Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Wirth P. Inhibin. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsinhibina.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Dimeric glycoprotein consisting of alpha and beta subunits that is mainly produced in the gonads
- Regulates follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) secretion through negative feedback mechanisms with paracrine and autocrine actions on gonads and adrenal glands
Essential features
- Dimeric protein consisting of an alpha subunit and 2 closely related beta subunits: βA and βB
- Member of the transforming growth factor beta family (TGF beta) serving as a marker of follicular growth, ovarian function and spermatogenesis
- Inhibin alpha is expressed in ovary, endometrium, brain, adrenal gland and testis
- Inhibin is highly expressed in sex cord stromal tumors including ovarian granulosa cell tumors (GCT) and Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors (Rom J Morphol Embryol 2017;58:753)
Terminology
- Inhibin alpha
- Inhibin beta
- Folliculostatin
Pathophysiology
- Inhibin is produced by different cell types at different times during the male and female life cycle
- 2 most clinically important subunits are alpha and beta (other isoforms include betaC and betaE) (Reprod Biol Endocrinol 2010;8:143)
- Inhibin suppresses the production and release of FSH from the pituitary gland in a negative feedback loop (Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2021;95:702)
- Reproductive organs are the main source of inhibin; however, it can be found in the prostate, brain, placenta and adrenal glands
- Both subunits are produced by Sertoli cells in men before puberty
