Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Dall C, Zynger D. Teratoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/testisteratoma.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Tumor originating from germ cells with more than one embryonic germ layer
Terminology
- Prepubertal and postpubertal teratoma: currently accepted categories of teratoma
- Either category may occur in either age group
- Teratoma with somatic type malignancy: teratoma with malignant transformation that occupies at least a 4x magnification (0.5 cm) (Moch: WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs (IARC WHO Classification of Tumours), Fourth Edition, 2016)
- Do not divide into mature and immature as both are malignant and this nomenclature is misleading, no longer accepted and has no clinical relevance (Med Surg Urol 2014;3:1)
Epidemiology
- Teratoma is second most common germ cell tumor type in pediatrics, after yolk sac tumor (Rev Urol 2004;6:11)
- Incidence increasing, as testicular germ cell tumors are increasing (Hum Reprod 2001;16:972)
- Most commonly presents at age 25 - 35 years
- Postpubertal teratoma more frequent that prepubertal teratoma
- Pure teratomas (5%) are more rare than mixed germ cell tumors as malignant germ cells differentiate into other malignant phenotypes prior to teratoma (Med Surg Urol 2014;3:1)
- Teratoma is a component of 50% of mixed germ cell tumors (Moch:WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs (IARC WHO Classification of Tumours), Fourth Edition, 2016)
Pathophysiology
- Postpubertal type associated with germ cell neoplasia in situ (GCNIS) and chromosome 12p amplification (Med Surg Urol 2014;3:1)
- Thought to arise from GCNIS
- Prepubertal is not associated with GCNIS or chromosome 12p amplification (Med Surg Urol 2014;3:1)
- Prepubertal type significantly less likely to metastasize or recur
Etiology
- Genetic component; higher incidence with family history and Caucasians (Int J Dev Biol 2013;57:201)
- Possible contribution of environmental exposures but the data is inconclusive (Arch Environ Occup Health 2006;61:87, PLoS One 2013;8:e77130)
- Animal studies have demonstrated associations with diethylstilbestrol (J Urol 1987;138:1446), other groups have hypothesized links between in utero and early life exposure to endocrine disrupting agents (J Urol 1979;122:36, Int J Androl 2008;31:275)
