Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Sample pathology report | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Ellis A, Zhang L. PAX5. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsPAX5.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- 1 of 9 paired box transcription factors (NIH: PAX5 Paired Box 5 [Homo Sapiens (Human)] [Accessed 18 April 2022])
- Involved in the differentiation and maturation of lymphoid progenitor cells into B cells, development of the nervous system and spermatogenesis
Essential features
- Nuclear marker expressed in most mature and immature B cell neoplasms
- Especially useful when the B cell neoplasm does not express CD20 (such as in classic Hodgkin lymphoma, B lymphoblastic leukemia / lymphoma or status post rituximab therapy)
- Not expressed in plasma cells due to repression by BLIMP1
- Variable expression in Merkel cell carcinoma, small cell carcinoma, rectal neuroendocrine tumors and acute myeloid leukemia with t(8;21)(q22;q22)
Terminology
- Also known as B cell lineage specific activator protein (BSAP)
Pathophysiology
- Encoded by PAX5 at 9q13
- Paired box transcription factors have a novel, highly conserved DNA binding motif and regulate early tissue development
- Activates B cell specific genes and represses genes specific for other hematopoietic lineages (Oncogene 2012;31:966)
- Regulates distinct target genes in early and late B cell development (EMBO J 2012;31:3130)
- Activates expression of factors required for the BCR signaling pathway (Med Oncol 2015;32:360)
