Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Sample pathology report | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Baniak N. DOG1. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsdog1.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Discovered on GIST 1
- Primarily used in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST)
Essential features
- Monoclonal (SP31, K9, DOG1.1) and polyclonal antibodies (Cancer Control 2015;22:498)
- Most sensitive and specific marker for GIST
Terminology
- Discovered on GIST 1 (Adv Anat Pathol 2017;24:336)
- TMEM16A (Adv Anat Pathol 2017;24:336)
- ANO1 (Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- FLJ10261 (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1401)
- ORAOV2 (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1401)
Pathophysiology
- Encoded by a locus at chromosome 11q13 and has 3 known splice variants (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1401, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Transmembrane protein that encodes the chloride channel protein anoctamin 1 (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:896, Adv Anat Pathol 2017;24:336)
- Present in many sites, such as the luminal surface of the gastric body and antral mucosa, salivary glands, pancreatic acini, intrahepatic bile ducts, gallbladder glandular elements, as well as breast and prostatic myoepithelial / basal cells (Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:896)
- In the interstitial cell of Cajal, found to contribute to the generation of pacemaker electrical activity that is important for the physiologic motility of the gastrointestinal tract (Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- DOG1 does not appear to bear mutations in its protein coding sequence in GIST (Adv Anat Pathol 2017;24:336, Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8:5721)
- Biologic significance of increased DOG1 expression in tumors is not entirely known (Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
Interpretation
- Membranous and cytoplasmic
Uses by pathologists
- Sensitive and specific marker for GIST (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Sensitivity has been observed to be in the range of ~87 - 97% (Adv Anat Pathol 2017;24:336, Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:210, Mod Pathol 2011;24:866, Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1401)
