Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Iczkowski KA. Varicocele. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/testisvaricocele.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Mass of tortuous and dilated veins of pampiniform plexus and internal testicular vein of spermatic cord
- Occurs posterior and superior to the testis, may extend into the inguinal ring
Essential features
- Probably due to incompetent valves of left internal spermatic vein as it empties into renal vein
- 90% on left
- 10% bilateral
- Right internal spermatic vein is less often involved since it empties directly into the inferior vena cava and tends not to have incompetent valves
Epidemiology
- Affects 15% of adults (Ultrastruct Pathol 2010;34:260) and 13% (Fertil Steril 2017;107:74) to 40% (J Assist Reprod Genet 2017;34:839) of men seeking fertility treatment
- Only 20% of men with a varicocele will have lowered fertility (Asian J Androl 2016;18:276)
- Associated with decreased sperm count and motility (J Assist Reprod Genet 2017;34:839)
- Testicular atrophy is the main indication for surgical repair
Sites
- Right sided varicocele is unusual; isolated right sided varicocele is associated with situs inversus, venous thrombosis or inferior vena cava compression from space occupying lesion such as soft tissue sarcoma; less commonly paraganglioma (Ann Saudi Med 2016;36:148)
- It suggests the presence of a vascular abnormality (Urology 2015;85:e39)
Etiology
- Most cases are idiopathic
- Renal tumor may invade the left renal vein and block the drainage of the spermatic vein
- Possible association with maternal exposure to diethylstilbestrol (Am J Obstet Gynecol 1981;140:186)
- Rare association with sertoliform cystadenoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:141)
- Kidney donation usually involves a left kidney; a study showed left pampiniform venous plexus diameter increased after kidney donation in men, suggesting that this can predispose to varicocele (Transplant Proc 2009;41:2738)
