Table of Contents
Definition / general | Clinical features | Radiology images | Case reports | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Weisenberg E. Glomus tumor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stomachglomus.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Mesenchymal tumor composed of modified smooth muscle cells; neoplastic counterpart of perivascular glomus bodies
- Common site is distal extremities; rare in GI tract; most common GI site is stomach
Clinical features
- More common in women, median age 55 years (range, 19-90 years, Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:301)
- Presents with bleeding (may be life threatening), ulcer symptoms or as incidental finding
- Much less common than GIST
- Usually benign, may metastasize to liver and cause death; malignant behavior more likely if > 5 cm, but cannot predict based on histology
Radiology images
Case reports
- 53 year old woman with pain in left hypochondrium (upper abdomen) x 4 months (Case of the Week #393)
- 55 year old man (Indian J Surg 2011;73:230)
- Multiple tumors involving stomach wall and perigastric adipose tissue (Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:291)
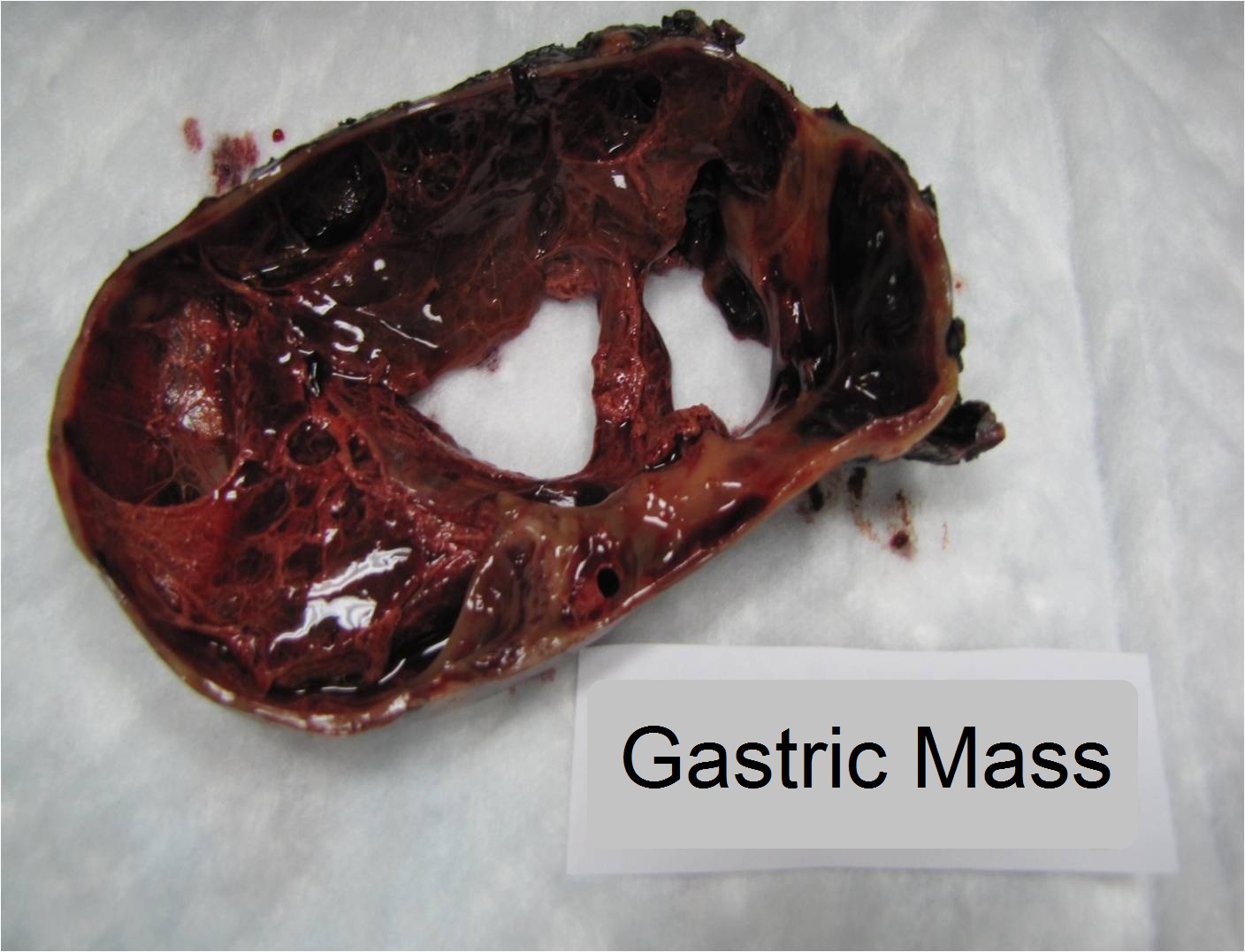
Gross description
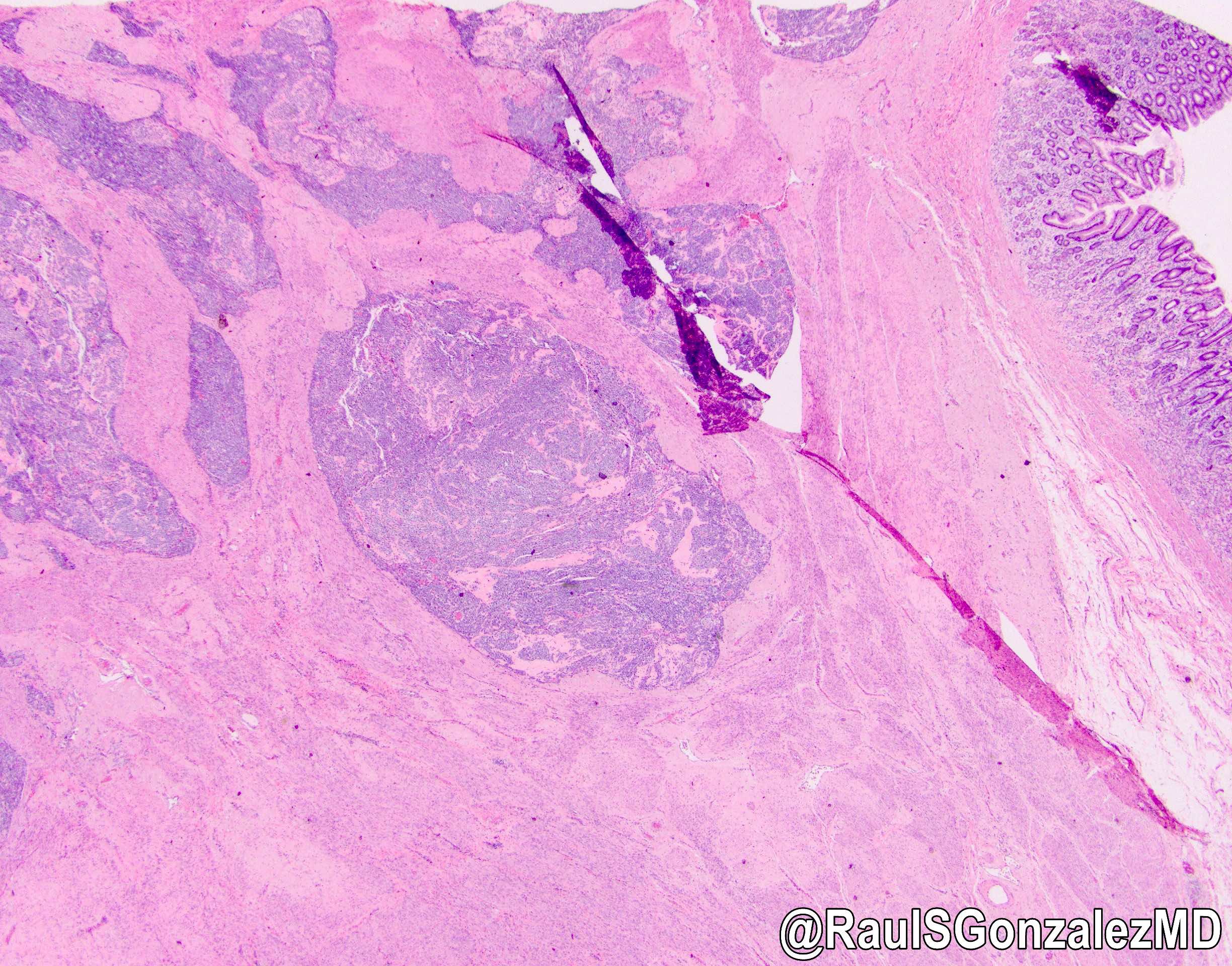
- 2-5 cm (range, 1.1 to 7 cm) intramural mass, usually antral
- Circumscribed, often with overlying mucosal ulceration and multinodular
Gross images
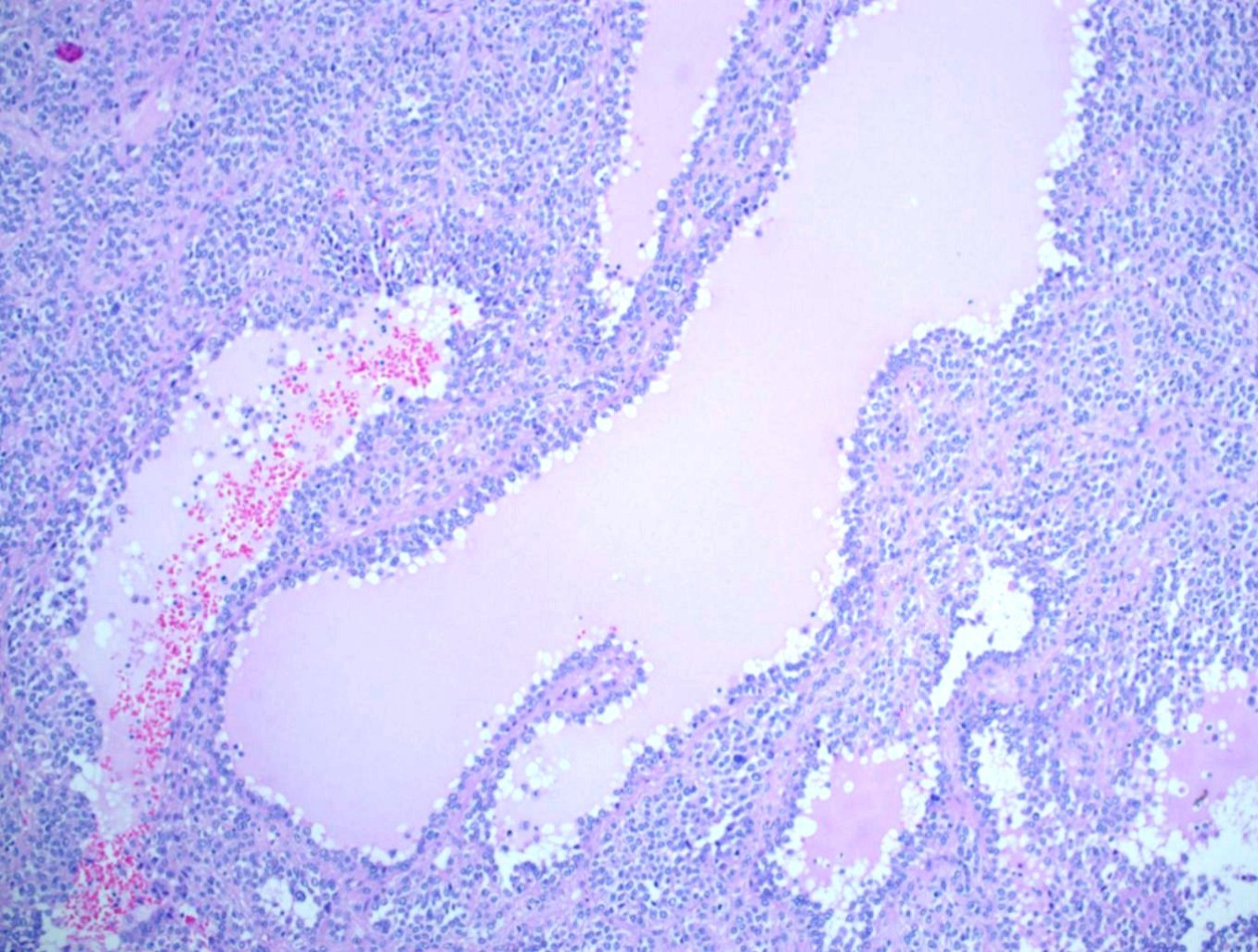
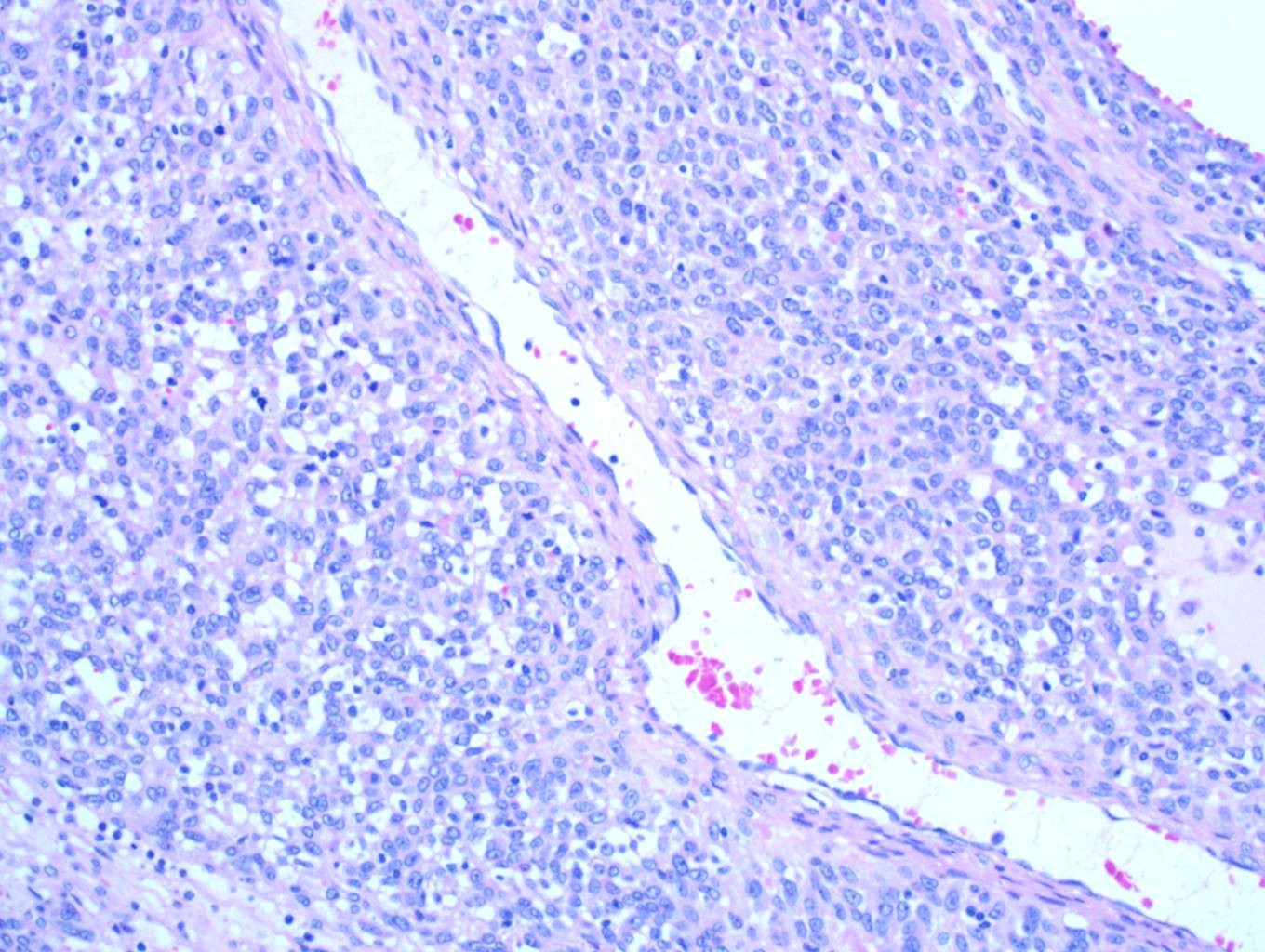
