Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Yoest J, Sadri N. MDM2. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsMDM2.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Murine double minute 2
- Located on 12q15
- Encodes protein that inhibits p53
- Amplified in various malignancies
Essential features
- MDM2 amplified on supernumerary ring or marker chromosomes in many tumors, leading to suppression of p53
- Common in atypical lipomatous tumor / well differentiated liposarcoma and dedifferentiated liposarcoma; often used to distinguish these entities from mimickers
- Distinguish low grade osteosarcoma and parosteal osteosarcoma (positive) from benign fibrous and fibro-osseous lesions (negative)
- Commonly tested by FISH or IHC, also dual color chromogenic in situ hybridization (DISH / CISH); FISH widely accepted as gold standard
Terminology
- Murine double minute 2
- Hdm2
- E3 ubiquitin ligase MDM2
- MDM2 proto-oncogene
- p53 binding protein MDM2
Pathophysiology
- Discovered in 1987 when screening for amplified genes in a transformed mouse cell line (Somat Cell Mol Genet 1987;13:235)
- Protein product inhibits p53 by blocking transcriptional activation domain, targeting for ubiquitination and exporting to cytoplasm (Cell 1992;69:1237, Nature 1993;362:857, Nature 1997;387:296, FEBS Lett 1997;420:25, EMBO J 1998;17:554)
- Oncogene when upregulated through genetic amplification or overexpressed through promoter single nucleotide polymorphisms (Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2016;6:a026336)