Clinical features
- Most commonly presents with painless swelling of the testicle (Histopathology 1988;12:491)
- Pain may be associated with hemorrhage or hematoma (Med Surg Urol 2014;3:1)
- About 1/3 of pure testicular teratomas present with advanced disease (Cancer 1995;75:2244)
- Mediastinal masses may present with cough, dyspnea or cyanosis (Histopathology 1988;12:491)
- Intracranial masses may present with headache, vomiting or visual disturbances (Histopathology 1988;12:491)
- Growing teratoma syndrome, an enlarging mass during or following chemotherapy for mixed germ cell tumor, may occur (Case Rep Urol 2014;2014:139425)
Diagnosis
- Ultrasound is used to evaluate a testicle mass
- Avoid biopsies to prevent cancer seeding
- Radical orchiectomy is initial procedure to diagnose a testicular mass in an adult
- Increasing rate of antenatal diagnoses (J Pediatr Surg 2006;41:1513)
- May use intraoperative frozen sections to guide therapy in pediatric populations
Laboratory
- In pure testicular teratomas, serum markers (b-hCG and AFP) are usually normal (Med Surg Urol 2014;3:1)
Radiology description
- Ultrasound is used to help exclude benign pathology
- Imaging may demonstrate calcifications or predominantly cystic lesions
- Computed tomography of the chest and abdomen used for staging purposes
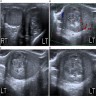
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- The International Germ Cell Consensus Classification guides prognosis and risk of recurrence for testicular germ cell malignancies (IGCCCG) (J Clin Oncol 1997;15:594, J Clin Oncol 2007;25:1033)
- Presence of teratoma is associated with better prognosis and therefore histologic recognition and documentation is required (Eur J Cancer 2001;37:576)
- Germ cell tumors with > 50% teratoma have fewer metastases (J Clin Oncol 1988;6:1467)
- Germ cell tumors with > 25% teratoma have less lymphovascular invasion (pT1) (Am J Clin Pathol 2016;145:341)
Case reports
- Antenatal diagnosis of teratoma in an undescended testicle (Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2016;47:527)
- 23 year old man with growing teratoma syndrome (Case Rep Urol 2014;2014:139425)
Treatment
- Radical orchiectomy is first line therapy for testicular mass in an adult
- Increasing rate of testis sparing surgery for prepubertal tumors (Rev Urol 2004;6:11)
