Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Sample pathology report | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Maccio U. Adipophilin. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsadipophilin.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Monoclonal antibody against a protein of perilipin family on the surface of intracellular lipid droplets (Mod Pathol 2010;23:567)
Essential features
- Monoclonal antibody against a protein of perilipin family used to identify lipid droplets in the cells
- Only a vacuolar / membranous staining pattern is considered positive, whereas granular positivity is nonspecific
- Mainly used as diagnostic marker for sebaceous lesions in combination with other markers
- Positive also in a subset of clear cell renal cell carcinomas
- Adipophilin positivity in other tumors has been associated with worse prognosis (but not routinely used for diagnosis or as biomarker)
Terminology
- Also known as adipocyte differentiation related protein (ADRP) or perilipin 2
Pathophysiology
- Lipid droplets (organelles that store neutral lipids like triglycerides and cholesterol esters) are coated with 1 or more of 5 members of the perilipin family of proteins: perilipin 1, perilipin 2 (adipophilin / ADRP), perilipin 3 (TIP47), perilipin 4 (S3-12) and perilipin 5 (MLDP) (Histopathology 2013;62:617)
- Adipophilin is a 48kDa protein encoded by PLIN2 gene, located on the short arm of chromosome 9 (9p22.1) (NIH: PLIN2 Perilipin 2 [Homo Sapiens (Human)] [Accessed 27 August 2024])
- Transcription regulated by peroxisome proliferator activated receptor (PPAR) subtypes α and δ (Biochim Biophys Acta 2005;1728:95)
- First member of the perilipin family of proteins to emerge during differentiation of adipocytes (J Clin Pathol 2023;76:98)
- Affects the level of key enzymes and lipids to maintain the structure and function of lipid droplets
- Plays role in the process of fatty acids passing through the cell membrane and the formation of lipid droplets in the cytoplasm
- Mainly expressed on the membrane of adipose precursor cells and the surface of lipid droplets in adipose cells during differentiation
- Controls intracellular lipid accumulation by maturation in cells involved in synthesis of sebum and steroid hormones
- Stable only when associated with lipid droplets, otherwise degraded through ubiquitin proteasome pathway
- Adipophilin is a marker of early adipocyte differentiation and lipid deposition in other cells (e.g., macrophages) as demonstrated by immunofluorescence and electron microscopy
- During pathology processing, most of the lipid droplets are dissolved in xylene, while adipophilin is retained in tissue cells (J Clin Pathol 2023;76:98)
Interpretation
