Table of Contents
Definition / general | Uses by pathologists | Clinical features | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Additional referencesCite this page: Pernick N. Alpha-synuclein. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsalphasynuclein.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Member of the synuclein family of soluble proteins (alpha-synuclein, beta-synuclein and gamma-synuclein) that are commonly present in CNS of vertebrates
- Expressed in the neocortex, hippocampus, substantia niagra, thalamus and cerebellum
- Main location is within the presynaptic terminals of neurons in both membrane-bound and cytosolic free forms
- Can be seen in neuroglial cells and melanocytic cells; highly expressed in the neuronal mitochondria of the olfactory bulb, hippocampus, striatum and thalamus
- Three isoforms have been isolated by alternative splicing
- Most research is the full length isoform with 140 amino acids
- Others are alpha-synuclein-112 and alpha-synuclein-126 (Wikipedia)
Uses by pathologists
- Diagnosis of (a) Parkinson disease (PD) / brainstem predominant type of Lewy body disease, and (b) dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), the two most frequent synucleinopathies.
- These neurodegenerative multisystem disorders have widespread occurrence of α-synuclein containing deposits in the central, peripheral, and autonomic systems. For both, staging/classification systems are based on semiquantitative assessment of the distribution and progression pattern of α-synuclein pathology, which are considered to be linked to clinical dysfunction (Biochimica et Biophysica Acta;2009:1792;730, Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7:1714, Mov Disord 2016;31:193
Clinical features
- Forms insoluble aggregates in the group of pathological disorders known as synucleopathies, characterized by:
- Formation of neuronal Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites in idiopathic Parkinson disease and dementia with Lewy bodies
- Oligodendroglial cytoplasmic inclusions in multiple system atrophy
- Large axonal spheroids in several rarer neuroaxonal dystrophies
- Both the sporadic and the familial form of Alzheimer disease also demonstrate alpha-synuclein protein
- In recent years, several studies have shown that alpha-synuclein aggregation can also be detected outside the central nervous system, particularly in the enteric nervous system of the gastrointestinal tract of PD patients using immunohistochemistry
- This has the potential to enable an early diagnosis of the disease as well as enhance the neuroprotective effects of the available therapeutic modalities
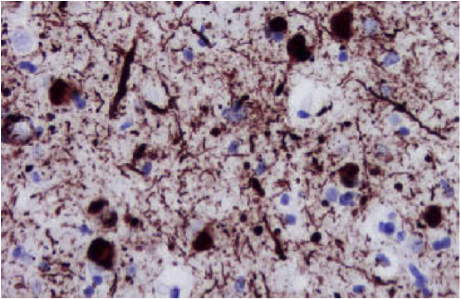
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Brain tissue: neocortex, hippocampus, substantia niagra, thalamus and cerebellum (within the presynaptic terminals of neurons in both membrane bound and cytosolic free forms)
- Olfactory bulb, hippocampus, striatum and thalamus (highly expressed in mitochondria)
- Also neuroglial cells, melanocytic cells