Table of Contents
Definition / general | Diagrams / tables | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Molecular / cytogenetics descriptionCite this page: Bradish J. HRAS. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsHRAS.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- HRAS, Harvey rat sarcoma viral oncogene homologue, is a proto-oncogene located on chromosome 11p
- This gene encodes for transforming protein 21, which binds GTP for activation and contains intrinsic GTPase activity (Genes Cancer 2011;2:344)
- HRAS is very similar to NRAS and KRAS in its structure
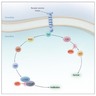
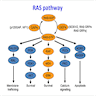
- HRAS is involved in both the MAPK pathway and AKT pathway
- HRAS activates RAF enzymes (i.e. CRAF or BRAF) in the MAPK pathway
Treatment
- No specific targeted therapy against HRAS currently exists
- No mechanisms of resistance have been evaluated
- No resistance therapies have been evaluated
Microscopic (histologic) description
- HRAS mutations are most often associated with Spitz nevi (Am J Pathol 2000;157:967)
- HRAS mutations are not associated with Spitzoid melanoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:1436)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- HRAS mutations are most frequently found in codons 12, 13 and 61
- Amplification of HRAS / 11p is also not infrequently identified
- Amplification and mutations of HRAS are not mutually exclusive (Am J Pathol 2000;157:967)
- HRAS mutations are associated with Costello syndrome (Wikipedia: Costello Syndrome [Accessed 12 June 2018]), which is associated with delayed development, intellectual disability, cardiomyopathy, coarse facial features, loose skin and a predilection for developing rhabdomyosarcoma, bladder cancer or neuroblastomas
- Detection of HRAS / 11p amplification can be performed using FISH probes
- Detection of specific HRAS mutations can be performed using PCR assays (Am J Pathol 2000;157:967)