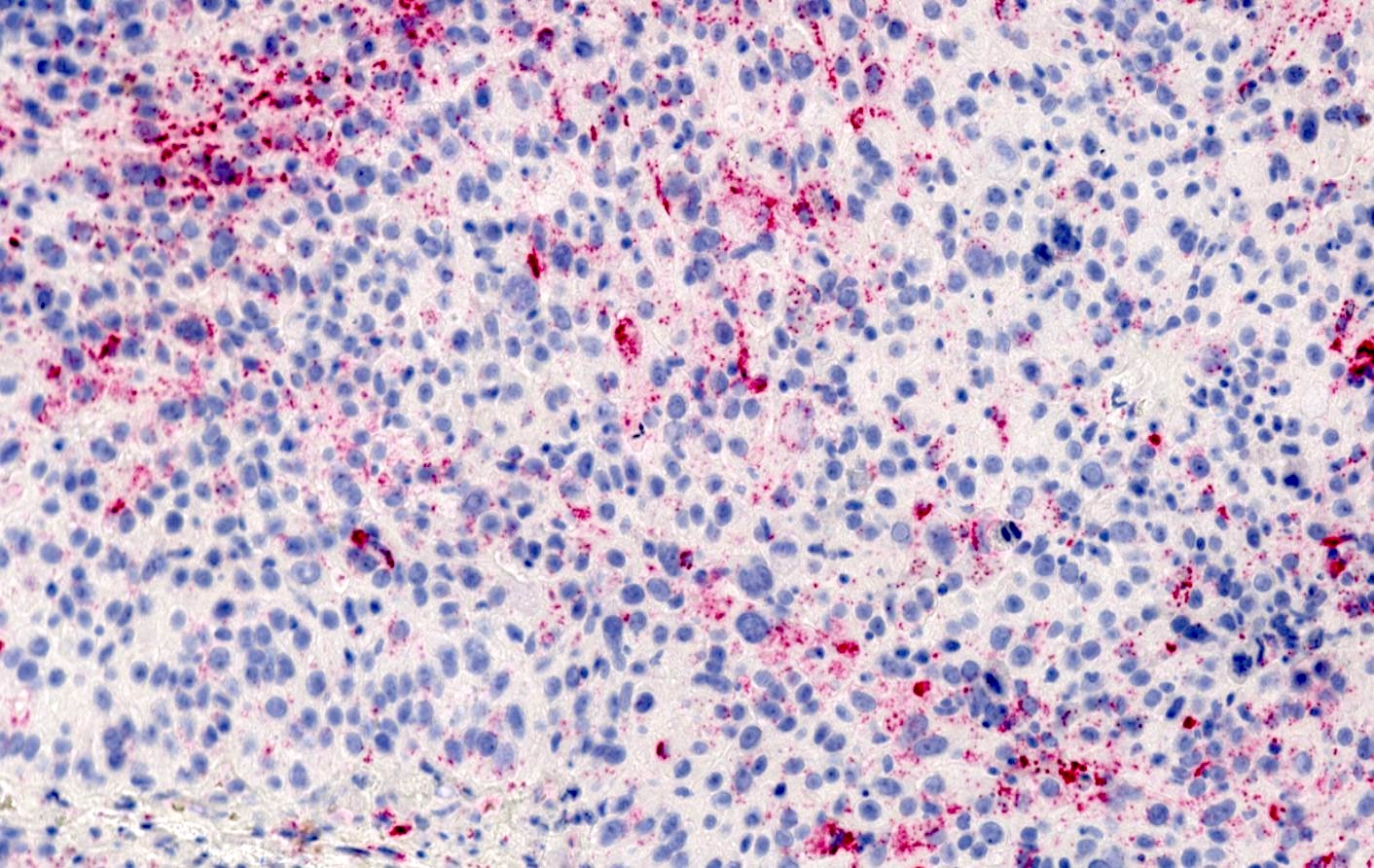
- Cytoplasmic staining
- Vacuolar / membranous staining pattern (membranous staining around intracytoplasmic lipid vesicles)
- Granular staining (i.e., uptake by keratohyalin granules or in cytoplasm of macrophages) is considered nonspecific / negative
- Staining intensity and pattern may vary from mature sebaceous neoplasms (intense and foamy) to less differentiated sebaceous carcinomas (weak and punctate staining)
- Reference: Mod Pathol 2010;23:567
Uses by pathologists
- Differential diagnosis of skin tumors with foamy or clear cell morphology (e.g., sebaceous carcinoma versus clear cell squamous cell carcinoma) (Mod Pathol 2010;23:567)
- Caveat: not useful if a differential diagnosis is clear cell renal cell carcinoma (see Positive staining - disease)
Prognostic factors
- Adipophilin expression has been correlated with aggressive clinical behavior in certain types of tumors (Histopathology 2017;70:232)
- Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) (PLoS One 2020;15:e0242563)
- Adipophilin expression in TNBC is associated with high rate of relapse
- Cutaneous malignant melanoma (Lab Invest 2020;100:727)
- Adipophilin expression is associated with poor metastasis free survival, disease specific survival and overall survival rates
- Lung adenocarcinoma (J Pathol Transl Med 2018;52:357)
