other organs
- Papillary carcinoma with foci of squamous differentiation (occurs in 15 to 45% of papillary carcinomas)
- Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma with squamous differentiation
- Other thyroid carcinomas with squamous differentiation, including mucoepidermoid carcinoma, sclerosing mucoepidermoid carcinoma with eosinophilia, CASTLE
Essential features
- Squamous cell carcinoma is regarded as a variant of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma
- Aggressive clinical behavior
Epidemiology
- Similar to anaplastic carcinoma, affects older patients with chronic goiter
Clinical features
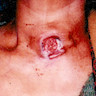
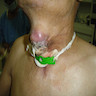
- Older patients present with a rapidly enlarging neck mass
- Patients may have a long history of preexisting thyroid disease
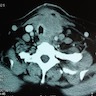
- Extrathyroidal extension and cervical nodal metastases are common, distant metastases are rare
Prognostic factors
- Poor prognosis with median survival < 6 months
- Death in almost all cases, usually due to local progression (Int Semin Surg Oncol 2007;4:8) or airway compression
Case reports
- Teenage girl with Hashimoto thyroiditis (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2006;9:496)
- 49 year old woman without coexisting thyroid carcinoma (Case Rep Pathol 2015;2015:838079)
- 65 year old woman with a 20 year history of thyroid goiter (J Surg Case Rep 2014 Dec 8;2014(12))
- 66 year old man with hypercalcemia and leukocytosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1987;111:373)
Treatment
- Radical resection and radiation (often radioresistant)
Clinical images
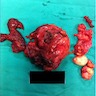
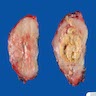
Gross description
- Firm infiltrating mass with necrosis
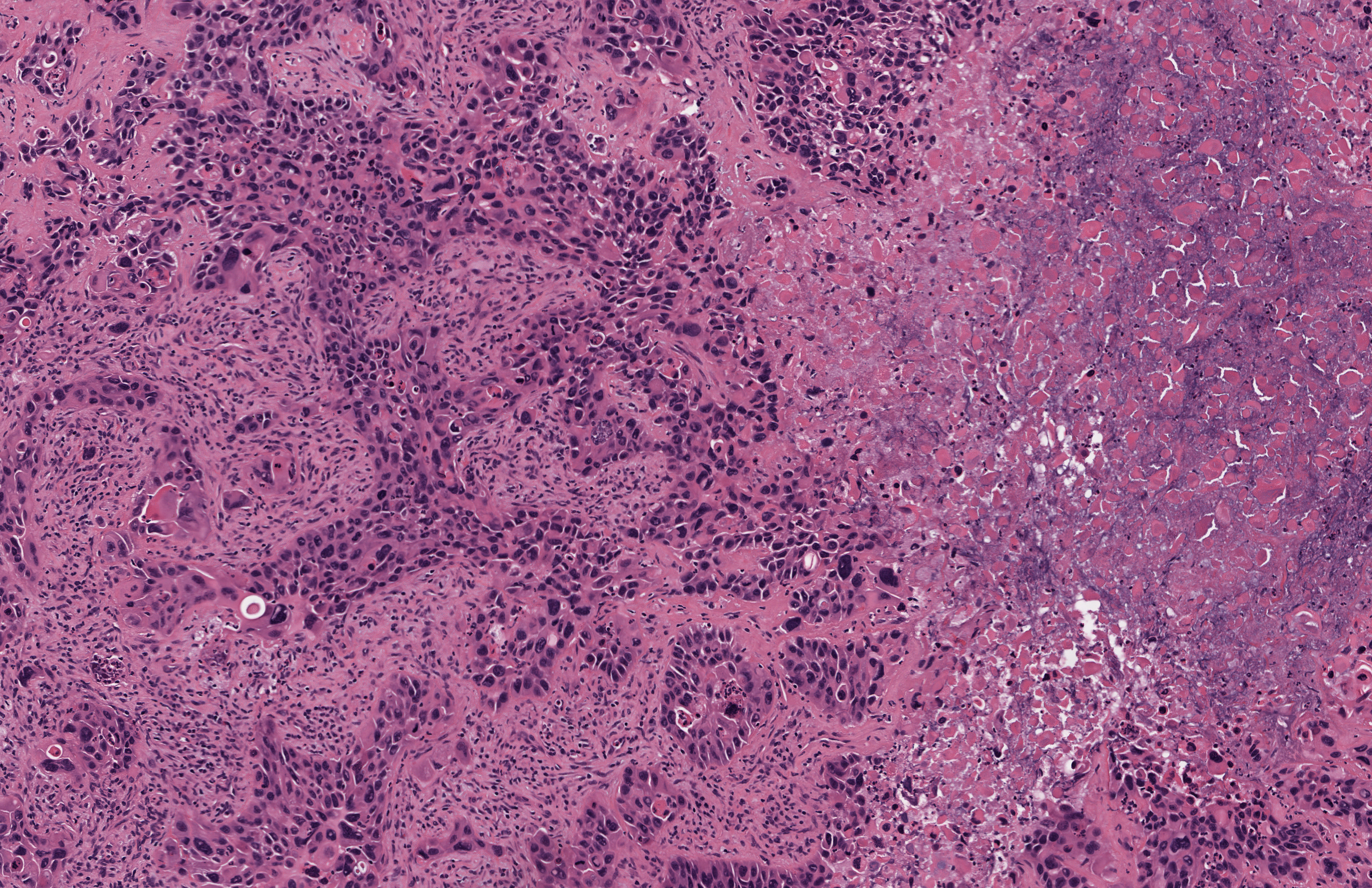
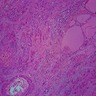
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Invasive squamous carcinoma, with or without keratinization
- High mitotic index
- Extrathyroid, vascular and perineural invasions are common
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- CK5, CK6, CK19
- Thyroglobulin (focally), PAX8 (91%), TTF1 (9%) (Endocr J 2015;62:991)
- p40, p53 (40 - 50%), p63, high Ki67 proliferation index (Thyroid 2006;16:89)
Negative stains
Differential diagnosis
- CASTLE: circumscribed, slowly growing tumor, CD5+, CD117+
- Metastasis or direct invasion of squamous cell carcinoma from other organs: history of squamous cell carcinoma, PAX8-
- Papillary thyroid carcinoma with squamous differentiation: squamous component is small portion of the well differentiated thyroid carcinoma
- Squamous metaplasia: benign squamous cells