Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Interpretation | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - not malignant | Positive staining - malignant | Negative staining - disease | Sample pathology report | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Skorobogatko V, Umphress B. Factor XIIIa. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsfactorxiiia.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- FXIIIa is widely expressed in a variety of cell types; however, it is most commonly recognized as a marker of fibrohistiocytic proliferations
- Derived from monocyte / macrophage myeloid lineage and expressed in dermal dendrocytes, primarily surrounding microvasculature in the adventitial dermis near the dermoepidermal junction and near skin appendages (Int J Mol Med 2008;22:403)
- Active form of factor XIII, the last enzyme in the coagulation cascade
Essential features
- Cytoplasmic marker with expression in normal epithelial tissue and various pathologic states
- Mainly used to distinguish dermatofibroma from dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
- Generally expressed (with some variation) in benign sebaceous neoplasms, fibroblasts in fibrovascular tumors and a proportion of histiocytomas
- Generally negative (with some variation) in malignant sebaceous neoplasms and clear cell tumors
Terminology
- Factor XIIIa, FXIIIa, F13a, fibrin stabilizing factor
Pathophysiology
- Synthesized by cells in the bone marrow, FXIIIa exists as a tetrameric molecule with 2 A subunits and 2 B subunits in plasma and a dimer composed of 2 A subunits in cells (J Thromb Haemost 2007;5:181)
- Zymogen that crosslinks fibrin molecules which stabilizes blood clots
- Enhances proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of peripheral monocytes and fibroblasts (Cell Physiol Biochem 2007;19:113)
- Participates in wound healing and keloid formation (Thromb Haemost 2002;88:967, Pathol Int 2007;57:337)
Uses by pathologists
- Marker of fibrohistiocytic proliferations
- Marker of dermal dendrocytes
- Differentiates dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (CD34+, factor XIIIa-) from dermatofibroma or benign fibrous histiocytoma (FH) (CD34-, factor XIIIa+)
- FXIIIa (AC-1A1) is a sensitive and specific marker for sebaceous differentiation (J Cutan Pathol 2018;45:1)
- Shown to be expressed in higher numbers in indeterminate leprosy compared to normal skin (Am J Dermatopathol 2015;37:269)
Prognostic factors
- FXIII has been shown to have a role in metastatic potential by impeding NK cell mediated clearance of tumor cells (J Thromb Haemost 2008;6:812)
- Lung squamous cell carcinoma: plays a role in cell invasion and disease progression; extensive fibrin linkage correlated with worse prognosis (Nat Commun 2018;9:1988)
- Low levels of FXIIIa following an acute myocardial infarction have been correlated with worse prognosis with increased complications, such as heart failure and death (Thromb Haemost 2015;114:123)
