Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Cai C. Alkaline phosphatase. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsalkphos.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- An enzyme histochemical stain that relies on endogenous alkaline phosphatase activity to hydrolyze exogenous alpha naphthyl acid phosphate substrate to form naphthol, which in turn reacts with fast blue RR salt to form a black reaction product (Zhou: A Case-Based Guide to Neuromuscular Pathology, 1st Edition, 2020)
- Alkaline phosphatase reaction generates air bubbles if the section is cover slipped prematurely; to minimize this, it is advisable to wait at least 45 minutes before placing the coverslip over the stained section
Essential features
- In skeletal muscle, alkaline phosphatase is normally only present in the endothelium of arterioles but not in capillaries, myofibers or connective tissue (Nature 1962;195:611, J Histochem Cytochem 1970;18:55, Arch Histol Cytol 1998;61:215)
- The main use in a skeletal muscle biopsy is to highlight regenerating myofibers and connective tissue injury (Zhou: A Case-Based Guide to Neuromuscular Pathology, 1st Edition, 2020)
- Immune myopathies with perimysial pathology (IMPP), highlighted by alkaline phosphatase, are more commonly associated with antisynthetase syndrome associated autoantibodies, particularly Jo1 autoantibody; these patients are more likely to have interstitial lung disease, arthritis, Raynaud phenomenon, mechanic hands and excellent response to immune modulation therapy (Brain 2015;138:2485, Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm 2018;5:e434)
- Elsewhere in the body, alkaline phosphatase enzyme activity is also widely present in bone, cartilage, biliary tract, kidney, intestine and a variety of human tumors (Burstone: Enzyme Histochemistry and Its Application in the Study of Neoplasms, 1st Edition, 1962)
Terminology
- Other names: Gomori alkaline phosphatase stain, nonspecific alkaline phosphatases
Interpretation
- Assess for black reaction product
Uses by pathologists
- In muscle biopsies:
- Identify regenerating myofibers of all causes (not limited to inflammatory myopathies) (J Histochem Cytochem 1970;18:55, Dubowitz: Muscle Biopsy - A Practical Approach, 4th Edition, 2013, Zhou: A Case-Based Guide to Neuromuscular Pathology, 1st Edition, 2020)
- Identify connective tissue injury in immune myopathies with perimysial pathology (IMPP) (Brain 2015;138:2485, Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm 2018;5:e434)
