Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Ismail S, Elshimali JYI. OCT2. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsOCT2.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- B cell restricted transcription factor (Science 1988;241:577)
- Encoded by the gene POU2F2 (Genes Dev 1988;2:1570, GeneCards: POU2F2 Gene [Accessed 8 August 2022])
- Member of the POU domain family of transcription factors (Genes Dev 1988;2:1570, Int J Biochem Cell Biol 1996;28:1081)
Essential features
- B cell restricted transcription factor
- Encoded by the gene POU2F2
- Binds to an octamer DNA motif 5'-ATGCAAAT-3'
- Essential for B cell maturation and immunoglobulin production
Terminology
- Octamer binding protein 2 (OCT2)
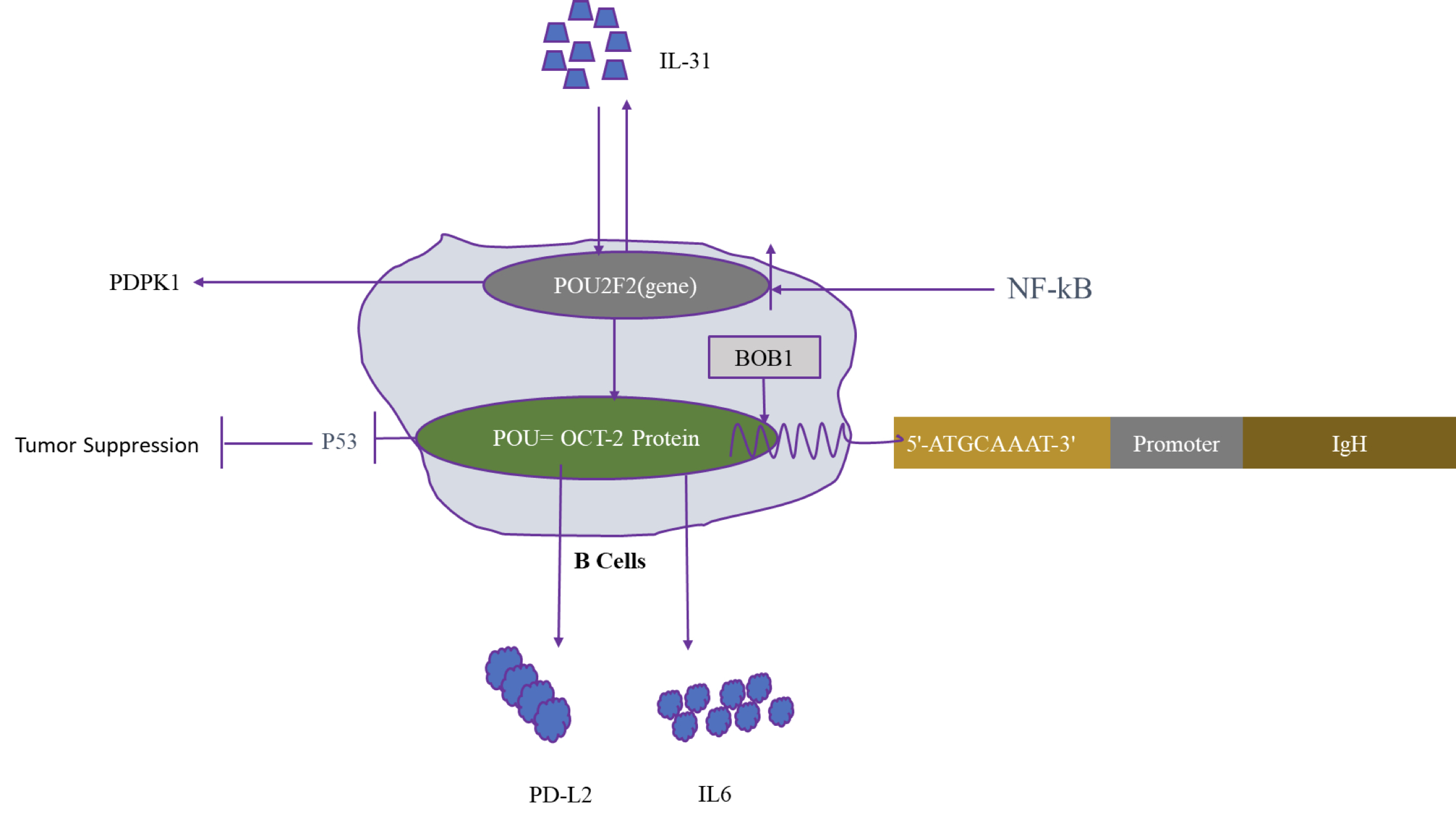
Pathophysiology
- Binds to an octamer DNA motif 5'-ATGCAAAT-3' (Semin Immunol 1998;10:155, Nucleic Acids Res 1991;19:237)
- Binding leads to activation of IgH enhancer (Immunity 1999;11:517)
- Activated by interacting with BOB1 to express immunoglobulin genes in B cells (Nature 1995;373:360, Cell 1995;80:497)
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features
