Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Sample pathology report | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Terlević R, Vranić S. Cytokeratin 5/6 and CK5. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsck5and6.html. Accessed January 21st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Basic (type II) cytokeratins of molecular weight 58 kDa (CK5) and 56 kDa (CK6) (Cell 1982;31:11)
- Common antibodies are directed against both cytokeratin 5 and 6
- Major partner of CK5 is CK14, while CK6 pairs with CK16/17 (Exp Cell Res 2007;313:2244, Eur J Cell Biol 2004;83:735)
- CK5 is also detected by antibodies against high molecular weight cytokeratins (such as 34 beta E12, also known as K903) and pan-CK markers (such as CK AE1 / AE3)
Essential features
- Stains basal cells of prostate and basal / myoepithelial cells of breast (can be used to rule out invasion)
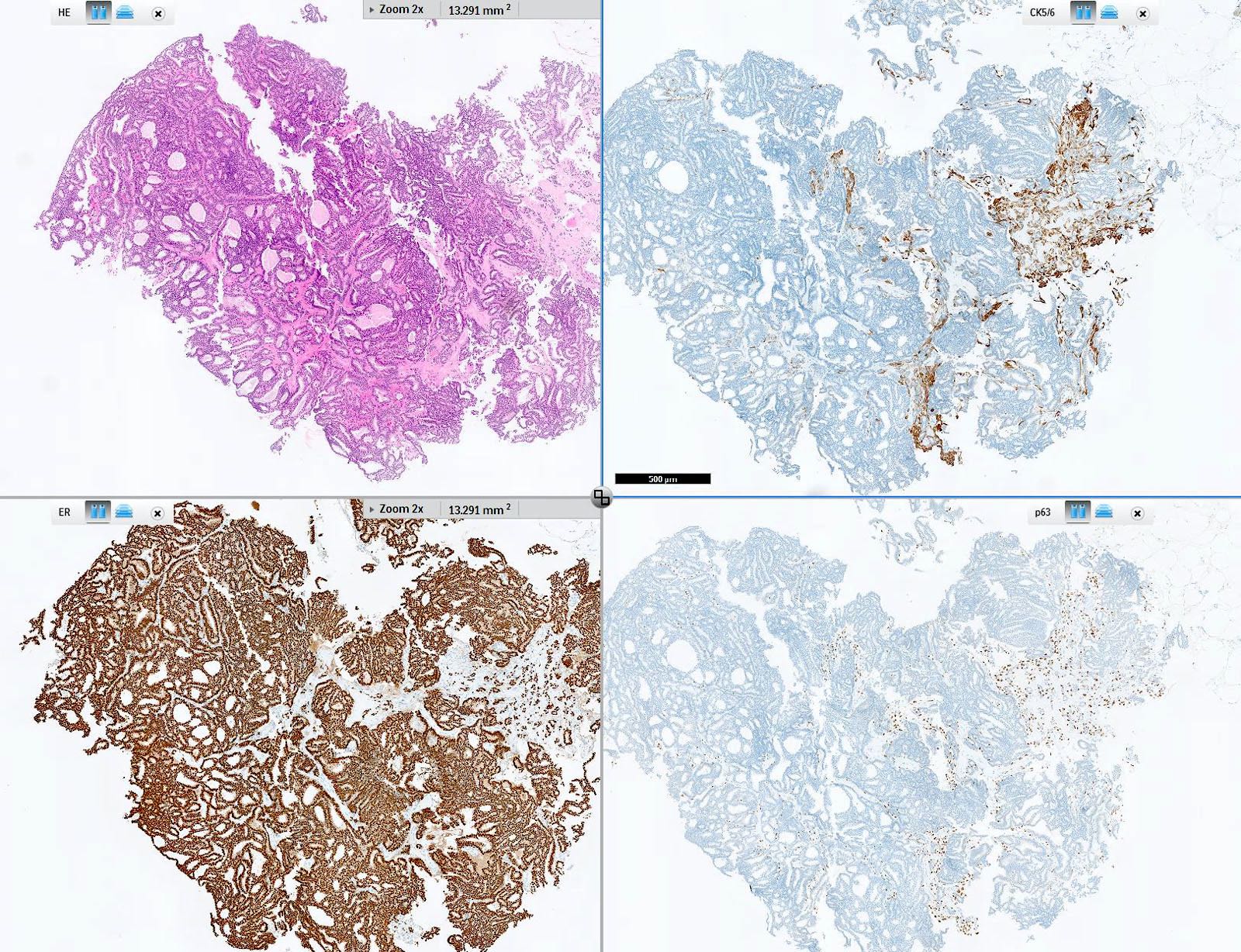
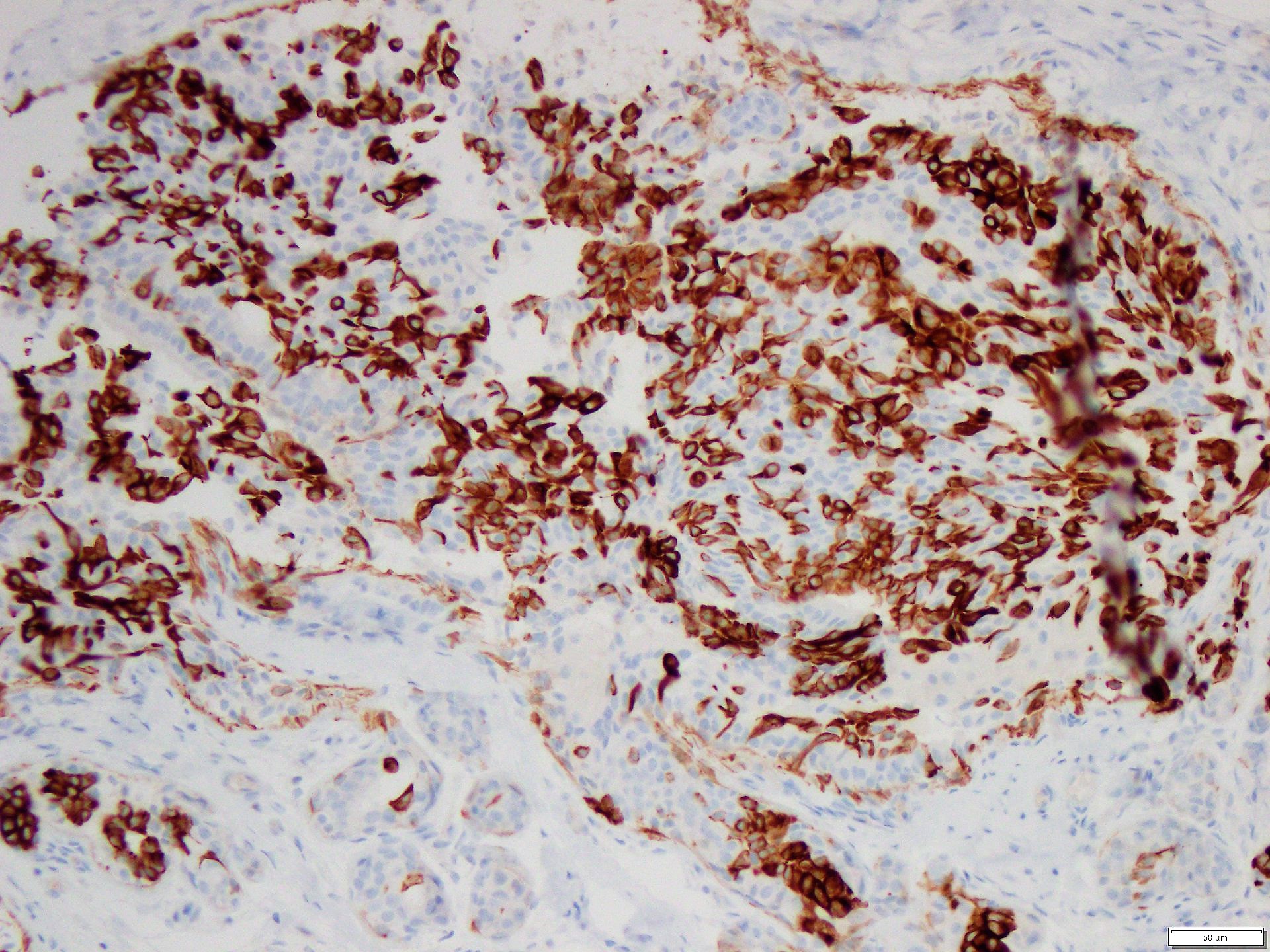
- Useful for detecting benign breast proliferations (mosaic-like pattern) versus ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) (negative or rarely diffusely positive) (Pathology 2009;41:68)
- Together with p63, used to detect squamous cell origin in poorly differentiated carcinomas (Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:823)
Terminology
- K5, K6, keratin 5, keratin 6, basal cytokeratins, intermediate molecular weight cytokeratins
Pathophysiology
