Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Wirth P. HMGA2. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsHMGA2.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Transcription factor involved in maintenance and regulation of replication, recombination, transcription and DNA repair that is strongly upregulated in many cancers
Essential features
- HMGA 2 (high mobility group AT hook 2) belongs to nonhistone chromosomal high mobility group protein family
- Consists of 4 proteins: HMGA1a, HMGA1b, HMGA1c and HMGA2
- Highly expressed in embryonic stem cells during embryogenesis
- Highly expressed in many human malignancies
Terminology
- HMG1C
Pathophysiology
- Involved in maintenance and regulation of replication, recombination, transcription and DNA repair
- Activates signaling via MAPK / ERK, TGFβ / Smad, PI3K / Akt / mTor, NFkβ and STAT3 pathways
- Transcription factor that increases cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting apoptosis and cell cycle entry
- Promoter of epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) (Genes (Basel) 2021;12:269)
- Enhances expression of EMT regulators such as Snail, Twist, Slug and ZEB1 resulting in the downregulation of E-cadherin and upregulation of vimentin (J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2021;147:3313)
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features
- Can be part of the panel used for differential diagnosis between benign thyroid lesions (such as nodular goiter) and malignant thyroid tumors (such as papillary thyroid carcinoma)
- High expression in papillary carcinoma and anaplastic carcinoma; negative in normal thyroid (Eur J Cancer 2008;44:1015)
- HMGA2 positivity can be seen in some soft tissue subtypes like lipomas or aggressive fibromatosis
- Helpful for the distinction of normal adipose tissue (negative) from well differentiated lesions (positive)
- Expressed almost exclusively by atypical lipomatous tumor / well differentiated and dedifferentiated liposarcomas
- HMGA2 is expressed in benign fibrous histiocytoma, nodular fasciitis and vulvovaginal benign mesenchymal tumors (Mod Pathol 2010;23:1657)
Interpretation
- Nuclear expression in most tissues
- Some cytoplasmic expression is correlated with lymph vessel and venous invasion in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2021;147:3313)
- May show cytoplasmic expression in luminal A and triple negative breast cancer, which is associated with a more favorable overall survival (Int J Biol Markers 2020;35:20)
Uses by pathologists
- Helpful for the distinguishing normal adipose tissue from well differentiated adipose lesions
- Useful for the diagnosis of benign fibrous histiocytoma, nodular fasciitis and vulvovaginal benign mesenchymal tumors (Mod Pathol 2010;23:1657)
- High nuclear expression is associated with tumor progression, metastasis and resistance to chemotherapy in various cancers (Sci Rep 2018;8:14008)
