Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Terlević R, Vranić S. OCT 3/4. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsoct34.html. Accessed January 21st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Octamer binding transcription factor (OCT) 3/4 is essential for pluripotency and self renewal of stem cells (Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med 2009;1:228)
- 18 kDa domain transcription factor encoded by POU5F1 gene (POU domain, class 5, transcription factor 1) at 6p21.3
- Together with SOX2, essential for reprogramming somatic cells into pluripotent stem cells (Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med 2009;1:228)
- Expressed in germ cells and stem cells, downregulated in all somatic tissues (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:368)
- Likely to be involved in maintaining the stemness of cancer stem cells (Brain Tumor Pathol 2015;32:31)
Essential features
- Marker of germ cells, not expressed in somatic tissues
- Strong diffuse nuclear expression seen in seminoma (dysgerminoma) and embryonal carcinoma components of germ cell neoplasia, including metastatic disease
- Can be expressed focally in advanced epithelial and lymphatic malignancy
Terminology
- Also known as OCT 4, OCT 3 and encoded by POU5F1 (Cell Struct Funct 2001;26:137)
Pathophysiology
- Ectopic expression of OCT 3/4 in epithelial tissues induces dysplasia via inhibition of cellular differentiation, similarly to mechanisms in embryonic stem cells (Cell 2005;121:465)
- Increased expression of OCT 3/4 correlates with tumor progression and worse prognosis in various human solid tumors (J Clin Pathol 2010;63:879, Brain Tumor Pathol 2015;32:31)
- OCT 3/4 is involved in the pathogenesis of testicular germ cell derived tumors (Cancer Cell 2003;4:361)
- OCT 3/4 promotes survival in glioblastoma cells by upregulating HIF1α (Brain Tumor Pathol 2015;32:31)
Interpretation
- Nuclear staining, typically intense and diffuse
- Cytoplasmic only staining in non germ cell derived tumors
Uses by pathologists
- Marker for primary and metastatic germ cell derived tumors of the testis and ovary and extragonadal sites
- Highly sensitive and specific for primary intracranial germinomas (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:368)
Prognostic factors
- Poor prognostic factor in breast cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), gastric cancer, cervical squamous cell carcinoma, right sided colon cancer, tongue squamous cell carcinoma (Oncotarget 2014;5:10803, World J Gastroenterol 2012;18:712, Int J Mol Sci 2012;13:7663, Med Oncol 2015;32:433, J Histochem Cytochem 2014;62:499, Future Oncol 2018;14:2279, Head Neck 2018;40:1759)