- Artificial overexpression induced tumorigenesis (sarcomas) in mice and lower expression is protective of tumor formation in vitro (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998;95:15608, Mol Cell Biol 2007;27:5479, EMBO J 2003;22:1442)
- Mutually exclusive with TP53 mutations (Nucleic Acids Res 1998;26:3453)
- Frequently amplified in human sarcomas and less frequently in many other tumor types (Nature 1992;358:80, Nucleic Acids Res 1998;26:3453)
- Potential target for treatment by MDM2 inhibiting compounds or derivatives (nutlins) (Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2016;6:a026336, ClinicalTrials.gov: MDM2 [Accessed 25 November 2020])
- CDK4, located on 12q14, co-amplified with MDM2 (Virchows Arch 2010;456:167, Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2016;6:a026336)
Clinical features
- Amplification detected by comparative genomic hybridization, qualitative PCR, FISH or DISH; MDM2 immunostaining correlates with gene amplification (Virchows Arch 2010;456:167, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2019;27:758, Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2016;6:a026336)
- MDM2 amplification and overexpression in tumors is associated with radiation, chemotherapy, tyrosine kinase inhibitor and immune checkpoint inhibitor resistance (Cancer Cell Int 2019;19:216)
- MDM2 SNP309 (rs2279744) GG genotype (minor allele) associated with higher MDM2 expression levels and may be associated with slightly higher cancer risk, particularly in tumors related to ER signaling pathways (Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2016;6:a026336)