- Adipophilin expression in solid subtype is associated with shorter overall and progression free survival
- Pancreatic adenocarcinoma (Pancreatology 2019;19:443)
- Adipophilin expression is associated with high grade histology, high CA19-9 level, R1 status and shorter overall and progression free survival
- Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (Clin Cancer Res 2007;13:152)
- Adipophilin expression is possibly correlated with better cancer specific survival, low stage and low grade histology
- Salivary duct carcinoma (Virchows Arch 2020;477:291)
- Adipophilin expression is associated with shorter overall and progression free survival and more aggressive histopathology
- Liposarcoma (J Clin Pathol 2023 May 31 [Epub ahead of print])
- Adipophilin expression is associated with shorter overall survival in myxoid liposarcoma and dedifferentiated liposarcoma
- Hepatoblastoma (Histol Histopathol 2021;36:1169)
- Adipophilin expression may predict better prognosis
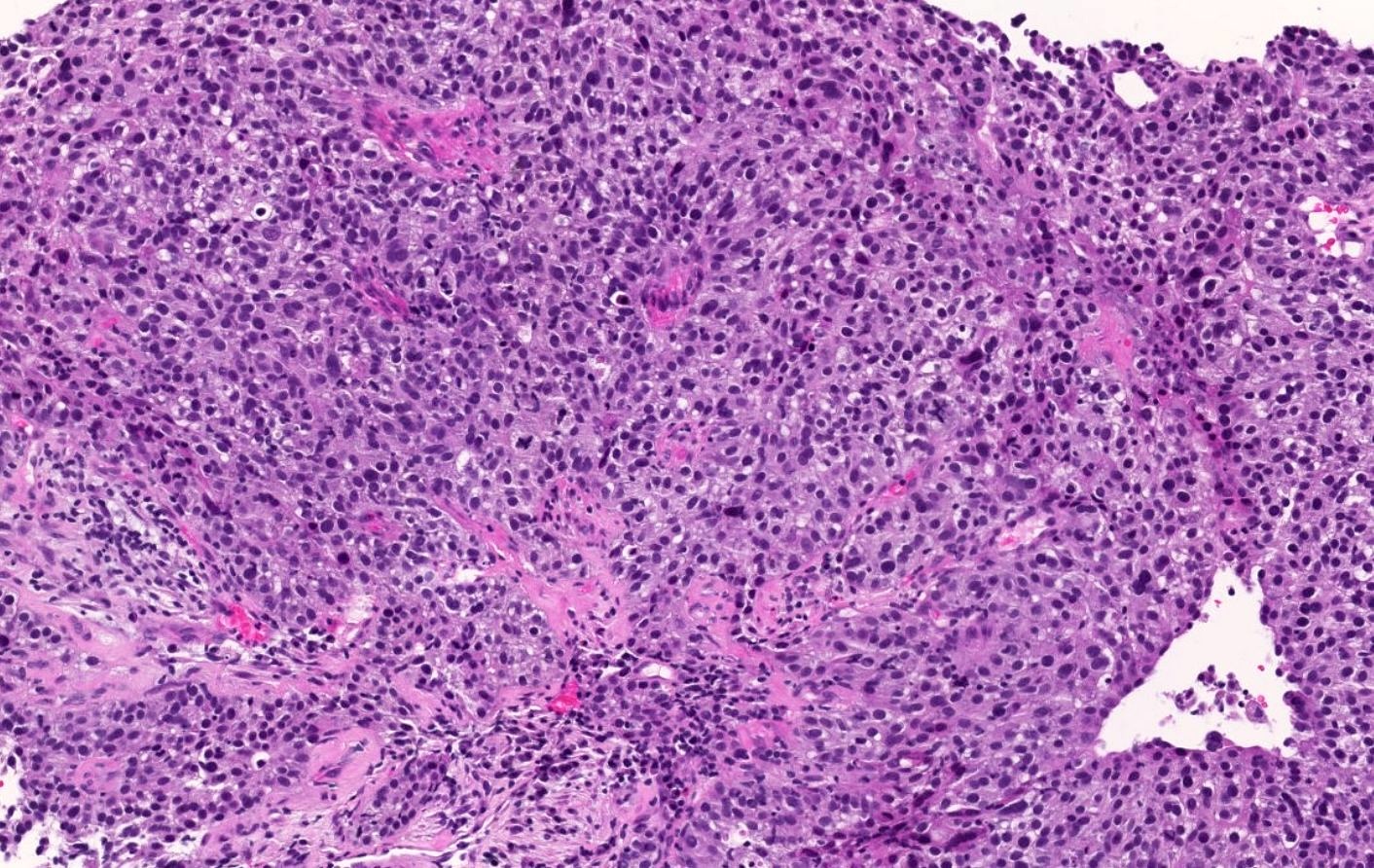
Microscopic (histologic) description
- See Interpretation
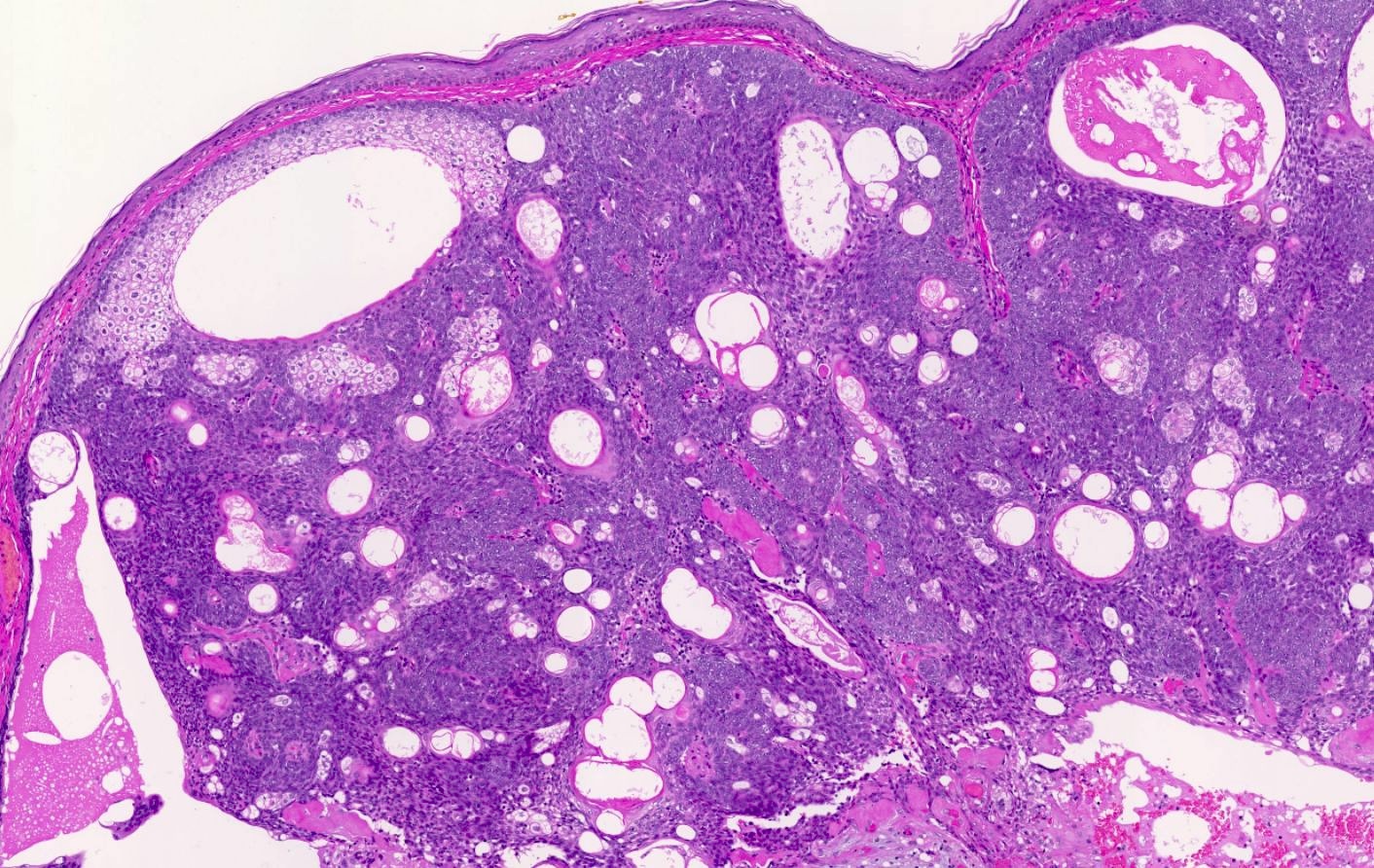
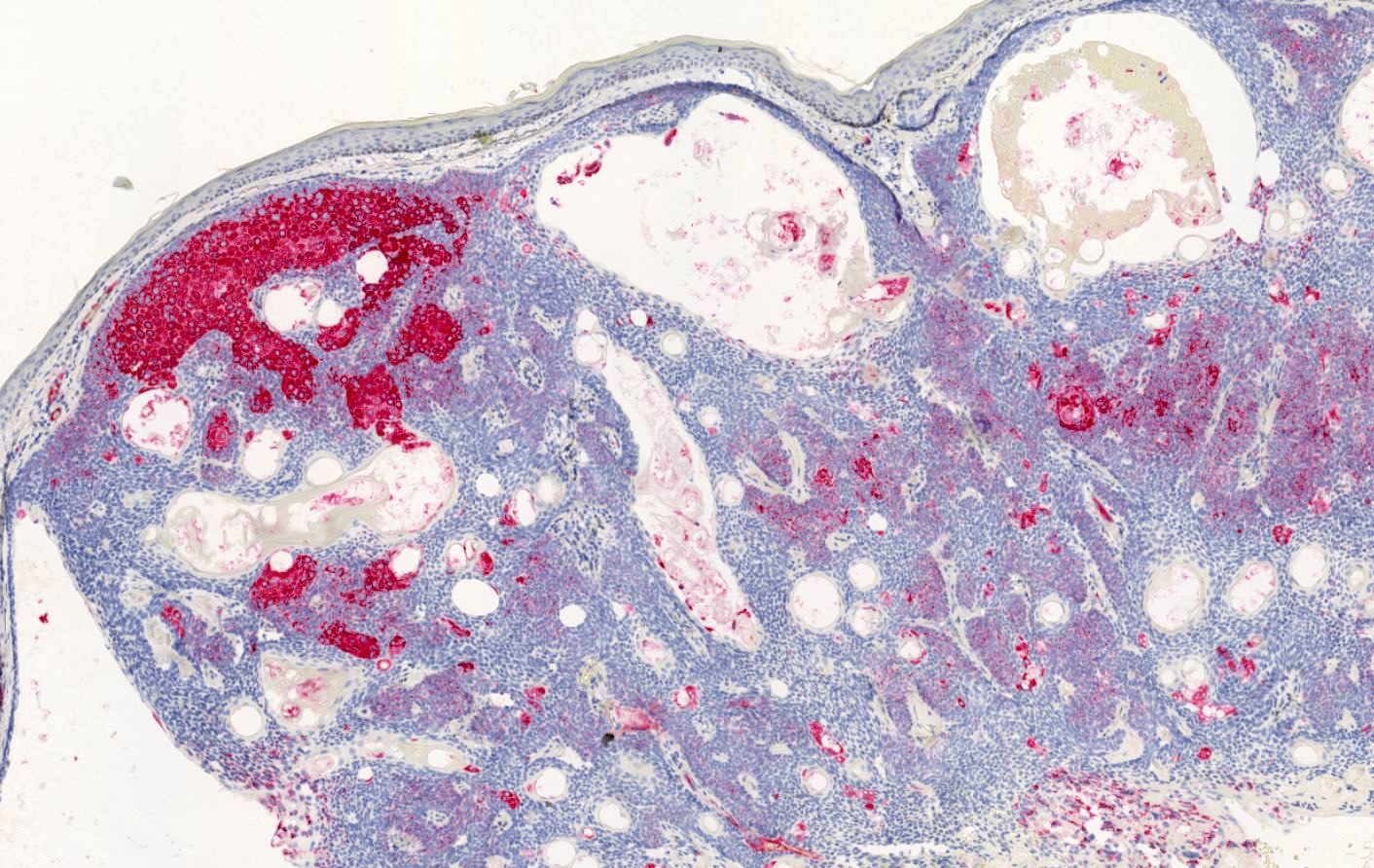
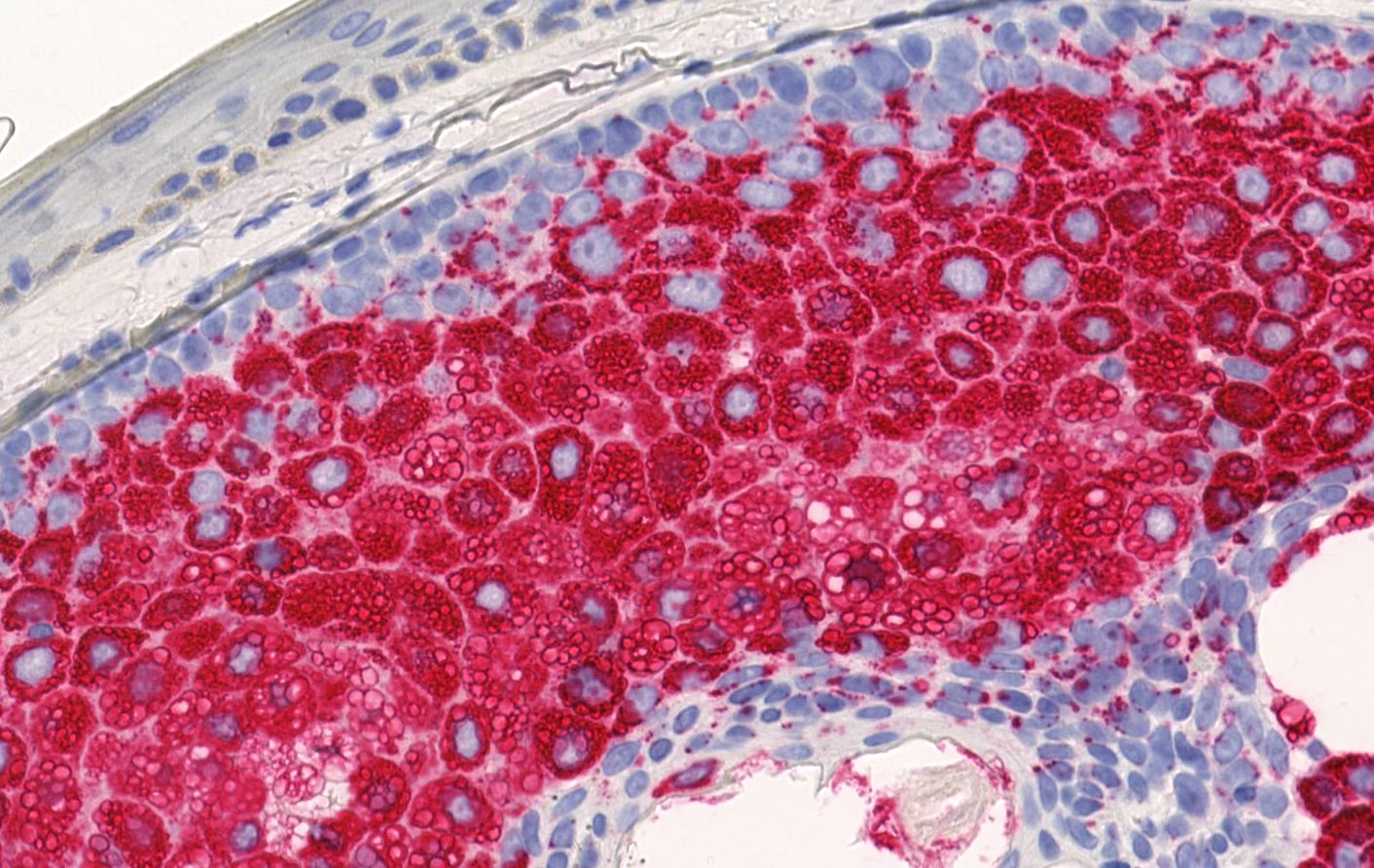
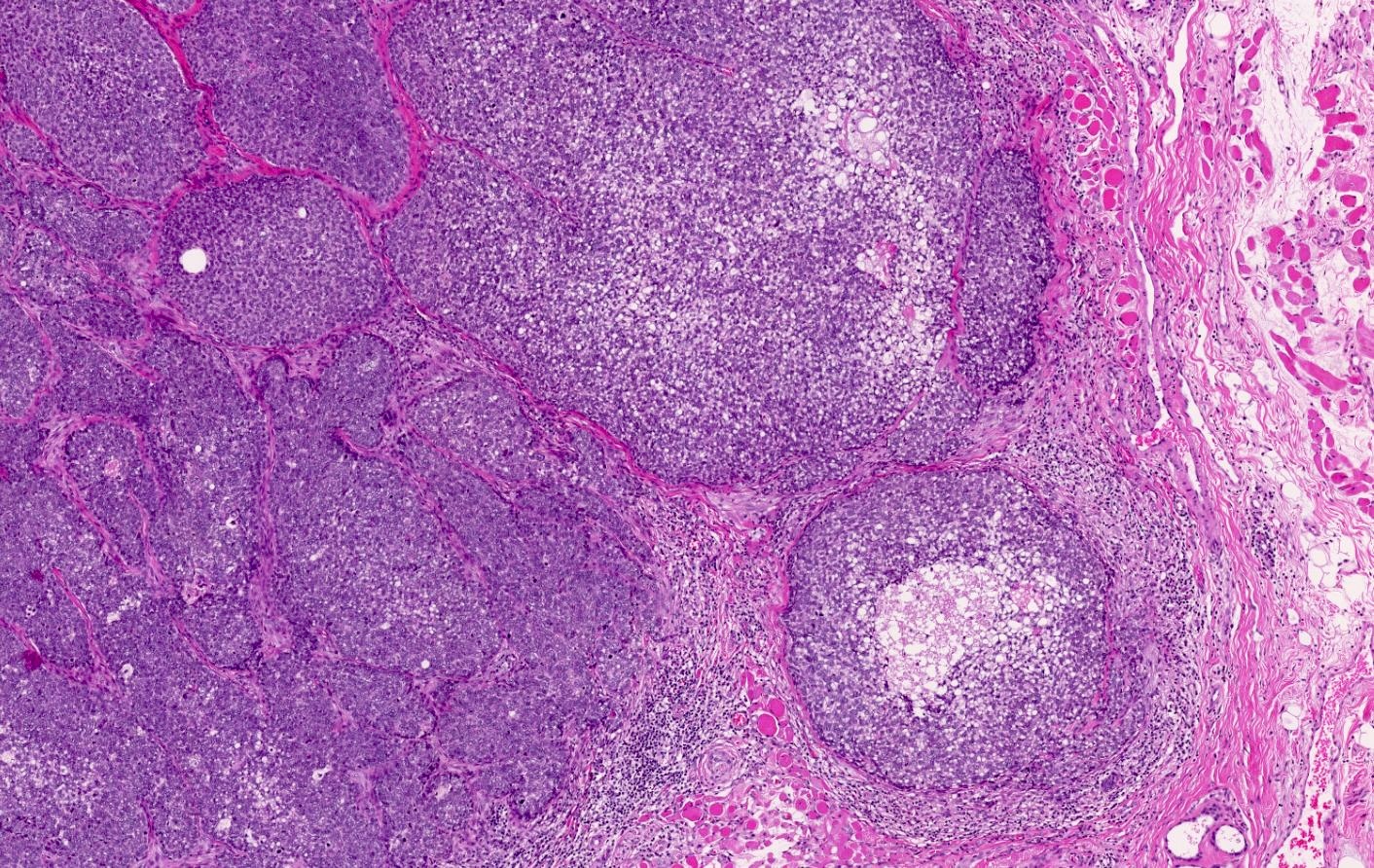
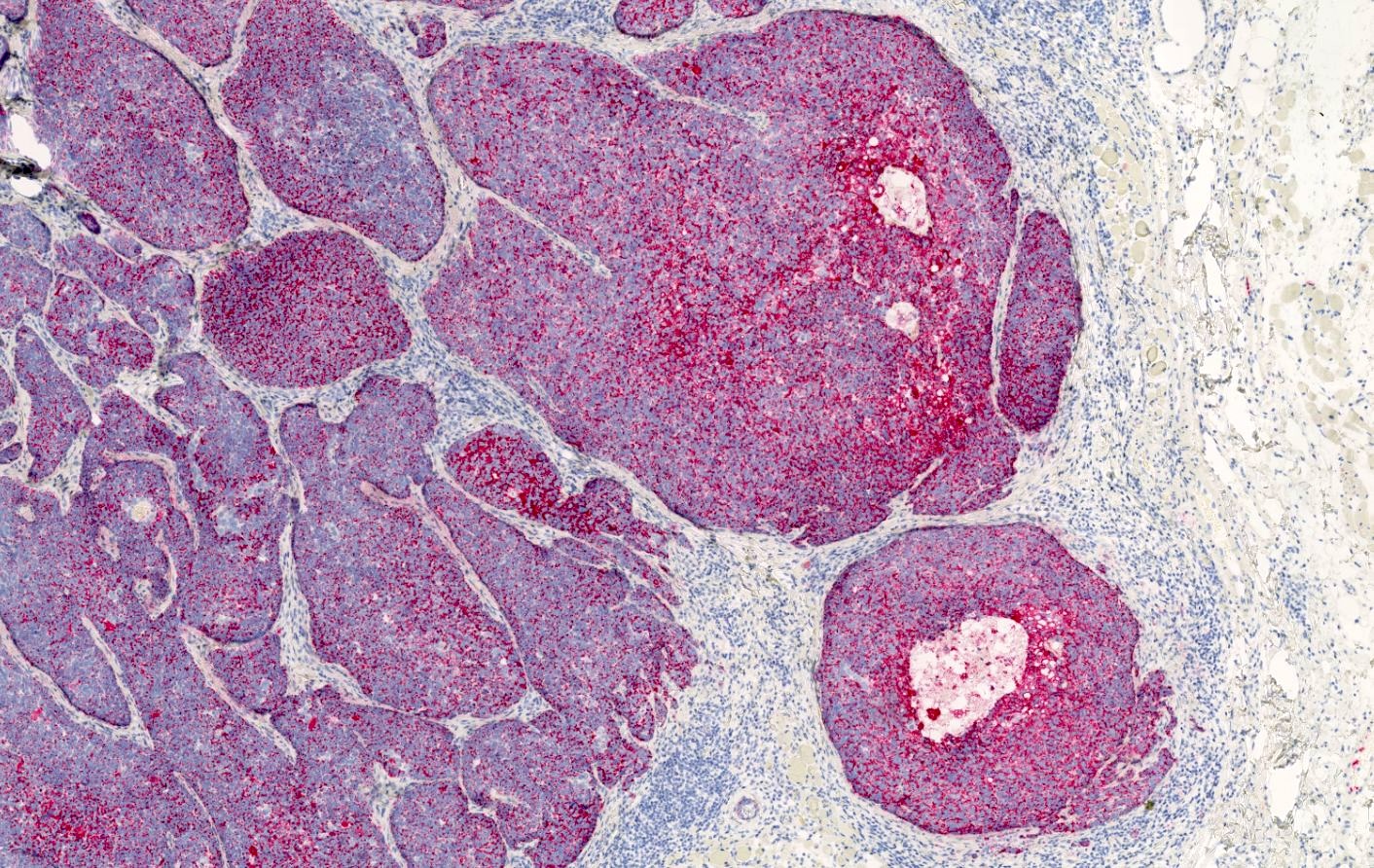
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