- Cytoskeletal constituents of the intermediate filament family of proteins, which provide the cell with a structural framework stretching from around the nucleus to desmosomes and hemidesmosomes (Science 1998;279:514)
- In stratified epithelia, CK5 preferentially stains basal layer, while CK6 stains suprabasal layer (Virchows Arch 2022;480:433)
- CK5 and its partner CK14 constitute up to 25% of total cell protein in basal cells of epidermis; expression in skin correlates with mitotic activity (Science 1998;279:514, J Biol Chem 1995;270:21362, Development 1994;120:2369)
- CK6 is expressed in wound healing and hyperproliferative cancer cells (J Biol Chem 1995;270:21362)
- CK5/6 expression may be useful in subclassifying epidermolysis bullosa cases (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2018;26:586)
- CK5 is a marker of breast luminal progenitor and stem cells (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2011;128:45)
- CK5 positive cells may represent a chemoresistant population in breast and ovarian cancer (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2011;128:45, Int J Gynecol Cancer 2015;25:1565)
Clinical features
- CK5 and CK14 mutations may cause epidermolysis bullosa simplex and Dowling-Degos disease (Hum Mutat 2006;27:719, Am J Hum Genet 2006;78:510)
- Important in tooth enamel formation (J Biol Chem 2003;278:20293)
- CK6 mutations involved in pachyonychia congenita (Nat Genet 1995;10:363)
Interpretation