- In early puberty, inhibin beta levels rise then plateau (Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2021;95:702)
- Serum levels of inhibin beta are decreased in boys with delayed puberty and bilateral cryptorchidism (J Urol 2022;207:701)
- Serum levels of inhibin beta are a marker for male infertility in adults
- Inhibin is produced by granulosa, theca and luteal cells of the ovary with variable expression patterns during the menstrual cycle
- Secretion of both inhibin subunits in women is stimulated by FSH in the early follicular phase, reaching their highest concentrations in the middle of the luteal phase
- Inhibin alpha levels are highest during the late follicular and luteal phases, while the beta subunit is most prominent during early and mid follicular phases
- Decreased inhibin beta levels are associated with a decrease in the number of ovarian follicles and can lead to infertility (Hum Reprod Update 2010;16:39)
Clinical features
- Elevations of both inhibin subunits have been detected in GCT
- Inhibin beta may be a tumor marker for determining response to therapy in GCT (Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1999;50:381)
- Mutations in the inhibin gene are associated with premature ovarian failure caused by a reduction in inhibin beta (Hum Reprod Update 2010;16:39)
- Serum levels of both inhibin subunits may be useful when assessing ovarian function in patients with Turner syndrome (Pol Merkur Lekarski 2009;26:258)
- Serum levels of inhibin alpha are part of a quadruple test for prenatal screening of Down syndrome (Semin Reprod Med 2004:22:235)
Interpretation
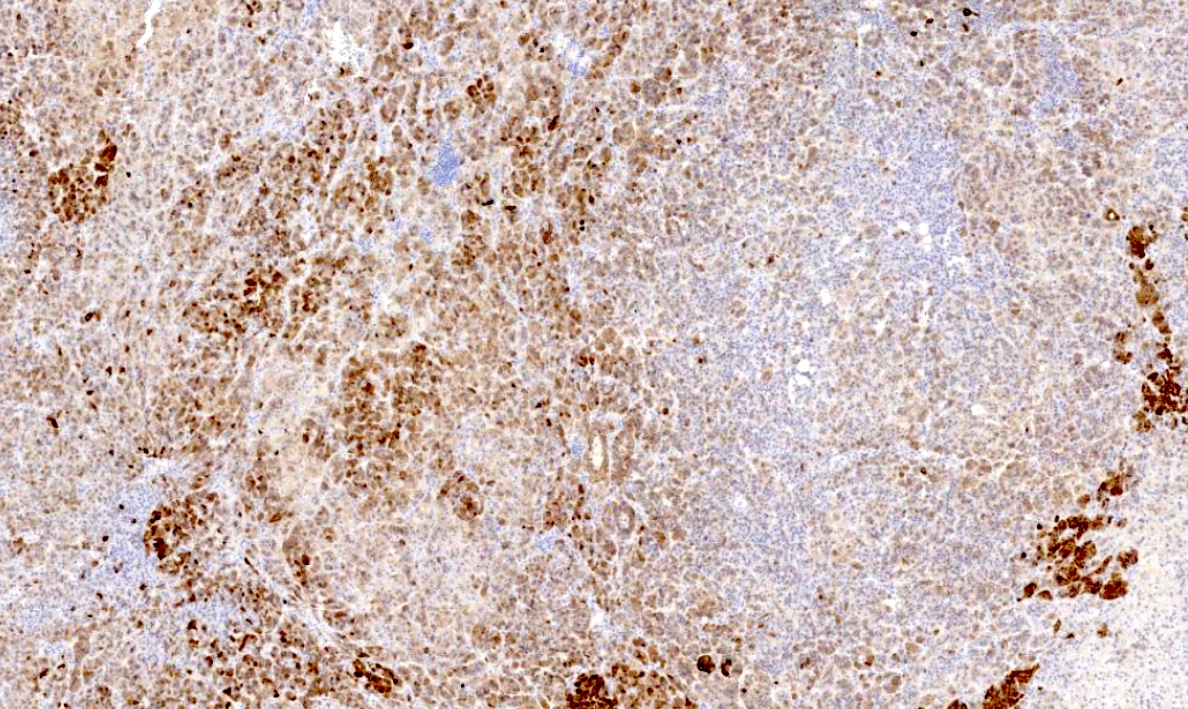
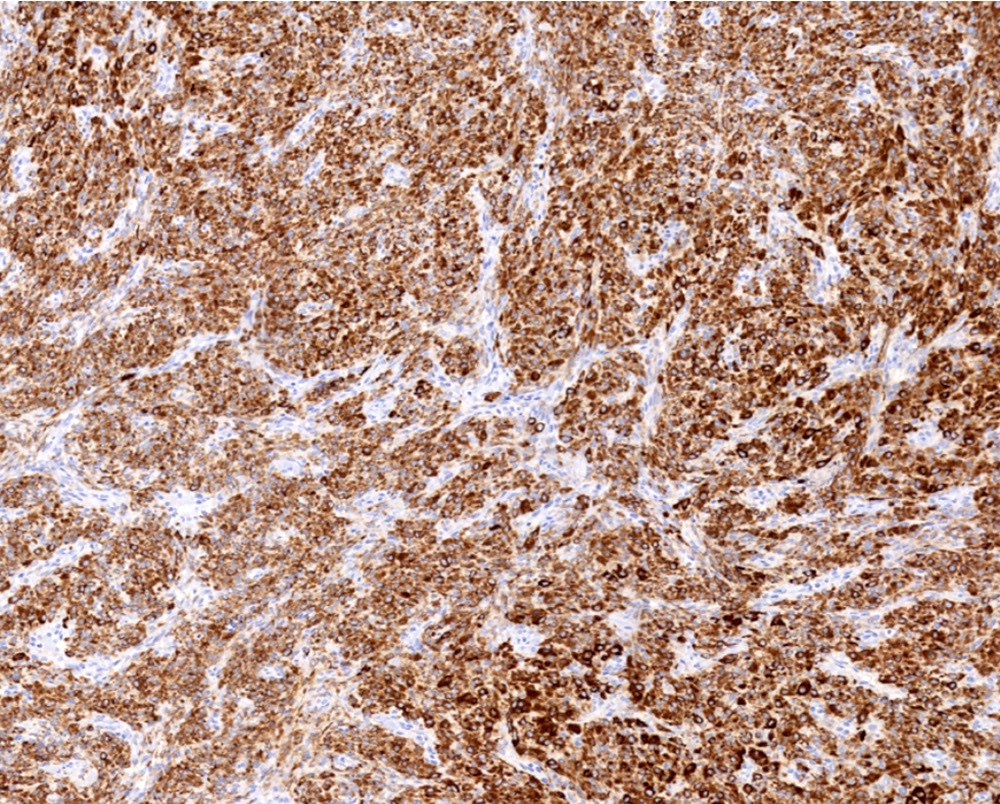
- Granular cytoplasmic staining (Rom J Morphol Embryol 2017;58:753)