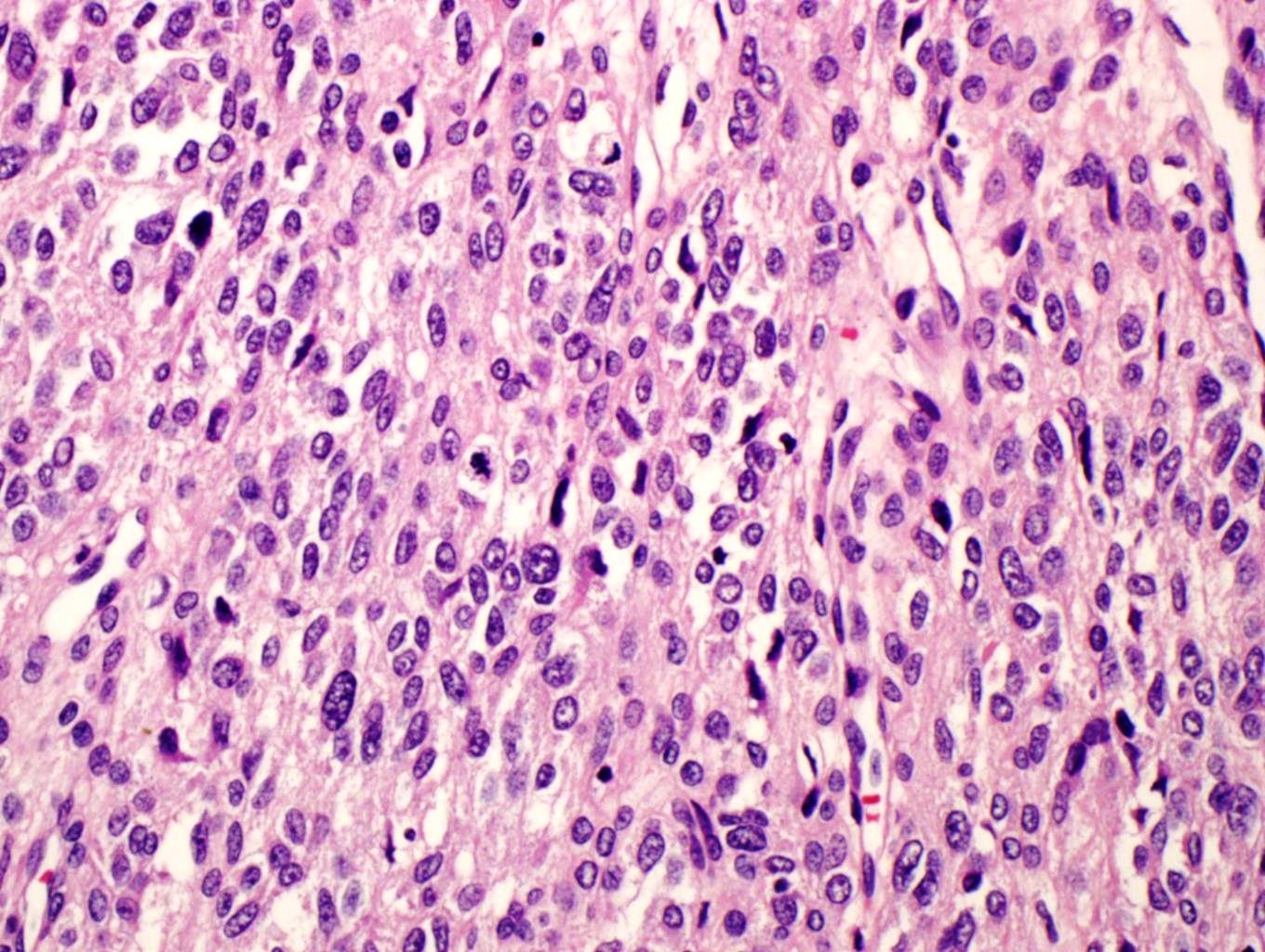
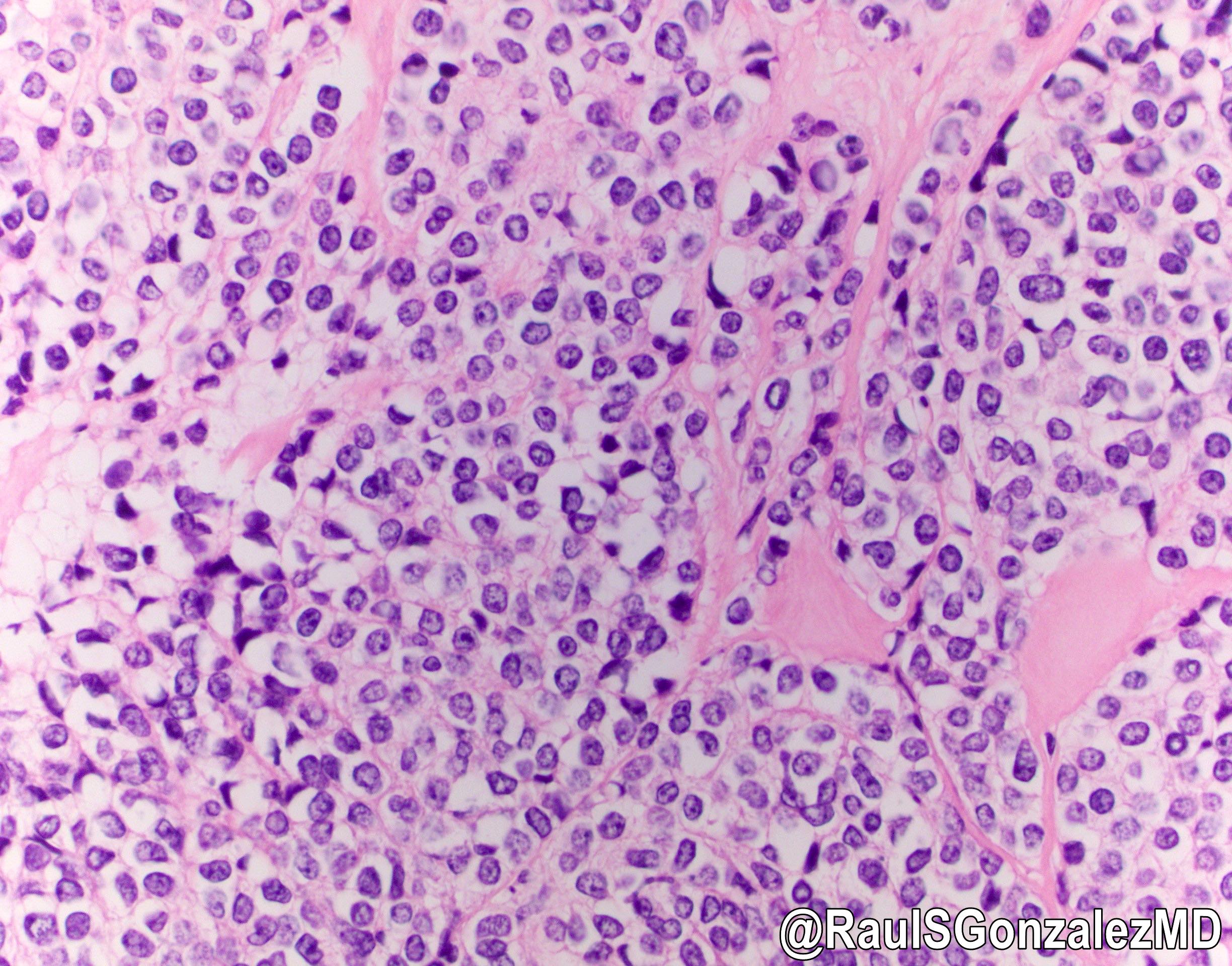
Microscopic (histologic) description
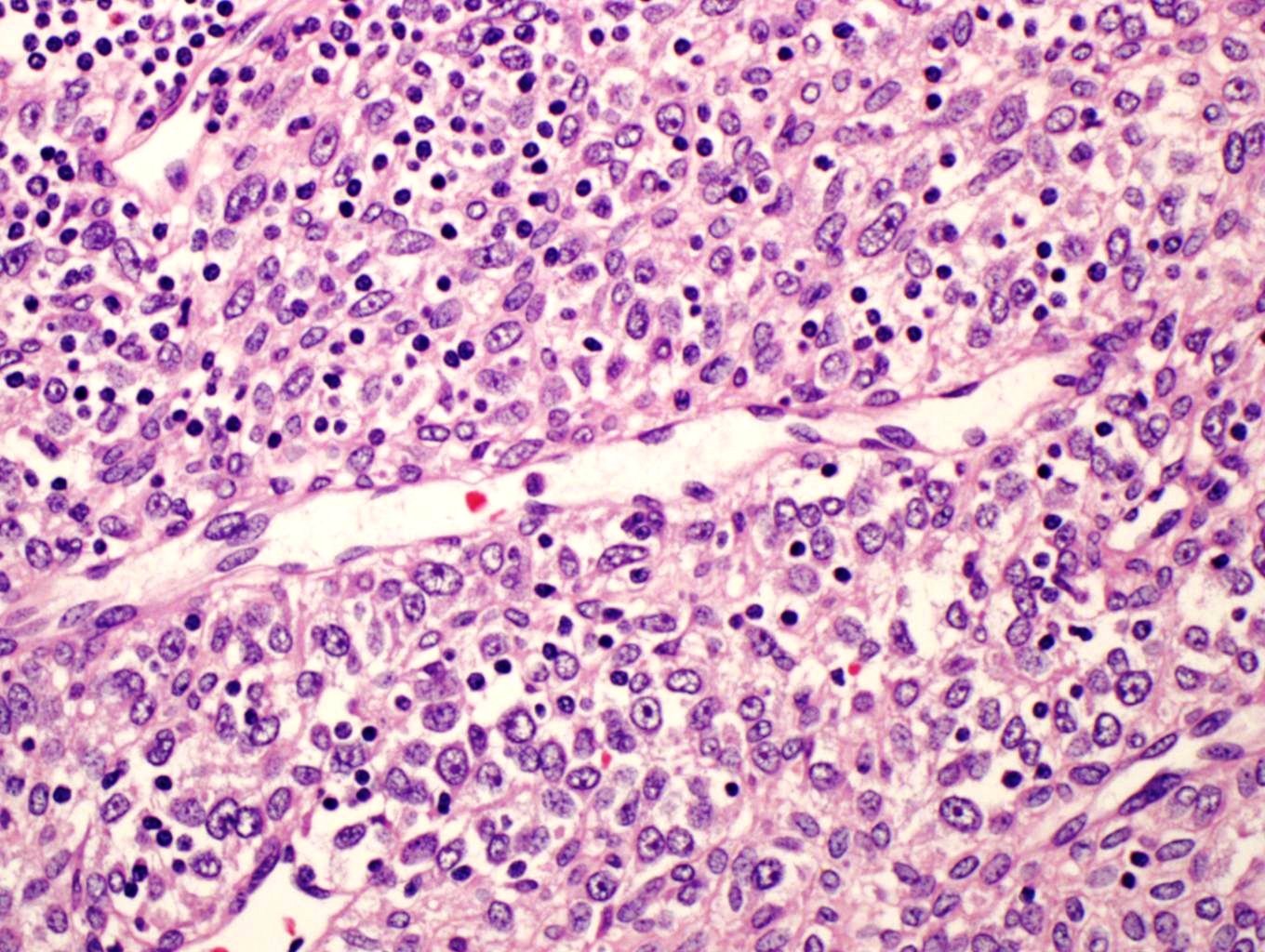
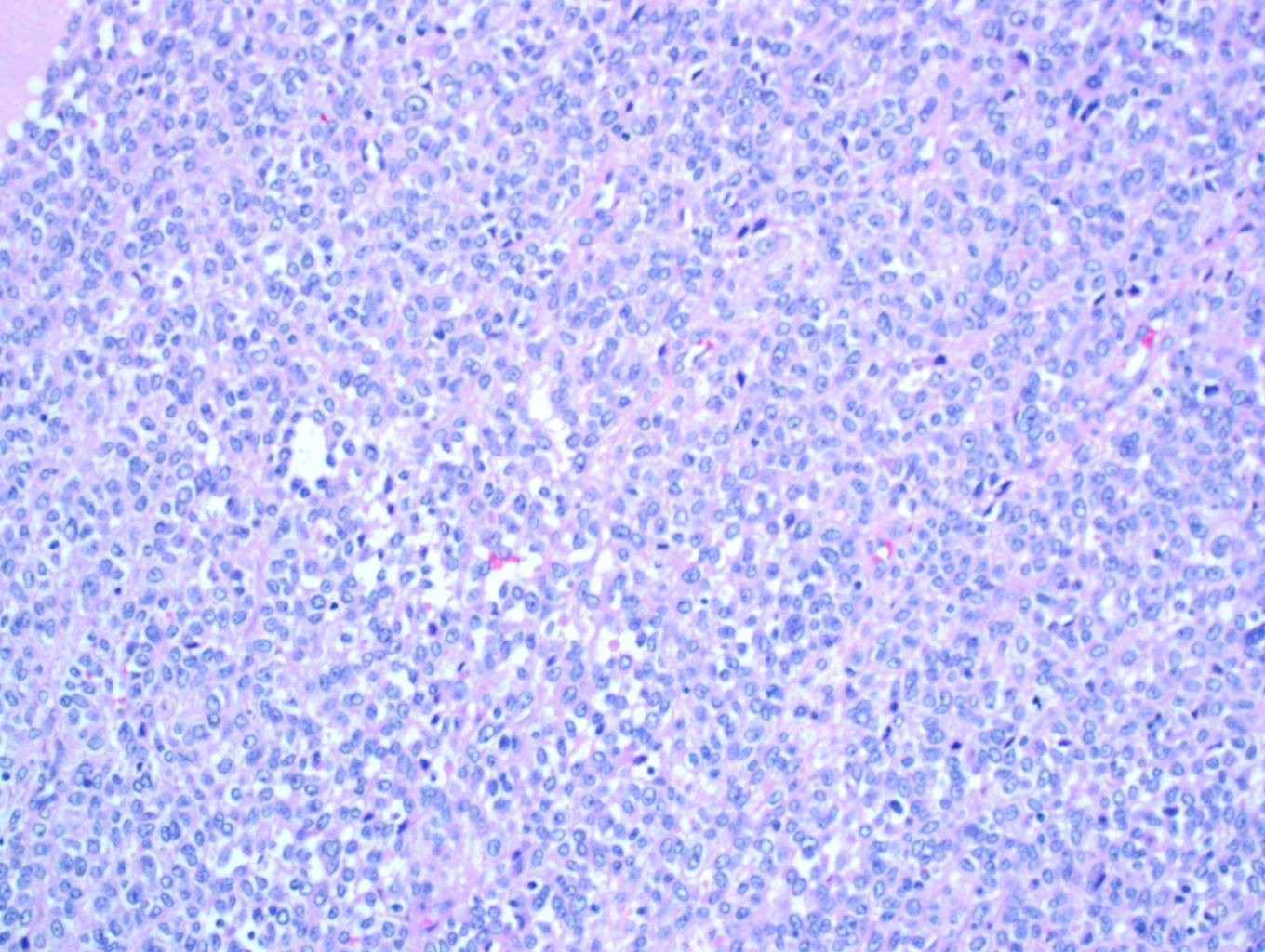
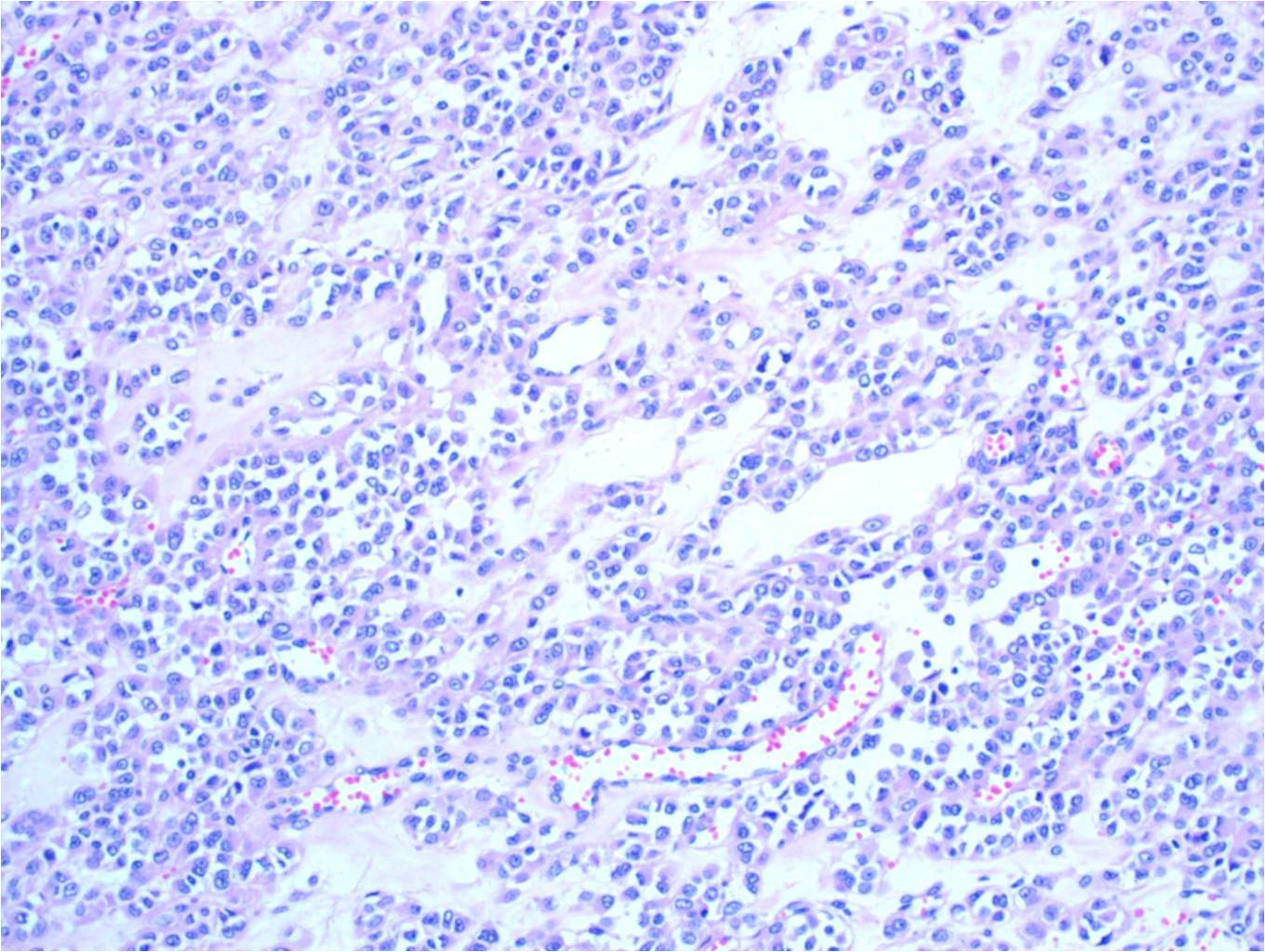
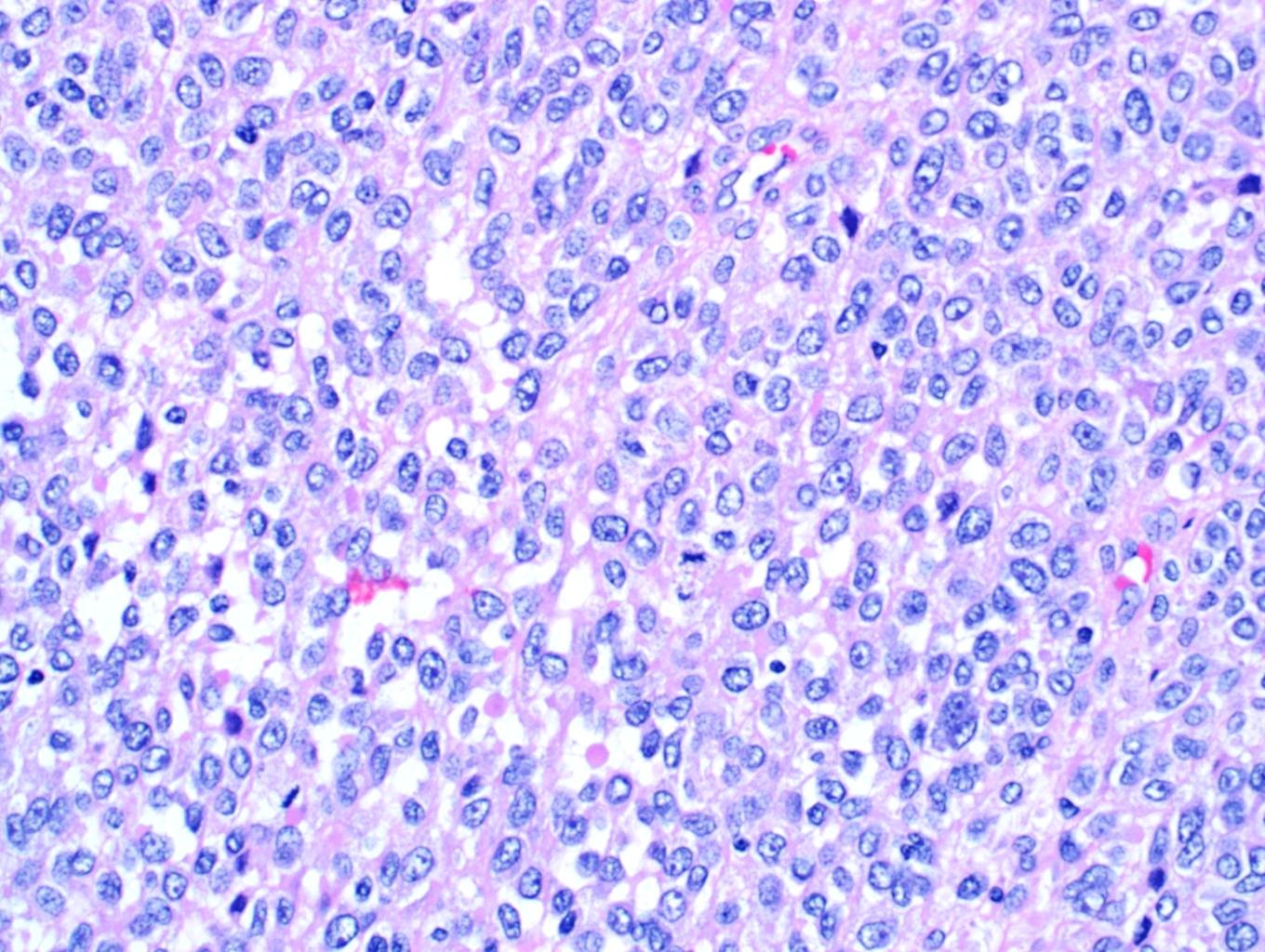
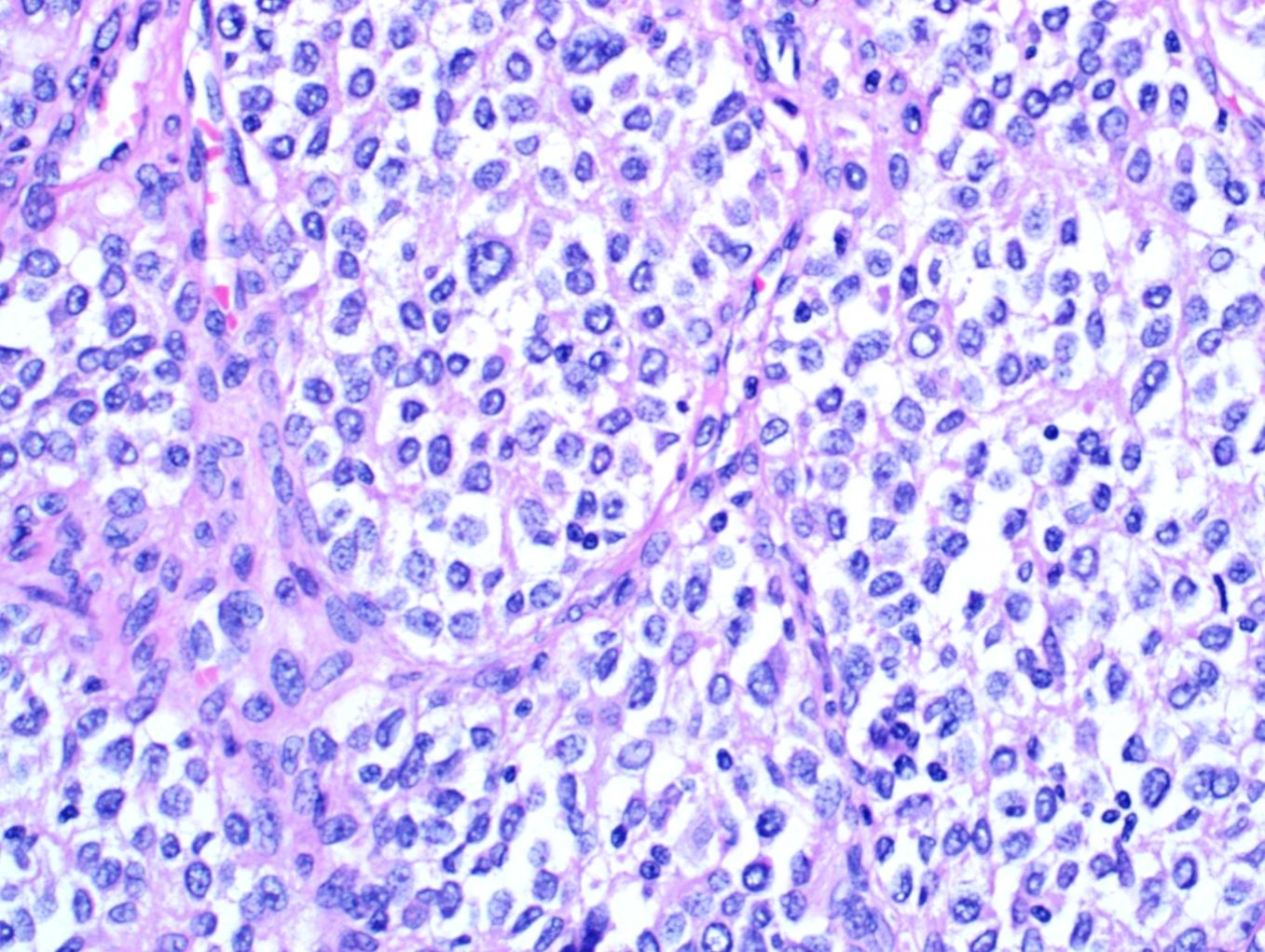
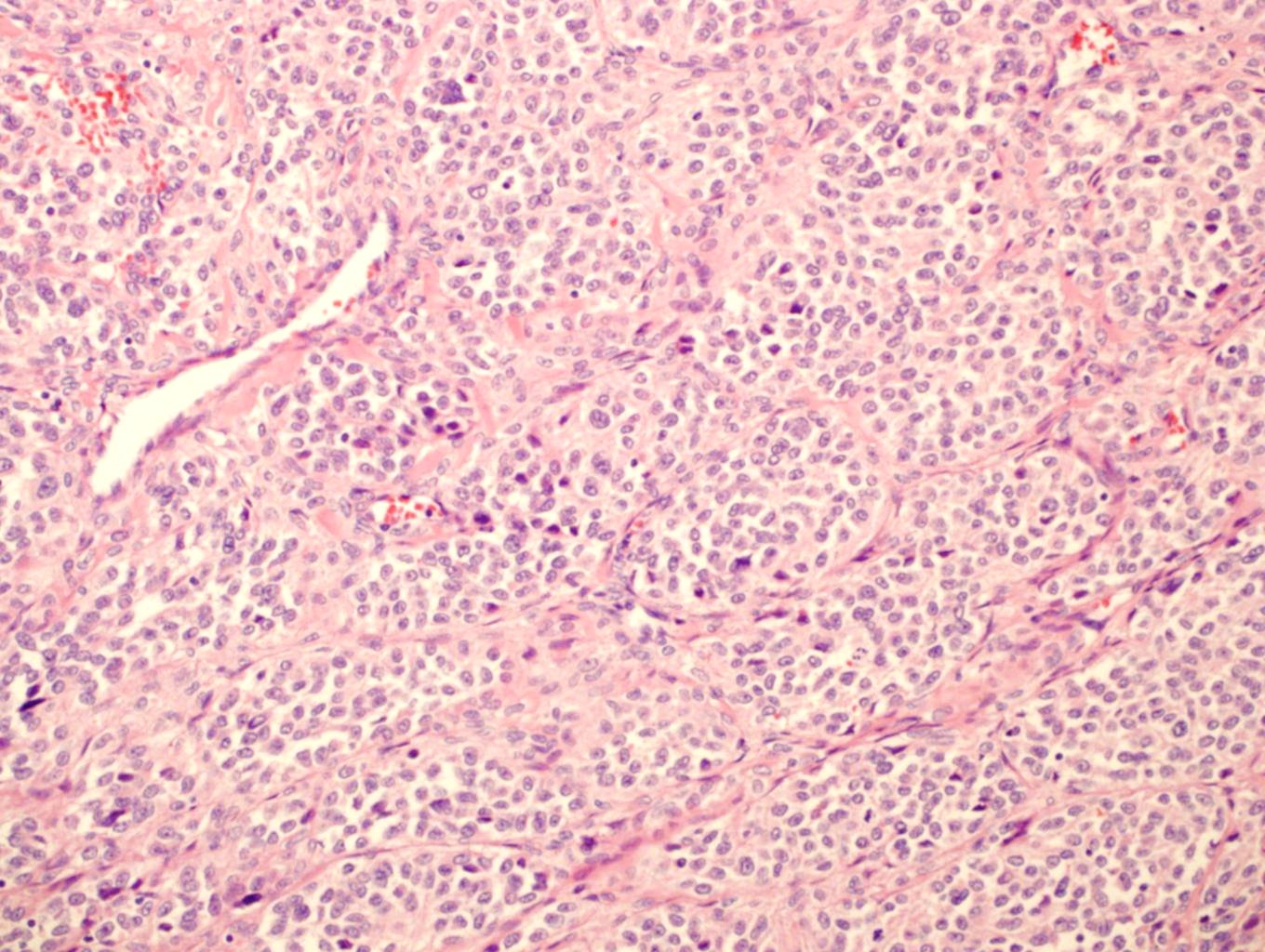
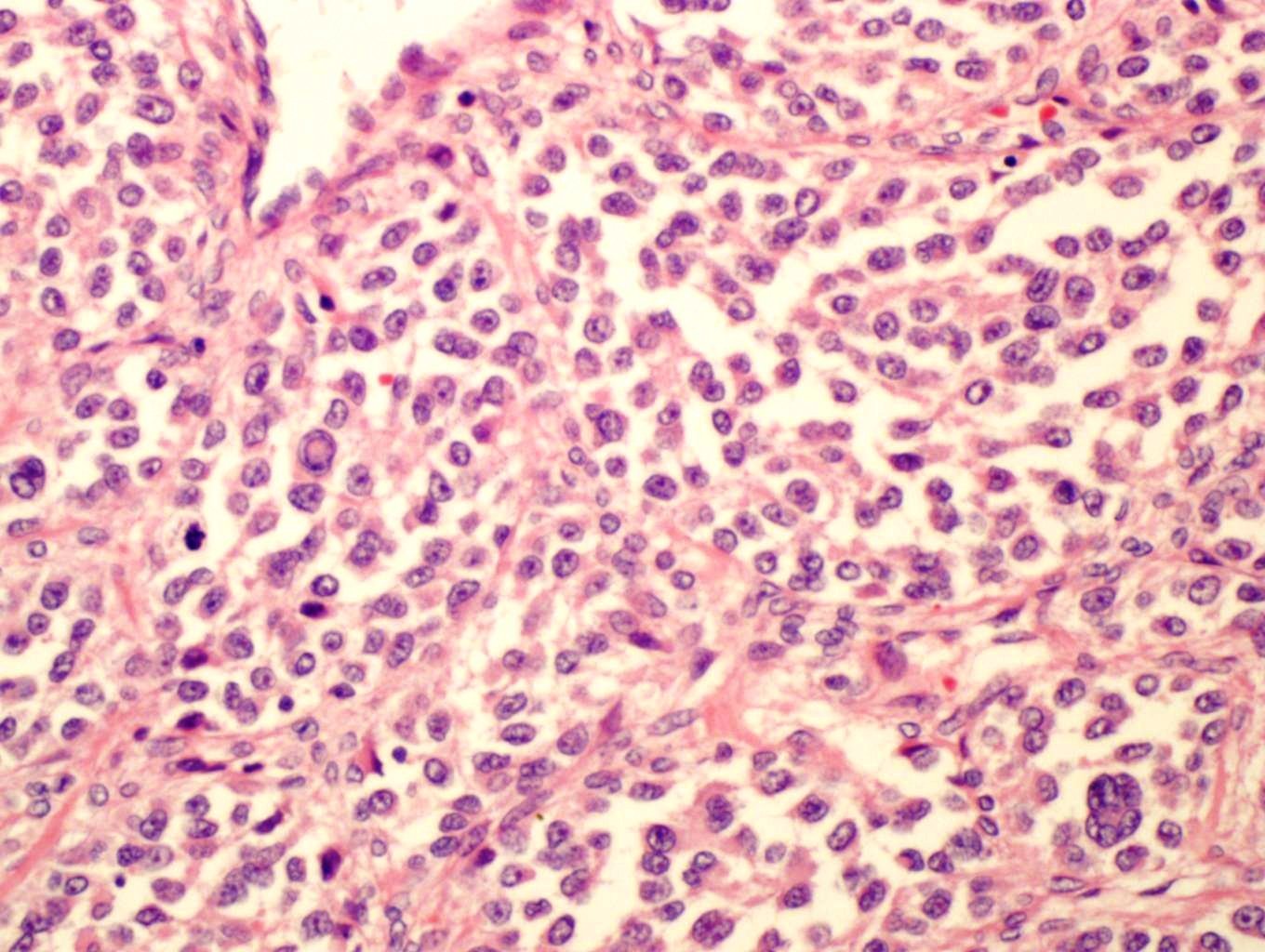
