Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Cai C. Acid phosphatase. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsacidphosphatase.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Acid phosphatase is not a single enzyme but rather a group of enzymes that hydrolyze and release phosphate group from different substrates
- By definition, they function best in an acidic environment and are normally localized in the lysosomes (Mol Pathol 2002;55:65)
- In muscle biopsies, the acid phosphatase stain is an enzyme histochemical stain that relies on endogenous acid phosphatase activity in the muscle specimen to hydrolyze the artificial naphthol AS-B1 phosphate substrate into naphthol, producing a brick red reaction product (Dubowitz: Muscle Biopsy: A Practical Approach, 4th Edition, 2013)
- Therefore, the acid phosphatase stain must be performed on cryosections of snap-frozen fresh muscle tissue
- Acid phosphatase should be differentiated from the antibody based immunohistochemical stains Prostatic Acid Phosphatase (PAP or PSAP) and Tartrate Resistant Acid Phosphatase (TRAP)
- PAP is a marker for prostate cancer (Biochem Mol Biol Int 1994;33:567)
- TRAP is a marker for osteoclasts (Calcif Tissue Int 1982;34:285)
Essential features
- In muscle biopsies, acid phosphatase stain is mainly used to highlight macrophages, red rimmed vacuoles in inclusion body myositis, lysosome storage disorders and other hereditary or acquired vacuolar myopathies associated with abnormal lysosomal activity
Terminology
- Nonspecific acid phosphatase(s)
Interpretation
- Lysosomes
Uses by pathologists
- Highlights degenerating fibers and macrophages (Dubowitz: Muscle Biopsy: A Practical Approach, 4th Edition, 2013)