Prognostic factors
- Overexpression is an unfavorable prognostic marker in urothelial cancer, head and neck cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer and metastatic breast cancer (Clin Cancer Res 2011;17:2570)
- Associated with progression, metastasis and chemotherapy resistance in pancreatic ductal carcinoma (Sci Rep 2018;8:14008)
- Associated with metastasis and reduced survival for patients with stage 3 and 4 colorectal cancer
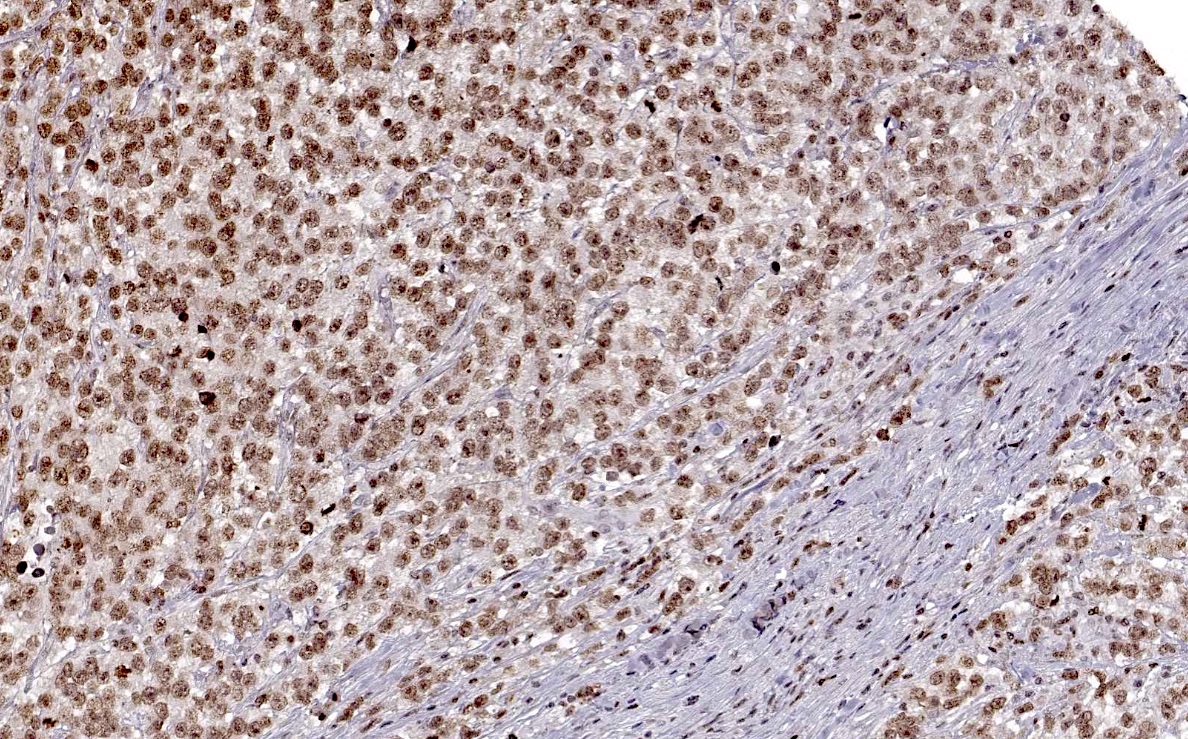
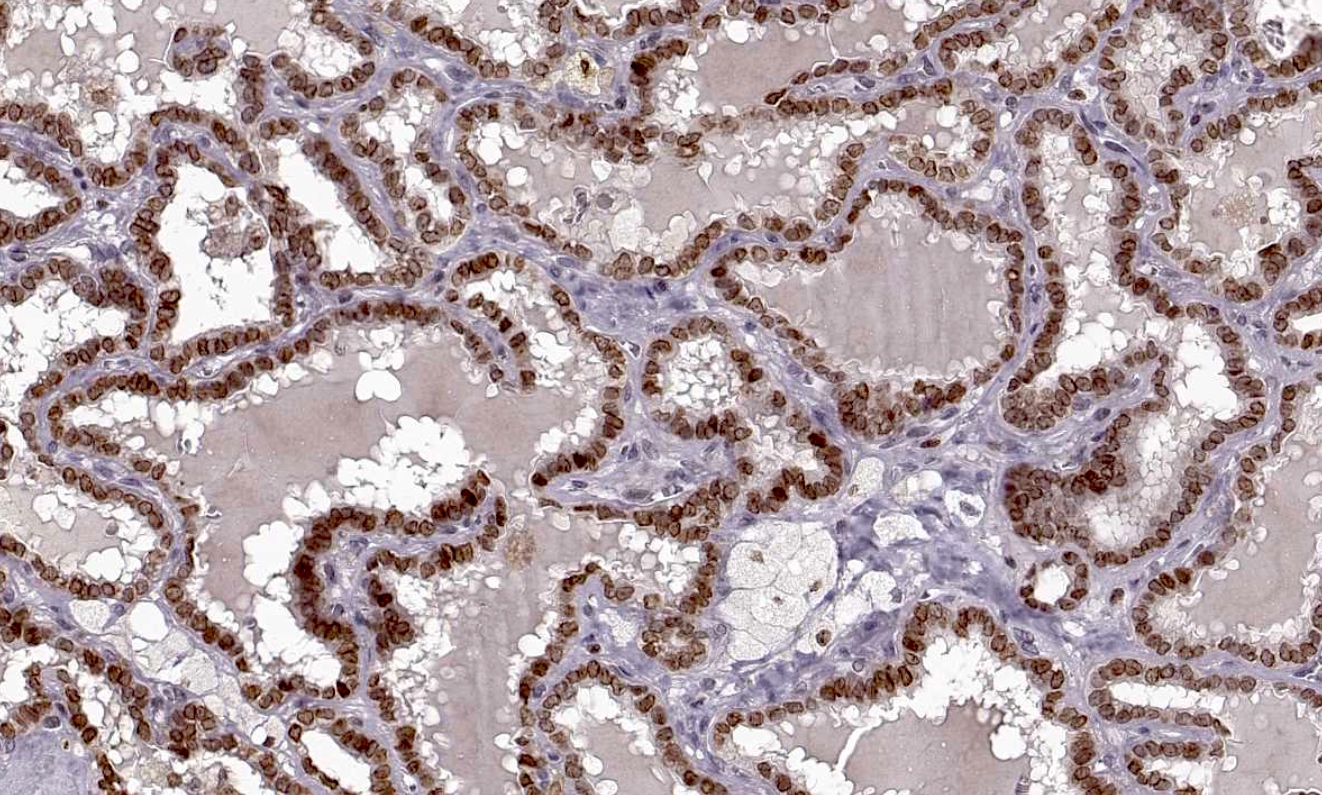
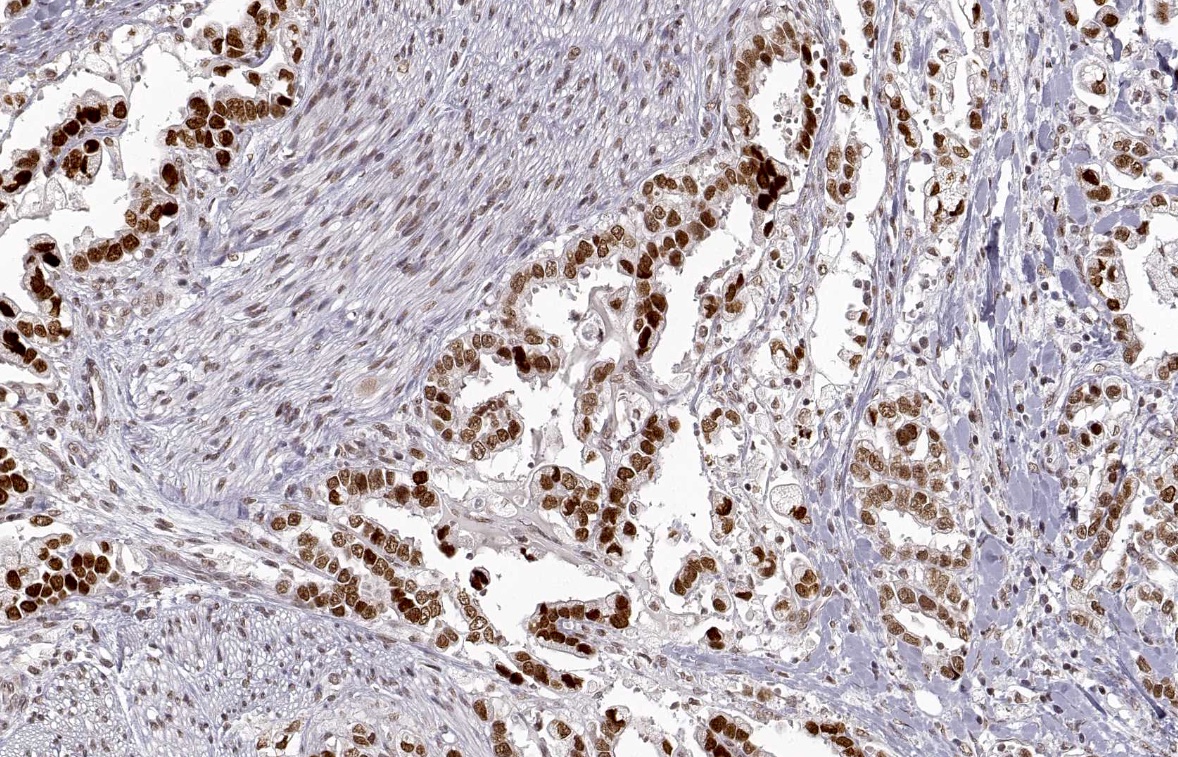
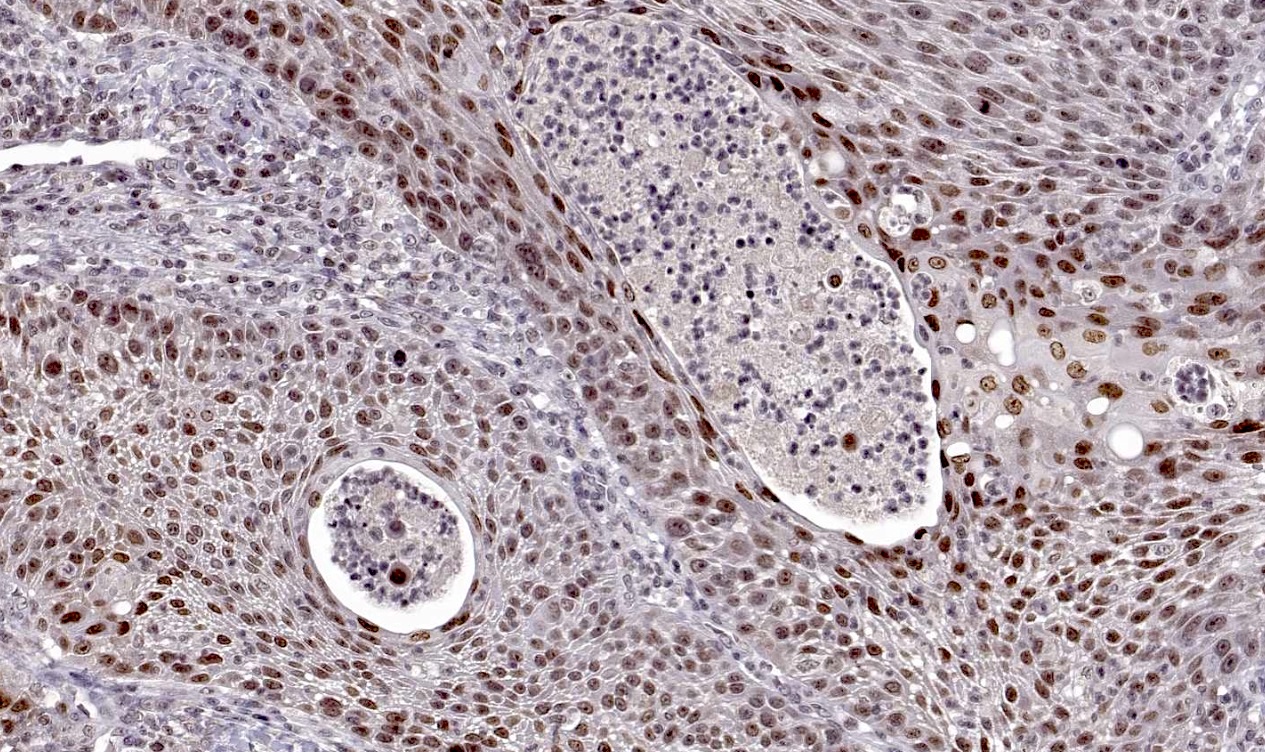
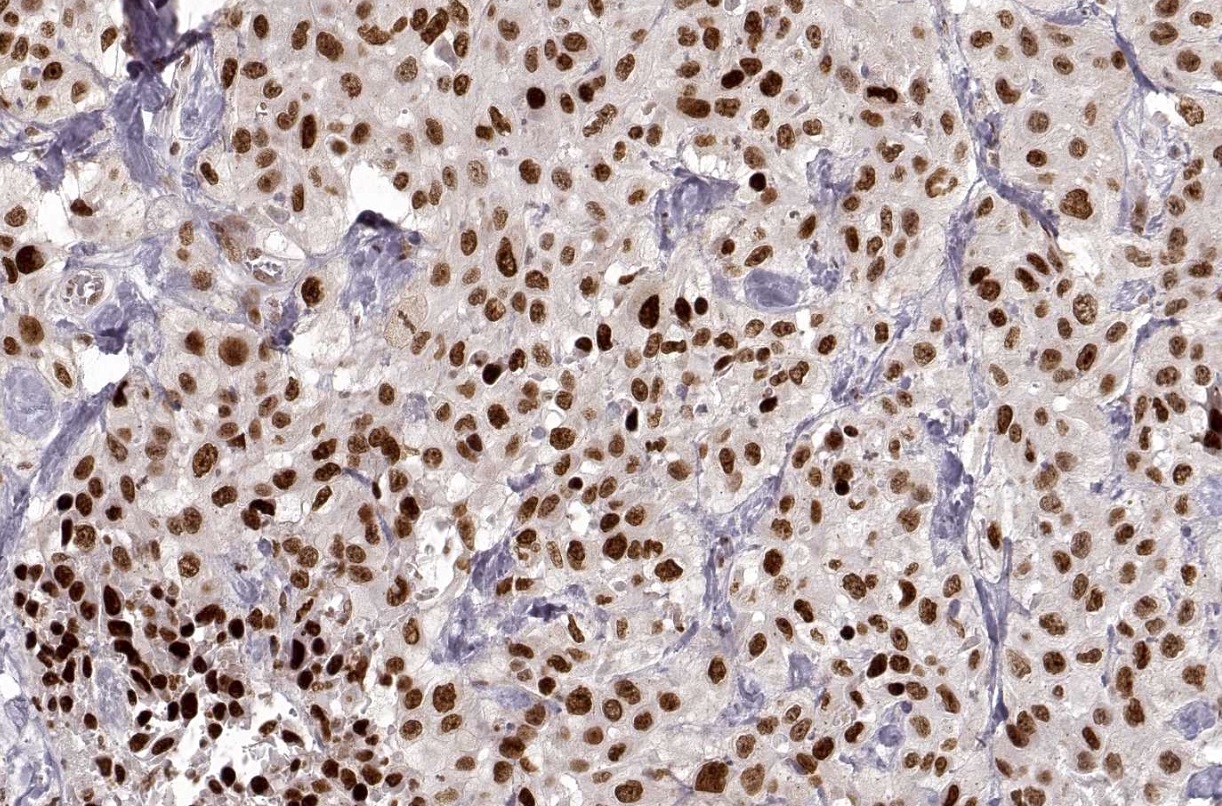
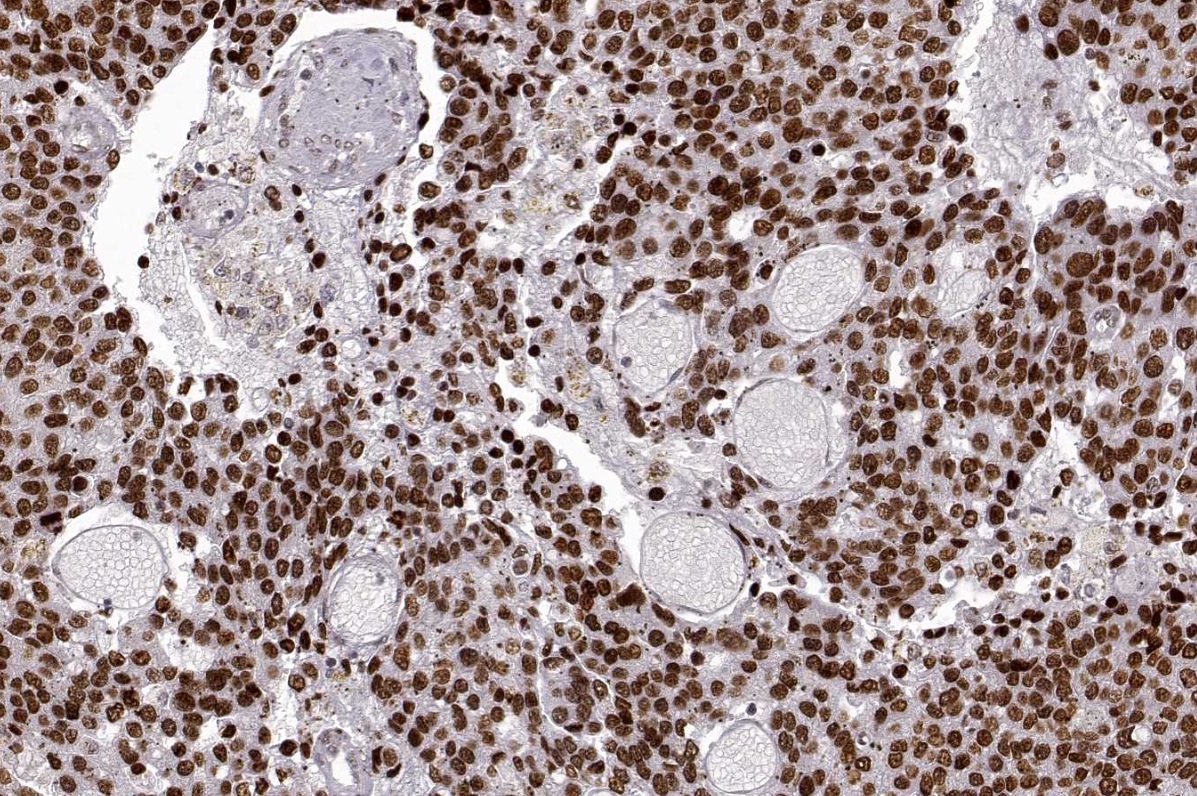
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
- Many fetal tissues express HMGA2, especially kidney, liver and uterus (Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol: HMGA2 (High Mobility Group AT-Hook 2) [Accessed 19 April 2024])
Positive staining - disease
- Positive staining in many carcinomas including those found in breast, pancreas, ovary, lung, colon, nerve system and oral cavity (squamous cell carcinomas) (Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol: HMGA2 (High Mobility Group AT-Hook 2) [Accessed 19 April 2024])
- Strong protein expression in pleomorphic adenomas
- Highly specific (92%) but low sensitivity (30%) (Histopathology 2017;71:511)
- Helpful for distinguishing normal adipose tissue (negative) from well differentiated adipose lesions
