Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Sample pathology report | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Cai C. IDH1 (R132H). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsidh1.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
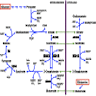
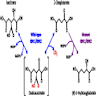
- Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 and 2 (IDH1 and IDH2) are metabolic enzymes that catalyze the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to produce α ketoglutarate (also known as 2 oxoglutarate [2OG]), NAPDH and CO2 (Genes Dev 2013;27:836)
Essential features
- IDH mutations were first identified in a small percent of glioblastomas and later found in the majority of adult low grade diffuse gliomas (Science 2008;321:1807, N Engl J Med 2009;360:765)
- IDH mutant gliomas have a better prognosis than the IDH wild type counterparts
- Over 90% of IDH mutations in gliomas are a missense mutation of IDH1 amino acid 132 (from arginine [R] to histidine [H]), which can be detected by mutation specific immunostain IDH1 R132H (Acta Neuropathol 2009;118:599, Neuropathology 2020;40:68)
- IDH mutations have also been identified in some nonglioma tumor types (outlined in Positive staining - disease); however, those tumors are dominated by non IDH1 R132H mutations and thus have very little utility for the IDH1 R132H immunostain
Pathophysiology
- Mutant IDH enzymes produce (R)-2-hydroxyglutarate ([R]-2HG) instead of 2OG, which results in widespread DNA hypermethylation and a unique glioma CpG island methylator phenotype (G CIMP) in IDH mutant gliomas (Nature 2012;483:479)
- Abnormal accumulation of tumor metabolite 2HG allows detection of IDH mutant glioma in live patients by magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) (Neuro Oncol 2016;18:1559)
Diagrams / tables
Uses by pathologists
- IDH1 R132H immunostain is widely used in pathology laboratories on brain tumors in order to classify diffuse gliomas and provide prognostic implications
- Multispecific mutant IDH1 / IDH2 immunostain (clone MsMab1) that detects mutant IDH1 (R132H, R132S, R132G) and IDH2 (R172S, R172G) or monoclonal antibody (clone 11C8B1) that detects mutant IDH2 R172T
- These antibodies have been used in research studies on glial or nonglial tumors; however, they have not gained significant clinical utility in pathology laboratories (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1067, Cancer Med 2013;2:803, Cancer Sci 2014;105:744, Mod Pathol 2019;32:205)
