Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Pathophysiology | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Sample pathology report | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Ohashi R. Vimentin. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsvimentin.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Intermediate filament for mesenchymal tissue
Essential features
- Vimentin staining confirms mesenchymal origin of some tumors but there are numerous exceptions, so relatively nonspecific
- Carcinomas and epithelial tumors are usually negative but there are many exceptions
- Thus, helps distinguish renal cell carcinoma and uterine carcinoma as part of panel
Pathophysiology
- Intermediate filament protein expressed primarily by cells of mesenchymal origin; the human gene (VIM gene) is located on chromosome 10 (Am J Hum Genet 1987;41:616, J Invest Dermatol 1993;101:383, NCBI: VIM vimentin [Accessed 11 January 2021])
Interpretation
- Cytoplasmic staining
Uses by pathologists
- Vimentin staining confirms mesenchymal origin of some tumors; may be the only positive stain in certain cases and thus confirms that the tissue is capable of staining (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1722)
- May confirm mesenchymal origin but there are numerous exceptions, so relatively nonspecific
- Helps distinguish clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC) from mimics as part of panel
- Absence of vimentin staining may confirm that fat-like or other spaces actually lack a cellular lining (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1823)
- Distinguishes endocervical adenocarcinoma (vimentin negative) and endometrial carcinoma (vimentin positive), as part of panel (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:915)
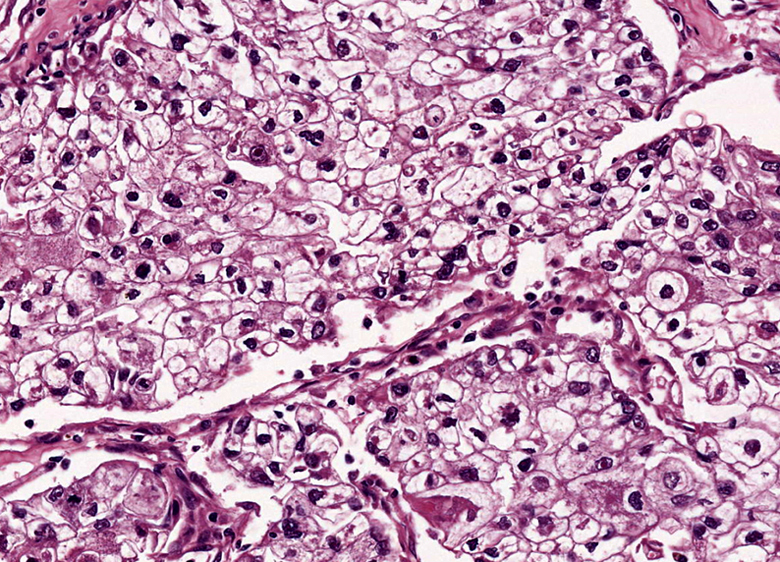
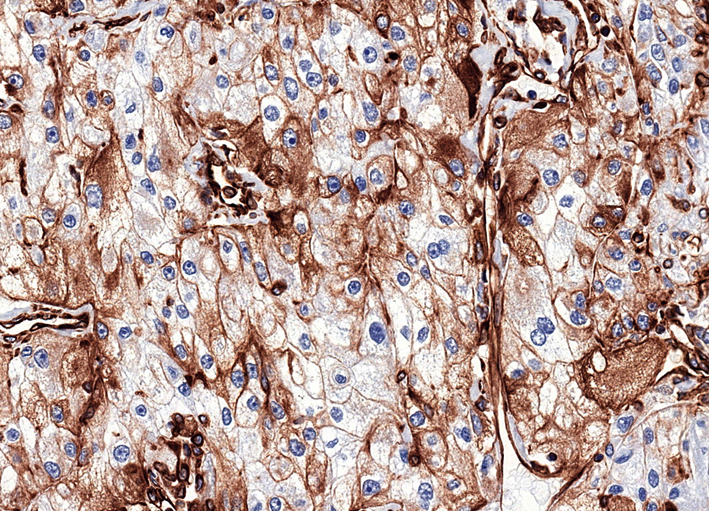
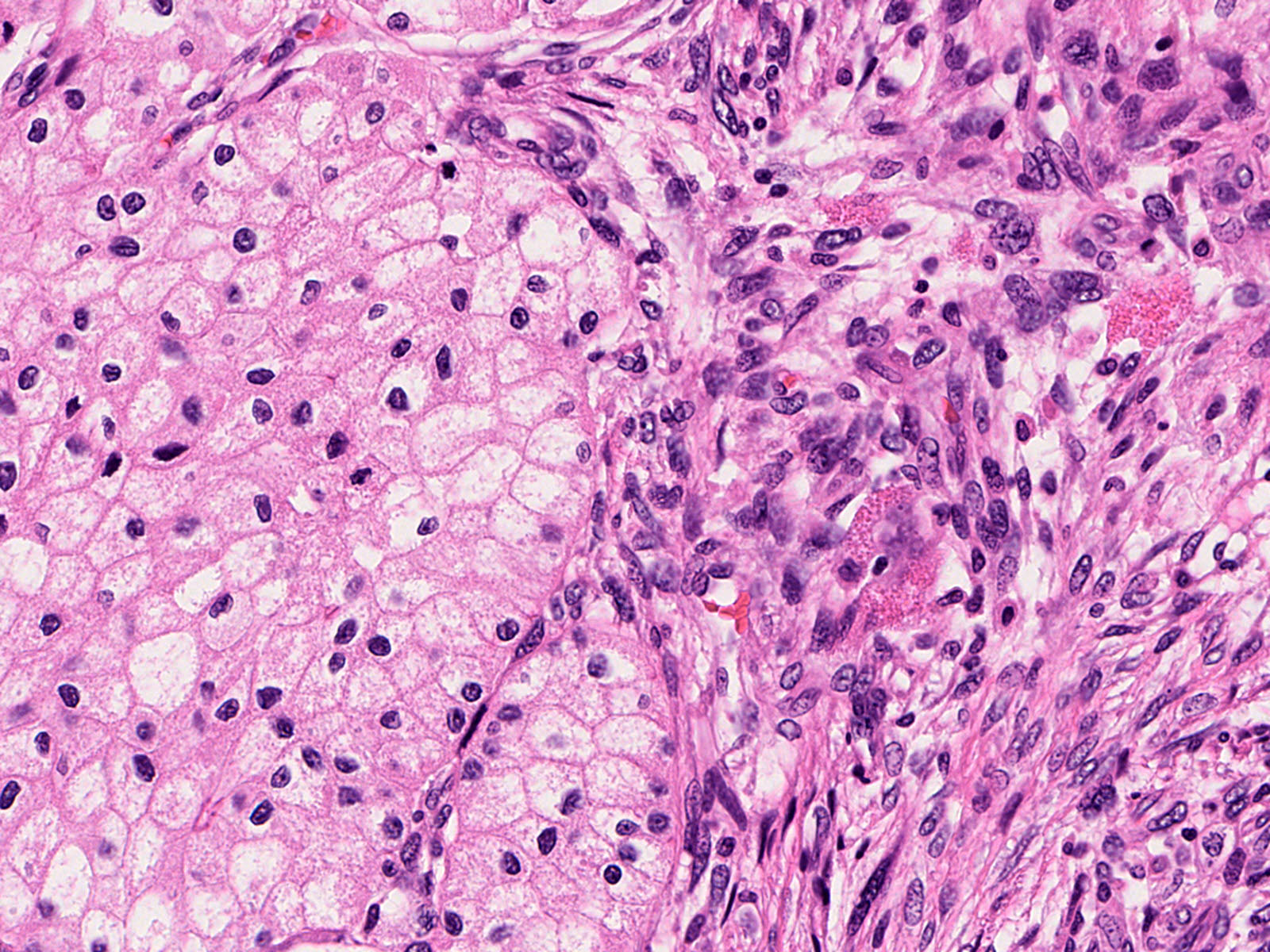
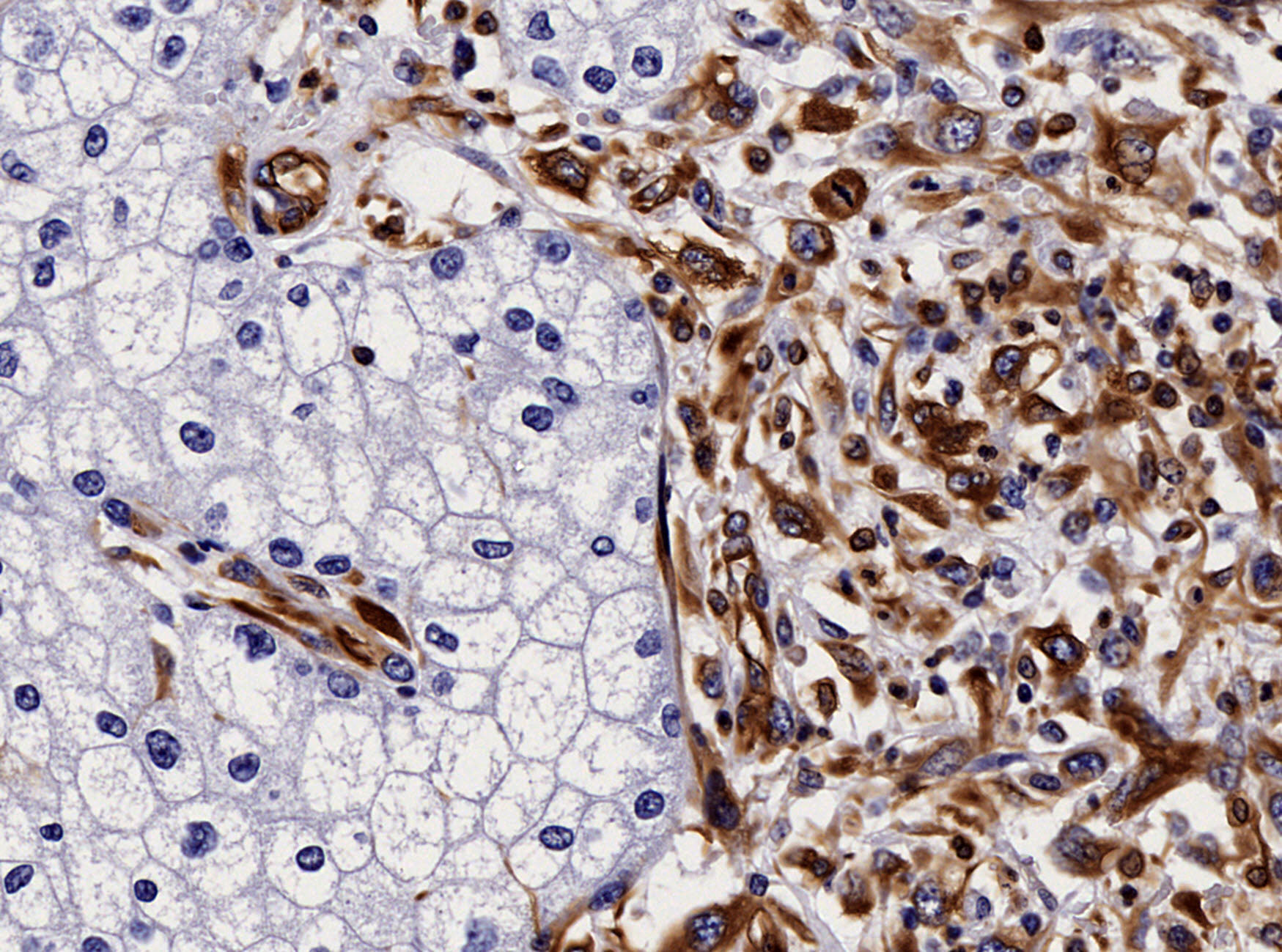
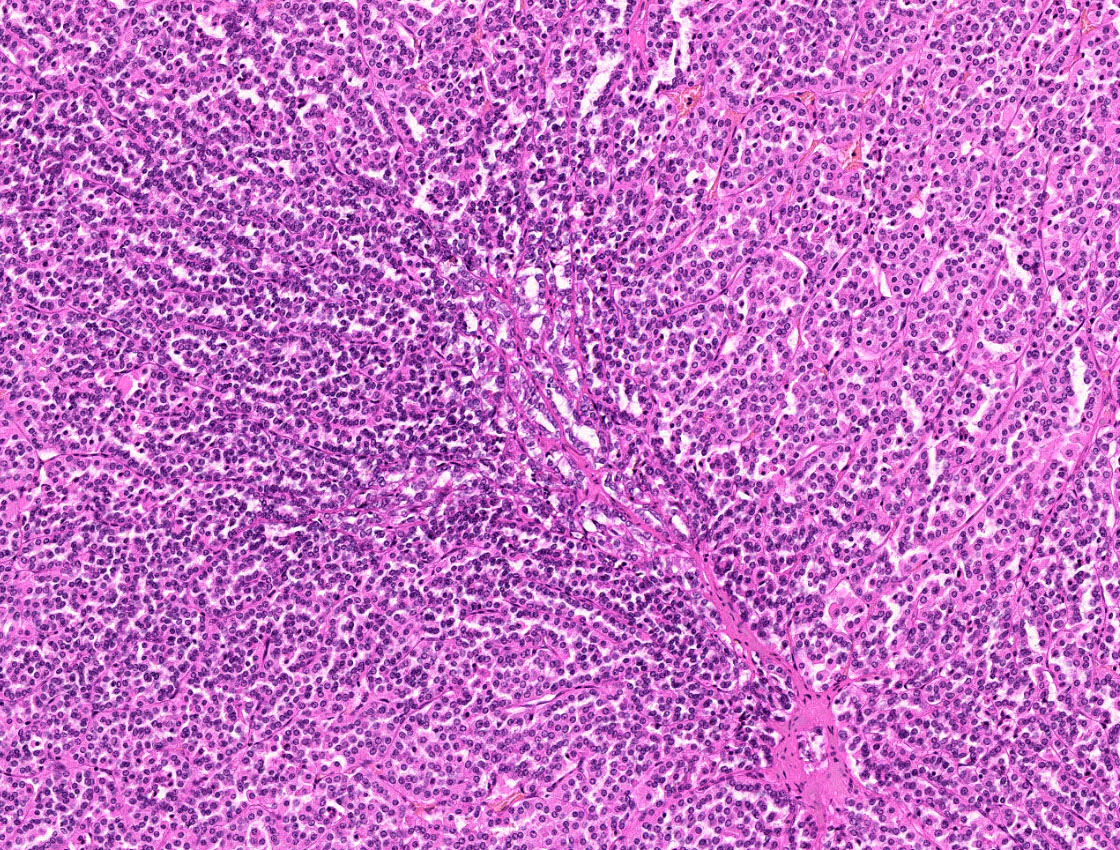
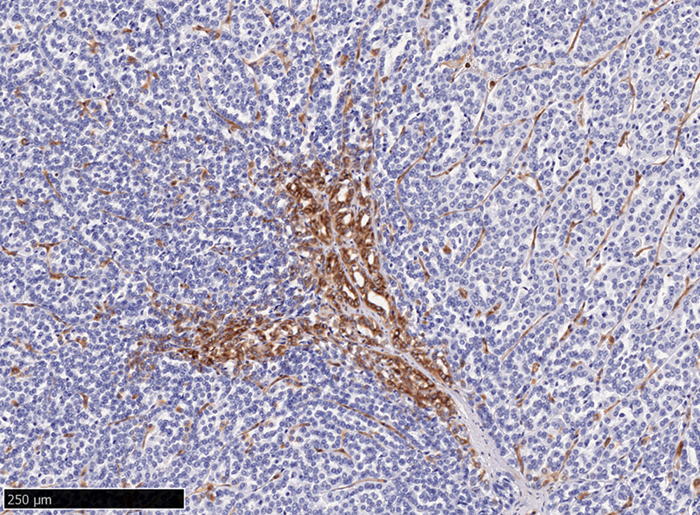
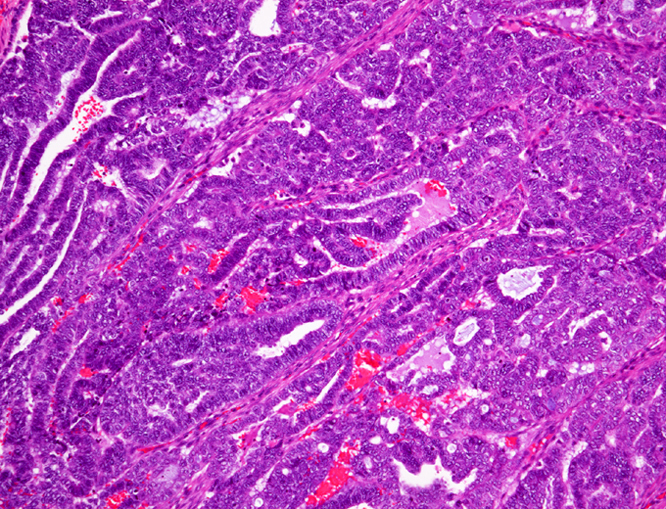
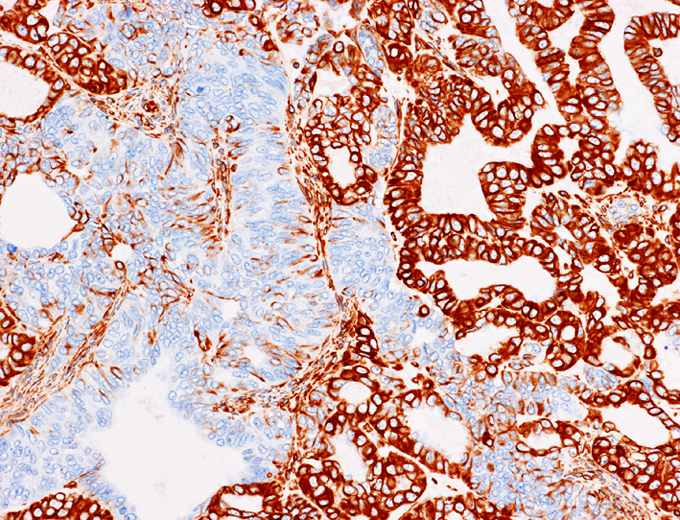
