Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Sample pathology report | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Moayed-Alaei L, Colebatch A. RAS Q61R IHC. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsNRAS.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- RAS family of oncogenes includes NRAS, HRAS and KRAS
- NRAS (neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog) is a proto-oncogene located on chromosome 1p13.2 (My Cancer Genome: NRAS [Accessed 31 January 2023], Cancer Discov 2017;7:818)
- Mutant NRAS was first identified as a transforming gene in a neuroblastoma cell line (SK-N-SH) (Cell 1983;34:581, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1983;80:2112)
Essential features
- RAS Q61R immunohistochemistry (IHC) is mutation specific, with immunoreactivity against NRAS Q61R, KRAS Q61R and HRAS Q61R
- Strong and diffuse cytoplasmic or membranous staining of RAS Q61R is interpreted as positive
Terminology
- Neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog
Pathophysiology
- NRAS is a proto-oncogene located on chromosome 1p13.2
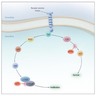
- NRAS encodes a protein with GTPase activity (Clin Cancer Res 2014;20:4186)
- In its normal state, NRAS protein transmits proliferation signals (i.e., cytokines, hormones and growth factors in to the cell), which are critical for proliferation, differentiation and survival (My Cancer Genome: NRAS [Accessed 31 January 2023], Nucleic Acids Res 2019;47:D506)
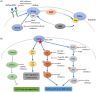
- Downstream signaling pathways triggered by NRAS include RAF-MEK-ERK (MAP) kinases and PI3-AKT kinases (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014;111:4179)
- Point mutations in hotspot codons within exon 2 [codons 12 and 13] and exon 3 [codon 61] lead to aberrant activation of the RAS pathway; this mutation disrupts GTPase activity and keeps RAS in the activated state (GTP bound) (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014;111:4179)
