Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Yeh YA. YAP1. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsyap1.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- YAP1 (yes associated protein 1) is a transcriptional regulator that activates gene transcription involved in cellular survival and proliferation and suppresses apoptotic genes
Essential features
- Loss of YAP1 C terminus expression for detecting YAP1 fusion in porocarcinoma and poroma (J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:403)
- YAP1 break apart FISH probe for detecting YAP1 rearranged tumors, including epithelioid hemangioendothelioma, sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma, retiform and composite hemangioendothelioma and pediatric meningioma (Genes Chrom Cancer 2013;52:775, Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:368, Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1677, Acta Neuropathol 2020;139:215)
- Increased expression of YAP1 is associated with unfavorable disease and biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer (Sci Rep 2020;10:8916)
- Overexpression of YAP1 is associated with poor prognosis in many cancers, including colorectal cancer, breast cancer, bladder cancer and non small cell lung cancer (Cancer Sci 2010;101:1279, BMC Cancer 2013;13:349)
Terminology
- YAP
- YAP2
- YAP65
- YKI
- Protein yorkie homolog
- COB1
Pathophysiology
- When Hippo signaling pathway is on, mammalian STE20-like protein kinase 1 / 2 (MST1 / 2) and salvador family WW domain containing protein 1 (SAV1) are activated
- These kinases phosphorylate and activate large tumor suppressor 1 / 2 (LATS1 / 2) (Nat Rev Cancer 2015;15:73)
- LATS1 / 2 kinases phosphorylate YAP or transcriptional coactivator with PDZ binding motif (TAZ) through the interaction with MOB kinase activator 1A / 1B (MOB1A / 1B)
- As a result, the active phosphorylated YAP / TAZ binds to 14-3-3, leading to cytoplasmic retention and ubiquitin mediated proteasomal degradation
- Neurofibromin 2 (NF2) can activate LATS1 / 2 through a nonkinase reaction
- Unknown kinase(s) may phosphorylate LATS1 / 2 in an MST1 / 2 independent fashion
- When the Hippo signaling pathway is off, YAP / TAZ are not phosphorylated by LATS1 / 2
- YAP and TAZ translocate to the nucleus and bind to transcription factor TEAD, leading to transcription activation of target genes, including AMOTL2, AREG, BIRC5, CTGF and CYR61, and promoting cell survival and proliferation (Nat Rev Cancer 2015;15:73)
Clinical features
- YAP1 expression is associated with cancer development, including promoting malignant transformation, proliferation of cancer stem cells and drug resistance (Int J Cancer 2018;143:2133)
- Loss of YAP1 is seen in neuroendocrine differentiation of lung cancer (Cancer Sci 2016;107:1527)