- Breast cancers with mutated TP53 are more likely to have MDM2 SNP309 TT or TG than GG genotype (Int J Mol Sci 2019;20:509)
- MDM2 SNP309 may be a risk factor for leukemia among Asians but not Caucasians (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:2245)
- MDM2 SNP285 (rs117049649) C genotype is linked to SNP309 G, found in a minority of Caucasians and may modify or offset the effects of the SNP309 G genotype (Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2016;6:a026336)
- After analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas data, overall effect of MDM2 single nucleotide polymorphisms on MDM2 expression levels across wide range of human tumors is probably minor but cannot be ruled out as significant in specific settings; overall effects on cancer risk is currently poorly understood due to conflicting findings (Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2016;6:a026336)
Interpretation
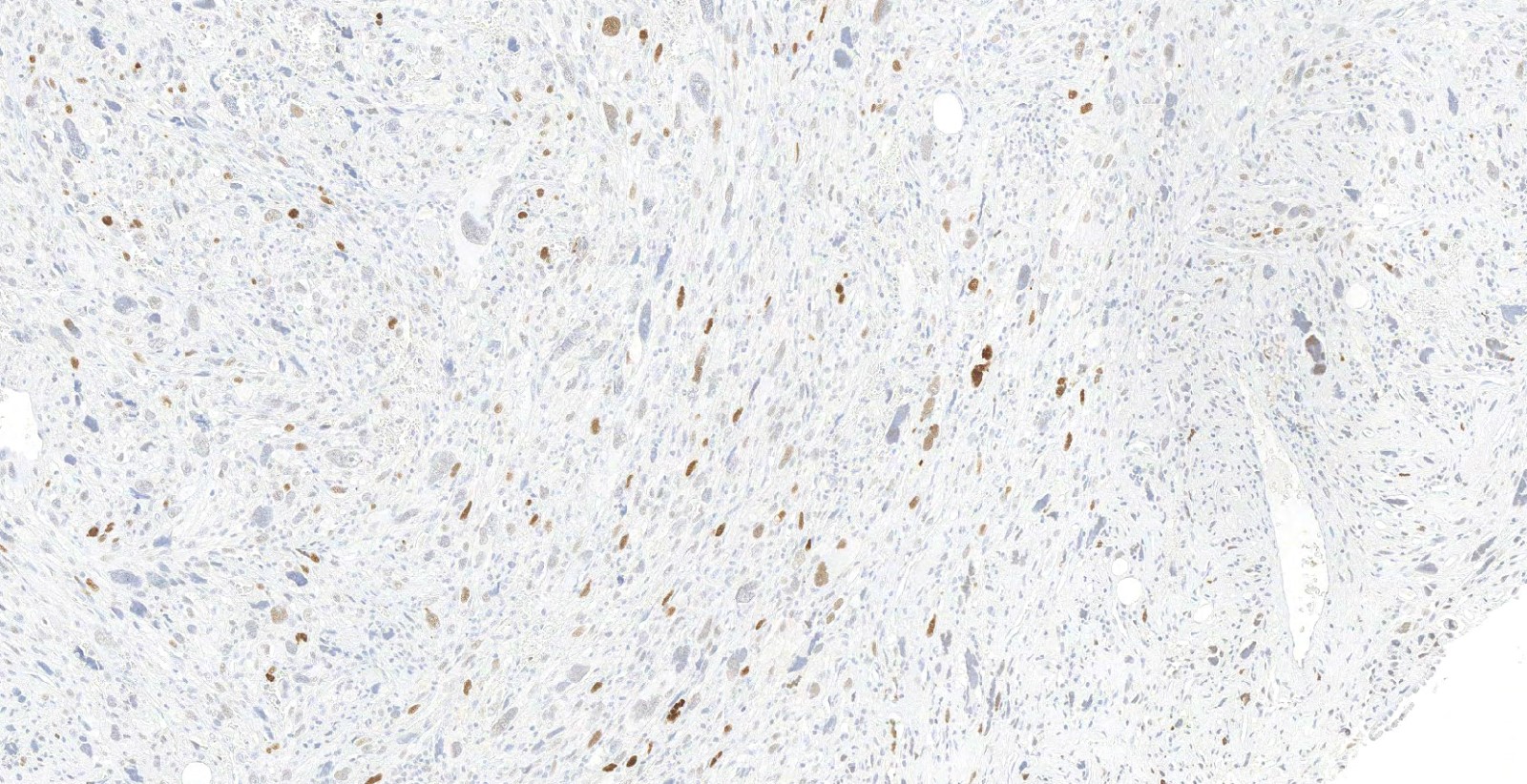
- IHC: strong diffuse nuclear staining (Virchows Arch 2010;456:167)
Uses by pathologists
- Distinguish well differentiated liposarcoma (positive) from benign adipose tumors (negative) (Virchows Arch 2010;456:167)
- In the setting of appropriate histology, FISH ranges from 93 - 100% sensitive for atypical lipomatous tumor / well differentiated liposarcoma and dedifferentiated liposarcoma (Sarcoma 2015;2015:812089, Mod Pathol 2012;25:1384, Mod Pathol 2010;23:1301)
