Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Sample pathology report | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2 | Board review style question #3 | Board review style answer #3Cite this page: Van Bockstal MR. Cytokeratin AE1 / AE3. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsae1ae3.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Mixture of 2 different clones of anticytokeratin (CK) monoclonal antibodies (AE1 and AE3), which functions as a broad spectrum cytokeratin marker (Ann Surg Oncol 2011;18:S261)
- AE1 detects the high molecular weight cytokeratins 10, 14, 15 and 16 and the low molecular weight cytokeratin 19
- AE3 detects the high molecular weight cytokeratins 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 and the low molecular weight cytokeratins 7 and 8
- Not reactive to cytokeratins 17 and 18
Essential features
- Mixture of 2 different clones of anticytokeratin monoclonal antibodies (AE1 and AE3), which functions as a broad spectrum cytokeratin marker for cytokeratins 1 - 8, 10, 14 - 16 and 19
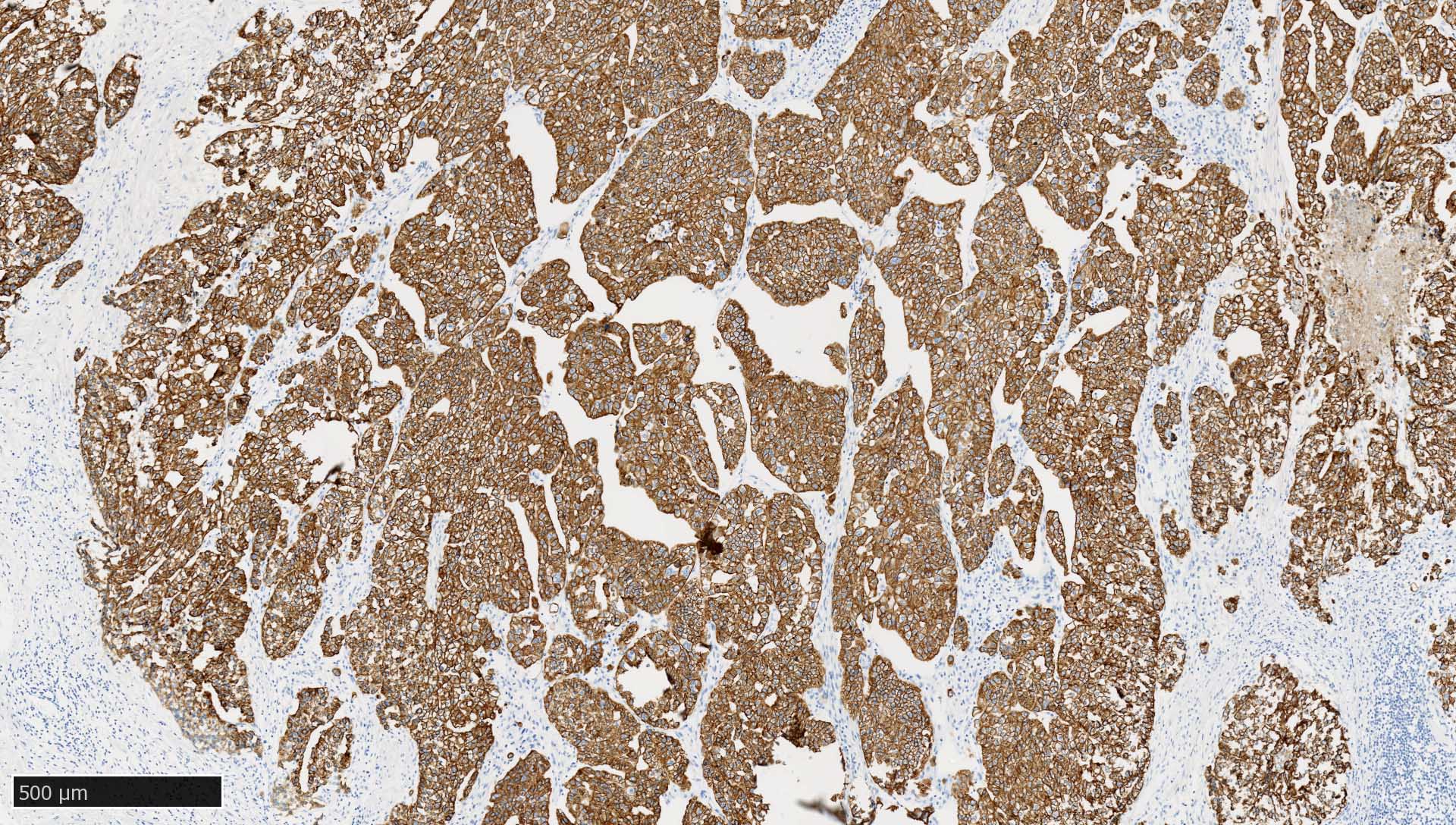
- Immunoreactivity is observed in epithelia and most carcinomas (i.e., tumors of epithelial origin), with cytoplasmic and membranous positivity
- Normal liver is recommended as an on slide positive external control
- CK AE1 / AE3 immunohistochemistry is used for assessment of occult lymph node metastases, residual disease after neoadjuvant therapy, invasion depth and tumor budding in multiple carcinomas
- CK AE1 / AE3 is rarely used as a standalone immunohistochemical analysis but rather as part of a panel when used to confirm or rule out epithelial nature of tumors
Terminology
- Pankeratin, broad spectrum keratin or keratin: not preferred as this can also refer to cytokeratin MNF116 and (to a lesser extent) CAM5.2
Pathophysiology
- Cytokeratins are proteins of the cytoskeletal intermediate filaments, which allow cells to cope with mechanical stress
- Type I cytokeratins are acidic and type II cytokeratins are basic, either with high or low molecular weight; acidic and basic cytokeratins often form heterodimeric pairs (Ann N Y Acad Sci 1985;455:282)