- Diffuse cytoplasmic staining with perinuclear enhancement
Uses by pathologists
- Identify breast basal / myoepithelial cells and prostate basal cells
- Distinguish breast usual ductal hyperplasia (UDH) and papillary lesions (mosaic-like pattern) from DCIS (usually negative, rarely diffusely positive) (Pathology 2009;41:68)
- Distinguish epithelioid mesothelioma (CK5/6+ in 83%) from lung adenocarcinoma (CK5/6- in 85%), including in pleural effusions (CK5/6+ in 90% mesothelioma, 0% adenocarcinoma) (Histopathology 2006;48:223, Diagn Cytopathol 2006;34:801)
- Distinguish cutaneous spindle squamous cell carcinoma (CK5/6+ in 100%) from superficial epithelioid sarcoma (rare focal positivity) (J Cutan Pathol 2003;30:114)
- Together with p63+, identify squamous origin in poorly differentiated metastatic carcinomas (e.g., cervical) (Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:823)
- CK5 preferred to K903 in antibody cocktails for the detection of prostate carcinoma (Diagn Pathol 2012;7:81)
- As part of panel to discriminate between undifferentiated sinonasal carcinoma (CK5/6-) and other poorly differentiated head and neck tumors (poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma, olfactory neuroblastoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma) (Ann Diagn Pathol 2014;18:261)
- CK5 used as part of panel to distinguish cutaneous metastasis of breast cancer from sweat gland carcinoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2011;135:975)
