Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Haghi L, Jorns JM. Estrogen receptor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsER.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Estrogen receptor (ER) gene on chromosome 6 encodes ER protein
- Member of hormone receptor family of ligand dependent transcription factors
Essential features
- Hormone receptor with roles in development, physiologic processes and reproduction
- Frequent expression in breast cancer and can serve as a good prognostic factor in invasive breast carcinomas and endometrial carcinomas; can also be an indicator of response to hormonal treatment
- Nuclear positivity via immunohistochemical staining
Terminology
- ERα
- ER alpha
- ERa
- ESR1
Pathophysiology
- 2 isoforms: ERα and ERβ, with variants (Exp Hematol Oncol 2018;7:24)
- ESR1 gene encodes ERα and ESR2 gene encodes ERβ
- ERα and ERβ are expressed in many organs and tissues, with impact on normal physiologic processes (J Clin Invest 2006;116:561)
- ERα is the driver of proliferation in breast cancer and is thus the target of common ER antibodies used for immunohistochemistry (Mol Oncol 2012;6:428)
- ER is in the nuclei of the cells (J Clin Invest 2006;116:561)
- Estrogen / ER binding activates transcription factors and cell signaling proteins that mediate gene expression (Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol 2019;116:135)
Interpretation
- Nuclear staining
- Evaluate percentage of tumor cell staining and staining intensity (weak, moderate or strong)
- Cytoplasmic staining or < 1% nuclear staining of cells is considered negative
- ≥ 1% nuclear staining is considered positive
- Standardized process for initial test validation is recommended (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2020;144:545)