- Lactating mammary epithelium (Cell Tissue Res 1998;294:309)
- Adrenal cortex
- Sertoli and Leydig cells
- Steatotic hepatocytes
Positive staining - disease
- Tumors with sebaceous differentiation (Mod Pathol 2010;23:567)
- Sebaceoma (100%)
- Sebaceous adenoma (100%)
- Sebaceous carcinoma (92%)
- Metastatic clear cell carcinoma of the kidney (62.5%) (J Cutan Pathol 2010;37:1193)
- Hepatocellular carcinoma with fatty changes (Pathol Int 2020;70:199)
- Adrenocortical carcinoma (Lipids Health Dis 2017;16:83)
- Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type (NST) with lipid rich pattern (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:861)
- Xanthelasma (100%) (Mod Pathol 2010;23:567)
- Xanthogranuloma (90%) (Mod Pathol 2010;23:567)
- Liposarcoma (88%) (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2021;29:152)
- Malignant apocrine and eccrine tumors (58%) (Hum Pathol 2013;44:1811)
- Tumors with ameloblastic differentiation (ameloblastoma and ameloblastic carcinoma) (J Oral Pathol Med 2021;50:708)
Negative staining
- Squamous cell carcinoma (Mod Pathol 2010;23:567)
- Basal cell carcinoma (Mod Pathol 2010;23:567)
- Hidradenoma (Mod Pathol 2010;23:567)
- Melanocytic nevus (balloon cell) (Mod Pathol 2010;23:567)
- Mucinous carcinomas of the skin (J Cutan Pathol 2018;45:886)
Sample pathology report
- Eyelid, excision biopsy:
- Sebaceous carcinoma (see comment)