- FISH more sensitive in the setting of atypical lipomatous tumor / well differentiated liposarcoma versus benign mimics (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6:1306)
- One study identified much lower positivity rates among tumors with inconclusive histology (28% and 32% positivity rates among tumors suspected atypical lipomatous tumor / well differentiated liposarcoma versus benign, respectively) (Sarcoma 2015;2015:812089)
- Immunohistochemistry less sensitive (45%) in histologically ambiguous cases (atypical lipomatous tumor / well differentiated liposarcoma versus benign lipomatous tumors); only seen in atypical neoplastic nuclei and may be seen in histiocytes or multinucleated giant cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1647)
- Distinguish dedifferentiated liposarcoma (positive) from poorly differentiated sarcomas (negative) (Virchows Arch 2010;456:167)
- Distinguish low grade osteosarcoma and parosteal osteosarcoma (positive) from benign fibrous and fibro-osseous lesions (negative) (Mod Pathol 2010;23:1279, Mod Pathol 2011;24:624, J Chin Med Assoc 2019;82:889)
- MDM2 and CDK4 coexpression in high grade osteosarcoma suggests progression from low grade osteosarcoma and degree of amplification higher in dedifferentiated osteosarcomas (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:423, J Chin Med Assoc 2019;82:889)
- MDM2 and CDK4 IHC together is more specific but less sensitive than MDM2 IHC alone (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1340)