- Decalcification, alternate fixatives, prolonged cold ischemia time and fixation time out of recommended range are among variables that may negatively impact expression / interpretation (J Clin Oncol 2020;38:1346)
Uses by pathologists
- ER testing is recommended in invasive breast cancers by validated immunohistochemistry as the standard for predicting which patients may benefit from endocrine therapy; no other assays are recommended for this purpose (J Clin Oncol 2020;38:1346)
- Testing of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) for ER is recommended to determine potential benefit of endocrine therapies to reduce risk of future breast cancer, while testing DCIS for PR is considered optional (J Clin Oncol 2020;38:1346)
- Breast carcinoma is evaluated based on percentage of cancer cells staining and staining intensity
- 1 - 100% nuclear staining is interpreted as positive
- < 1% or 0% nuclear staining or cytoplasmic staining is interpreted as negative
- If 1 - 10% of tumor cell nuclei are immunoreactive for ER, the sample should be reported as ER low positive with a recommended comment (J Clin Oncol 2020;38:1346)
- Sample may be deemed uninterpretable for ER if
- Sample is inadequate (insufficient cancer or severe artifacts present, as determined at the discretion of the pathologist)
- External and internal controls (if present) do not stain appropriately
Prognostic factors
- In breast cancers, ER serves as a crucial marker for predicting sensitivity to endocrine therapy and guiding treatment decisions with hormonal agents such as tamoxifen
- ER positive status, particularly ERα positivity, is associated with favorable survival rates in patients with breast cancer, including patients with tumors with a lower proliferation rate and histological evidence of tumor differentiation (i.e., lower grade) (Clin Exp Med 2023;23:1)