- CK5/6 full thickness positivity specific for bladder condyloma acuminatum versus basal / patchy staining in papillary noninvasive urothelial carcinoma (Int J Surg Pathol 2022;30:260)
Prognostic factors
- CK5/6+ / p63+ breast intraductal papillomas show lower risk of subsequent invasive carcinoma (Pathol Int 2015;65:81)
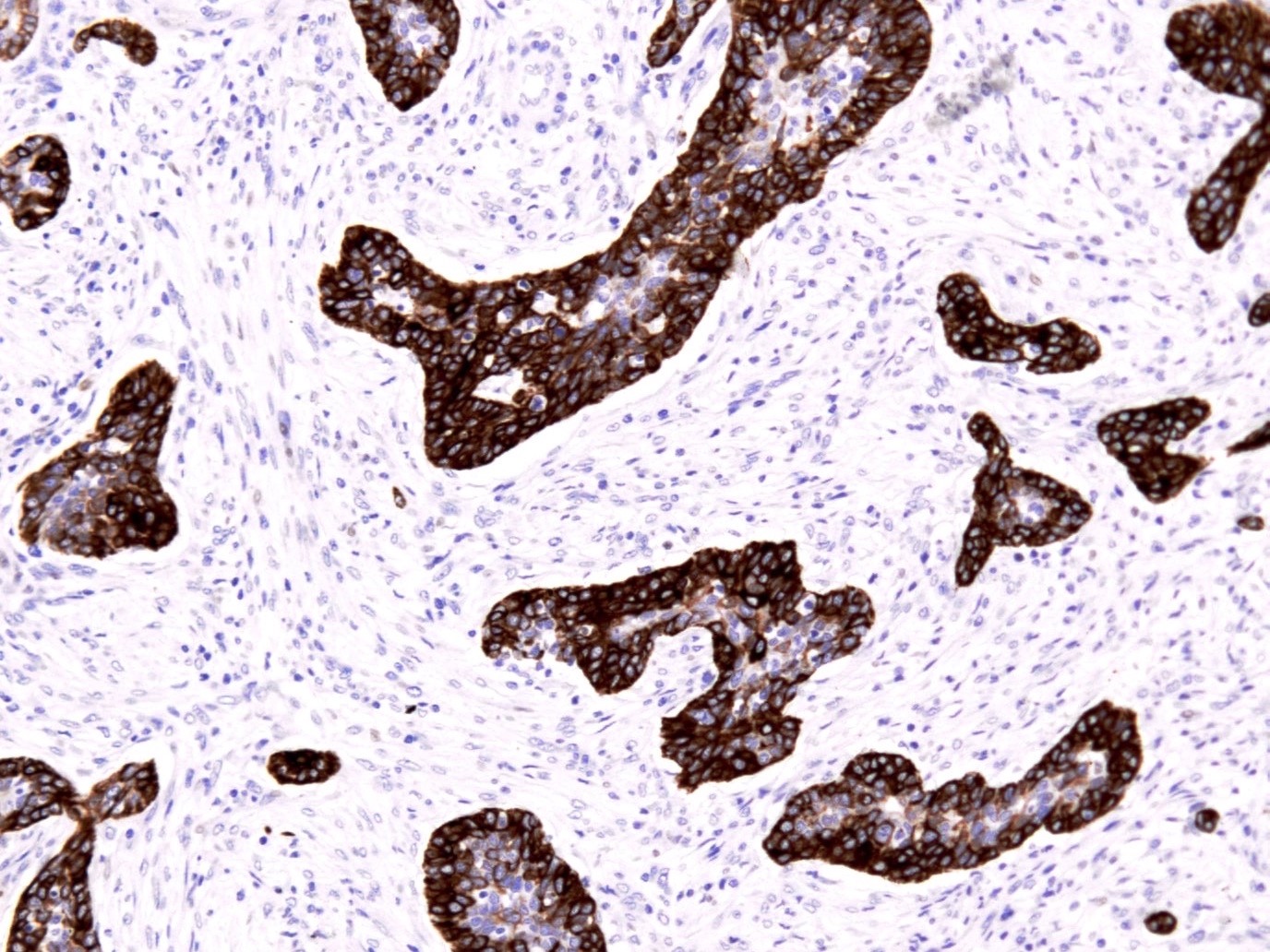
- Diffuse positivity in DCIS defines basal-like subtype with poorer prognosis (Hum Pathol 2007;38:197)
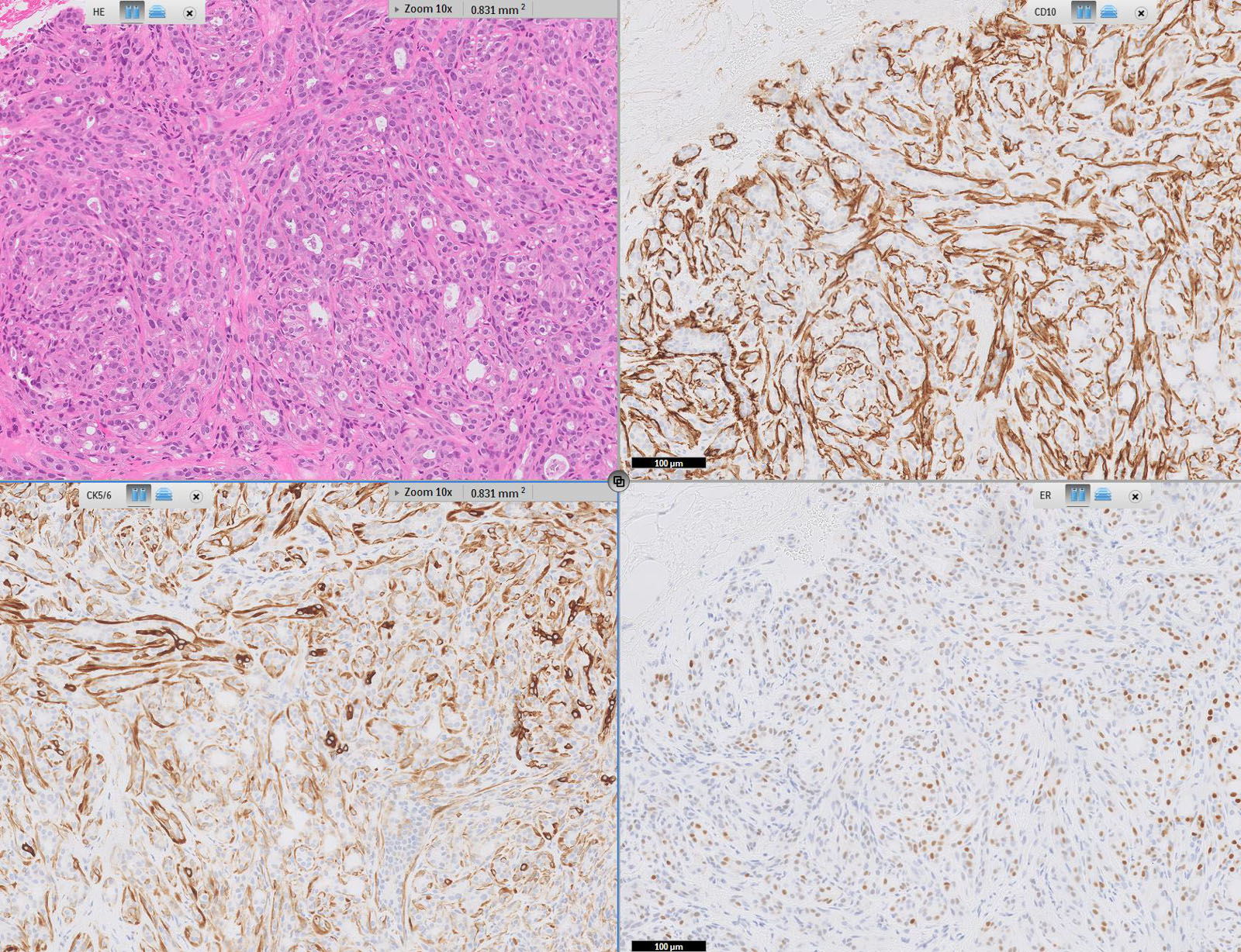
- CK5/6 positivity helps define a basal-like subtype of triple negative breast carcinoma (TNBC) with poorer prognosis; associated with premenopausal African American women, BRCA1 mutations and higher propensity for brain metastases (Transl Cancer Res 2021;10:1193, Clin Cancer Res 2006;12:1533, JAMA 2006;295:2492, Mod Pathol 2005;18:1321, J Natl Cancer Inst 2003;95:1482, Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:1097)
- CK5/6+ muscle invasive urothelial carcinoma associated with poor survival (Int J Mol Sci 2021;22:628)
- CK5+ together with CD44+ defines invasive and noninvasive basal-like urothelial carcinoma subtype associated with more aggressive behavior (Pathol Res Pract 2015;211:610, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2016;24:575, Sci Rep 2021;11:21186)
- CK5/6-, CD44-, CK20+ nonmuscle invasive papillary upper tract urothelial carcinoma associated with worse outcome (Histopathology 2019;74:483)