Interpretation
- Cytoplasmic staining ranging from focal to diffuse and weak to strong
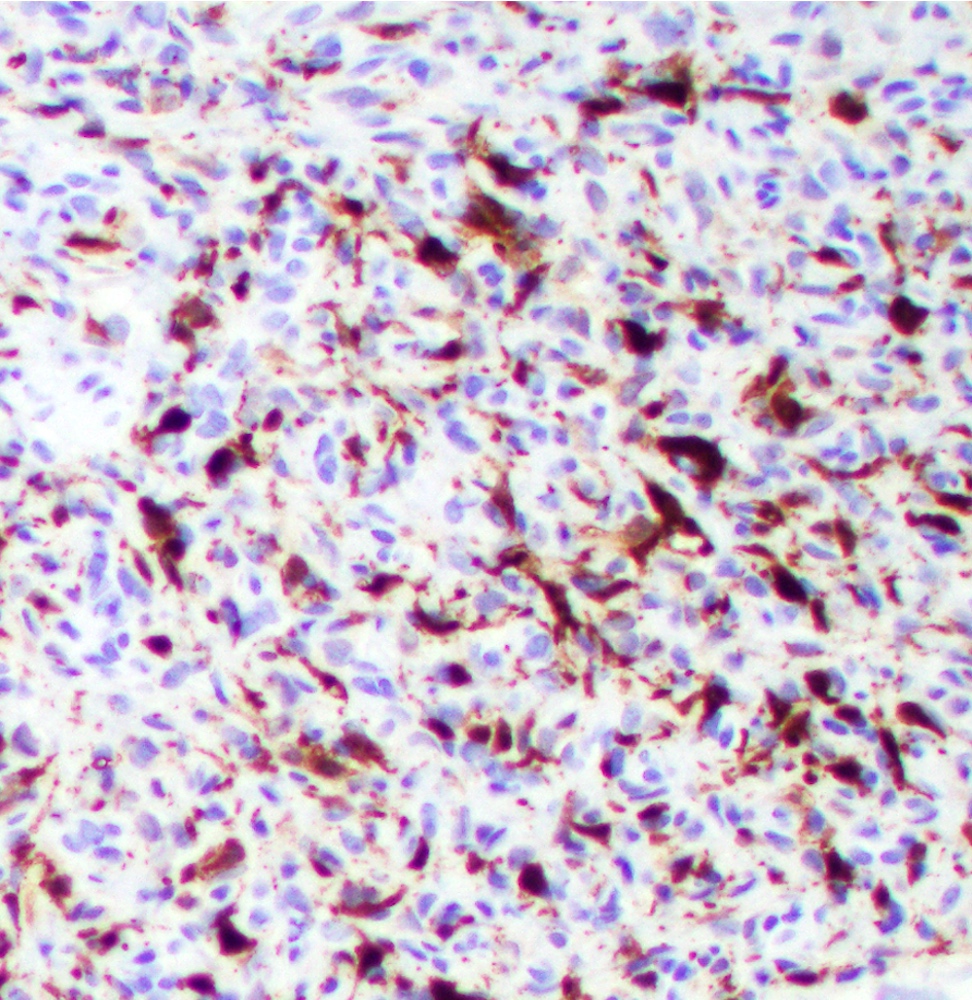
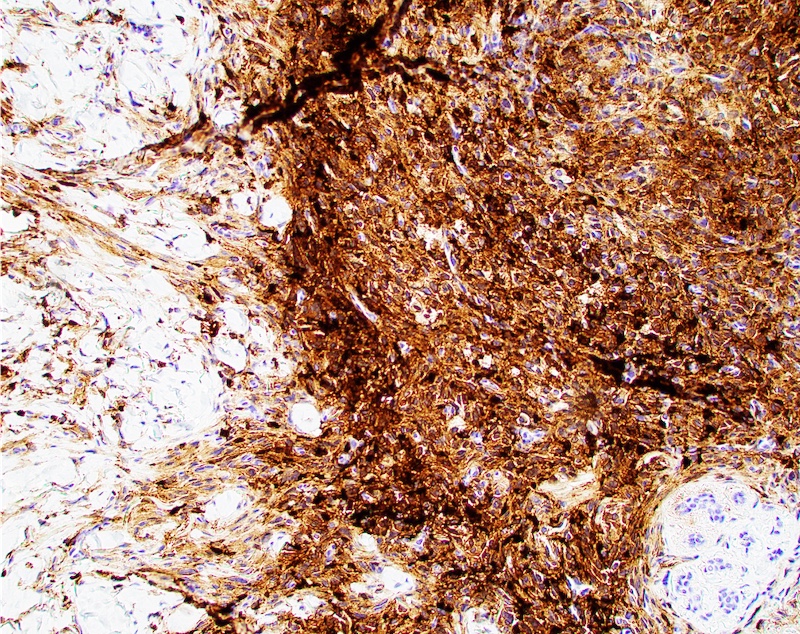
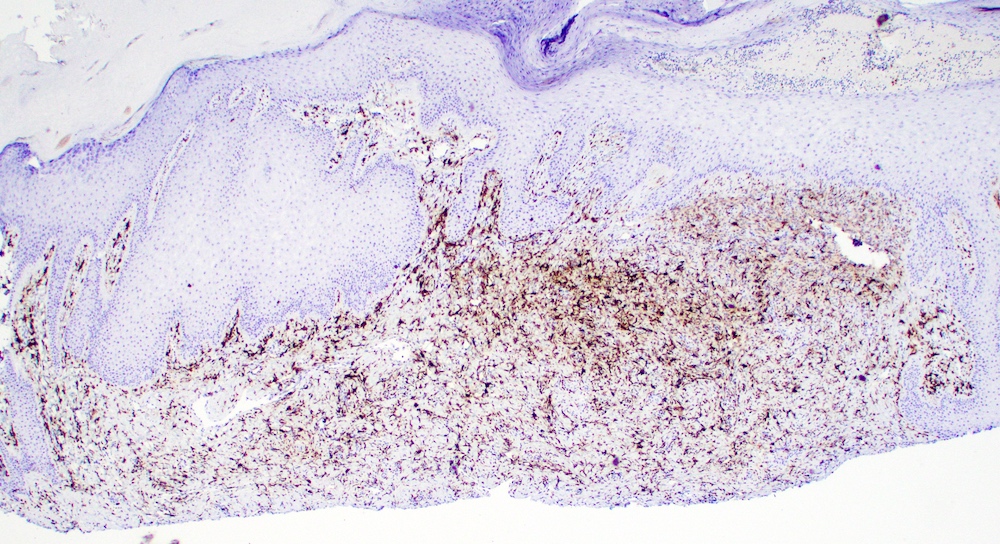
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
- Dermal dendrocytes
- Small subset of resident spindle cells in conjunctival stroma, Tenon capsule and tarsal plate (Ocul Oncol Pathol 2020;6:196)
- Sebaceous glands (FXIIIa, AC1-1A1 clone) (J Cutan Pathol 2016;43:657)
Positive staining - not malignant
- Ocular surface fibroma (60%) (Ocul Oncol Pathol 2020;6:196)
- Elastofibroma (Pol J Pathol 2014;65:120)
- Angiofibroma of eyelid (diffuse) (Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 2019;35:e199)
- Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma (in giant, stellate fibroblast-like stromal cells) (Head Neck Pathol 2018;12:52)
- Dendritic cell neurofibroma with pseudorosettes (Am J Dermatopathol 2020;42:604)
- Desmoplastic fibroblastoma of oral cavity (focal) (J Clin Exp Dent 2016;8:e89)
- Cellular neurothekeoma (focal) (J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:980)
- Nonneural granular cell tumor (J Cutan Pathol 2020;47:1026)
- Benign fibrous histiocytoma (dense); reduced in FH with retiform morphology (Hum Pathol 2020;99:107)
- Epithelioid cell histiocytoma (diffuse) (Diagn Pathol 2018;13:28)
- Perianal atypical fibrous histiocytoma (focal) (Am J Dermatopathol 2014;36:171)
- Multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma (interstitial histiocytes) (J Cutan Pathol 2013;40:1048)
- Sinonasal hemangiopericytoma (Am J Otolaryngol 2017;38:87, Int J Clin Oncol 2012;17:169)
- Cerebellopontine hemangiopericytoma (focal) (Pathol Res Pract 2012;208:493)
- Xanthogranuloma (Eur J Dermatol 2020;30:32)
- Calcifying fibrous tumor of the pleura and GI tract (Ann Pathol 2015;35:515, World J Gastroenterol 2020;26:5597)
- Calcifying fibrous pseudotumor of the epicardium (diffuse) (Cardiovasc Pathol 2015;24:191)
- Fibrous papules of the face; positive in classic, hypercellular, inflammatory, pleomorphic, pigmented and granular variants (Ann Dermatol Venereol 2013;140:763)
- Congenital medallion-like dermal dendrocyte hamartoma (MDDH) (Ann Dermatol 2013;25:382)
- Acquired bilateral melanosis of the neck in perimenopausal women (majority) (Br J Dermatol 2012;166:662)
- Chronic actinic dermatitis / actinic reticuloid (strong) (Am J Dermatopathol 2014;36:875)
- Dermal plexiform spindle cell lipoma (widely positive) (Rom J Morphol Embryol 2016;57:875)
- Sebaceous hyperplasia, adenoma (100%) and sebaceoma (80%); FXIIIa clone AC-1A1 (J Cutan Pathol 2016;43:657)
- CNS and pulmonary involvement with Erdheim-Chester disease (Autops Case Rep 2021;11:e2021321, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004;128:1428)
- Verruciform xanthoma (weak) (Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:479)
- Storiform collagenoma (scattered) (J Clin Pathol 2007;60:840)