- Retroperitoneal lymph node dissection and platinum based chemotherapy are adjunctive therapies for testicular germ cell tumor
- Treatment guidelines are based on postorchiectomy TNM stage (NCCN guidelines: Testicular Cancer)
- Consider sperm preservation options
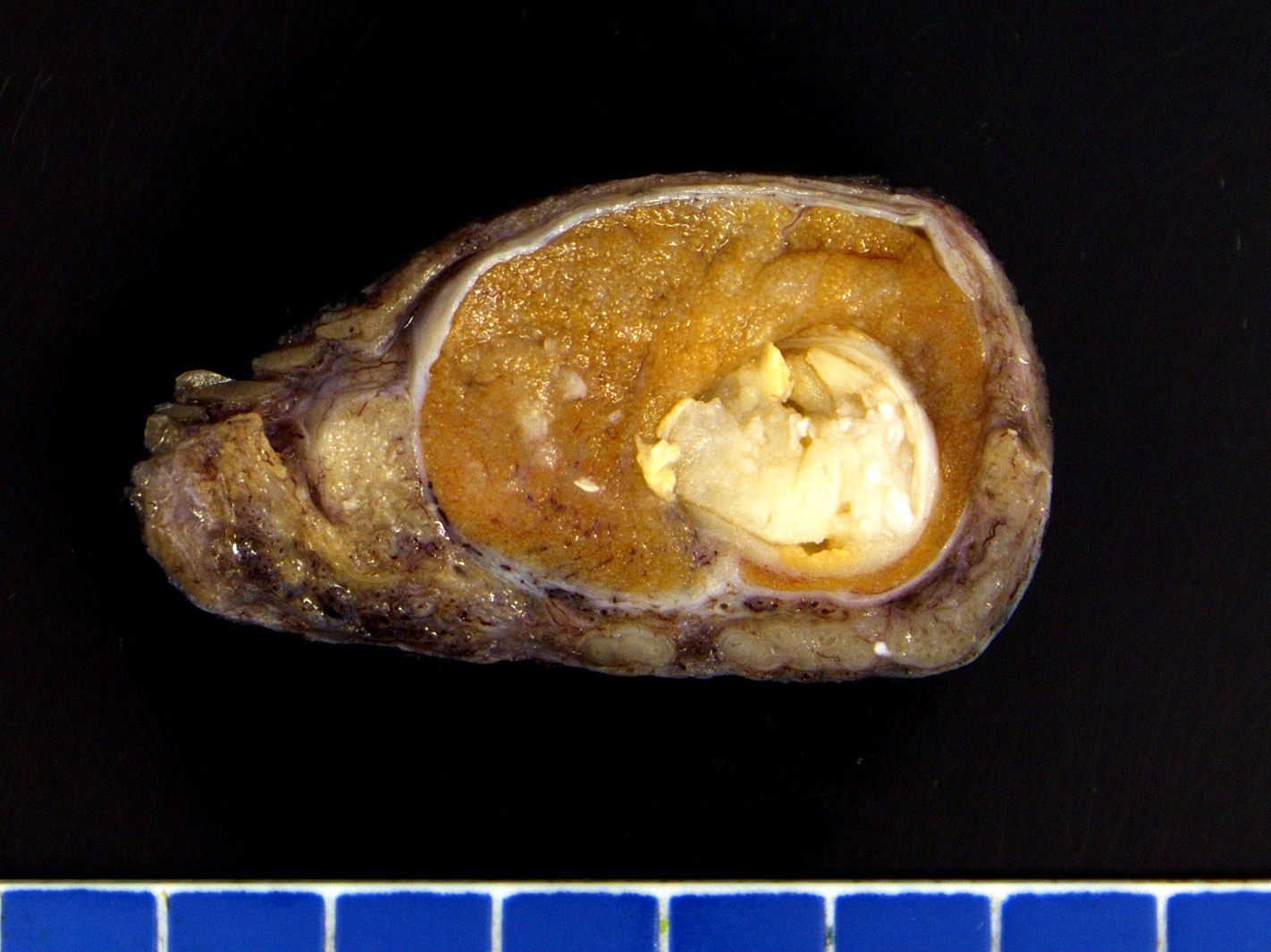
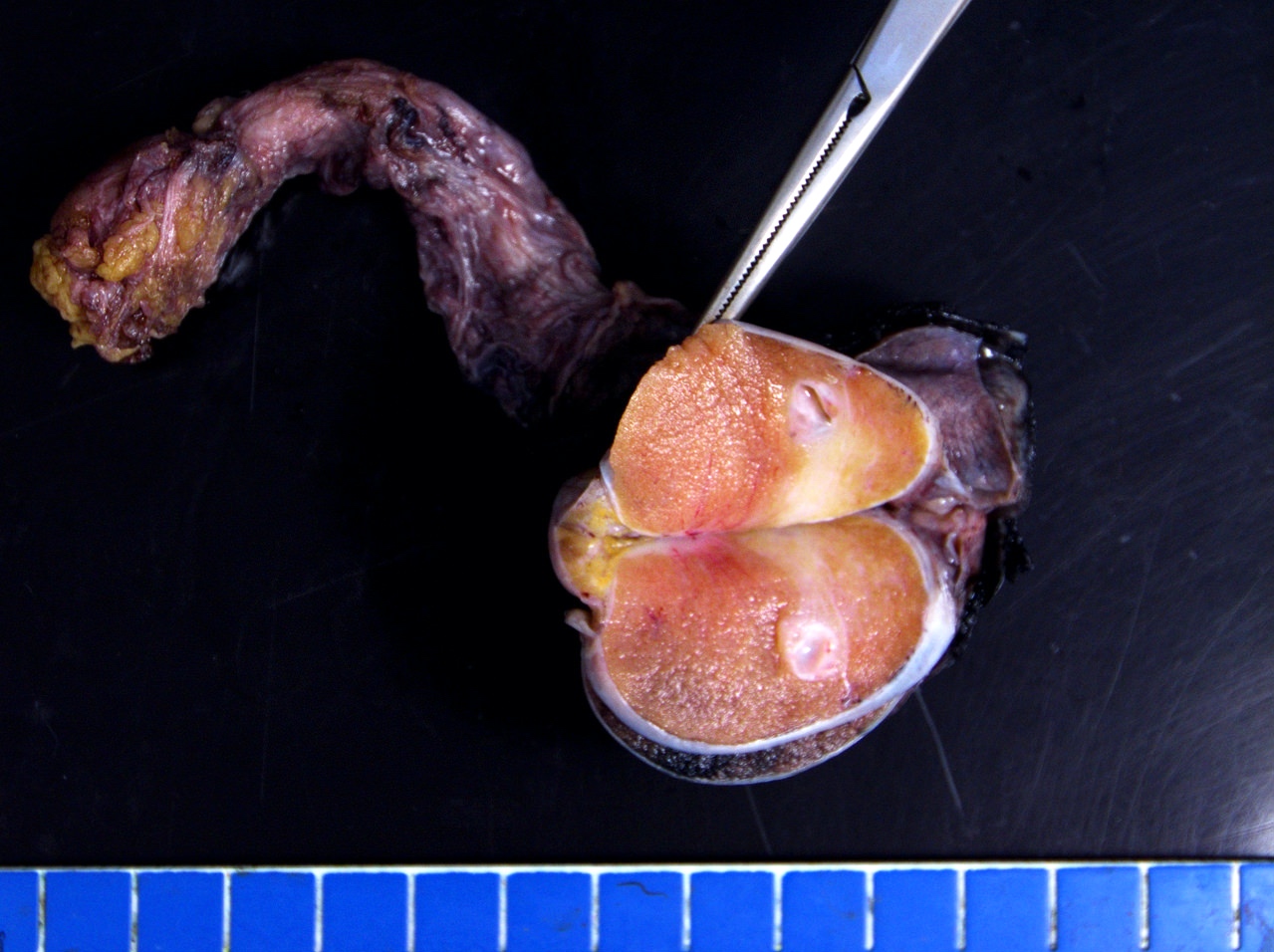
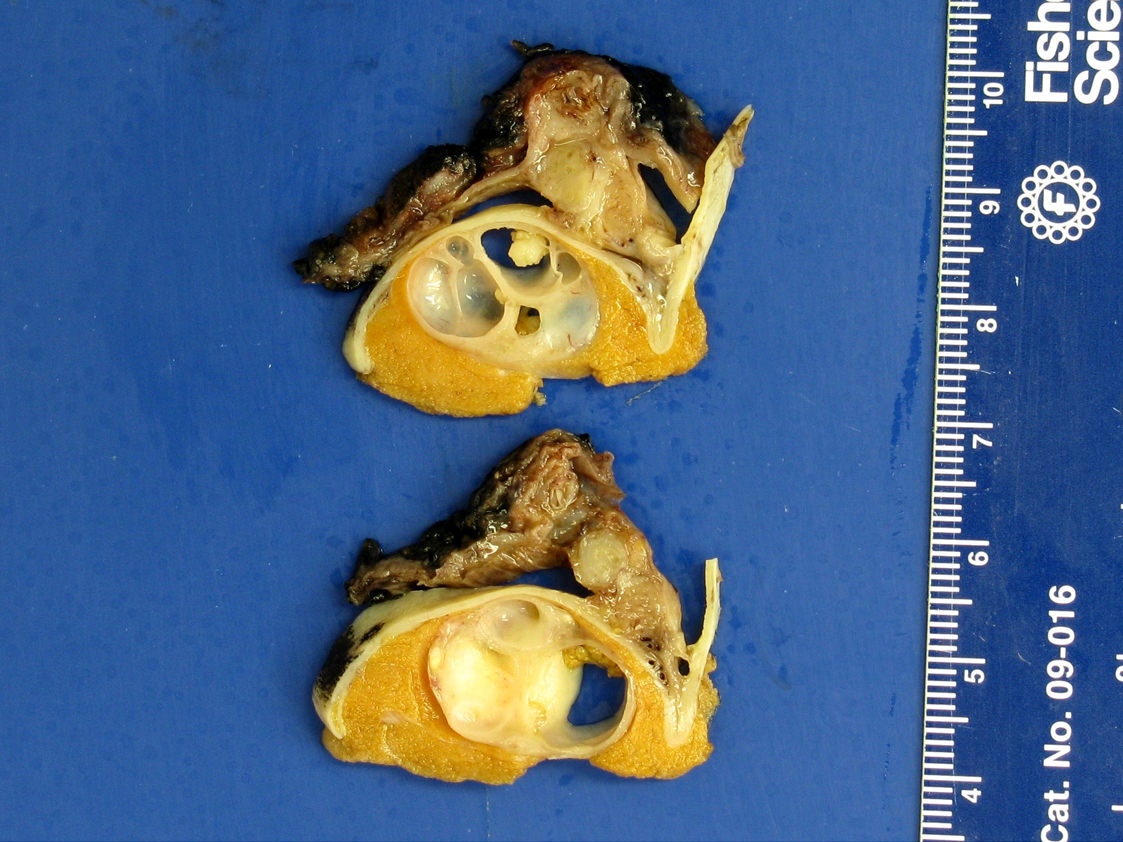
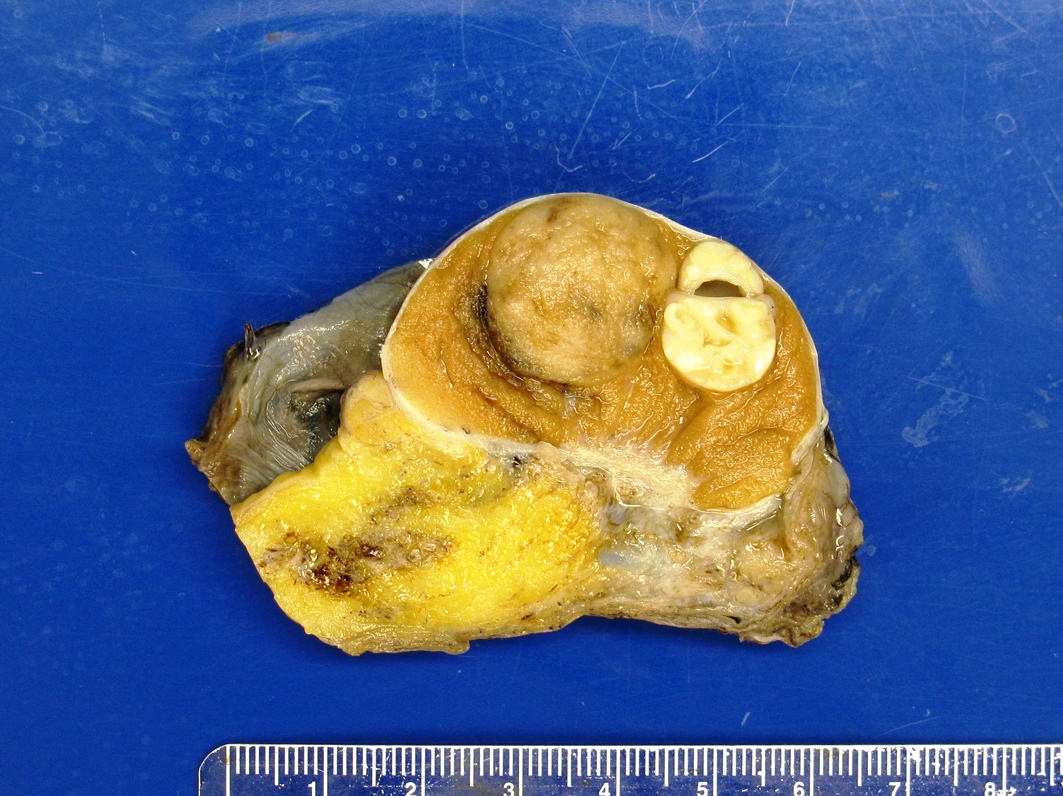
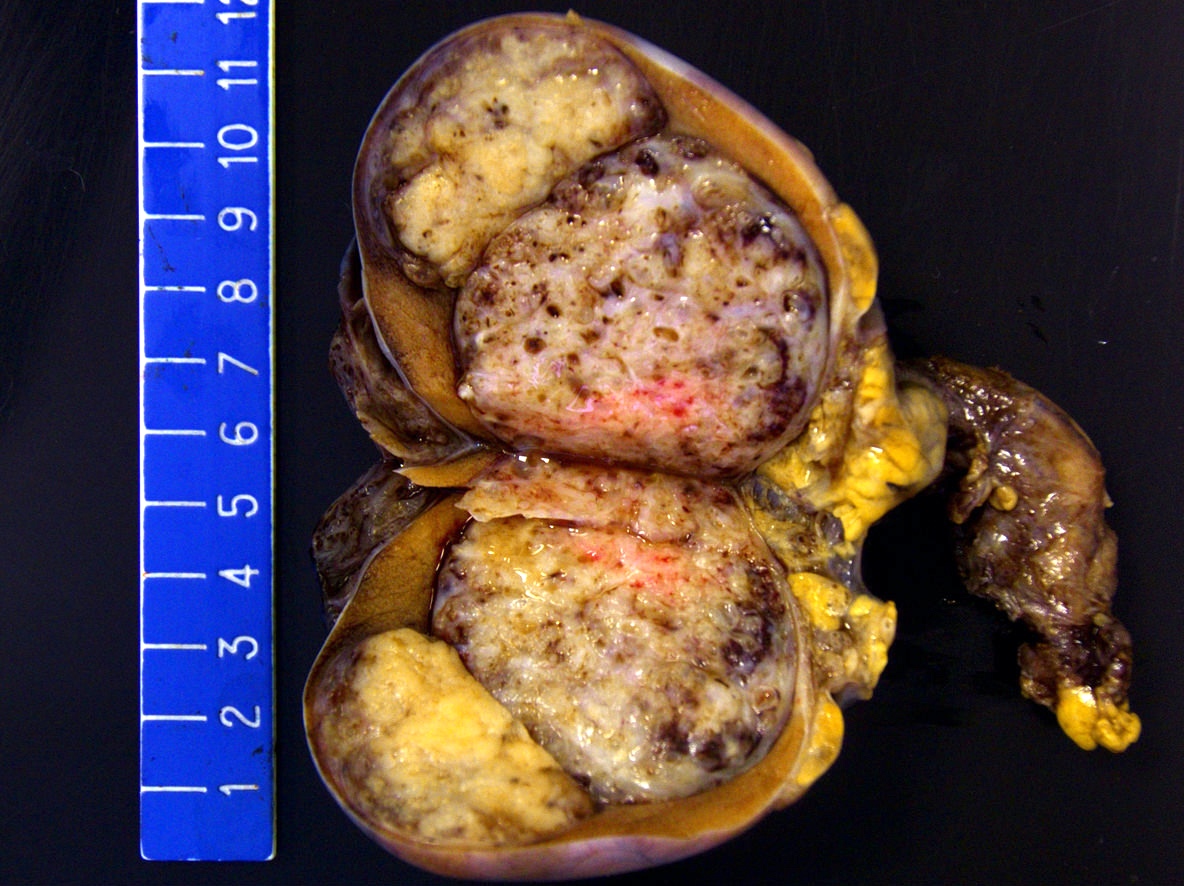
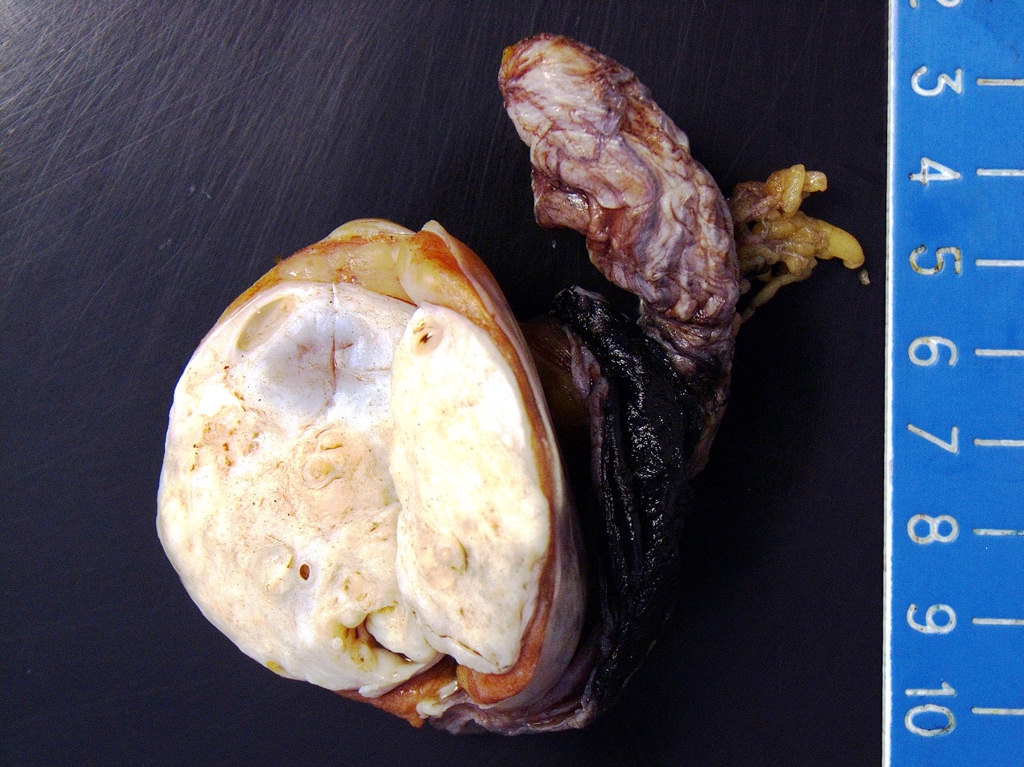
Gross description
- Lobulated, with cysts of mucinous, gelatinous or serous material
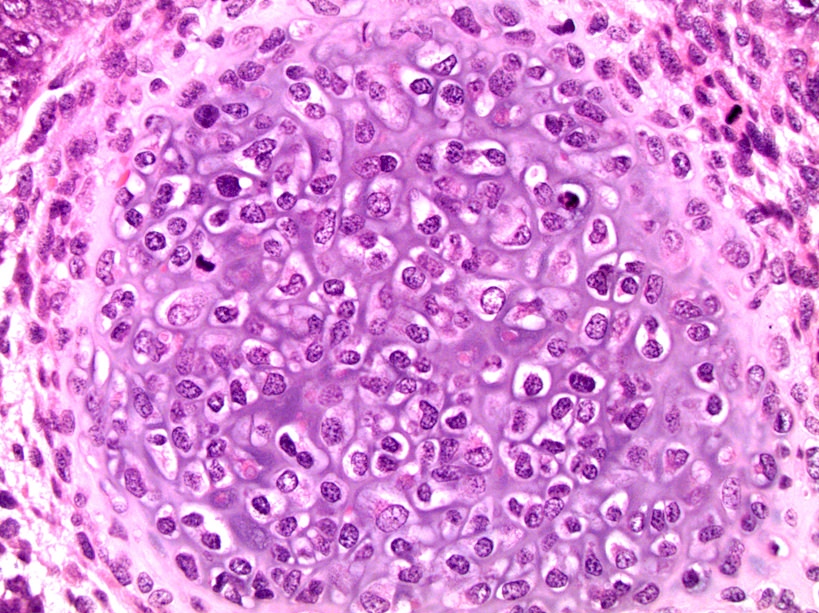
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Postpubertal type
- Recognition is important as the percentage of teratoma must be documented in orchiectomy specimens and metastatic lesions
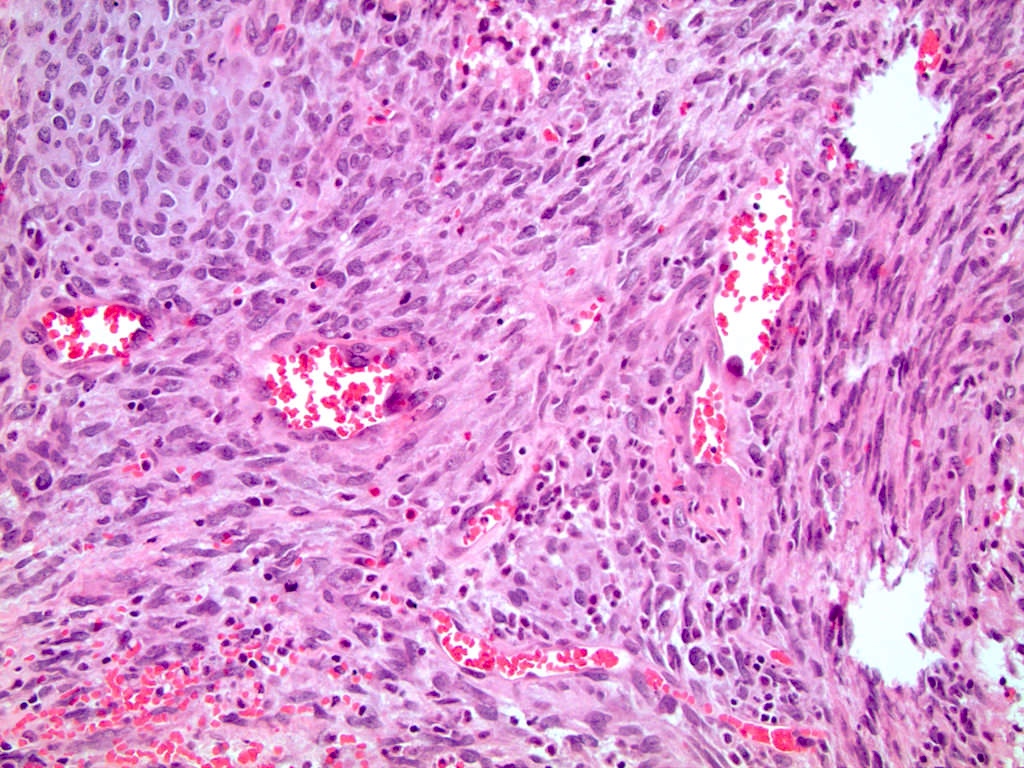
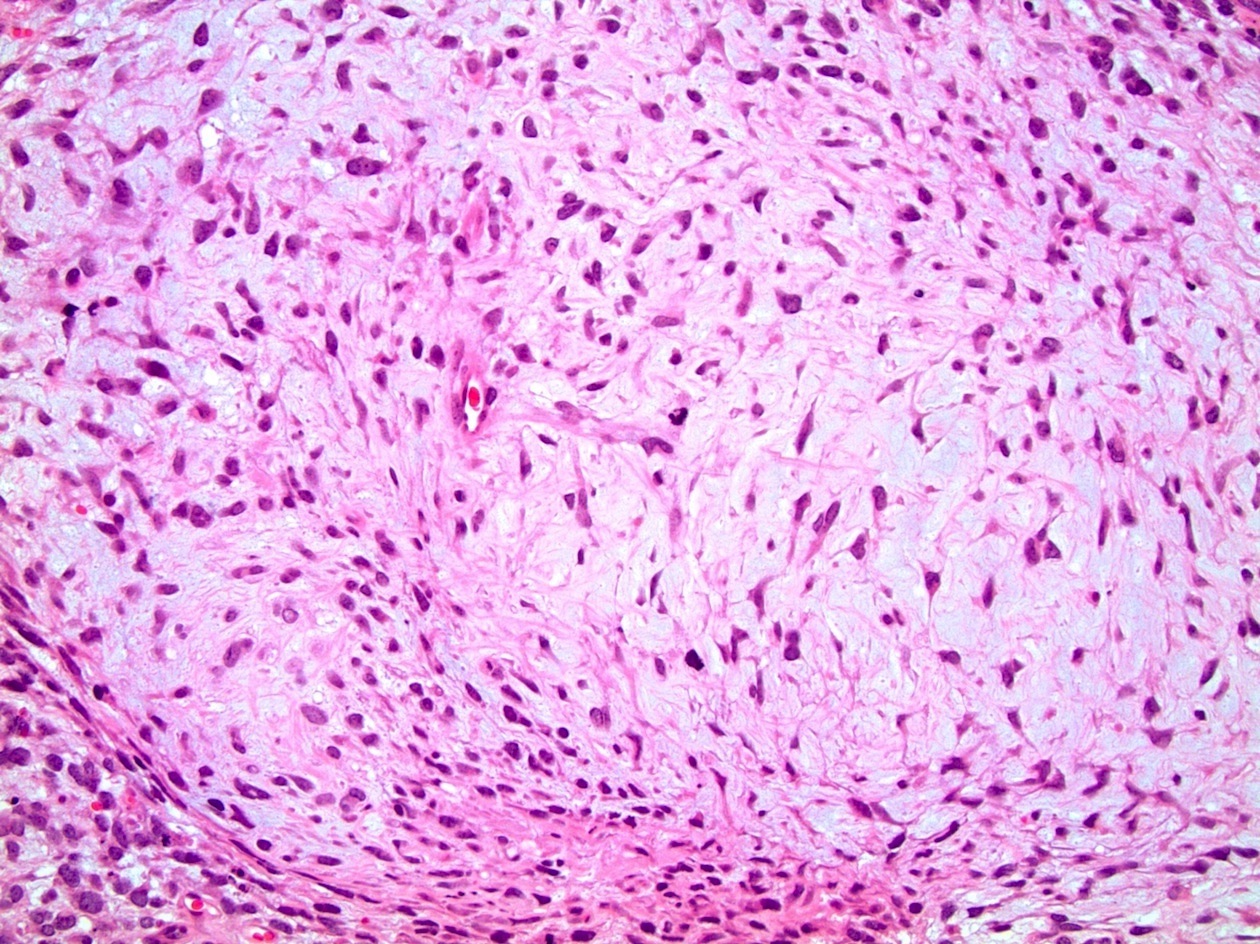
- Demonstrate varying degrees of atypia
- Any type of tissue may be present, such as gastrointestinal glands, respiratory epithelium, cartilage, squamous epithelium with keratinization, primitive undifferentiated spindle cells, or neuroepithelium