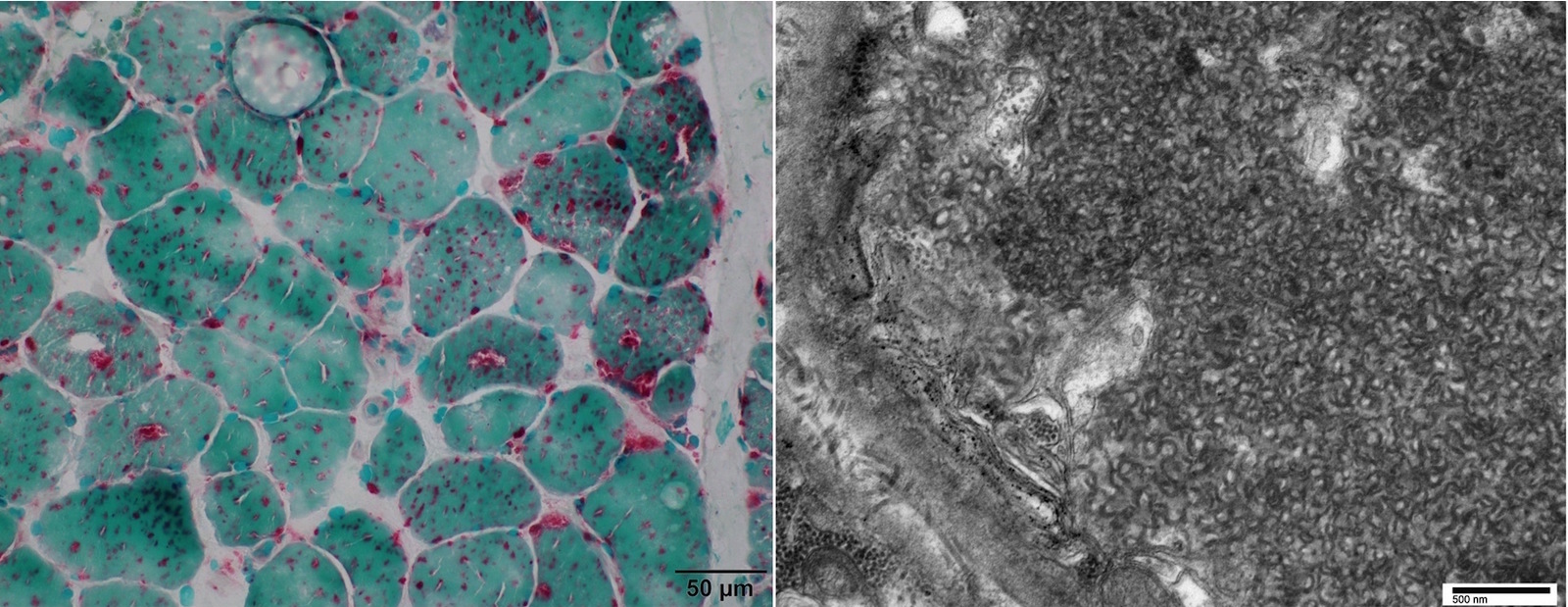
- Detects muscle disorders with lysosomal abnormalities, including lysosomal storage diseases and variable hereditary or acquired vacuolar myopathies associated with lysosomal dysfunction or excessive autophagic activity; see disease specific references under Positive staining - disease section
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Staining of lipofuscin in myofiber is punctate granular, predominantly subsarcolemmal (Dubowitz: Muscle Biopsy: A Practical Approach, 4th Edition, 2013)