- Cardiac myxoma (Histopathology 1996;28:529)
- Oral lichen planus, predominately in the superficial dermis (Actas Dermosifiliogr 2009;100:46, J Oral Pathol Med 1994;23:114)
- Increased number in recurrent aphthous ulcers (J Oral Pathol Med 1997;26:408)
Positive staining - malignant
- Biphenotypic sinonasal sarcoma (focal, 80%) (Hum Pathol 2016;55:44)
- Pleomorphic hyalinizing angiectatic tumor (focal) (J Cutan Pathol 1997;24:377, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2000;124:423)
- Kaposi sarcoma (Arch Dermatol 1993;129:1291)
Negative staining - disease
- Sebaceous carcinoma (Am J Dermatopathol 2015;37:809)
- Sebaceous adenocarcinoma of the major salivary glands (Histopathology 2018;73:585)
- Agminated clear cell tumor (Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:212)
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans generally negative, with exceptions (Am J Dermatopathol 2014;36:414)
- Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma (Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat 2018;27:225)
- Papular xanthoma (J Cutan Pathol 2002;29:200)
- Solitary fibrous tumor (of the uterine cervix) (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2010;29:189)
- Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis (Skinmed 2005;4:71)
Sample pathology report
- Skin, thigh lesion, biopsy:
- Dermatofibroma (see comment)
- Comment: Immunohistochemical studies with FXIIIa demonstrate diffuse positivity within tumor cells, while CD34 is negative. The findings are supportive of the diagnosis of dermatofibroma.
- Skin, back mass, excision:
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, margins free (see comment)
- Comment: Immunohistochemical studies with CD34 demonstrate diffuse positivity within the tumor, while FXIIIa is negative. The immunohistochemical findings are in support of the diagnosis.
Board review style question #1
A 37 year old woman presents with a 1 year history of a lumpy mass on her midback. On physical exam, the lesion is 3 cm, slightly raised, resembling a scar that feels rubbery upon palpation. Histologic examination shows a spindle cell neoplasm that is diffusely positive for CD34 and negative for factor XIIIa and S100 staining. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- Cutaneous melanoma
- Dermatofibroma
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
- Myxoid liposarcoma
Board review style answer #1
C. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is CD34+, factor XIIIa- and S100-. Dermatofibroma is typically CD34- and factor XIIIa+. Myxoid liposarcoma is usually vimentin+, S100+ and CD34-. Cutaneous melanoma would express S100.
Comment Here
Reference: Factor XIIIa
Comment Here
Reference: Factor XIIIa
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2
B. Factor XIIIa is a general marker for fibrohistiocytic proliferations
Comment Here
Reference: Factor XIIIa
Comment Here
Reference: Factor XIIIa