- Their expression varies throughout the tissue type and is mainly organ specific, which allows their use to identify the primary origin of a metastatic tumor (Ann N Y Acad Sci 1985;455:282, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1014)
Interpretation
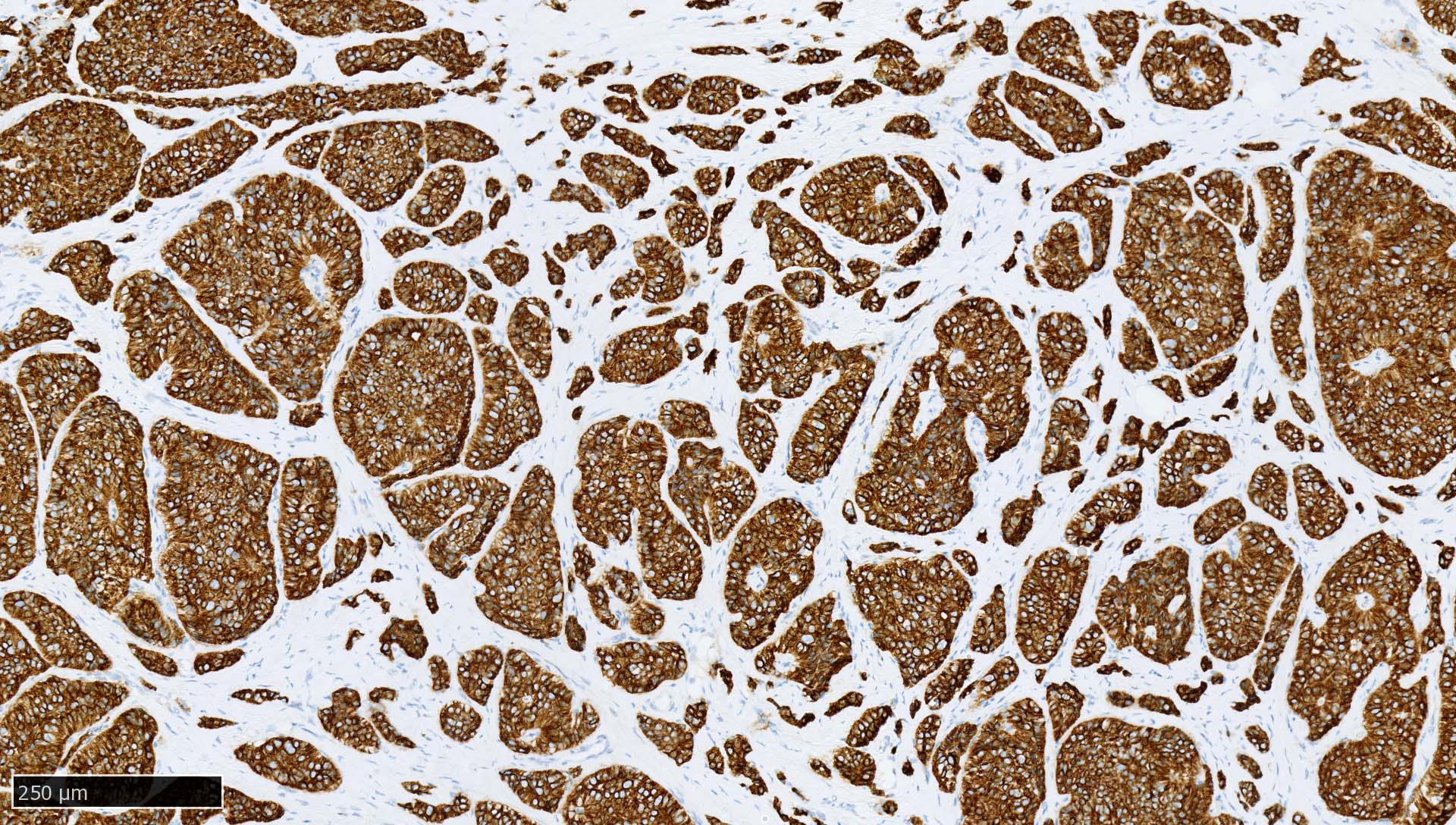
- Normal pattern in epithelium: cytoplasmic staining reaction with accentuation of the cellular membrane
- Dot-like pattern in certain tumors, such as neuroendocrine neoplasms
Uses by pathologists
- Confirm or rule out epithelial nature of tissue, tumors or components of tumors (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1014)
- As such, usually not performed as a standalone immunohistochemical analysis but rather used as part of a panel of immunohistochemical stains to avoid misinterpretation (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2014;138:1583)
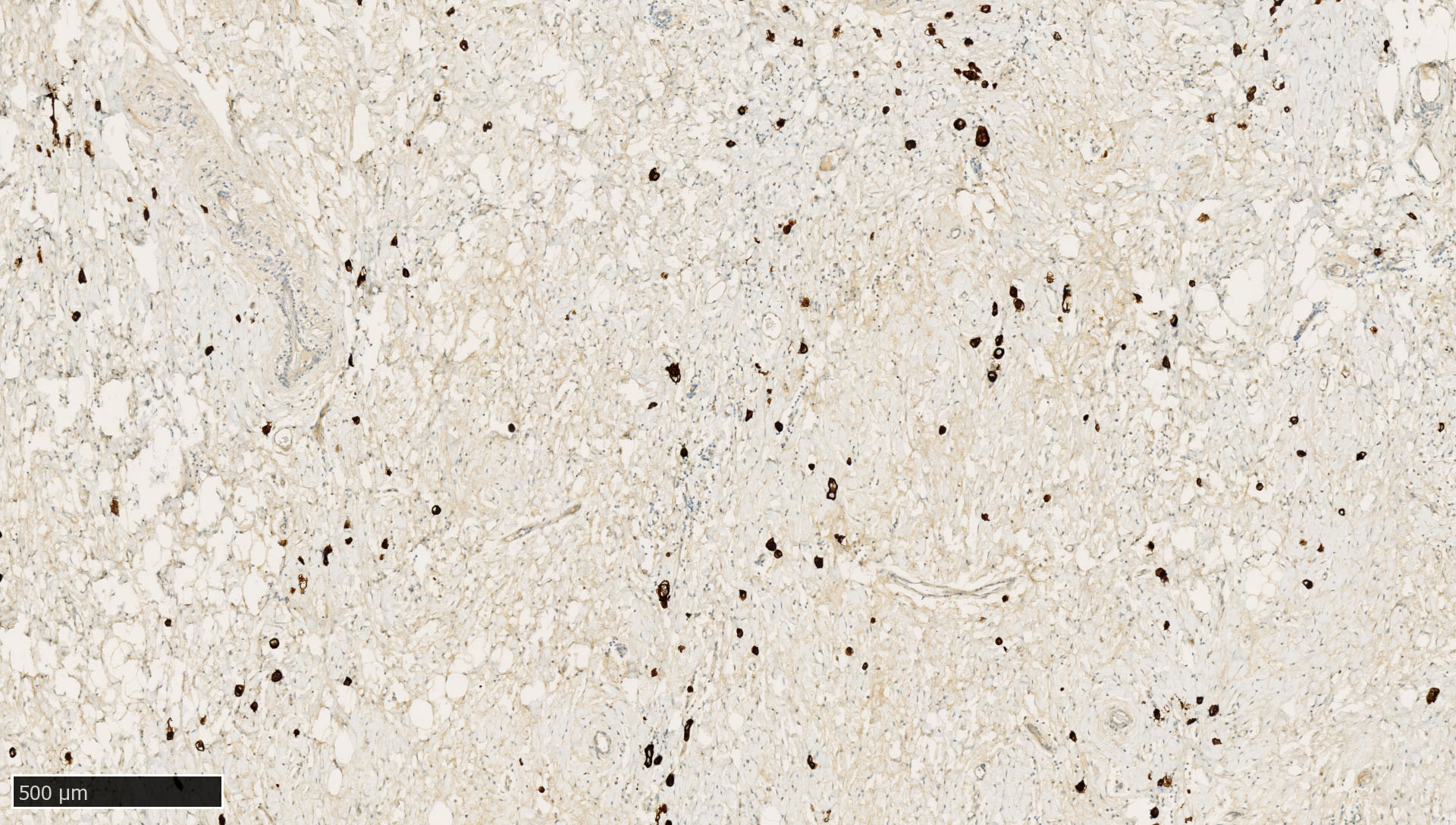
- Identification of occult tumor cells of carcinomas (either isolated tumor cells or micrometastases) in lymph nodes or bone marrow or (less common) at frozen section (Ann Surg Oncol 2020;27:4204, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:1212, J Clin Oncol 2003;21:3469, BMC Cancer 2012;12:403, Acta Histochem Cytochem 2011;44:133)
- Note: per current invasive breast cancer NCCN guidelines, routine cytokeratin IHC to define node involvement is not recommended in clinical decision making (NCCN: Breast Guidelines [Accessed 9 June 2022])
- Epithelial cells in lymph nodes may represent an artefact (displaced epithelium by recent biopsy) instead of true metastasis (Histopathology 2015;66:283, J Clin Oncol 2006;24:2013)
- Hyalinized cytokeratin particles without tumor cell nuclei may mimic isolated tumor cells and may cause misinterpretation (J Surg Res 2002;107:75, Hepatogastroenterology 2014;61:1235)
- Dispersed interstitial reticulum cells with dendritic / reticular pattern show weak to moderate cytoplasmic immunoreactivity (J Cutan Pathol 2016;43:1231, NordiQC: Pan Cytokeratin (CK-PAN) [Accessed 5 May 2022])
- Identification of tumor cells of epithelial origin in difficult cases in which there are few cells, there are significant cautery artifacts or there is a dense inflammatory infiltrate obscuring infiltrating cancer cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:e20)