Uses by pathologists
- Inhibin alpha protein expression is generally considered an important diagnostic feature for adrenocortical tumors and sex cord stromal tumors of the testis and the ovary (Biomedicines 2022;10:2507)
- Inhibin protein expression helps to distinguish sex cord stromal tumors from other malignant ovarian neoplasms since it is highly expressed in GCT and Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors, whereas other ovarian carcinoma subtypes are mostly negative
- Sex cord and stromal histology elements are confirmed by reticulin stains that show the framework surrounding individual tumor cells
- Most clinical tests for inhibin measure serum levels along with other reproductive hormones to test for ovarian or testicular function
- When used together, serum levels for inhibin and CA125 (marker for epithelial tumors) improved the specificity for identifying GCT from 82% to 95% in postmenopausal women (Mol Cell Endocrinol 2002;191:97)
- It is important to note that tissue staining of inhibin does not always correlate with serum levels (Am J Cancer Res 2022;12:3495)
Prognostic factors
- Negative staining for inhibin is associated with poorer prognosis in adrenocortical cancer (Acta Chir Belg 2020;120:23)
- High expression levels of inhibin βA protein in non-small cell lung cancer are significantly associated with advanced tumor stage (Mol Med Rep 2021;24:789)
- Decreased staining reactivity and intensity for inhibin alpha is likely associated with advanced stages of GCT according to more recent studies; however, the data on prognostic applications have varied and requires further evaluation (J Ovarian Research 2023;16:50)