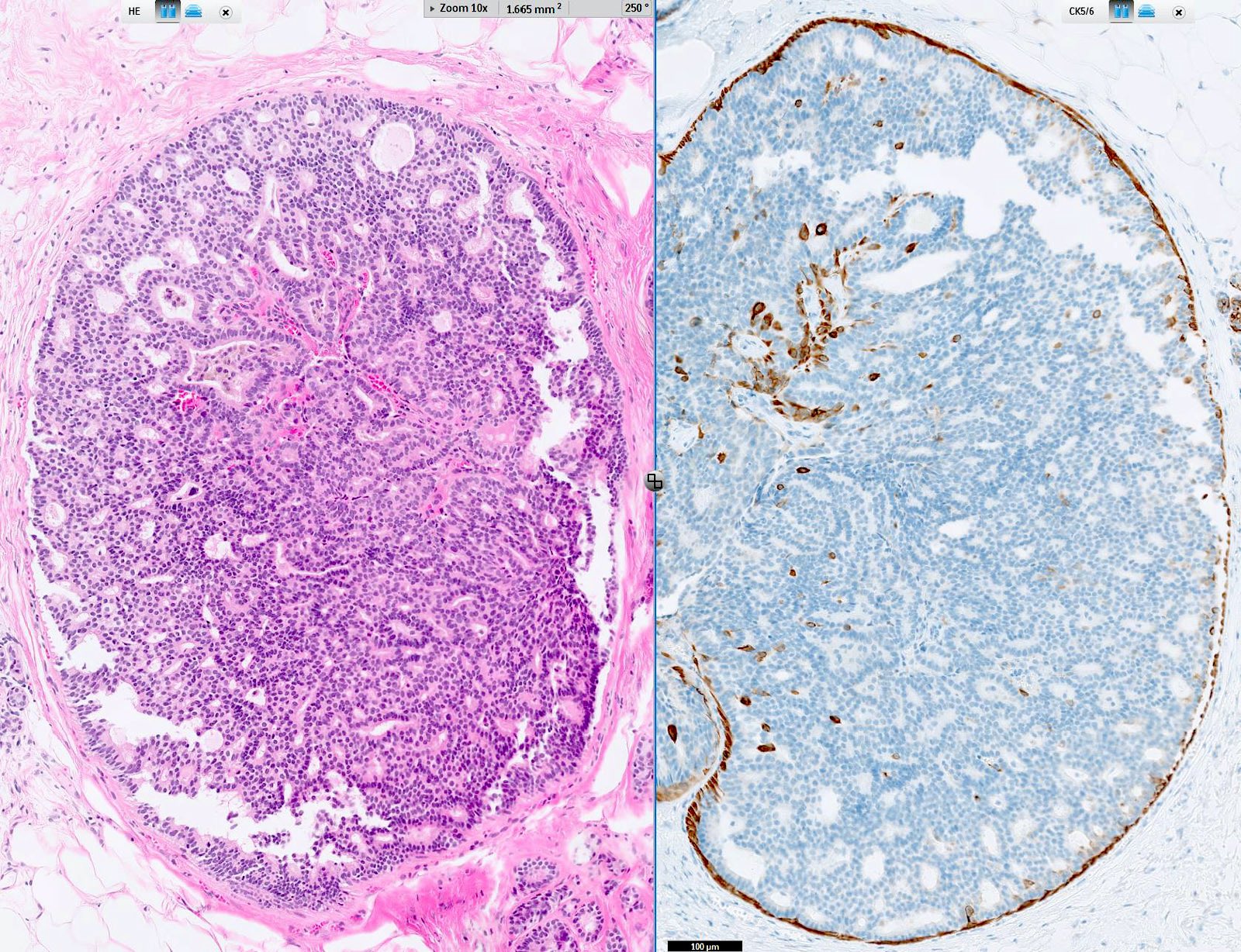
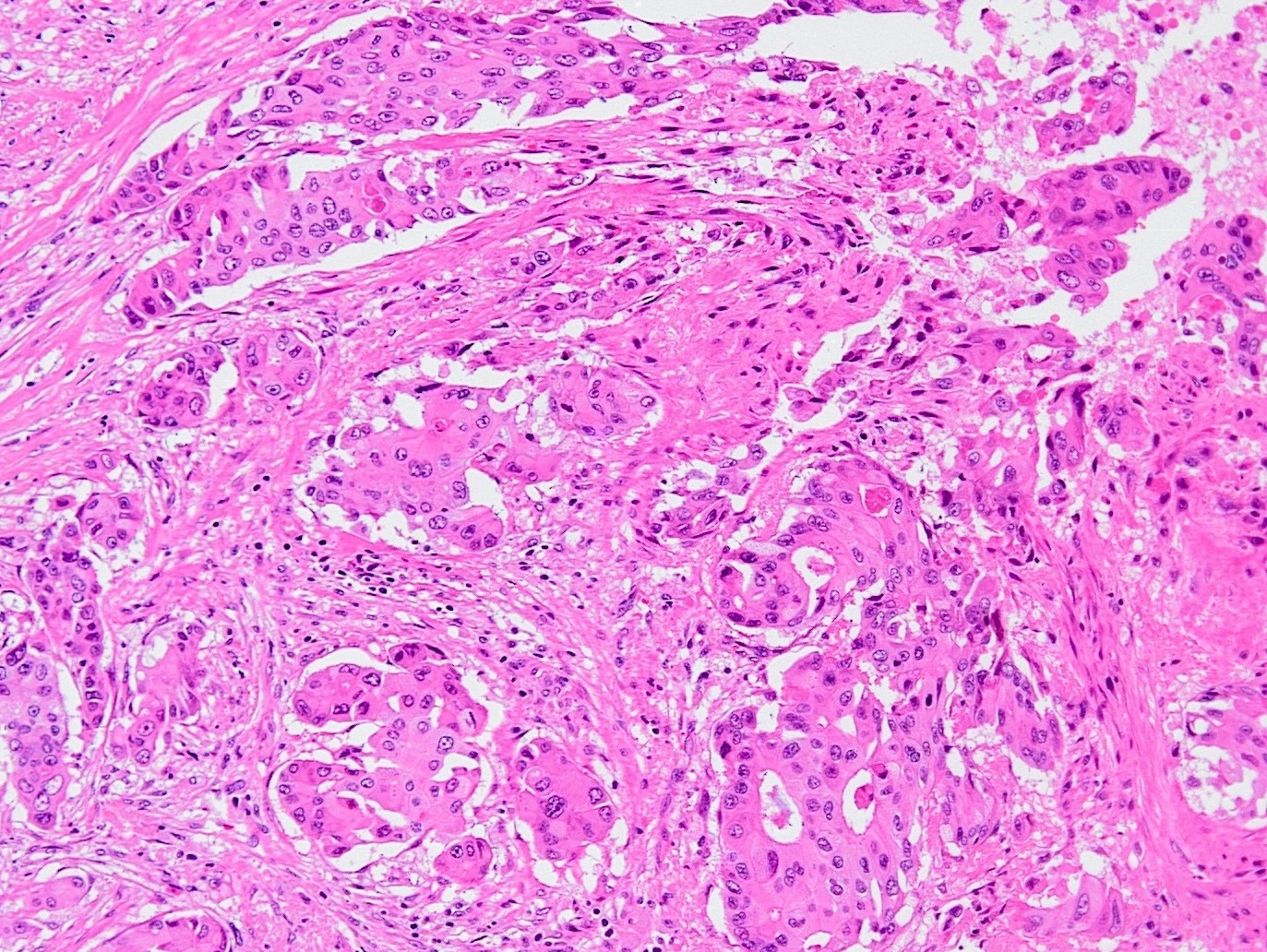
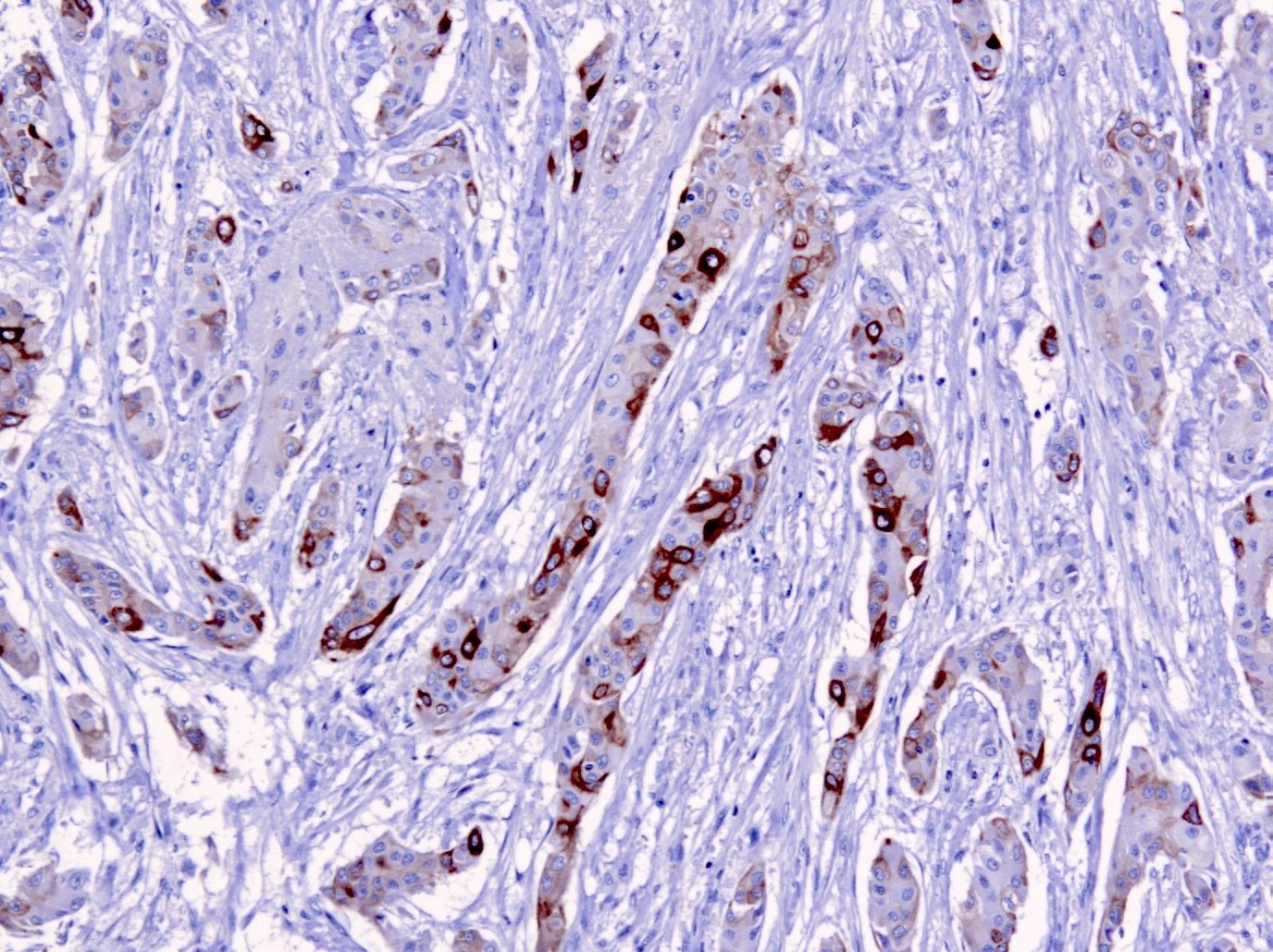
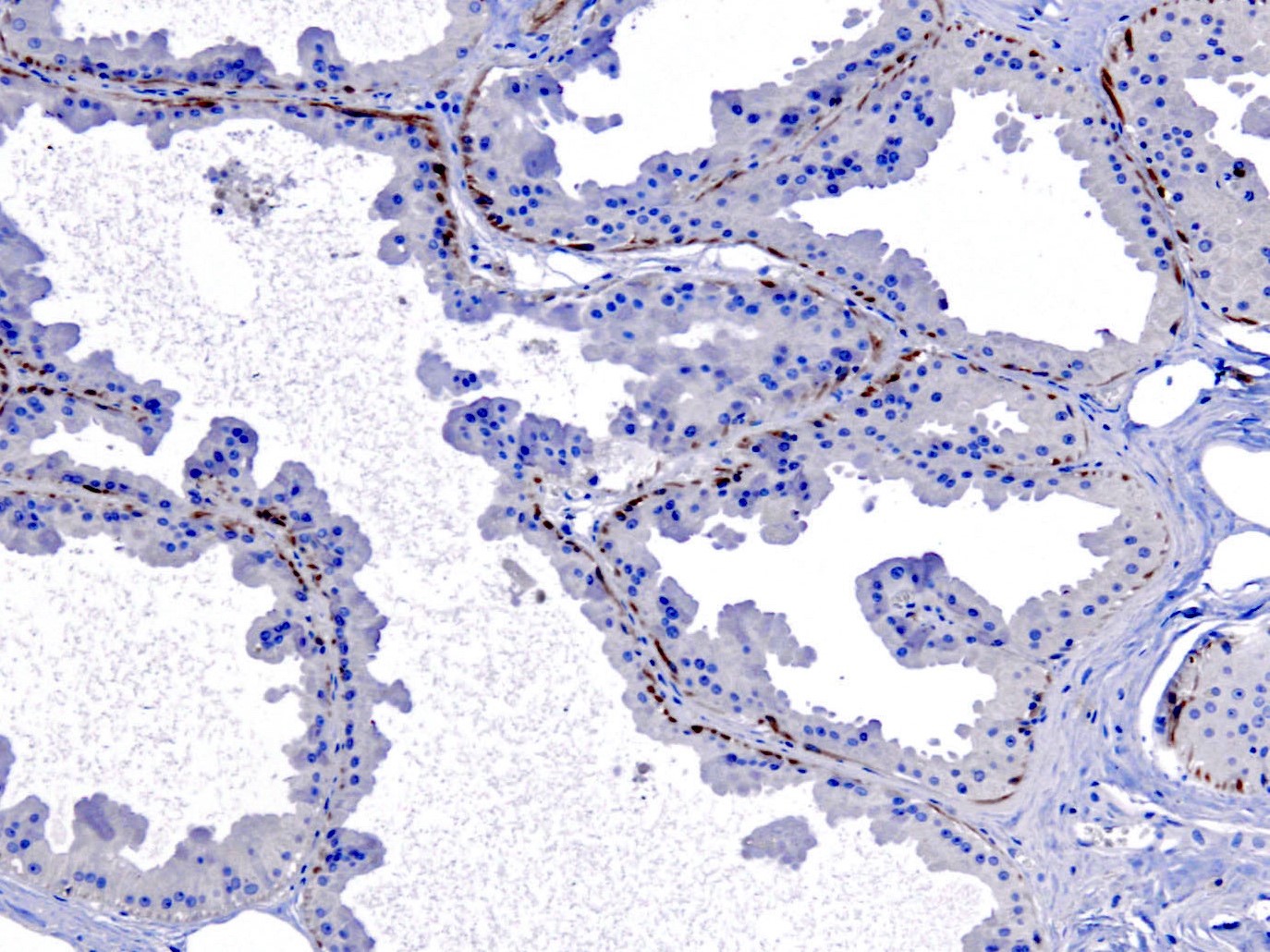
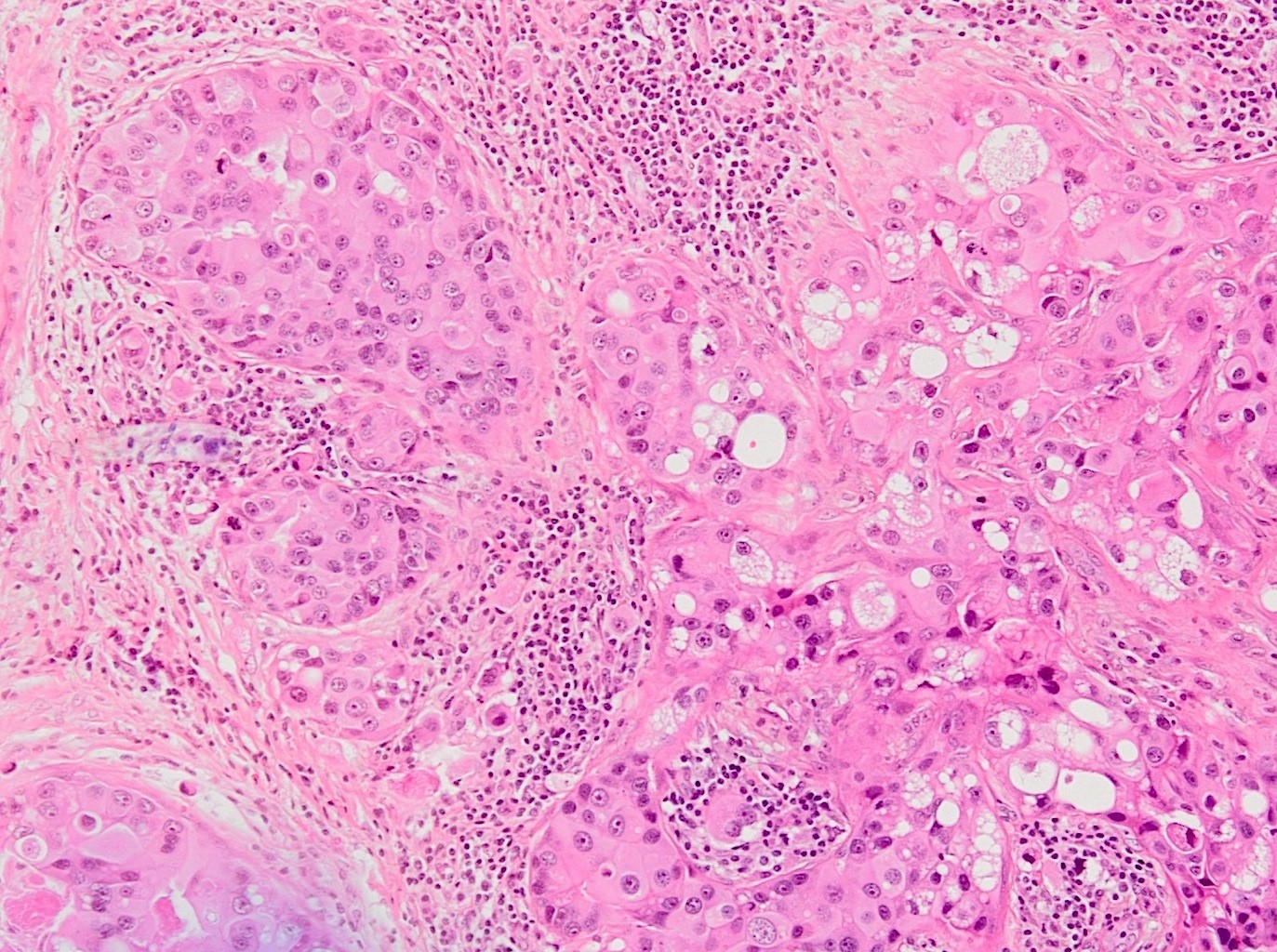
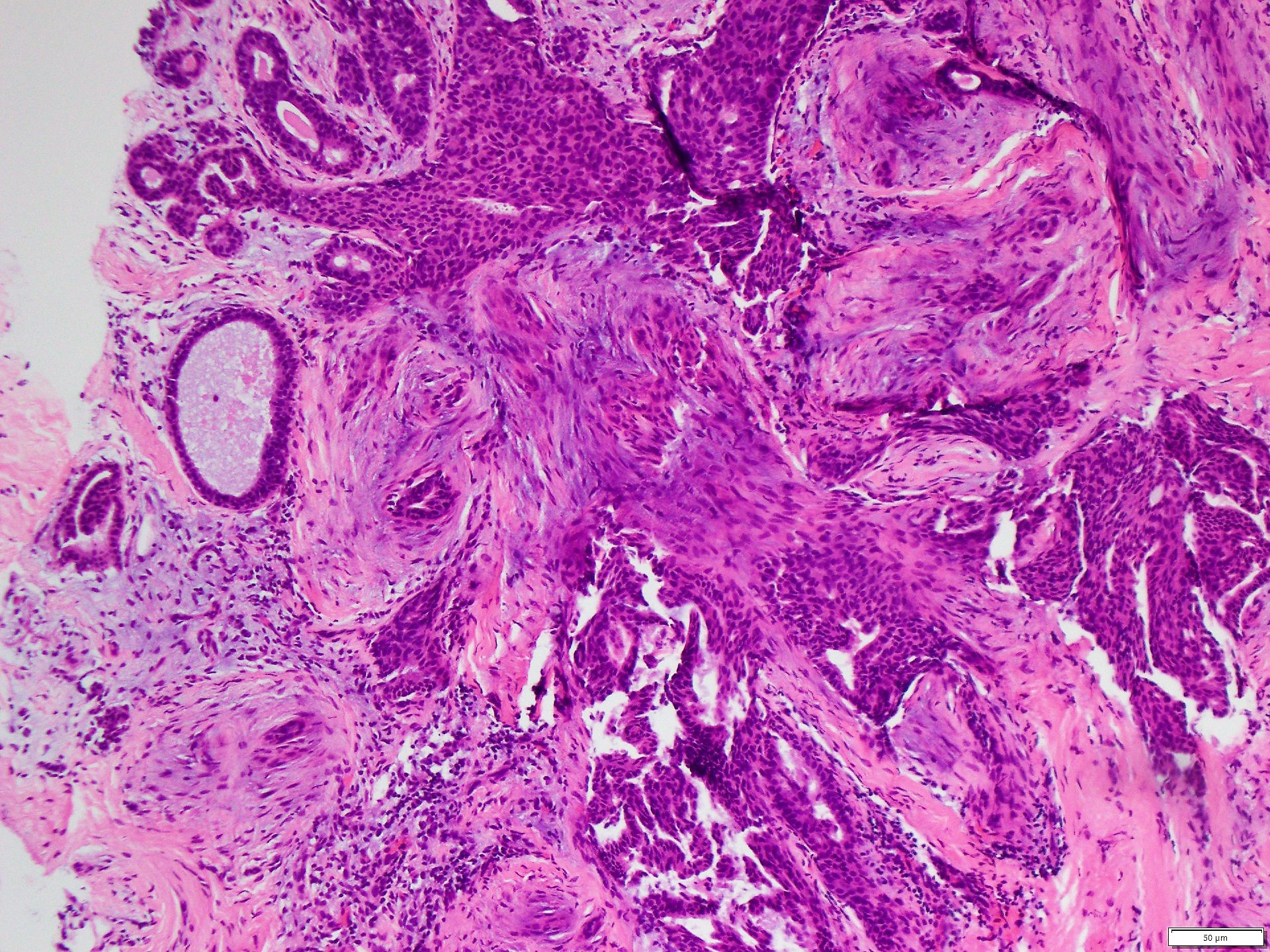
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Jijgee Munkhdelger, M.D., Ph.D., Andrey Bychkov, M.D., Ph.D. and Semir Vranić, M.D., Ph.D.
Positive staining - normal
- CK5 is the major keratin of basal cells in the epidermis, while CK6 preferentially stains the suprabasal layer (Exp Cell Res 2007;313:2244, Virchows Arch 2022;480:433)
- Also expressed in basal cells of respiratory epithelium, male genital tract (efferent ducts, epididymis, deferent duct and seminal vesicle), breast basal / myoepithelial cells, mesothelium, prostate basal cells, cornea, endocervical squamous metaplasia, spermatogenic cells, basal cells of urinary tract transitional epithelium (J Pathol 2001;195:563, Ann N Y Acad Sci 1985;455:282, Mol Reprod Dev 2002;61:1, J Histochem Cytochem 1985;33:415, Mol Cell Proteomics 2002;1:269)
- CK5 stains thyroid solid cell nests (Endocr Pathol 2016;27:83)
- CK5 and CK6 are both expressed in palmar and plantar epidermis; basal cells of eccrine and apocrine glands; hair follicle; myoepithelial cells of salivary gland acini; basal cells of excretory ducts; mucosal stratified epithelia of the oral cavity, esophagus, female genital tract and glans penis; thymus epithelial cells (J Biol Chem 1995;270:21362, Ann N Y Acad Sci 1985;455:282)