- Utility in the identification of PDGFRα mutant GIST, which is more likely to be KIT and CD34 negative (Adv Anat Pathol 2017;24:336, Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:210, Mod Pathol 2011;24:866)
- Sensitive for CD117 negative GIST tumor (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1287, Mod Pathol 2011;24:866)
- Sensitive and specific marker for GIST in cell blocks (Cancer Cytopathol 2011;119:202, Am J Clin Pathol 2011;135:448)
- Marker for interstitial cells of Cajal (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:72)
- Differentiate salivary gland carcinoma subtypes (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Mod Pathol 2012;25:919, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:333, Ann Diagn Pathol 2019;43:151408)
- Characterize sloughed cells in testicular biopsies for infertility (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1123)
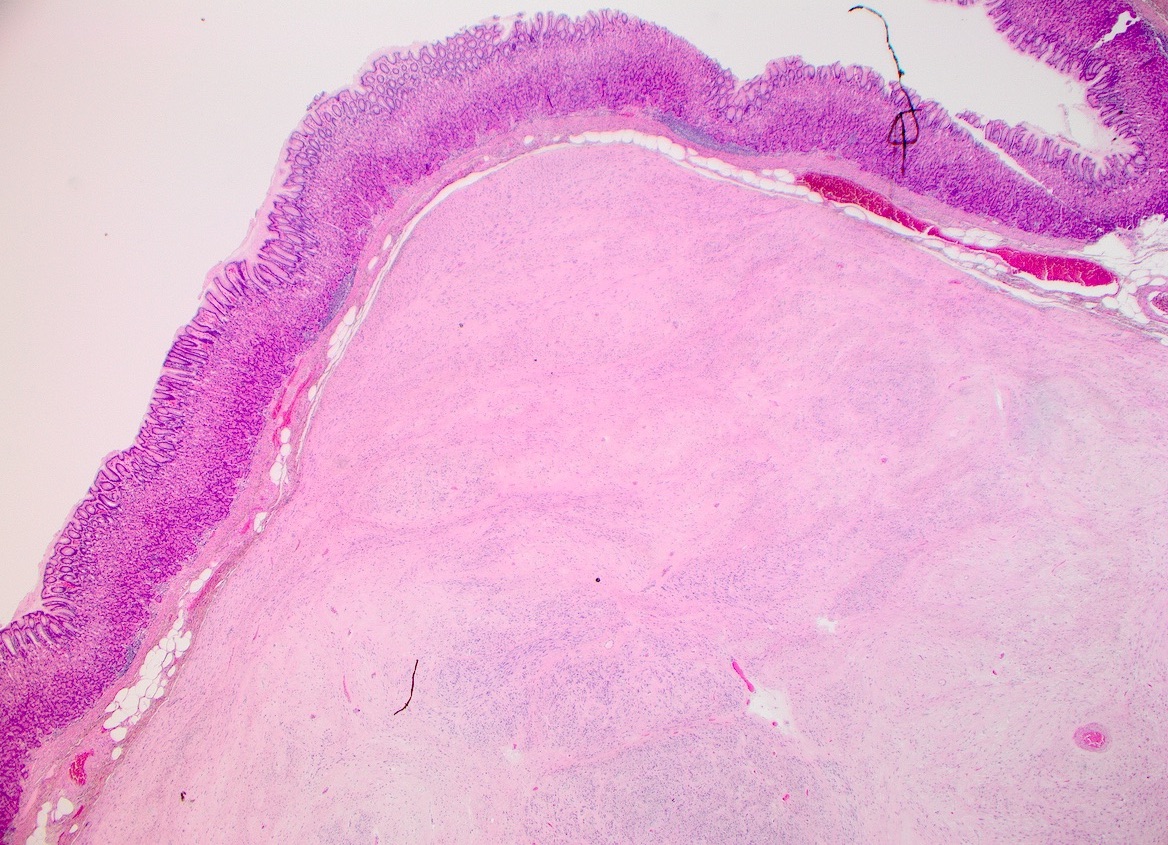
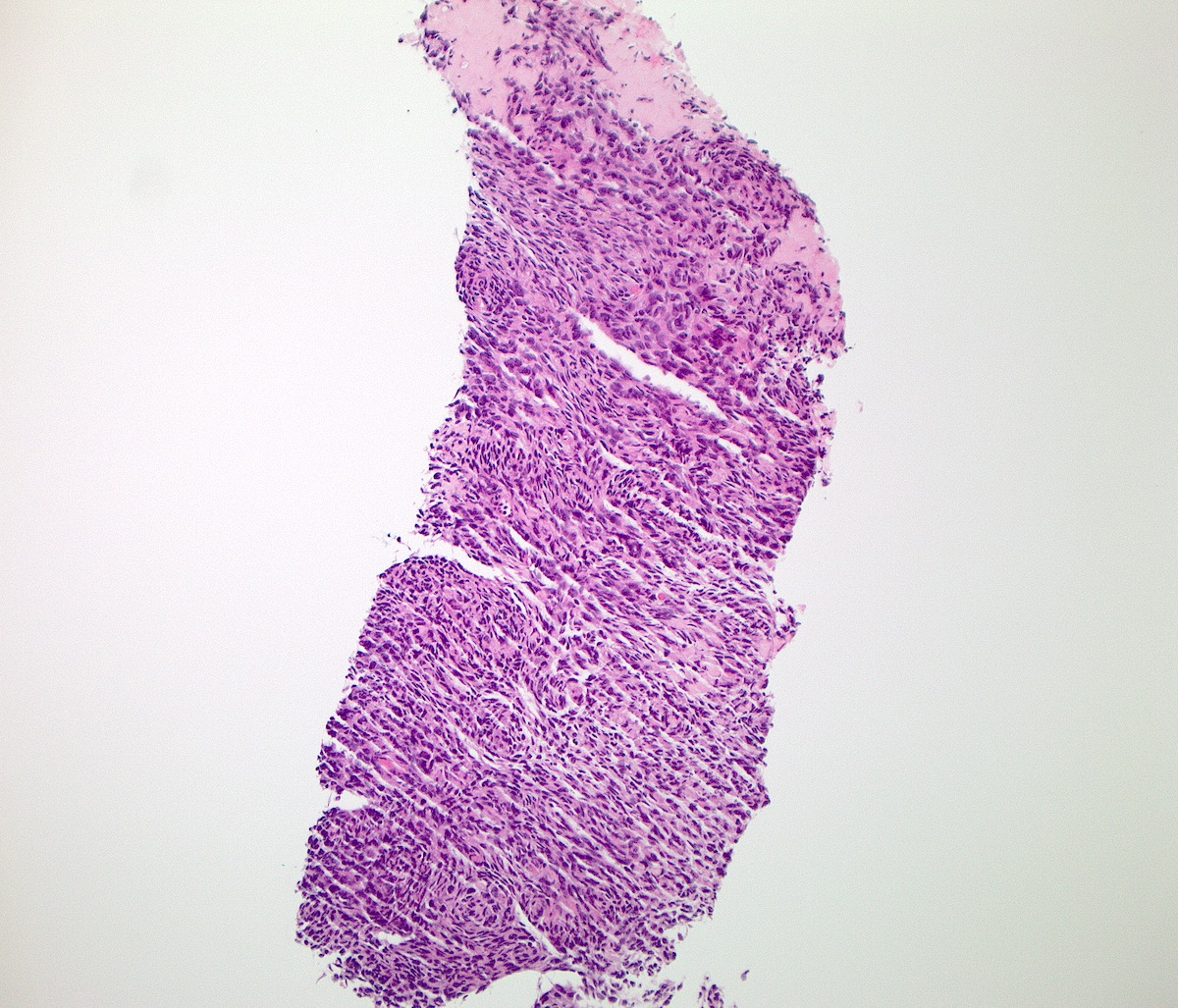
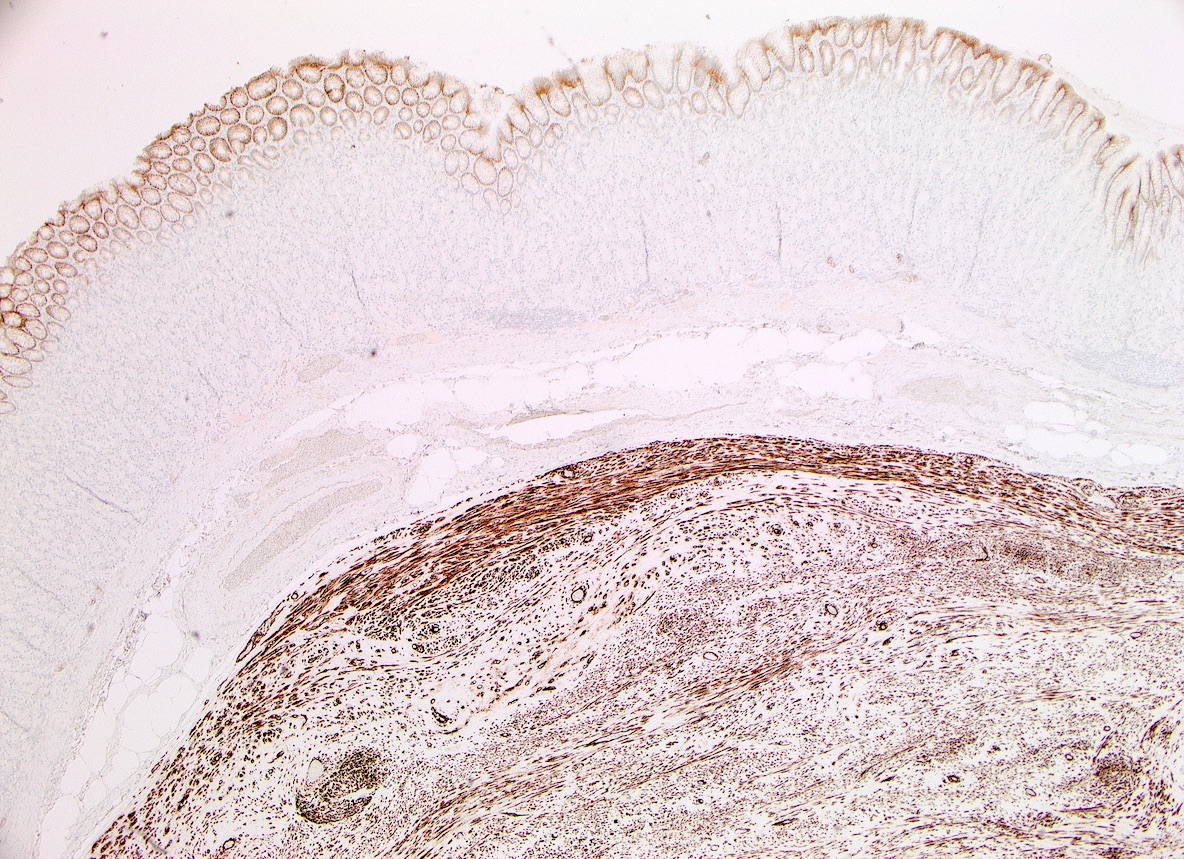
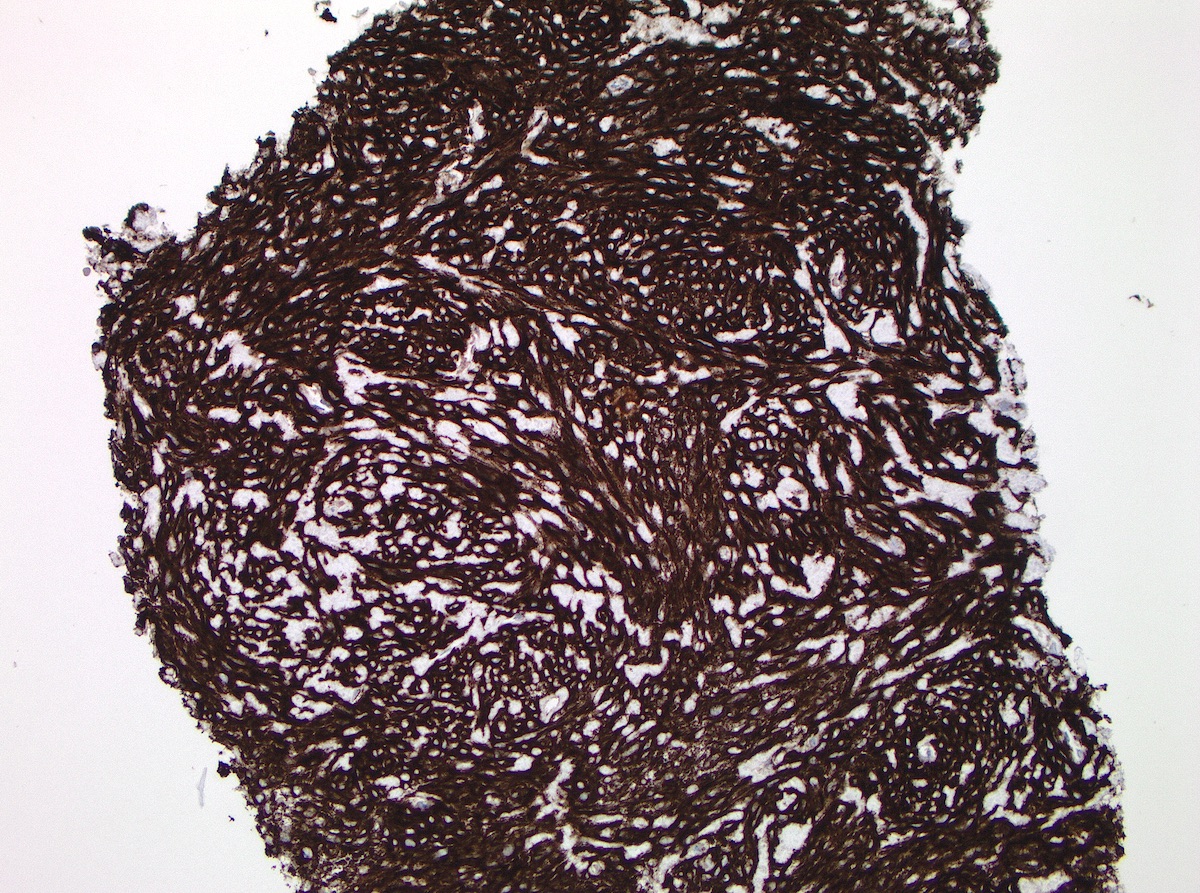
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
- Gastric epithelium, pancreatic centroacinar cells (Hum Pathol 2011;42:817, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Interstitial cells of Cajal (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:72)
- Pancreatic endocrine cells (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2009;17:413)
- Late germ cells (spermatocytes and spermatids) (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1123, Ann Diagn Pathol 2019;40:18)
- Skin adnexa: canalicular expression in eccrine glands and weak expression in myoepithelial cells of apocrine glands, germinative cells of sebaceous glands and outer root sheath of follicular infundibulum (Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:896, J Cutan Pathol 2016;43:974)
- Liver bile ducts *clone dependent (Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Gallbladder *clone dependent (Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Bladder mucosa (Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Normal salivary gland tissues (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Mod Pathol 2012;25:919, Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:140)
- Minor salivary glands (apical region of the mucous acini, intercalated ducts and partial striated ducts) (Ann Diagn Pathol 2019;43:151408)
Positive staining - disease
- Acinic cell carcinoma (97 - 100%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Mod Pathol 2012;25:919, Acta Cytol 2015;59:384, Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:140)