- Staining of lysosomes or lysosomal vacuoles in myofiber is punctate and predominantly sarcoplasmic; see disease specific references under Positive staining - disease section
- Staining of degenerating myofibers and paraspinal myofibers is a weak diffuse blush in the sarcoplasm
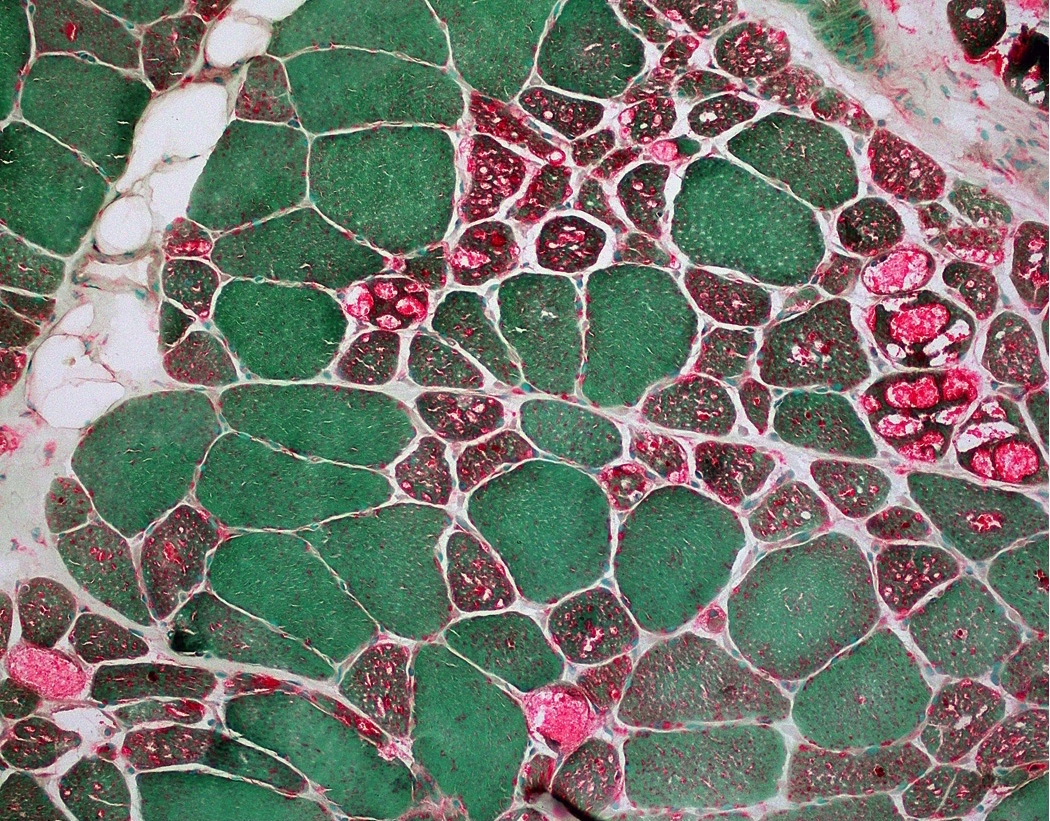
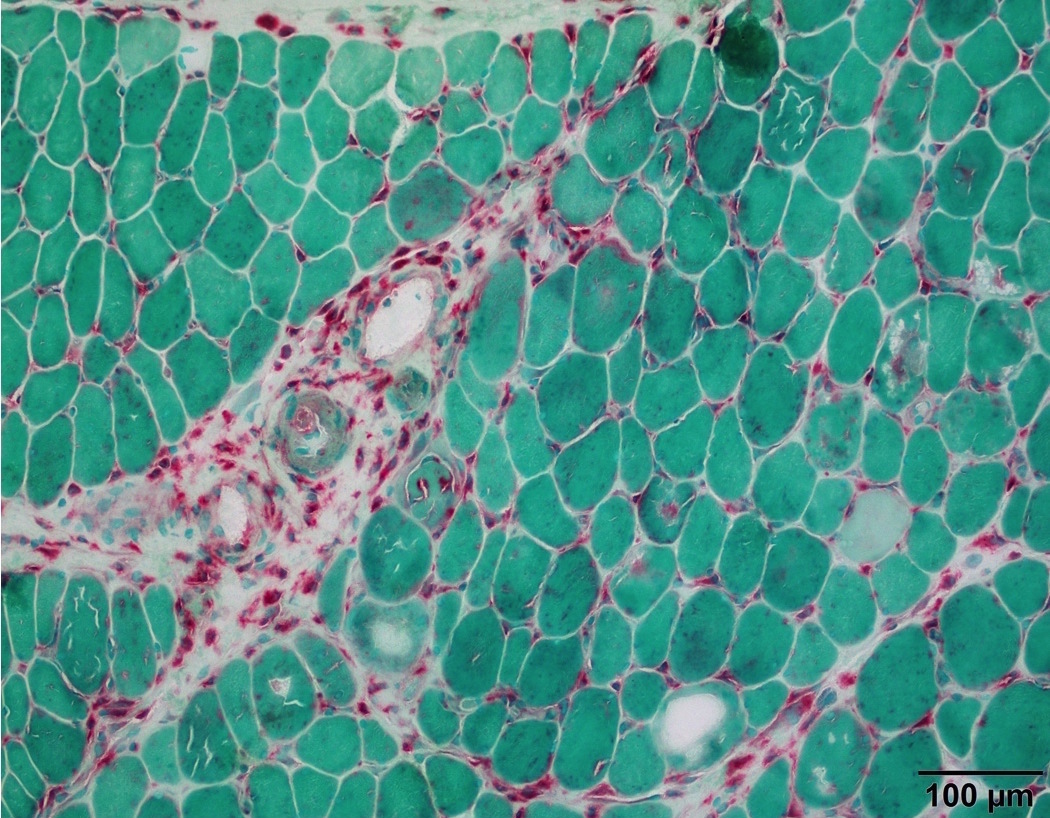
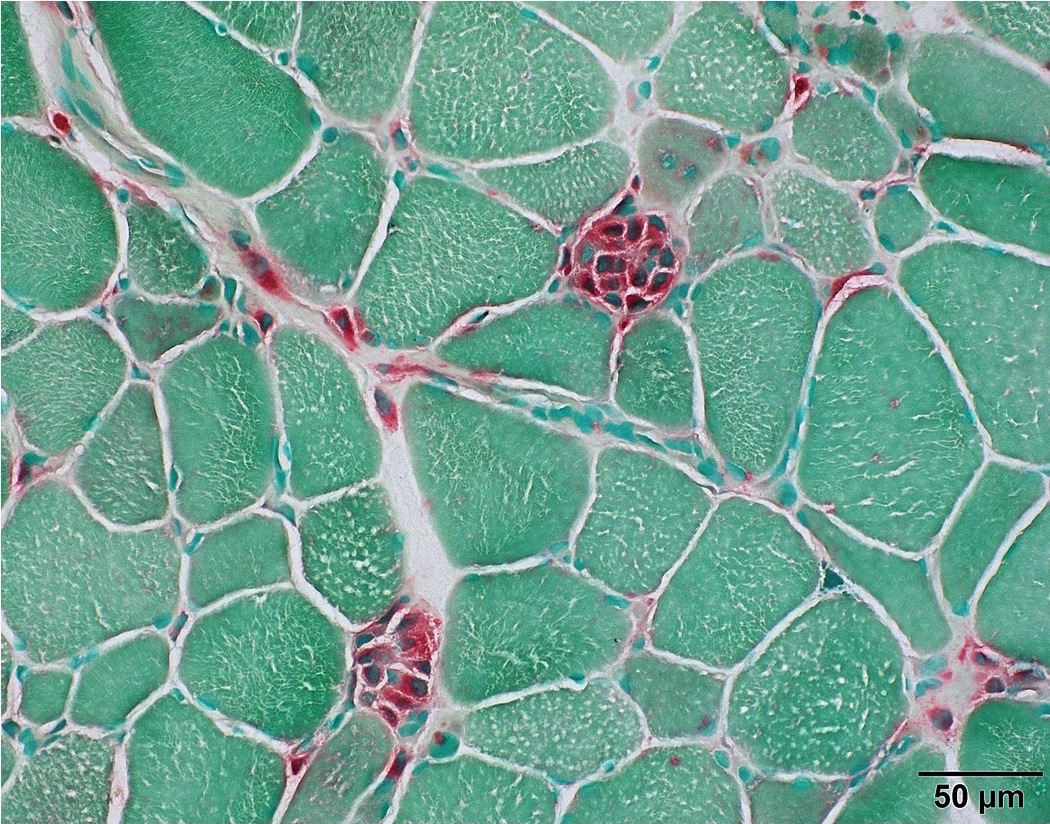
- Staining of macrophages is strong cytoplasmic
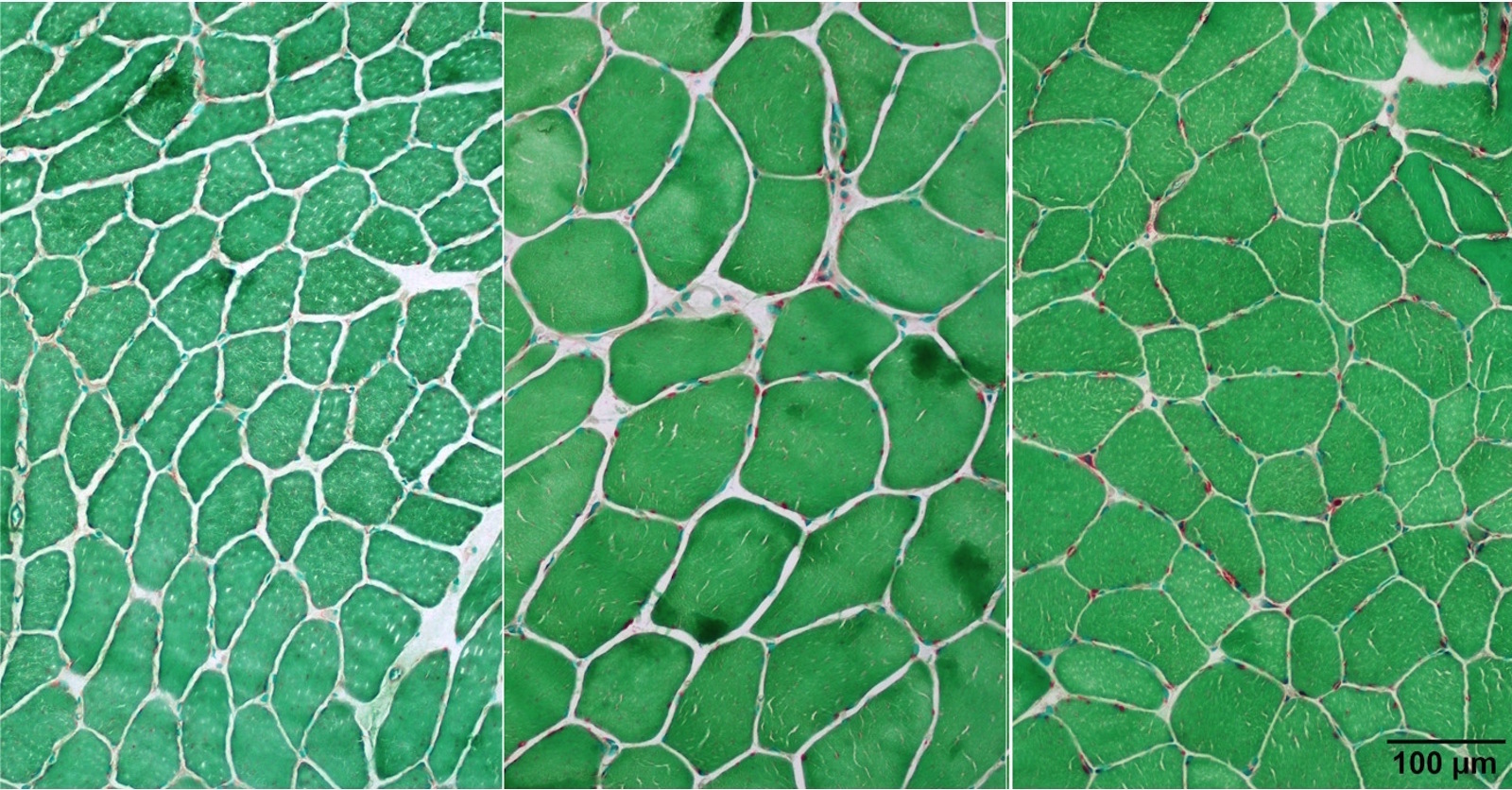
Microscopic (histologic) images