- Somatic mutations of NRAS in cancer commonly occur at codon 61, including Q61R; similar mutations occur in HRAS and KRAS, at lower relative frequencies
- RAS Q61R mutation specific antibody (SP174) was initially designed to detect NRAS Q61R mutations; however, it is also reactive against KRAS and HRAS Q61R mutations due to homology (Histopathology 2021;79:650)
- Anti-RAS Q61R antibody cannot distinguish between NRAS Q61R, KRAS Q61R and HRAS Q61R mutations due to sequence homology at these loci
Clinical features
- Binimetinib has evidence of efficacy in patients with NRAS Q61R in melanoma (My Cancer Genome: NRAS Q61R [Accessed 31 January 2023], Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2017;17:985)
Interpretation
- Diffuse and strong cytoplasmic or membranous staining confined to myoepithelial cells in salivary glands neoplasm (Am J Surg Pathol 2021;45:885)
- Moderate to strong granular cytoplasmic or membranous staining in thyroid neoplasm (Histopathology 2021;79:650)
- Moderate to strong cytoplasmic staining in > 60% of metastatic melanoma; 100% correlation with molecular testing (J Am Acad Dermatol 2015;72:786)
- Pitfall in IHC: not specific for NRAS Q61R mutation and will stain HRAS Q61R and KRAS Q61R as well (Am J Surg Pathol 2021;45:885, Hum Pathol 2021;112:35)
Uses by pathologists
- RAS Q61 IHC is used by pathologists to identify mutation in codon 61 of HRAS, KRAS and NRAS genes (Histopathology 2021;79:650)
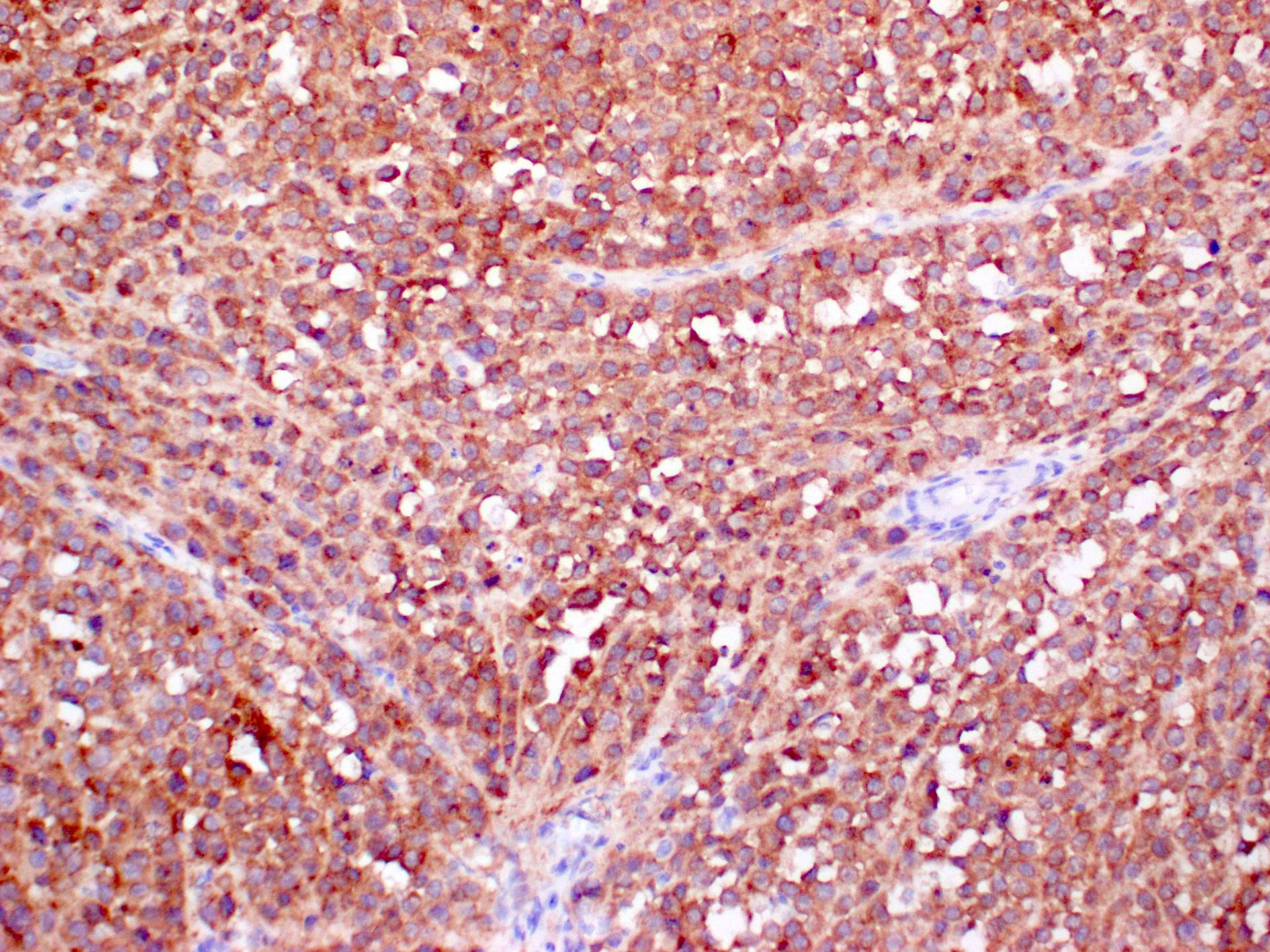
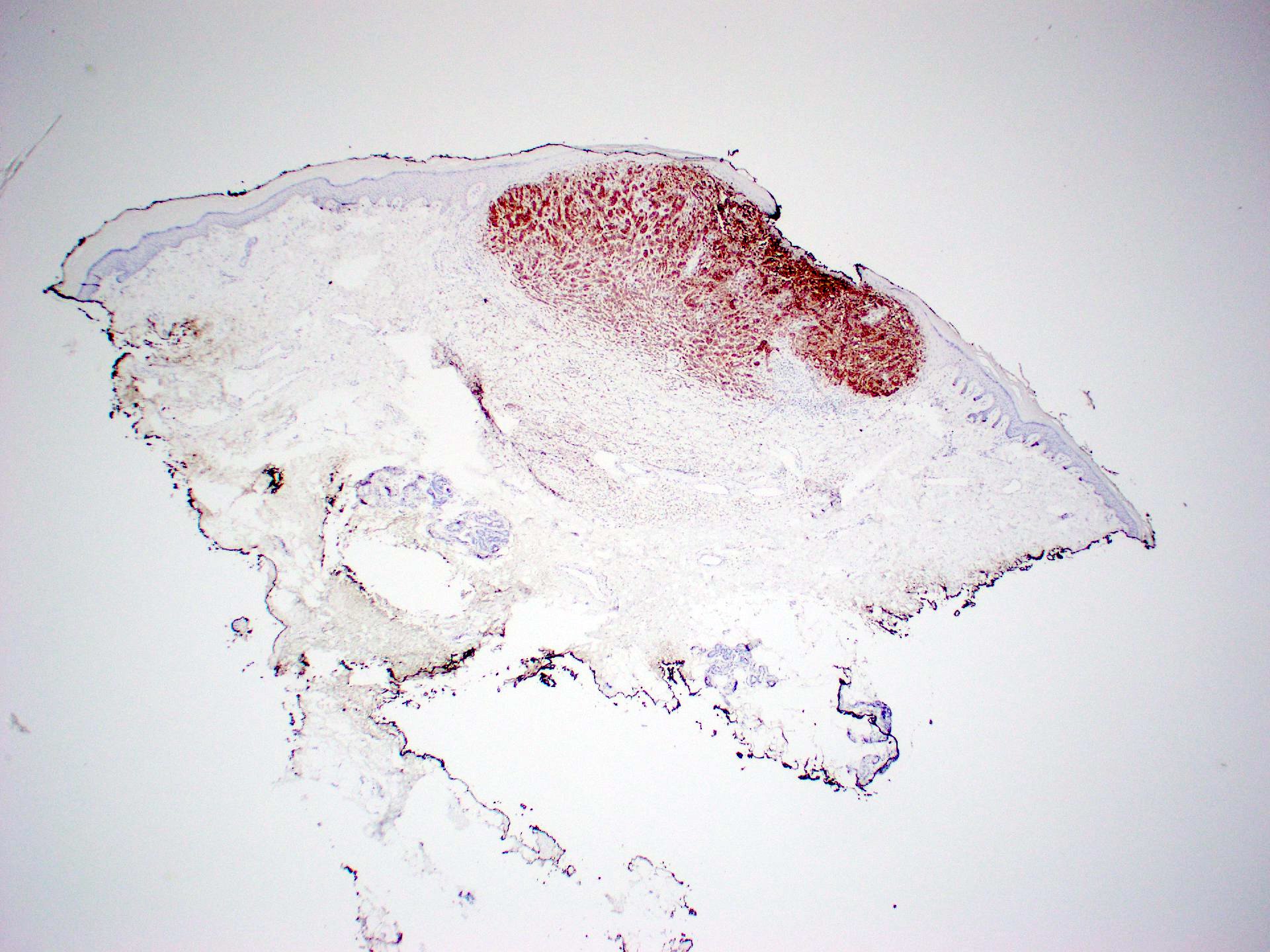
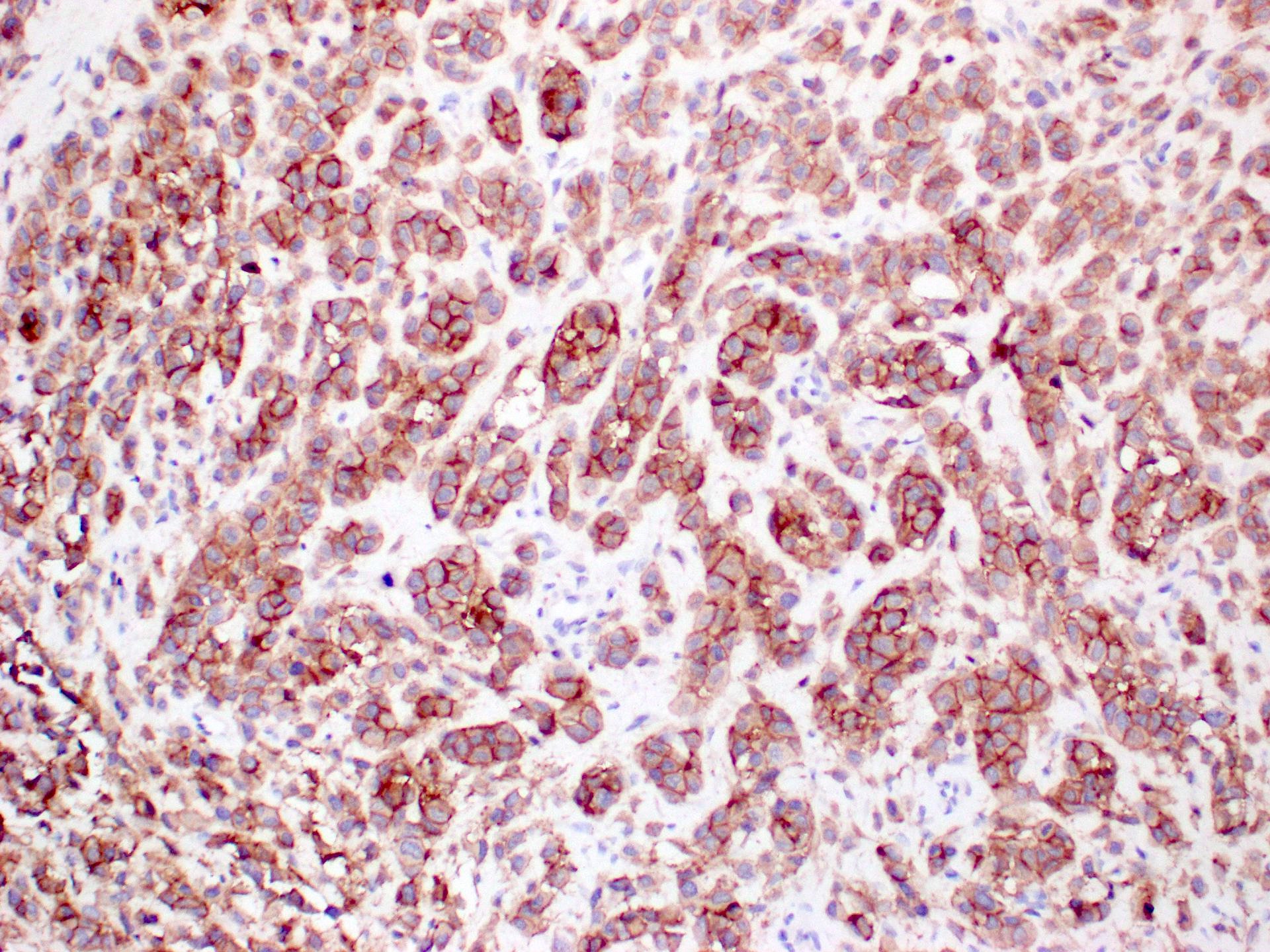
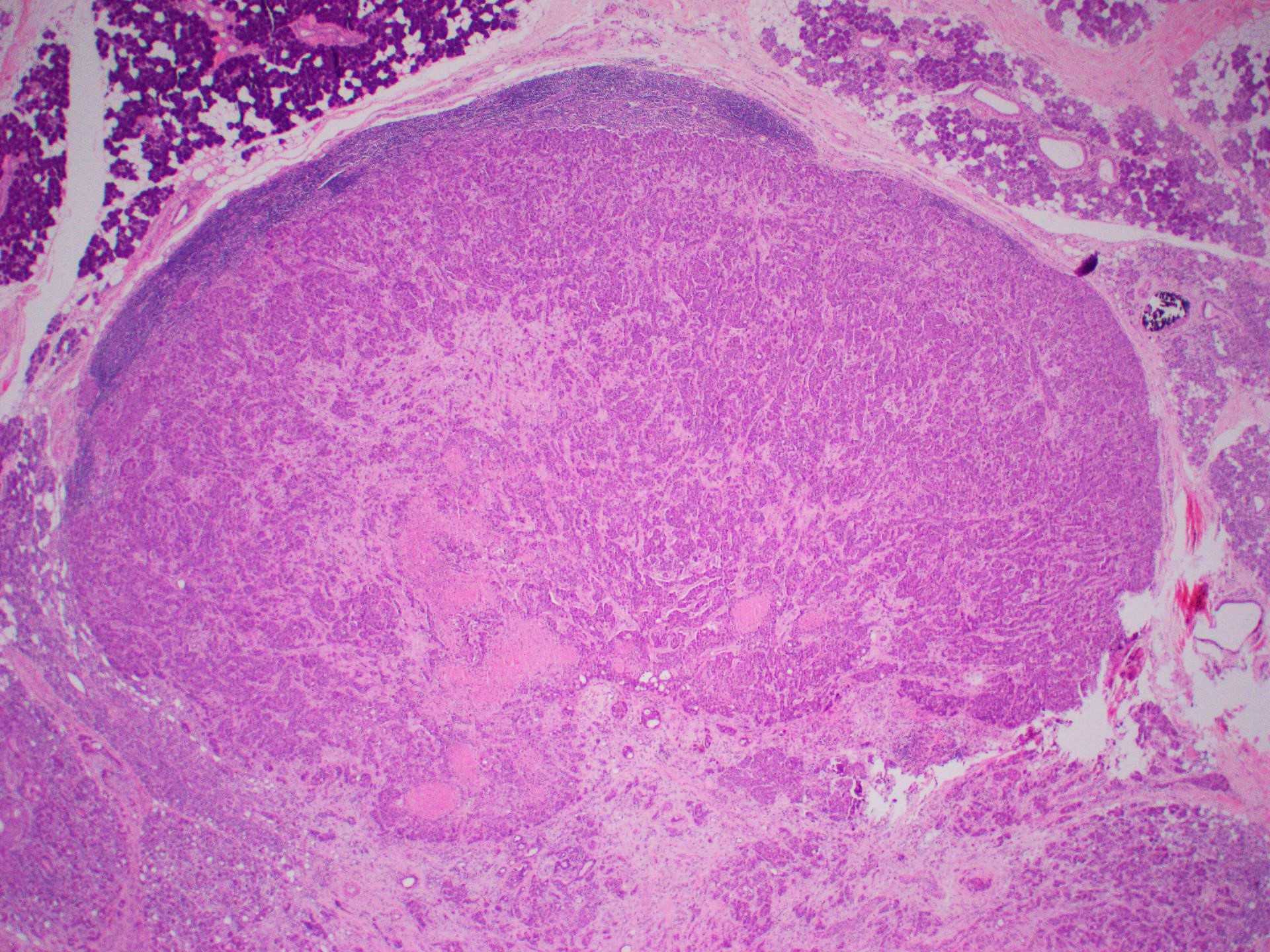
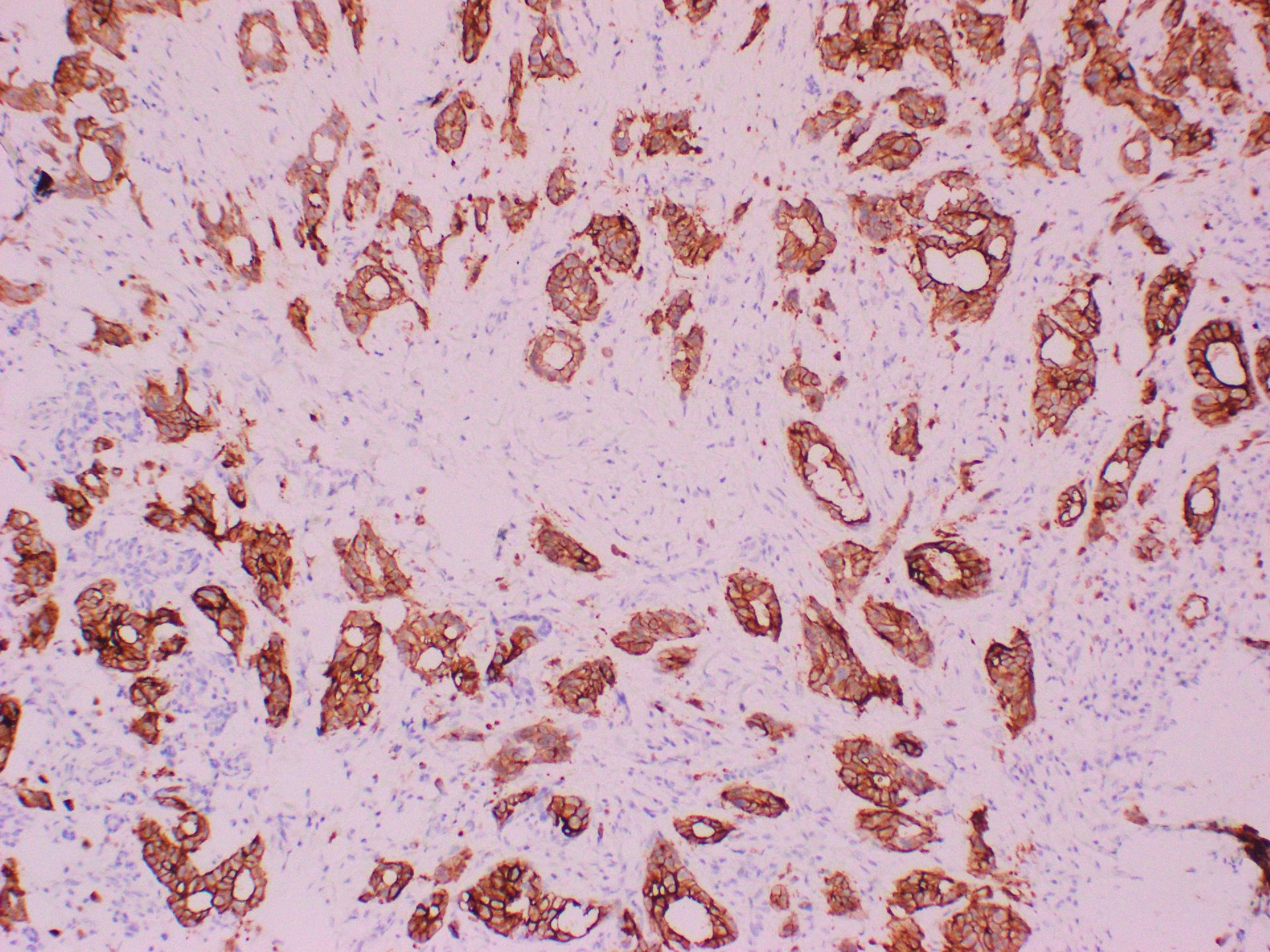
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
- RAS Q61R staining is not seen in normal human tissue, as it results from a gain of function oncogenic mutation