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma (30 - 71%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:333, Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:140)
- Apocrine carcinoma (50%) (J Cutan Pathol 2016;43:974)
- Breast fibroadenoma (82%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:333)
- Chondroblastoma (84 - 100%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Histopathology 2012;60:1099, Ann Diagn Pathol 2020;44:151440)
- Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma (86 - 100%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Histopathology 2012;61:170, Pathol Res Pract 2015;211:303)
- Cylindroma (87.5%) (Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:896)
- Epithelial myoepithelial carcinoma (53%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Histopathology 2012;61:170)
- Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (60%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1401)
- Extramammary Paget disease (60%) (J Cutan Pathol 2016;43:974)
- GIST
- Hidradenoma papilliferum (100%) (J Cutan Pathol 2016;43:974)
- Hidrocystadenoma (100%) (J Cutan Pathol 2016;43:974)
- Mixed tumor of the skin, apocrine type (100%) (J Cutan Pathol 2016;43:974)
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma (73%) (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:140)
- Pilomatrixoma (50%) (J Cutan Pathol 2016;43:974)
- Polymorphous adenocarcinoma (66%) (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:140)
- Renal oncocytoma (100%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Pathol Res Pract 2015;211:303)
- Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas (51%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Hum Pathol 2011;42:817)
- Squamoid eccrine ductal carcinoma (100%) (J Cutan Pathol 2016;43:974)
- Steatocystoma (100%) (J Cutan Pathol 2016;43:974)
Negative staining
- Alveolar soft part sarcoma (0%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2012;20:397)
- Angiosarcoma (0 - 3%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1401, Histopathology 2012;61:170, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Basal cell adenocarcinoma (0%) (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:140)
- Basal cell adenoma (35%) (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:140)