- Inhibin immunopositive GCT was correlated with longer patient survival times (Eur J Gynaecol Oncol 2000;21:187, Gynecol Oncol 2000;77:232)
- One study was unable to confirm an association of inhibin alpha immunoreactivity with stage or prognosis (J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005;90:6529)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Inhibin is a useful marker to differentiate GCT from other epithelial neoplasms with similar histology; inhibin staining in other epithelial neoplasms is usually weak or negative and limited to nontumoral stromal theca cells (Rom J Morphol Embryol 2017;58:753)
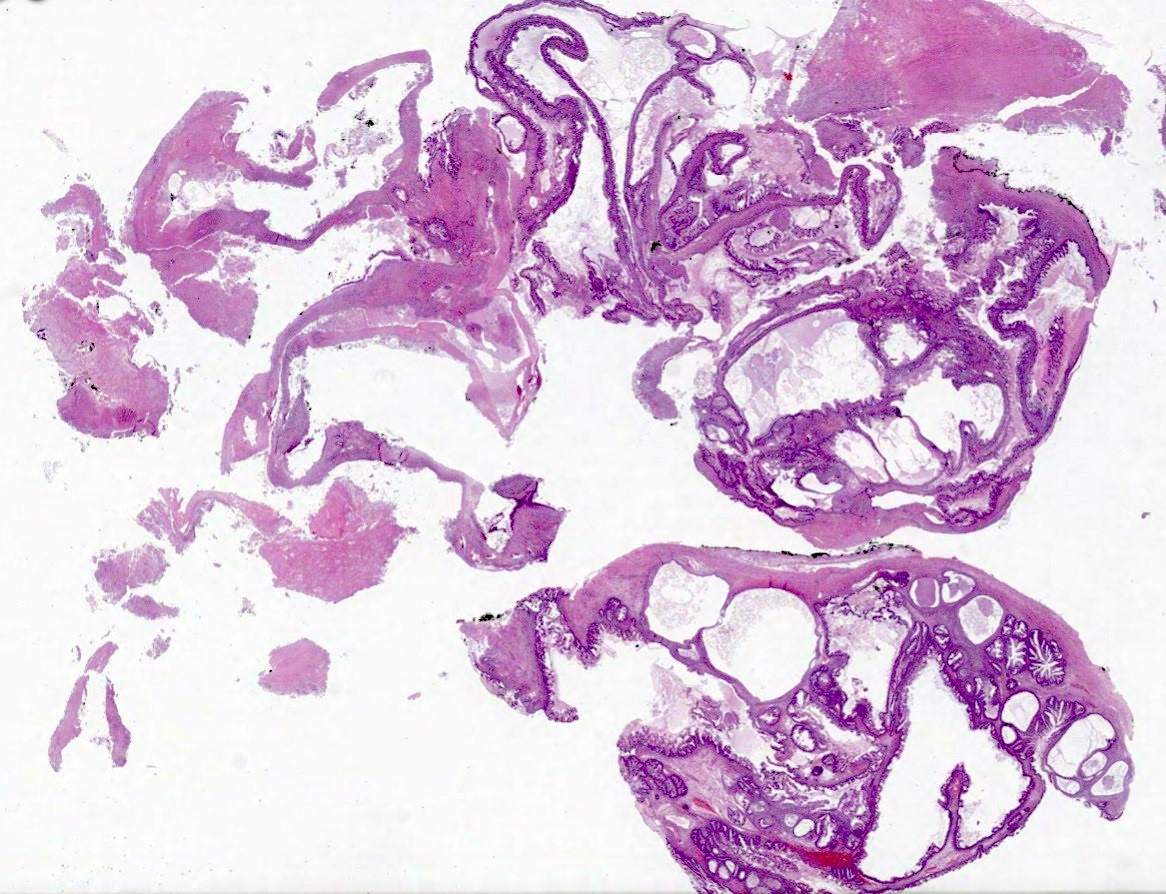
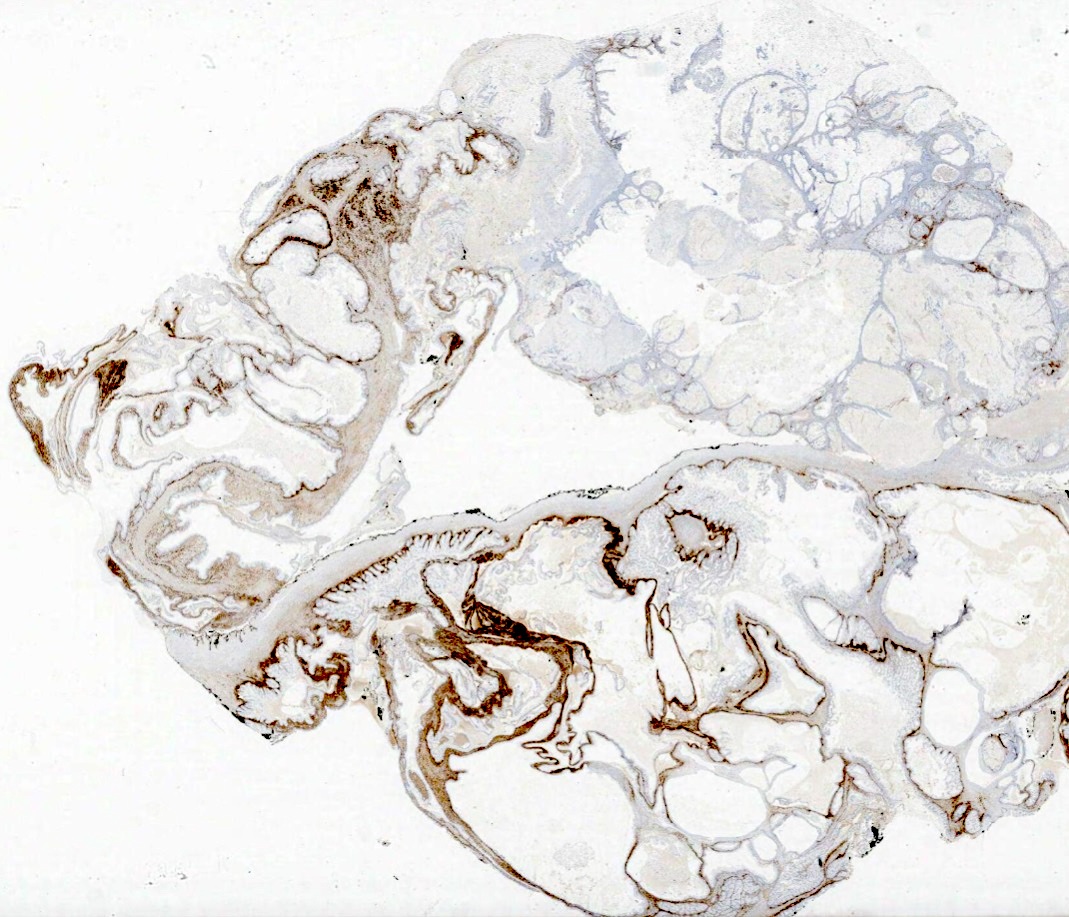
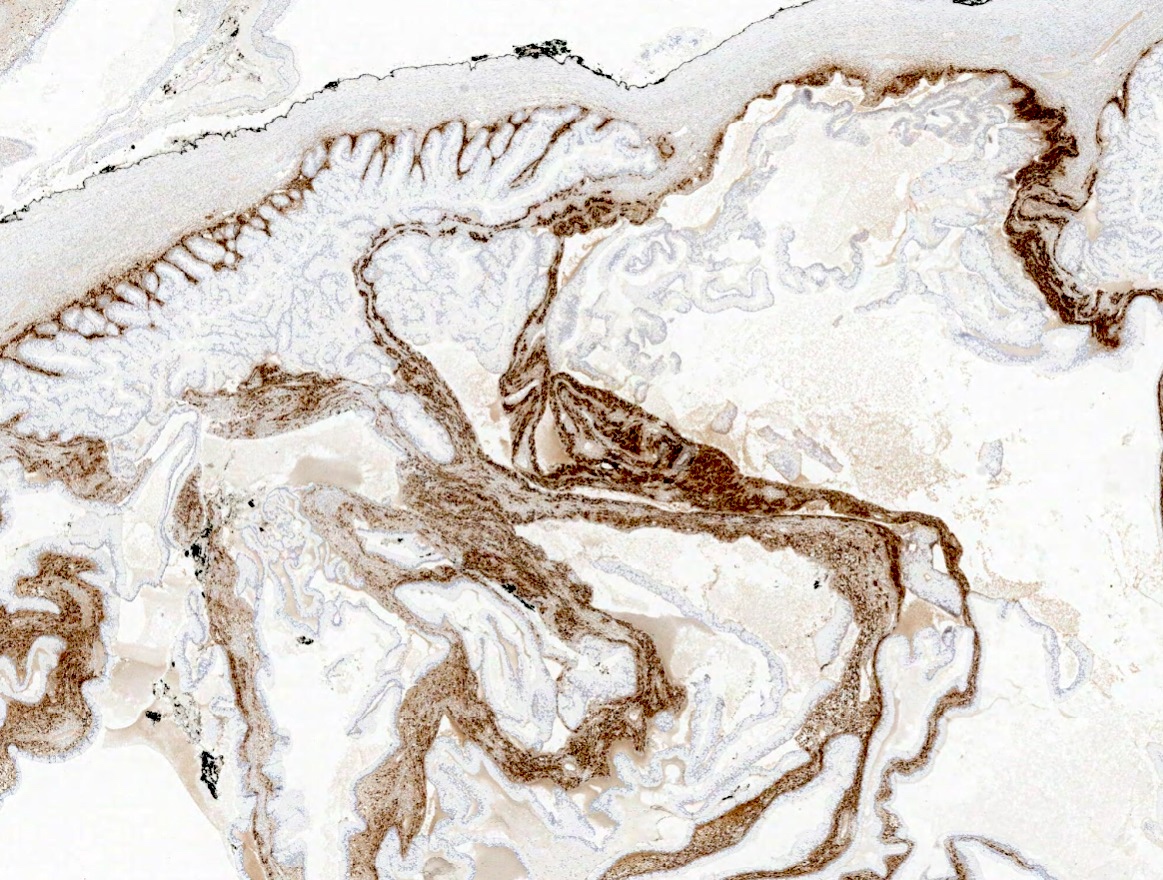
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
- Sertoli cells (diffuse and strong), granulosa cells, prostate, brain, adrenal glands
- Leydig cells of the testis (Mod Pathol 1998;11:774)
- Corpus luteum of the ovary, cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast, chorion cells of the placenta (stronger staining in the first trimester than in mature placenta), cortical cells of adrenal gland and granulosa cells of the ovary (Biomedicines 2022;10:2507)
Positive staining - disease
- Sex cord stromal tumors including granulosa cell tumors, Sertoli cell tumors, Leydig cell tumors and ovarian fibrothecomas (Mod Pathol 1998;11:774)
- Adrenocortical tumors (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2012;20:462)
- Placental and gestational trophoblastic lesions
- Adrenocortical and sex cord stromal tumors usually show a moderate to strong level of cytoplasmic inhibin staining
- GCT of the ovary (100%)
- Adrenal cortical adenomas (93%) and carcinomas (80%)