- Beginning to be used clinically for sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma (SNUC)
- Multiple monoclonal antibodies that target other individual IDH1 / IDH2 mutations and another multispecific mAbs (i.e., MsMab2) that recognizes IDH1 R132L and IDH2 R172M are available but have not gained significant clinical utility in pathology laboratories (Brain Tumor Pathol 2015;32:3)
Prognostic factors
- Diffuse glioma: IDH mutant gliomas have better prognosis than their IDH wild type counterparts (N Engl J Med 2009;360:765)
- Acute myeloid leukemia (AML): IDH1 mutations are associated with worse overall survival (hazard ratio: 1.17; 95% CI: 1.02 - 1.36) and a lower complete remission rate (risk ratio: 1.30; 95% CI: 1.04 - 1.63) (Am J Blood Res 2012;2:254)
- Chondrosarcoma: IDH1 / IDH2 mutations are associated with worse overall survival (hazard ratio: 1.90; 95% CI: 1.06 - 3.42; p: 0.03) (Cancer Med 2021;10:4415)
Microscopic (histologic) description
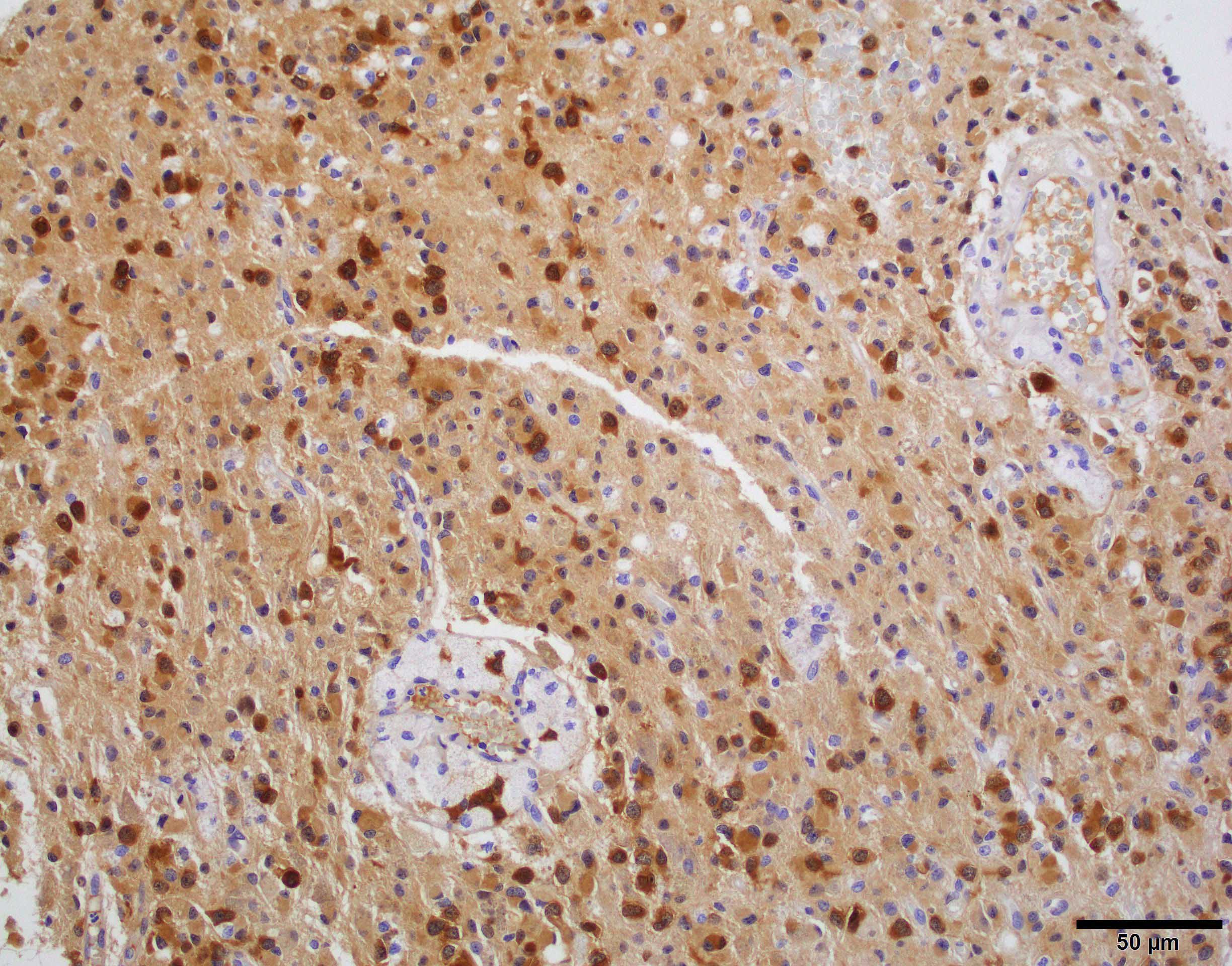
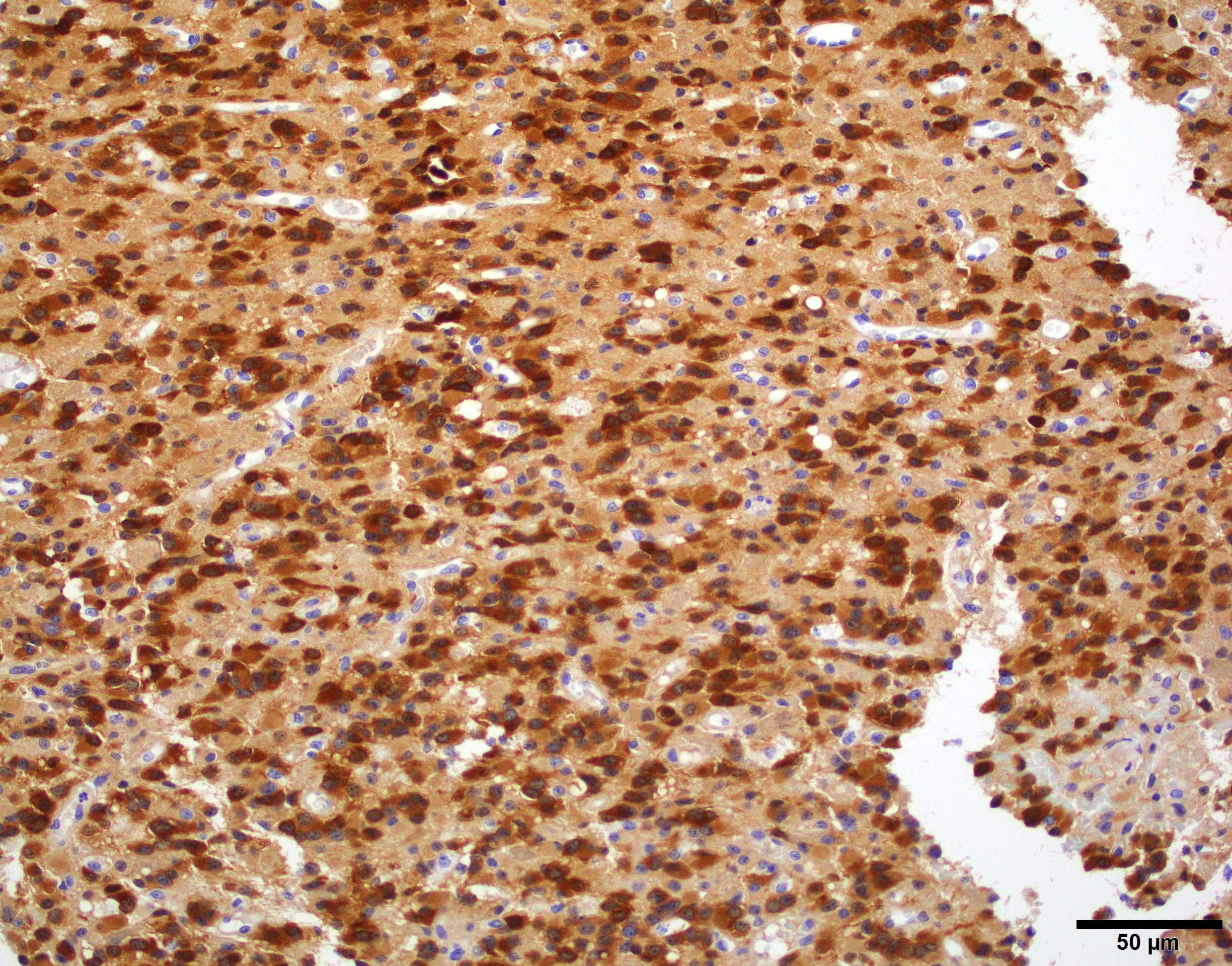
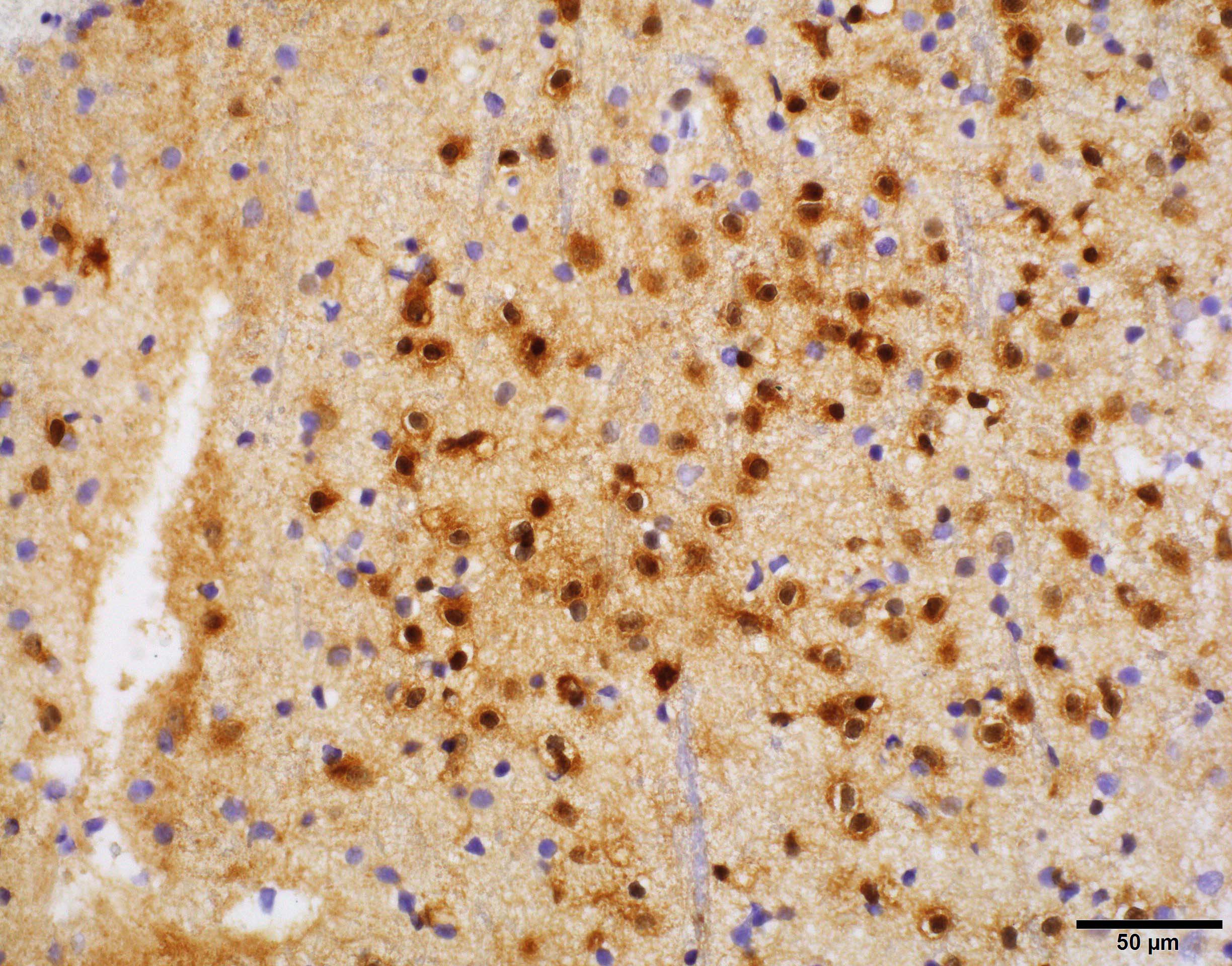
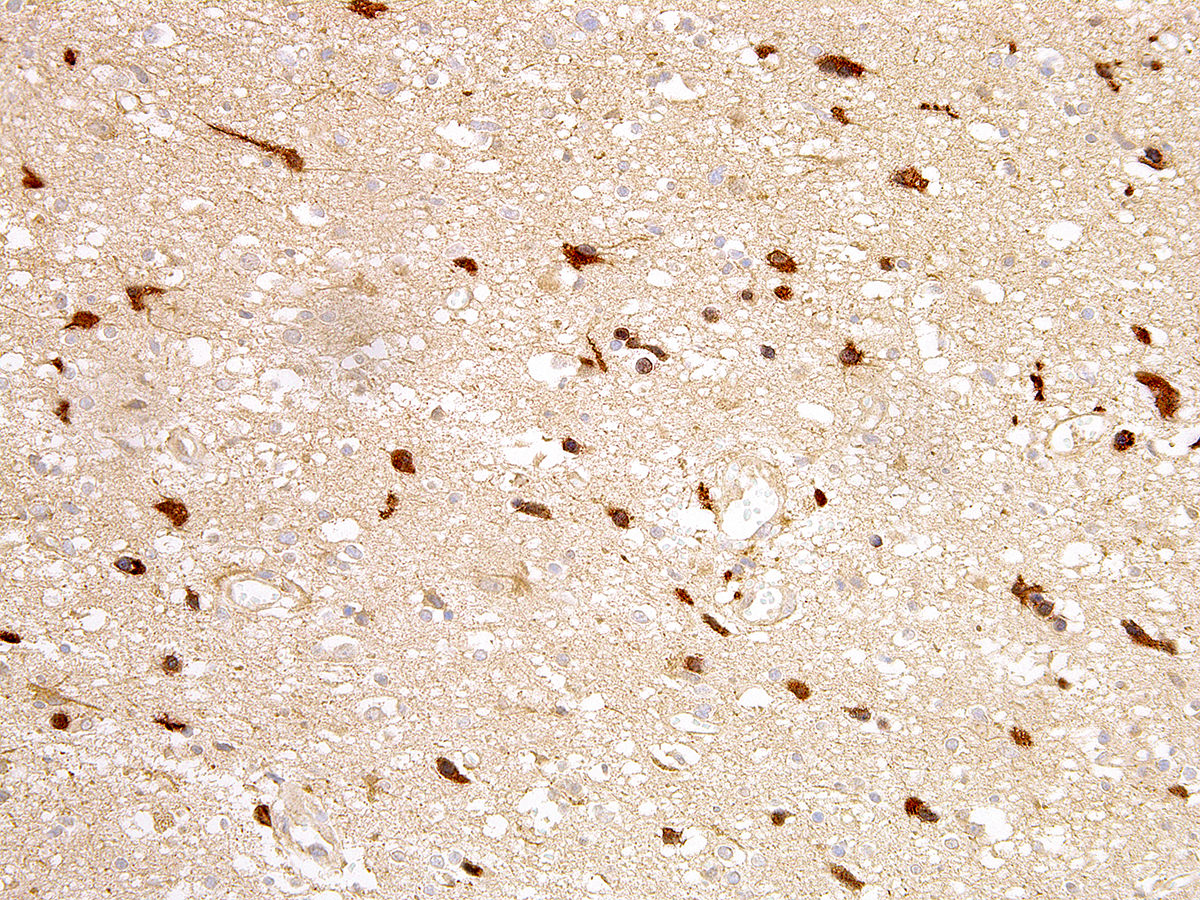
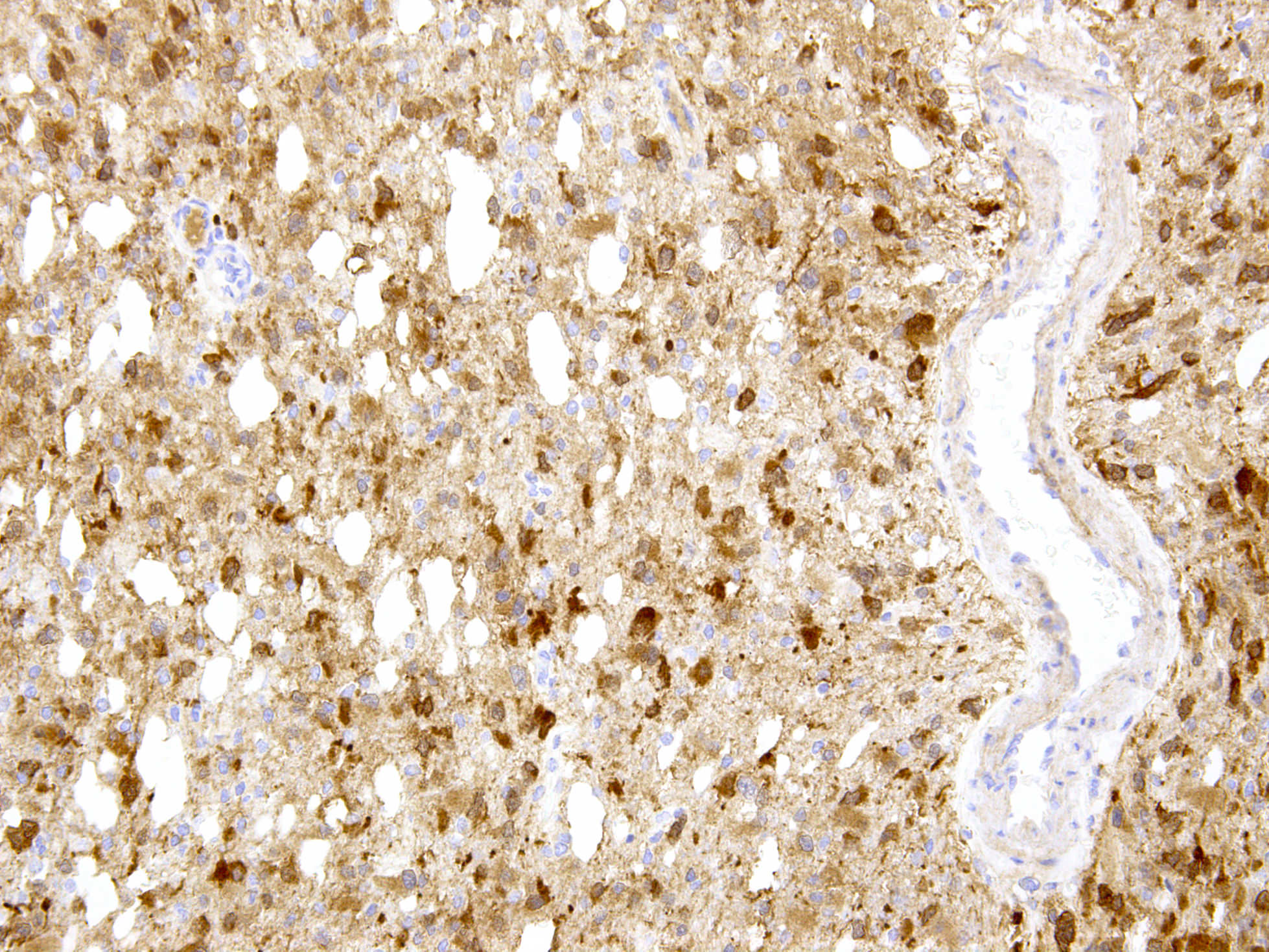
- IDH1 (R132H) mutant gliomas show diffuse cytoplasmic reactivity in all tumor cells on IDH1 R132H immunostains
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
