Table of Contents
Definition / general | Case reports | Clinical features | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normalCite this page: Obeng, R. TSC1 and TSC2. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsTSC1/2.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- TSC1 (hamartin) and TSC2 (tuberin) are tumor suppressor genes in chromosomes 9 and 16 respectively
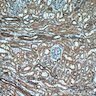
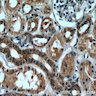
- TSC1 and TSC2 are expressed in a wide variety of normal tissues including skeletal muscle, brain, heart, liver, lung, kidney, pancreas, placenta, biliary epithelium, fibroblasts, lymphocytes
- TSC1 complexes with and stabilizes TSC2 resulting in the activation of the GTPase function of TSC2 and the negative regulation of the mTOR signaling pathway (Nat Cell Biol 2002;4:648, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002;99:13571, Am J Hum Genet 2001;68:64)
- Mutations in TSC1 or TSC2 lead to autosomal dominant inheritance of tuberous sclerosis complex with hamartomatous lesions in many tissues and organs
- Mutations in TSC2 are more common than mutations in TSC1
- Mutations in TSC2 also tend to lead to a more severe clinical phenotype than mutations in TSC1
Case reports
- Tuberous sclerosis, immunohistochemistry expression of tuberin and hamartin (Fetal Pediatr Pathol 2004;23:241)
- Gastric adenocarcinoma in association with tuberous sclerosis (Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J 2009;9:75)
- Dissociate expression of tuberous sclerosis complex 1 product hamartin in a skin and pulmonary lesion (Hum Pathol 2009;40:430)
Clinical features
- Expression of TSC1 has also been associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer (Eur J Cancer 2005;41:1628)
- Tuberin may play an important role in pathogenesis of sporadic fundic gland polyps (Mod Pathol 2002;15:862)
- Reduction or loss of staining of TSC2 is associated with uterine leiomyomas (Mod Pathol 2005;18:179)
Positive staining - normal
- Skeletal muscle, brain, heart, liver, lung, kidney, pancreas, placenta, biliary epithelium, fibroblasts, lymphocytes