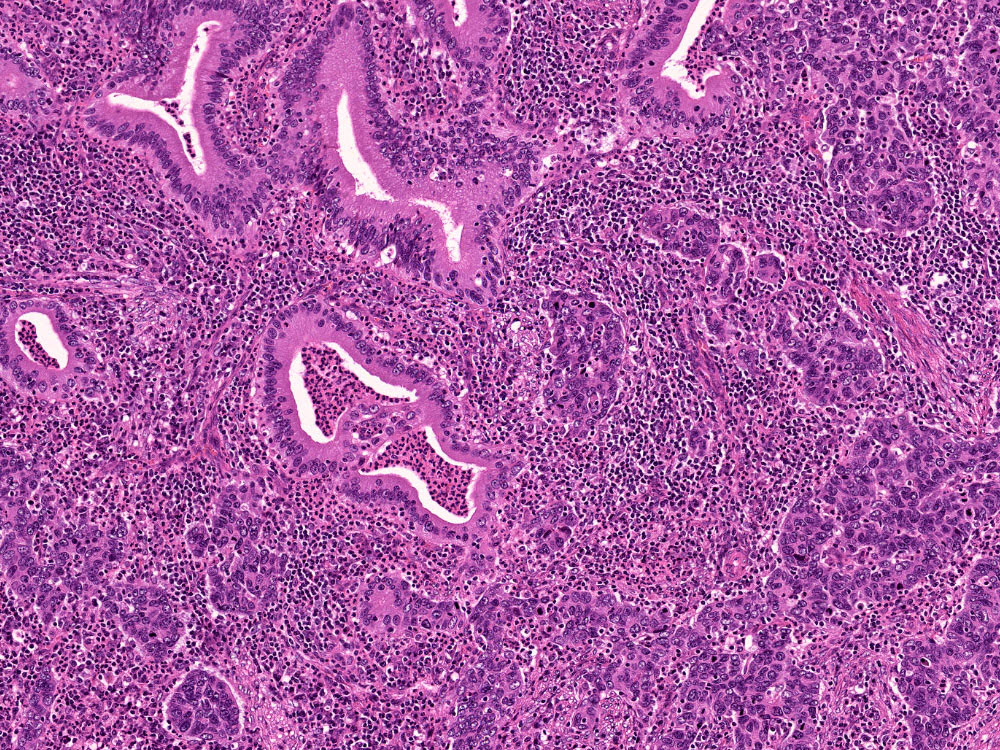
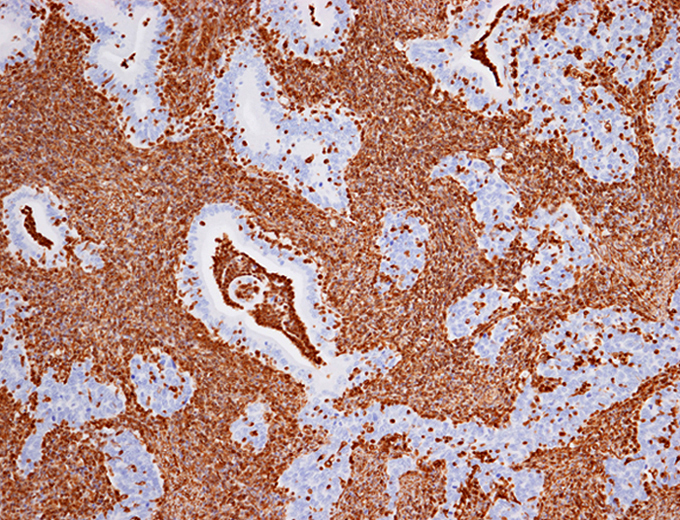
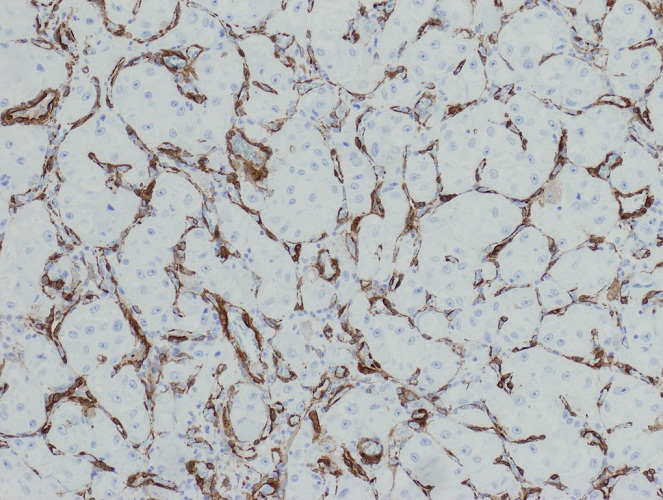
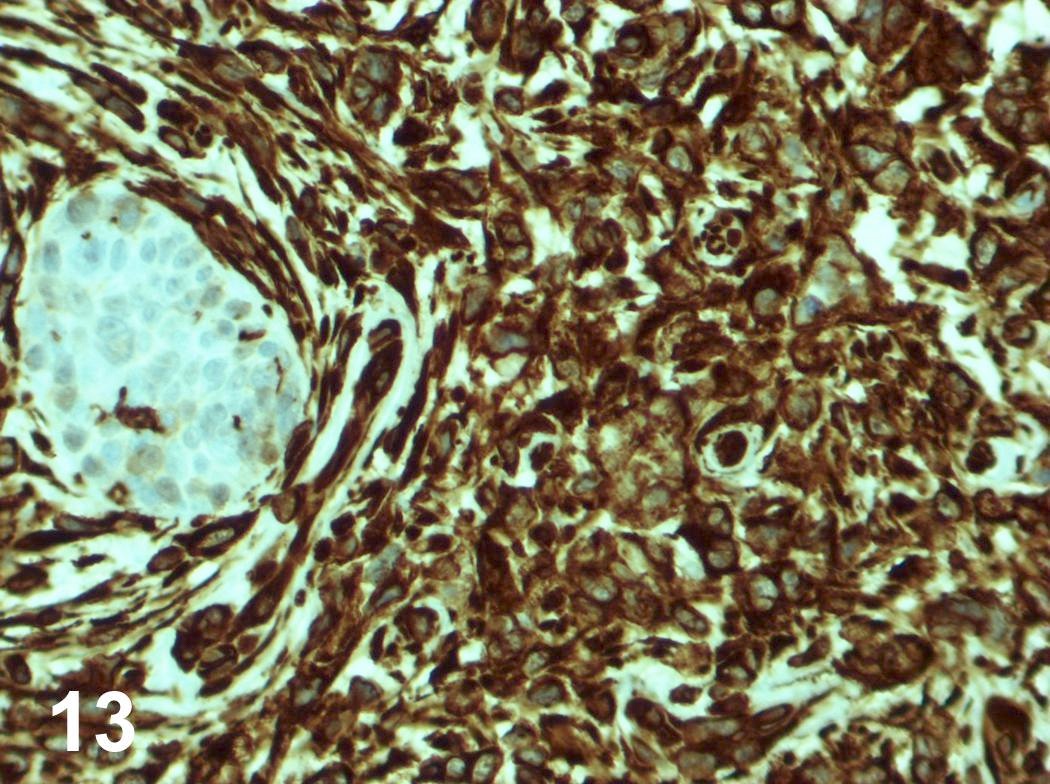
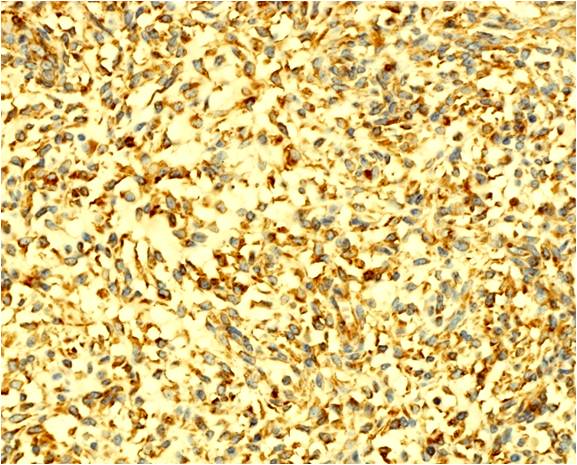
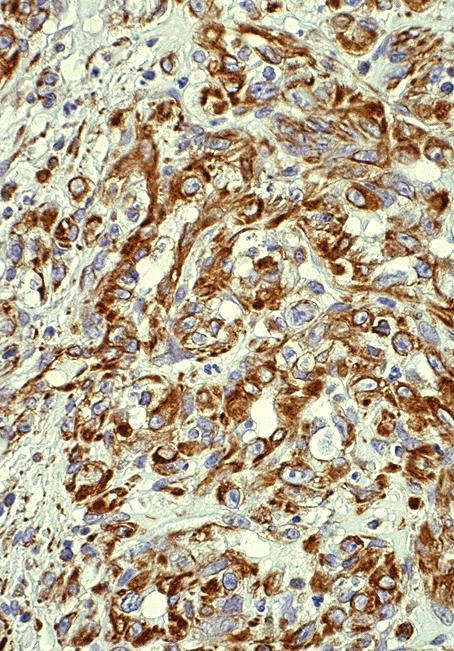
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Riuko Ohashi, M.D.
Contributed by Dr. Steven Catinchi-Jaime, Mowafak Hamodat, M.B.Ch.B., AFIP images and Cases #149, 184, 216, 222 and 241
Positive staining - normal
- Mesenchymal cells, including:
- Endothelial cells, fibroblasts (Am J Clin Pathol 1991;96:669, Dabbs: Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry - Theranostic and Genomic Applications, 5th Edition, 2018)
- Vascular smooth muscle cells (Anat Rec 1997;247:439)
- Endometrial stromal cells (Am J Surg Pathol 1991;15:861)
- Blood and immune cells, including:
- Macrophages, neutrophils, platelets (Int J Mol Sci 2020;21:4675)
- Dendritic cells, Langerhans cells, melanocytes (J Invest Dermatol 1983;81:46)
- Lymphocytes (with some exceptions) (EMBO J 1983;2:1509)