- YAP1 contributes to multidrug resistance of small cell lung cancer (Cancer Med 2020;9:259)
- YAP / TAZ is hyperactivated in breast cancer (Expert Rev Mol Med 2015;17:e14)
- Upregulation of EGFR by YAP1 contributes to chemoresistance in esophageal cancer cells (Clin Cancer Res 2015;21:2580)
- YAP1 expression is associated with aggressive behavior in papillary thyroid carcinoma (Endocrine 2018;59:209)
- YAP1 promotes invasion and metastasis of melanoma cells (Oncogene 2020;39:5267)
- YAP1 is overexpressed in hedgehog associated medulloblastoma (Genes Dev 2009;23:2729)
- YAP1 signaling pathway may be a target for the combination chemotherapy of childhood rhabdomyosarcoma (Cancer Res 2020;80:3046)
- Dysregulation of YAP / TAZ is involved in lung cancer, obstructive lung disease and pulmonary fibrosis (Life Sci 2018;214:176)
- YAP1 is identified as a susceptible gene for polycystic ovary syndrome (J Med Genet 2012;49:254)
- YAP1 loss of function mutation is associated with optic fissure closure defect (Am J Hum Genet 2014;94:295)
- YAP1 may serve as a potential target for cancer chemotherapy (Pharmacol Res 2016;103:270)
Interpretation
- Cytoplasmic and predominantly nuclear staining
Uses by pathologists
- Loss of YAP1 C terminus expression for detecting YAP1 fusion in porocarcinoma and poroma (J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:403)
- YAP1 break apart FISH probe for detecting YAP1 rearranged tumors, including:
- Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (Genes Chrom Cancer 2013;52:775)
- Sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:368)
- Retiform and composite hemangioendothelioma (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1677)
- Pediatric meningioma (Acta Neuropathol 2020;139:215)
Prognostic factors
- Overexpression of cytoplasmic YAP1 predicted unfavorable prognosis in colorectal cancer (PeerJ 2020;8:e10397)
- Increased expression of nuclear YAP1 is associated with worse prognosis in gallbladder cancer (Cancer Lett 2014;355:201)
- YAP1 activation is associated with poor prognosis in ovarian cancer (Anticancer Res 2014;34:811)
- YAP1 activity is associated with progression in oral squamous cell carcinoma (Sci Adv 2020;6:eaay3324)
- Nuclear expression of YAP1 correlated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer (Anticancer Res 2012;32:3827)
- High expression of YAP1 contributed to poor outcome in urothelial carcinoma of the bladder (BMC Cancer 2013;13:349)
- YAP1 overexpression is associated with poor tumor differentiation in hepatocellular carcinoma (Cancer 2009;115:4576)
- YAP1 hyperactivation tumors are linked to worse overall survival rate in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (Carcinogenesis 2011;32:389)
- YAP1 overexpression is associated with progression and poor prognosis of non small lung cancer (Cancer Sci 2010;101:1279)