Positive staining - disease
- Tumors derived from stratified epithelia (skin and mucosa) are positive (Mod Pathol 2002;15:6)
- Some adenocarcinomas may show focal staining (pancreas, breast, lung, uterine endometrioid, cholangiocarcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma, lung) (Mod Pathol 2002;15:6, Hum Pathol 2019;84:221)
- Poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma identified by both CK5/6+ and p63+ with 77% sensitivity and 96% specificity (Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:823)
- Urothelial carcinoma (63%) (Mod Pathol 2002;15:6)
- Breast usual ductal hyperplasia and papillary lesions (mosaic-like pattern) (Pathology 2009;41:68)
- Basal-like breast DCIS (Hum Pathol 2007;38:197)
- In breast and salivary gland adenoid cystic carcinoma, CK5/6 stains cells lining true lumina (Virchows Arch 2016;469:213, Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2011;4:336)
- Metaplastic breast cancer (87%) (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2021;29:265)
- High grade serous ovarian carcinoma (focal or diffuse pattern in 69%) (Hum Pathol 2017;67:30)
- Epithelioid mesothelioma (CK5/6+ in 83%) (Histopathology 2006;48:223)
- Stains both glandular and myoepithelial components of salivary gland tumors (Mod Pathol 2002;15:6)
- Thymoma (100%, 8/8 cases) (Mod Pathol 2002;15:6)
- Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (90%) and poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma of the nasal tract (100%) (Ann Diagn Pathol 2014;18:261)
- Cutaneous adnexal neoplasms (97%) (Am J Dermatopathol 2004;26:447)
- Primary cutaneous SMARCB1 deficient carcinoma (100%) (J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:1051)
- Amyloid deposits in cutaneous macular amyloidosis (50%) (Cureus 2020;12:e7606)
- Adenocarcinoma of the rete testis (80%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:670)
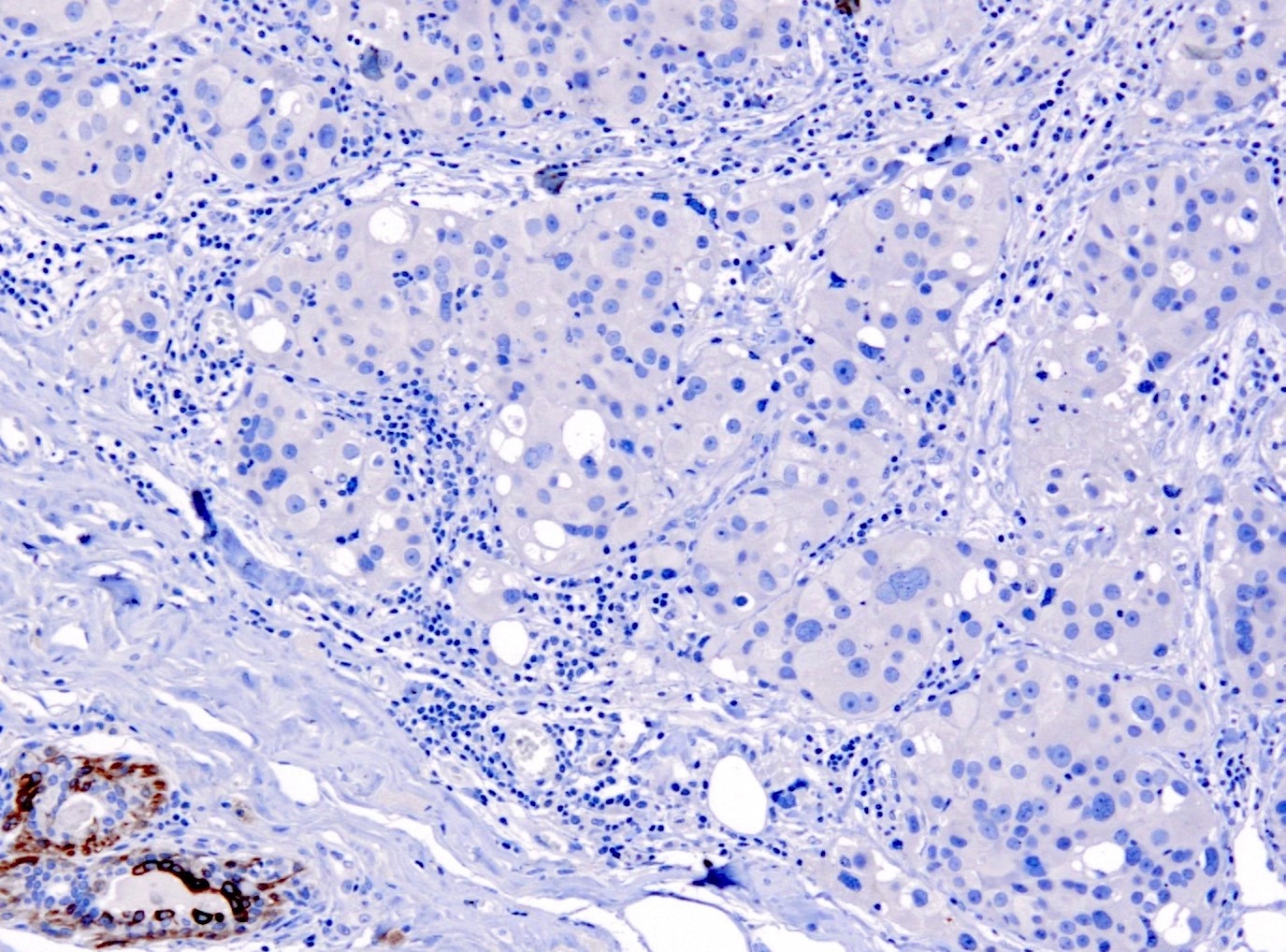
Negative staining
- Adenocarcinoma (colon, stomach), renal cell carcinoma, germ cell tumors, thyroid carcinomas, neuroendocrine carcinoma (lung, skin and gastrointestinal), epithelioid sarcoma, synovial sarcoma (Mod Pathol 2002;15:6)
- Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma (Ann Diagn Pathol 2014;18:261)
- SMARCA4 deficient sinonasal carcinoma (0%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:703)
- Well differentiated neuroendocrine tumors of skin (0%) (J Cutan Pathol 2017;44:557)
Sample pathology report
- Breast, core biopsy:
- Benign breast tissue with usual ductal hyperplasia (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show mildly distended breast gland lumina filled with a mixed population of cells showing a mosaic pattern expression of CK5/6, consistent with usual ductal hyperplasia.
Board review style question #1
- Which of the following is an important use of the CK5/6 immunostain?