- Critical regulator of human primordial germ cell development (Nat Cell Biol 2018;20:655)
Interpretation
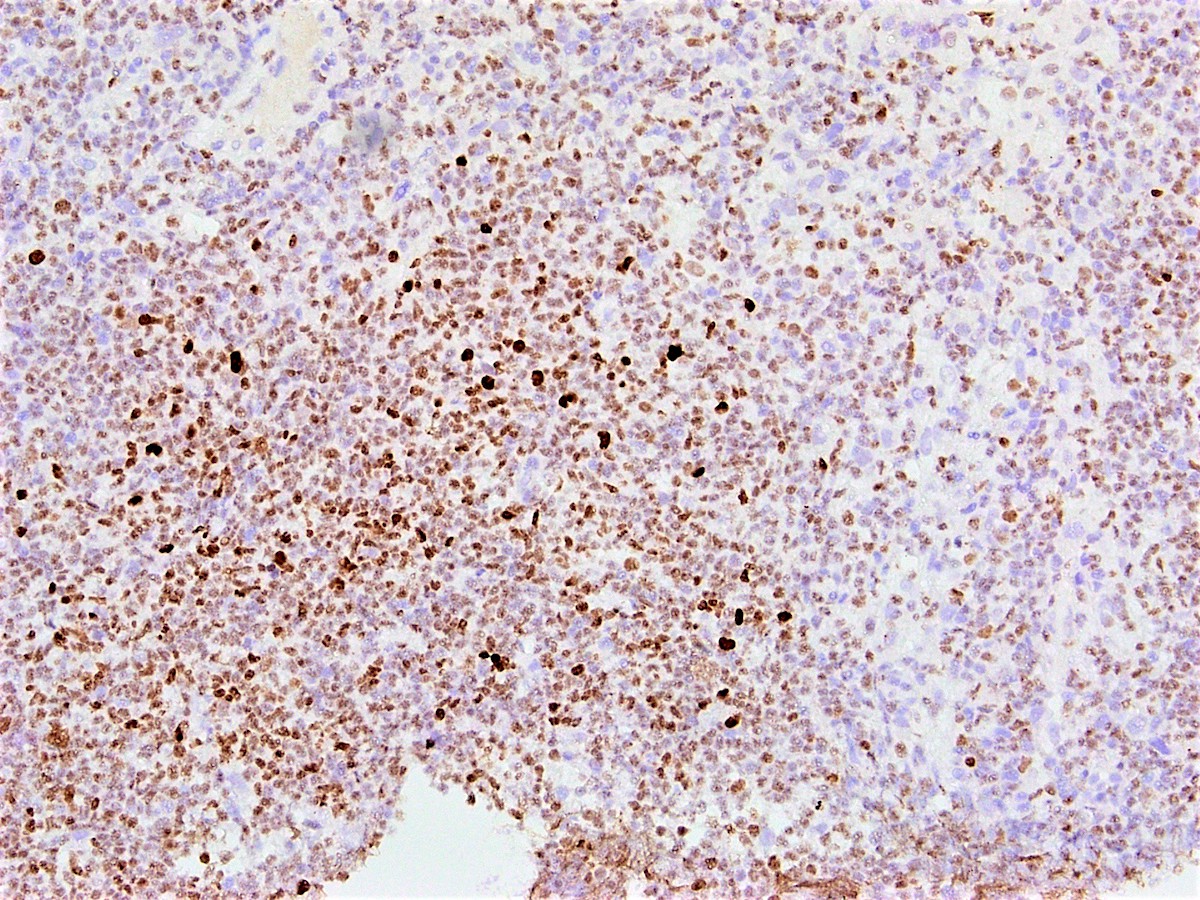
- Nuclear stain
Uses by pathologists
- Identification of mature and immature B cell neoplasms
- Determining B cell lineage in lymphomas that lack CD20 expression
- Reference: Adv Anat Pathol 2007;14:323
Prognostic factors