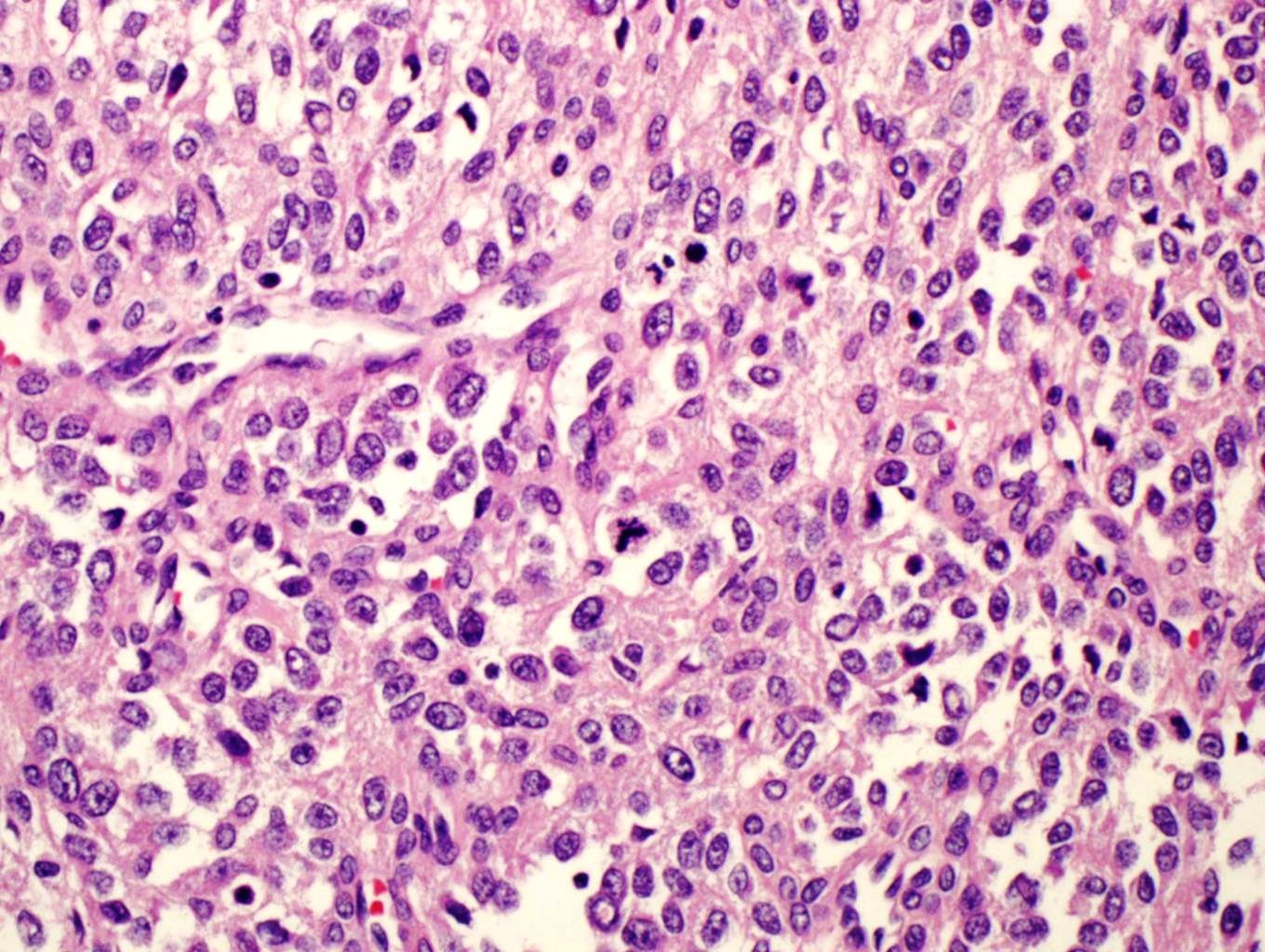
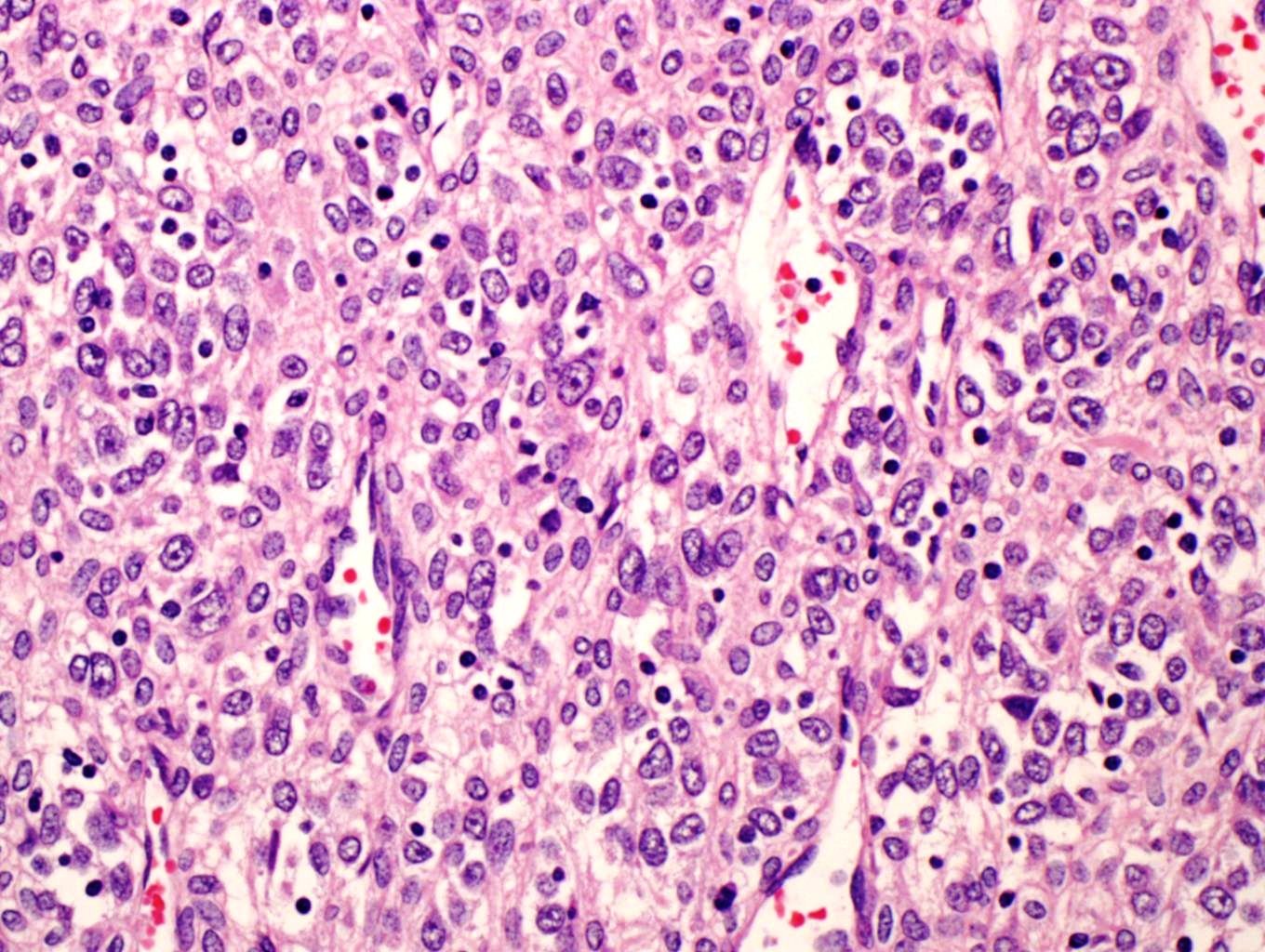
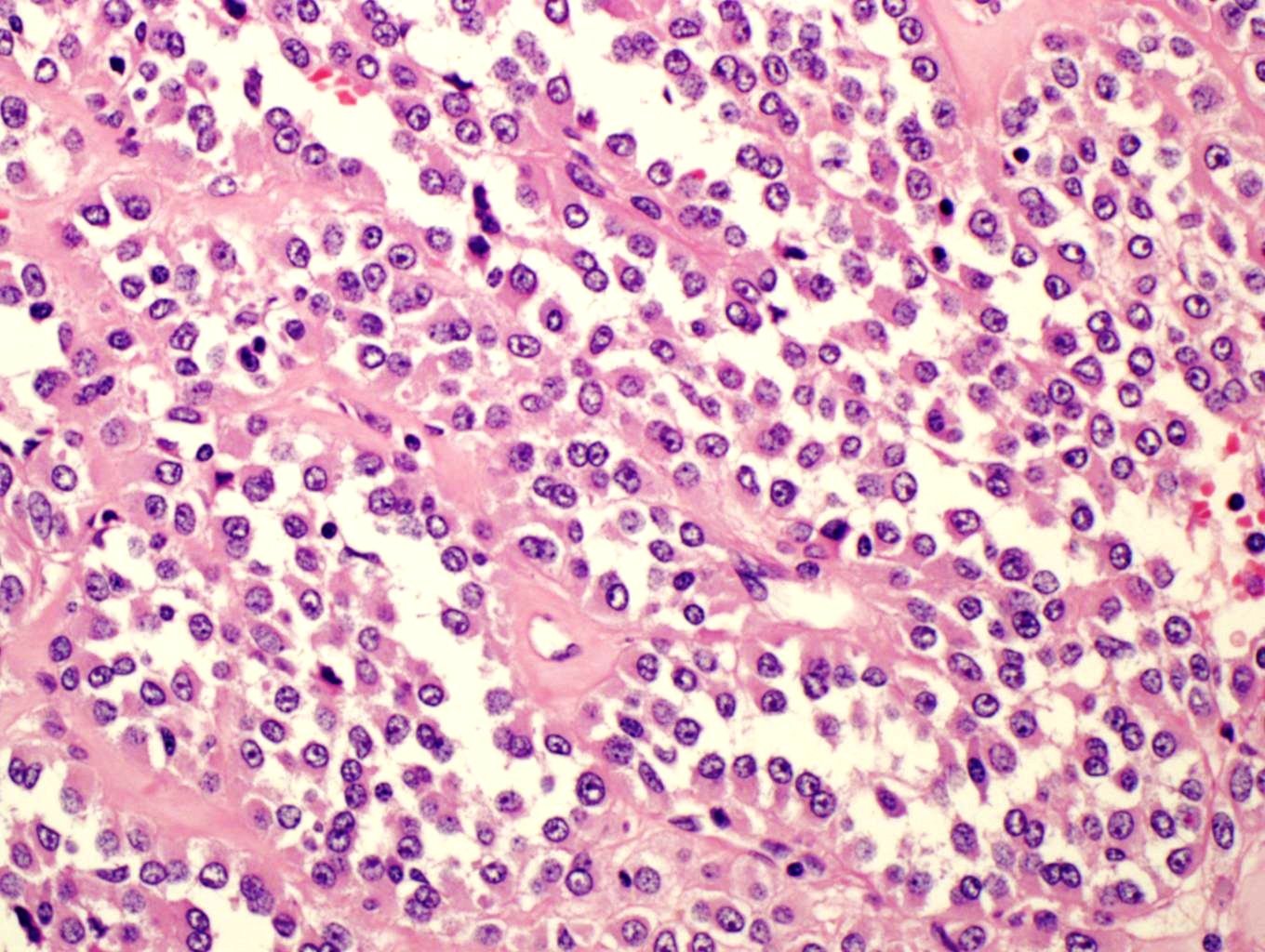
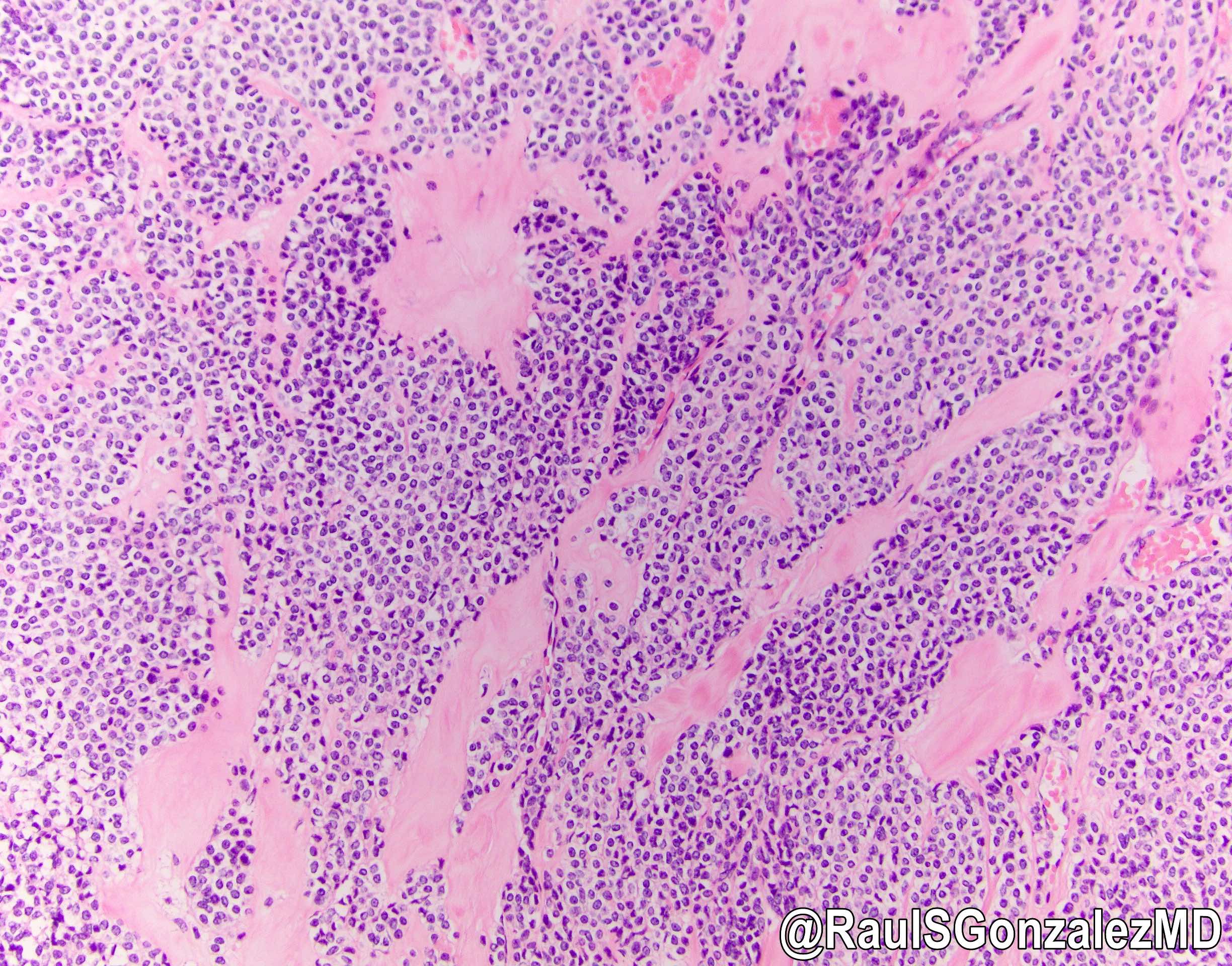
- Multiple cellular nodules often separated by streaks of gastric smooth muscle
- Glomus cells are round, sharply demarcated, with cytoplasmic clearing
- Hyaline and myxoid change often in center of tumor
- Mildly dilated pericytoma-like vessels
- Vascular invasion and focal atypia common
- 1-4 mitotic figures / 50 HPF
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Smooth muscle actin, calponin, h-caldesmon, net-like pericellular laminin and collagen type IV
Electron microscopy description
- Cytoplasm packed with myofilaments with focal condensations
- Resembles smooth muscle cells
Differential diagnosis
- Carcinoid: less prominent cell borders, coarser chromatin, keratin+, chromogranin+, synaptophysin+
- Epithelioid GIST: pericellular clearing, polygonal and not oval / round, less prominent veins / capillaries
- Hemangiopericytoma / solitary fibrous tumor: very rare in GI tract, actin-
- Paraganglioma: zellballen surrounded by sustentacular cells; chromogranin+, synaptophysin+, S100+