Prognostic factors
- MDM2 amplification is a proposed radiation, chemotherapy, tyrosine kinase inhibitor and immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy resistance mechanism (Cancer Cell Int 2019;19:216)
- MDM2 amplification linked to hyperprogression after immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy; requires further study (Clin Cancer Res 2017;23:4242, JCO Precis Oncol 2018;2018:PO.17.00235)
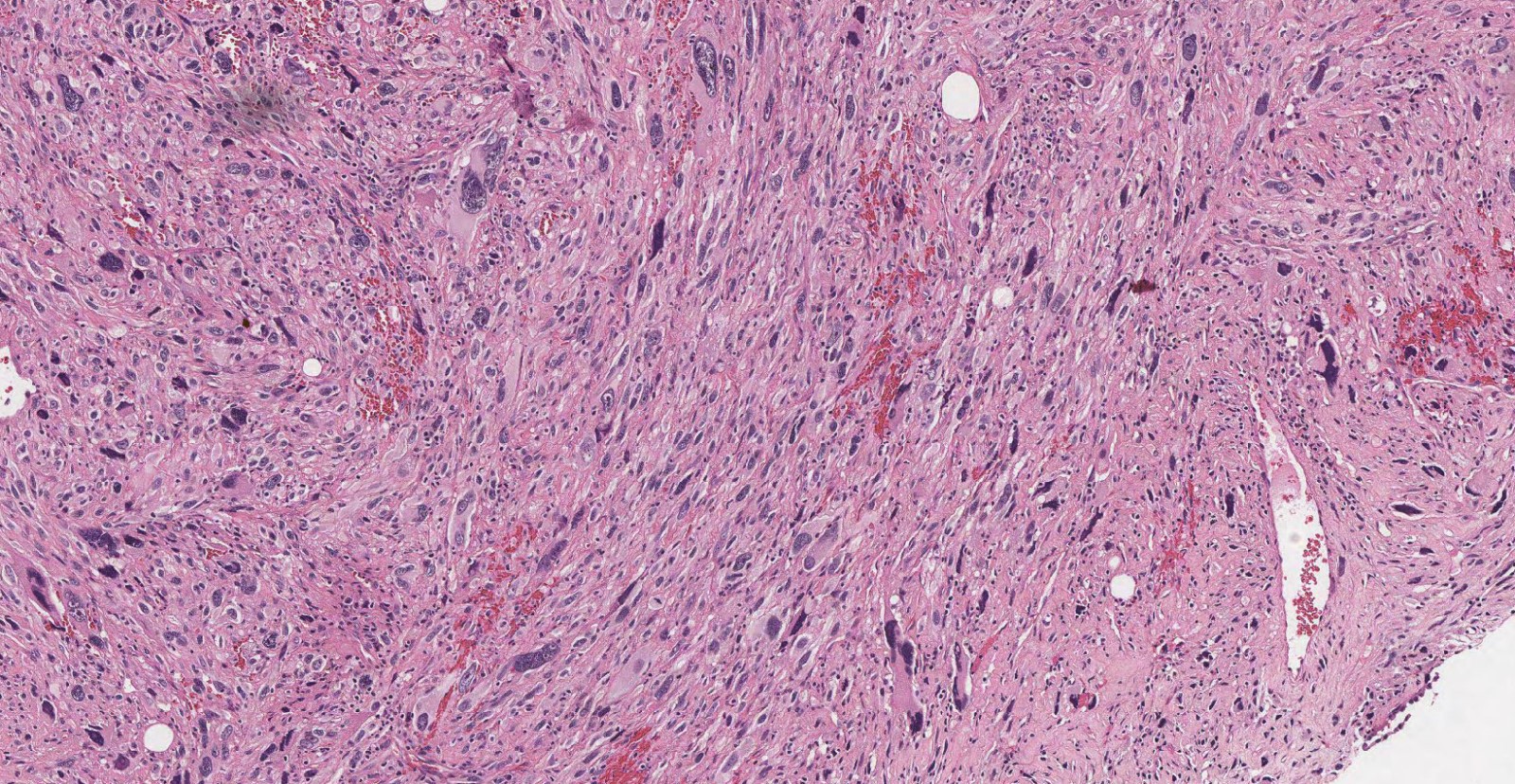
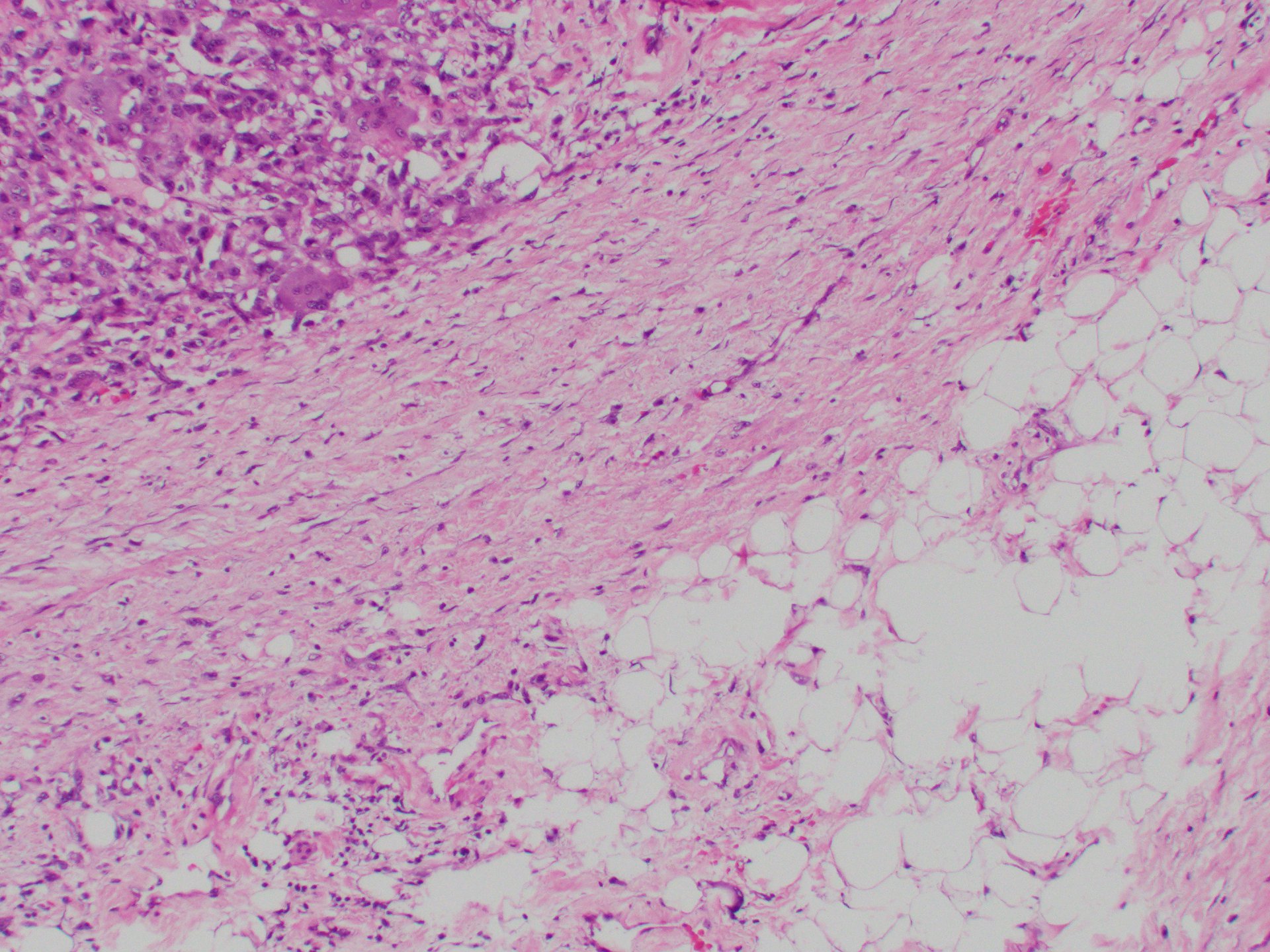
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
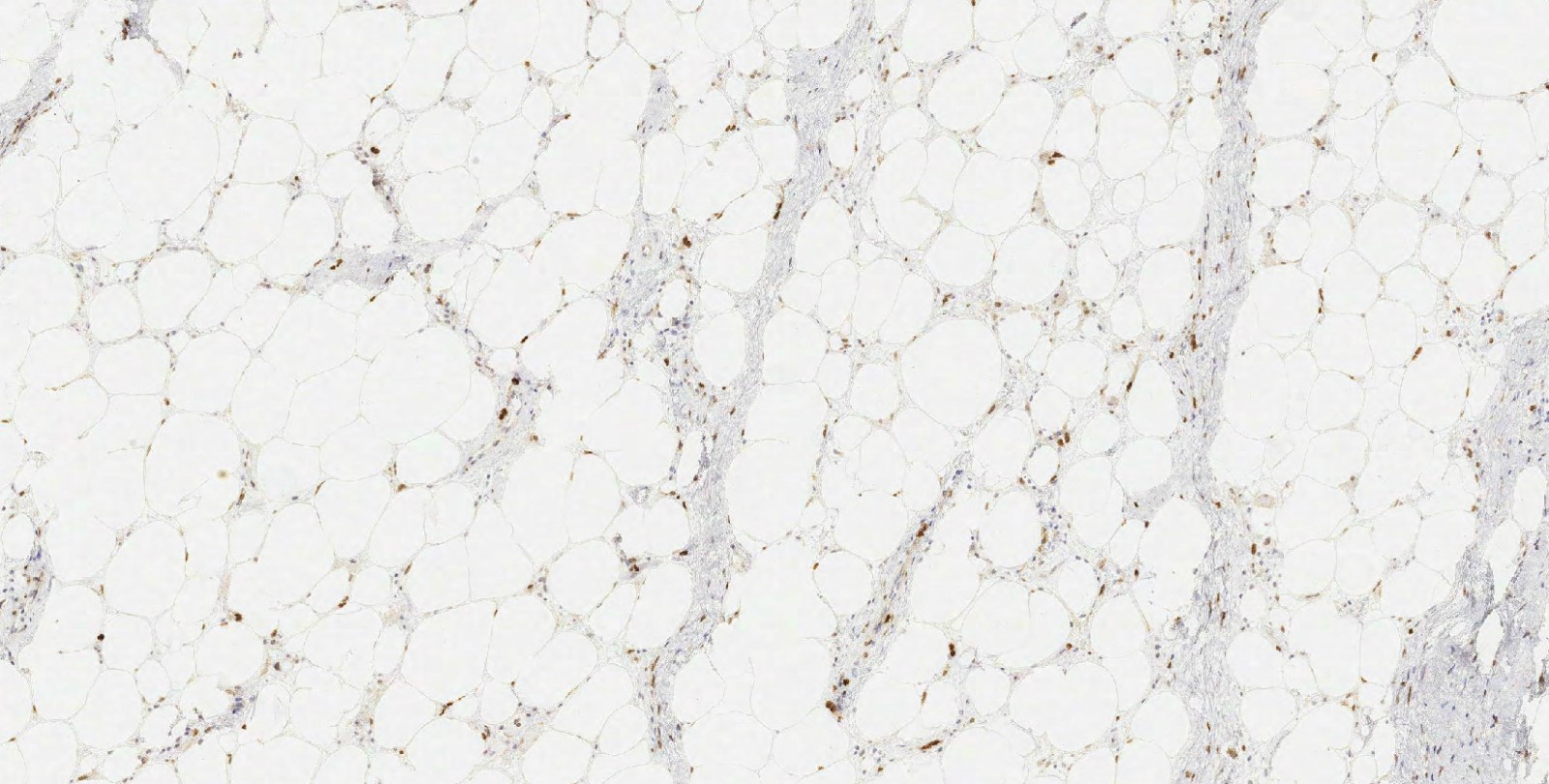
- Strong nuclear staining can be seen in multinucleated giant cells and foamy macrophages in lipomatous tumors (Virchows Arch 2010;456:167, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1647)
Positive staining - disease
- Liposarcoma: well differentiated and dedifferentiated (Virchows Arch 2020;476:29, Semin Diagn Pathol 2019;36:112, Virchows Arch 2010;456:167)
- Osteosarcoma, low grade and parosteal and those that dedifferentiate to high grade osteosarcoma (Mod Pathol 2011;24:624, J Chin Med Assoc 2019;82:889, Mod Pathol 2010;23:1279)
- Intimal sarcoma (Cardiovasc Pathol 2019;43:107142)
- Rhabdomyosarcoma, sclerosing (some cases) (Sarcoma 2013;2013:520858, Hum Pathol 2009;40:1347)
Negative staining
- Benign adipose tumors, poorly differentiated sarcomas (Virchows Arch 2010;456:167)
- Atypical spindle cell / pleomorphic lipomatous tumor (polysomy 12 may be seen) (Virchows Arch 2020;476:29, Virchows Arch 2010;456:167, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:234)