- Comment: Histopathological examination reveals a lesion composed of polygonal cells with atypical pleomorphic nuclei and abundant intracytoplasmic vacuoles imparting a foamy appearance. Mitotic figures are easily identified. Centrally in the lesion, an area of comedo-like necrosis is found. On immunohistochemical examination, the tumor cells express pancytokeratin, adipophilin (vacuolar / membranous staining pattern) and AR. PAX8, S100, HMB45 and SOX10 are negative with adequate on slide control. There is loss of MSH2 and MSH6 expression with adequate expression of MLH1 and PMS2. This pattern suggests a sebaceous carcinoma with microsatellite instability. Notably, sebaceous carcinomas can be associated with genetic syndromes on the Lynch syndrome spectrum (e.g., Muir-Torre syndrome), so genetic counseling is recommended.
Additional references
Board review style question #1
An ulcerated tumor in upper eyelid underwent excision. Histology of the lesion (H&E) is shown above. What combination of immunohistochemical markers would be consistent with the diagnosis of sebaceous carcinoma?
- Adipophilin+, AR-, PAX8+
- Adipophilin+, AR+, PAX8-
- Adipophilin-, AR+, PAX8-
- Adipophilin-, AR-, PAX8-
Board review style answer #1
B. Adipophilin+, AR+, PAX8- would be the typical combination expected in the case of a sebaceous carcinoma. Answer A is incorrect because adipophilin can also be positive in up to 62.5% of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. In combination with positive staining for PAX8, the diagnosis would be more consistent with clear cell renal carcinoma (rather than with sebaceous carcinoma). Answer C is incorrect because positive staining for adipophilin would be expected in sebaceous carcinoma. Additionally, positive staining for AR alone is nonspecific and may occur in many tumors (e.g., prostate cancer, apocrine carcinoma, etc.) and should be further investigated with other markers. Answer D is incorrect because negative results for all of those markers may suggest another diagnosis (e.g., squamous cell carcinoma) that needs to be verified by other markers.
Comment Here
Reference: Adipophilin
Comment Here
Reference: Adipophilin
Board review style question #2
Which of the following statements about adipophilin is correct?
- In a cutaneous lesion, positivity for adipophilin can distinguish between a sebaceous carcinoma and a metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Indicates the presence of lipids in the cells and may help in the diagnosis of tumors with clear cell morphology, although it is not specific for sebaceous differentiation
- It is a sensitive and specific diagnostic marker for sebaceous lesions
- Tumors with adipophilin expression have a better prognosis in general, so adipophilin can be used a marker for favorable prognosis
Board review style answer #2
B. Indicates the presence of lipids in the cells and may help in the diagnosis of tumors with clear cell morphology, although it is not specific for sebaceous differentiation. Adipophilin indicates the presence of intracellular lipids and can be helpful in identifying tumors with clear cell morphology but it is not specific for sebaceous differentiation and can be seen in a variety of lipid containing tumors. Answer C is incorrect because while adipophilin is a useful marker for identifying lipid droplets in sebaceous lesions, it is not entirely specific or sensitive. It can also be positive in other types of tumors that contain lipid, such as clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Answer A is incorrect because adipophilin positivity is insufficient to distinguish between sebaceous carcinoma and clear cell renal cell carcinoma metastasis. Both tumor types can stain positive for adipophilin. Answer D is incorrect because adipophilin expression has been linked in many studies to a worse prognosis and is not routinely used as a prognostic marker. Its main role is in identifying lipids within cells rather than indicating prognosis.
Comment Here
Reference: Adipophilin
Comment Here
Reference: Adipophilin