- OCT 3/4 and NANOG co-expression is a poor prognostic marker in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (Sci Rep 2018;8:11739)
- High expression related to increased biochemical relapse in prostate cancer (Hum Pathol 2016;51:1)
- Overexpression in cervical cancer is an independent risk factor for overall survival (BMC Cancer 2015;15:1015)
- Expression in bladder cancer correlates with recurrence (Med Oncol 2012;29:82)
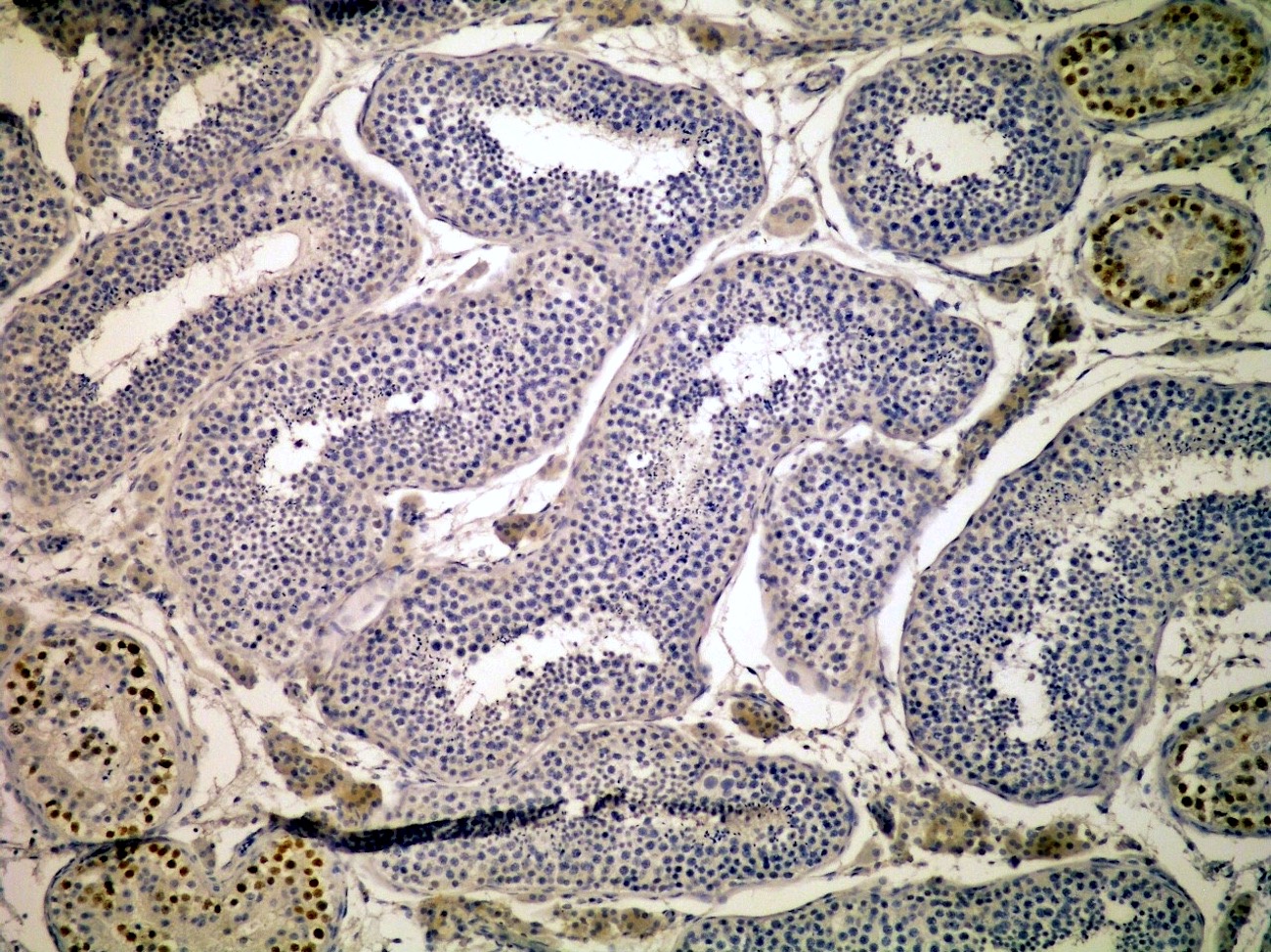
Positive staining - normal
- Embryonic stem cells (Nature 1990;345:686)
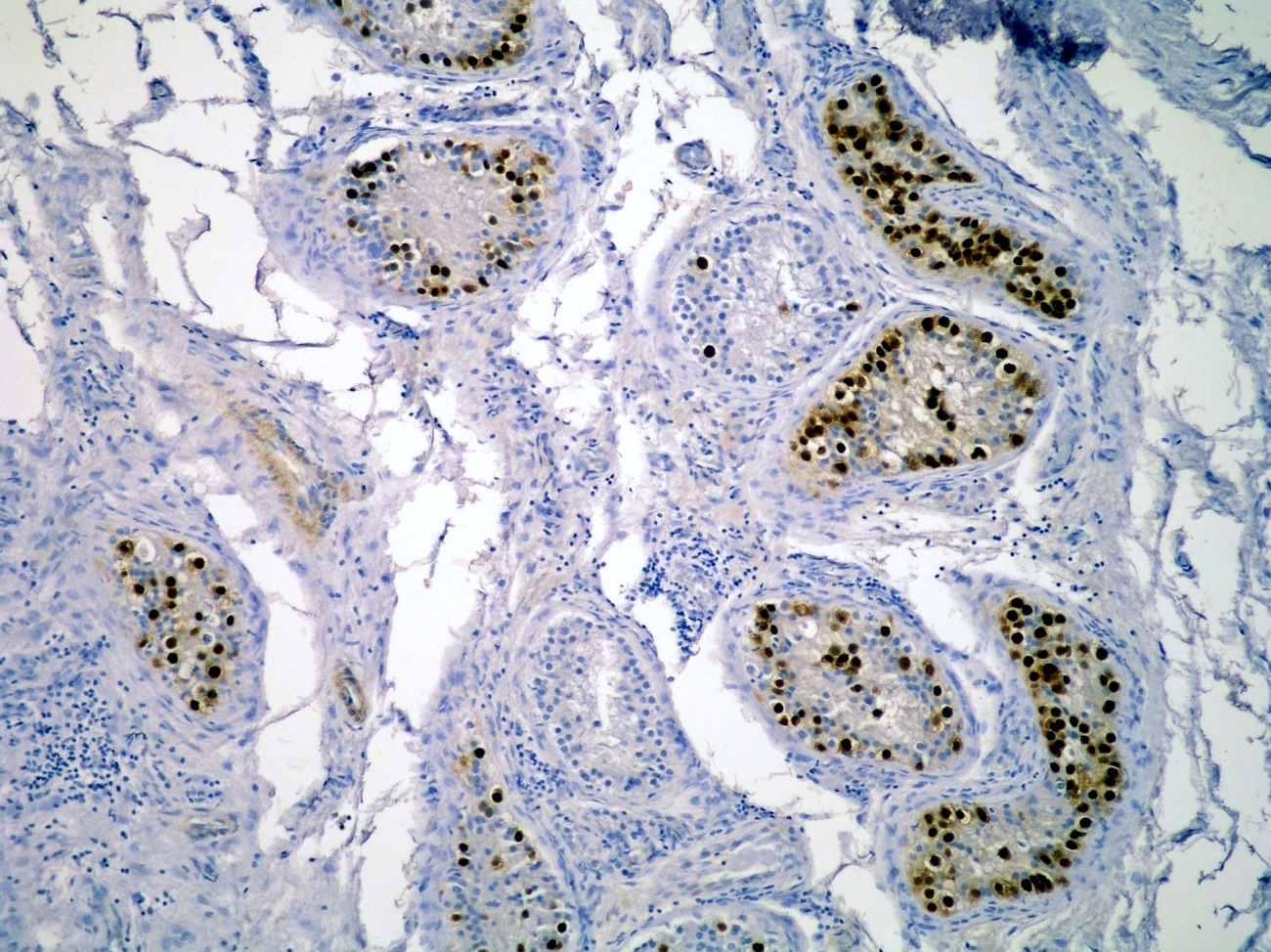
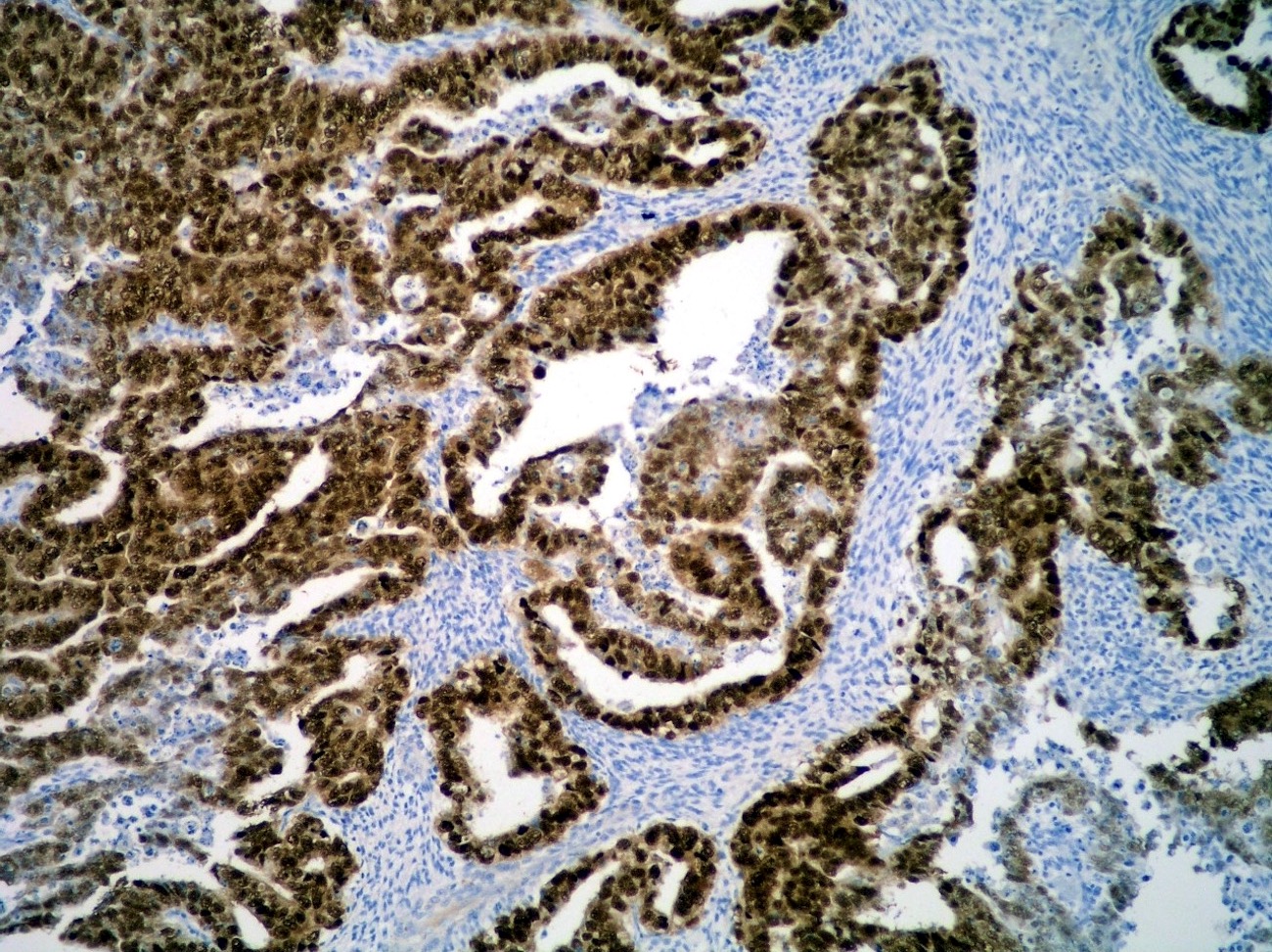
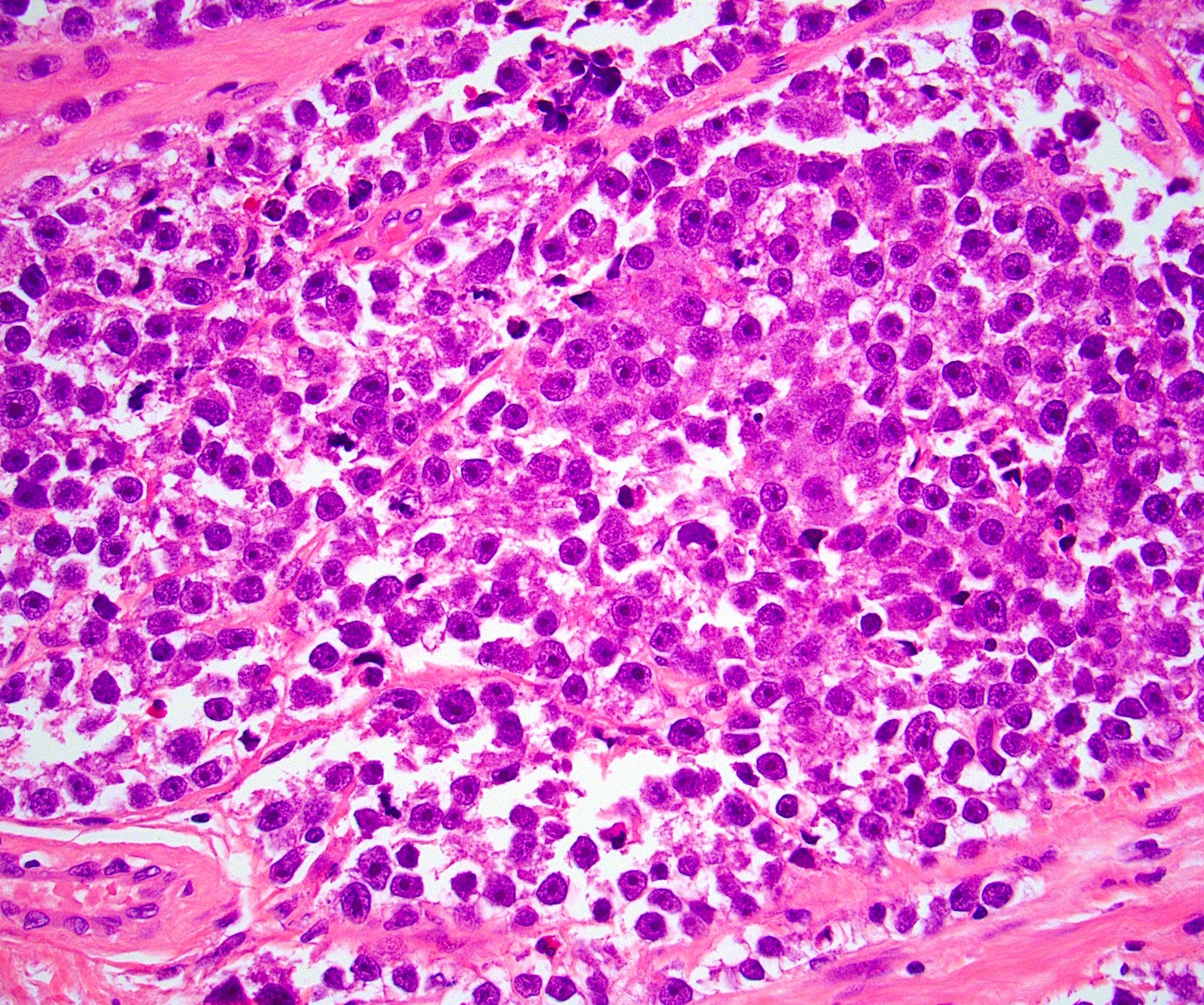
Positive staining - disease
- Seminoma (100%), dysgerminoma of the ovary (100%), intrathecal germinoma (100%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:368)
- Embryonal carcinoma (100%)
- Germ cell neoplasia in situ (GCNIS) (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:935, J Pathol 2005;206:242)
- Germ cell component of ovarian gonadoblastoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1341)