- Essential for immunoglobulin production and germinal center formation (J Immunol 2003;171:6589)
- Required for activation of IgH enhancer (Immunity 1999;11:517, J Immunol 2003;171:6589)
- Required for embryogenesis, maturation and postnatal survival of B cells (Genes Dev 1993;7:570)
- Directly regulates production of IL6 by activated B cells
- Possible therapeutic target in myeloma (Leuk Lymphoma 2011;52:659)
- In mammary gland: plays a role in mammary gland development and expression increased in lactation stage (Gen Comp Endocrinol 2014;204:185, Nucleic Acids Res 1992;20:4311)
- Regulates expression of PDL2 gene in B1 cells (Genes Immun 2010;11:55)
Interpretation
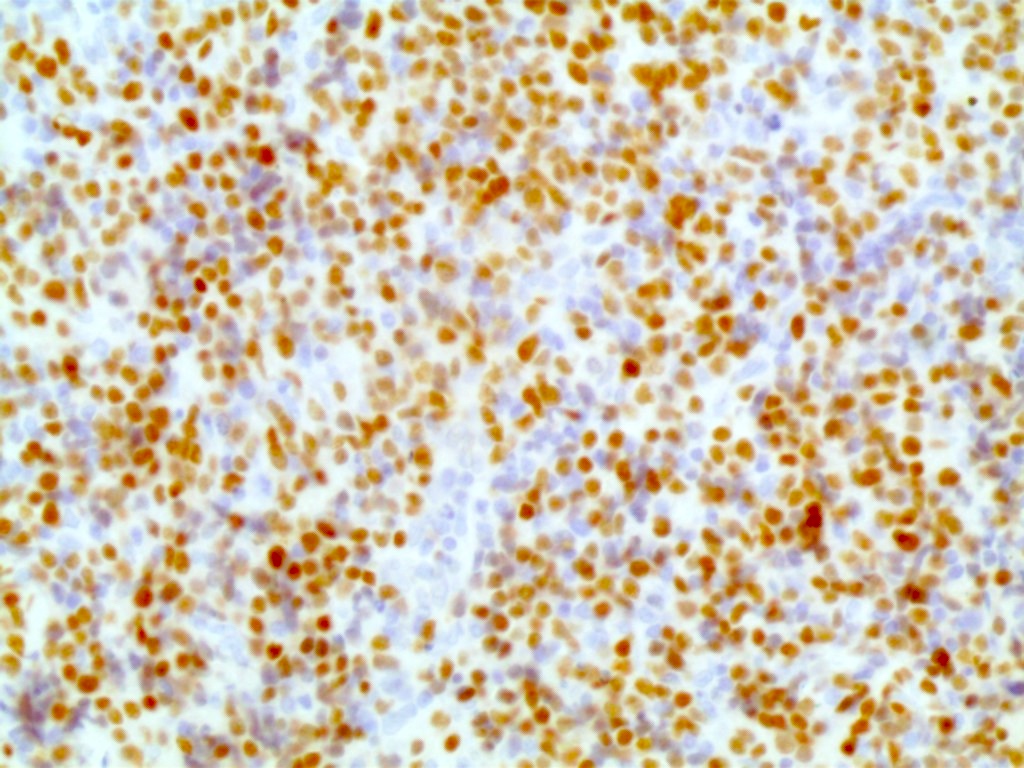
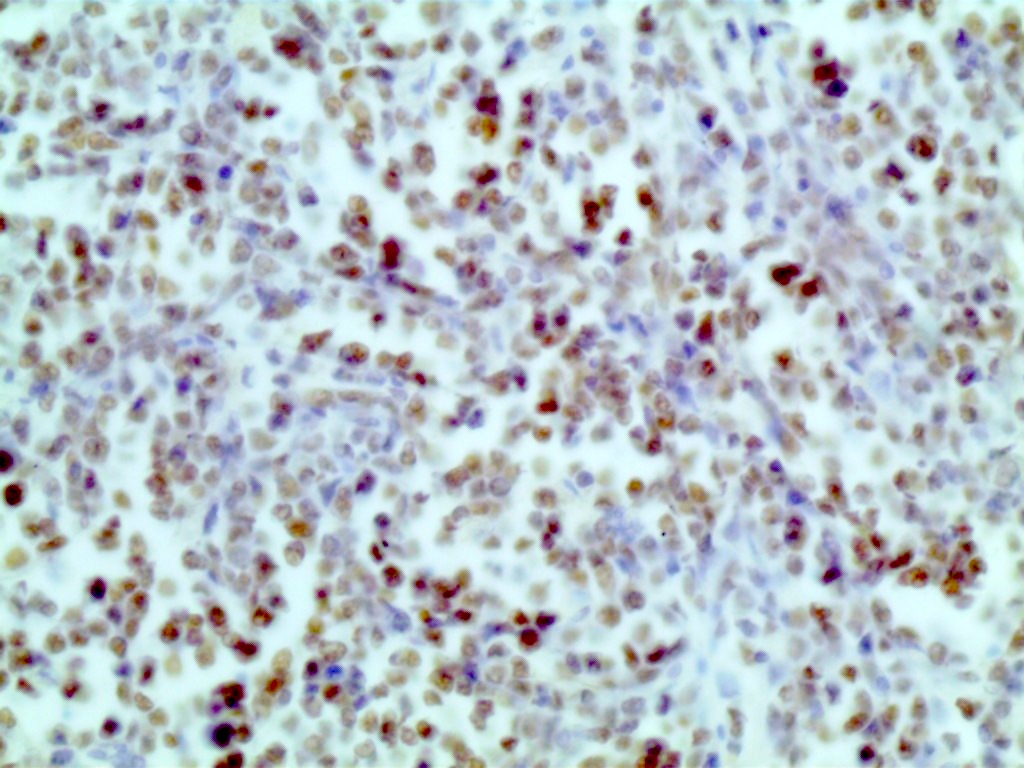
- OCT2 immunostaining demonstrates nuclear expression
Uses by pathologists
- Definite B cell lineage determiner in CD20-, PAX5- and CD79a- B cell lymphomas (Histopathology 2016;69:775)
- Differentiate nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (NLPHL) from classical Hodgkin lymphoma (CHL) (Rom J Morphol Embryol 2011;52:69)
Prognostic factors
