Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Additional referencesCite this page: Enwere E, Thakur S. FOXP3. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsfoxp3.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- FOXP3 (Forkhead box P3) is a member of the FOX protein (forkhead / winged helix) family and acts as a master regulator of the development and function of regulatory T cells (Science 2003;299:1057)
- It is a specific marker of both natural T regulatory cells (nTregs) and adaptive / induced T regulatory cells (a / iTregs) (Immunity 2005;22:329)
- This can play an important role in immune destruction of cancer cells and various autoimmune diseases
Essential features
- Acts as a transcriptional regulator of regulatory T cells (Tregs)
- Plays an essential role in maintaining homeostasis of the immune system by regulating the suppressive function, stability and expansion of the Tregs
- Depending upon its interaction with various histone deacetylases or acetylases, FOXP3 can act both as a transcriptional activator or repressor in Tregs (GeneCards - FOXP3)
- Orchestrates the expression levels of proteins like CTLA4, IL2, IL17, IFN-ϒ, RORA, RORC and RELA, resulting in inhibition of effector and helper T cells as well as expansion of Tregs (Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005;102:5138, Nature 2007;446:685, Nature 2008;453:236, J Immunol 2008;180:4785)
Terminology
Also known as:
- Scurfin, IPEX, DIETER, AIID, PIDX, XPID, JM2, FOXP3delta7
- Mutations cause IPEX syndrome - Immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, x-linked immunodeficiency (GeneCards - FOXP3)
Sites
- Expressed in nucleus excluding nucleoli (The Human Protein Atlas - FOXP3)
Pathophysiology
- Induction of FOXP3 positive Treg cells has been reported to markedly reduce autoimmune disease severity in animal models of diabetes, multiple sclerosis, asthma, inflammatory bowel disease, thyroiditis and renal disease (Springer Semin Immunopathol 2006;28:3)
- In mice, a 'Scurfy' phenotype is observed due to a mutant FOXP3 (lacking Forkhead domain); these mice demonstrate hyperproliferation of CD4+ T lymphocytes, extensive multiorgan infiltration and elevation of numerous cytokines (Nat Genet 2001;27:68)
- In humans, patients with solid tumors show increased local FOXP3 positive T cells, which can inhibit the suppression of cancerous cells by the immune system (Blood 2006;108:804); conversely, FOXP3 positive Tregs are dysfunctional in autoimmune disease such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) (J Autoimmun 2006;27:110)
Clinical features
- Apart from Tregs, FOXP3 expression has been reported in normal breast, prostate and ovarian epithelium, and is downregulated in the corresponding tumor tissue (Cell 2007;129:1275, Cancer Lett 2010;287:91)
- As a transcription factor, FOXP3 represses the expression of HER2, SKP2, SATB1 and MYC oncogenes (Cancer Cell 2009;16:336, Oncogene 2012;31:1045, J Clin Invest 2007;117:3765, Cell 2007;129:1275) , and to induce the expression of p21 (Cancer Res 2009;69:2252) and LATS2 tumor suppressor genes (Cancer Res 2011;71:2162)
- Overexpression of FOXP3 inhibits cell growth in vitro and in vivo in various glioma (Oncotarget 2012;3:1146), breast (Cell 2007;129:1275), prostate (Cancer Cell 2009;16:336) and ovarian (Cancer Lett 2010;287:91) cancer cell lines
- Conversely, increased FOXP3 expression has been reported in melanoma (Cancer Res 2008;68:3001); pancreatic adenocarcinoma (Cancer Res 2007;67:8344); leukemia (Leuk Res 2011;35:e10); bladder cancer (BJU Int 2011;108:1672) and cervical cancer (Cancer Immunol Immunother 2013;62:481)
- FOXP3 also facilitates tumorigenesis by enabling tumor cells to evade anti-tumor immunity by inhibiting T cell proliferation (Cancer Res 2007;67:8344)
- In humans with immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, x-linked (IPEX) syndrome, mutations in FOXP3 result in lack of normal Tregs and consequent development of multisystem autoimmunity (Ann N Y Acad Sci 2016 Feb 25 [Epub ahead of print])
Prognostic factors
- Increased FOXP3 expression in muscle invading urinary bladder cancer is associated with reduced long term survival (BJU Int 2011;108:1672)
- In breast cancer, increasing FOXP3 expression is associated with reduced overall survival; FOXP3 is also a strong prognostic factor for distant metastases free survival (J Clin Oncol 2009;27:1746)
- In colorectal carcinoma, high FOXP3 expression in cancer cells are associated with poor prognosis: in these patients, FOXP3 levels in tumor infiltrating Treg cells did not correlate with overall patient survival (PLoS One 2013;8:e53630)
- In smokers with adenocarcinoma of the lung, high FOXP3 / CD4 T cells correlated with poor survival (Ann Oncol 2016 Aug 8 [Epub ahead of print])
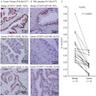
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Appendix, bone marrow, tonsil, spleen and lymph node show high to medium expression of FOXP3 (The Human Protein Atlas - FOXP3)
Negative stains
- Muscle tissue, pancreas, ovary and kidney stain negative for FOXP3 (The Human Protein Atlas - FOXP3)
Additional references