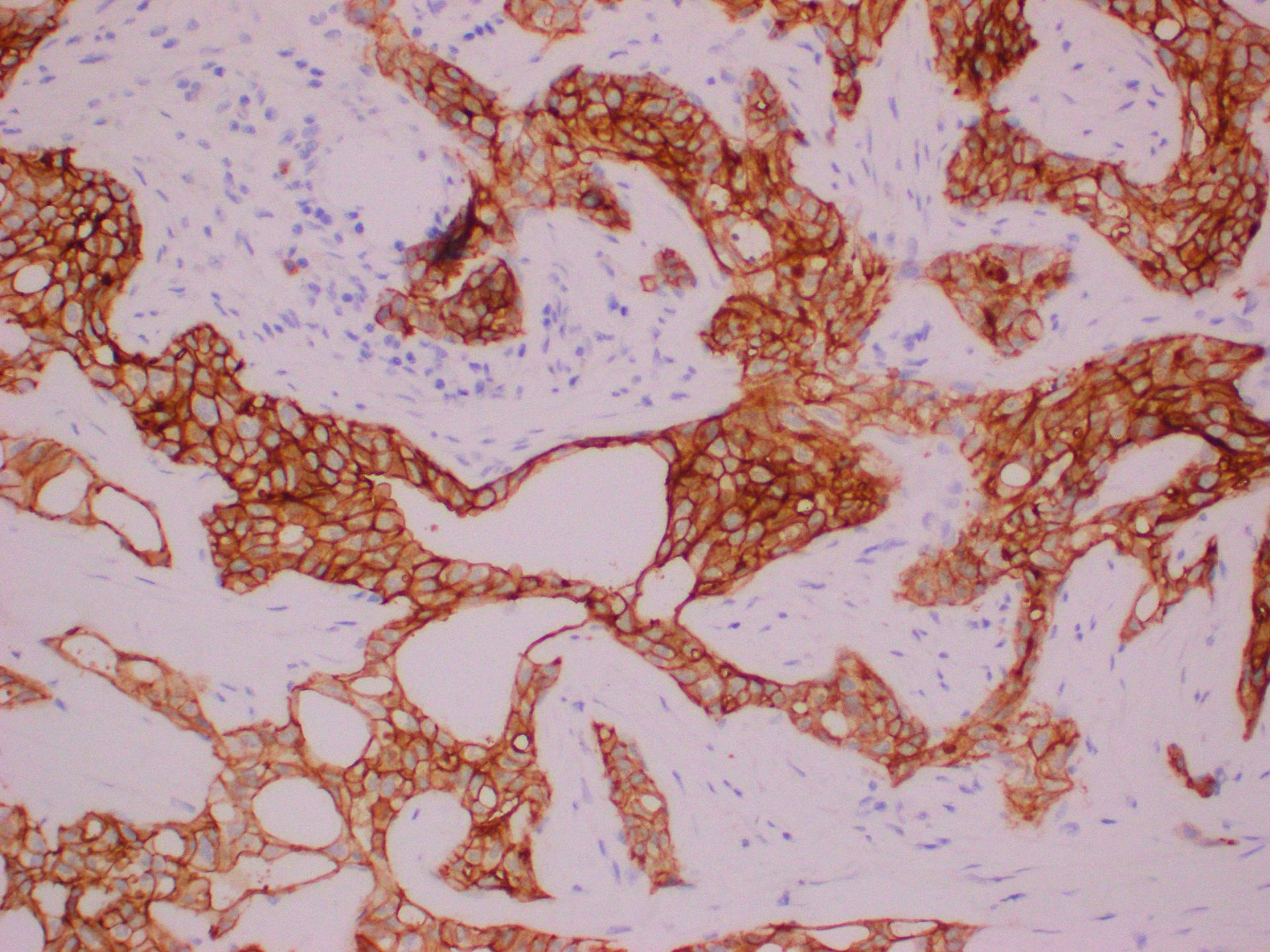
Positive staining - disease
- Melanocytic lesion (NRAS Q61R present in about 8% of all melanoma patients)
- Cutaneous melanoma
- Acral lentiginous melanoma
- Mucosal melanoma
- Approximately 20% of Spitz nevi harbor HRAS Q61 mutations, of which a proportion have HRAS Q61R - this subset of cases with HRAS Q61R mutations shows immunostaining with RAS Q61R antibody; of note, Spitz nevi do not harbor NRAS Q61R mutations (Am J Pathol 2000;157:967, Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1145)
- HRAS mutated Spitz nevi are generally located in the dermis, have low cellularity, show desmoplasia and an infiltrative base (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:1436)
- Thyroid (Histopathology 2021;79:650)
- Follicular cell carcinoma: 14.3%
- Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC)
- 48% in follicular variant
- 25% of infiltrative variant
- 20% of solid variant
- 3.3% of classic variant
- Poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma
- 25% of primary lesions
- 50% of metastatic lesions
- Anaplastic carcinoma (primary): 33%
- Follicular adenoma (20%) and Hürthle cell adenoma (33%)
- Gastrointestinal tract
- 0.8% of colorectal adenocarcinoma (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2017;25:475)
- 8.33% of pancreatic duct adenocarcinoma (KRAS Q61R mutation) ( My Cancer Genome: KRAS Q61R [Accessed 31 January 2023], Cancer Discov 2017;7:818)
- Non-small lung adenocarcinoma (NRAS Q61R present in 0.11%, KRAS Q61R in 0.06%) (My Cancer Genome: KRAS Q61R [Accessed 31 January 2023], Cancer Discov 2017;7:818)
- Gynecology
- Low grade ovarian serous carcinoma: 3.6%
- Salivary gland neoplasm (highlighting HRAS Q61R mutation) (Am J Surg Pathol 2021;45:885)
- 65% of de novo epithelial myoepithelial carcinoma
- 8.6% of salivary duct carcinoma
- 44% of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm
- 20% of sialadenoma papilliferum
- Breast
- 71% of ER negative adenomyoepithelioma (Histopathology 2020;76:865)
Sample pathology report
- Skin, excision:
- Melanoma (see comment)
- Comment: Histologic section of skin to subcutis demonstrates melanoma. Immunohistochemistry shows moderate cytoplasmic and membranous staining for RAS Q61R and is negative for BRAF V600E.
Board review style question #1
Which of the following statements is true regarding RAS Q61R?
- NRAS gene encodes for a nuclear transcription factor that promotes cell growth
- Positive staining for RAS Q61R can be found in lesions with either NRAS Q61R, KRAS Q61R or HRAS Q61R mutations
- Positive staining for RAS Q61R is specific to NRAS Q61R mutation
- RAF is one of the upstream pathways that trigger NRAS
Board review style answer #1
B. Positive staining for RAS Q61R can be found in lesions with either NRAS Q61R, KRAS Q61R or HRAS Q61R mutation.
Comment Here
Reference: NRAS
Comment Here
Reference: NRAS