- Identification of residual tumor cells of epithelial origin in fibrous scars or cauterized tissue of patients with prior surgical resections or after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (Urology 1997;49:721, Int J Colorectal Dis 2010;25:805)
- Keratin positive tumor cells should be distinguished from keratin positive myofibroblasts; simultaneous staining for actin may be useful (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:e20)
- Identification of areas of interest (hotspots) for the assessment of tumor budding on hematoxylin / eosin stained slides in colorectal cancer (Am J Clin Pathol 1991;95:137, Ann Surg 2022;275:e549, Virchows Arch 2021;479:459, Mod Pathol 2017;30:1299)
- Visualization of Mallory bodies in a variety of liver diseases, although CK8/18 might be more effective (Med Electron Microsc 2004;37:114)
- Assessment of the depth of tumor invasion (Diagn Pathol 2015;10:200, PLoS One 2020;15:e0225958)
- Establish the presence of noninvasive epithelial downgrowth after penetrating keratoplasty (Cornea 2006;25:727)
- Part of flow cytometry strategy to enrich epithelial cells in sputum (Cytometry A 2004;60:1)
- Identification of lymphoepithelial lesions in MALT lymphomas of the stomach and other sites (Respir Med Case Rep 2019;27:100826)
- Identification of trophoblastic tissue (i.e., cytotrophoblast, syncytiotrophoblast and intermediate trophoblast) in curettages of missed and habitual abortions (Am J Clin Pathol 1991;95:137)
Prognostic factors
- Micrometastases and isolated tumor cells are generally associated with poorer prognosis in many cancer types:
- Occult tumor cells are associated with poor recurrence free survival and increased risk of cancer related death in gastric cancer patients staged as pN0 (Ann Surg Oncol 2020;27:4204)
- Micrometastasis is associated with worse recurrence free survival and overall survival in stage I lung adenocarcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:1212)
- Lymph node micrometastasis is more frequently observed in stage I lung adenocarcinoma with a micropapillary component (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:1212)