- Breast carcinoma (ductal / lobular) (0%) (Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Canalicular adenoma (0%) (Ann Diagn Pathol 2019;43:151408, Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:140)
- Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma (36%) (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:140)
- Cholangiocarcinoma (0 - 17%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Histopathology 2010;57:250, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Chondromyxoid fibroma (0%) (Histopathology 2012;60:1099)
- Chondrosarcoma (0%) (Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Chordoma (0%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:333)
- Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (0%) (Pathol Res Pract 2015;211:303, Histopathology 2012;61:170)
- Clear cell sarcoma (0%) (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:333, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Colonic adenocarcinoma (0 - 13%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1401, Histopathology 2012;61:170)
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (0%) (Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Desmoid tumor (0%) (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:333, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Desmoplastic small round cell tumor (0%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1401, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Endometrial adenocarcinoma (40%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Histopathology 2012;61:170)
- Endometrial stromal sarcoma (0%) (Histopathology 2012;61:170, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (0%) (Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Epithelioid sarcoma (0%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:333)
- Esophageal adenocarcinoma (0%) (Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Ewing sarcoma (0 - 3%) (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:333, Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1401, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma (0%) (Histopathology 2012;61:170, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Ganglioneuroma (0%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Histopathology 2012;61:170)
- Gastric adenocarcinoma (28%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, J Clin Pathol 2013;66:40)
- Glomus tumor (22%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Histopathology 2010;57:250)