- Melanocytes (J Invest Dermatol 1983;81:46)
- Leydig cells and Sertoli cells (Reproduction 2001;121:287)
- Endometrial glands (Am J Surg Pathol 1986;10:568)
Positive staining - disease
- Mesenchymal tumors of soft tissue or other organs (Dabbs: Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry - Theranostic and Genomic Applications, 5th Edition, 2018)
- Carcinomas of adrenal cortex, thyroid (Am J Pathol 1986;122:343, Cancer 1992;70:2326)
- Breast: pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia, mesenchymal component of metaplastic carcinoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2010;134:1070, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:819)
- CNS: ependymoma, meningioma, pituicytoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2010;134:1063)
- Melanoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2014;138:1583)
- Mesothelioma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2014;138:1583)
- Pancreas: solid pseudopapillary neoplasm (Am J Clin Pathol 2009;132:831)
- Perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2011;135:499)
- Renal cell carcinoma: most carcinomas except for chromophobe renal cell carcinoma (see Negative staining, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:410, Pathol Res Pract 2015;211:303)
- Renal cell carcinoma: sarcomatoid differentiation and rhabdoid differentiation (Histol Histopathol 2003;18:551, BMC Cancer 2017;17:293, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:253)
- Salivary gland: mammary analog secretory carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:27, Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1370)
- Type A and AB thymoma (Diagn Pathol 2007;2:13)
- Testis: Leydig cell tumor (> 90%), Sertoli cell tumor (> 85%) (Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 1992;421:163, Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:615, Mod Pathol 1998;11:769, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2002;10:159)
- Uterus: mucinous carcinoma (not of cervix), most endometrial carcinoma, carcinosarcoma (malignant mixed Müllerian tumor) (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:915, Hum Pathol 1993;24:132)
Negative staining
- Carcinomas (usually but there are many exceptions), Krukenberg tumor
- Renal oncocytoma, although usually focal staining with a pattern different from carcinomas (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2007;131:1782)
- Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma (Pathol Res Pract 2015;211:303)
- Thymic carcinoma, type B thymoma (Diagn Pathol 2007;2:13)
- Alveolar soft part sarcoma (positive in < 50% cases) (J Clin Pathol 2006;59:1127)
Sample pathology report
- Left kidney, tumor, core needle biopsy:
- Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma, eosinophilic variant (see comment)
- Comment: Epithelial tumor showing solid growth pattern composed of comprised of eosinophilic cells with fine granular eosinophilic cytoplasm, perinuclear halo and round, oval to raisinoid nuclei. No pale cell was observed. Immunohistochemistry positive for CK7 and c-kit and negative for vimentin. These findings are consistent with chromophobe renal cell carcinoma.
