Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics descriptionCite this page: Obeng R. Dicer. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsdicer.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Protein encoded by DICER1 gene on chromosome 14
- A ribonuclease that produces 21 - 23 nucleotide short interfering RNAs (siRNAs) and microRNAs (miRNAs) by cleaving long double stranded RNAs (dsRNAs) and pre-miRNAs
Essential features
- Mutations in gene can lead to an autosomal dominant familial syndrome known as dicer syndrome that results in a predilection for malignant and benign tumors with pleuropulmonary blastoma being the most common tumor (U.S. National Library of Medicine, Schultz, Stewart: DICER1-Related Disorders, 2014)
- Important in posttranscriptional gene silencing
- Involved in DNA repair (Int J Mol Sci 2012;13:16769)
Terminology
- Dicer 1, ribonuclease III, Dcr-1 homolog, helicase MOI, HERNA, helicase with RNA motif, Double stranded RNA specific endoribonuclease
Epidemiology
- The prevalence and penetrance of the mutations are not known
- Dicer syndrome is a rare disorder
Sites
- Ubiquitously expressed
Pathophysiology
- Dicer syndrome: autosomal dominant inheritance of mutations in dicer gene that increases susceptibility to tumors
- Pleuropulmonary blastoma (most common), ovarian sex cord stromal tumors (Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor, juvenile granulosa cell tumor, gynandroblastoma), thyroid gland neoplasia (multi nodular goiter, adenomas, thyroid carcinoma), cystic nephroma, ciliary body medulloepithelioma, botryoid-type embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma, nasal chondromesenchymal hamartoma, renal sarcoma, pituitary blastoma, pineoblastoma (Schultz, Stewart: DICER1-Related Disorders, 2014)
- Macular degeneration: decreased levels of dicer in retinal pigment epithelial cells leads to accumulation of Alu RNA (due to the inability to cleave Alu dsRNA) and subsequent degeneration of rental pigment epithelium (Nature 2011;471:308, Cell 2012;149:847)
- Decreased levels of dicer is associated with increased DNA damage (Int J Mol Sci 2012;13:16769)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Depends on the neoplastic process
Diagnosis
- The levels of dicer may be useful in the diagnosis of cancer
- Decreased expression identified in patients with tumors (Cancer Res 2010;70:2571)
Radiology description
- Radiologic features depends on the presenting disease
Prognostic factors
- Elevated levels of dicer associated with poor prognosis in prostatic and esophageal cancers (Am J Path 2006;169:1812, Clin Cancer Res 2006;12:7322)
- Decreased levels of dicer correlates with poor prognosis and decreased survival in lung and ovarian cancers (Cancer Res 2010;70:2571, N Engl J Med 2008;359:2641, Cancer Sci 2005;96:111)
Case reports
- Dicer syndrome (PLoS One 2015;10:e0119142)
Treatment
- Depends on the present disease
- Surgical resection with or without chemotherapy
- Patients with pleuropulmonary blastoma may also undergo radiation therapy
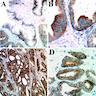
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Cytoplasmic staining
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Normal tissues
- Basal cells in benign prostatic epithelium (Am J Pathol 2006;169:1812)
Negative stains
- Luminal cells in benign prostatic epithelium (Am J Pathol 2006;169:1812)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Deletions, insertions, missense mutations, nonsense mutations, splice variants