- Presence of micrometastases and isolated tumor cells in (early stage) breast cancer is associated with poorer disease free and overall survival; however, NSABP-32 findings support that local radiation and systemic therapy, particularly endocrine therapy, may attenuate the unfavorable effect (J Natl Cancer Inst 2010;102:410, Br J Cancer 2018;118:1529, N Engl J Med 2011;364:412)
- CK AE1 / AE3 immunohistochemistry is not recommended for routine evaluation of pelvic lymph nodes in prostate cancer patients as it does not reveal additional information to a standard hematoxylin and eosin section (Virchows Arch 2014;464:45)
- Although tumor budding is assessed in one hotspot at the invasive front (in a field measuring 0.785 mm2) of a single hematoxylin / eosin stained slide, CK AE1 / AE3 immunohistochemistry may help to identify hotspots (Virchows Arch 2021;479:459, Mod Pathol 2017;30:1299)
- Tumor budding is associated with poor prognosis in several cancer types:
- High budding in colorectal carcinoma is associated with higher tumor grade, higher TNM stage, vascular invasion and reduced survival (Mod Pathol 2013;26:295)
- Tumor budding in colorectal carcinoma is classified as follows (Mod Pathol 2017;30:1299):
- Bd1 (low budding) : 0 - 4 buds per 0.785 mm2
- Bd2 (intermediate budding) : 5 - 9 buds per 0.785 mm2
- Bd3 (high) : ≥ 10 buds per 0.785 mm2
- Tumor budding in tongue squamous cell carcinoma and colorectal carcinoma is defined as a single cancer cell or small cluster of < 5 cancer cells at the tumor's invasive front (Hum Pathol 2018;76:1, Mod Pathol 2017;30:1299)
- Tumor budding score ≥ 4 is a significant predictor of occult metastasis in cT2N0 tongue squamous cell carcinoma (Hum Pathol 2018;76:1)
- High tumor budding is associated with worse overall survival in resected esophageal adenocarcinoma (Virchows Arch 2021;478:393)
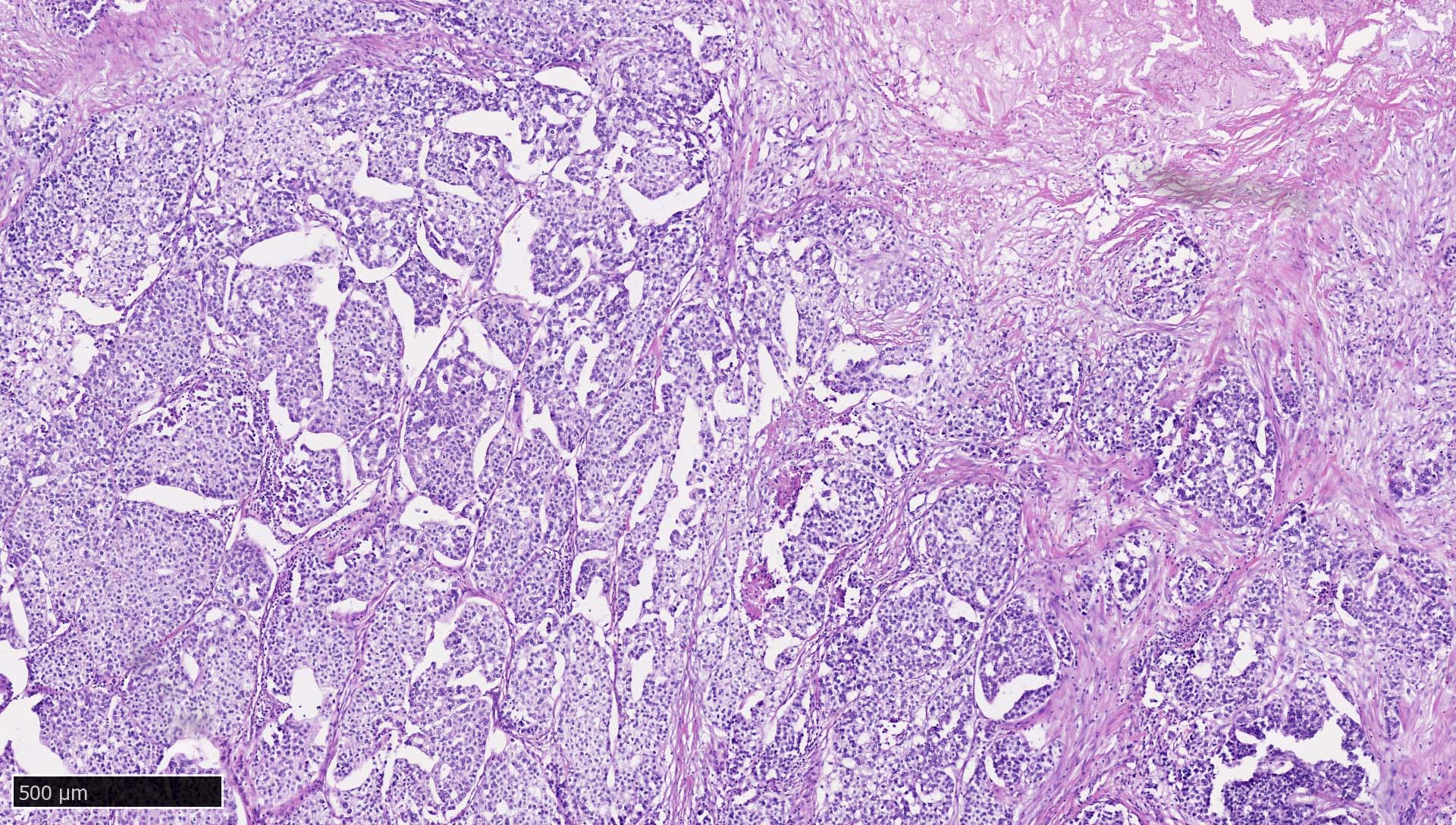
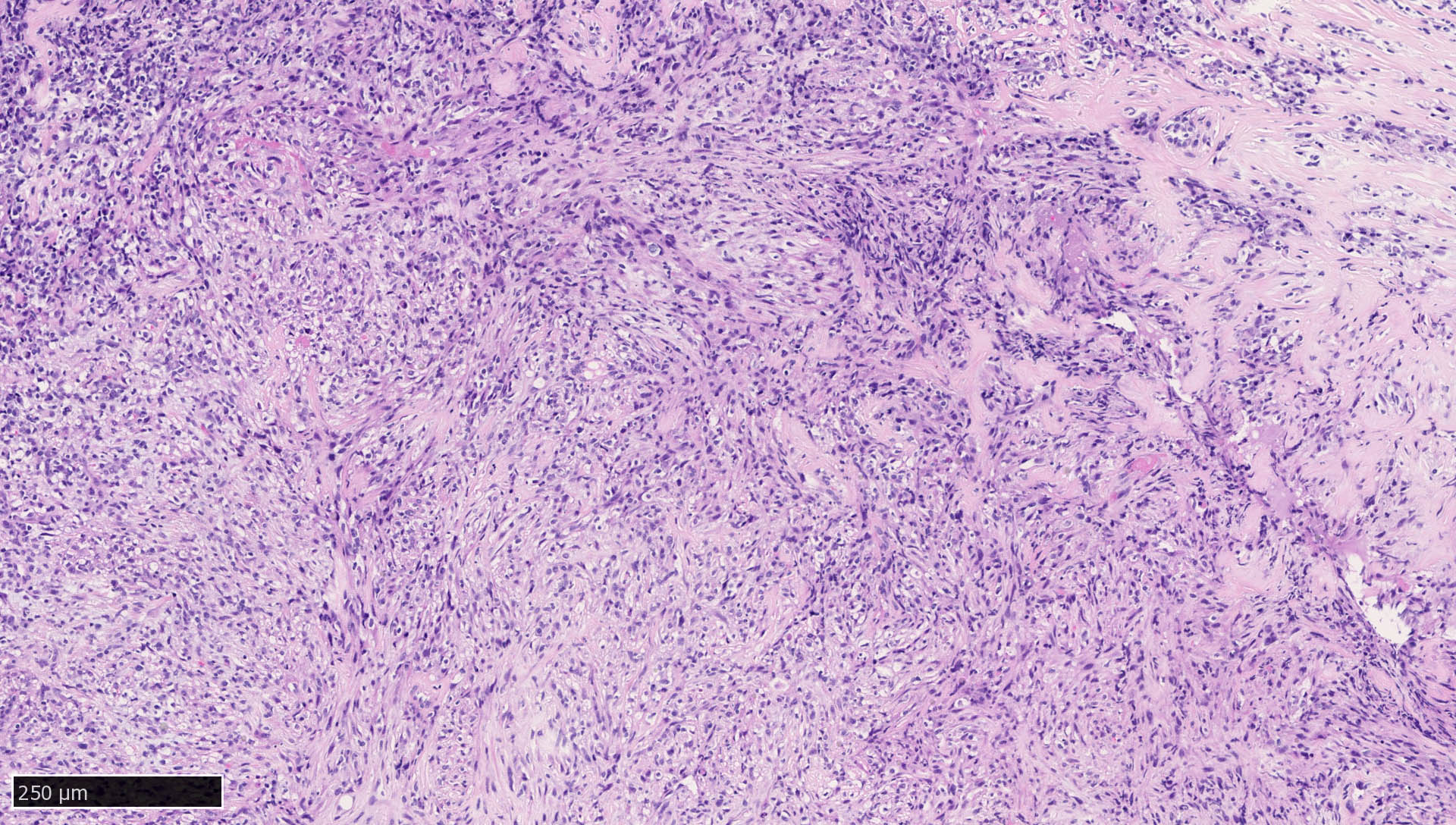
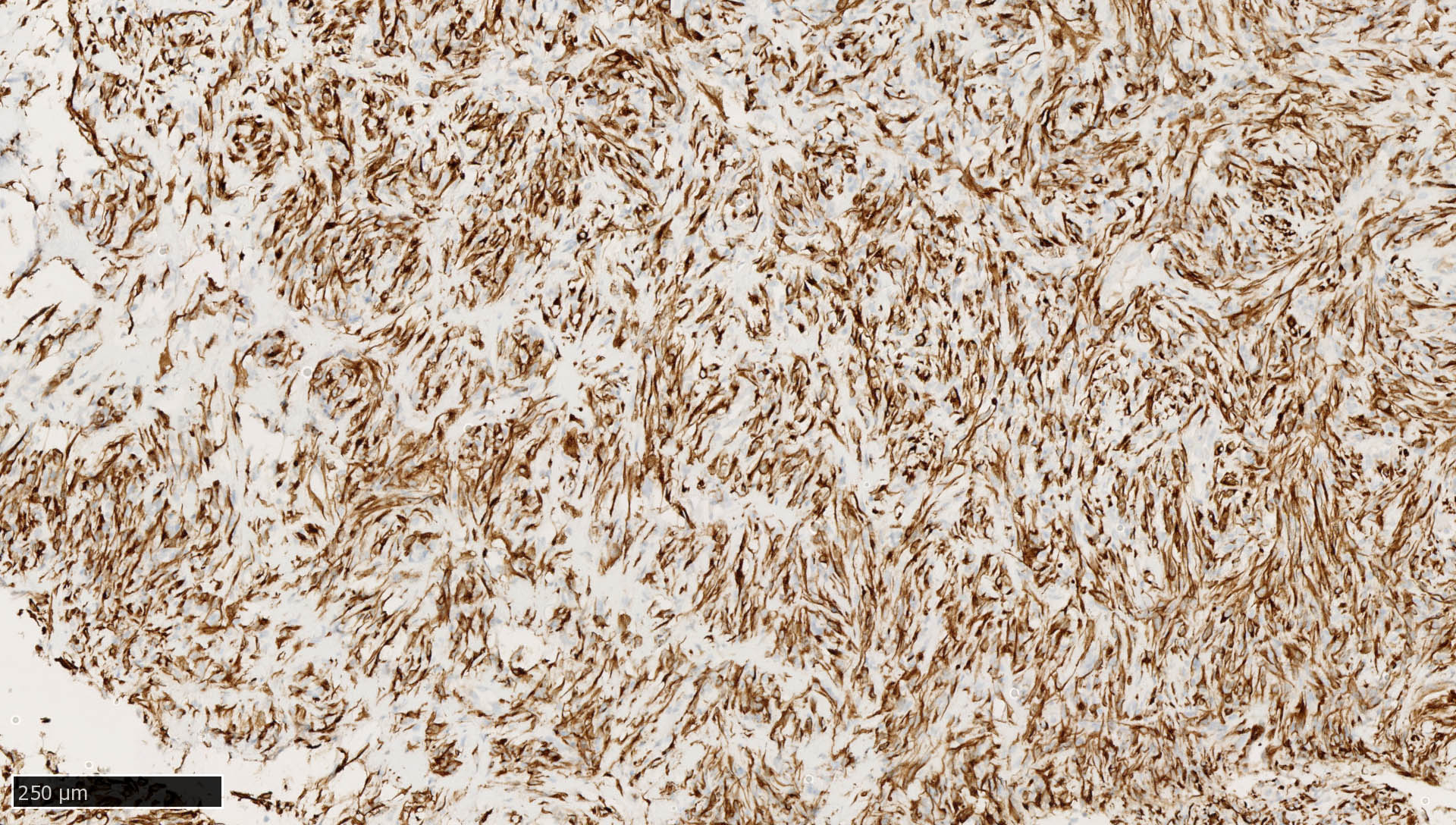
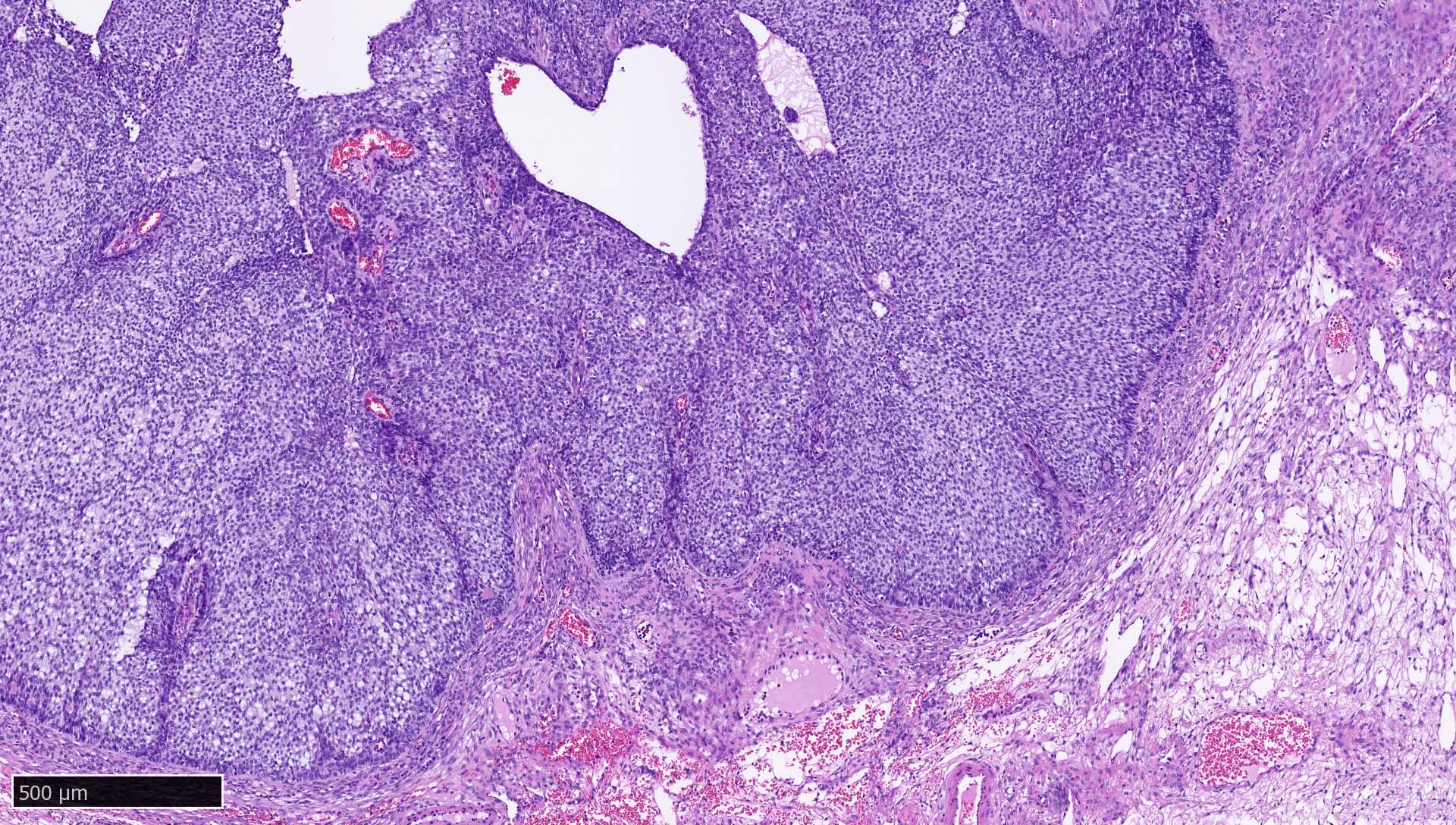
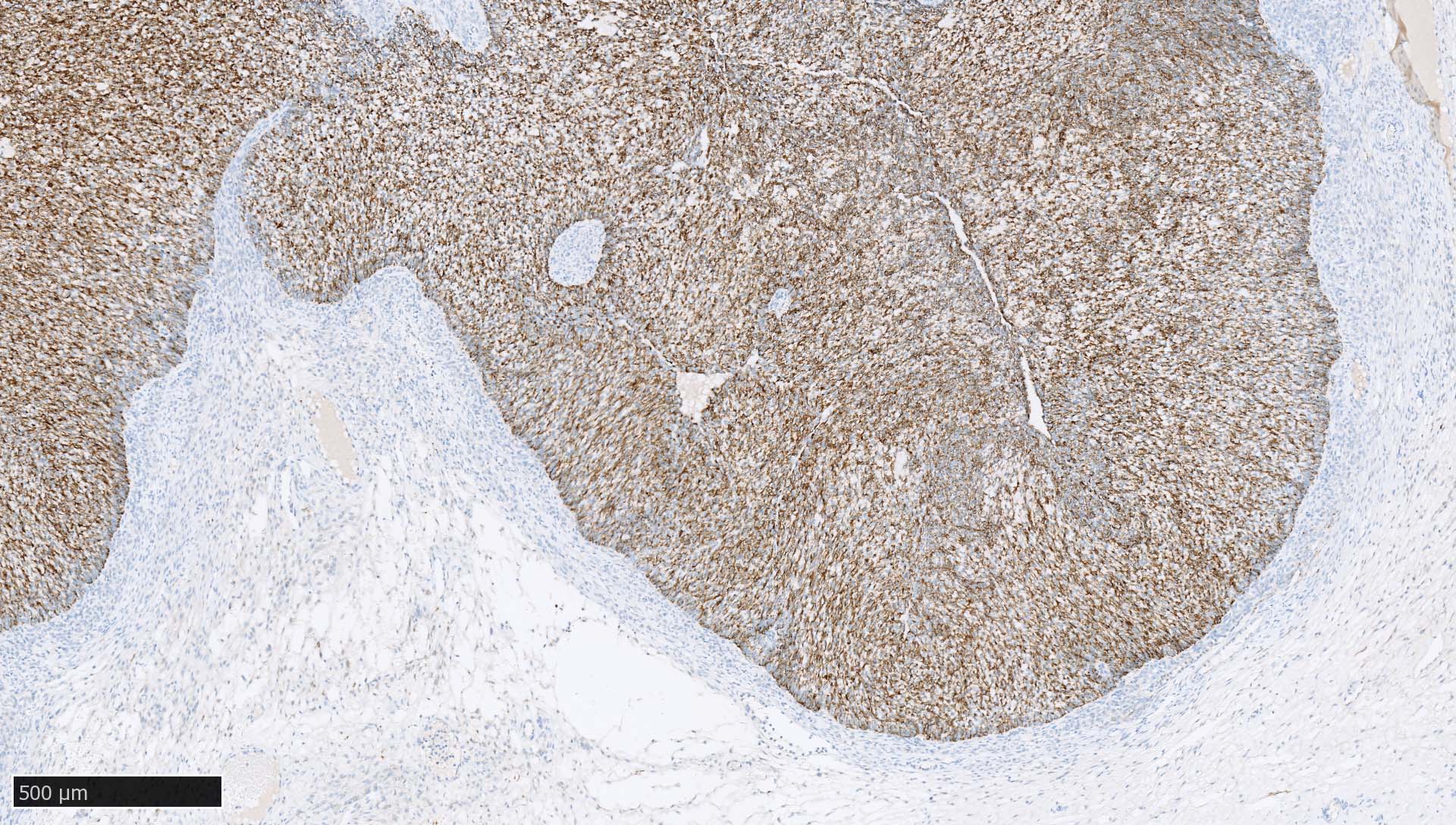
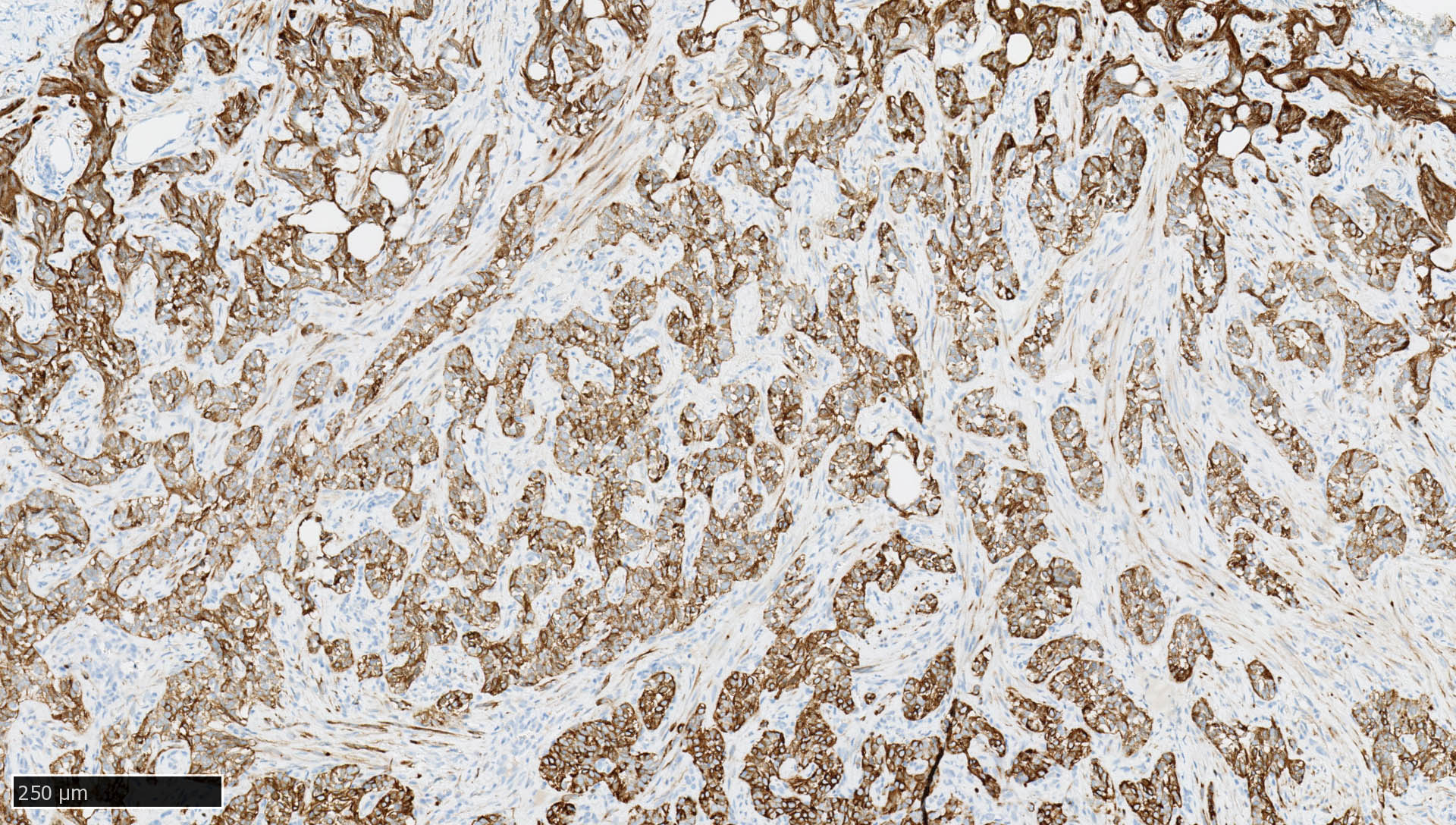
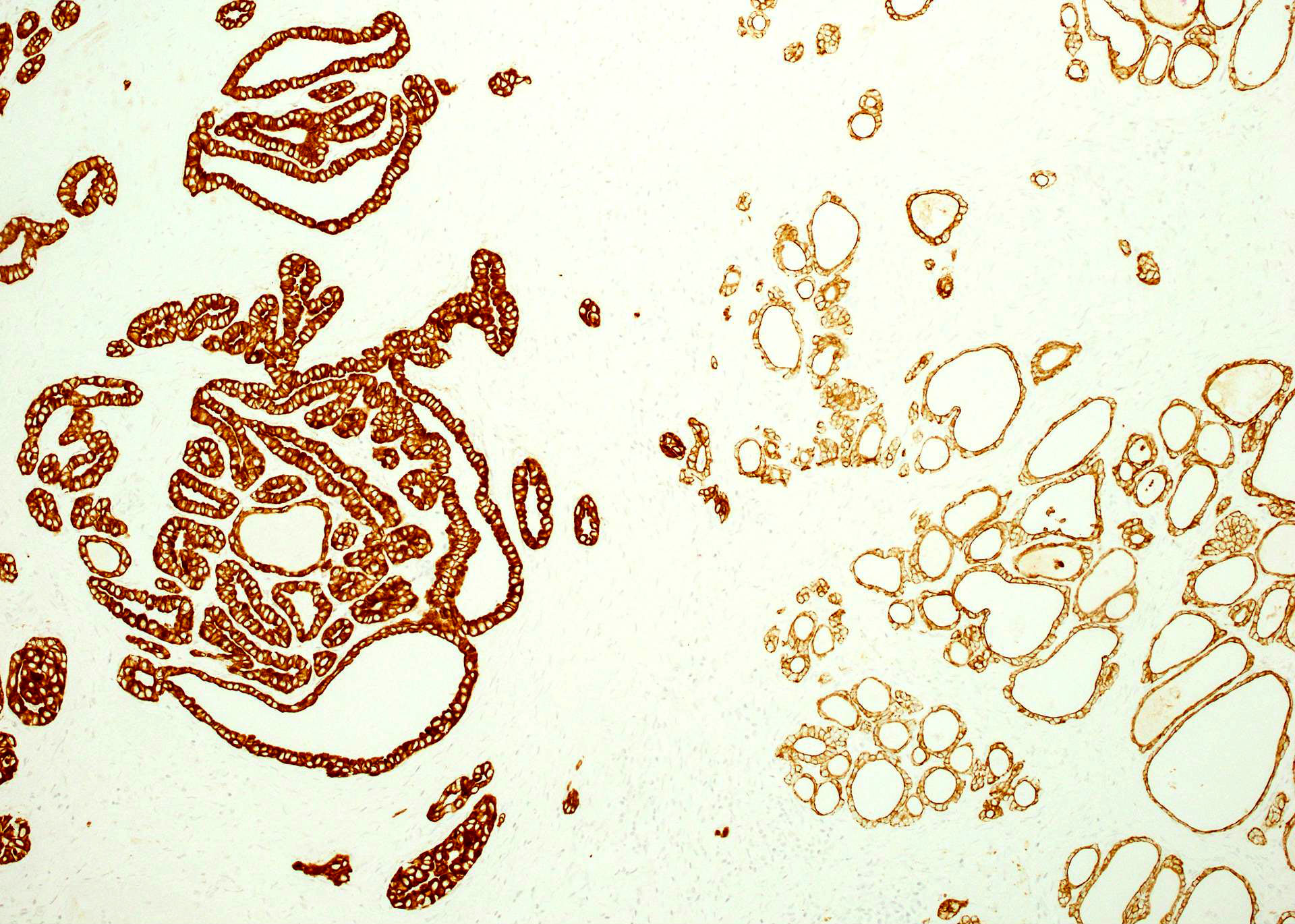
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Mieke R. Van Bockstal, M.D., Ph.D., Christine Galant, M.D., Ph.D. and Andrey Bychkov, M.D., Ph.D.
