Table of Contents
Definition / general | Clinical features | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - diseaseCite this page: Stuart L. Fontana-Masson. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsfontana.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Melanin stain
- Interpretation: melanin granules reduce ammonia-silver nitrate and turn black, but difficult to interpret faint staining in sparsely positive cells
Clinical features
- Melanin is normally found in skin, eye, substantia nigra, melanoma
- Melanin stains are Fontana-Masson (stains melanin black) and Schmorl method (stains melanin blue-green)
- Bleaching with potassium permanganate or hydrogen peroxide is used to remove melanin to examine cellular morphology
- Note: pseudomelanin of melanosis coli, usually found in macrophages, is PAS positive; true melanin is not
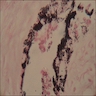
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
- Any cell containing melanin (e.g. melanocyte, Hum Pathol 2012;43:898)
Positive staining - disease
- Any melanin containing cell; also some forms of yeast and yeast-like organisms (Hum Pathol 2012;43:898)