- Increased expression is associated with poor prognosis in multiple myeloma and acute myeloid leukemia (Leuk Lymphoma 2011;52:659, Leuk Lymphoma 2010;51:606)
- In follicular lymphoma: activation is associated with overexpression of BCL2 (Oncogene 2006;25:888)
- Promotes latency of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and Kaposi sarcoma associated herpesvirus (KSHV) (PLoS Pathog 2012;8:e1002516, J Virol 2009;83:4308)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Positive cells should demonstrate a moderate to strong nuclear staining pattern
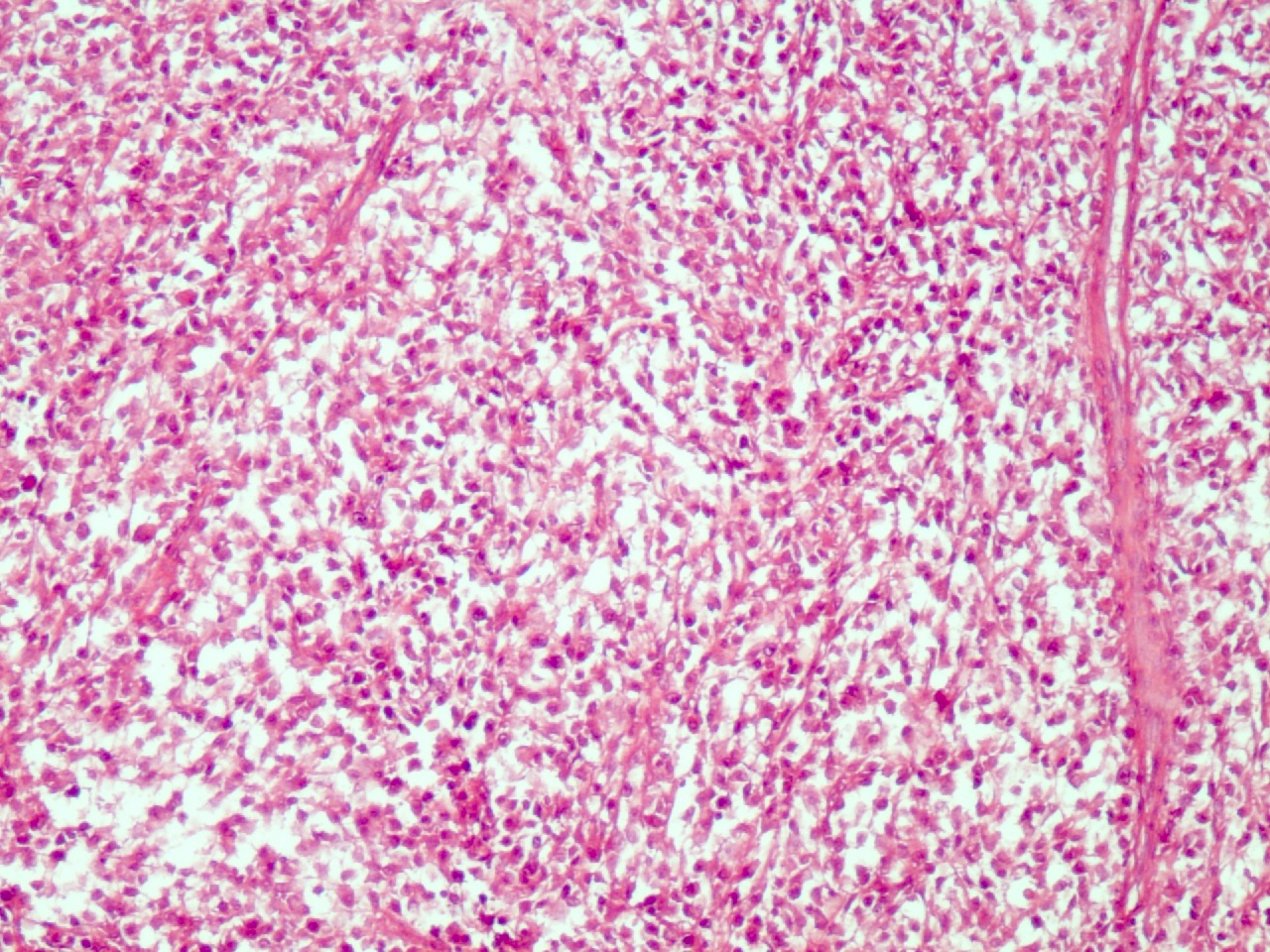
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
- Immature and mature B cells (Genes Dev 1993;7:570, Int J Biochem Cell Biol 1996;28:1081)
- Expression is increased in areas with increased activation, mainly in follicular center B cells (Genes Dev 1993;7:570)
- Neurons: isoforms OCT2.4, OCT2.5 (J Biol Chem 1992;267:24960)
- Alveolar epithelial cells of mammary gland in mouse (Cell Tissue Res 2007;328:595)
Positive staining - disease
- Pseudo B cell lymphomas: mantle cells, germinal center B cells (Mod Pathol 2006;19:1270)