Positive staining - normal
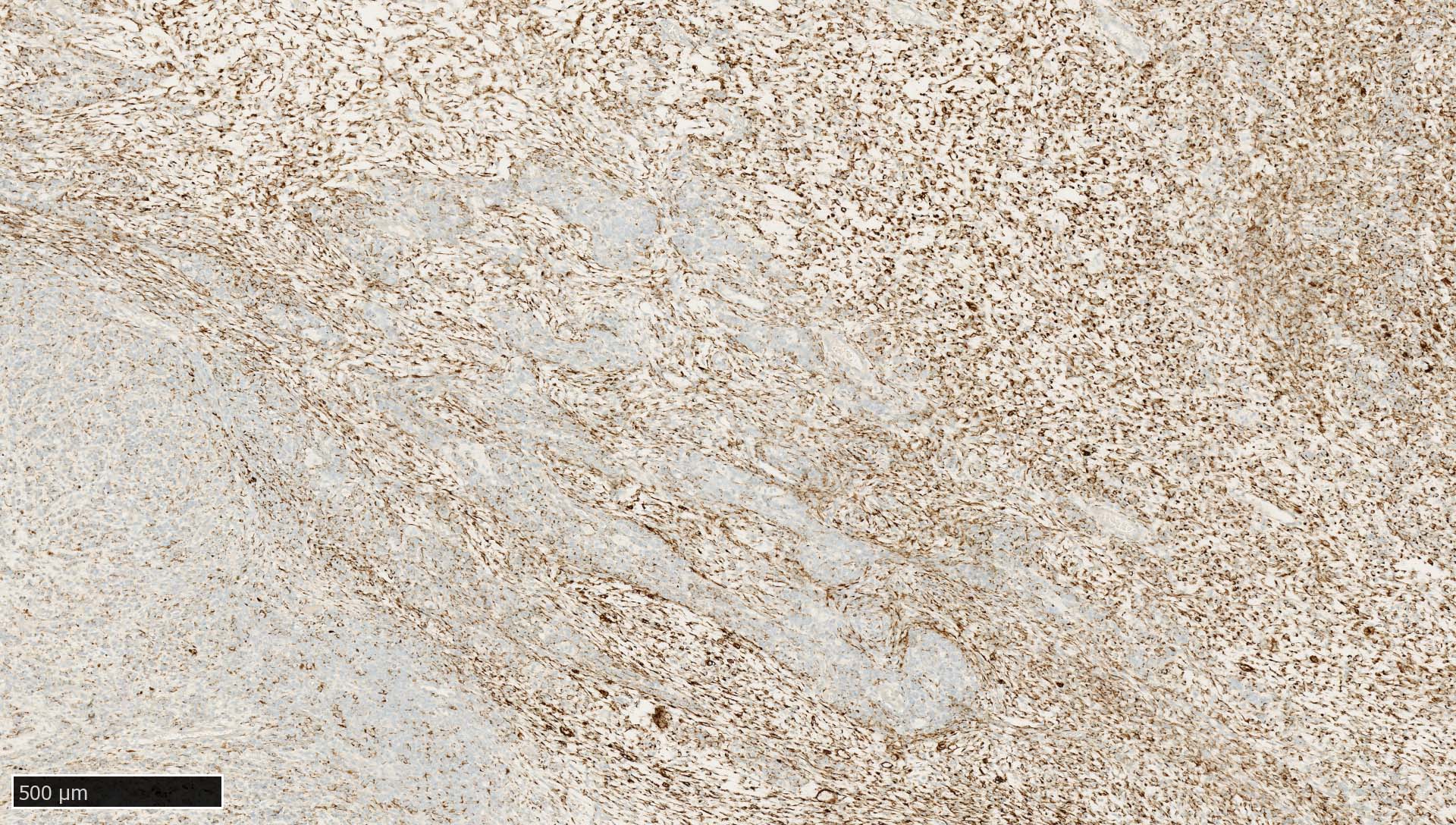
- Epithelium (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1014, J Clin Pathol 1991;44:660)
- Trophoblast (Am J Clin Pathol 1991;95:137)
- Follicular cells in the adenohypophysis (Pathol Int 2005;55:244, Hum Pathol 2021;114:1)
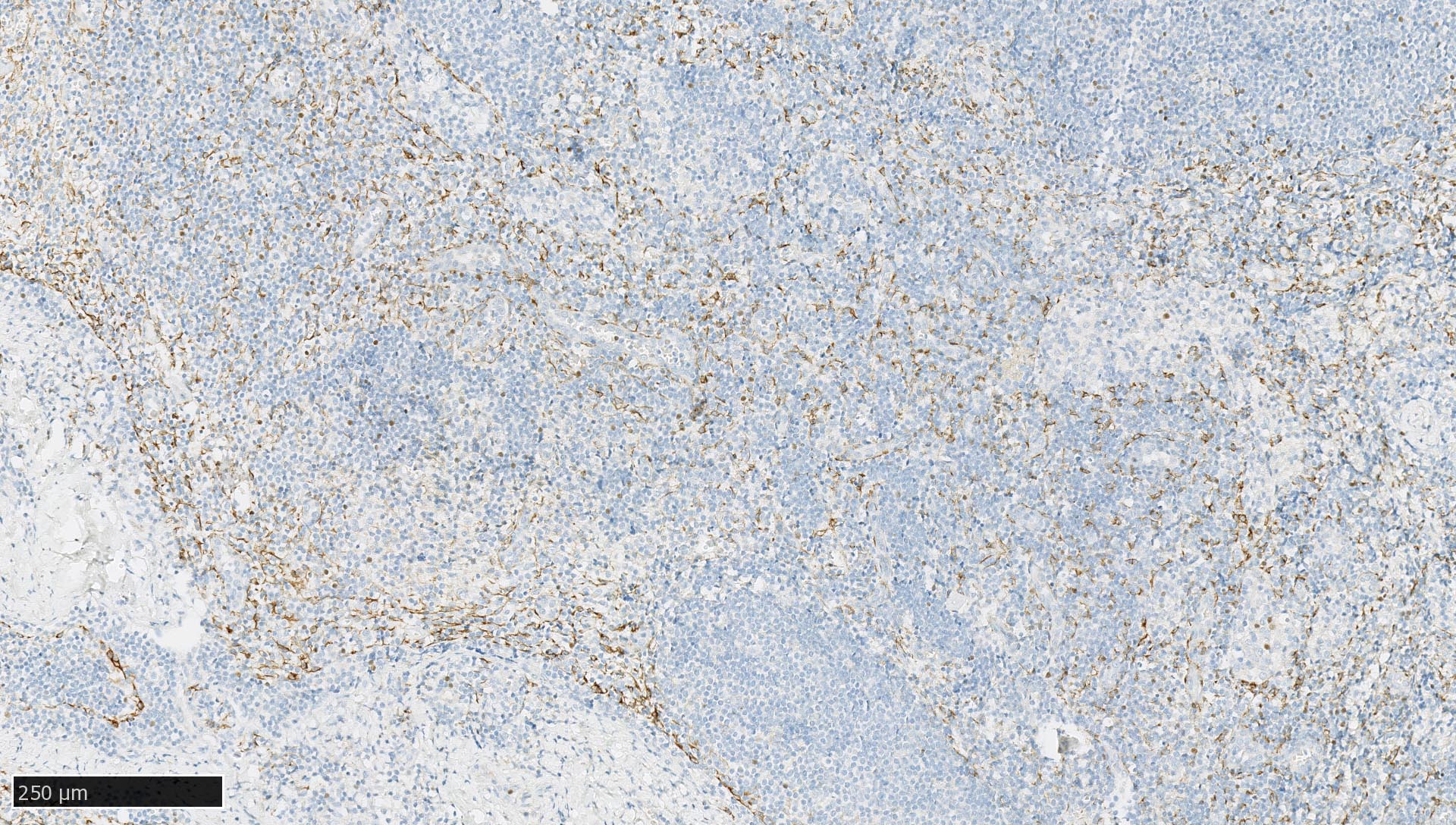
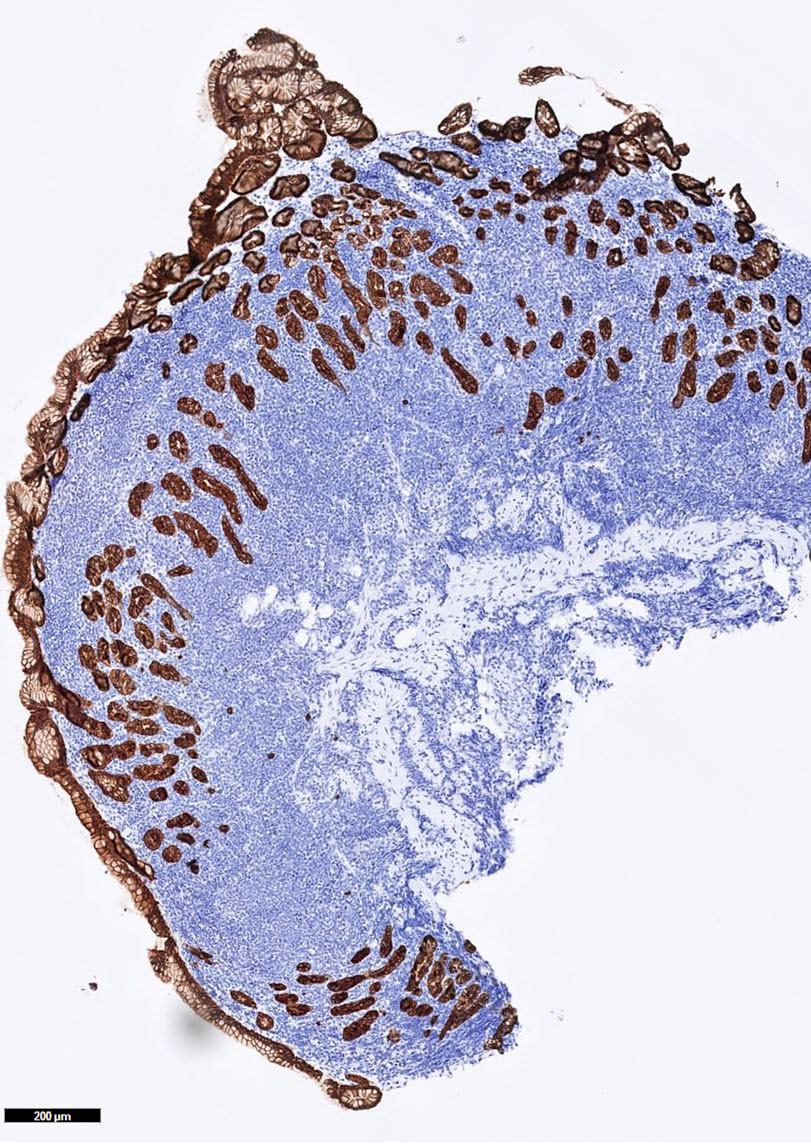
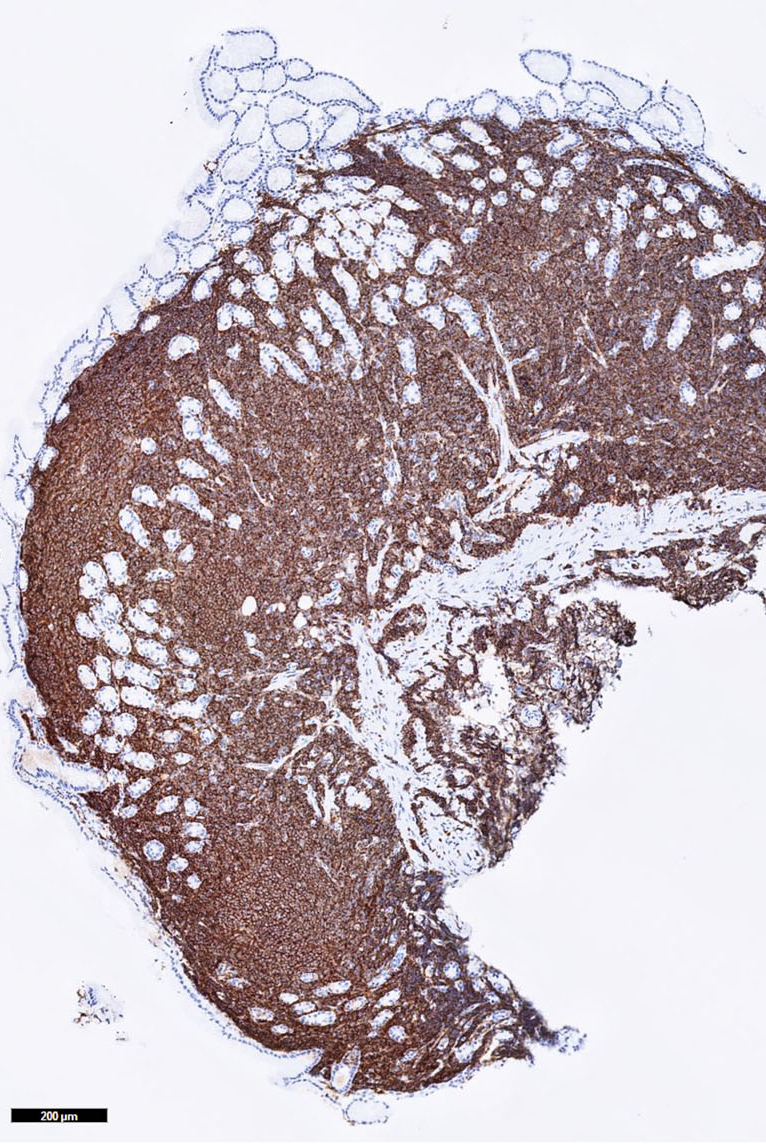
- Lymph nodes and lymphoid tissues: lymphocytes are negative but dispersed interstitial reticulum cells with dendritic / reticular pattern show weak to moderate cytoplasmic immunoreactivity (J Cutan Pathol 2016;43:1231, NordiQC: Pan Cytokeratin (CK-PAN) [Accessed 5 May 2022])
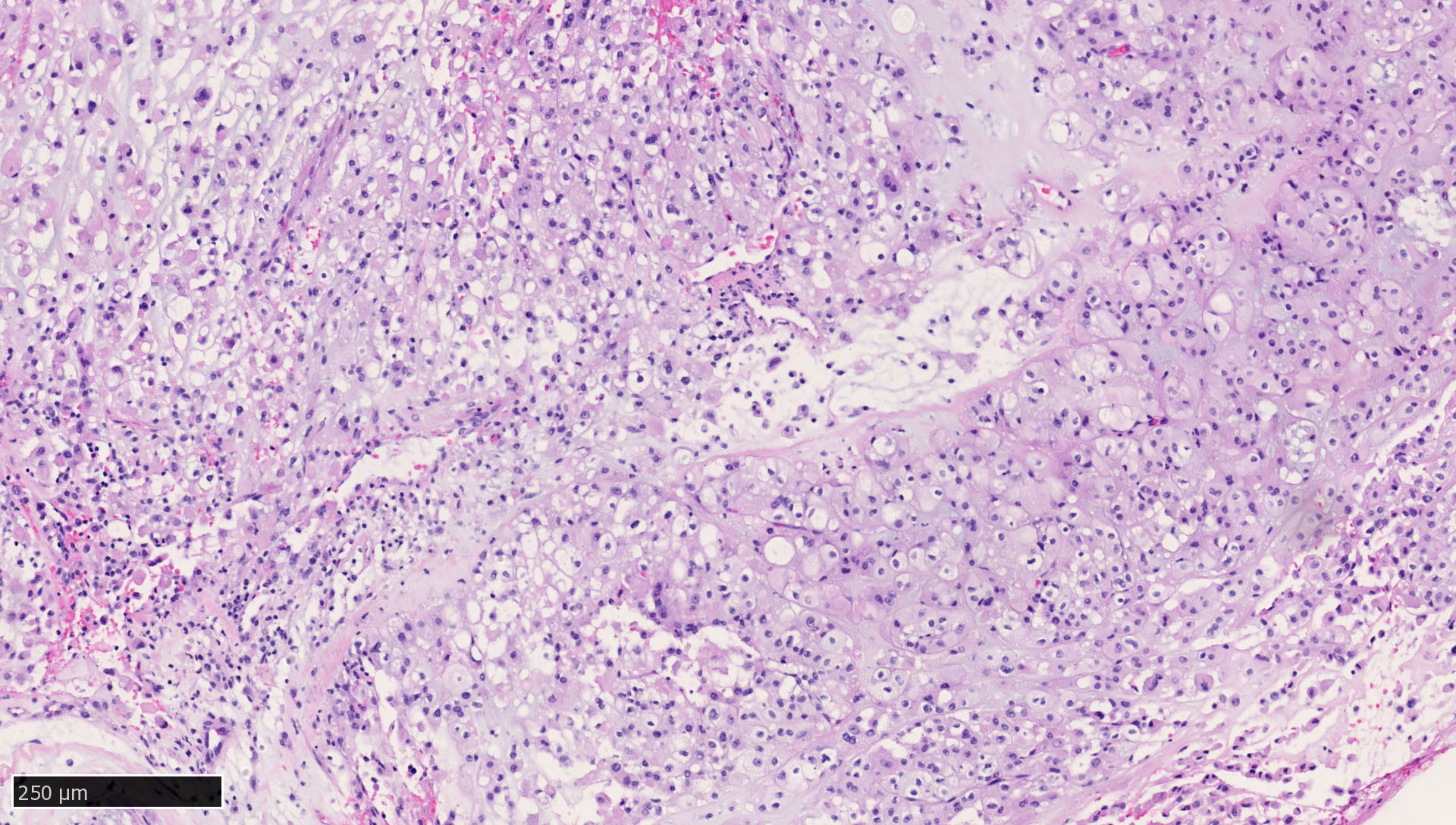
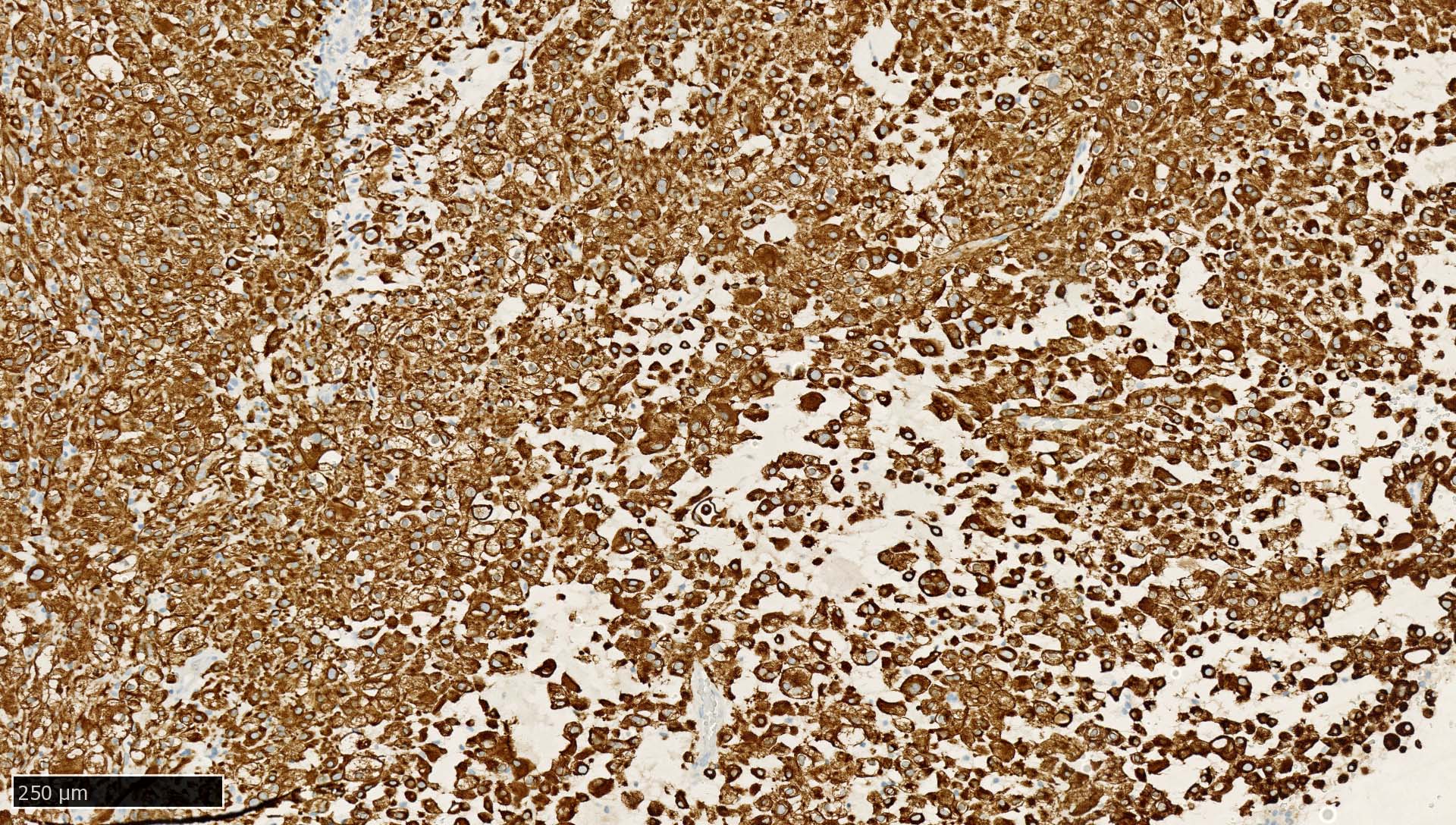
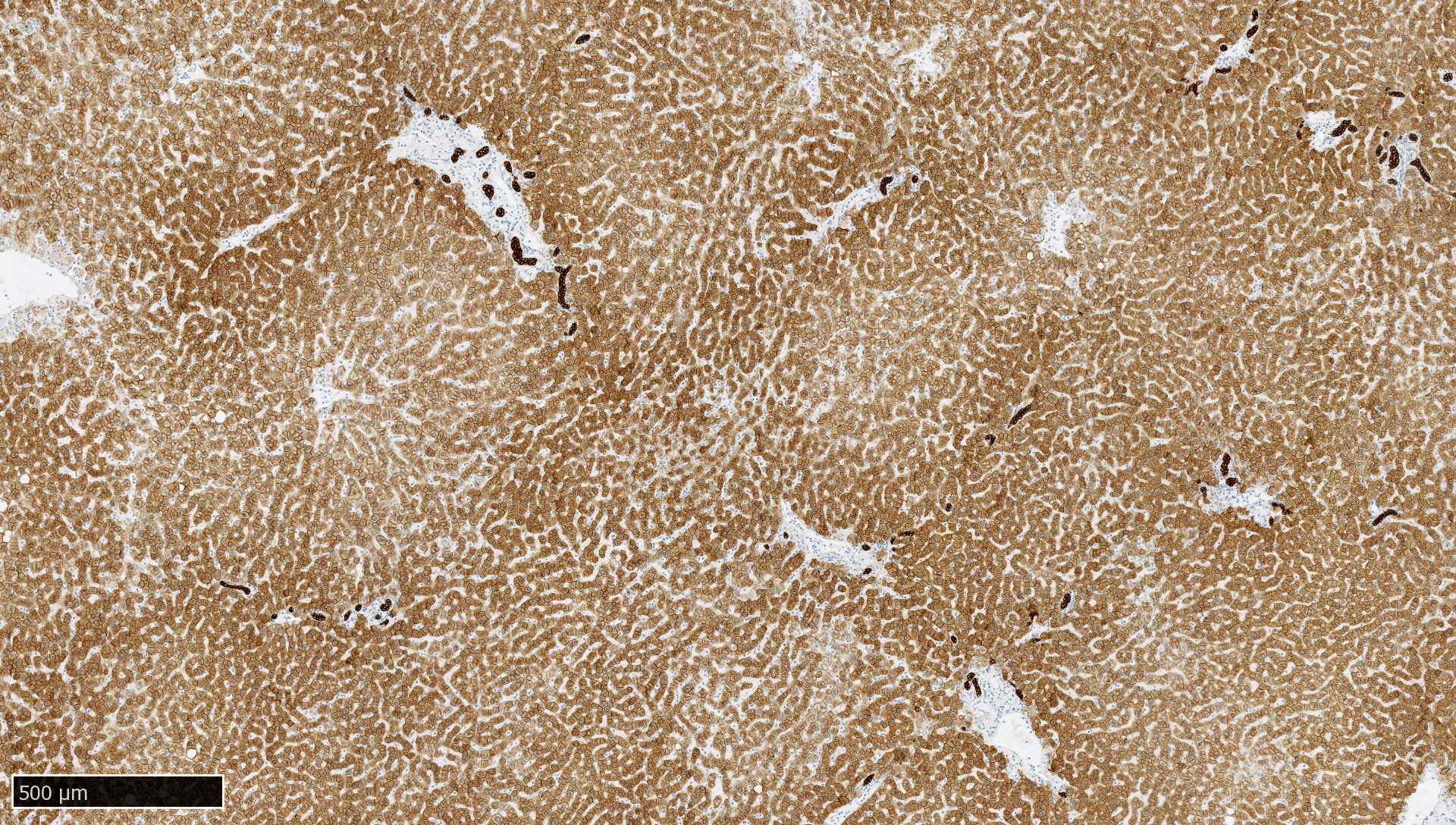
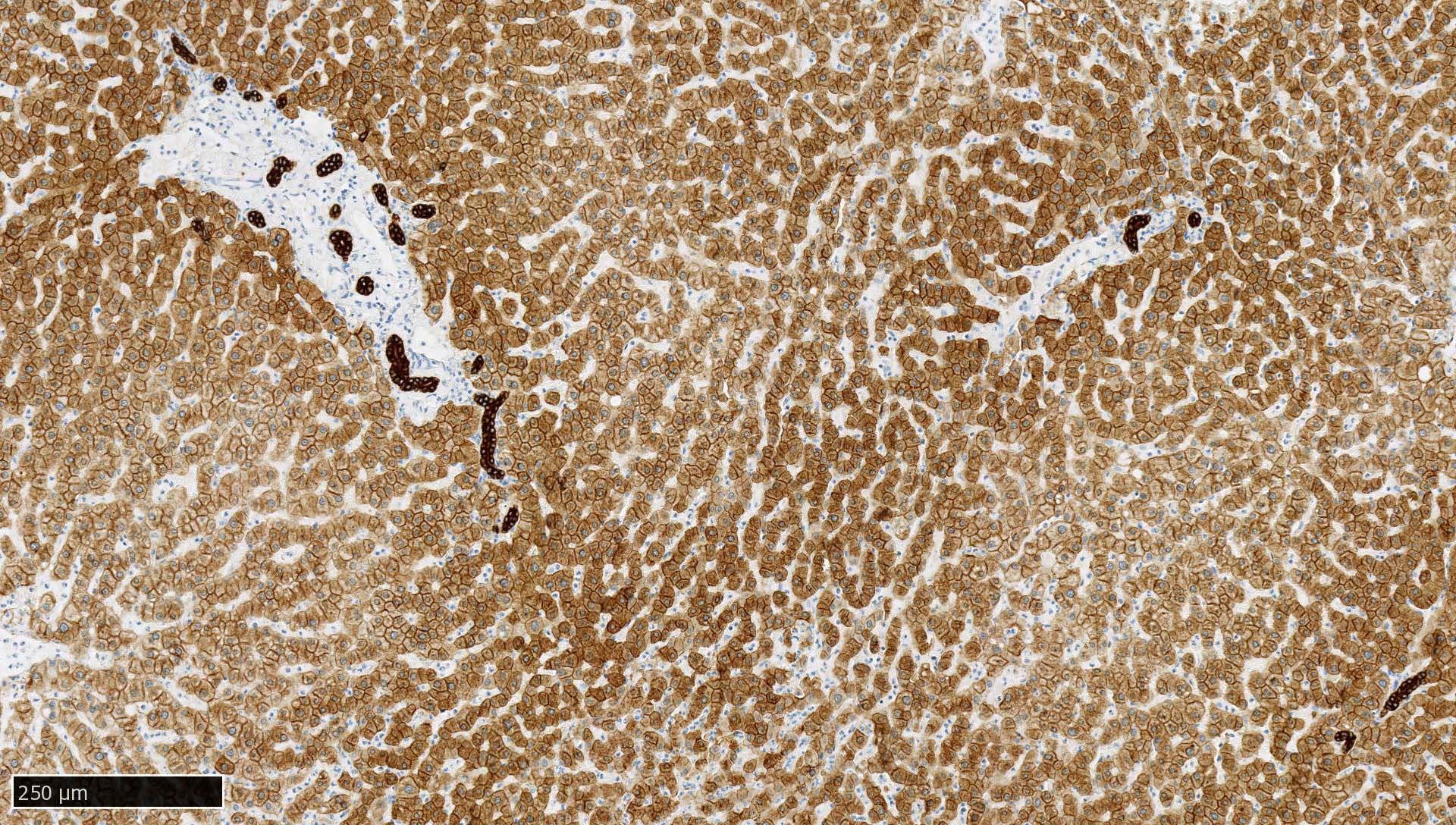
- Liver:
- Recommended as an on slide positive control for CK AE1 / AE3 immunohistochemistry by NordiQC (NordiQC: Pan Cytokeratin (CK-PAN) [Accessed 5 May 2022])
- Vast majority of hepatocytes show a distinct cytoplasmic staining reaction with membrane accentuation, while bile ducts display a strong cytoplasmic and membranous staining reaction (NordiQC: Pan Cytokeratin (CK-PAN) [Accessed 5 May 2022])
- Acinar gradient should be present: zone 1 hepatocytes stain more intensely and a rim of hepatocytes around terminal hepatic venules and adjacent to subhepatic veins should also stain more intensely (Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 1987;412:63)
Positive staining - disease
- Most carcinomas (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1014)
- Adamantinoma-like Ewing sarcoma of the salivary glands: 100% (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:187)
- Adenocarcinoma of the rete testis: 100% (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:670)
- Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor: 100% (J Dent Sci 2021;16:7)
- Adenomatoid tumor: 100% (paratesticular), 100% (uterine), 100% (adrenal gland) (Histopathology 2000;36:109, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2012;20:173, Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:969)
- Anaplastic astrocytoma: 63% (Histopathology 1989;14:359)
- Anaplastic carcinoma of the pancreas with rhabdoid features: 100% (Virchows Arch 2014;465:531)
- Calcifying nested stromal and epithelial tumor of the liver: 100% (at least focal immunoreactivity) (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:976, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2019;143:264)
- Calcifying odontogenic cyst: 100% (J Dent Sci 2021;16:7)
- Chondroblastoma: 62% (Hum Pathol 2013;44:237)
- Chordoma: 100% (conventional chordoma), 94% (chondroid chordoma), 100% (poorly differentiated chordoma with loss of INI1) (Microsc Res Tech 1996;33:73, Ann Diagn Pathol 2021;55:151809)
- Choroid plexus carcinoma: 100% (Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2004;62:600)
- Choroid plexus papilloma: 100% (Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2004;62:600)
- Cutaneous myoepithelial neoplasms on acral sites: 100% (Am J Surg Pathol 2022 Mar 31 [Epub ahead of print])
- Cytokeratin positive interstitial reticulum cell tumor: 100% (Diagn Pathol 2020;15:121)
- Cytokeratin positive malignant tumor in the abdomen with EWSR1 / FUS::CREB fusion: 100% (Am J Surg Pathol 2022;46:134)
- Embryonal carcinoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:39, Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1293, Hum Pathol 2006;37:662)
- Ependymoma: 98% (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2000;8:25)
- Epididymal papillary cystadenoma: 100% (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2010;134:630)
- Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver: 67% (Ann Diagn Pathol 2020;49:151589)
- Epitheloid sarcoma: 93% (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1580)
- Ewing sarcoma of the uterine cervix: 50% (Am J Surg Pathol 2021;45:523)
- Female adnexal tumor of probable Wolffian origin: 100% (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2022;146:166)
- Glioblastoma multiforme: 97% (Pathol Oncol Res 2015;21:817)