- Ovarian fibrothecomas (70 - 80%)
- Acinar cell carcinomas of the pancreas (80%) (Biomedicines 2022;10:2507)
Negative staining
- Primary ovarian carcinomas (some stromal cell staining may be present adjacent to tumor)
- Liver, bladder (Biomedicines 2022;10:2507)
- Renal cell carcinomas (limited expression; some expression in metastatic cases) (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:1152, Mod Pathol 2005;18:788)
- Inhibin alpha is rarely expressed in soft tissue neoplasms such as liposarcomas, schwannomas, leiomyomas and neurofibromas (Mod Pathol 2003;16:1205, Biomedicines 2022;10:2507)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Inhibin alpha gene (INHA) is located on chromosome 2 (2q33 - q36)
- Inhibin beta genes, βA and βB subunits (INHBA and INHBB), are located on chromosome 7 (7p15 - p13) and chromosome 2 (2cen - q13), respectively (Endocr Rev 2014;35:747)
- Mutations in the inhibin gene are associated with premature ovarian failure as a result of reduced inhibin beta activity (Hum Reprod 2000;15:2644)
- Variant in INHssA gene due to polymorphism
- Variant in INHalpha gene due to amino acid substitution
- Higher INHBA expression is significantly associated with reduced overall survival in cervical cancer (Front Genet 2022;12:705512)
Sample pathology report
- Biopsy, ovary:
- Granulosa cell tumor (see comment)
- Comment: A 60 year old woman presented with abnormal uterine bleeding and abdominal pain. Ultrasound revealed a solid mass on the right ovary. Microscopic examination of the biopsy revealed sheets of tumor cells arranged in a trabecular pattern. Diagnosis of granulosa cell tumor was supported by positive diffuse cytoplasmic immunostaining for inhibin alpha.