- Myxoid liposarcoma (rarely positive), pleomorphic liposarcoma, pleomorphic myxoid liposarcoma (Virchows Arch 2020;476:29, Virchows Arch 2010;456:167)
- Periosteal osteosarcoma (Hum Pathol 2015;46:549)
- Benign fibrous and fibro-osseous lesions (fibrous dysplasia, myositis ossificans, reactive periostitis, osteochondroma, others) (Mod Pathol 2010;23:1279)
- Pleomorphic liposarcoma of skin / subcutis usually (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1047)
- Neurofibroma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:95)
- Schwannoma (MDM2 gains in 15% of vestibular schwannomas but no amplifications) (Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2013;270:2433)
- Rhabdomyosarcoma, pediatric (Sarcoma 2012;2012:492086)
- Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor - positivity varies: amplification detected in 6 - 20% (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:95, Mod Pathol 2018;31:1694, JCO Precis Oncol 2018;2018:PO.17.00235)
- Focal / weak / moderate (10%) or strong (26%) IHC staining corresponding to polysomy / weak gain / weak amplification (34%) or high level amplification (1.5%) by FISH (H3K27me3 IHC recommended instead) (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:656)
- Angiosarcoma (Cardiovasc Pathol 2019;43:107142)
- Pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma 14% (Cardiovasc Pathol 2019;43:107142)
- Myxofibrosarcoma (Virchows Arch 2010;456:167)