- Other ovarian tumors: serous borderline tumor (88%), ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma (89%), mucinous borderline tumor (68%), mucinous adenocarcinoma (63%) (J Clin Pathol 2010;63:879)
- Renal medullary carcinoma (71%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:583)
- Prostatic adenocarcinoma (77%) (Genet Mol Res 2015;14:6844)
- Salivary gland mucoepidermoid carcinoma (71%)
- Non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (54%) (Int J Mol Sci 2012;13:7663), more frequently in poorly differentiated tumors (81%) (Oncol Lett 2016;11:234)
Negative staining
- Yolk sac tumor, primary and metastatic (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:360)
- Teratoma, mature and immature
- Choriocarcinoma and syncytiotrophoblastic components of testicular germ cell neoplasia (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:935, Cancer 2004;101:2006)
- Spermatocytic tumor
- Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1341)
- Other non germ cell derived testicular tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:935)
- Adult type granulosa cell tumor, variable intensity and proportion (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1341, Int J Gynecol Pathol 2009;28:347)
- Small cell carcinoma hypercalcemic type (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1341)
- Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (testicular 18%, nontesticular 4%, CNS 33%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:950)
- Adrenal cortical carcinoma, primary and metastatic (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:727)
- Pheochromocytoma, primary and metastatic, diffuse and strong cytoplasmic staining (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:727)
- Urothelial carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:583, APMIS 2013;121:982)
- Collecting duct carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:583)
- Clear cell adenocarcinoma (focal positivity, 28%)
- Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (31%) (World J Gastroenterol 2012;18:712)
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (22%) (Genet Mol Res 2015;14:6844)
- Glioblastoma multiforme, pineoblastoma, pituitary adenoma, melanoma, capillary hemangioblastoma, meningioma, schwannoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:368)
- Skin Merkel cell carcinoma, frequent cytoplasmic staining (Am J Dermatopathol 2014;36:274)
Board review style question #1
- Which of the following testicular germ cell tumors consistently stain with OCT 3/4?
- Choriocarcinoma
- Embryonal carcinoma
- Immature teratoma
- Mature teratoma
- Yolk sac tumor
Board review style answer #1