Board review style question #1
A biopsy removed from the ovary of a 56 year old woman with abnormal bleeding showed cells with ill defined cytoplasmic membranes and distinctive pale gray cytoplasm. The biopsy was positive for inhibin (image above) and reticulin. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Clear cell carcinoma of the ovary
- Endometrioid carcinoma
- Granulosa cell tumor
- Ovarian thecoma
Board review style answer #1
D. Ovarian thecoma. Ovarian thecomas typically present in postmenopausal women with abnormal bleeding as the main symptom. Histologic characteristics of thecomas are poorly defined cytoplasmic membranes with a pale gray cytoplasm. Thecomas stain positive for both reticulin and inhibin. Answer C is incorrect as granulosa cell tumors will stain strongly for inhibin; however, they typically show minimal staining for reticulin. Answers A and B are incorrect because inhibin is typically negative or weakly expressed in these tumor types.
Comment Here
Reference: Inhibin
Comment Here
Reference: Inhibin
Board review style question #2
Inhibin protein expression is useful for identifying which of the following types of tumors?
- Adrenocortical tumors
- Liposarcomas
- Neurofibromas
- Schwannomas
Board review style answer #2
A. Adrenocortical tumors. Inhibin, as part of a staining panel, can be a valuable marker for differentiating adrenal cortical tumors from medullary tumors. Answers B, C and D are incorrect because inhibin staining is most often negative in soft tissue neoplasms like liposarcomas, schwannomas and neurofibromas and may only be useful as part of an antibody panel in very limited cases.
Comment Here
Reference: Inhibin
Comment Here
Reference: Inhibin