- Expression may be associated with aggressive clinical course in olfactory neuroblastoma (Pol J Pathol 2016;67:130)
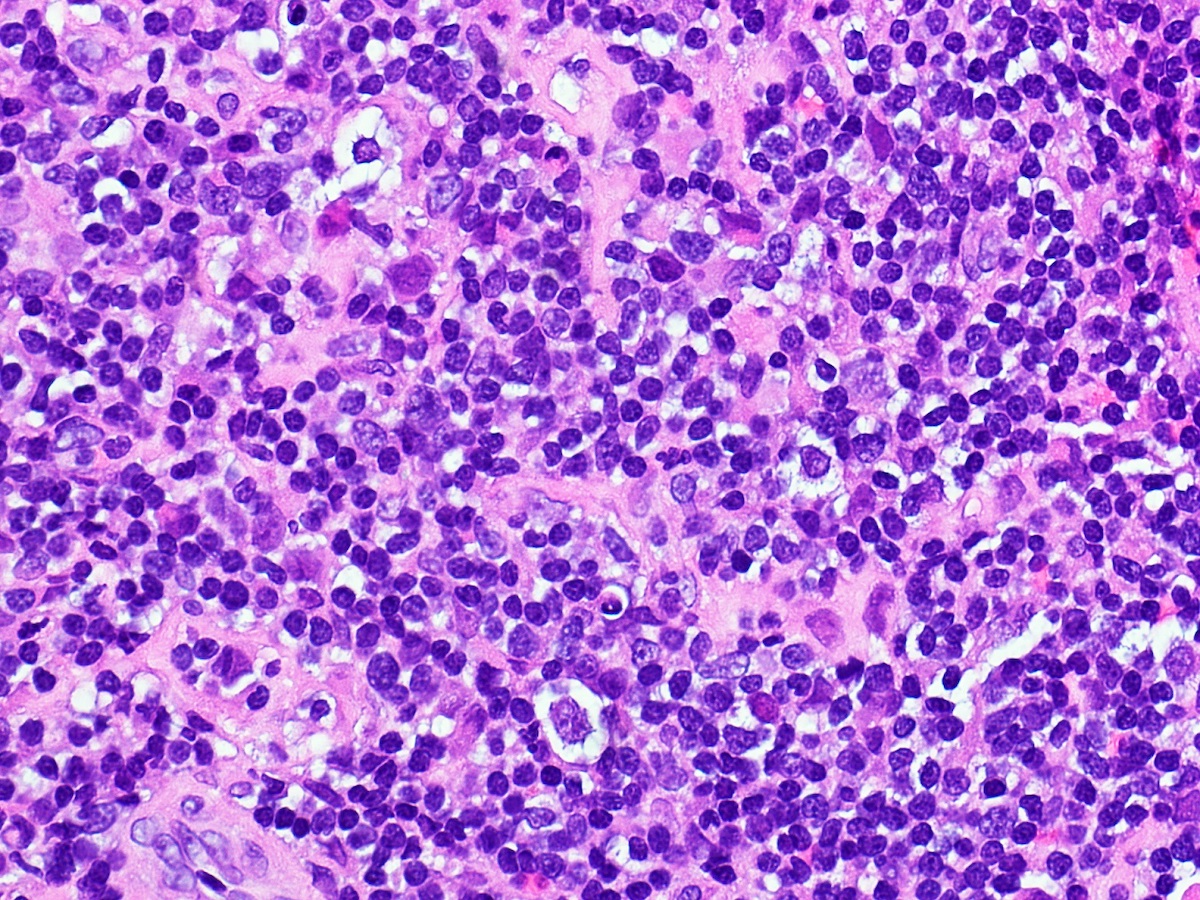
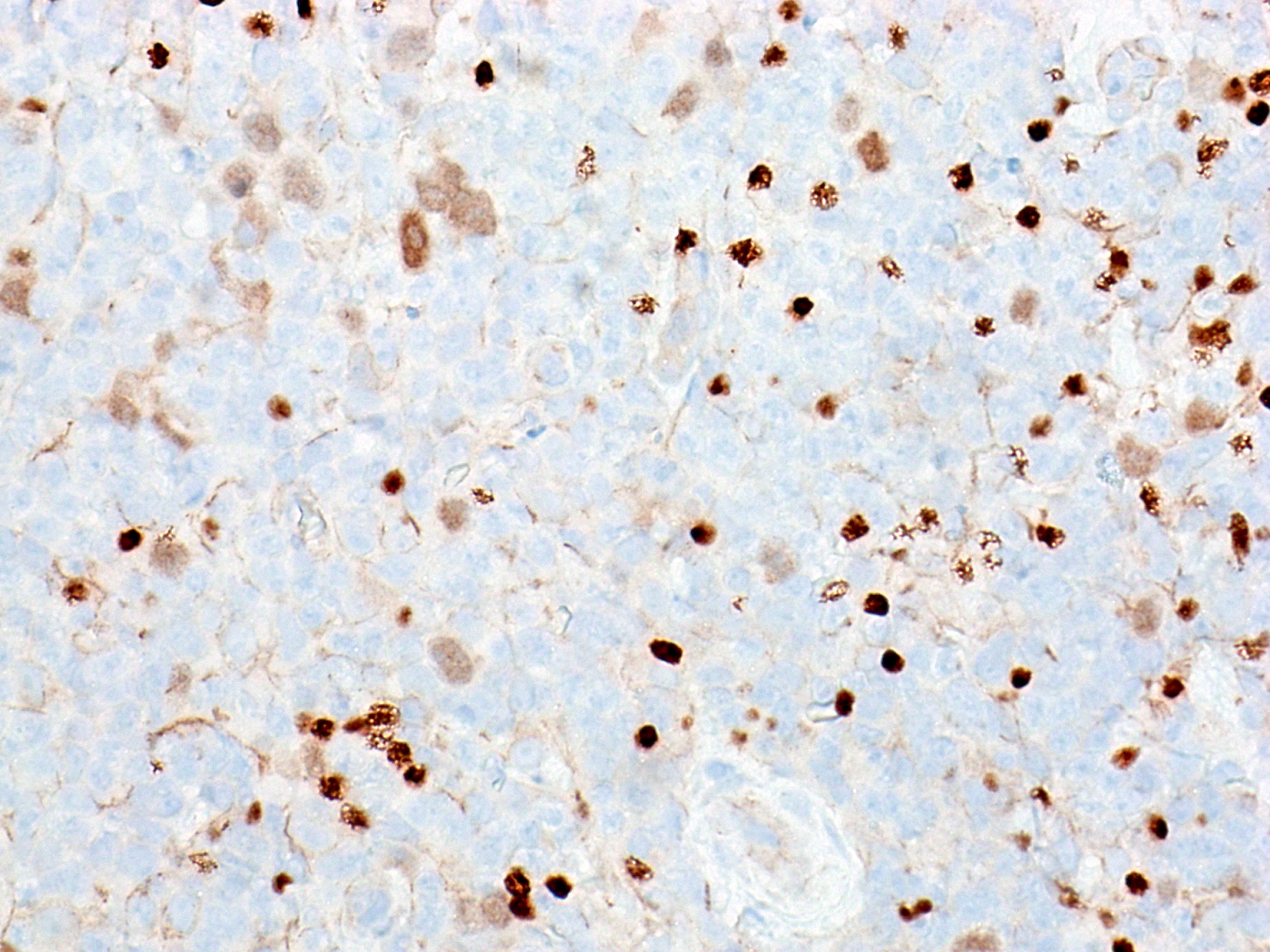
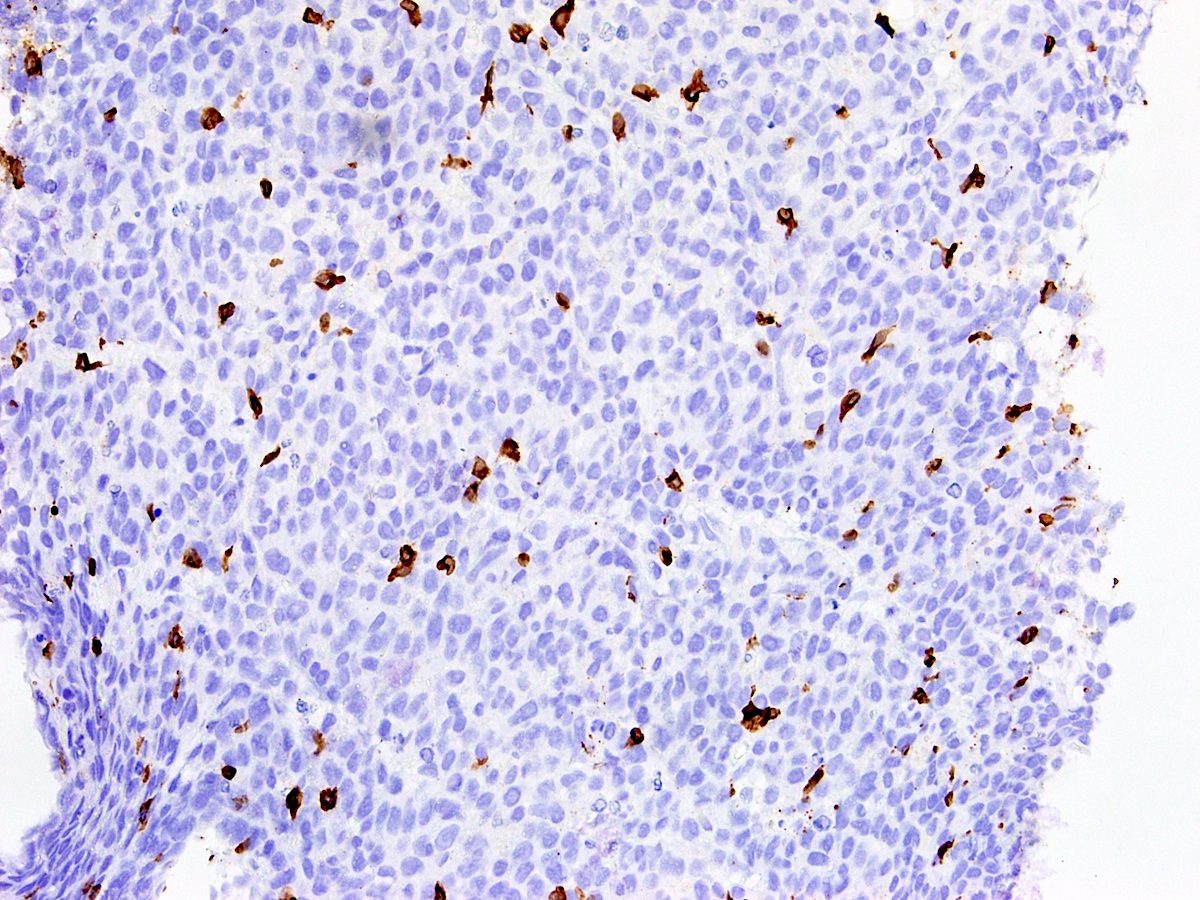
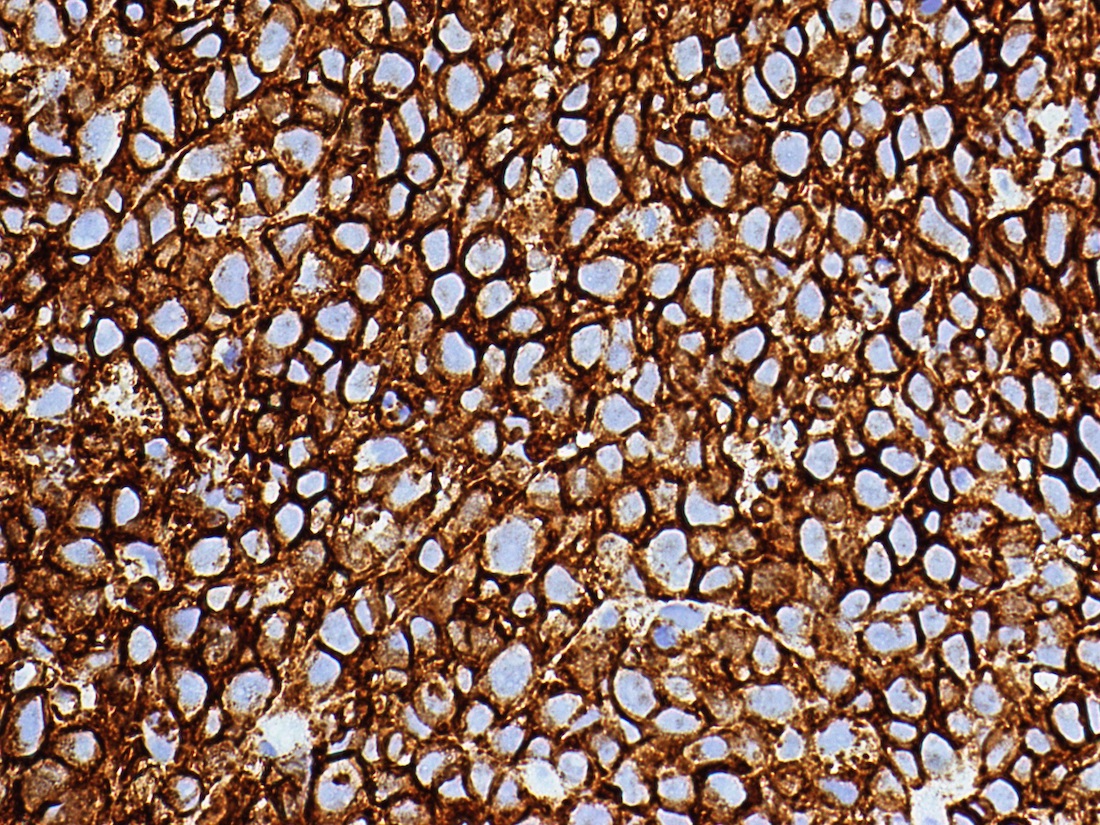
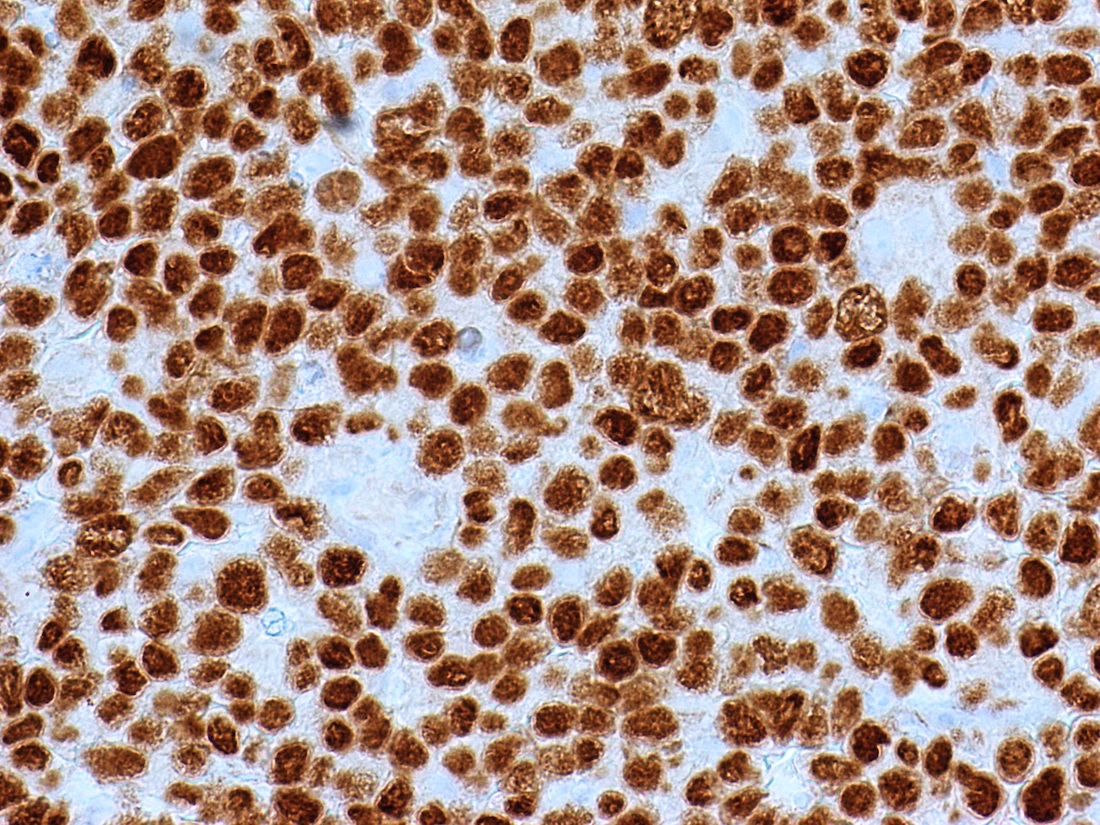
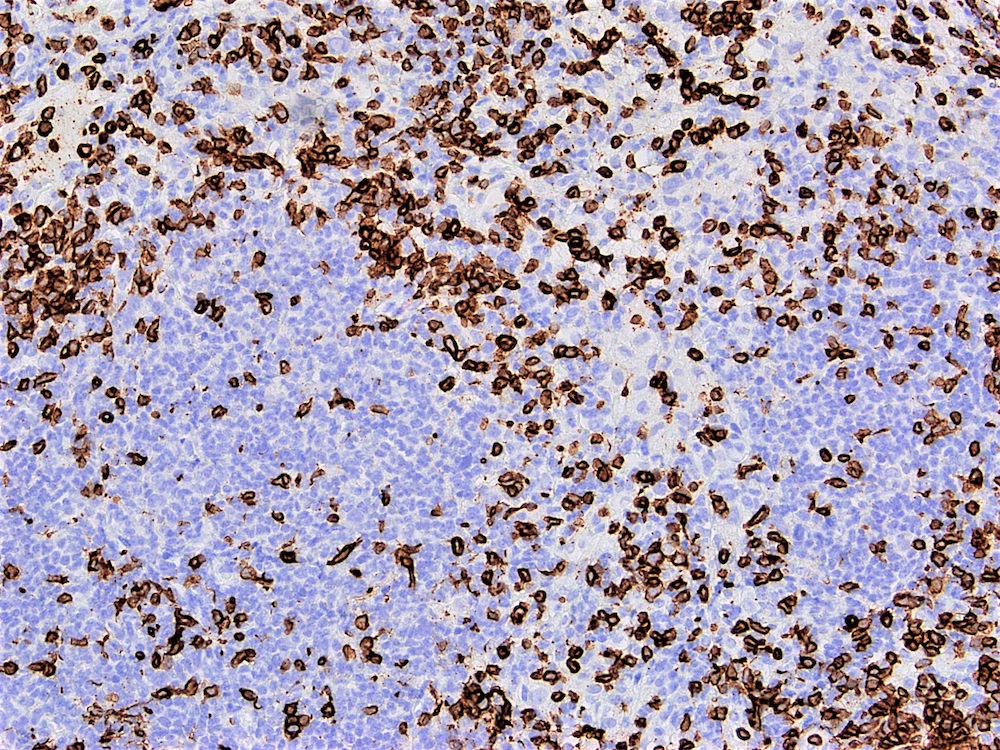
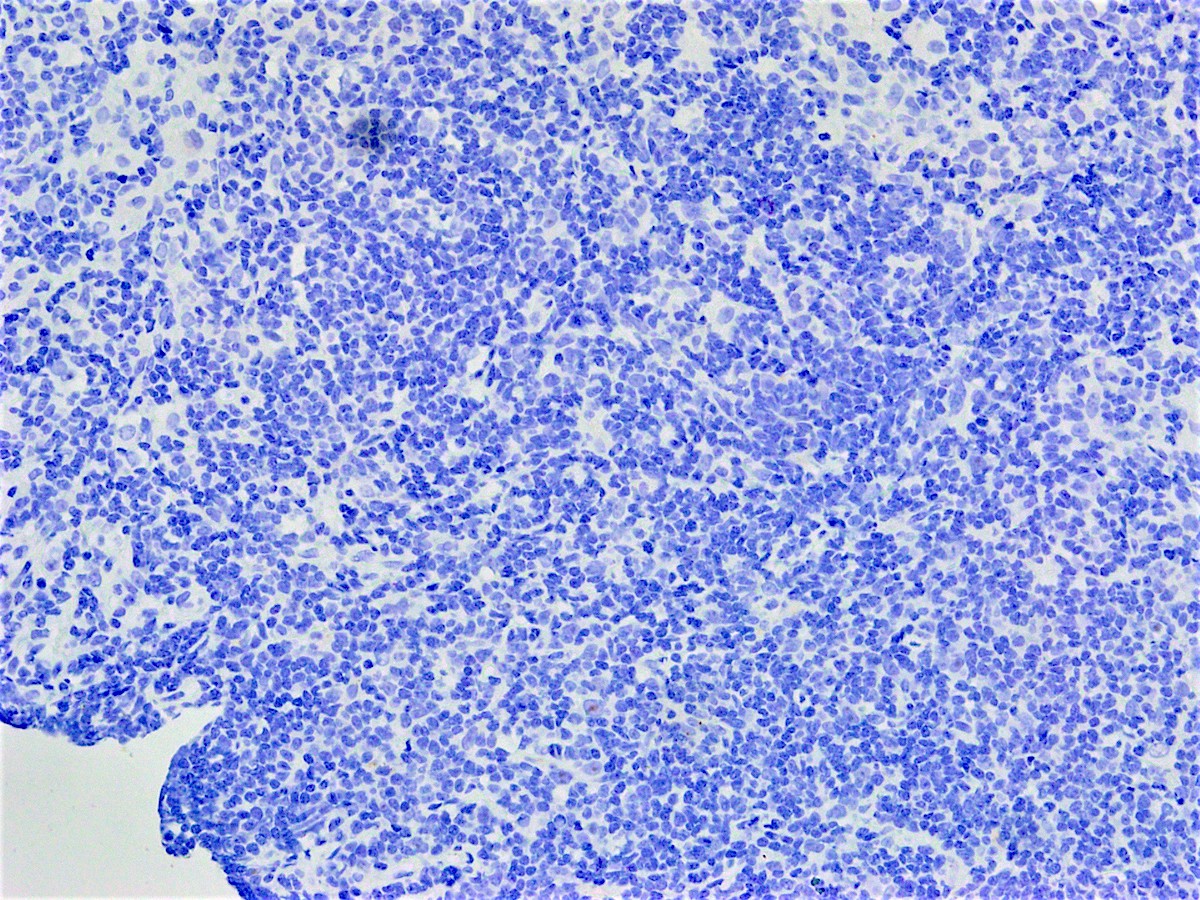