- IDH1 R132H is a mutation specific monoclonal antibody and is negative in normal tissue
Positive staining - disease
- Glial neoplasms:
- By definition, all oligodendrogliomas harbor IDH1 / IDH2 mutation
- Vast majority of adult type diffuse astrocytomas are IDH mutant
- Nonglial neoplasms:
- Acute myeloid leukemia (AML): prevalence of IDH1 and IDH2 mutations was 8.7% (20/230) and 10.4% (24/230), respectively (Blood 2010;116:2122, J Clin Oncol 2010;28:3636, J Hematol Oncol 2012;5:5)
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL): 3 of 54 adult ALL cases had IDH1 mutations (R132H, R132G, R132S - one of each); there were no IDH2 mutations and no IDH1 or IDH2 mutations in the 34 pediatric ALL cases (Genet Test Mol Biomarkers 2012;16:991)
- Chondrosarcomas: IDH1 and IDH2 mutations were detected in 38.7% and 12.1% of chondrosarcomas; IDH1 R132H only accounts for 7% of the IDH1 mutations (Cancer Med 2021;10:4415)
- Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma (SNUC) and poorly differentiated carcinomas have high rates (49 - 80%) of IDH2 R172X mutations (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1067, Mod Pathol 2017;30:650, J Pathol 2017;242:400, Mod Pathol 2019;32:205)