- Positive HMGA2 staining found in the following lesions
- 86% of conventional and intramuscular lipomas
- 67% of dedifferentiated liposarcomas
- 66.7% of papillary renal cell carcinomas (Cancer Med 2023;12:14851)
- 83.3% of atypical teratoid / rhabdoid tumors (Clin Cancer Res 2014;20:1179)
- 90% of esophageal squamous carcinomas (predominantly nuclear but may have some cytoplasmic staining) (Oncotarget 2016;7:25872)
- 98.1% of pancreatic ductal carcinomas (strong nuclear staining, some cytoplasmic) (J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2021;147:3313)
Negative staining
- Normal adipose tissue (Mod Pathol 2010;23:1657)
- 15% of non-well differentiated liposarcomas / dedifferentiated liposarcomas may show HMGA2 protein expression (Mod Pathol 2010;23:1657)
- HMGA2 levels are undetectable in most adult cells; however, low levels may be present in lungs, kidneys and benign mesenchymal tumor tissues (BMC Biology 2022;20:171)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Protein is encoded by HMGA2 gene located at chromosomal band 12q14-15 (Int J Mol Sci 2020;21:3151)
- HMGA2 gene may be involved in various rearrangements involving 12q15
- Salivary gland neoplasms associated with recurrent translocations (Histopathology 2017;71:511)
- Deregulation in mesenchymal tumors (such as lipomas) often due to rearrangement of HMGA2 locus in 12q15 (Mol Cancer 2009;8:36)
- Pleomorphic adenomas are associated with rearrangement of HMGA2 locus (Histopathology 2017;71:511)