- Can be caused by May-Thurner syndrome, which is reflux in the left spermatic vein caused by iliac vein compression between the right iliac artery and the spine [Ann Vasc Surg 2017;42:305)
- Certain genetic and epigenetic changes are associated with varicocele (J Assist Reprod Genet 2017;34:839)
Clinical features
- Often associated with infertility; after treatment, 40 - 55% recover fertility
- Testicular pain may be associated with sexual activity
- If longstanding, testicular atrophy and infertility of the affected testis may result
Diagnosis
- Based on palpation while patient is at rest compared to during Valsalva
- Graded based on physical exam findings:
- Grade 1: palpable only during Valsalva
- Grade 2: palpable at rest but not visible
- Grade 3: visible and palpable at rest
- Ultrasound if physical exam is inconclusive (J Ultrason 2016;16:359)
Laboratory
- May decrease Leydig cell function, causing a lower serum testosterone, which can be improved after varicocelectomy (Urology 2013;81:1213)
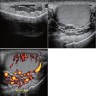
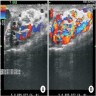
Radiology description
- Ultrasound can demonstrate vessel size, reversal of blood flow and testicular volume
Radiology images
Case reports
- 64 year old Asian man with varicocele due to renal arteriovenous malformation (J Med Case Rep 2018;12:2)
- 68 year old man with thrombosed varicocele (BMC Urol 2018;18:34)
- Fighter pilot with an asymptomatic varicocele precipitated by centrifuge training (Aerosp Med Hum Perform 2015;86:1063)
Treatment
- Varicocelectomy
- Some patients have improved fertility after microsurgery, perhaps because DNA fragmentation is reduced / DNA integrity is improved (Syst Biol Reprod Med 2012;58:274)
- Ligation or occlusion of left spermatic vein at the internal inguinal ring
- Motile sperm were found in 11 of 19 patients after varicocele repair; testicular histology was also improved (Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:709452)
Gross description
- Thin walled cystically dilated membrane
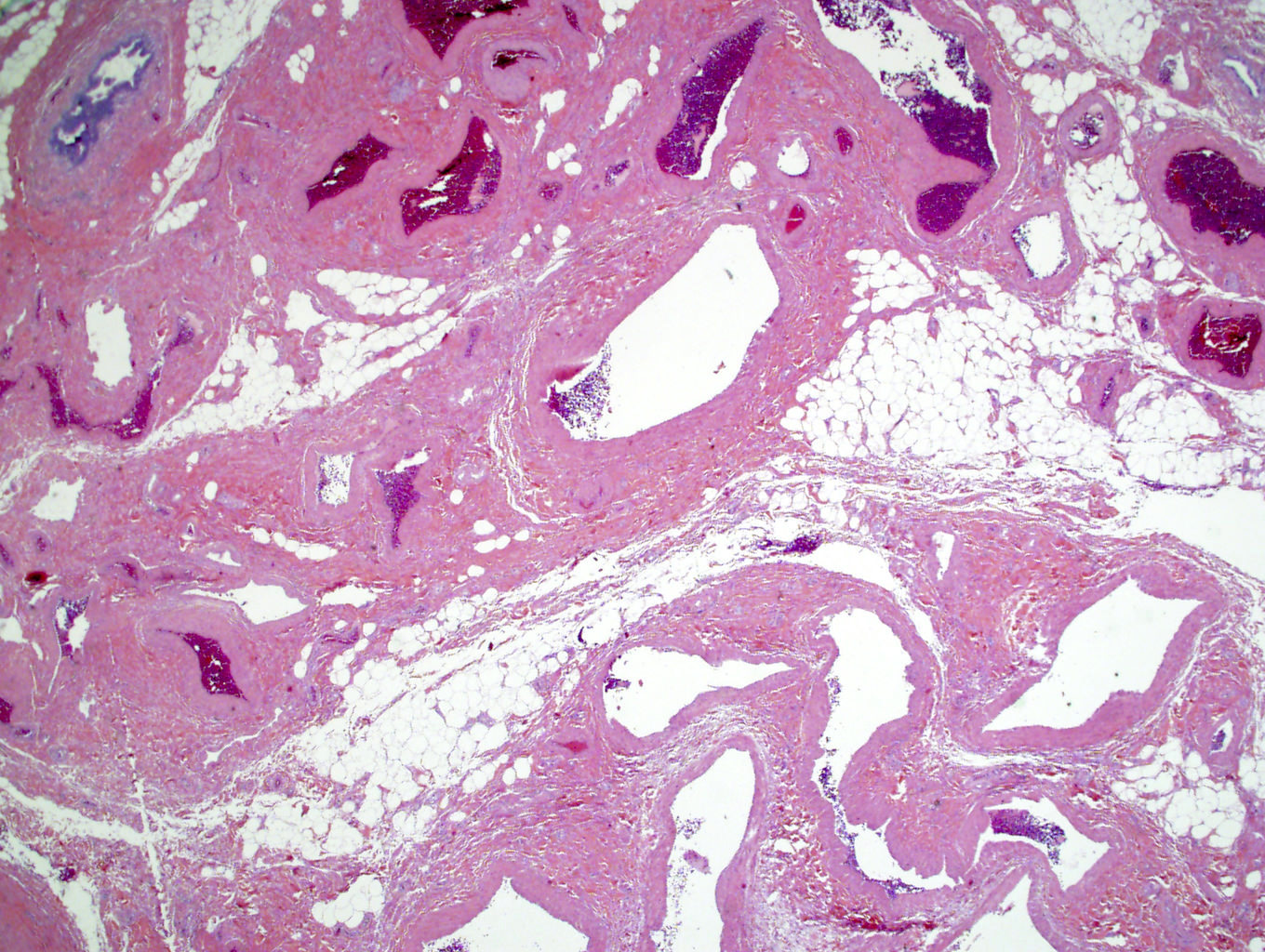
