Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Sample pathology report | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Pernick N. HGAL. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsHGAL.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
Essential features
- Germinal center marker
- Useful to diagnose diffuse large cell lymphoma, particularly if CD10-
- Marker of T follicular helper (TFH) cells - useful to diagnose TFH derived lymphomas including angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma
Terminology
- Also known as germinal center expressed transcript 2 (GCET2), germinal center associated signaling and motility (GCSAM) (Blood Adv 2021;5:5072)
Pathophysiology
- Regulates B cell receptor signaling and cell motility; may interact with tubulin and other cytoskeletal proteins to regulate lymphoma motility and spread (Blood 2010;116:5217, Blood Adv 2021;5:5072)
Interpretation
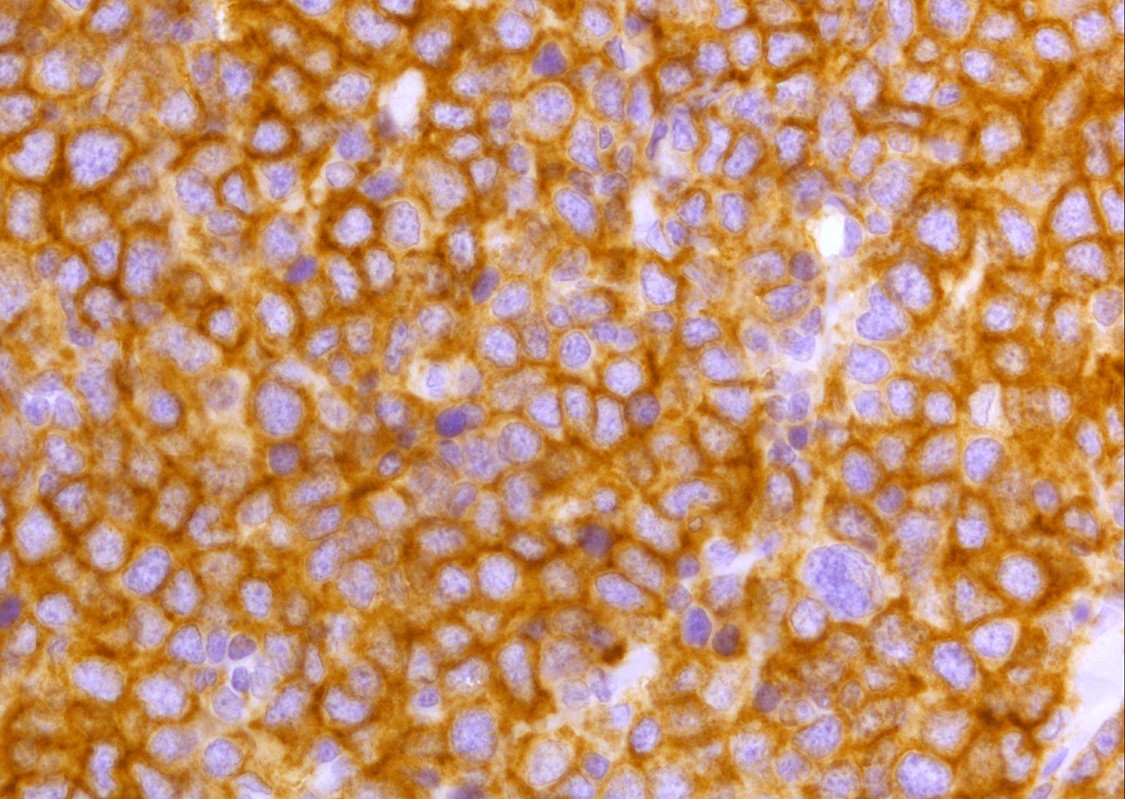
- Cytoplasmic staining
Uses by pathologists
- Can increase the accuracy of classification of diffuse large cell lymphoma cases, particularly CD10- cases (Turk J Haematol 2023;40:162)
- For follicular lymphoma, more sensitive than BCL6 and CD10
- Particularly helpful in detecting its interfollicular and diffuse components