- Patients with pathogenic variants in HMGA2 have been reported in Silver-Russell syndrome (J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2020;105:dgaa273)
Sample pathology report
- Core biopsy, pancreas:
- Poorly differentiated pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (see comment)
- Comment: Core biopsy of the pancreas showed irregular glands embedded within a prominent desmoplastic stroma containing a mixture of dense collagen, fibroblasts and inflammatory cells. Immunohistochemistry was positive for CK7, CK19, CEA, MUC1 and HMGA2. These findings are consistent for poorly differentiated pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Board review style question #1
Which of the following statements about HMGA2 is correct?
- HMGA2 enhances the proliferation of cancer cells by inhibiting the cell cycle and promoting apoptosis
- HMGA2 is downregulated in many human malignancies
- HMGA2 is primarily expressed in adult tissues and is absent in fetal tissues
- HMGA2 is primarily expressed in the cytoplasm and membrane of normal and neoplastic cells
Board review style answer #1
A. HMGA2 enhances the proliferation of cancer cells by inhibiting the cell cycle and promoting apoptosis. This is supported by its role as a transcription factor that promotes tumor growth and survival along with its documented upregulation in many cancer types. Answer C is incorrect because HMGA2 is widely expressed in undifferentiated cells during embryogenesis but declines as fetal development progresses with very limited expression in adult tissues. Answers B and D are incorrect because HMGA2 activates many signaling pathways related to growth and differentiation and is highly expressed in the nucleus of many cancer types as shown in the associated image of seminoma.
Comment Here
Reference: HMGA2
Comment Here
Reference: HMGA2
Board review style question #2
HMGA2 gene alterations are associated with which of the following conditions?
- Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
- Laron syndrome
- Silver-Russell syndrome
- SOX2 anophthalmia syndrome
Board review style answer #2
C. Silver-Russell syndrome (SRS). SRS, a condition of delayed growth, has been associated with genetic variants in HMGA2 due to microdeletions in chromosomes 12p14. Answer D is incorrect because although SOX2 has similar functions to HMGA2 in the maintenance of embryonic and neural stem cells, anophthalmia syndrome is not a condition associated with HMGA2. Answer A is incorrect because Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome is a growth affecting disorder commonly involving mutations to the CDKN1C gene but is not associated with mutations in HMGA2. Answer B is incorrect because although Laron syndrome is a condition characterized by growth abnormalities, it is caused by mutations in the growth hormone receptor gene.
Comment Here
Reference: HMGA2
Comment Here
Reference: HMGA2