Table of Contents
Definition / general | Uses by pathologists | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative stainingCite this page: Pernick N. FOXL2. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsfoxl2.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Forkhead Box L2; belongs to large family of forkhead FOX transcription factors (PLoS One 2012;7:e46270)
- One of first genes expressed in female gonad development, required for proper granulosa cell differentiation during folliculogenesis
- Expression strongly maintained in granulosa cells throughout life
- FOXL2 expression has role in developing eyelid, associated with blepharophimosis ptosis epicanthus inversus syndrome (BPES), with or without accompanying premature ovarian failure (Mol Vis 2011;17:436, J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2013 Sep 13:1)
FOXL2 mutation
- FOXL2 mutation (402C→G / C134W) present in 70 - 95% of ovarian adult granulosa cell tumors (Mod Pathol 2010;23:1477, Gynecol Oncol 2013;131:325) but not in ovarian fibromas (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1450); also present in 2 of 5 men with adult granulosa cell tumor (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:825)
- Mutation absent in ovarian juvenile granulosa cell tumors (Mod Pathol 2011;24:1360)
- FOXL2 mutation (402C→G / C134W) may contribute to development of adult granulosa cell tumors by reducing expression of GnRH receptor, thus conferring resistance to GnRH-induced cell apoptosis (PLoS One 2013;8:e55099)
- Blepharophimosis-ptosis-epicanthus inversus syndrome (BPES) cases may have different mutations (Horm Res Paediatr 2012;77:2, Hum Reprod 2012;27:3347, Mol Vis 2012;18:211)
- Germline mutations lead to disorders of ovarian function ranging from premature follicle depletion and ovarian failure to unregulated granulosa cell proliferation leading to tumor formation (Endocrinology 2011;152:1199)
Uses by pathologists
- FOXL2 mutation analysis distinguishes diffuse adult granulosa cell tumor ( 402C→G mutation present) from cellular fibroma (mutation absent) (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1450, Mod Pathol 2013;26:860)
- Note: FOXL2 staining is not specific for the FOXL2 mutation
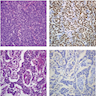
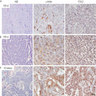
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
- Nuclear stain
- Ovary: granulosa cells
Positive staining - disease
- Breast cancer: Int J Oncol 2011;38:1145
- Ovary: most sex cord stromal tumors (>95% of adult and juvenile granulosa cell tumors, fibromas, and sclerosing stromal tumors; 50% of Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors, 9% of steroid cell tumors, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:484)
- Pituitary adenoma: gonadotropin-subunit-producing adenomas (87%), null cell adenoma cases (73%, Mod Pathol 2011;24:765)
- Testis: granulosa cell tumors (2 of 5, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:825)
Negative staining
- Ovary: most non sex cord stromal tumors
- Ovary: gonadoblastoma - germ cells in gonadoblastoma and dysgerminoma components (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2011;14:391)