- Giant cell tumor (0%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:333)
- Granular cell tumor (0%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:333)
- Hidradenoma (0 - 9%) (Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:896, J Cutan Pathol 2016;43:974)
- Inflammatory fibroid polyp (0%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Histopathology 2012;61:170)
- Kaposi sarcoma (0%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Histopathology 2012;61:170)
- Leiomyoma (0 - 23%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:333, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Leiomyosarcoma (0 - 4%) (J Clin Pathol 2013;66:40, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Liposarcoma (0%) (Histopathology 2010;57:250, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma (0 - 42%) *clone dependent (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:333, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222, Ann Diagn Pathol 2017;30:8)
- Lung adenocarcinoma (0%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:333)
- Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (0 - 3%) (Histopathology 2010;57:250, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Mastocytoma (0%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:333)
- Melanoma (2%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1401, Histopathology 2010;57:250, Am J Clin Pathol 2011;136:74, Histopathology 2012;61:170, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:333)
- Neuroblastoma (0%) (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:333, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Neurofibroma (0%) (Histopathology 2012;61:170, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Osteosarcoma (0%) (Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Ovarian carcinoma (serous / mucinous / clear cell) (0%) (Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Pancreatic adenocarcinoma (0 - 7%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2012;20:397, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor (2%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2012;20:397)
- Perineurioma (0%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:333)
- Perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (0%) (Histopathology 2012;61:170, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Pleomorphic adenoma (29%) (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:140)
- Porocarcinoma (0%) (J Cutan Pathol 2016;43:974)