- Granulosa cell tumor (GCT) - cystic: 57% (focal and patchy expression) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2022 Mar 30 [Epub ahead of print])
- Granulosa cell tumor (GCT) - juvenile: 100% (Mod Pathol 2003;16:584)
- Hepatoblastoma: 100% (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2006;9:196)
- High grade oncocytic renal tumor: 100% (Virchows Arch 2018;473:725)
- Leiomyosarcoma of bone: 57% (Virchows Arch 2012;461:561)
- Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of the upper urinary tract: 100% (Virchows Arch 2017;470:703)
- Malignant meningioma: 75% (Mod Pathol 2004;17:1129)
- Mesothelioma - sarcomatoid: 100% (Int J Surg Pathol 2021;29:820)
- Mesothelioma - epithelioid: 100% (Pathol Int 2007;57:190)
- Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast: 100% (fibromatosis-like spindle cell carcinoma), 98% (matrix producing carcinoma), 88% (squamous cell carcinoma), 83 - 100% (low grade adenosquamous carcinoma), 80% (spindle cell carcinoma) (Histopathology 2017;70:975)
- Myoepithelioma-like sarcoma: 50% (Virchows Arch 2012;461:561)
- Nonconventional papillary thyroid carcinoma with pleomorphic tumor giant cells: 100% (Virchows Arch 2010;456:661)
- Odontoma - complex and compound: 100% (J Dent Sci 2021;16:7)
- Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity: 100% (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1099)
- Paratesticular fibrous pseudotumor: 54% (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:569)
- Pituitary neuroendocrine tumors (PitNET) (Hum Pathol 2021;107:87)
- Polymorphous sweat gland carcinoma: 100% (Am J Dermatopathol 2018;40:580)
- Poorly differentiated nonkeratinizing squamous cell carcinoma of the thymus: 100% (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1224)
- Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma (Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat 2018;27:225, Pathologica 2018;110:96)
- Reactive nodular fibrous pseudotumor: 86% (Int J Surg Pathol 2004;12:365)
- Retroperitoneal schwannoma: 69% (Mod Pathol 2006;19:115)
- Rhabdoid and undifferentiated phenotype in renal cell carcinoma: 94% (variable intensity and extent) (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:253)
- Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor of the ovary: 100% (Mod Pathol 2003;16:584)
- Sex cord tumor with annular tubules (SCTAT): 66% (Mod Pathol 2003;16:584)
- Small cell carcinoma of hypercalcemic type: 60% (usually focally positive) (Histopathology 2017;70:1147, Int J Gynecol Pathol 2004;23:330)
- STK11 adnexal tumor: 93% (Am J Surg Pathol 2021;45:1061)
- Synovial sarcoma: 50% (focal reactivity); 100% in biphasic synovial sarcomas (Virchows Arch 2017;471:799, Mod Pathol 2005;18:40, J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2017;76:289)
- Testicular Sertoli cell tumor: 64% (Mod Pathol 1998;11:774)
- TFE3 gene fusion associated renal cell carcinoma: 71% (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1450)
- Thymoma: 100% (atypical thymomas with squamoid and spindle cell features), 100% (type A thymoma), biphasic expression in metaplastic thymoma and type AB thymoma (Mod Pathol 2022 Feb 10 [Epub ahead of print], Virchows Arch 2014;464:725)
- Undifferentiated / dedifferentiated urothelial carcinoma of the urinary tract: 100% (Virchows Arch 2016;469:321)
- Xanthogranulomatous epithelial tumor: 100% (Mod Pathol 2020;33:1889)
- Yolk sac tumor: 100% (also 100% in testicular sarcomatoid yolk sac tumors after chemotherapy) (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:360, Am J Surg Pathol 2022;46:309, Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:251)
Negative staining
- Adrenocortical carcinoma: 84% negative (Hum Pathol 2015;46:1799)
- Adult granulosa cell tumors: 65% negative (Mod Pathol 2003;16:584)
- Aggressive angiomyxoma: 72% negative (Virchows Arch 2005;446:157)
- Angiosarcoma: 97 - 100% negative (up to 31% positive in hepatic angiosarcoma) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2007;131:288, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1580, Ann Diagn Pathol 2020;49:151589)
- Atypical fibroxanthoma: 100% negative (Australas J Dermatol 2020;61:e22)
- Benign meningioma: 100% negative (Mod Pathol 2004;17:1129)