- Increased endomysial capillary alkaline phosphatase reactivity is seen in a subset of myositis with poor response to steroids (Am J Pathol 1980;101:159)
Prognostic factors
- Immune myopathies with perimysial pathology (IMPP) are associated with excellent response to immune modulation therapy (Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm 2018;5:e434)
- Inflammatory myopathies with high endomysial capillary alkaline phosphatase reactivity responded poorly to steroids (Am J Pathol 1980;101:159)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Staining pattern varies depending on structure highlighted:
- Regenerating fibers: sarcoplasmic (J Histochem Cytochem 1970;18:55)
- Arterioles and capillaries: endothelium cytoplasmic (Nature 1962;195:611)
- Perimysial connective tissue: connective tissue / collagen (Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm 2018;5:e434)
- Denervated myofibers: sarcoplasmic (J Histochem Cytochem 1970;18:55)
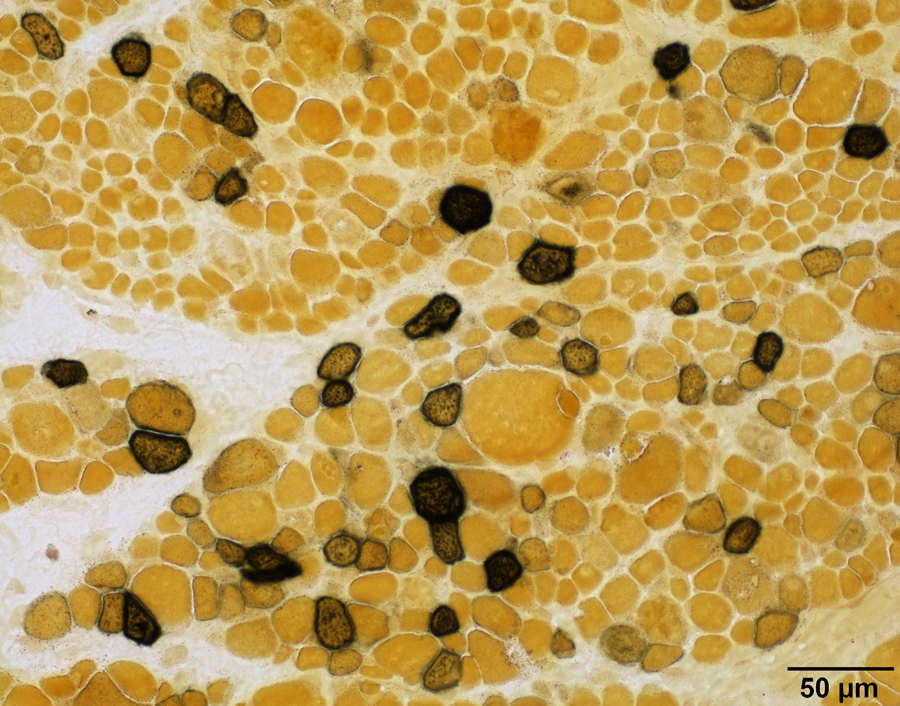
Microscopic (histologic) images
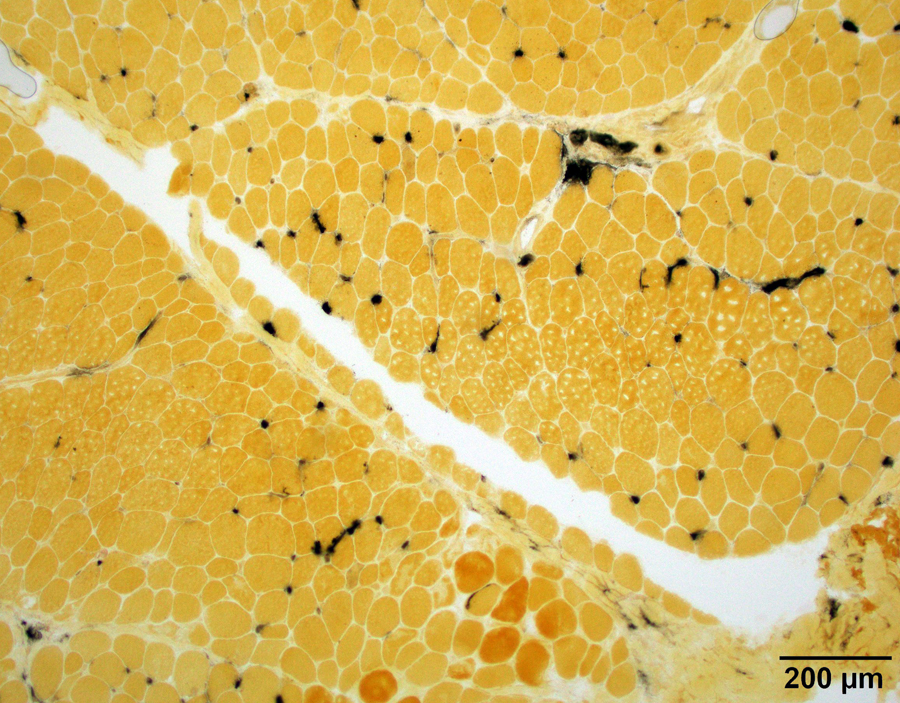
Positive staining - normal
- Endothelium of arterioles of skeletal muscle (Nature 1962;195:611, J Histochem Cytochem 1970;18:55, Arch Histol Cytol 1998;61:215)
Positive staining - disease
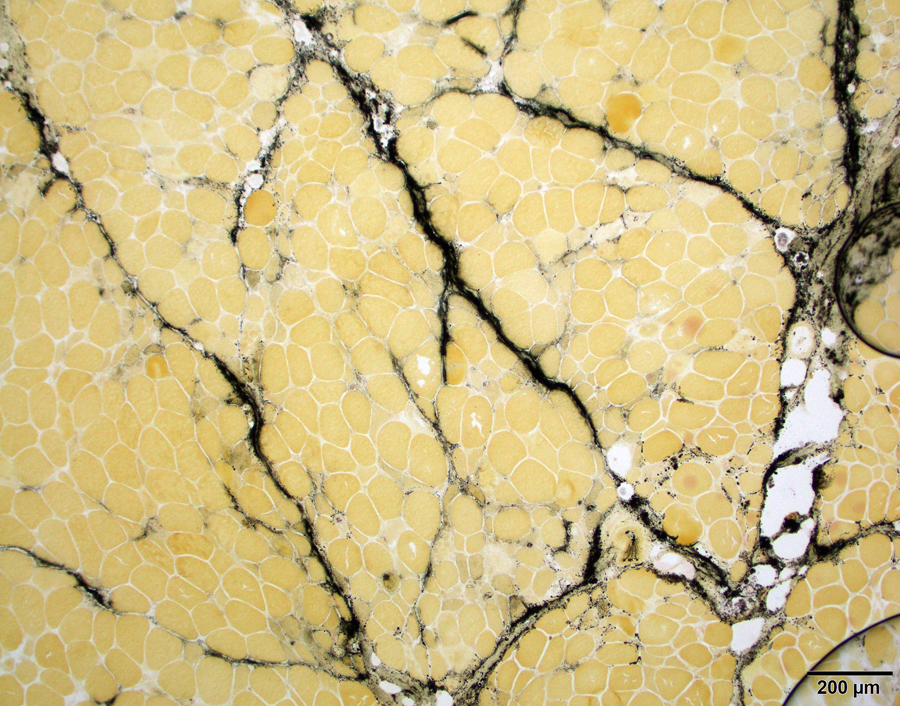