- Useful to detect tumors at nodal and extranodal sites, although less sensitive in the bone marrow (Diagn Pathol 2011;6:97, Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:1266, Am J Clin Pathol 2011;135:697)
- Helps classify cutaneous large B cell lymphomas (Mod Pathol 2008;21:653)
- Associated with prolonged survival in diffuse large B cell lymphoma and classical Hodgkin lymphoma (Blood 2003;101:433, Leuk Lymphoma 2009;50:1830, Blood 2007;109:298)
- Reliable marker of T follicular helper (TFH) cells; useful to diagnose TFH lymphomas, particularly early patterns of angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2022;46:643)
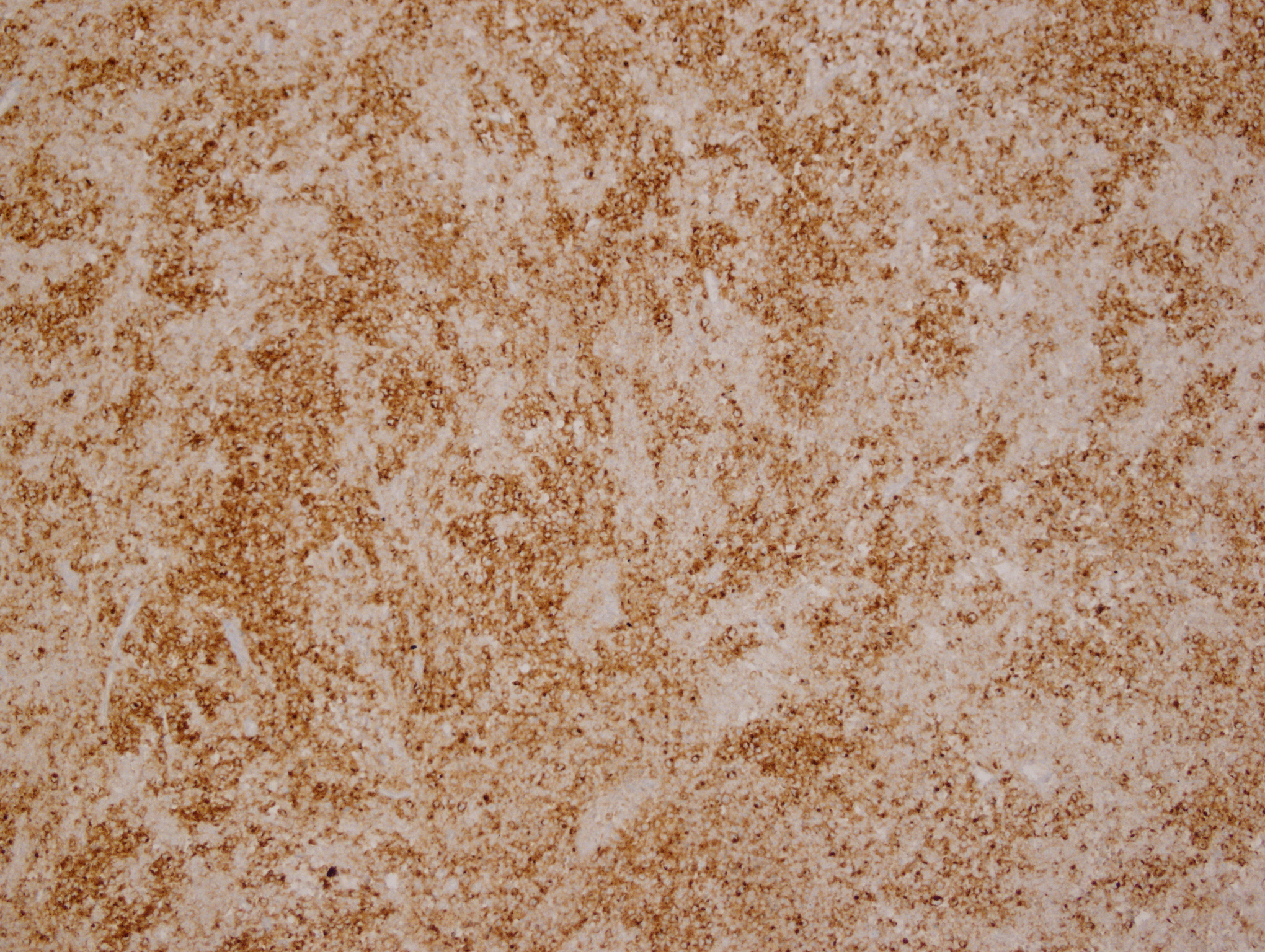
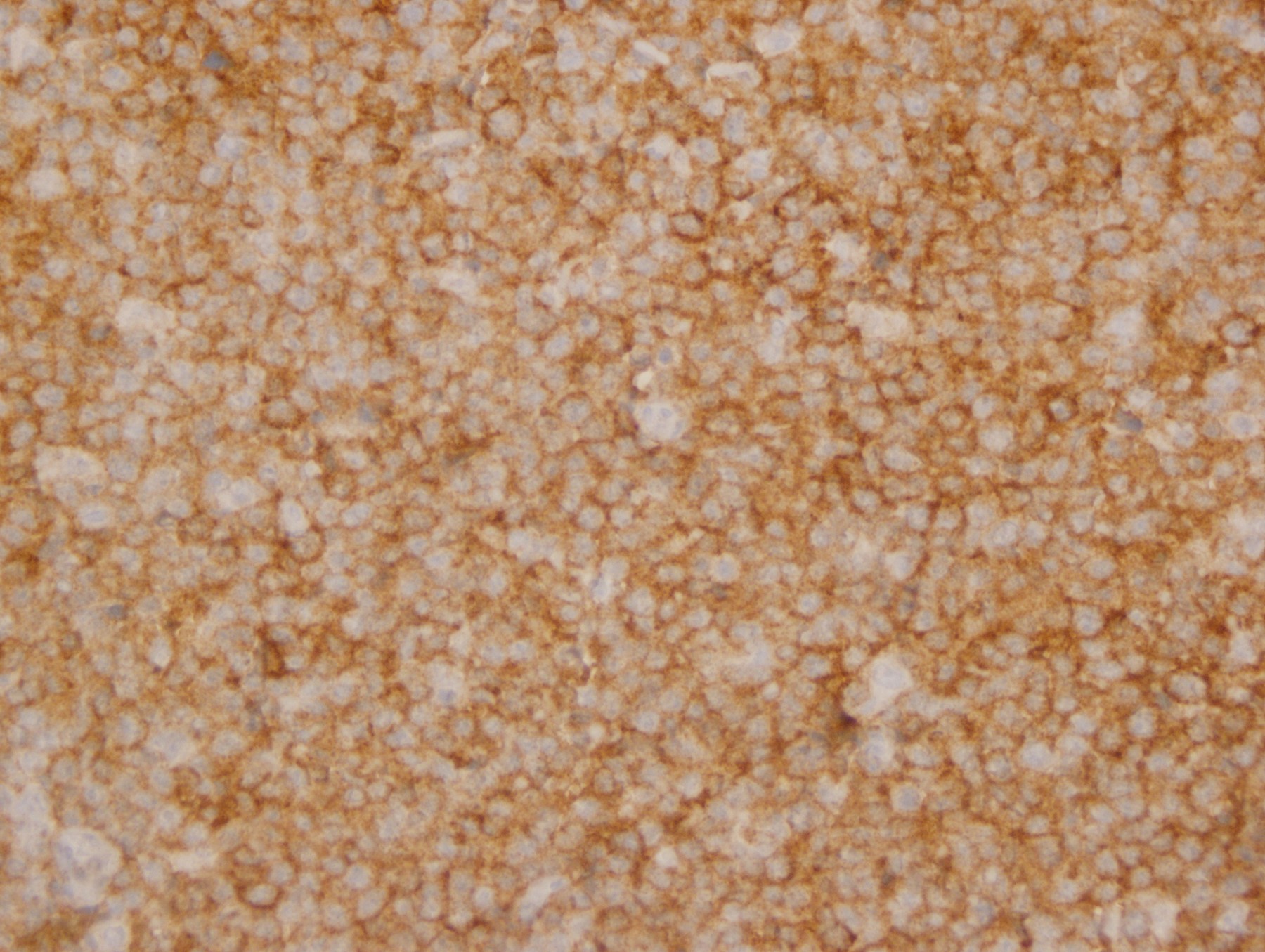
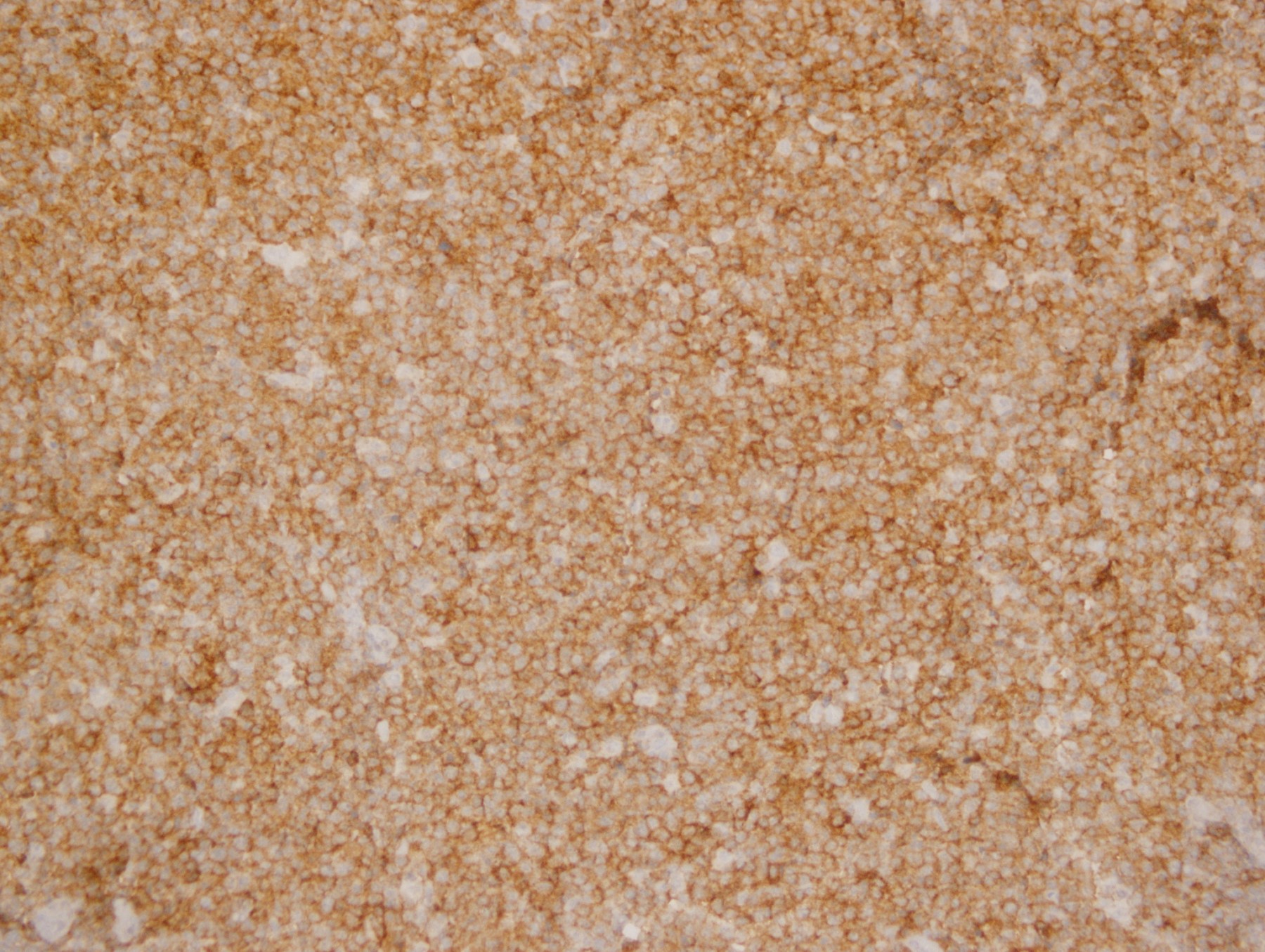