- Right lung, tumor, excision:
- Metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (see comment)
- Comment: Immunohistochemistry positive for vimentin, PAX8, CAIX and RCC and negative for CK7.
- Left lung, tumor, excision:
- Consistent with metastatic endometrioid carcinoma (see comment)
- Comment: Immunohistochemistry positive for vimentin, PAX8 and ER and negative for TTF1, consistent with endometrial primary.
Additional references
Board review style question #1
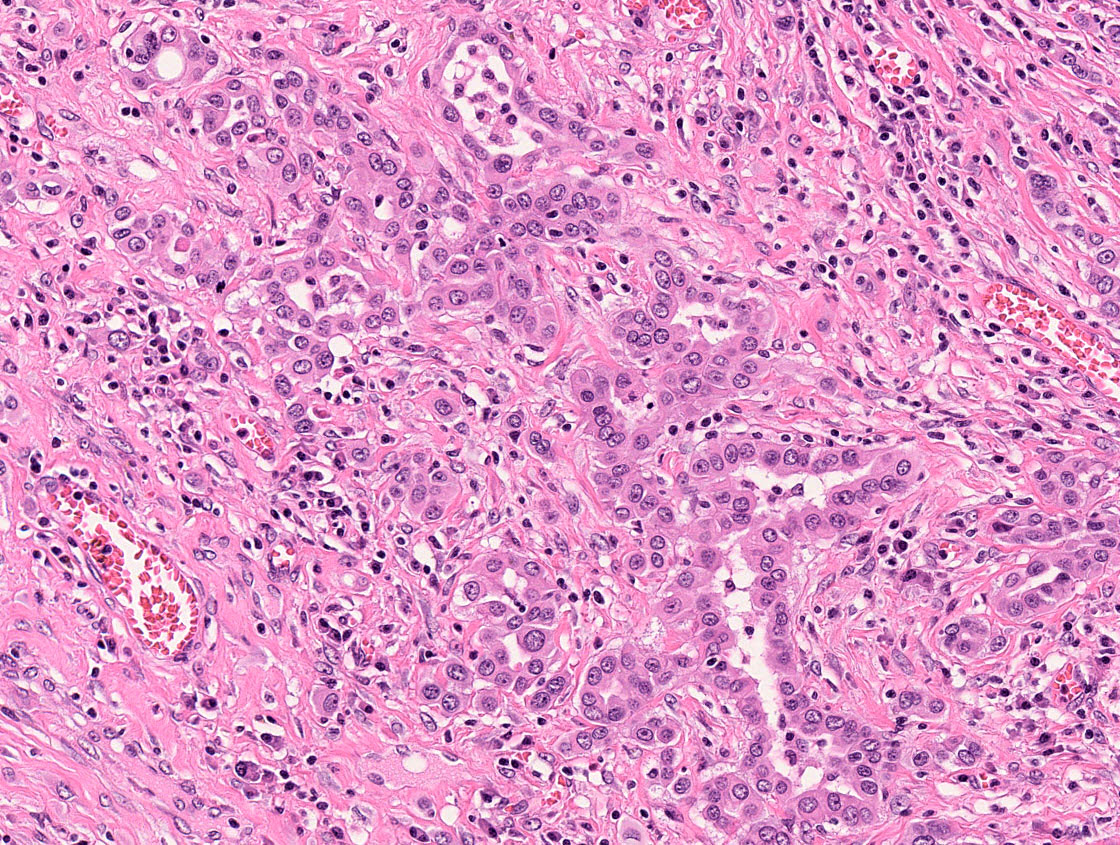
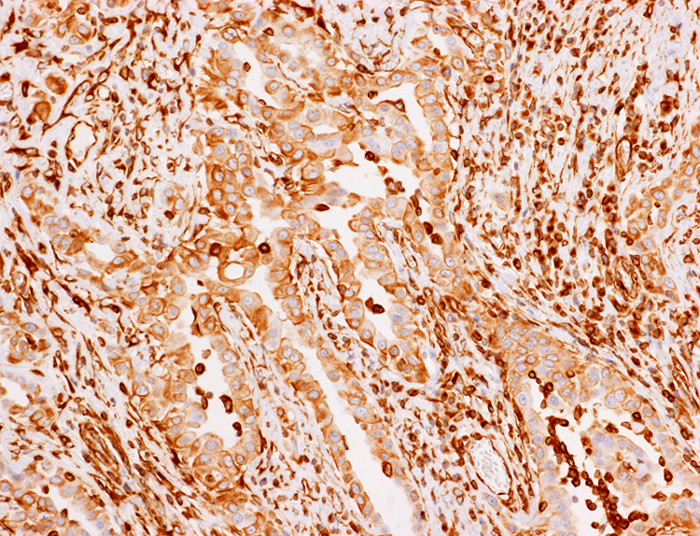
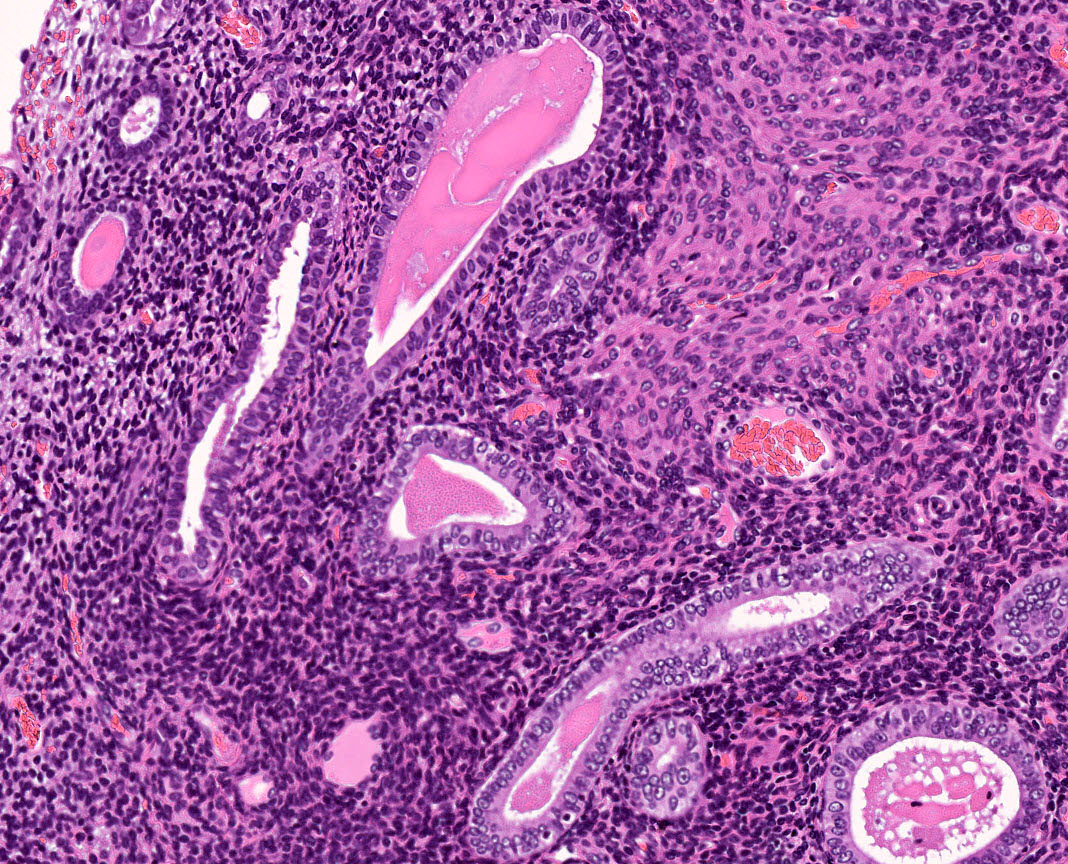
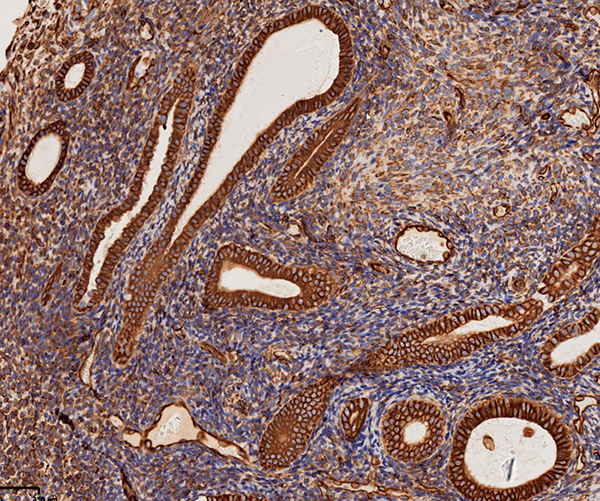
A 56 year old female is found to have a uterine tumor that involves both the endometrium and the endocervix. Histology and immunohistochemistry for vimentin are shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- Endocervical adenocarcinoma
- Endometrioid adenocarcinoma
- Endometrial stromal tumor
- Carcinosarcoma
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Which of the following tumors should be negative for vimentin?
- Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma
- Clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Endometrioid carcinoma
- Mammary analog secretory carcinoma
Board review style answer #2
A. Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. While most carcinomas are negative for vimentin, mammary analog secretory carcinoma, most endometrial carcinomas and most renal cell carcinomas, except for chromophobe renal cell carcinoma, are positive for vimentin.
Comment Here
Reference: Vimentin
Comment Here
Reference: Vimentin