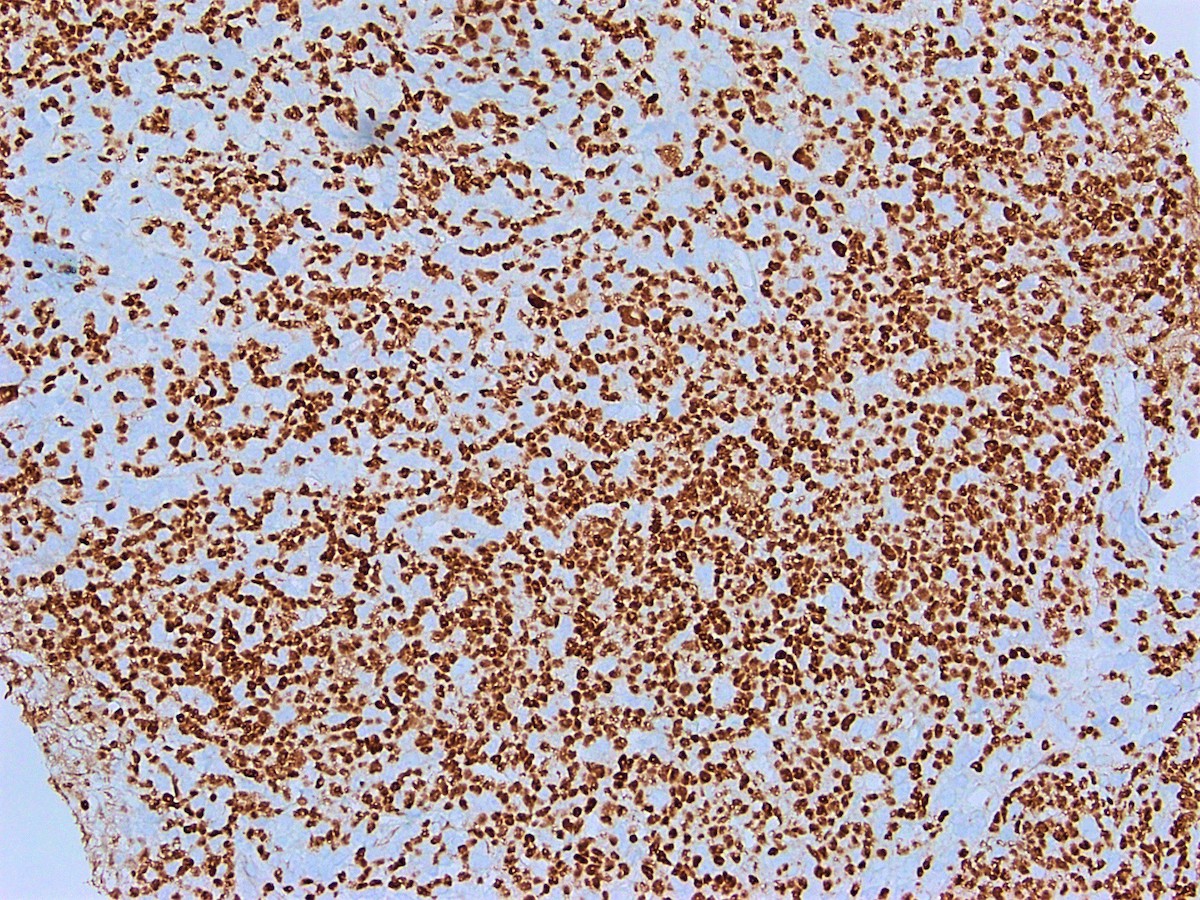
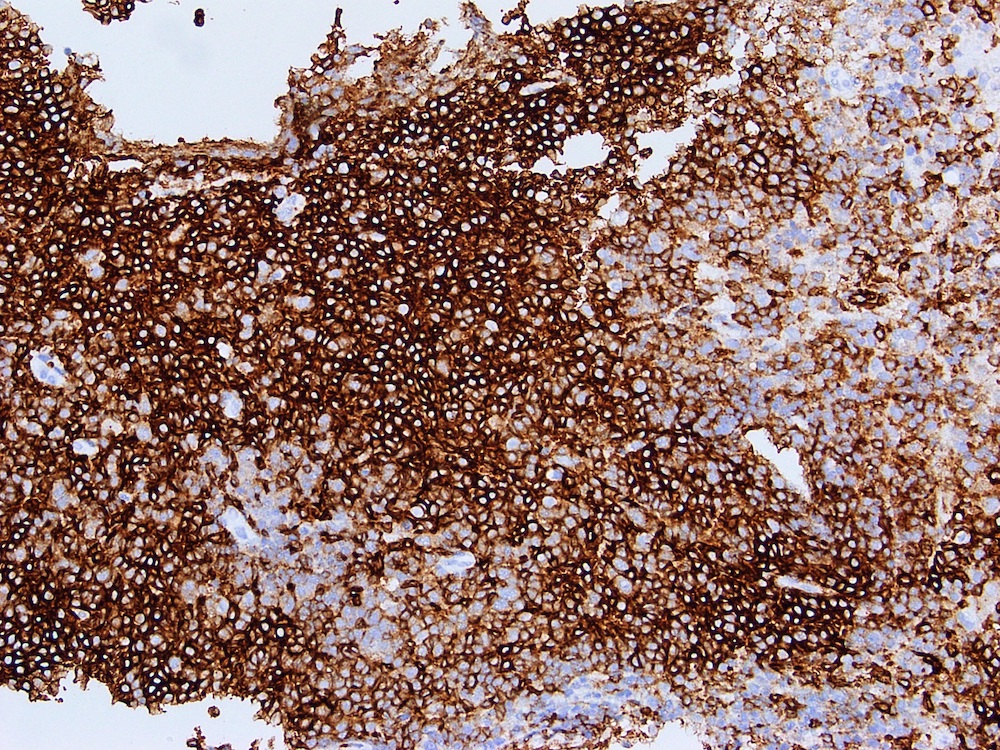
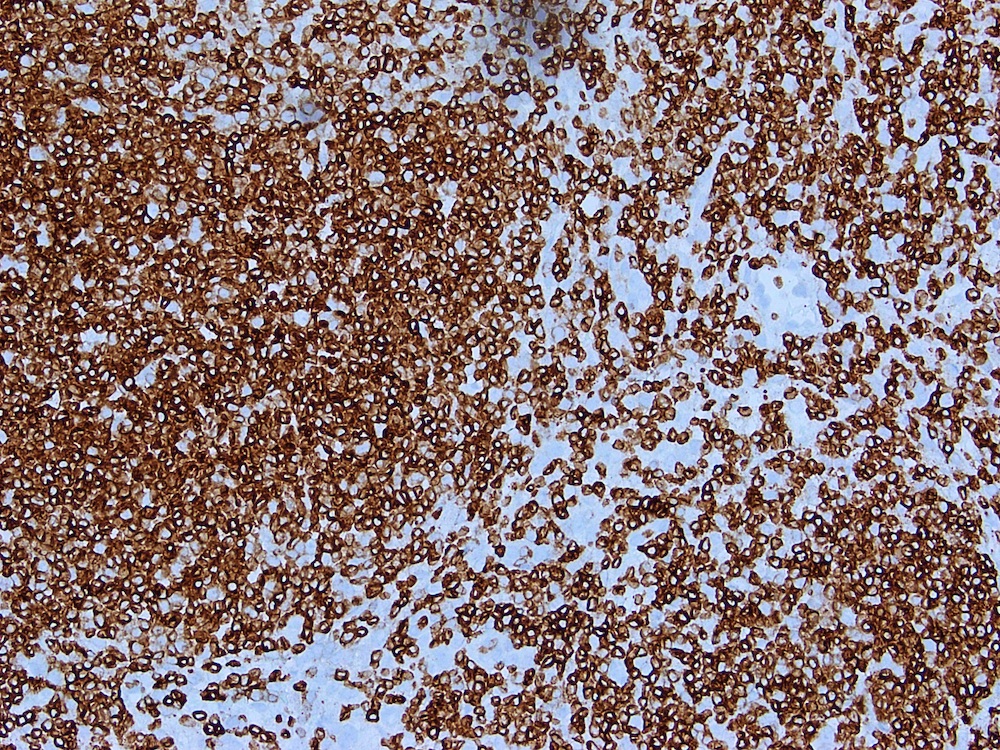
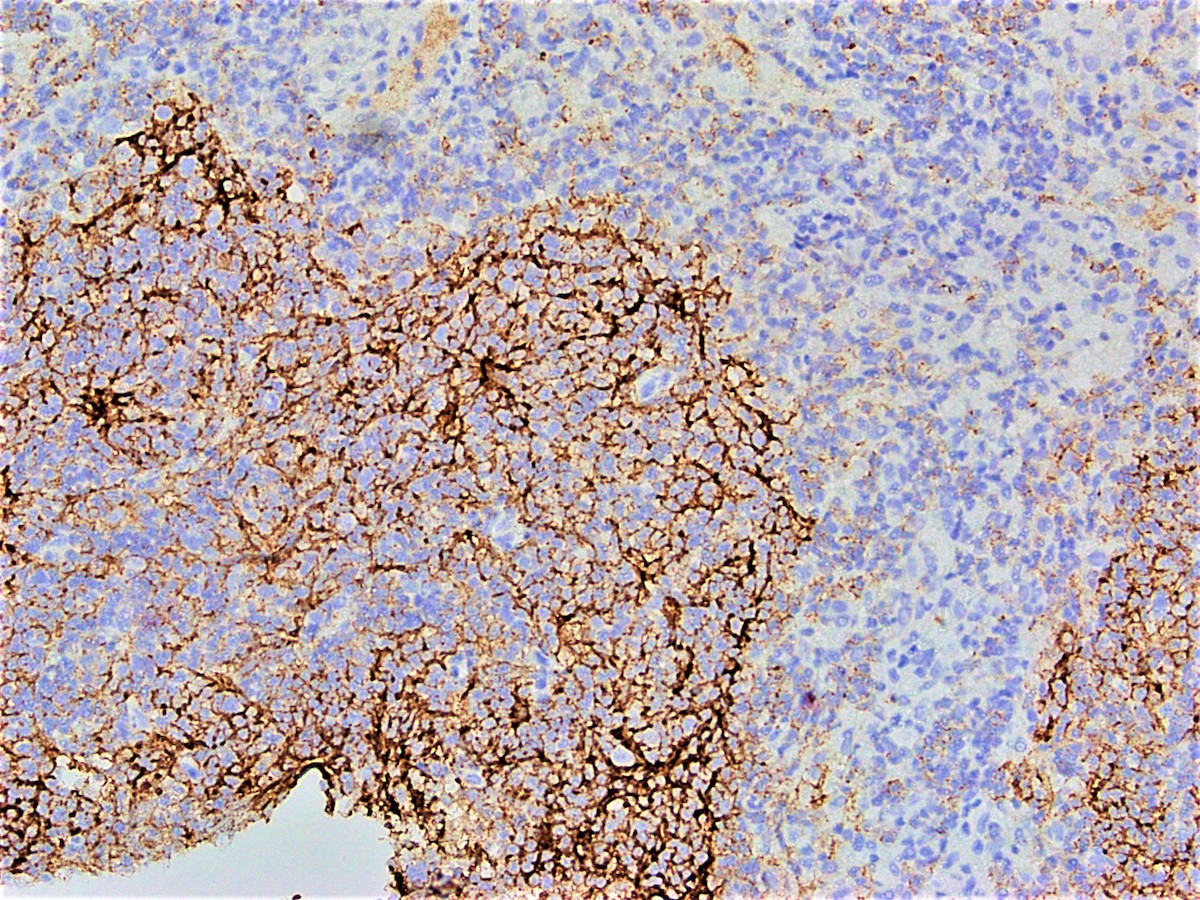
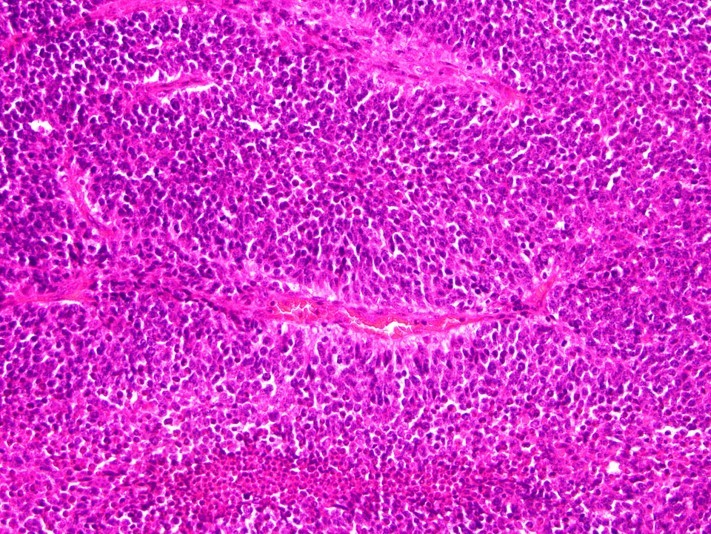
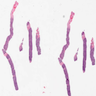
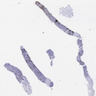
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Austin Ellis, M.D. and Ling Zhang, M.D.