- Cholangiocarcinoma IDH1 / IDH2 mutations have been detected in ~25% of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas (Cell Rep 2017;18:2780, Nature 2014;513:110)
- Ollier disease and Maffucci syndrome: enchondromas and spindle cell hemangiomas in Ollier disease and Maffucci syndrome are associated with somatic mosaic IDH1 and IDH2 mutations (Nat Genet 2011;43:1262, Nat Genet 2011;43:1256)
- Spindle cell hemangioma: 64% (18/28) of the spindle cell hemangioma cases had IDH1 R132C mutation, with or without association with Maffucci syndrome; 2/28 had IDH2 R172T or IDH2 R172M mutations (Am J Pathol 2013;182:1494)
- Osteosarcoma: ~25% (3/12) of osteosarcoma patients harbor IDH2 R172S mutation
- Giant cell tumors of bone (GCTB): up to 80% (16/20) of GCTB patients harbor IDH2 R172S mutation (Cancer Sci 2014;105:744)
- Prostate carcinoma: IDH1 (R132H) IHC expression is seen in 2.5% (3/118) of prostate carcinomas (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2014;22:284)
- High grade meningioma: mutations in IDH1 / IDH2 were identified in 2.2% (3/134) of high grade meningioma cases (Tumori 1988;74:555)
Negative staining
- CNS neoplasms:
- Within the CNS, IDH R132H is considered a specific marker for a subset of adult diffuse gliomas and is not expressed in pediatric type diffuse gliomas, circumscribed gliomas, glioneuronal tumors, ependymal tumors, choroid plexus tumors or mesenchymal tumors (N Engl J Med 2009;360:765)