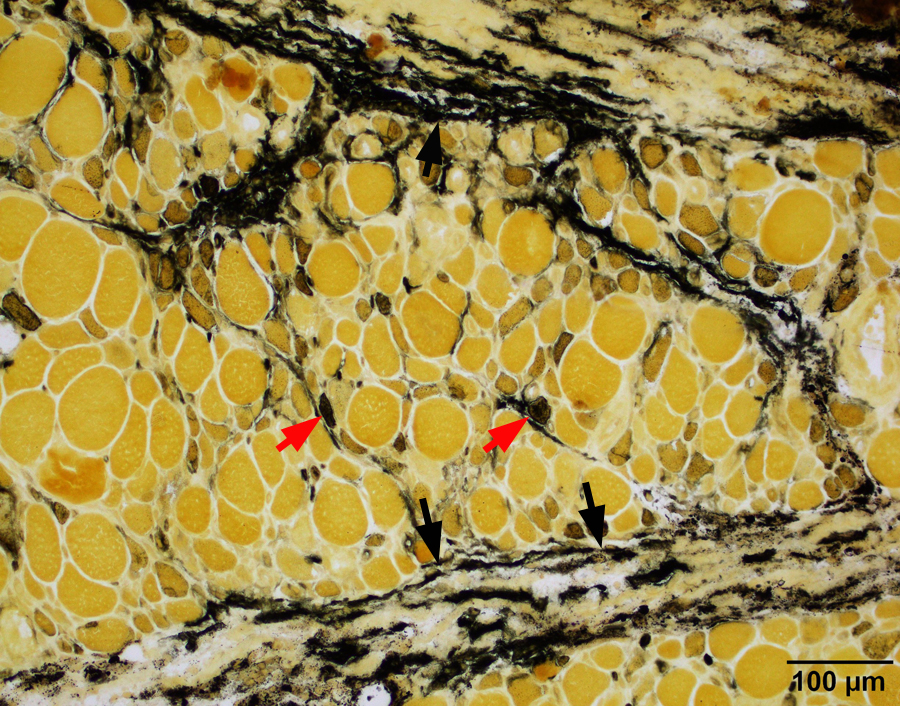
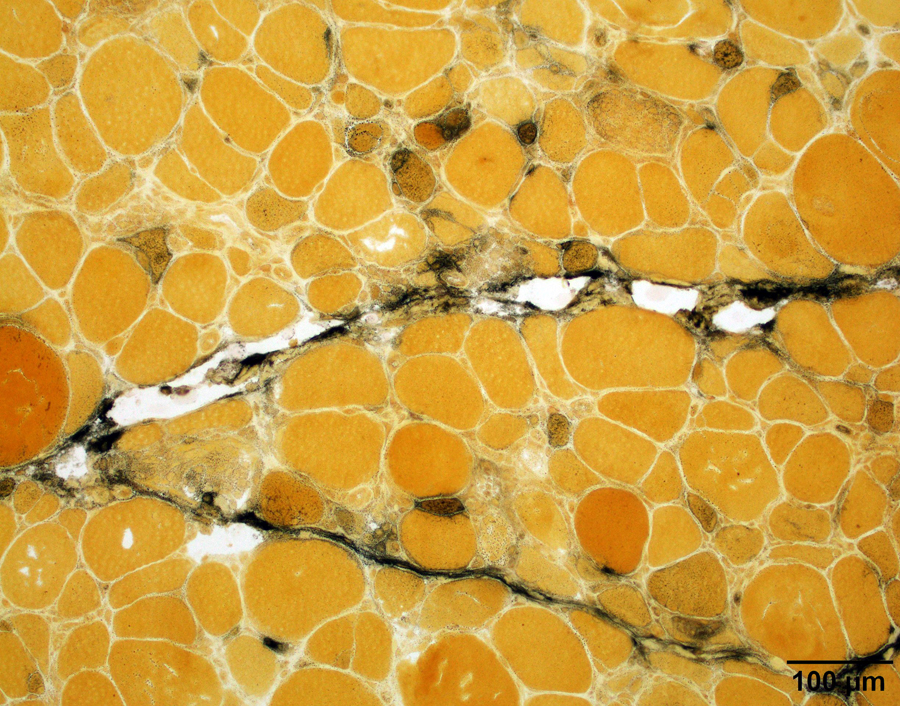
- Connective tissue reactivity:
- Perimysial connective tissue in antisynthetase syndrome associate myositis, necrotizing myopathy with anti-HMGCR autoantibody and a subset of dermatomyositis (Brain 2015;138:2485, Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm 2018;5:e434, Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm 2015;2:e124)
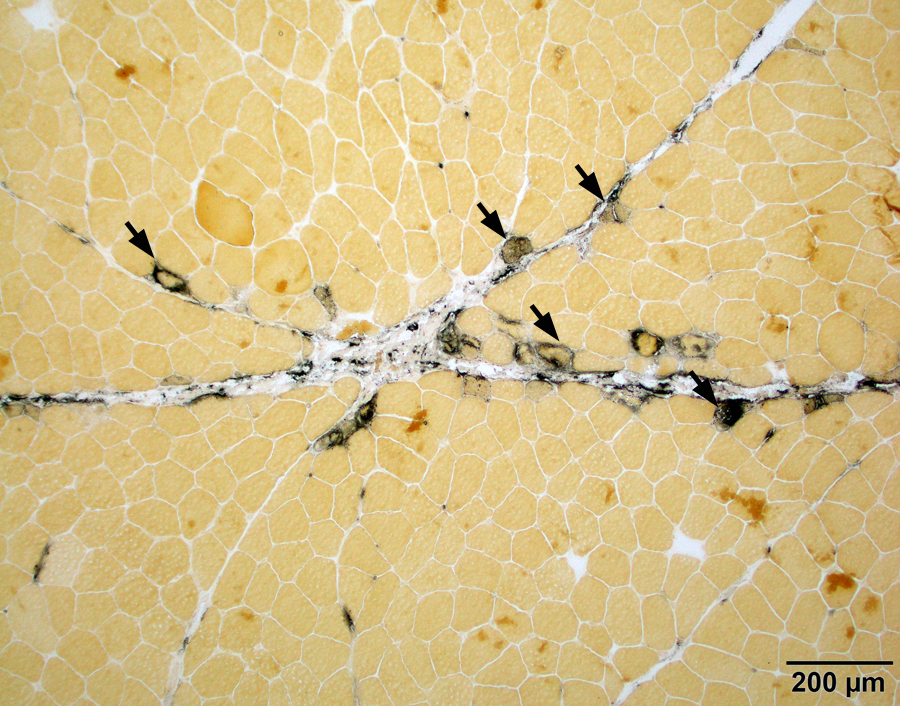
- Myofiber reactivity:
- Regenerating fibers of all causes (not limited to inflammatory myopathies) (J Histochem Cytochem 1970;18:55)
- Can be seen in a small subset of denervated myofibers in adults with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or peripheral neuropathies or young children with infantile spinal muscular atrophy (J Histochem Cytochem 1970;18:55)
- Capillary reactivity:
- Endomysial capillary reactivity is increased in a subset of dermatomyositis (Am J Pathol 1980;101:159)
Negative staining
- Myofibers undergoing active necrosis or phagocytosis
- Duchene muscular dystrophy, limb girdle muscular dystrophy or experimental ischemic myopathy do not show perimysial connective tissue reactivity (Am J Pathol 1980;101:159)
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1