Positive staining - normal
- B cells, from pro-B cells to mature B cells (J Immunol 2007;178:8222)
- Developing central nervous system (Eur J Histochem 2016;60:2563)
- Expressed in testis (Genes Dev 1992;6:1589)
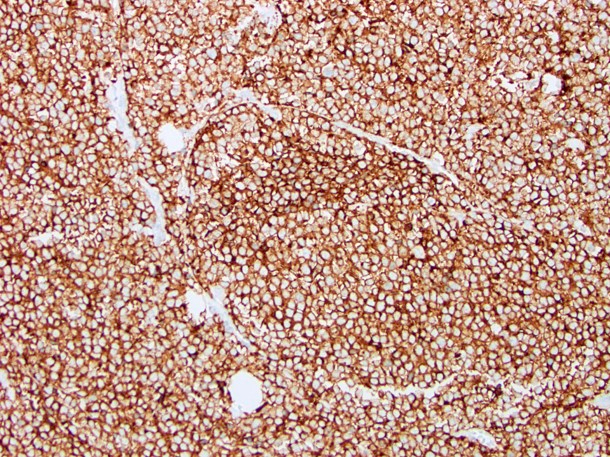
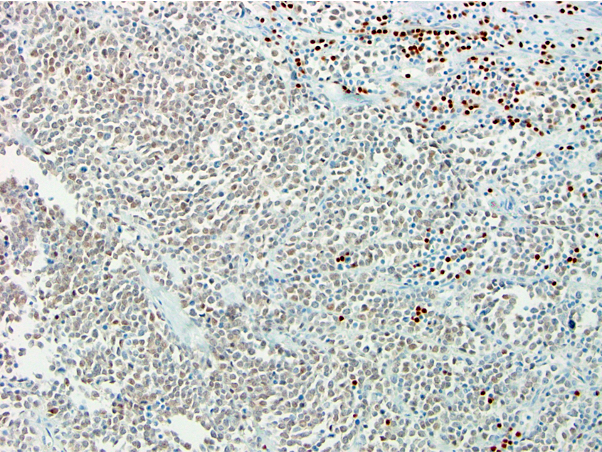
Positive staining - disease
- B cell lymphomas (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:561)
- B cell lymphoma status post rituximab therapy (Histopathology 2008;53:278, Am J Clin Pathol 2006;126:534)
- B lymphoblastic leukemia / lymphoma (Histopathology 2008;53:278, Clin Med Res 2010;8:84)
- Classic Hodgkin lymphoma (Mod Pathol 2004;17:1531)
- Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:561)
- Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (Clin Med Res 2010;8:84, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2010;134:759, Histopathology 2008;53:278, Hematol Oncol 2020;38:171)
- Primary mediastinal (thymic) large B cell lymphoma (Am J Pathol 2003;162:243)
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia / small lymphocytic lymphoma (Clin Med Res 2010;8:84)
- Follicular lymphoma (Mod Pathol 2006;19:1010)
- Mantle cell lymphoma (Cancer Biol Med 2015;12:46)
- Hairy cell leukemia (Am J Clin Pathol 2020;153:322, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:561)
- Nodal marginal zone lymphoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:762)
- Extranodal marginal zone lymphoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:1343)
- Splenic marginal zone lymphoma (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:561)
- Burkitt lymphoma (Am J Clin Pathol 2010;133:41)
- Merkel cell carcinoma (29/31, 24/34) (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:687, J Clin Pathol 2007;60:709)
- Small cell carcinoma (22/30, 42/53) (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:687, J Clin Pathol 2007;60:709)
- Acute myeloid leukemia with t(8;21)(q22;q22) (7/16, 30/40) (Am J Clin Pathol 2006;126:916, Am J Clin Pathol 2013;140:355)
- Rectal neuroendocrine tumors, granular cytoplasmic staining (90% [19/21]) (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2019;27:454)
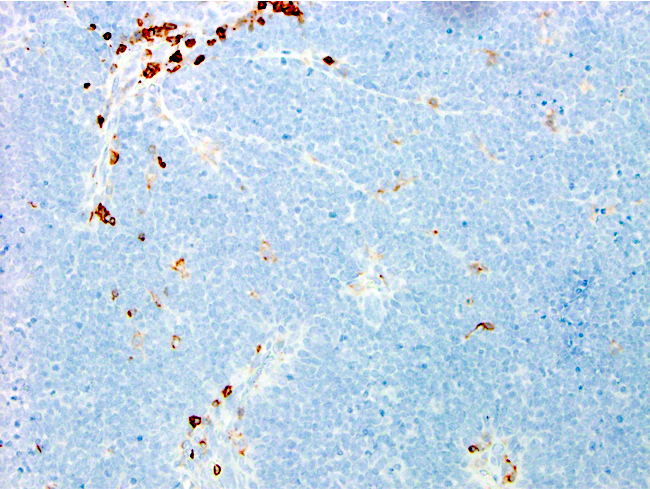
Negative staining
- Plasmacytomas (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:561)
- Plasmacytic component in B cell lymphomas with plasmacytic differentiation (FEBS Lett 1991;286:91)
- T / NK cell lymphomas (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:561)
- Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (Am J Clin Pathol 2003;120:767)
- Most nonhematologic malignancies (J Clin Pathol 2007;60:709, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:561)
Sample pathology report
- Lymph node, needle core biopsy:
- Diffuse large B cell lymphoma, germinal center B cell type (see comment)
- Comment: The needle core biopsy demonstrates sheets of large atypical lymphoid cells. The neoplastic cells are positive for CD20, PAX5, CD10, BCL6 and BCL2 and negative for CD3, CD5, MUM1 and MYC. Ki67 is variable, on average 70%. CD21 is negative. FISH for high grade B cell lymphoma is pending and will be reported in an addendum.
Board review style question #1
A 27 year old man presents with fever, drenching night sweats and supraclavicular lymphadenopathy. Excisional biopsy of the enlarged lymph node has architectural effacement by variable numbers of large cells with prominent nucleoli, mixed with inflammatory cells. The large cells are positive for CD30 and PAX5 and negative for CD3 and CD20. Which of the following is true regarding the large cells?
- PAX5 expression indicates that they are derived from B cells
- PAX5 expression indicates that they are plasma cells
- PAX5 expression supports a diagnosis of anaplastic large cell lymphoma
- PAX5 expression supports a diagnosis of seminoma
Board review style answer #1