Table of Contents
Definition / general | Clinical features | Uses by pathologists | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - disease | Negative stainingCite this page: Pernick N. Olig2. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsOlig2.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor with an important role in development (Nat Rev Neurosci 2012;13:819)
- Also marker of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (Brain Pathol 2010;20:399)
- Essential for selection of motor neuron and oligodendrocyte fates and choice of neural progenitors to either proliferate or differentiate (Neuron 2011;69:833)
Clinical features
- Variation in Olig2 gene is associated with psychosis in Alzheimer's disease (Neurosci Lett 2009;461:54)
Uses by pathologists
- May differentiate oligodendroglioma (Olig2+) from extraventricular neurocytoma (Olig2-, Brain Tumor Pathol 2011;28:157)
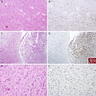
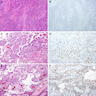
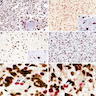
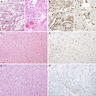
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - disease
- Adult gliomas: diffuse (nearly all)
- Glioblastoma variants:
- Giant cell (67%)
- Gliosarcoma (93% in glial component, 14% in sarcomatous component)
- Granular cell (100%)
- Small cell (98%), with oligodendroglial component (100%), with PNET-like foci (74%, staining in PNET-like foci) (Mod Pathol 2013;26:315)
- Glioneuronal tumors: dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor, papillary glioneuronal tumor, rosette-forming glioneuronal tumor of fourth ventricle (Neuropathology 2013;33:246)
- Oligodendroglioma
Negative staining
- Ependymoma (Clin Neuropathol 2008;27:118)