- Upregulation of YAP1 is associated with unfavorable disease and biochemical recurrence in prostate cancer (Sci Rep 2020;10:8916)
- Increased expression of YAP1 is linked to extraprostatic extension (Cancer Biol Med 2017;14:405)
- YAP1 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer (FEBS Open Bio 2019;9:437)
- High expression of YAP1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma is associated with poor prognosis (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2019;27:59)
Microscopic (histologic) description
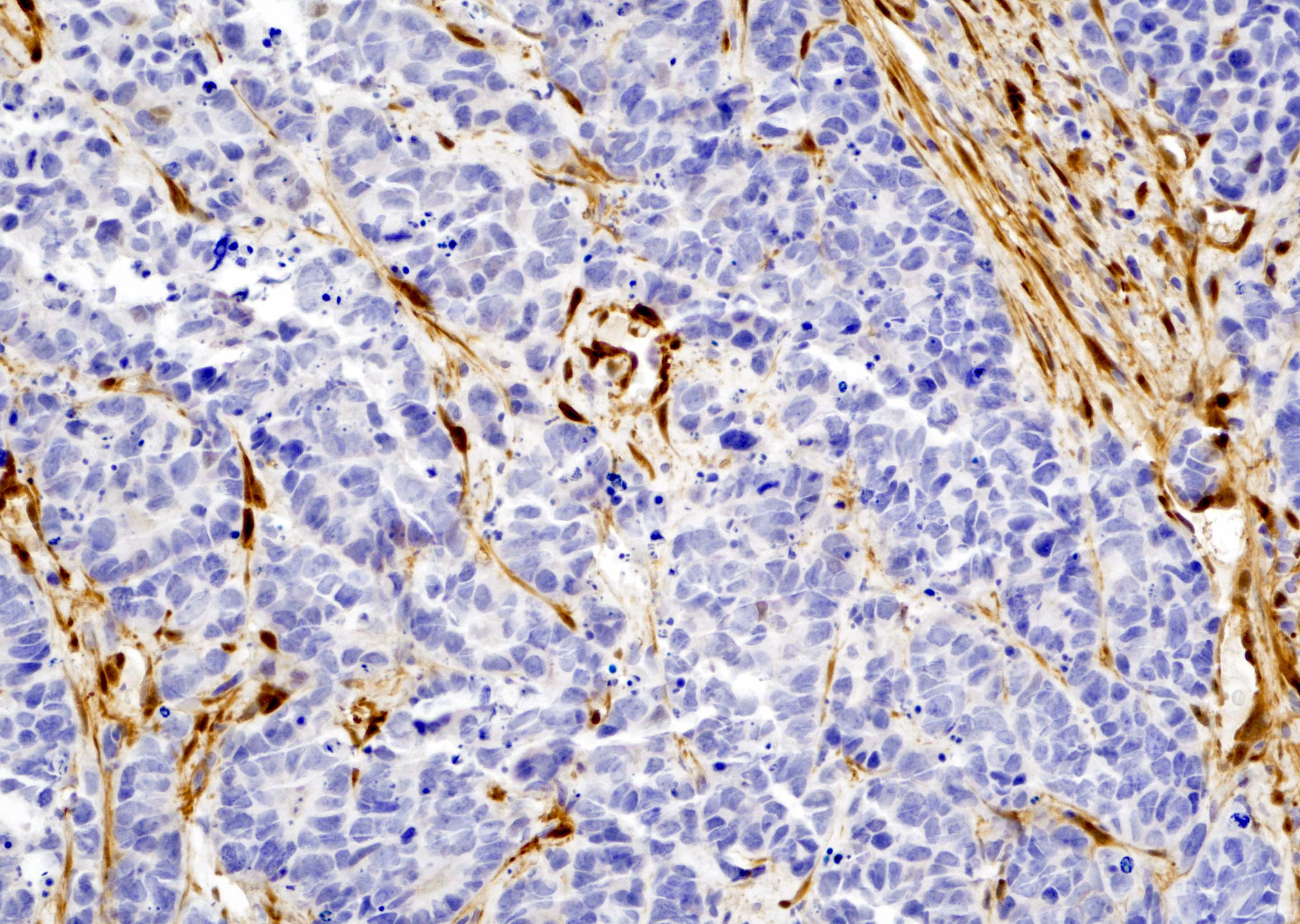
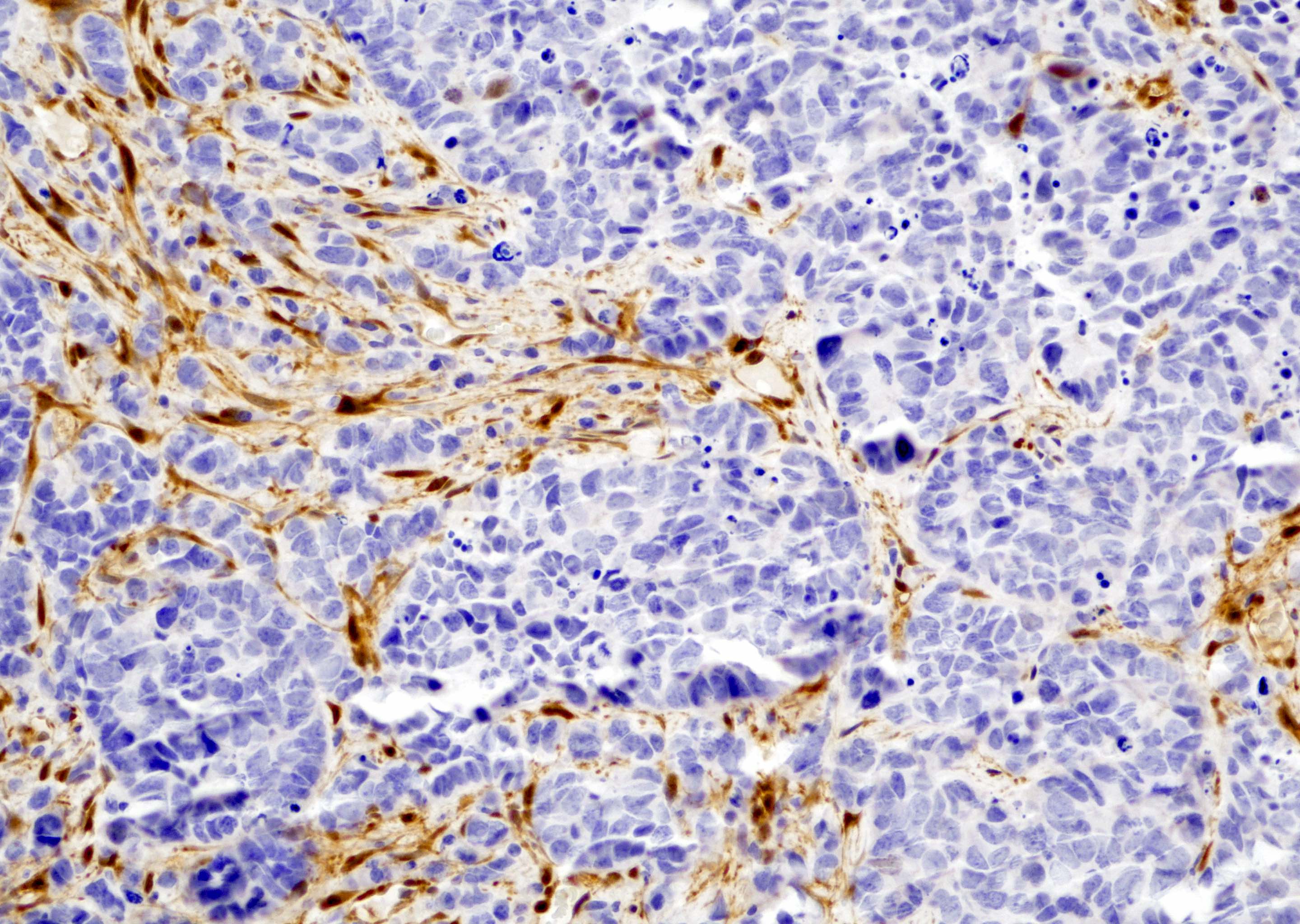
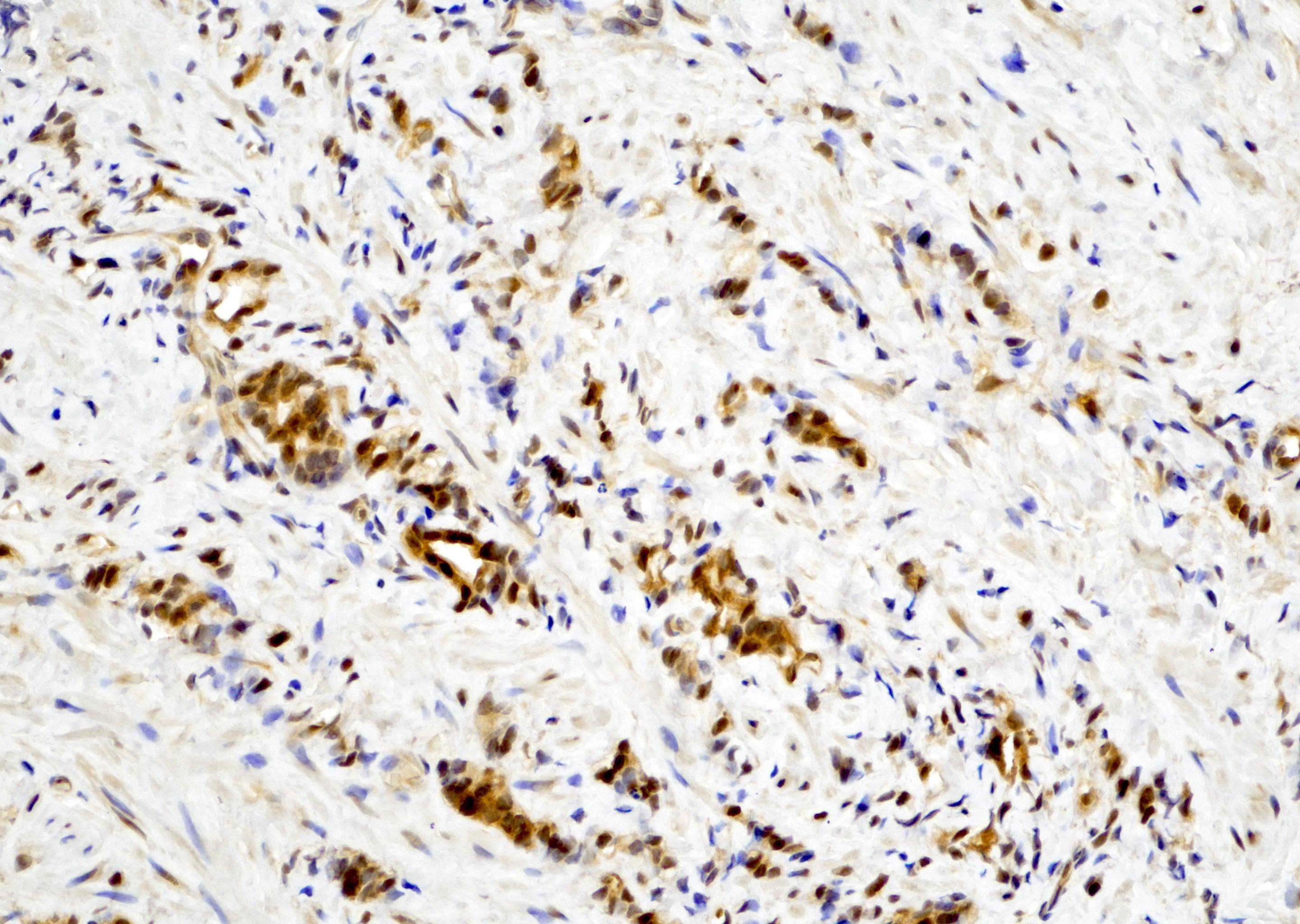
- Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate is negative for YAP1 (see Microscopic images 1, 2, 3)
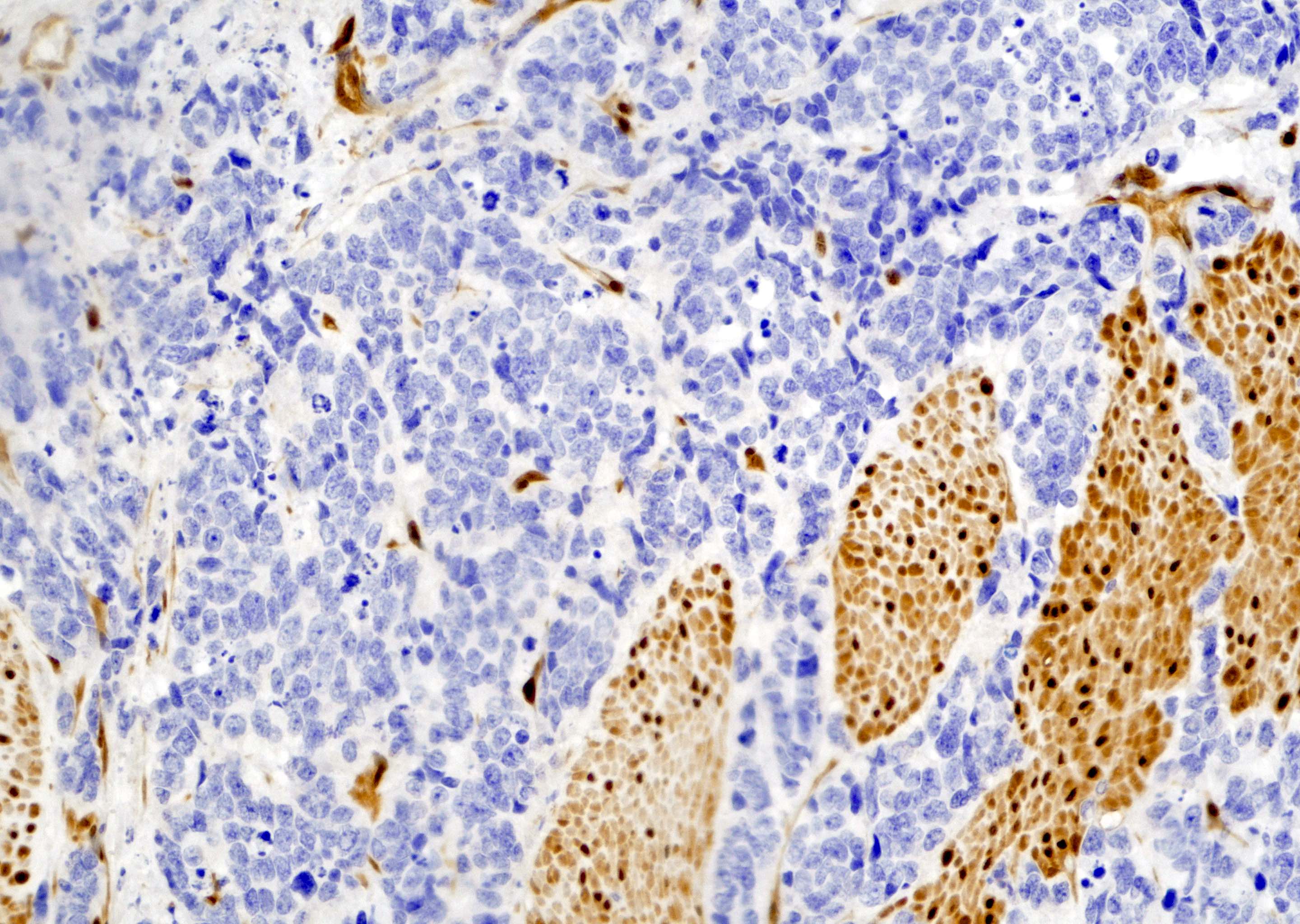
- Low risk prostatic adenocarcinoma cells (Gleason score 3+3=6, grade group 1) show focally positive nuclear staining for YAP1 (see Microscopic image 4)
- In prostatic adenocarcinoma, Gleason score 3+4=7 (grade group 2), many carcinoma cells show positive nuclear staining for YAP1 in the glomeruloid structure (Gleason pattern 4) (see Microscopic image 5)
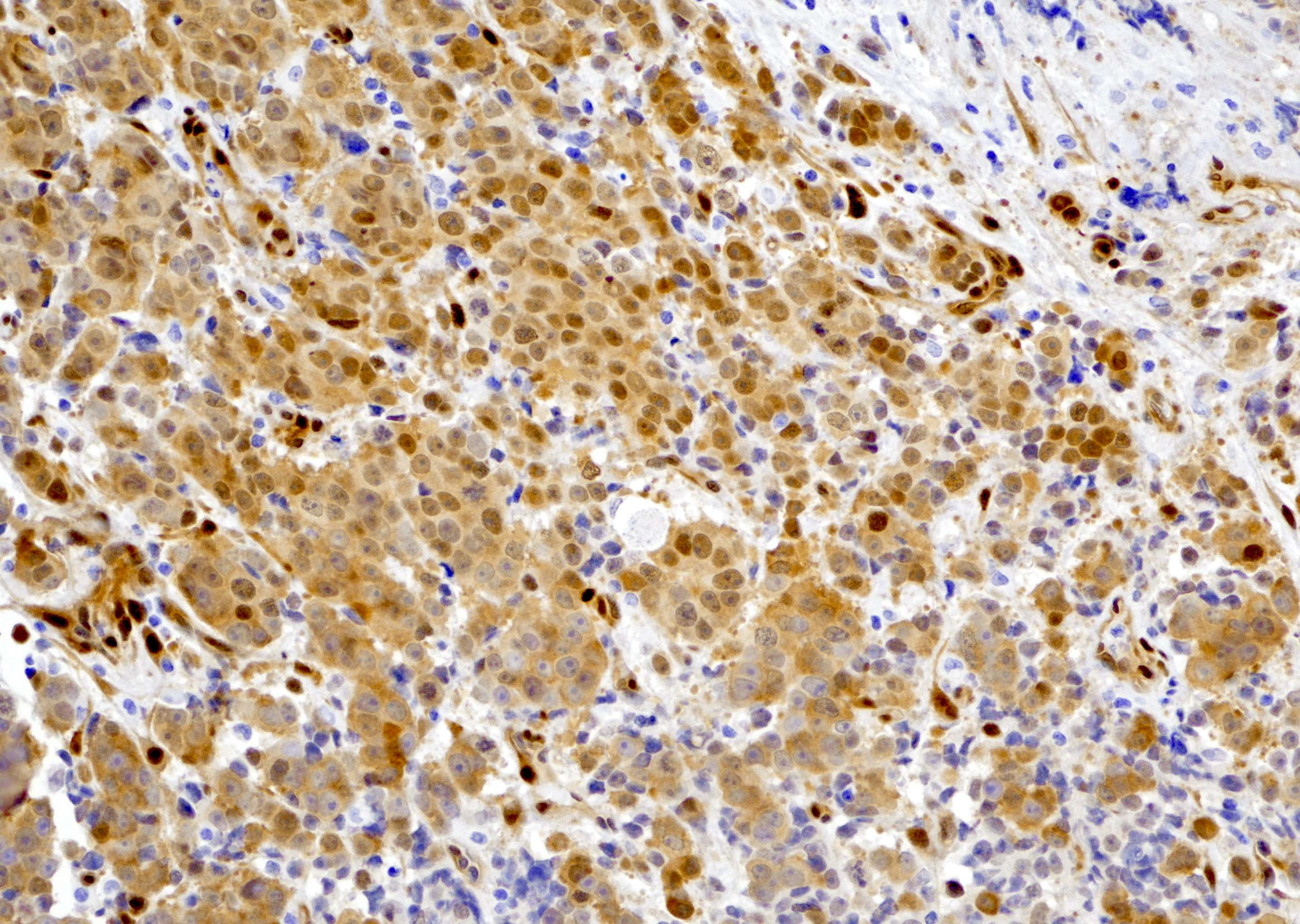
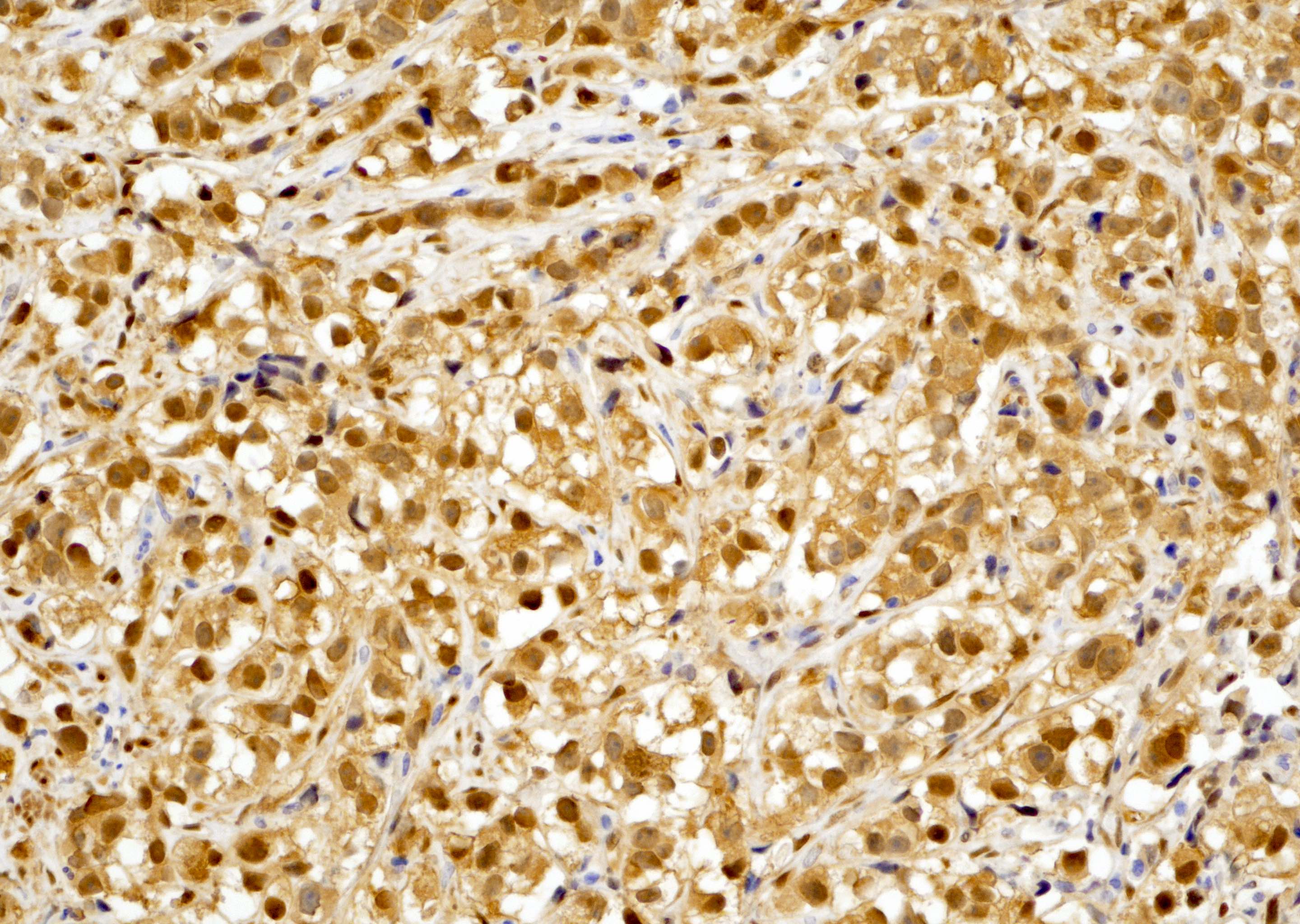
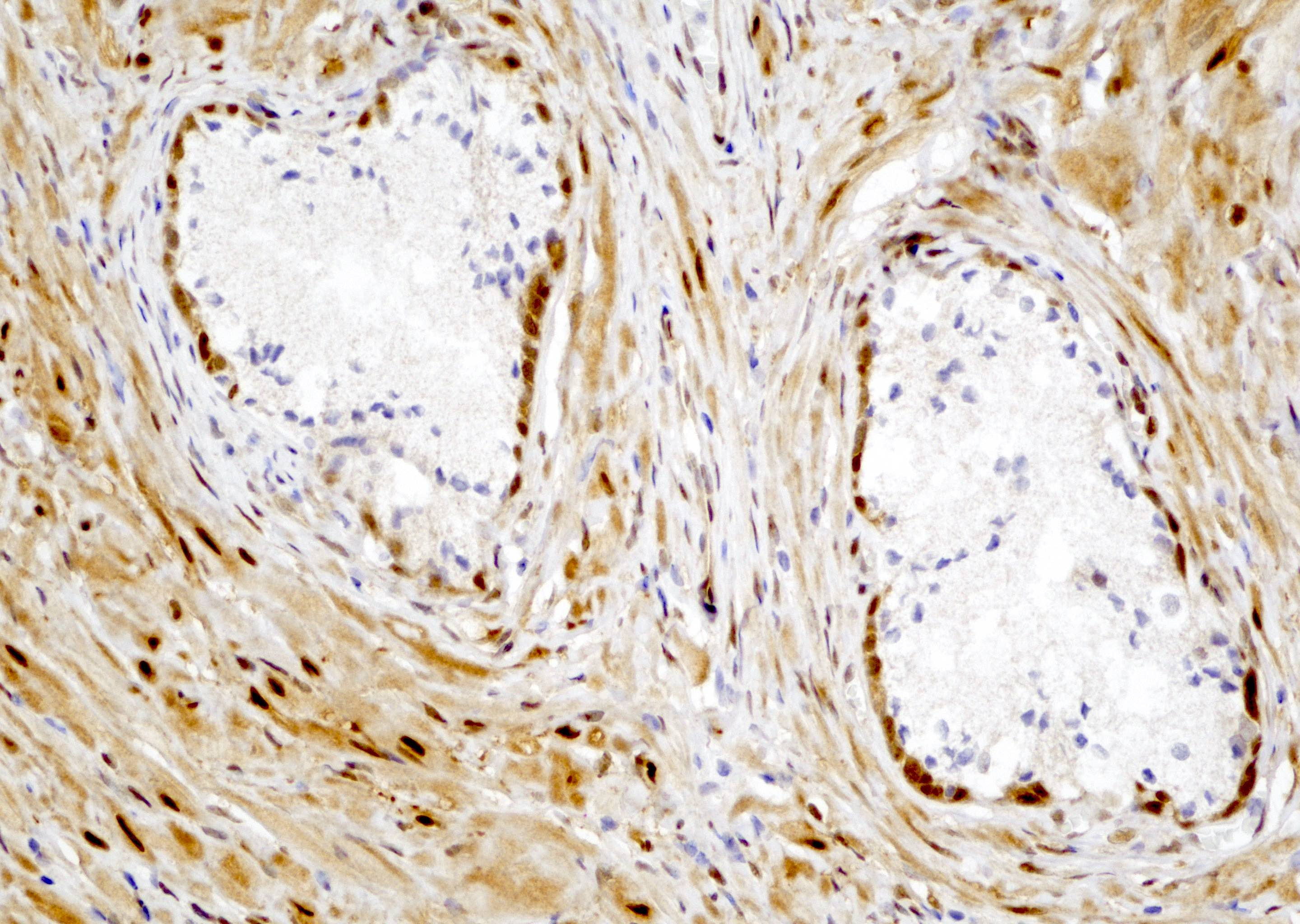
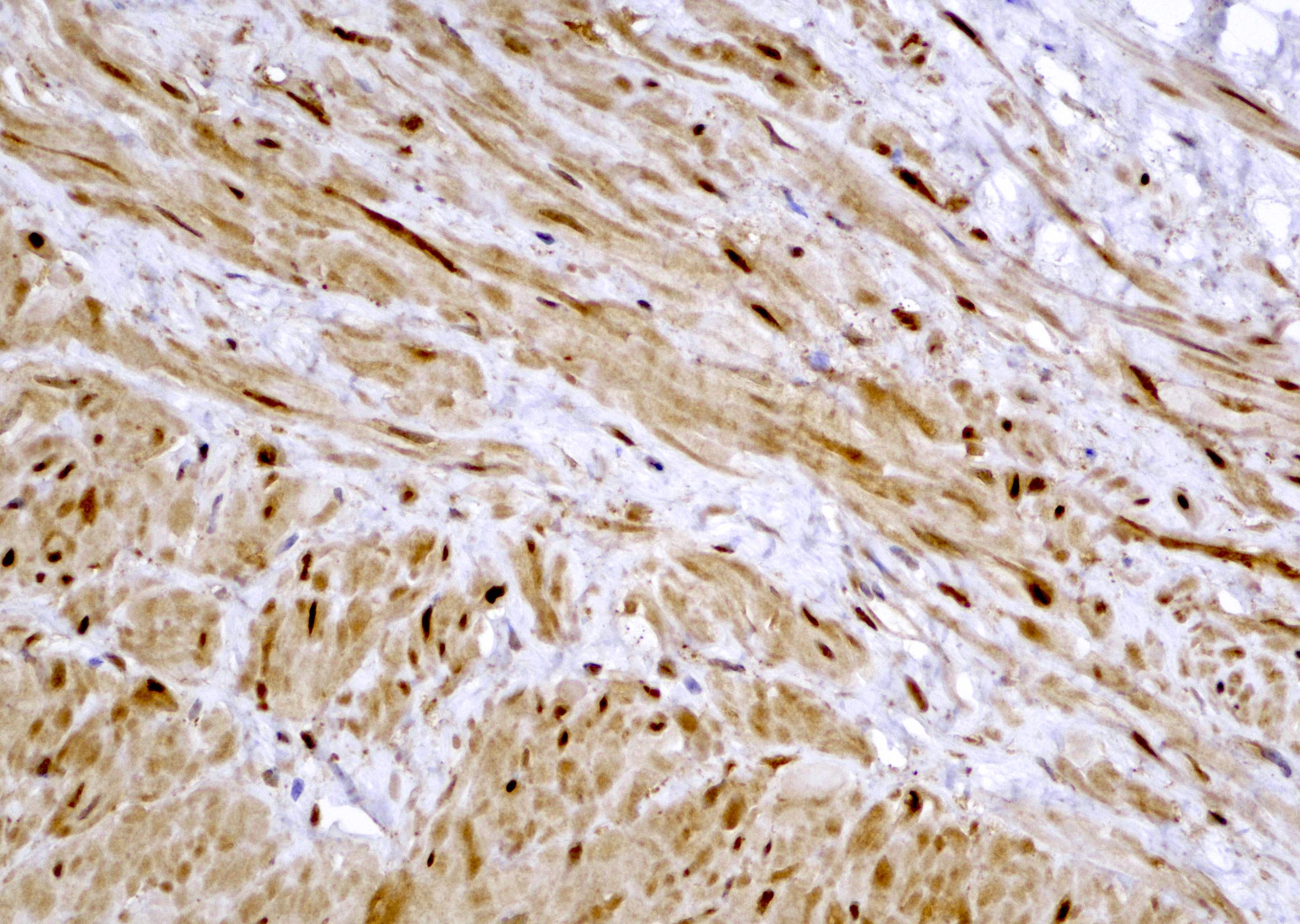
- In high risk prostatic adenocarcinoma (Gleason 4+4=8, 4+4=9, 5+5=10), tumor cells are diffusely stained positive for YAP1 (see Microscopic images 6, 7, 8)