- Poroma (0%) (Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:896, J Cutan Pathol 2016;43:974)
- Prostatic adenocarcinoma (0%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:333)
- Rhabdomyosarcoma (0%) (Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Salivary oncocytoma (0%) (Acta Cytol 2015;59:384, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222, Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:140)
- Schwannoma (0 - 1%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1401, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222, Int J Surg Pathol 2016;24:274)
- Sebaceoma (12.5%) (Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:896)
- Sebaceous adenoma (37.5%) (Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:896)
- Sebaceous carcinoma (31%) (Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:896)
- Secretory carcinoma (0 - 33%) (focal, weak) (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1483, Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:140)
- Serous cystadenoma (0%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2012;20:397)
- Small cell carcinoma (0%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Histopathology 2012;61:170)
- Small intestine neuroendocrine tumor (0%) (Cancer Control 2015;22:498, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:333, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Solitary fibrous tumor (0%) (Histopathology 2012;61:170, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Spiradenoma (10.5%) (Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:896)
- Synovial sarcomas (2.5 - 15%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1401, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Syringoma (0%) (Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:896)
- Testicular germ cell tumors (0%) (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:333, Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
- Trichoblastoma (0%) (Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:896)
- Trichoepithelioma (6%) (Am J Dermatopathol 2017;39:896)
- Urothelial carcinoma (0%) (Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:222)
Sample pathology report
- Stomach, biopsy:
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (see comment)
- Comment: Immunohistochemistry performed at X institution reveals the following immunoprofile (controls stained appropriately): positive - DOG1.
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1