- Will have GCNIS (Med Surg Urol 2014;3:1)
- Associated with atrophic testis with sclerosis and microliths (Ulbright: Atlas of Tumor Pathology, 4th Series - Tumors of the Testis and Adjacent Structures, First Edition, 2013)
- Prepubertal type
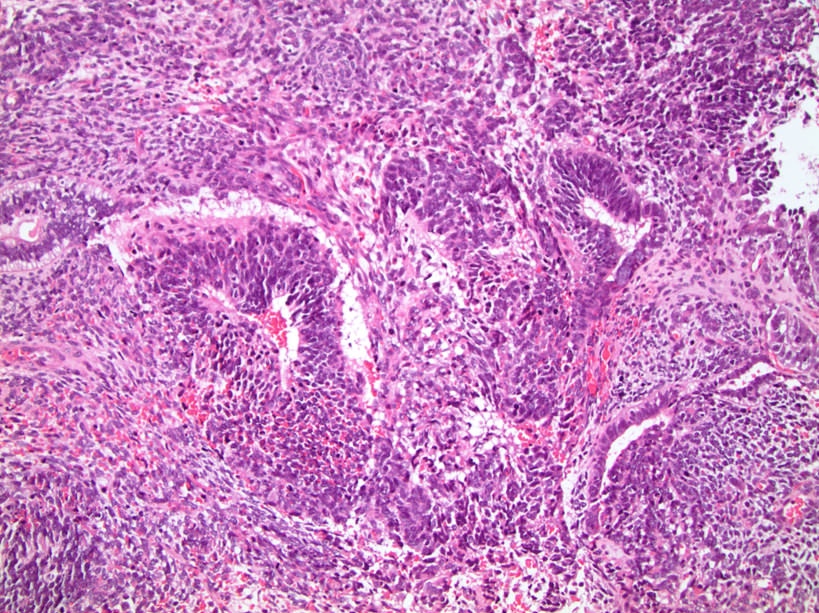
- More likely to have tissue arrangements mimicking organs (organoid morphology with tissue layers visible such as epithelium, lamina propria and muscularis propria) but any tissue type may be present (Moch: WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs (IARC WHO Classification of Tumours), Fourth Edition, 2016)
- Hair follicles may be seen (not in postpubertal type)
- No cytologic atypia, GCNIS or necrosis; minimal mitoses (Ulbright: Atlas of Tumor Pathology, 4th Series - Tumors of the Testis and Adjacent Structures, First Edition, 2013)
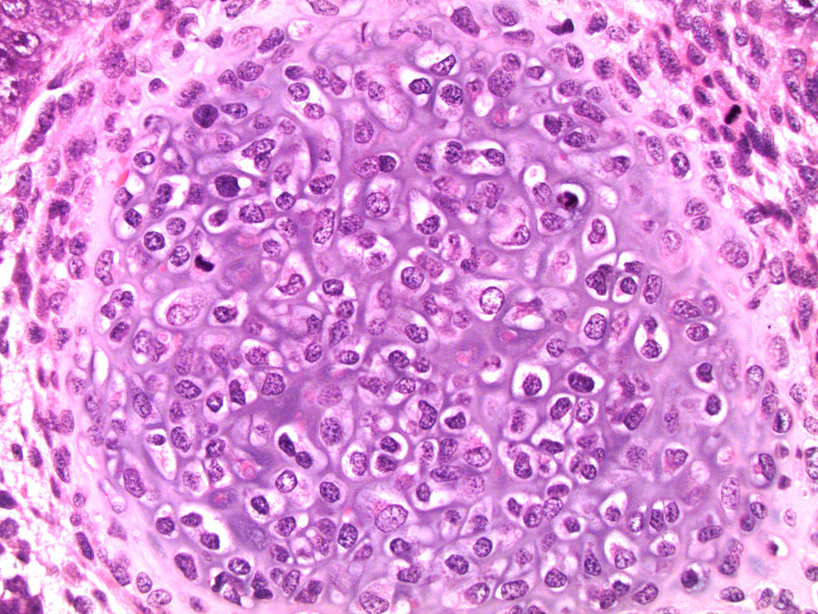
- Teratoma with somatic type malignancy
- Sarcoma is most prevalent somatic type malignancy but other tumor types occur, including adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET) (Moch: WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs (IARC WHO Classification of Tumours), Fourth Edition, 2016, J Urol 