- Low grade fibromyxoid sarcomas (Virchows Arch 2010;456:167)
- Gallbladder adenocarcinoma (11.2%), lung adenosquamous carcinoma (9.8%), glioblastoma (7.2 - 8.2%), urothelial carcinoma (2.9 - 10.4%), duodenal adenocarcinoma (7.8%), ovarian carcinosarcoma (7.8%) (Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2016;6:a026336, JCO Precis Oncol 2018;2018:PO.17.00235)
- Adrenal gland: adrenocortical carcinoma (1.1%), pheochromocytoma (Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2016;6:a026336)
- Brain: astrocytomas (not glioblastoma multiforme) (0.4%) (Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2016;6:a026336)
- Breast: invasive carcinoma (0.9%) (Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2016;6:a026336)
- Gastrointestinal tract: cholangiocarcinoma (2.8%), colorectal adenocarcinoma, esophageal carcinoma, gastric adenocarcinoma (1.6 - 5.5%), hepatocellular carcinoma, pancreatic adenocarcinoma (Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2016;6:a026336, JCO Precis Oncol 2018;2018:PO.17.00235)
- Genitourinary: clear cell renal cell carcinoma, papillary renal cell carcinoma, chromophobe renal cell carcinoma, prostate adenocarcinoma, testicular germ cell tumors (1.3%) (Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2016;6:a026336)
- Gynecologic: endometrial carcinoma, ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma (0.3%), cervical squamous carcinoma (0.3%), uterine carcinosarcoma (Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2016;6:a026336)