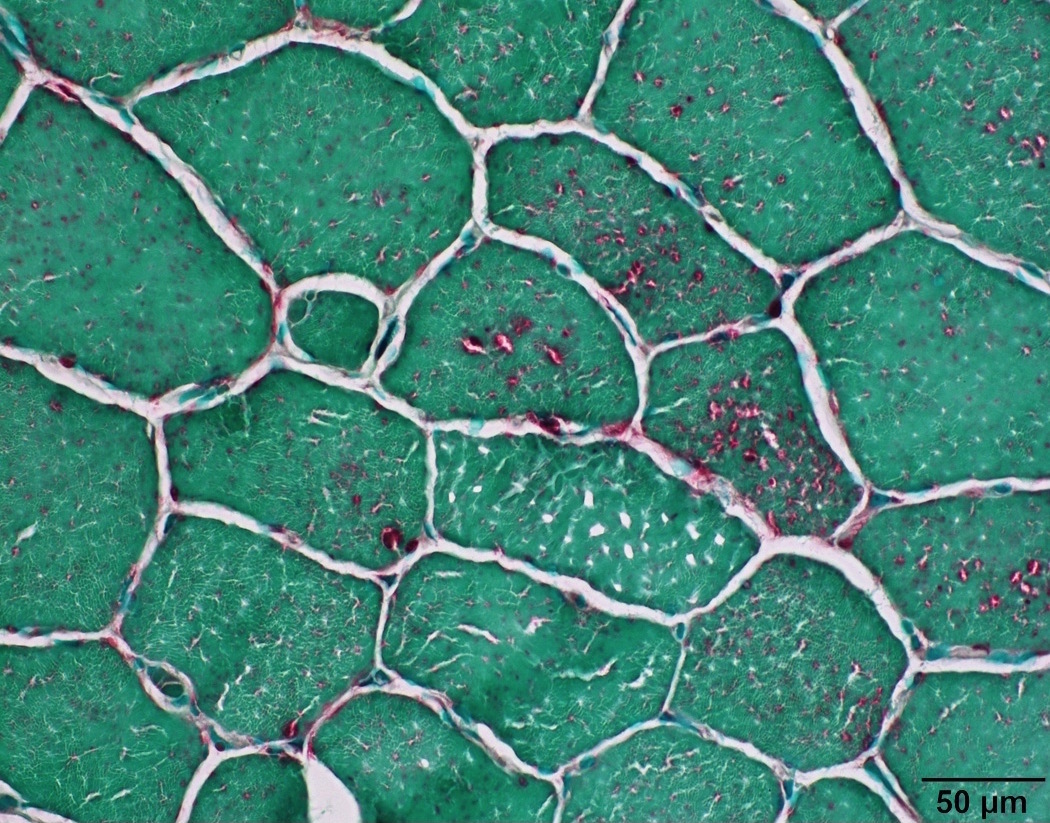
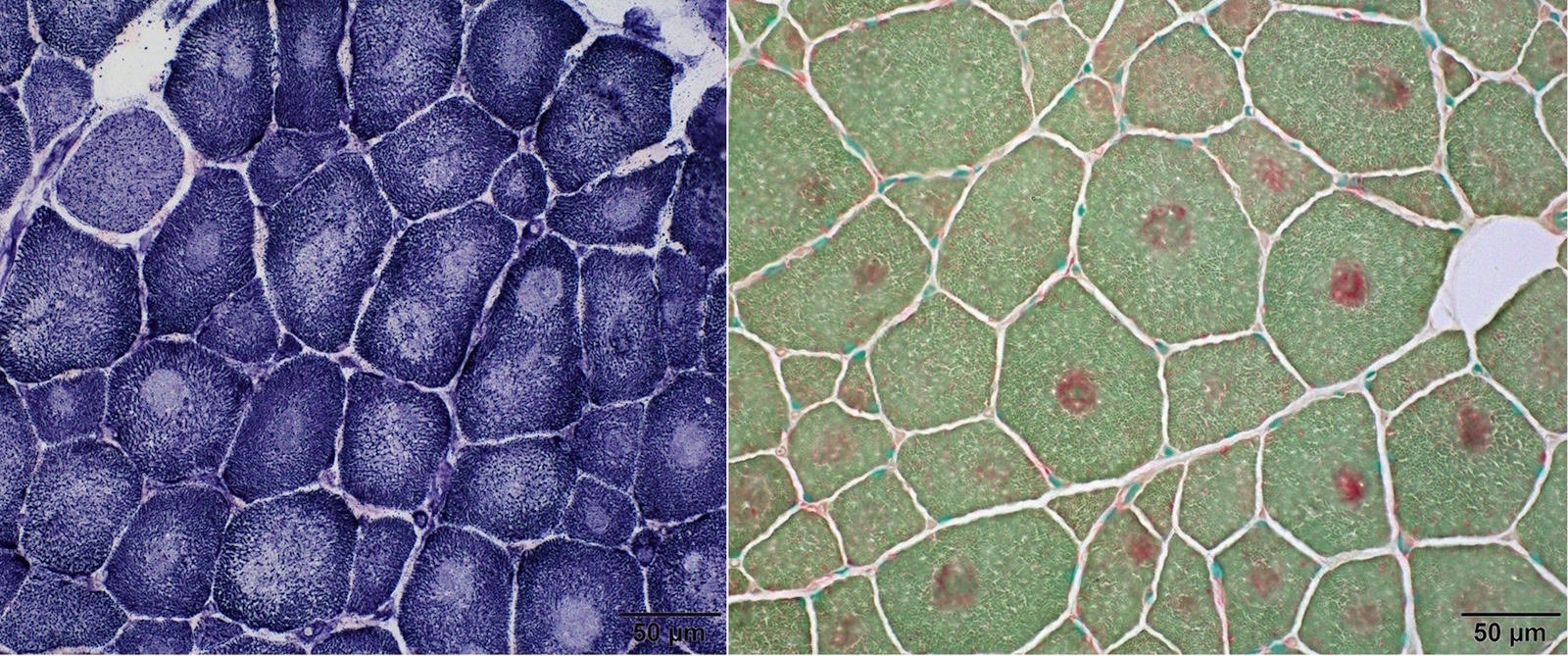
Positive staining - normal
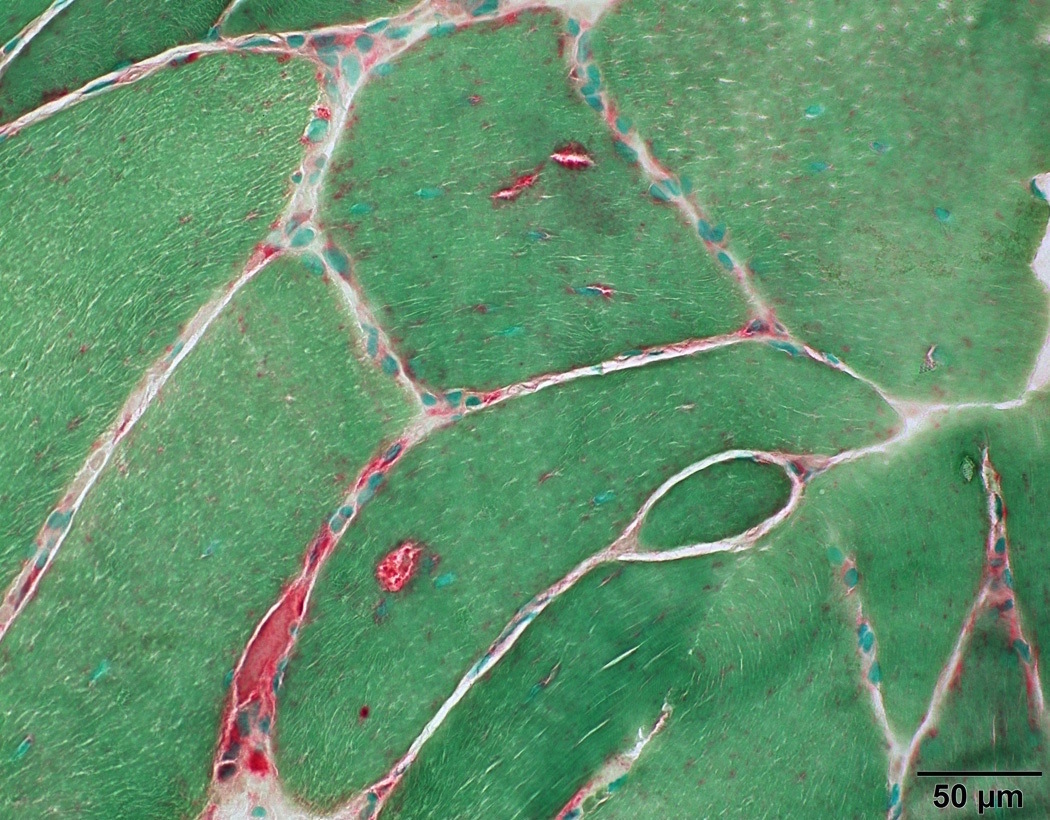
- Stains lysosomes in myofibers, which are inconspicuous in normal fibers
- Stains lipofuscin in muscle fibers, which are usually subsarcolemmally located and increase with age
- Increased in paraspinal muscles (Muscle Nerve 2015;52:45)
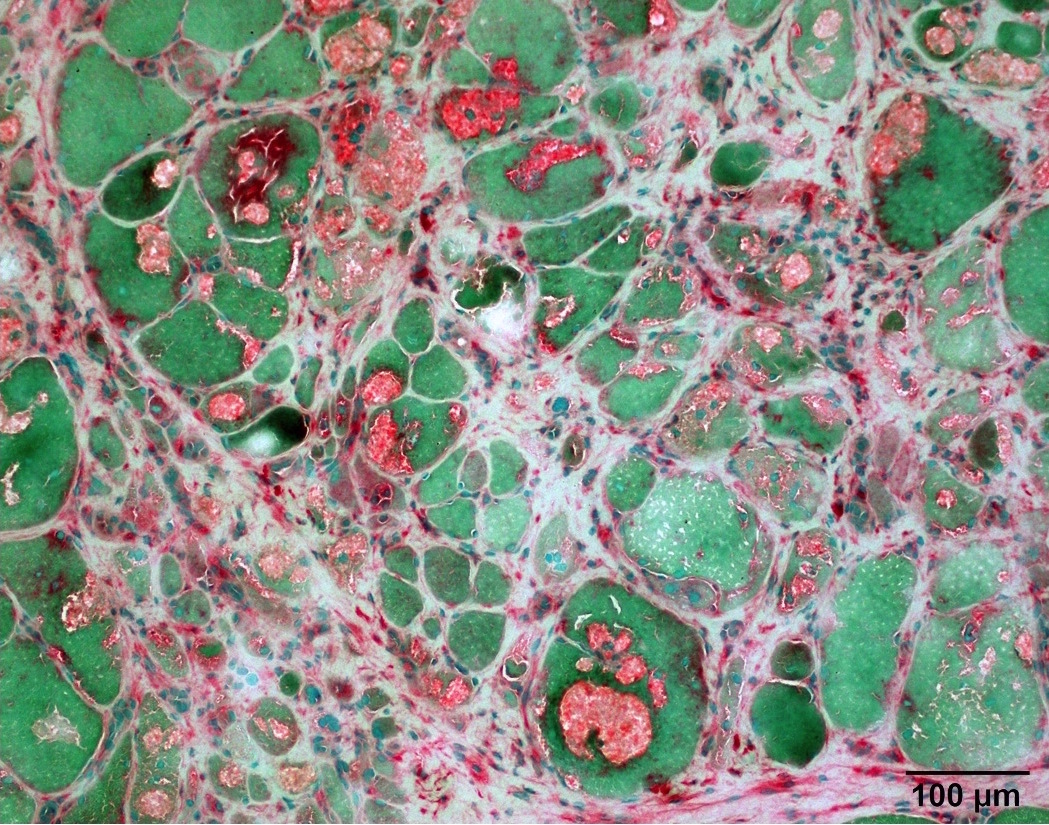
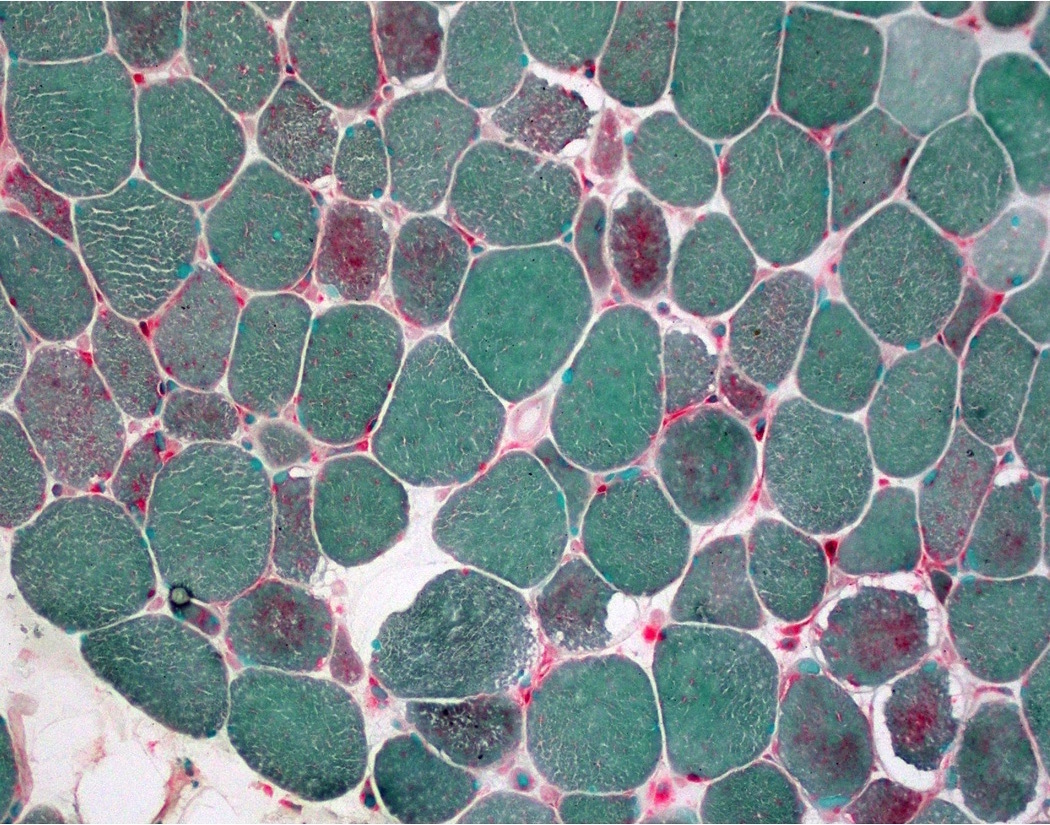
Positive staining - disease
- Degenerating and regenerating myofibers (J Neurol Sci 1977;33:95)
- Macrophages (Muscle Nerve 1995;18:242)
- Rimmed vacuoles in inclusion body myositis (Ann Neurol 1988;23:258)
- Acid maltase deficiency/Pompe disease/Glycogen storage disease type II (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2014;2:2)
- Vacuoles in cystinosis distal vacuolar myopathy (Ann Neurol 1994;35:181)
- Vacuoles in X-linked myopathy with excessive autophagy (XMEA) (Biomed Res Int 2018;2018:5069042)
- Vacuoles in Danon disease (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2005;64:513)
- Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine induced myopathy (Am J Med 1987;82:447)
- Colchicine induced myopathy (Acta Neuropathol 2002;103:100)
- Chronic vitamin E deficiency (Ann N Y Acad Sci 1982;393:84)
Negative staining
- Other types of glycogen storage diseases besides acid maltase deficiency (GSD II) (J Clin Neurosci 2015;22:1674)
Board review style question #1
- Which of the following components in muscle fiber stains acid phosphatase?
- Lipid droplet
- Lysosome
- Mitochondria
- Myosin filament
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Board review style answer #1