Table of Contents
Definition / general | Case reports | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Williamson S. Splenogonadal fusion. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/testissplenogonadal.html. Accessed December 26th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Also called ectopic scrotal spleen, testicular splenic fusion
- Rare congenital condition of gonad fusing with ectopic splenic tissue; patients usually present before age 20, 50%+ are less than age 10
- In males, involves left testis only; occurs in females also
- Fusion may be continuous (attaching to spleen) or discontinuous (intrascrotal splenic nodules attached to testis, spermatic cord, epididymis, appendix of testis or appendix of epididymis)
- Continuous form is associated with limb bud anomalies such as peromelia (severe congenital anomalies of extremities identical to thalidomide embryopathy) and micrognatia (small jaw)
- Discontinuous type is rarely associated with cardiac defects
Case reports
- 16 year old boy with chronic, painless testicular mass (Case of the Week #309)
- 27 year old man with associated nonseminomatous germ cell tumor (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2002;126:1222)
- 56 year old man with scrotal mass (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2003;127:e277)
Gross description
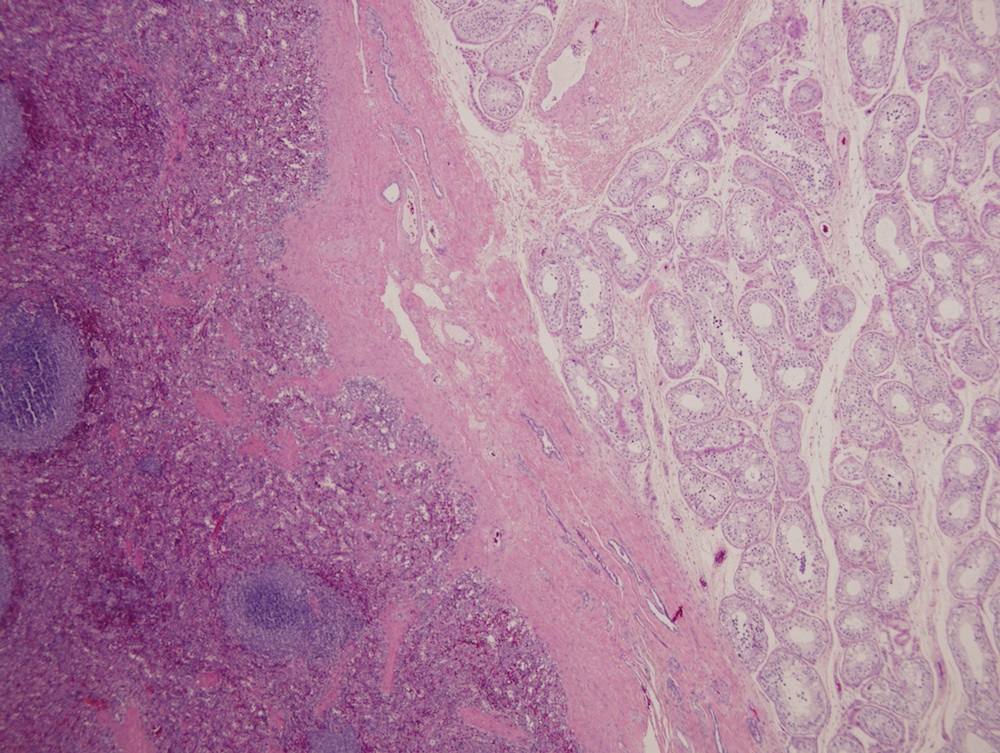
- Splenic tissue well demarcated from gonad
Microscopic (histologic) description
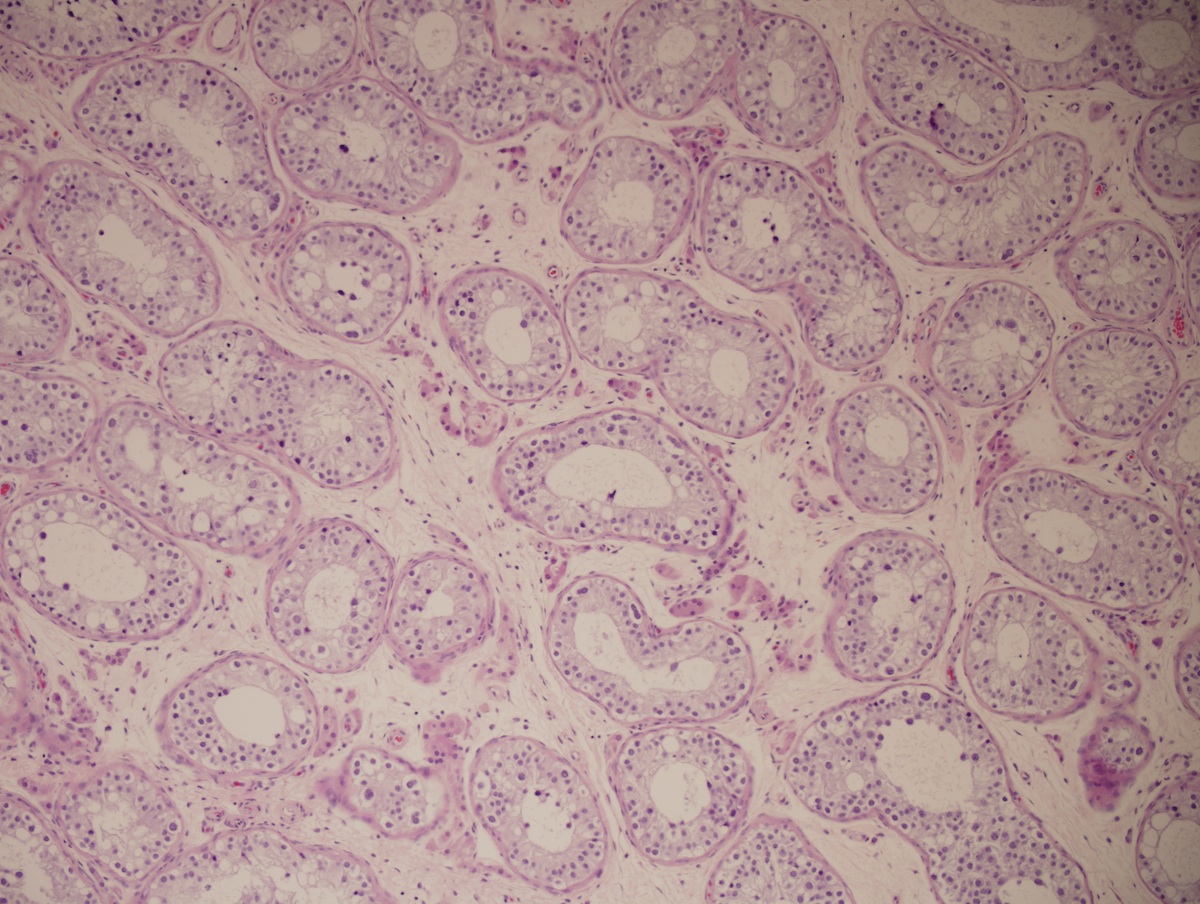
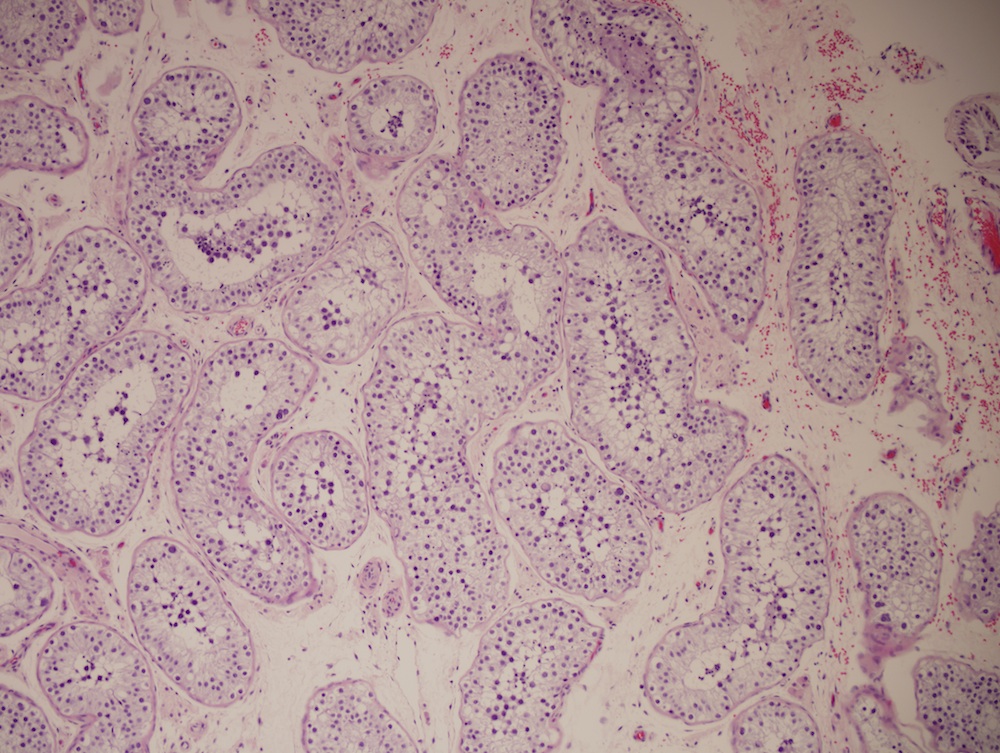
- Normal splenic parenchyma with variable fibrosis, thrombi, calcification, fatty degeneration, hemosiderin
Differential diagnosis
- Lymphoproliferative tumor
- Sarcoma
- Teratoma