- B cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (Mod Pathol 2006;19:1270)
- B lymphoblastic lymphoma (acute lymphoblastic leukemia)
- Lymphocyte predominant cells in nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (Mod Pathol 2006;19:1010, Rom J Morphol Embryol 2011;52:69)
- ALK positive large B cell lymphoma (ALK+ LBCL) (Histopathology 2016;69:775)
- Plasmablastic lymphoma (PBL) (Histopathology 2016;69:775)
- Primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) (Histopathology 2016;69:775, J Virol 2009;83:4308)
- Solid variant of PEL (Histopathology 2016;69:775)
- Extracavitary human gammaherpesvirus 8 positive large B cell lymphoma (HHV8+ LBCL) (Histopathology 2016;69:775)
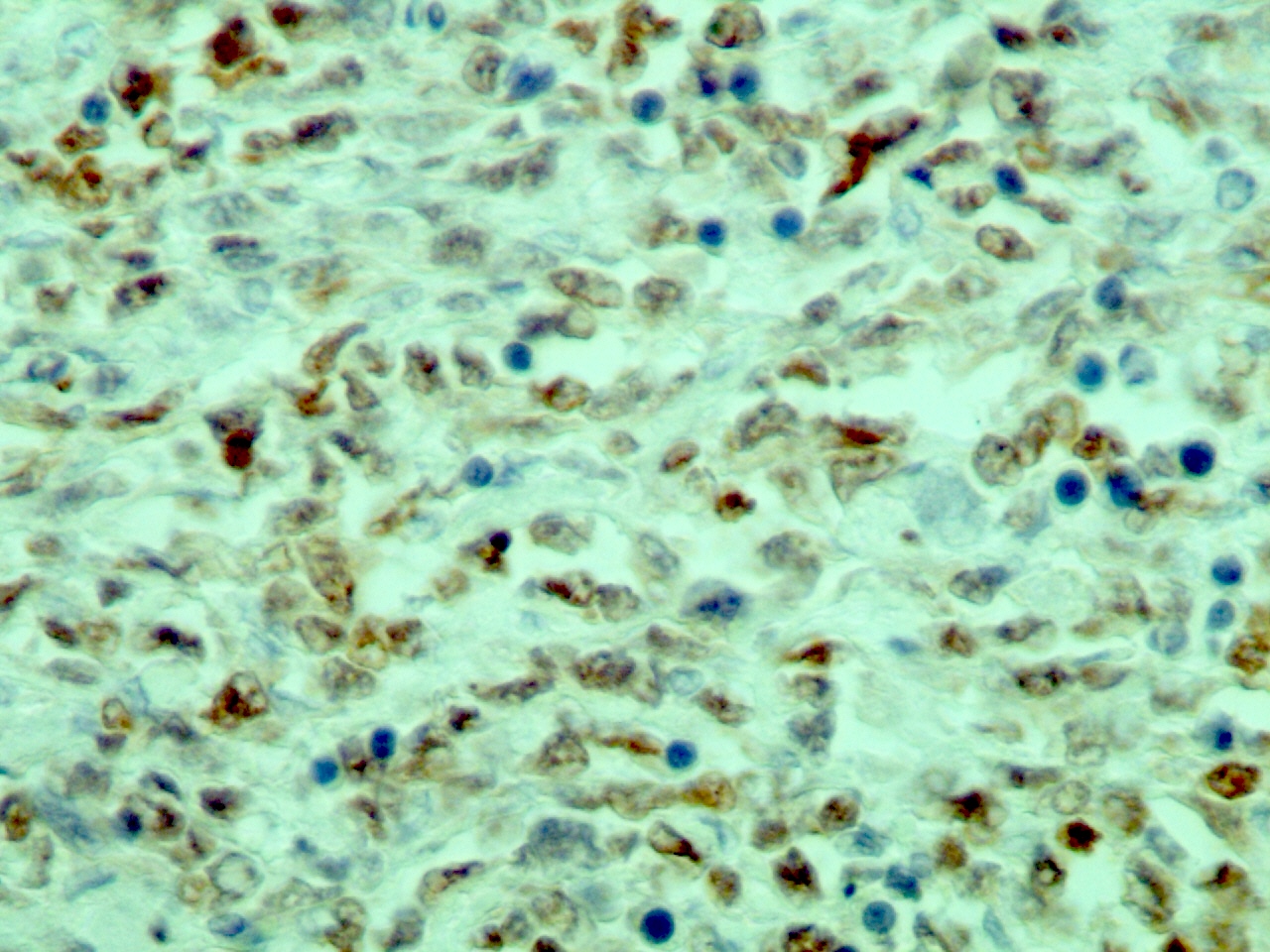
Negative staining
- T cell lineage: possible positive expression induced by NFAT and NFkB transcription factors (Nucleic Acids Res 2013;41:2138)
- Classical Hodgkin lymphoma (Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg [HRS] cells) (Cancer Res 2001;61:2080, Blood 2001;97:3191)
- Nonlymphoid malignancies (Nature 1986;323:640)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- POU2F gene is a large gene (43 kb) with complex splicing patterns