- Of diffuse gliomas, IDH R132H mutation is not found in wild type glioblastoma, H3F3A G34R or K27M mutant gliomas; IDH mutation is uncommon in infratentorial, spinal cord diffuse gliomas and pediatric gliomas under 14 years of age (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2016;4:60, Acta Neuropathol 2012;124:449, Childs Nerv Syst 2011;27:87)
- Non CNS neoplasms:
- IDH1 R132H immunostain is negative in 258 thyroid, 11 renal cell, 10 ovarian, 18 endometrial, 20 breast, 25 colorectal, 22 non small cell lung carcinomas, 25 melanomas and 8 thyroid follicular adenomas (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2014;22:284)
- In the initial study, IDH1 / IDH2 mutation was not detected in 494 non CNS tumors, including 35 lung cancers, 57 gastric cancers, 27 ovarian cancers, 96 breast cancers, 114 colorectal cancers, 95 pancreatic cancers, 7 prostate cancers, 4 chronic myelogenous leukemias, 7 chronic lymphocytic leukemias, 7 acute lymphoblastic leukemias and 45 acute myelogenous leukemias (N Engl J Med 2009;360:765)
Sample pathology report
- Brain, left frontal lobe mass, excision:
- Astrocytoma, IDH mutant, WHO grade 2
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1