- Chondrosarcoma: 100% negative (but up to 60% positive in clear cell chondrosarcoma) (Hum Pathol 2013;44:237, Neuroendocrinology 2020;110:836)
- Chordoid meningioma: 100% negative (J Neurooncol 2010;99:41)
- Clear cell sarcoma of soft tissue: 97% negative (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:452)
- Endometrial stromal sarcoma: 76% negative (Mod Pathol 2005;18:40)
- Epithelioid angiosarcoma of the bladder: 66% negative (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1377)
- Ewing sarcoma family of tumors / PNET: 81% negative (Virchows Arch 2011;459:409, Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:410)
- Gliosarcoma: 100% negative (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2017;76:289)
- Hemangioblastoma: 94 - 97% negative (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:1051, J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2017;76:289)
- Hepatocellular carcinoma: 72% negative (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2014;138:1583)
- Melanoma: 55% negative (epithelioid melanoma), 73% negative (spindle cell / desmoplastic melanoma) (Mod Pathol 2015;28:1033)
- Meningioma: 94% negative (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2017;76:289)
- Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST): 50 - 100% negative (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2017;76:289, Am J Clin Pathol 1999;112:641)
- Myofibroblastic-like sarcoma: 63% (Virchows Arch 2012;461:561)
- Myxofibrosarcoma: 100% negative (Virchows Arch 2012;461:561)
- Neurofibroma: 100% negative (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2017;76:289)
- Nodular fasciitis: 91% negative (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1404)
- Oncocytic adrenocortical neoplasm: 62% negative (Hum Pathol 2011;42:489)
- Ovarian fibroma: 80% negative (Mod Pathol 2003;16:584)
- Ovarian thecoma and fibrothecoma: 100% negative (Mod Pathol 2003;16:584)
- Paraganglioma: 98% negative (Hum Pathol 2019;93:16)
- Peripheral schwannoma: 100% negative (Mod Pathol 2006;19:115)
- Phyllodes tumor of the breast: 100% negative (benign and borderline phyllodes tumors), 79% negative (malignant phyllodes tumors) (Int J Surg Pathol 2018;26:232, Histopathology 1989;14:141)
- Plasmacytoma / multiple myeloma: 64% negative (occasional positivity can occur in up to 36%) (Int J Surg Pathol 2018;26:232, Histopathology 1989;14:141)
- Proliferative fasciitis: 54% negative (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1404)
- Renal epithelioid angiomyolipoma: 100% negative (Sci Rep 2015;5:10030)
- Solitary fibrous tumor (SFT): 89 - 95% negative (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1404, J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2017;76:289)
- Spindle cell sarcoma, NOS: 100% negative (Virchows Arch 2012;461:561)
- Testicular Leydig cell tumor: 58% negative (Mod Pathol 1998;11:774)
- Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma: 72% negative (Virchows Arch 2012;461:561)
- Well differentiated astrocytoma: 60 - 78% (Histopathology 1989;14:359, Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2007;50:478)
- YAP1::TFE3 fused hemangioendothelioma: 80% negative (Mod Pathol 2021;34:2211)
Sample pathology report
- Immunohistochemical analysis for cytokeratin AE1 / AE3, performed on an automated slide stainer (brand name):
- The tissue sample shows no / focal / diffuse* dot-like / cytoplasmic / membrane* staining with weak / moderate / strong* intensity.
- External on slide tissue control (liver - in accordance with the NordiQC recommendations): positive
- * Select the appropriate option
- Biopsy, left breast (external superior quadrant):
- Desmoid fibromatosis of the breast, with presence of an APC gene mutation (see comment)
- Number of biopsies: 2
- Maximum length of the biopsy: 14 mm
- Lesion type / histological description: Both biopsies show a spindle cell proliferation with fascicular architecture. In one of these biopsies, diffuse infiltration of the fatty stroma is observed. The spindle cells are bland, elongated and slender, with a pale slightly eosinophilic cytoplasm. They are surrounded by a densely collagenous stroma. There is no overt cytonuclear atypia, no clear nucleoli and no nuclear hyperchromasia. There are < 1 mitosis per 10 high power fields.