- Confirm a diagnosis of epithelioid sarcoma
- Confirm a diagnosis of well differentiated neuroendocrine tumors of skin
- Identify a basal-like subtype of triple negative breast carcinoma (TNBC) with poorer prognosis
- Identify sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma
Board review style answer #1
C. Identify a basal-like subtype of triple negative breast carcinoma with poorer prognosis (shown in the image above). Answers A, B and D are incorrect because CK5/6 is typically negative in epithelioid sarcoma, well differentiated neuroendocrine tumors of skin and sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Cytokeratin 5/6 and CK5
Comment Here
Reference: Cytokeratin 5/6 and CK5
Board review style question #2
- What is the typical immunohistochemical staining pattern in usual ductal hyperplasia?
- Diffuse CK5 negativity
- Diffuse CK5 positivity
- Diffuse ER negativity
- Diffuse ER positivity
- Mosaic pattern CK5
Board review style answer #2
E. Mosaic pattern CK5. Mosaic pattern of CK5 refers to partial staining of the intraductal myoepithelial cell population. Answers A, B, C and D are incorrect because diffusely negative or positive CK5 or ER would indicate a clonal (neoplastic epithelial) cell population. Rarely, a neoplastic cell population can be CK5 positive, therefore use of a panel (CK5, p63, ER) is usually recommended.
Comment Here
Reference: Cytokeratin 5/6 and CK5
Comment Here
Reference: Cytokeratin 5/6 and CK5