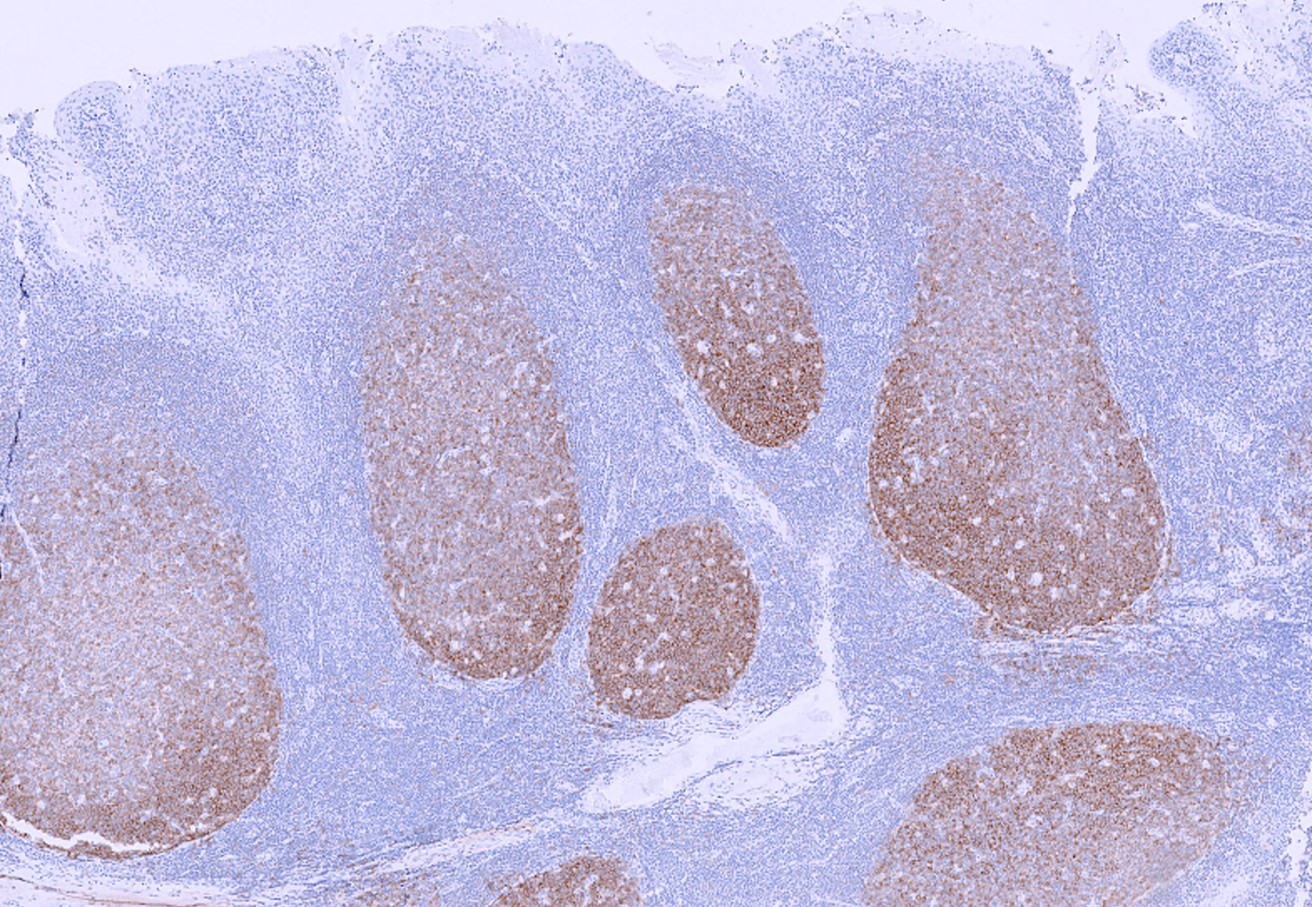
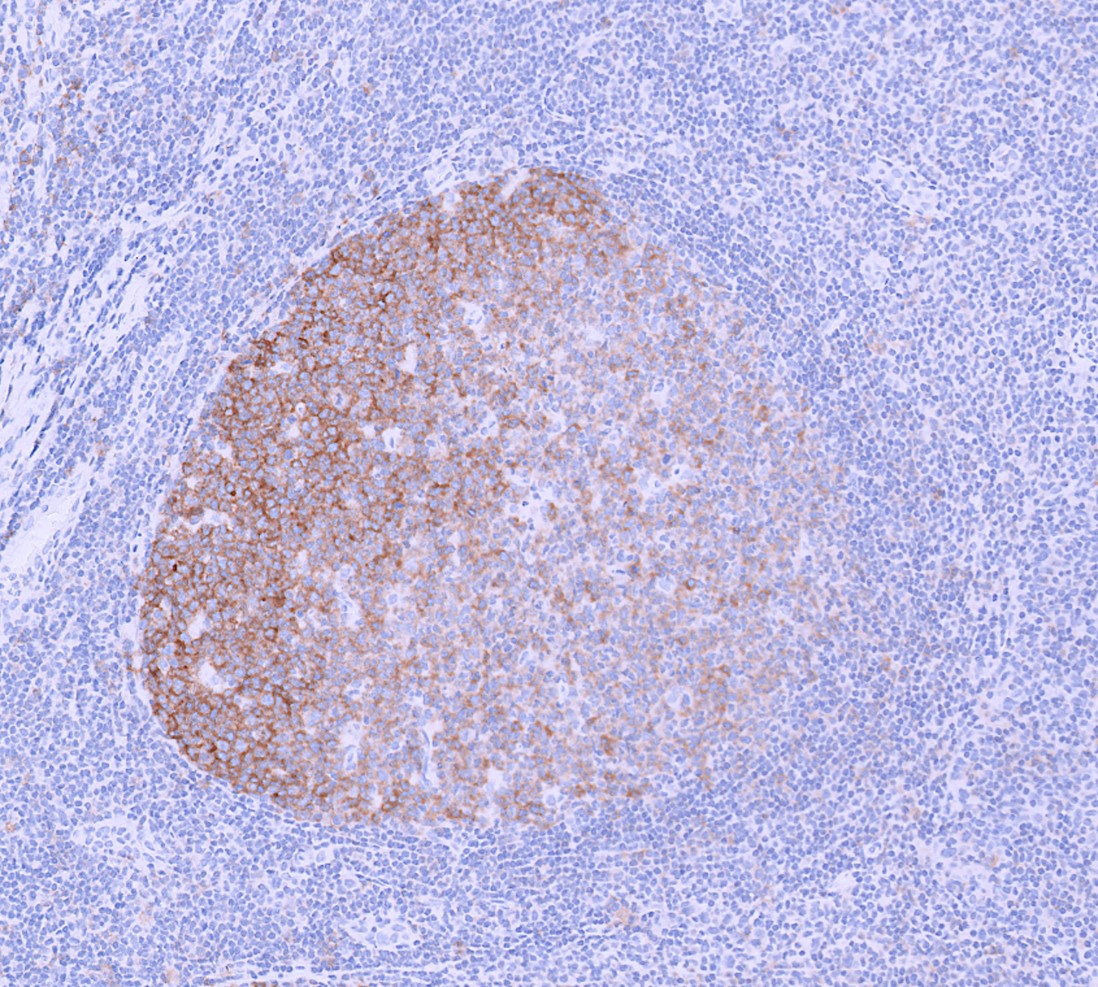
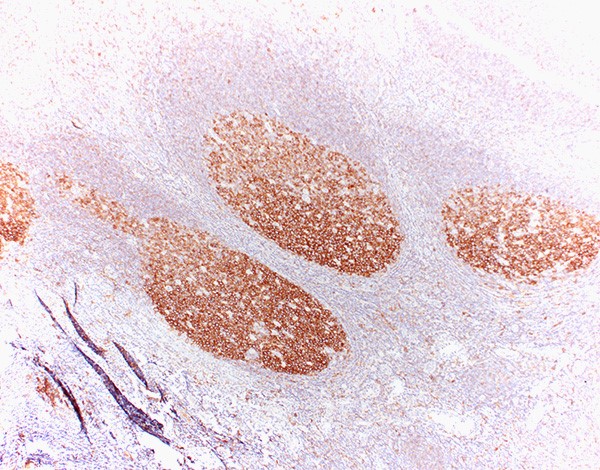
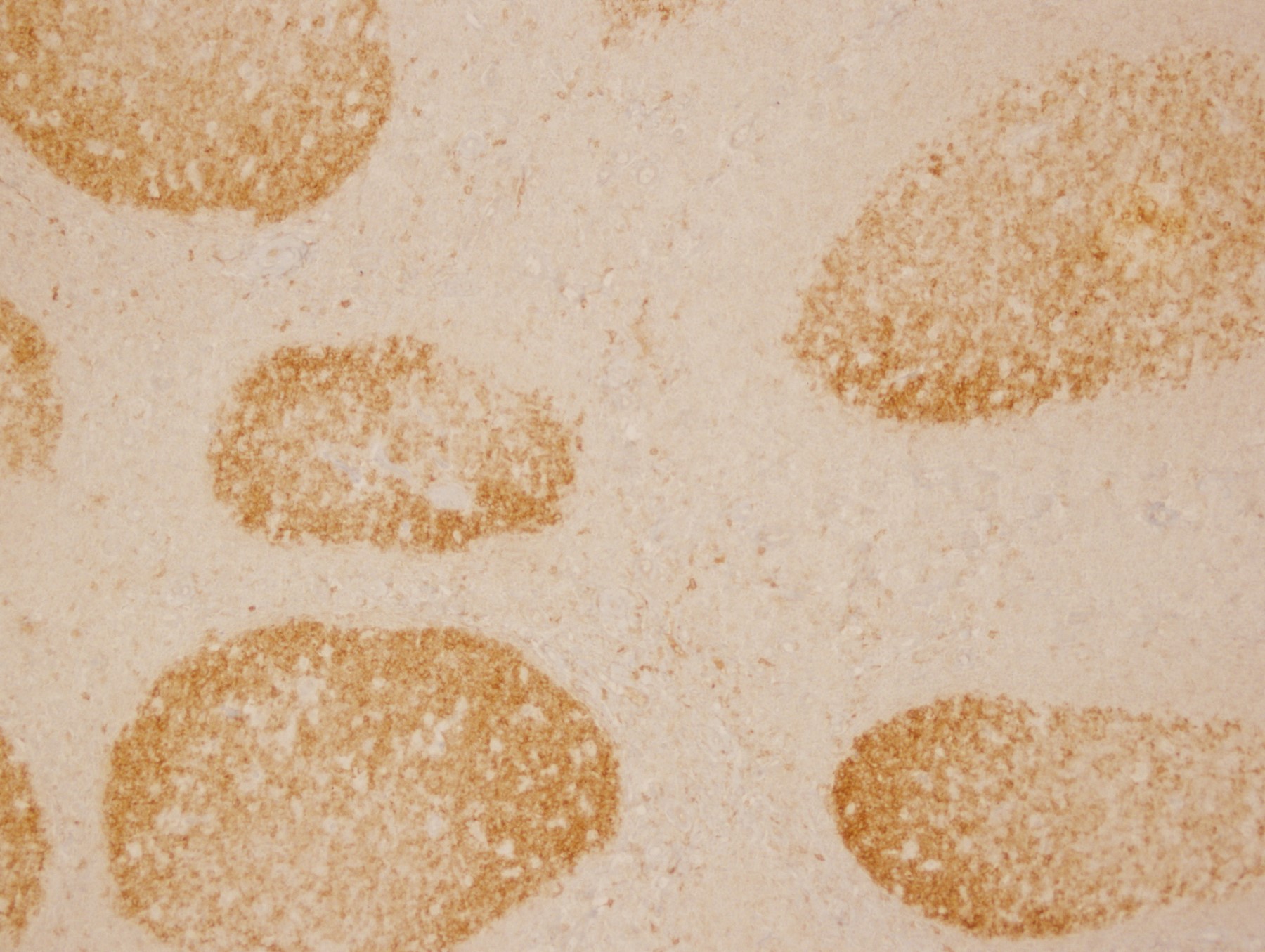
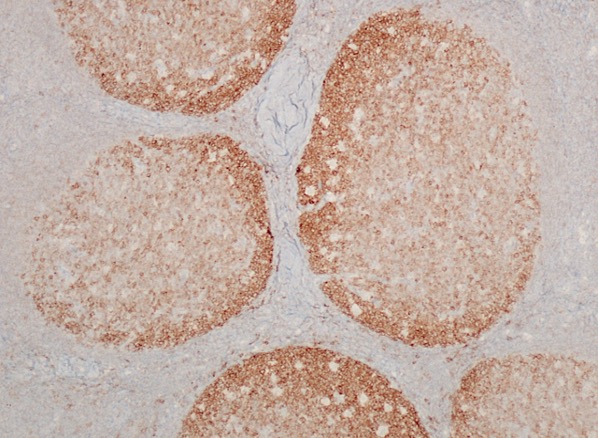
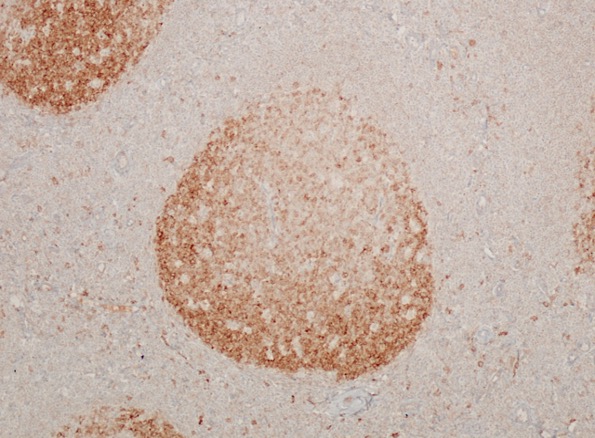
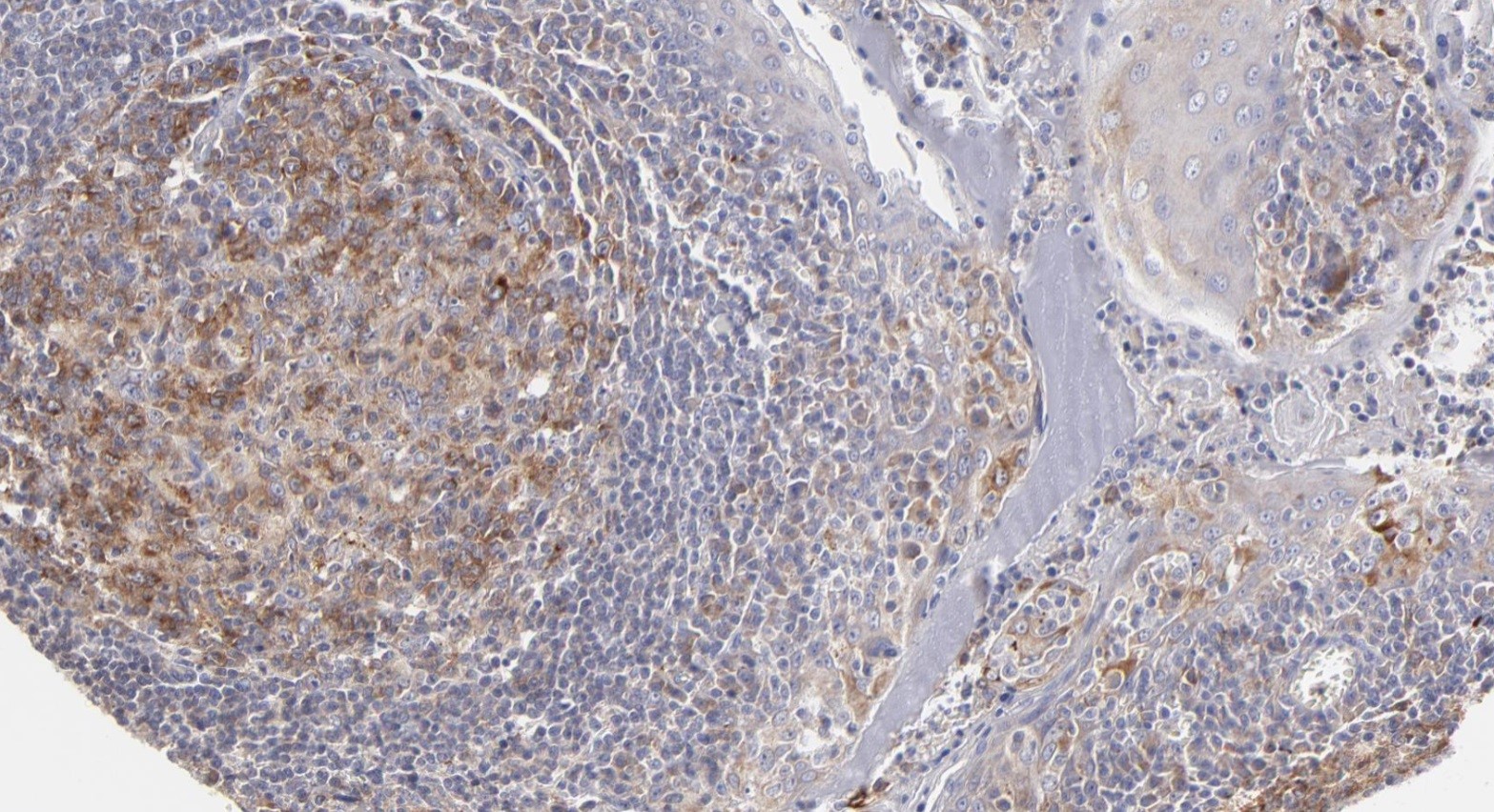
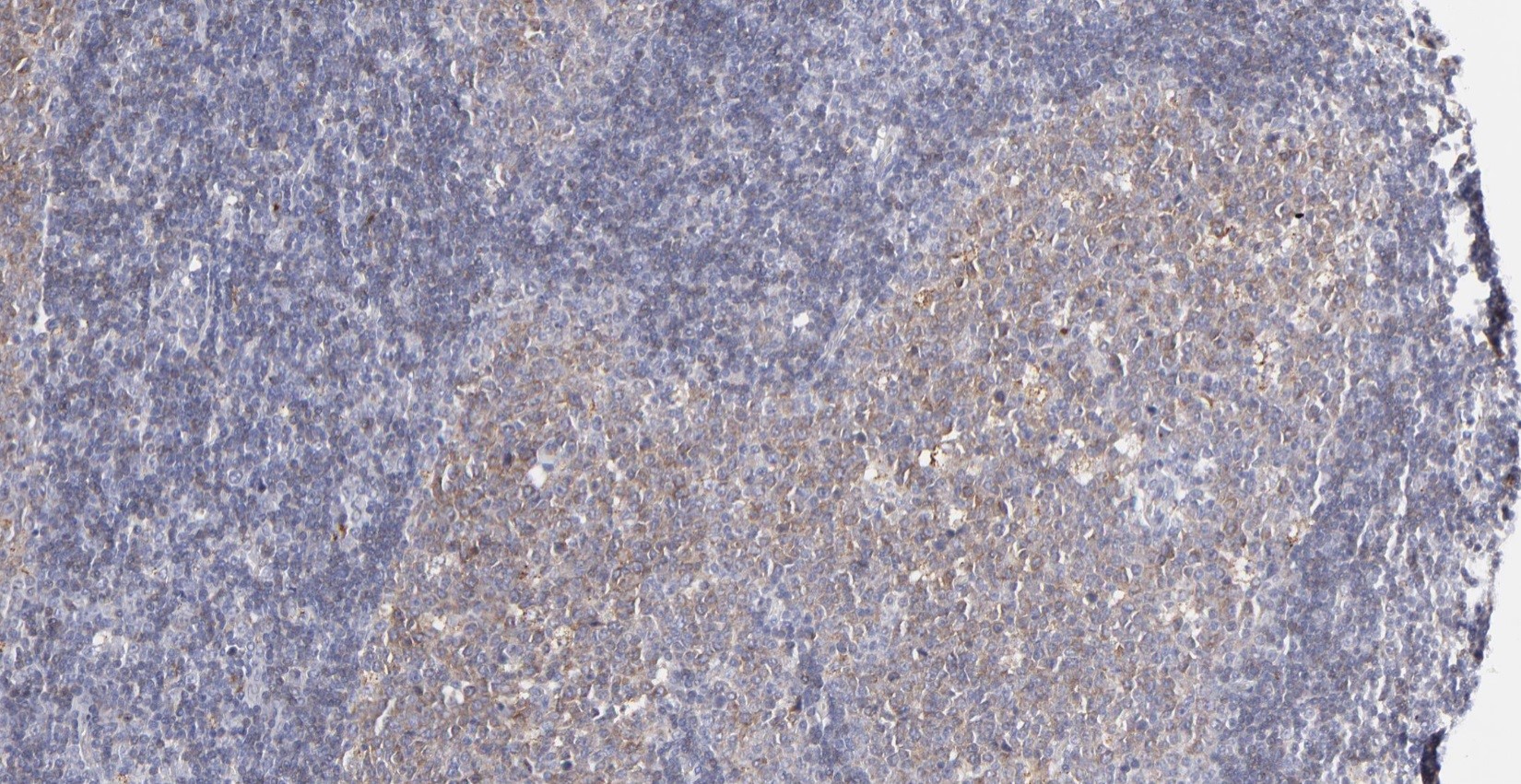
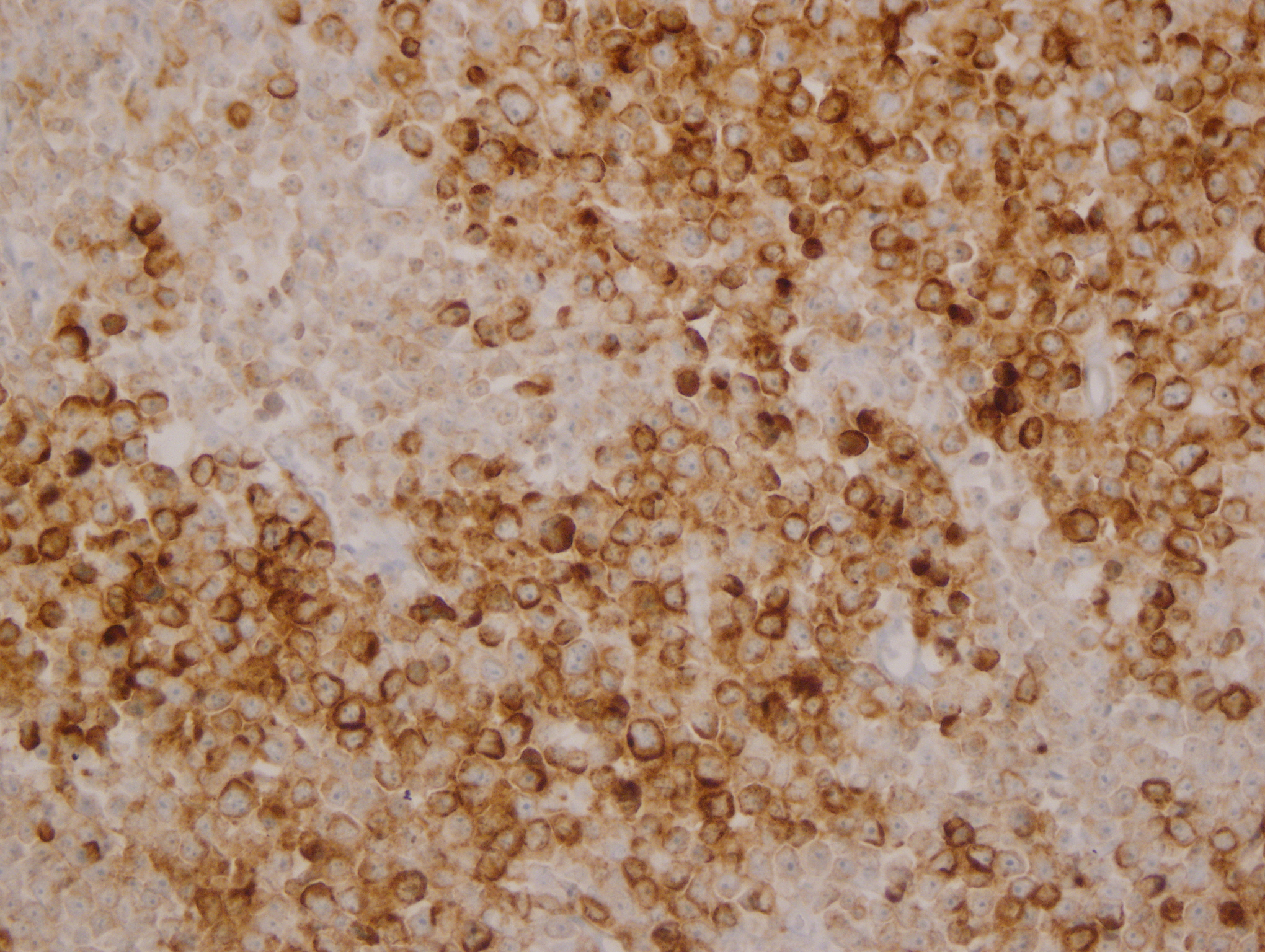
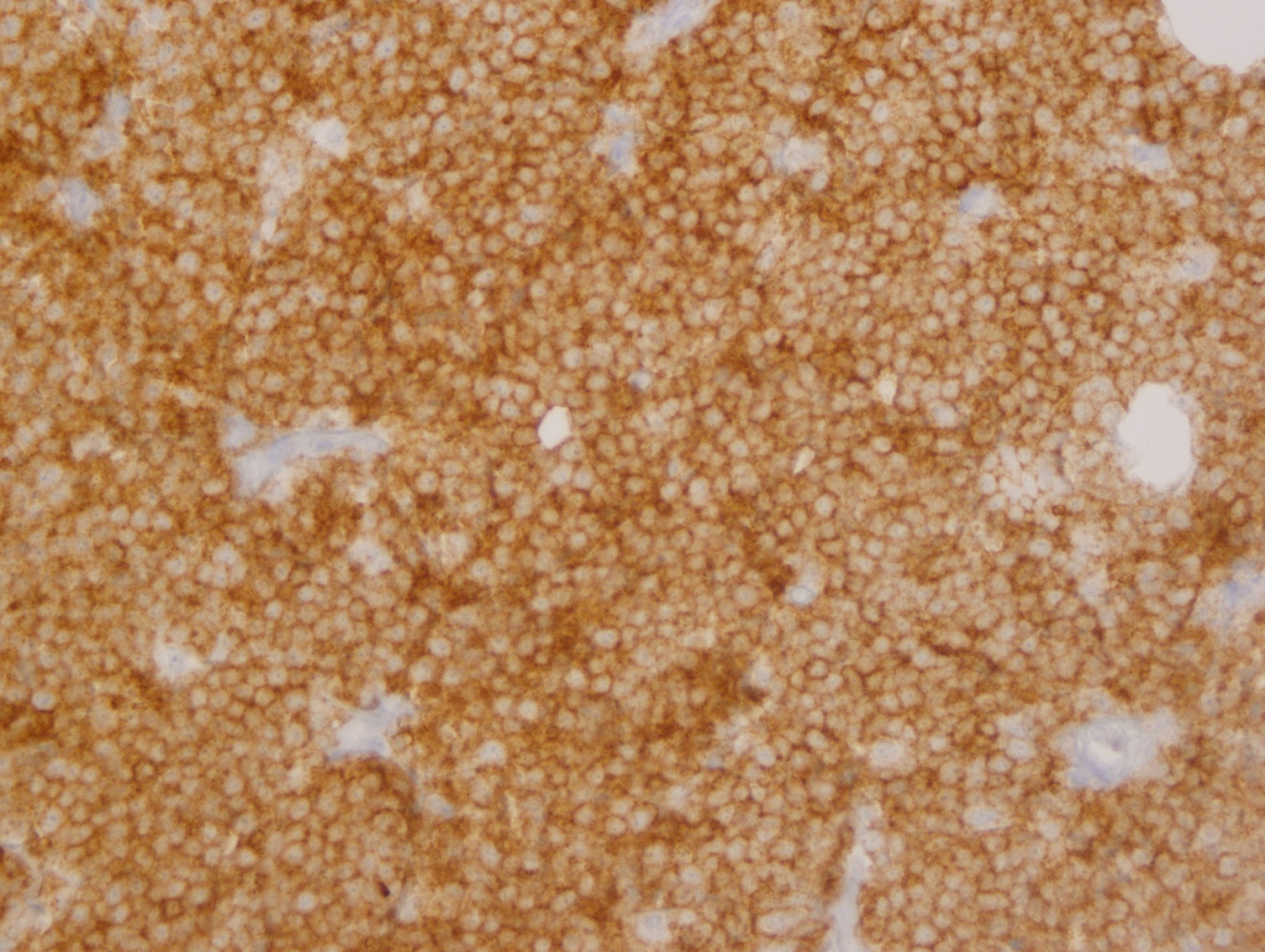
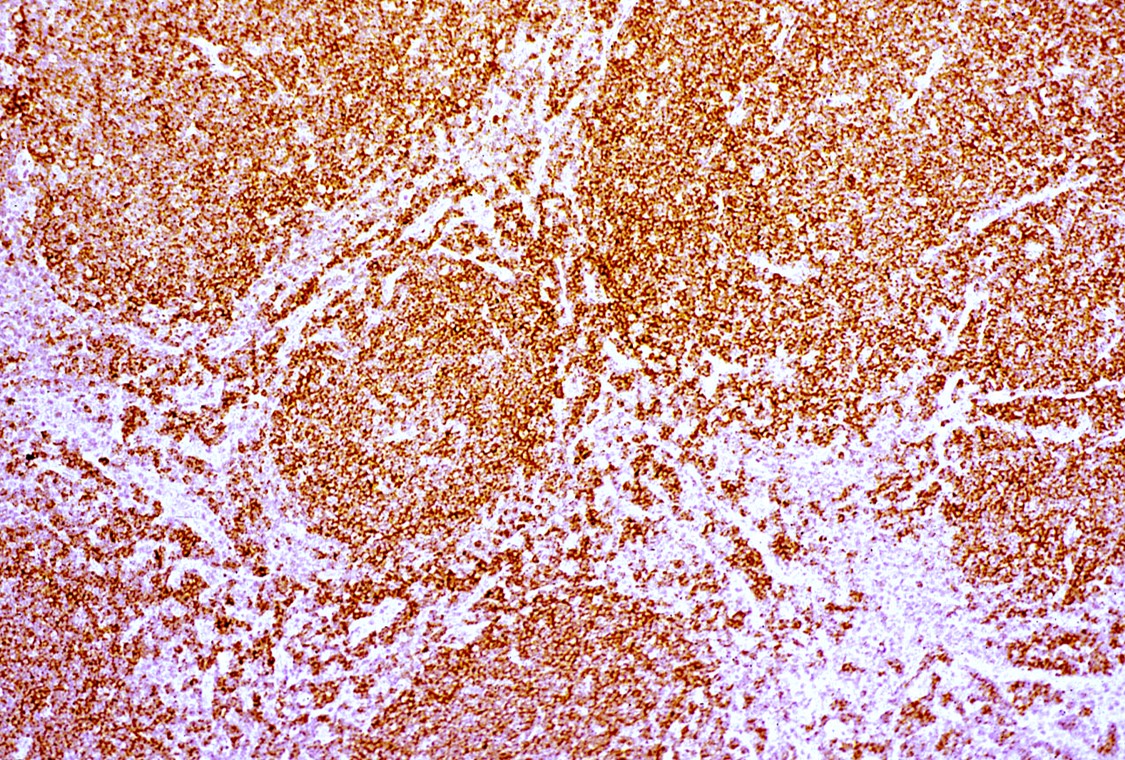
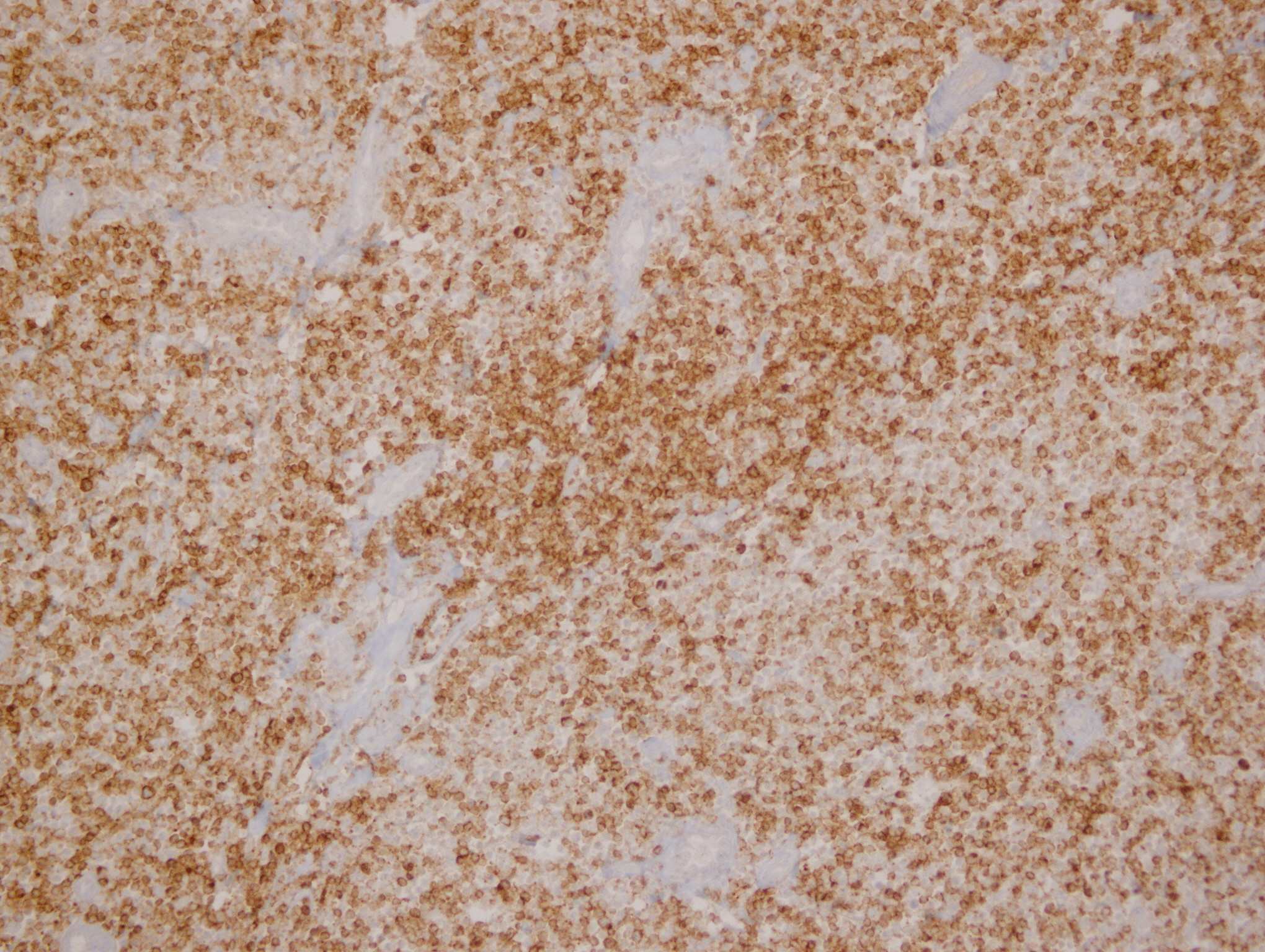
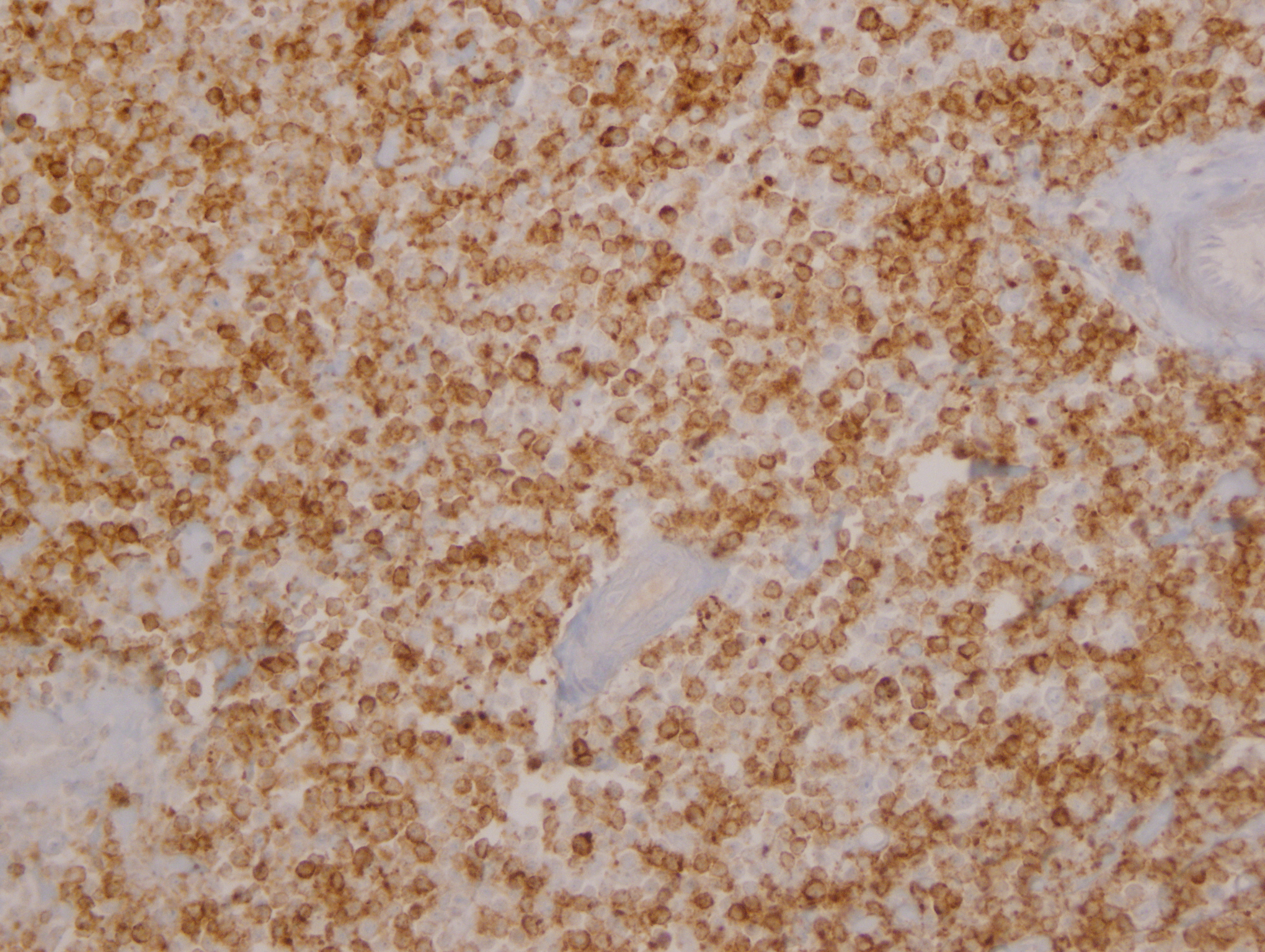
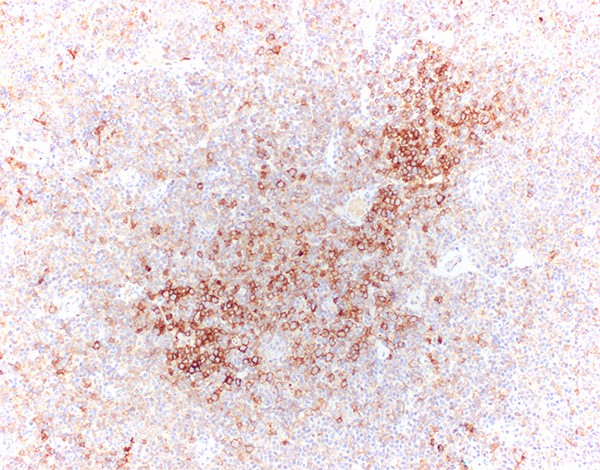