- Located on 19q13.2
- Octamer motif is a group of cis acting, sequence specific, DNA elements (Science 1988;241:577)
- Has 2 DNA binding domains: a homeodomain and a POU conserved sequence domain (Biochim Biophys Acta 1993;1173:1, Genes Dev 1988;2:1570)
- Binding specificity is regulated through phosphorylation by protein kinase A, C (Biochem J 1996;315:889)
- Has multiple splicing isoforms generated by alternative splicing: the major isoform OCT2.1 encoded by variant 2, the isoform OCT2.2 encoded by variant 1, the shorter isoform OCT2.7 encoded by variant 3 (Cell Tissue Res 2007;328:595, Nucleic Acids Res 1991;19:43)
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Sample pathology report
- Axillary lymph node, excisional biopsy:
- Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (see comment)
- Comment: The biopsy shows total replacement of the nodal architecture by expansive, vague nodules of small lymphocytes with sparse, relatively large tumor cells (LP cells) with multilobulated or round nucleus, a thin nuclear membrane, finely granular chromatin and variable small nucleoli (popcorn cells); the background shows numerous small B lymphocytes, epithelioid histiocytes and CD21+ follicular dendritic cells. The LP cells are immunoreactive for CD45 (LCA), CD20, CD19, BCL6, OCT2 (clone EP115), BOB.1 and PU.1 and are negative for CD3, CD15 and CD30. The morphologic and immunophenotypic findings are in support of the diagnosis.
Board review style question #1
Which of the following statements regarding OCT2 is true?
- Decreased expression is associated with poor prognosis in multiple myeloma
- OCT2 demonstrates positive nuclear expression in nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma
- OCT2 is used in the differential diagnosis of breast cancer
- OCT2.2 is the major isoform and is encoded by variant 3
Board review style answer #1
B. OCT2 demonstrates positive nuclear expression in nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. Increased expression is associated with poor prognosis in multiple myeloma. OCT2.1 is the major isoform and is encoded by variant 2. OCT2 is used in the differential diagnosis of Hodgkin lymphomas.
Comment Here
Reference: OCT2
Comment Here
Reference: OCT2