Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative staining | Flow cytometry description | Molecular / cytogenetics descriptionCite this page: Obeng R. Smooth muscle myosin heavy chain / SMMHC. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainssmmhc.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- The MYH11 gene (Chromosome 16) encodes a smooth muscle myosin protein (SMMHC) that is a subunit of a hexameric protein involved in contraction, the conversion of chemical energy into mechanical energy via ATP hydrolysis, and G protein coupled receptors / GPCR signaling
- Alternative splicing generates different isoforms (Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2006;38:1862)
- Fusion between core binding factor beta (CBF-beta) with SMMHC (CBFbeta-SMMHC; Inv(16)(p13q22)) is present in nearly all acute myeloid leukemia M4 eosinophilia subtype (AML M4Eo)
- Useful for differentiating between benign and malignant lesions (e.g. breast and lung lesions)
Essential features
- Expressed in the cytoplasm and cell membrane of myoepthelial and smooth muscle cells
- Useful for the differentiation of benign and malignant breast and lung (bronchoalveolar carcinoma) lesions
- Associated diseases
- Inv(16)(p13q22) with SMMHC fusion gene seen in nearly all acute myeloid leukemia M4 eosinophilia subtype (Nat Genet 1999;23:144; Cancer Cell 2006;9:57)
- Rare autosomal dominant mutations in the MYH11 gene seen in familial aortic aneurysm and dissection and patent ductus arteriosis (Nat Genet 2006;38:343; Hum Mol Genet 2007;16:2453; Int J Cardiol 2013;165:314; Hum Genome Variat 2015;2:15028)
Terminology
- Myosin heavy chain 11, myosin 11, myosin heavy chain, smooth muscle isoform, MYH11, SMHC, SMMHC
Sites
- Expressed in cytoplasm and cell membrane of myoepithelial and smooth muscle cells
Pathophysiology
- Acute myeloid leukemia of M4 eosinophilia subtype: the CBFbeta-SMMHC fusion protein inhibits myeloid differentiation and represses RUNX1; it also induces changes in gene expression in hematopoietic cells (Nat Genet 1999;23:144; J Cell Biochem 2010;110:1039)
- Aortic aneurysm and dissection: medial degeneration with smooth muscle cell disarray and hyperplasia in the medial layer of the aorta due to mutations in the MYH11 gene (Nat Genet 2006;38:343; Hum Mol Genet 2007;16:2453; Curr Atheroscler Rep 2012;14:219)
Diagnosis
- SMMHC IHC staining useful to evaluate restenosis in peripheral artery disease (Atherosclerosis 2016;251:226)
- SMMHC expression is decreased in diverticular disease (J Gastroenterol 2014;49:1241)
Laboratory
- Studies suggest serum levels of SMMHC are significantly higher in patients with acute aortic dissection and may be a good biomarker for early diagnosis (Heart Lung 2015;44:205; J Am Coll Cardiol 2010;56:1535)
Microscopic (histologic) description
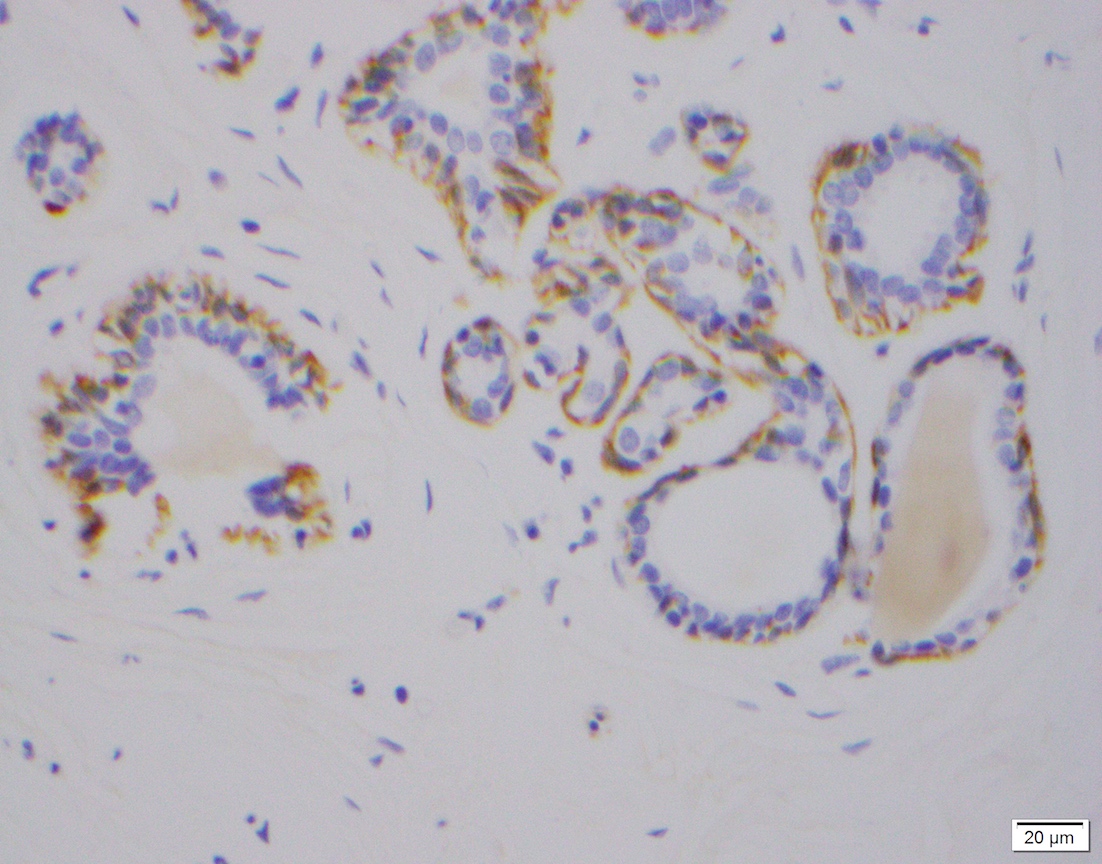
- Cytoplasmic and membranous staining in normal myoepithelial and smooth muscle cells
- Nuclear staining in acute myeloid leukemic cells with Inv(16)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Positive immunohistochemical staining in spindle cells between epithelial cells or along the edges of epithelial cells in benign breast lesions; negative staining in invasive breast carcinomas except for vascular smooth muscle cells (Diagn Cytopathol 1999;20:203)
Positive stains
- Myoepithelial and smooth muscle cells
- CBFbeta-SMMHC IHC staining in AML-M4Eo (nuclear stain) (Am J Surg Path 2006 30:1436)
Negative staining
- SMMHC can be a sensitive and specific marker for myoepithelial cells of the breast, helping to distinguish benign from malignant lesions (negative for SMMHC) (J Clin Pathol 2004:57:625)
- Staining may be reduced or patchy in carcinoma in situ (CIS) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2014;138:1629)
- Invasive papillary carcinomas are negative (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2011;135:422)
Flow cytometry description
- Intracellular staining for CBFbeta-SMMHC can be used for the identification of AML M4Eo leukemic cells (Blood 1998;91:1882)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Inv(16)(p13q22) or t(16:16)(p13q22) leads to fusion of CBFbeta and SMMHC that can be detected by fluorescent in situ hybridization