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Yasodha Natkunam, M.D., Ph.D., Izidore S. Lossos, M.D., Jennifer Rose Chapman, M.D., Nat Pernick, M.D. and Neslihan Berker, M.D.
Positive staining - normal
- Germinal center lymphocytes
- T follicular helper cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2022;46:643)
Positive staining - disease
- Germinal center derived lymphomas, including follicular center cell lymphoma
- Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (54% of cases, 84% of germinal center B cell [GCB] derived cases and 35% of non-GCB cases) (Turk J Haematol 2023;40:162)
- Lymphomas of TFH derivation, particularly early patterns of angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2022;46:643)
Negative staining
- Small lymphocytic lymphoma, plasmablastic lymphoma, marginal zone lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoma, peripheral T cell lymphoma, anaplastic large cell lymphoma (Turk J Haematol 2023;40:162)
Sample pathology report
- Axillary lymph node, excision:
- Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show partial or complete effacement of normal tissue architecture by a diffuse infiltrate of large atypical B lymphoid cells with vesicular chromatin and prominent nucleoli. The tumor cells are immunoreactive for B cell markers CD20 and CD79a. Although negative for the germinal center marker CD10, they are immunoreactive for HGAL and LMO2.
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
C. HGAL expression is associated with improved survival in diffuse large B cell lymphoma and classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Answers A, B and D are incorrect because HGAL stains follicular center cells, stains T follicular helper cells and is a germinal center cell marker.
Comment Here
Reference: HGAL
Comment Here
Reference: HGAL
Board review style question #2
HGAL is a useful marker in which of the following scenarios?
- Classification of cutaneous large B cell lymphomas
- Detection of follicular lymphoma involving the bone marrow
- Diagnosis of marginal zone lymphoma
- Helps classify CD10+ diffuse large cell lymphoma
Board review style answer #2
A. Classification of cutaneous large B cell lymphomas. HGAL marks germinal center B cells and can aid in the identification of tumors that arise from B lymphocytes such as primary cutaneous large B cell lymphoma. Answer B is incorrect because HGAL is less specific for follicular lymphomas involving the bone marrow and has shown downregulation in some studies. Answer C is incorrect because HGAL is a reliable marker for follicular lymphomas, not marginal zone lymphomas. Answer D is incorrect because HGAL helps classify CD10 negative diffuse large cell lymphomas, not CD positive ones.
Comment Here
Reference: HGAL
Comment Here
Reference: HGAL