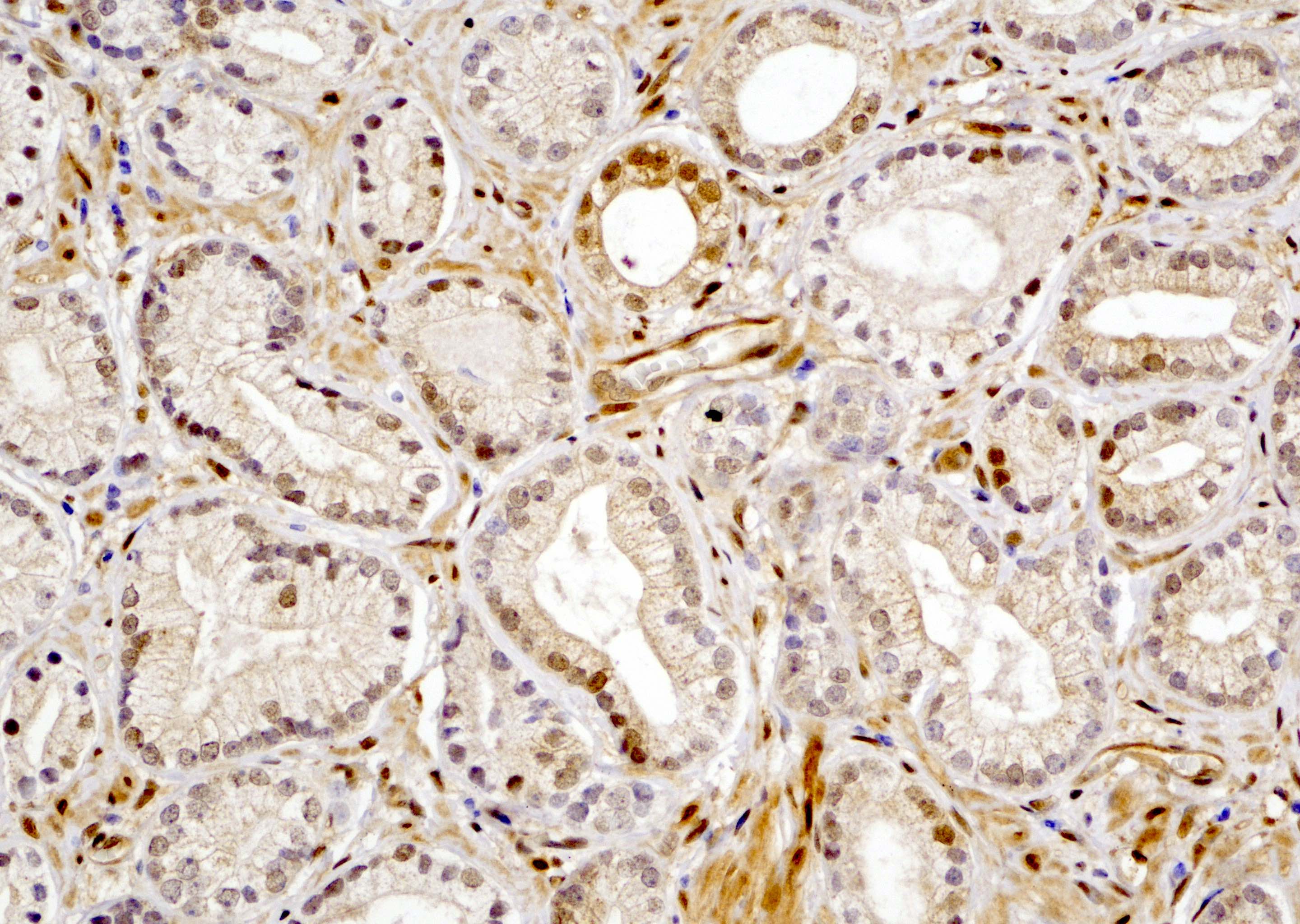
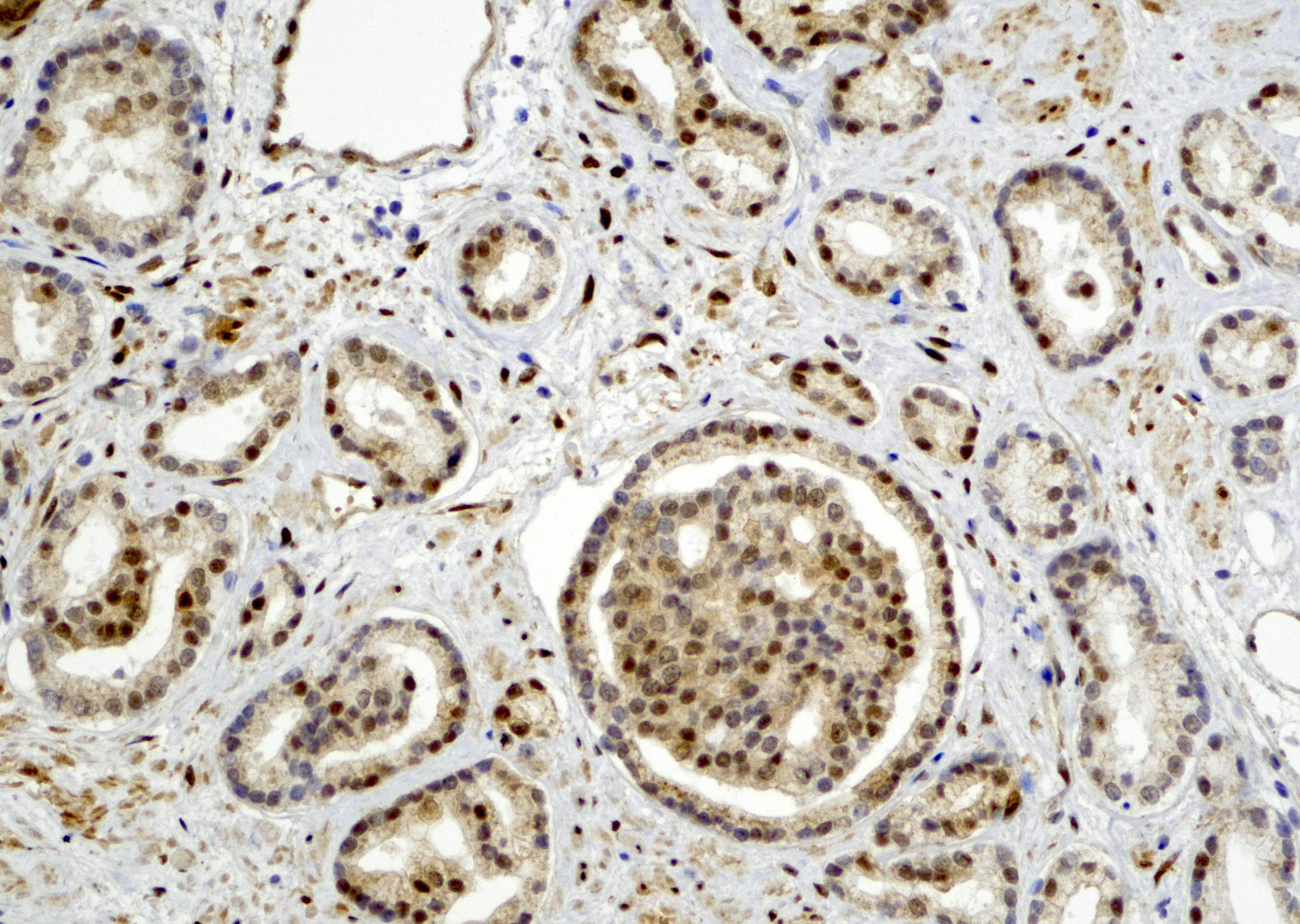
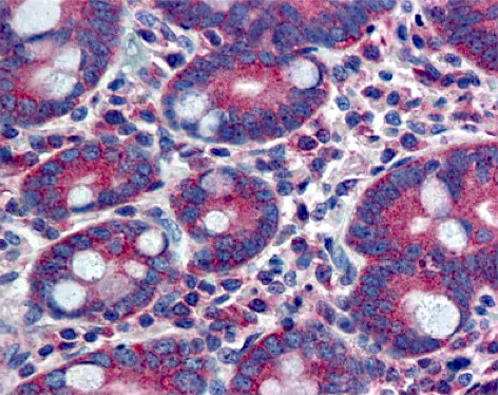
- In benign prostatic tissue, basal cells, fibromuscular stroma and smooth muscles are stained positive for YAP1; benign prostatic luminal cells show negative staining for YAP1 (see Microscopic images 9, 10)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
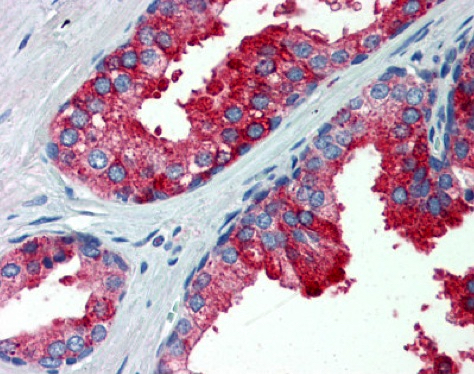
- Basal cells of prostate (Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2020;23:661)
- Myoepithelial cells (nuclear) and luminal cells (cytoplasmic) of breast (Arch Med Res 2014;45:223)
- Lung
- Esophagus
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
- Thyroid gland
- Adrenal gland
- Kidney (cells in glomeruli and renal tubules)
- Endometrium
- Ovary
- Adipose tissue
- Smooth muscle
- Reference: The Human Protein Atlas: YAP1 [Accessed 16 April 2021]
Positive staining - disease
- High risk prostatic acinar adenocarcinoma (Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2020;23:661)
- Lung cancer (Hum Pathol 2008;39:1582)
- Ductal carcinoma of the breast (Hum Pathol 2008;39:1582)
- Colonic adenocarcinoma (Hum Pathol 2008;39:1582)
- Urothelial carcinoma of the bladder (BMC Cancer 2013;13:349)
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity (Oncol Lett 2019;18:3561)
Negative staining
- Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate (Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2020;23:661)
- 98% of small cell neuroendocrine carcinomas and 60% of large cell neuroendocrine carcinomas of the lung (Cancer Sci 2016;107:1527)
- 58% of porocarcinomas with YAP1 fusion, including YAP1-MAML2 and YAP1-NUTM1 (J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:403)
- 80% of poromas with non-NUT YAP1 fusions (J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:403)
- Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and hidradenocarcinoma (J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:403)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
| YAP1 gene fusion | Tumor type | Reference |
| YAP1-MAMLD1 | Supratentorial ependymoma | Cancer Cell 2015;27:728 |
| YAP1-FAM118B | Supratentorial ependymoma | Cancer Cell 2015;27:728 |
| Meningioma | Am J Surg Pathol 2021;45:329 | |
| YAP1-MAML2 | Pediatric meningioma | Acta Neuropathol 2020;139:215 |
| Poroma and porocarcinoma | J Clin Invest 2019;129:3827 | |
| Retiform and composite hemangioendothelioma | Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1677 | |
| Metaplastic thymoma | Mod Pathol 2020;33:560 | |
| YAP1-PYGO1 | Pediatric meningioma | Acta Neuropathol 2020;139:215 |
| YAP1-LMO1 | Pediatric meningioma | Acta Neuropathol 2020;139:215 |
| YAP1-NUTM1 | Porocarcinoma | J Clin Invest 2019;129:3827 |