- Presence of calcifications: no
- Immunohistochemistry and discussion: Immunohistochemical stains for p63, cytokeratin AE1 / AE3, cytokeratin 8/18 and cytokeratin 34betaE12 are negative, which excludes a low grade fibromatosis-like metaplastic breast carcinoma. Immunohistochemical stains for SOX10 and S100 are negative, which excludes a neurofibroma. There is no immunoreactivity for desmin, which excludes a leiomyoma. Immunohistochemistry for CD34 is negative, which excludes a myofibroblastoma and PASH with fascicular architecture. The spindle cells show cytoplasmic immunoreactivity for SMA and beta catenin. There is no nuclear expression of beta catenin.
- Molecular analysis and discussion: FISH analysis did not show USP6 rearrangement, which excludes a nodular fasciitis. Next generation sequencing of the tumor sample did not show any mutations in the CTNNB1 gene but revealed a c.4626_4645del; p.(Lys1543Argfs*9) mutation in the APC gene, with a variant allele frequency of 52%.
- Comment: APC gene mutations are commonly observed in breast desmoid fibromatosis and might either be somatic or germline (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1266).
- Recommendation: These findings are to be correlated with the clinical history and family history of the patient, as a germline APC mutation (Gardner / familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome) should be excluded.
Board review style question #1
Which of the following tissues is the best choice as a positive on slide control for cytokeratin AE1 / AE3 immunohistochemistry?
- Adrenal gland
- Appendix
- Gastric mucosa
- Liver
- Placenta
Board review style answer #1
D. Liver. The liver shows strong, distinct cytoplasmic immunoreactivity of all bile ductal epithelial cells, as well as at least moderate cytoplasmic staining of the majority of hepatocytes. Hepatocytes show membrane accentuation. A low expressor (such as hepatocytes) is required to enable the detection of a slightly failing immunohistochemical staining reaction (resulting in insufficient intensity in low expressors), as strong expressors (such as most epithelia) will still present with an intense cytoplasmic staining.
Comment Here
Reference: Cytokeratin AE1 / AE3
Comment Here
Reference: Cytokeratin AE1 / AE3
Board review style question #2
Which of the following tumors is predominantly positive for cytokeratin AE1 / AE3?
- Adrenocortical carcinoma
- Aggressive angiomyxoma
- Benign meningioma
- Paraganglioma
- STK11 adnexal tumor
Board review style answer #2
E. STK11 adnexal tumor. 93% of STK11 adnexal tumors present at least some immunoreactivity for CK AE1 / AE3, whereas 72% of aggressive angiomyxomas are negative for CK AE1 / AE3. Nearly all benign meningiomas, 84% of adrenocortical carcinomas and 98% of paragangliomas do not present any immunoreactivity for CK AE1 / AE3.
Comment Here
Reference: Cytokeratin AE1 / AE3
Comment Here
Reference: Cytokeratin AE1 / AE3
Board review style question #3
This tissue was stained for cytokeratin AE1 / AE3. Which is the correct statement?
- The protocol of this immunohistochemical stain should be revised as lymphoid tissue should not show any immunoreactivity for cytokeratin AE1 / AE3
- This axillary lymph node contains isolated tumor cells from an invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast
- This axillary lymph node shows weak to moderate cytoplasmic staining in interstitial reticulum cells with dendritic / reticular pattern
- This immunohistochemical staining pattern is compatible with a nodal histiocytic sarcoma
Board review style answer #3
C. This axillary lymph node shows weak to moderate cytoplasmic staining in interstitial reticulum cells with dendritic / reticular pattern. The tissue shown in the photograph is a normal lymph node. A weak to moderate cytoplasmic staining reaction in the interstitial reticulum cells of a lymph node is normal and therefore the protocol of this stain should not be revised. Normal liver is a better external control tissue than a lymph node, as it contains both low and high expressors of CK AE1 / AE3.
Comment Here
Reference: Cytokeratin AE1 / AE3
Comment Here
Reference: Cytokeratin AE1 / AE3