Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Diagnosis | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Gordetsky J. Mucinous borderline tumor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/testisborderline.html. Accessed December 26th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Primary mucinous tumor of ovarian type surface epithelium with borderline malignant potential
Epidemiology
- Extremely rare testicular tumor reported in middle age men (age range 42 - 69) (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:1221)
Sites
- Intratesticular or paratesticular
Pathophysiology
- The histogenesis of the ovarian type surface epithelial tumors of the testis and paratestis remains unclear
- These tumors are possibly derived from Müllerian remnants or by metaplasia of the mesothelium of the tunica vaginalis (Hum Pathol 2011;42:1343)
Diagnosis
- Clinical evaluation is necessary to rule out metastatic spread from a primary adenocarcinoma of the appendix, colon, stomach, pancreas, lung or prostate
Case reports
- 55 year old man with primary testicular mucinous neoplasms (Can Urol Assoc J 2010;4:E112)
- 69 year old man with an ossified intratesticular mucinous tumor (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1999;123:244)
Treatment
- Radical orchiectomy
Gross description
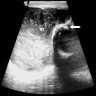
- Paratesticular or intratesticular mucinous cystic mass, most often unilocular
- Generally not as large as the ovarian tumor counterpart
Microscopic (histologic) description
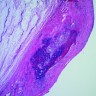
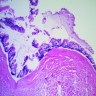
- Unilocular or multilocular cystic spaces lined by either endocervical or intestinal type mucinous epithelium
- Tufting and pseudostratification of cells with mild to severe nuclear atypia
- Occasional papillae
- Occasional mitotic figures
- Goblet cells are common
- Mucin extravasation and an associated fibrotic, calcific reaction with foci of dystrophic calcification and ossification
- Intracystic complex architecture diagnostic of intraepithelial carcinoma as well as foci of microinvasion have been reported
- No intratubular germ cell neoplasia (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:1221, Can Urol Assoc J 2010;4:E112)
Positive stains
Differential diagnosis
- Metastatic mucinous adenocarcinoma: appendix, colon, stomach, pancreas, lung, prostate
- Teratoma