| YAP1-TFE3 | Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma | Case Rep Gastrointest Med 2019;2019:7530845 |
| YAP1-KMT2A | Sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma | Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:368 |
| HMGA2-YAP1 | Aggressive angiomyxoma | BMJ Case Rep 2019;12:e227475 |
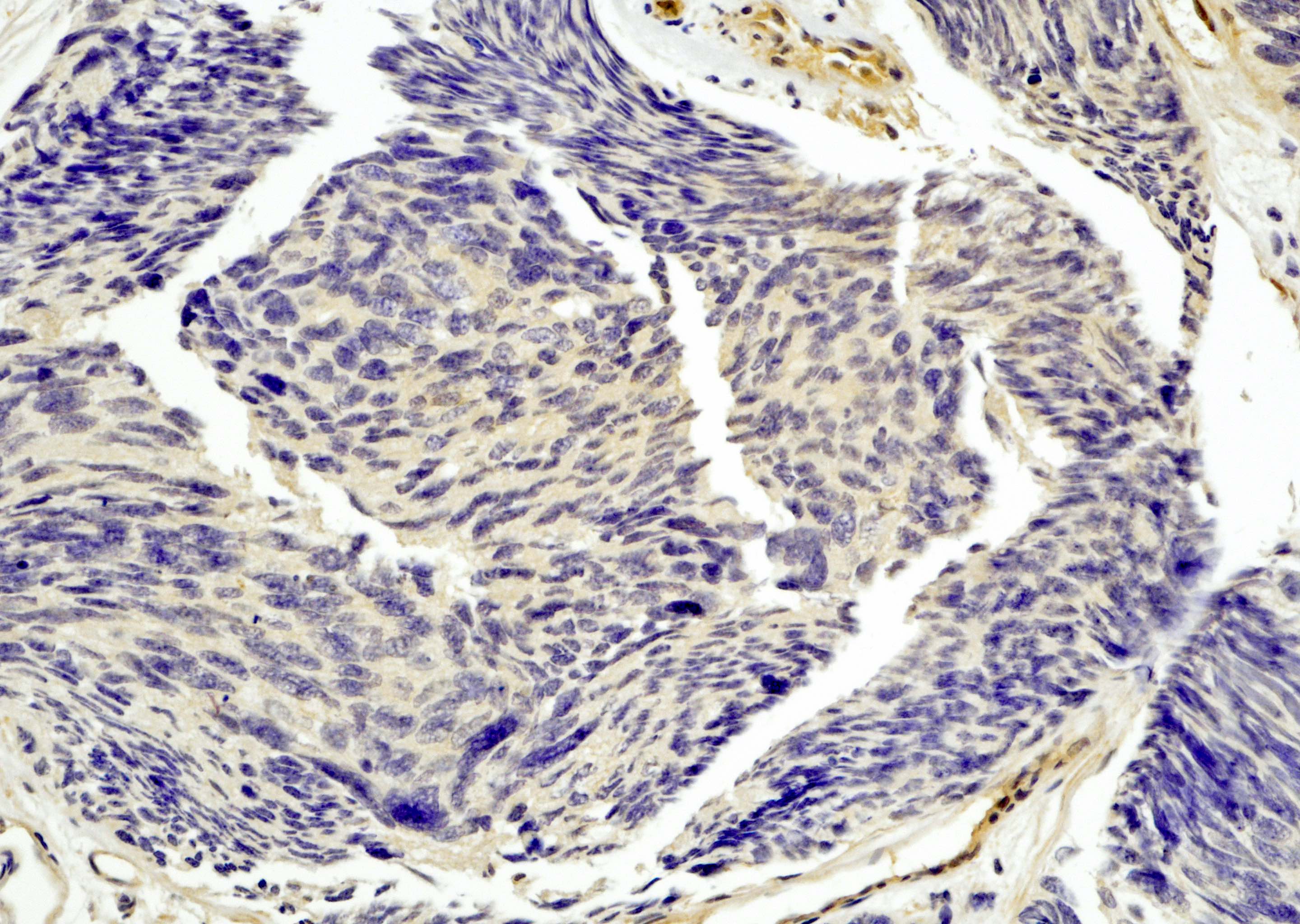
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Sample pathology report
- Skin, right lower leg, excision:
- Malignant cutaneous basaloid tumor with YAP1-NUTM1 fusion (see comment)
- Comment: The skin shows an infiltrating tumor composed of small basaloid cells arranged in anastomosing cords and nests with cystic formation. Tumor cells invade adipose tissue beneath the dermis. Focal tumor necrosis is present. Immunohistochemical stain shows positive nuclear staining of the N terminus of YAP1 but loss of staining of the C terminus. Fluorescence in situ hybridization using YAP1 break apart probe confirms rearrangement of YAP1 gene. RT-PCR testing reveals YAP1-NUTM1 translocation.
Additional references
- J Pathol Transl Med 2017;51:365, JCI Insight 2019;4:e130811, Oncotarget 2017;28:73745, Urol Int 2016;96:39, Pathol Res Pract 2018;214:335, Am J Pathol 2019;189:1091, Pathol Oncol Res 2014;20:805, Oncol Lett 2018;15:6825, J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2016;142:1765, Nat Rev Urol 2015;12:596, Pathology 2019;51:261
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1