Table of Contents
Definition / general | Uses by pathologists | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining - diseaseCite this page: Pernick N. Arginase1. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsarginase1.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Binuclear manganese metalloenzyme that catalyzes hydrolysis of arginine to ornithine and urea (Wikipedia: Arginase [Accessed 3 August 2023)
- Also called liver arginase
- Critical regulator of nitric oxide synthesis and vascular function
- Defects cause vascular disease, pulmonary disease, infectious disease, immune cell function or cancer
- Argininemia: rare autosomal recessive disorder of urea cycle due to mutations in arginase gene; arginine is elevated in blood and cerebrospinal fluid, causes periodic hyperammonemia, associated with developmental delay, seizures, intellectual disability, hypotonia, ataxia and progressive spastic quadriplegia (OMIM: 207800 [Accessed 3 August 2023])
Uses by pathologists
- Sensitive and specific marker of benign and malignant hepatocytes (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:1147)
- Helps distinguish hepatocellular carcinoma from metastatic carcinoma (Diagn Pathol 2012;7:149, Am J Clin Pathol 2012;138:203)
- But also stains some intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas (Oncol Lett 2011;2:1046)
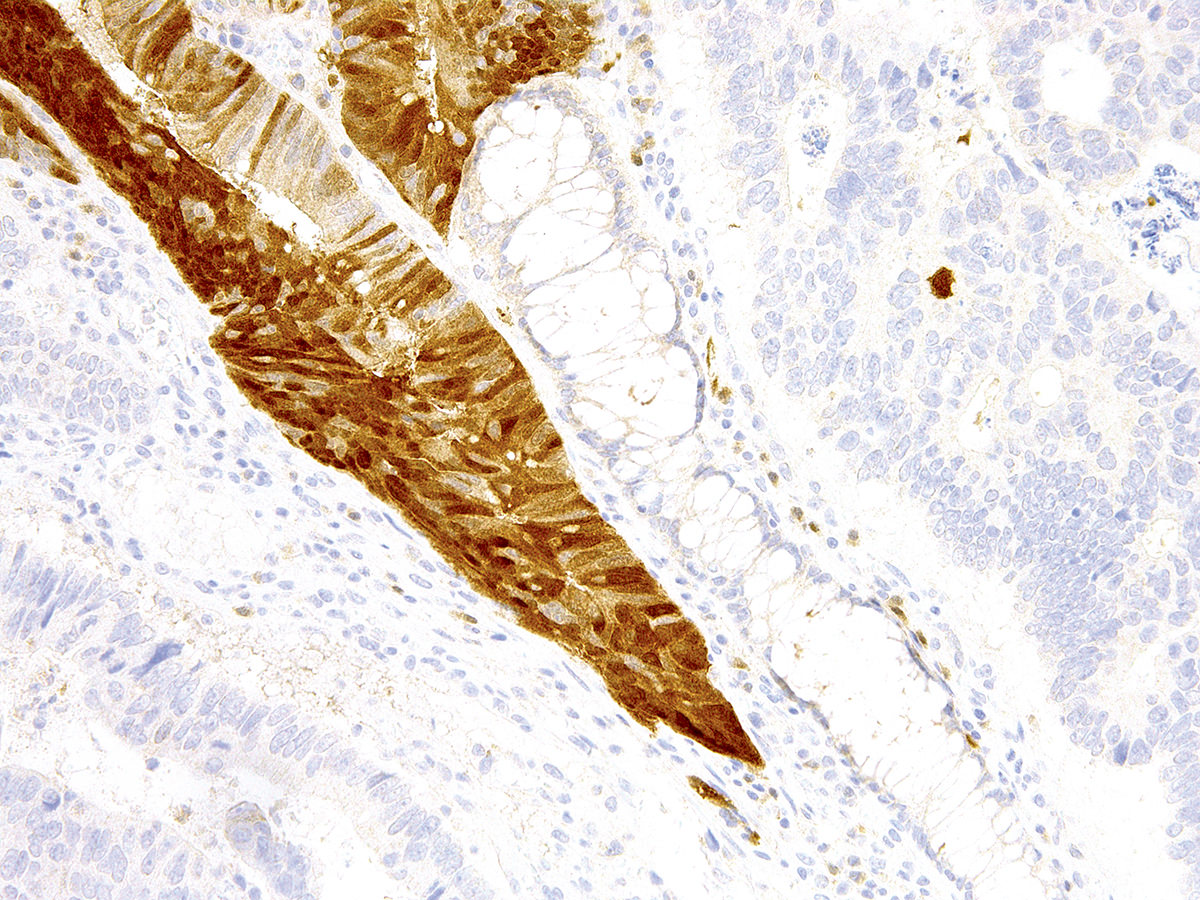
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by GenomeMe and Cell Marque Corporation
Images hosted on other servers:
Positive staining - normal
- Hepatocytes
Positive staining - disease
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Granuloma associated macrophages; lung: type II pneumocytes (FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 2012;66:265)
- Pancreatic adenocarcinoma (13%) (Cancer Cytopathol 2012;120:230)
Negative staining - disease
- Most cholangiocarcinomas, although intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas may be positive (Hepat Mon 2015;15:e30336, Oncol Lett 2011;2:1046)