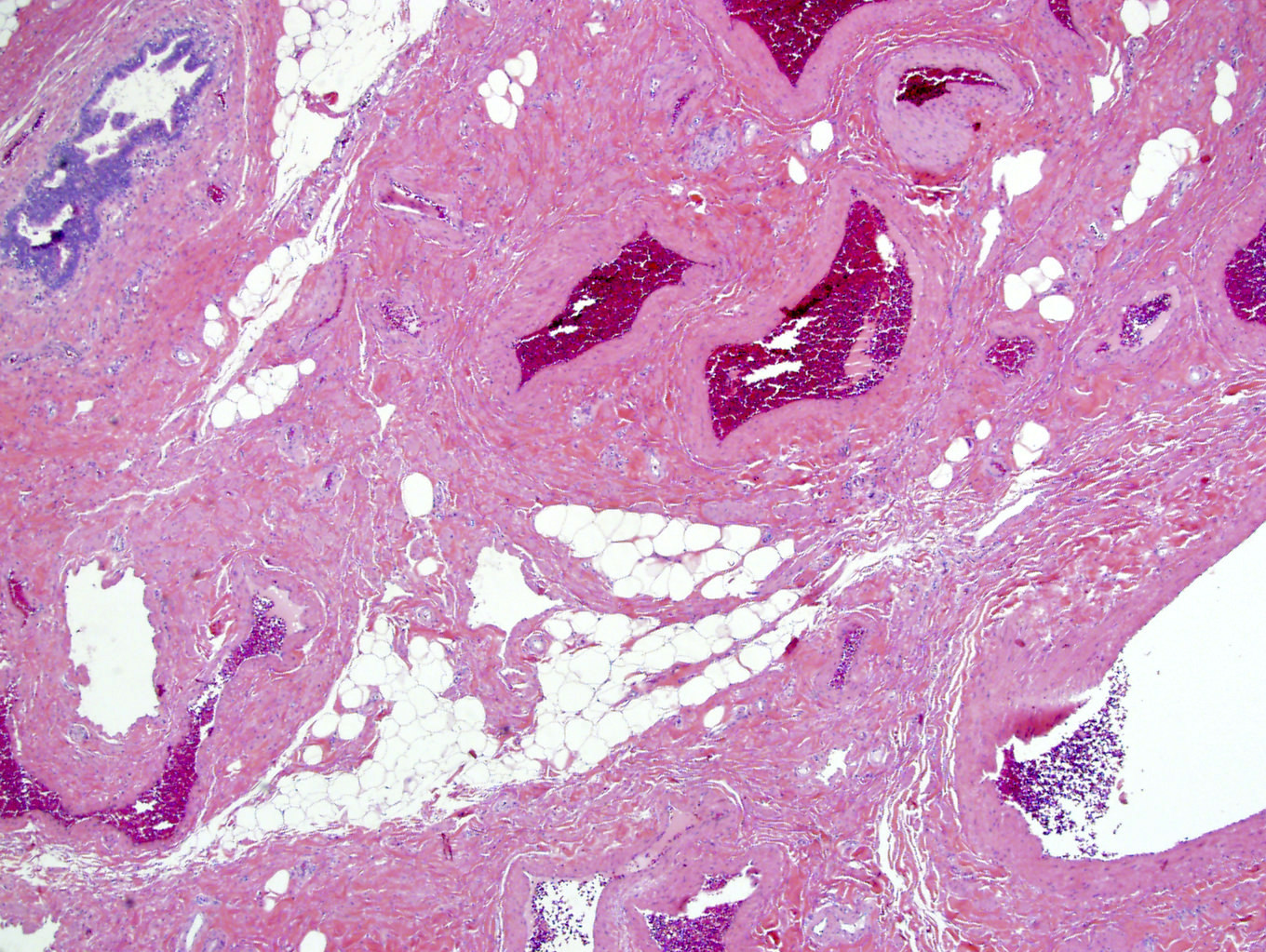
Microscopic (histologic) description
- From inside to outside, changes include (Ultrastruct Pathol 2010;34:260)
- Narrowing or obliteration of the vein lumens
- Segmental obliteration and occasional thrombi
- Internal elastic lamina fragmentation and invagination of intima
- Variable thickening of vein wall; the media contains hypertrophied smooth muscle fibers and deposition of collagen bundles (Ultrastruct Pathol 2012;36:201)
- If a testis is included: decreased spermatogenesis in tubules with germ cell degeneration and increased Leydig cells
- Adolescent varicocele: pathologic changes found at or soon after puberty, consisting of tubular sclerosis, premature germ cell sloughing, small vessel sclerosis and variable hypospermatogenesis (Am J Clin Pathol 1988;89:321)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- CD31 (stains endothelial layer)
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Endothelial cell damage and loss of internal elastic lamina (Ultrastruct Pathol 2010;34:260)
Differential diagnosis
- Hydrocele is lined by tunica vaginalis mesothelium (calretinin+, CD31-) whereas varicocele is lined by endothelium (CD31+, calretinin-)
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is not associated with varicocele?
- Destruction of vessel's external elastic lamina
- Endothelial cell damage
- Narrowing or obliteration of the lumen of the vein
- Thickening of the media by collagen deposition
Board review style answer #1
A. Destruction of vessel's external elastic lamina. It is the internal elastic lamina that is destroyed
Comment Here
Reference: Varicocele
Comment Here
Reference: Varicocele
Board review style question #2
In this orchiectomy specimen in a 30 year old with atrophic testis and varicocele, what is illustrated?
- Hematoma on the left and vas deferens on the right
- Hydrocele on the left and testis tubules on the right
- Spermatocele on the left and rete testis on the right
- Varicocele on the left and rete testis on the right
Board review style answer #2