Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Sites | Case reports | Radiology images | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Rane S. Fibrous pseudotumor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/testisepidfibrpseudotumor.html. Accessed December 22nd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Diffuse or localized, reactive fibromatous proliferation involving epididymis, tunica or spermatic cord
- May simulate a testicular tumor (Arch Surg 1978;113:814)
- May cause bowel wall perforation in infants with meconium periorchitis
Terminology
- Other terms used:
- Fibroma
- Nonspecific peritesticular fibrosis
- Nodular fibrous periorchitis, chronic proliferative periorchitis, reactive periorchitis or pseudofibrous periorchitis
- Fibrous periorchitis (for diffuse lesions)
- Proliferative funiculitis
- Nodular pseudotumor (if forms a mass)
- Inflammatory fibropseudotumor or pseudotumor (if forms a mass)
- Peritesticular fibromatosis
- Fibrous mesothelioma
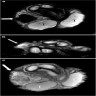
Sites
- Typically involves tunica albuginea
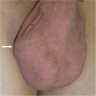
Case reports
- 28 year old man with paratesticular fibrous pseudotumor (J Med Case Rep 2013;7:225)
- 32 year old man with previous idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis (Eur Urol 1986;12:64)
- Fibrous pseudotumor of epididymis and tunica vaginalis (Can J Urol 2006;13:3279)
- Paratesticular fibrous pseudotumor (Front Med 2014;8:484)
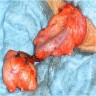
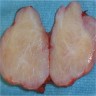
Gross description
- Can show diffuse band-like thickening, often encasing the testis
- Localized forms show single or multiple nodules, 2 mm to 9 cm
- Cut surface is usually firm, whitish
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Dense fibrosis, focal edema, lymphangiectasis and perivascular round cell infiltration
- Active epididymitis and chronic interstitial orchitis present in some cases
- Associated with fibrinous or hyalinized loose bodies in cavity
- Composed primarily of spindle cells with variable hyalinization and collagenization
- Variable component of lymphocytes, plasma cells, histiocytes and scattered eosinophils
- Nuclear atypia is usually absent, and if present is usually focal and restricted to the more cellular areas with more florid granulation tissue-like proliferation
- May have focal whorled arrangement, focal calcification and ossification
- Usually no mitoses
- No atypical mitoses
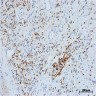
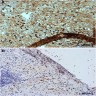
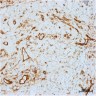
Microscopic (histologic) images
Differential diagnosis
- Sarcomas: generally are more cellular, with atypical mitoses and pleomorphism