1998;159:133, Ulbright: Atlas of Tumor Pathology, 4th Series - Tumors of the Testis and Adjacent Structures, First Edition, 2013)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- 12p amplification present in postpubertal teratomas and teratomas with somatic type malignancy (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:435, Moch: WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs (IARC WHO Classification of Tumours), Fourth Edition, 2016)
Sample pathology report
- Right testicle, radical orchiectomy:
- Mixed germ cell tumor, teratoma (55%), seminoma (20%), embryonal carcinoma (10%), yolk sac tumor (10%) and choriocarcinoma (5%) types (see synoptic report)
Differential diagnosis
- Dermoid cyst:
- Squamous epithelium, hair follicles / sebaceous glands
- May have adjacent lipogranulomas but no other embryonic germ cell types
- Lacks GCNIS and cytologic atypia (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:435)
- Epidermoid cyst:
- Nonneoplastic squamous epithelium producing keratin with lamellar targetoid appearance
- No other embryonic germ cell types
- Lacks GCNIS and cytologic atypia (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:435)
- Sarcoma:
- Can mimic teratoma with sarcoma as somatic type malignancy
- Lacks GCNIS and other germ cell tumor components
- Yolk sac tumor:
Board review style question #1
A 27 year old man presents with a painless enlarging testicular mass. He undergoes appropriate workup and orchiectomy confirms diagnosis of a pure postpubertal teratoma. Which of the following is likely to be true?
- AFP is likely elevated
- Cytogenetic analysis will reveal chromosomal abnormalities
- Few mitotic figures will be identified microscopically
- Hair follicles are likely to be seen microscopically
- He has a poor prognosis
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
A 37 year old woman gives birth to a male baby who is diagnosed with an undescended testicle. Further workup reveals a large intra abdominal mass, which is resected. Pathology is consistent with a pure teratoma. Which of the following is most likely present on microscopic examination?
- Adjacent areas of germ cell neoplasia in situ
- Areas with organoid morphology
- Many mitotic figures and cytologic atypia
- Sarcomatous elements
- Significant areas of testicular tubular atrophy
Board review style answer #2