- Head and neck: squamous cell carcinoma (Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2016;6:a026336)
- Hematolymphoid: diffuse large B cell lymphoma (Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2016;6:a026336)
- Lung: adenocarcinoma (0.9 - 5.6%), squamous cell carcinoma (0.2%), mesothelioma (JCO Precis Oncol 2018;2018:PO.17.00235, Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2016;6:a026336)
- Skin: cutaneous melanoma (Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2016;6:a026336)
- Thyroid: thyroid carcinoma (Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2016;6:a026336)
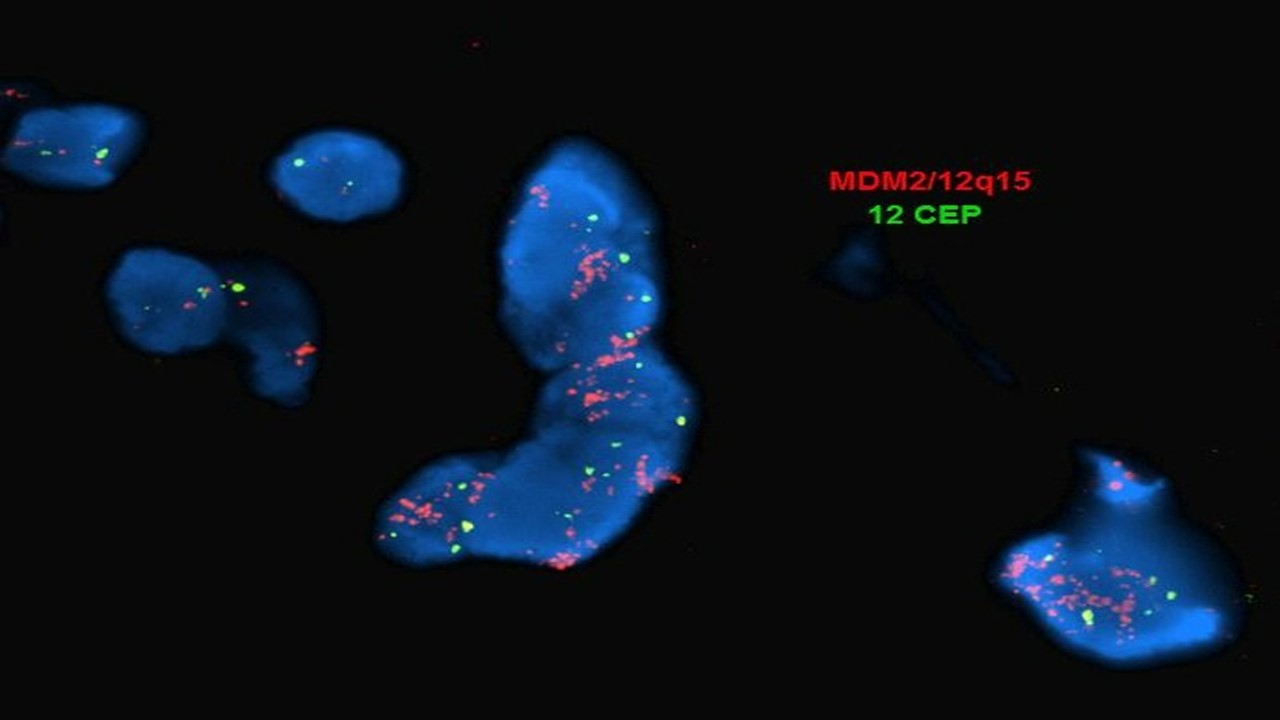
Molecular / cytogenetics description
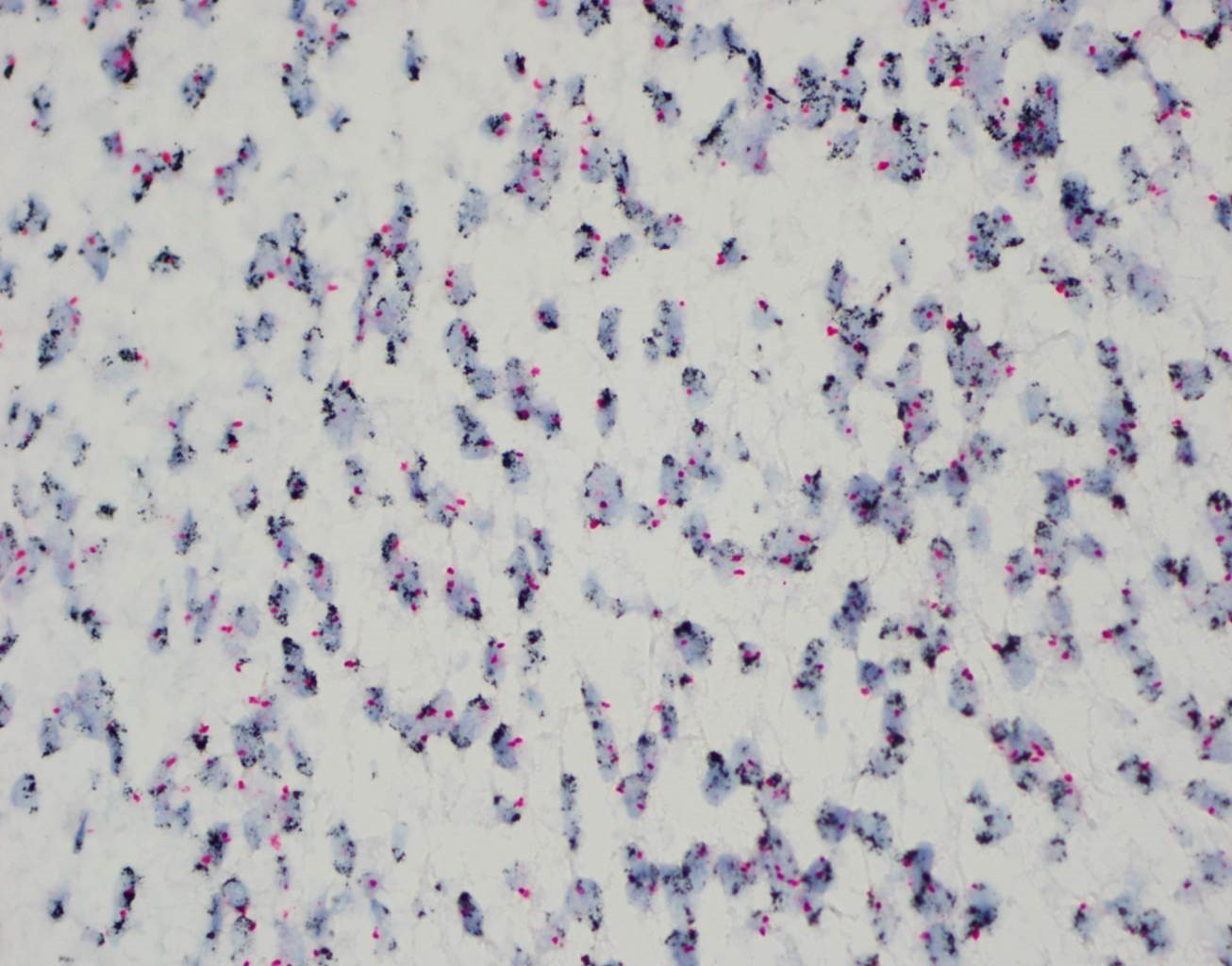
- FISH: true amplification indicated by increased number of MDM2 probe signals as compared with centromeric chromosome 12 probe (positive cutoff ratio set by lab); polysomy 12 (increased number of both MDM2 and centromeric chromosome 12 signals) seen in other sarcomas, especially with complex karyotype (Virchows Arch 2010;456:167, Cardiovasc Pathol 2019;43:107142)
- Dual color chromogenic in situ hybridization (DISH or CISH): same interpretation as FISH with high concordance between the 2 methods; benefits include light microscopy (rather than fluorescent), ability to store slides, ability to evaluate morphology of counterstained tissues and lower cost and turnaround time (J Clin Lab Anal 2015;29:462, Cardiovasc Pathol 2019;43:107142)
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1