- Most ER low (1 - 10%) positive, HER2 negative breast cancers are basal-like, with Oncotype Recurrence Score (RS) ≥ 26, indicating these tumors are similar to triple negative breast cancer (Ann Surg Oncol 2024;31:2244)
- ER has prognostic significance in endometrial adenocarcinomas, with association with type I versus type II carcinoma, via American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) / College of American Pathologists (CAP) scoring criterion (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2019;38:111)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Interpretation of percent and intensity (weak, moderate or strong) of nuclear staining in breast cancer (J Clin Oncol 2020;38:1346)
- < 1% is considered negative
- 1 - 10% is considered low positive
- ≥ 1% is considered positive
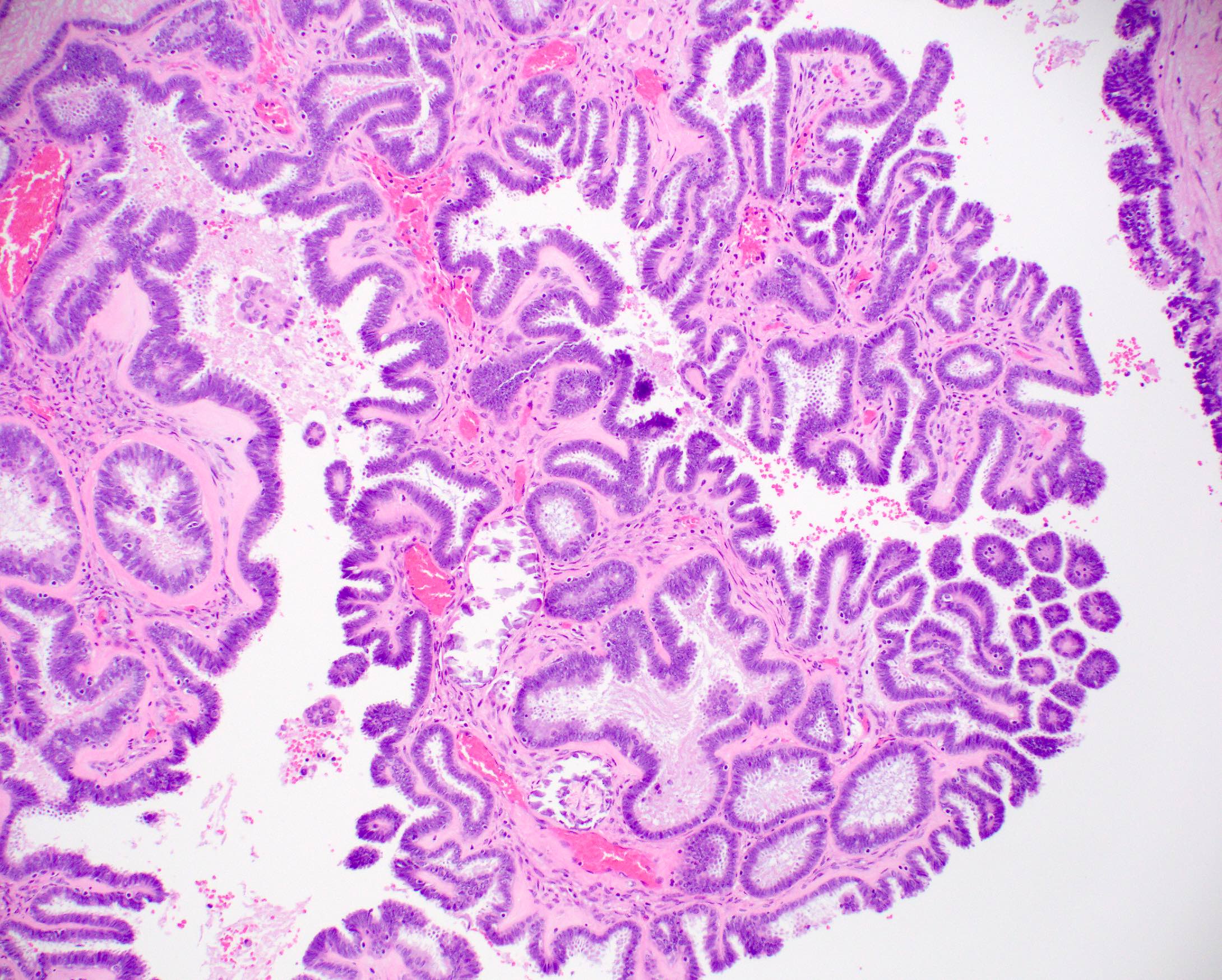
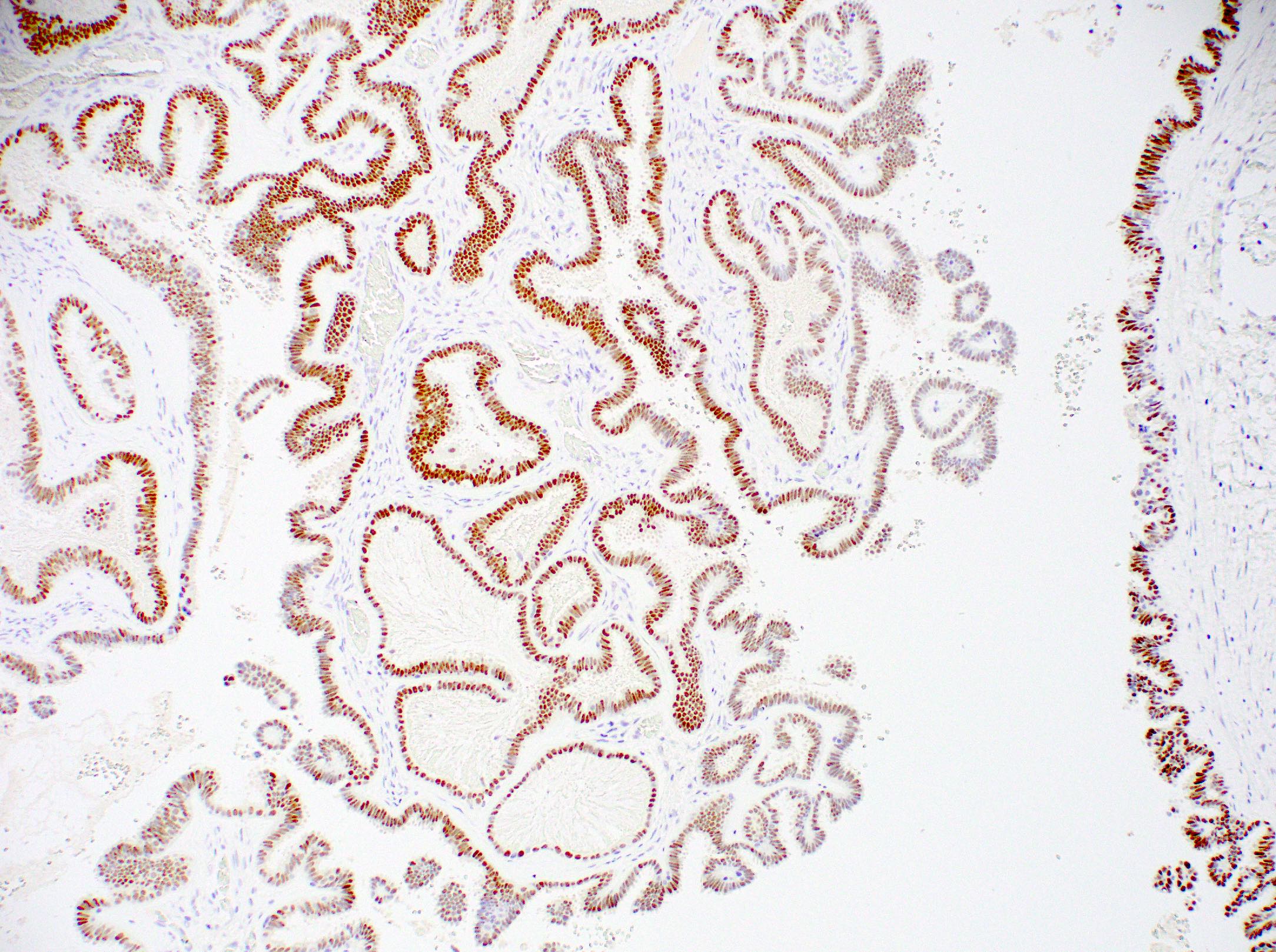
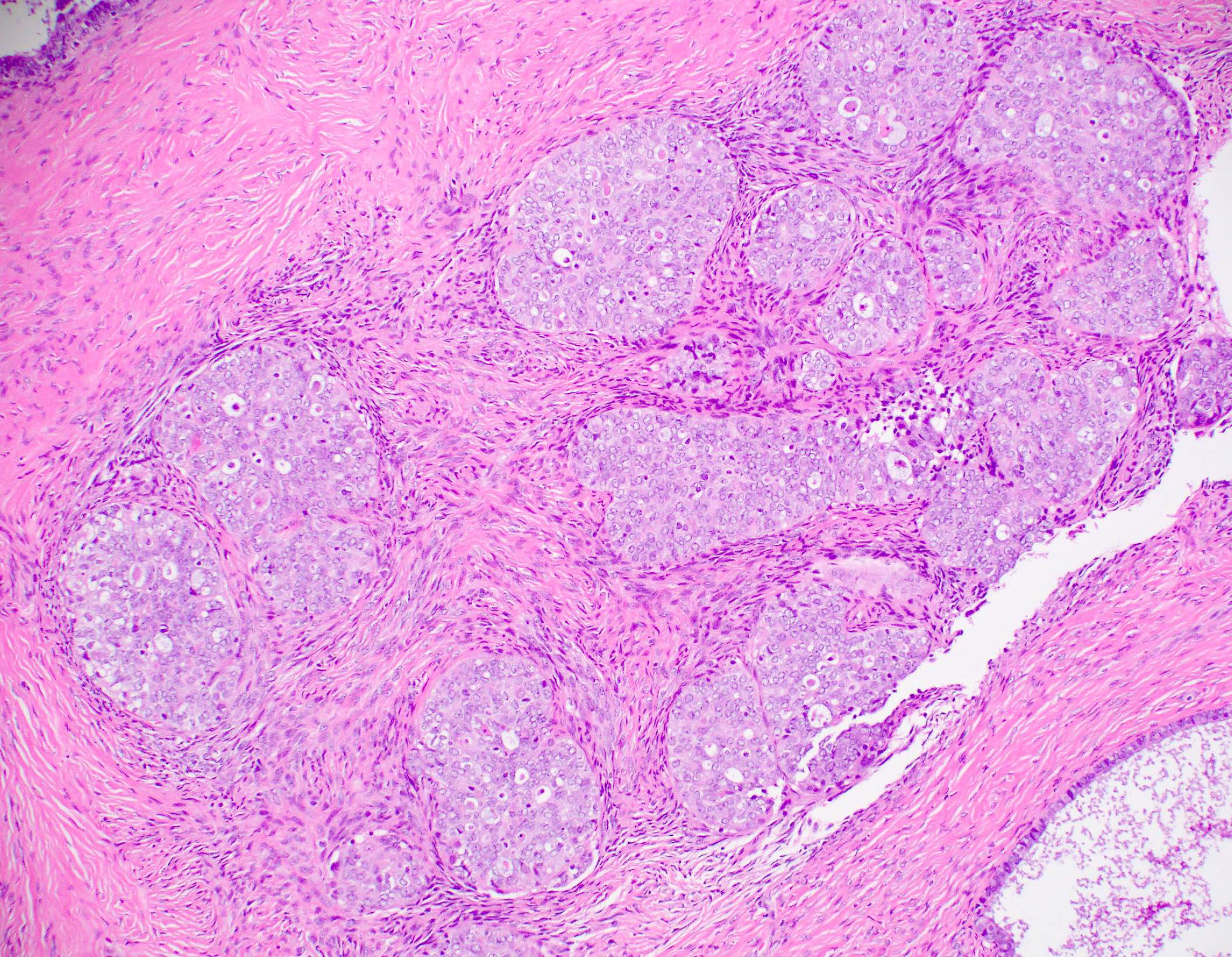
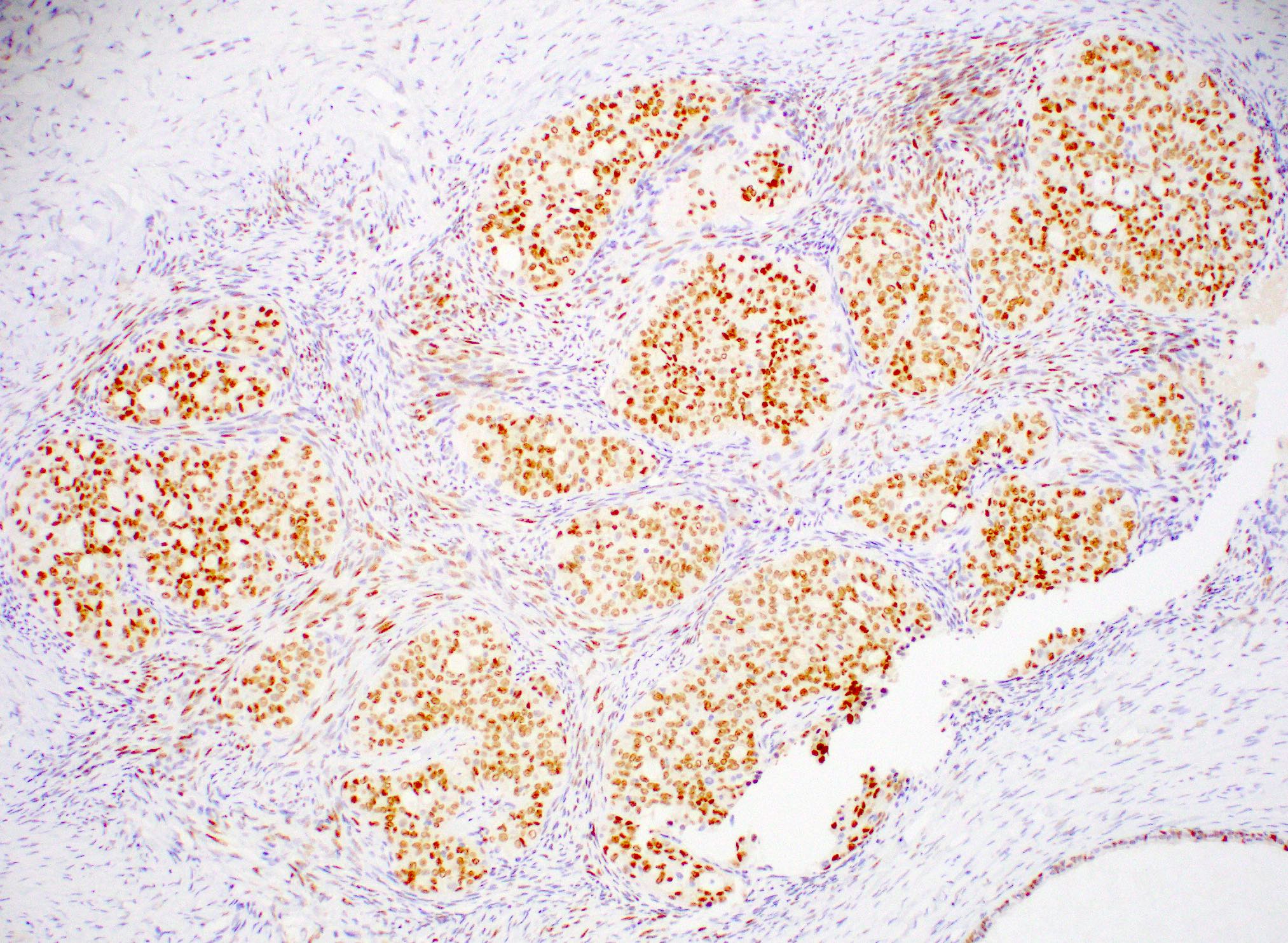
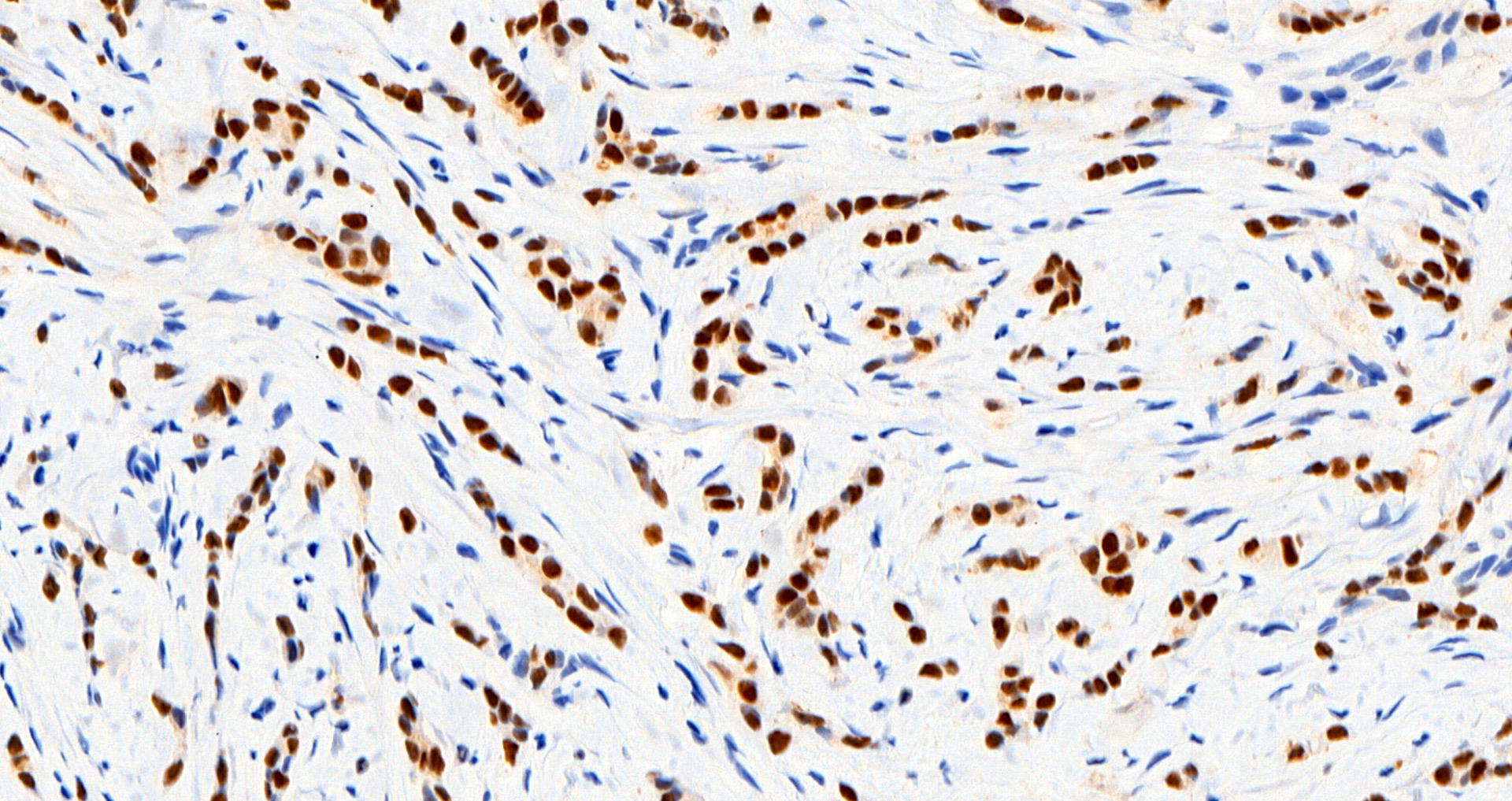
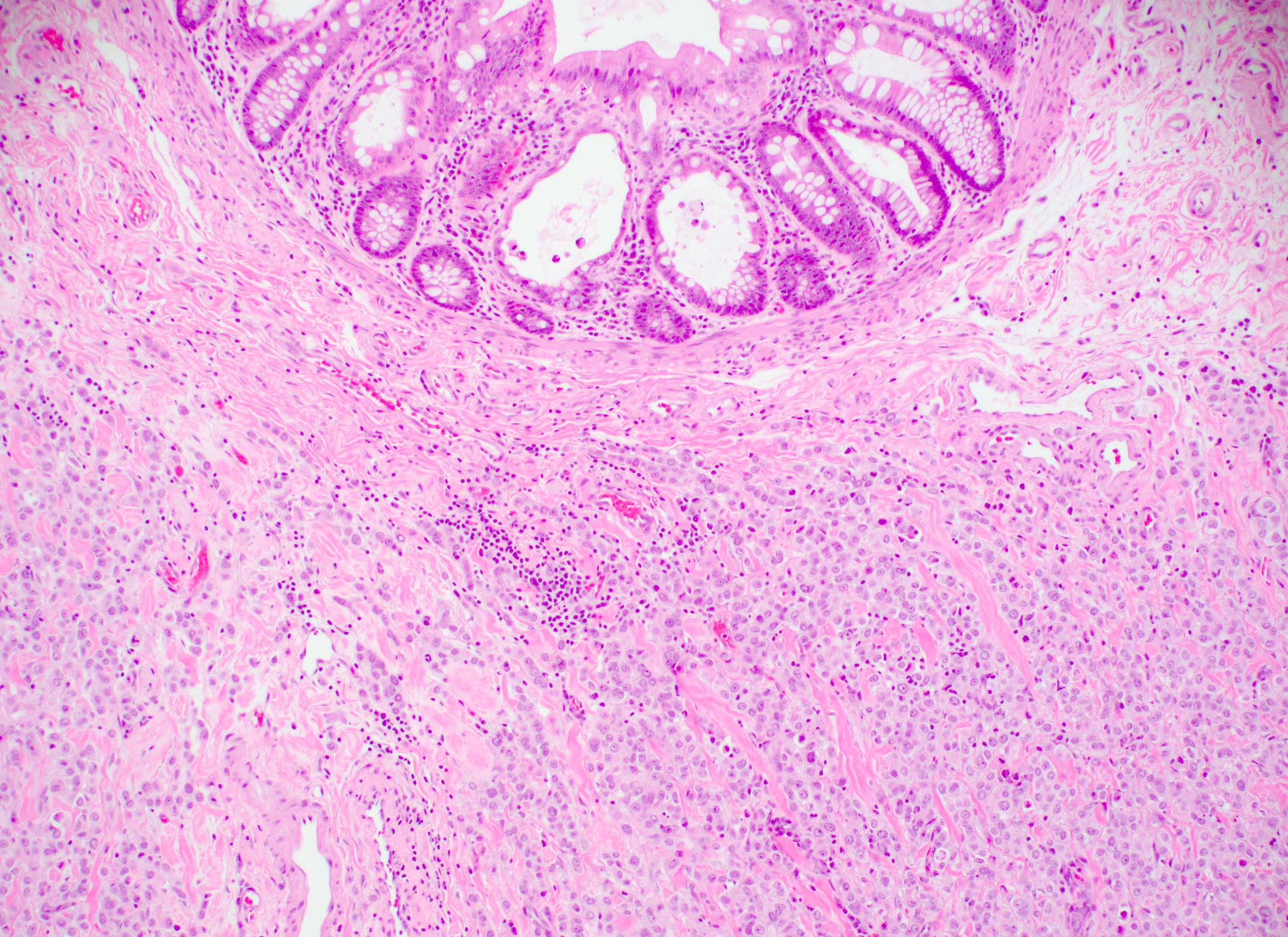
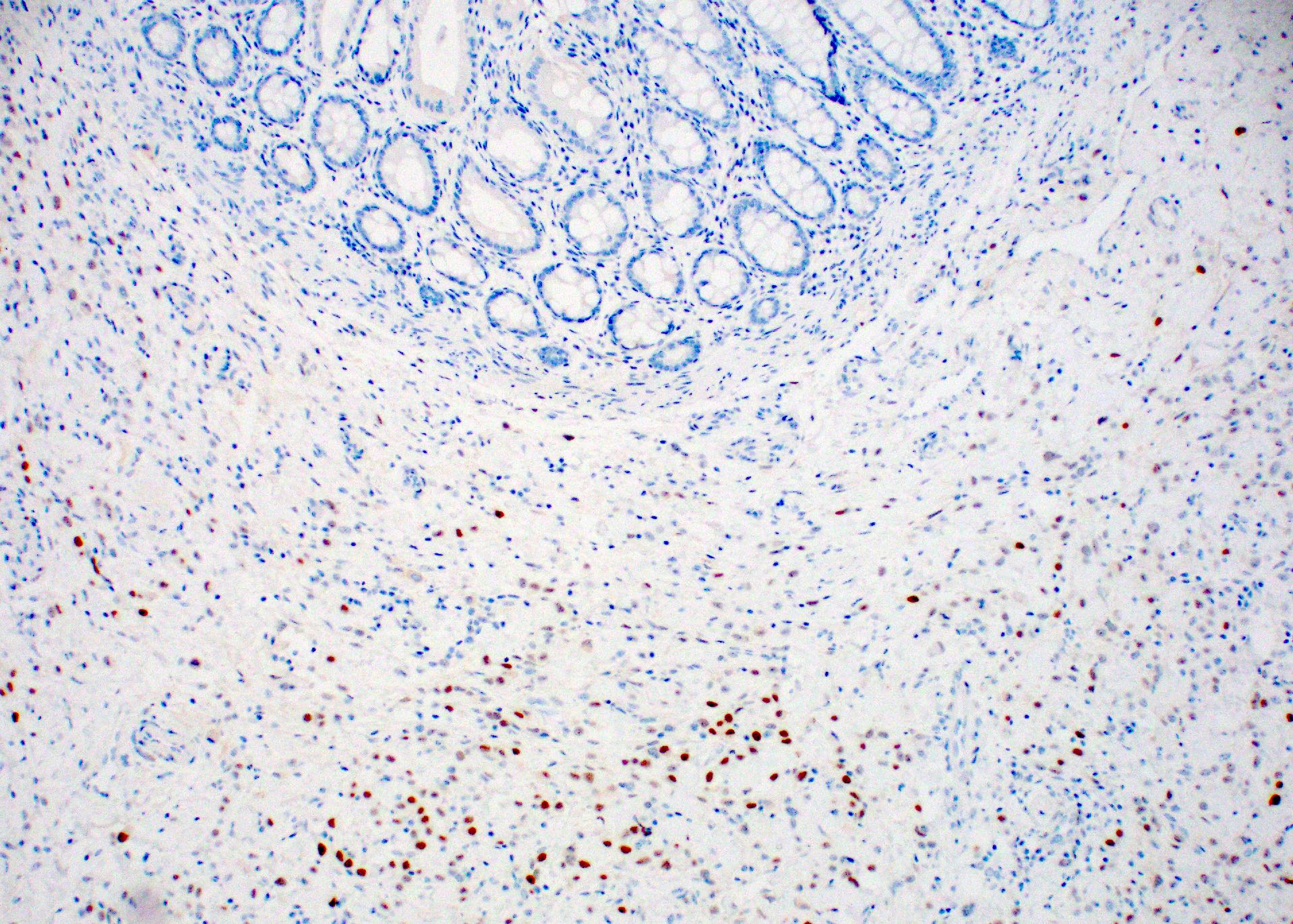
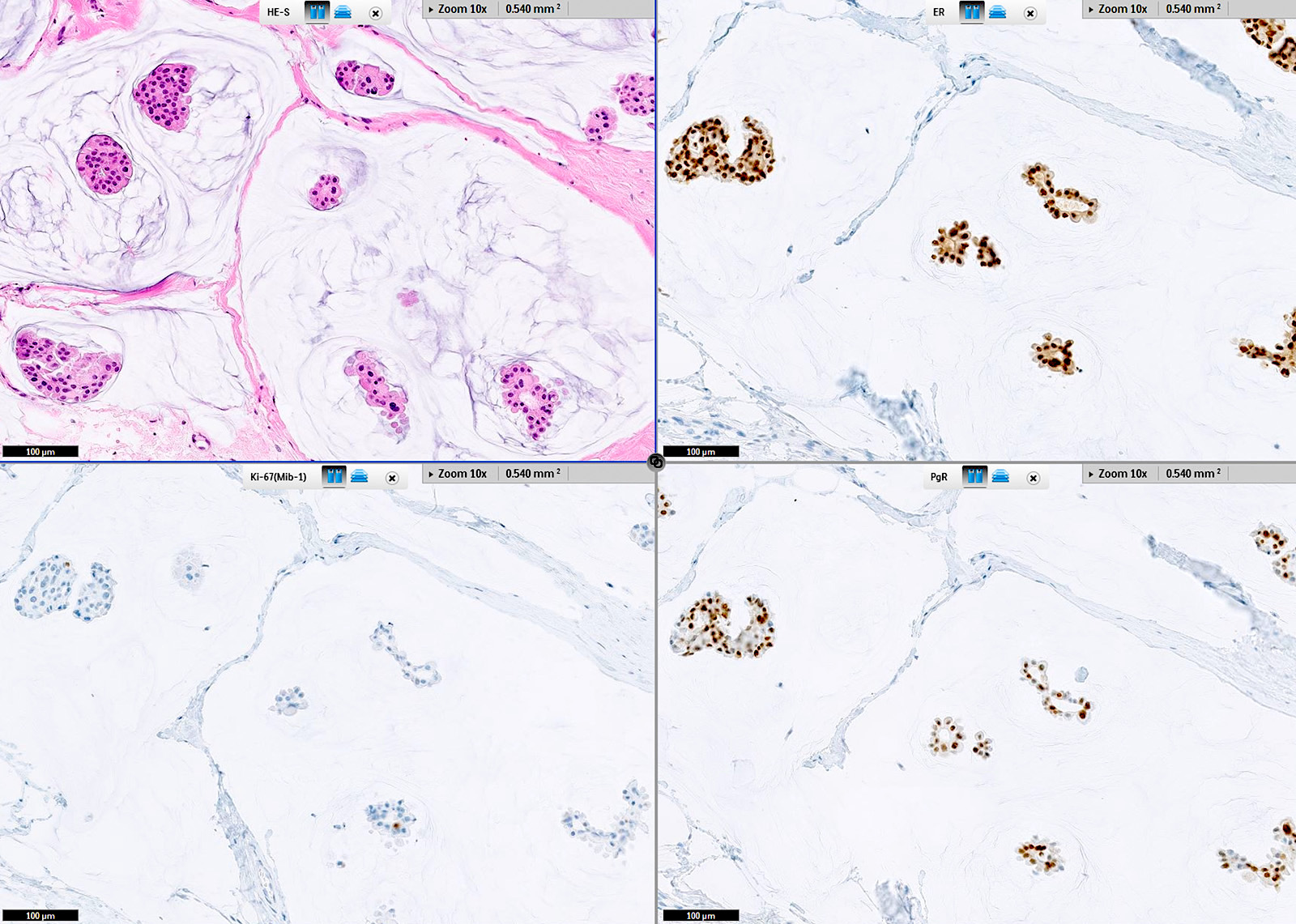
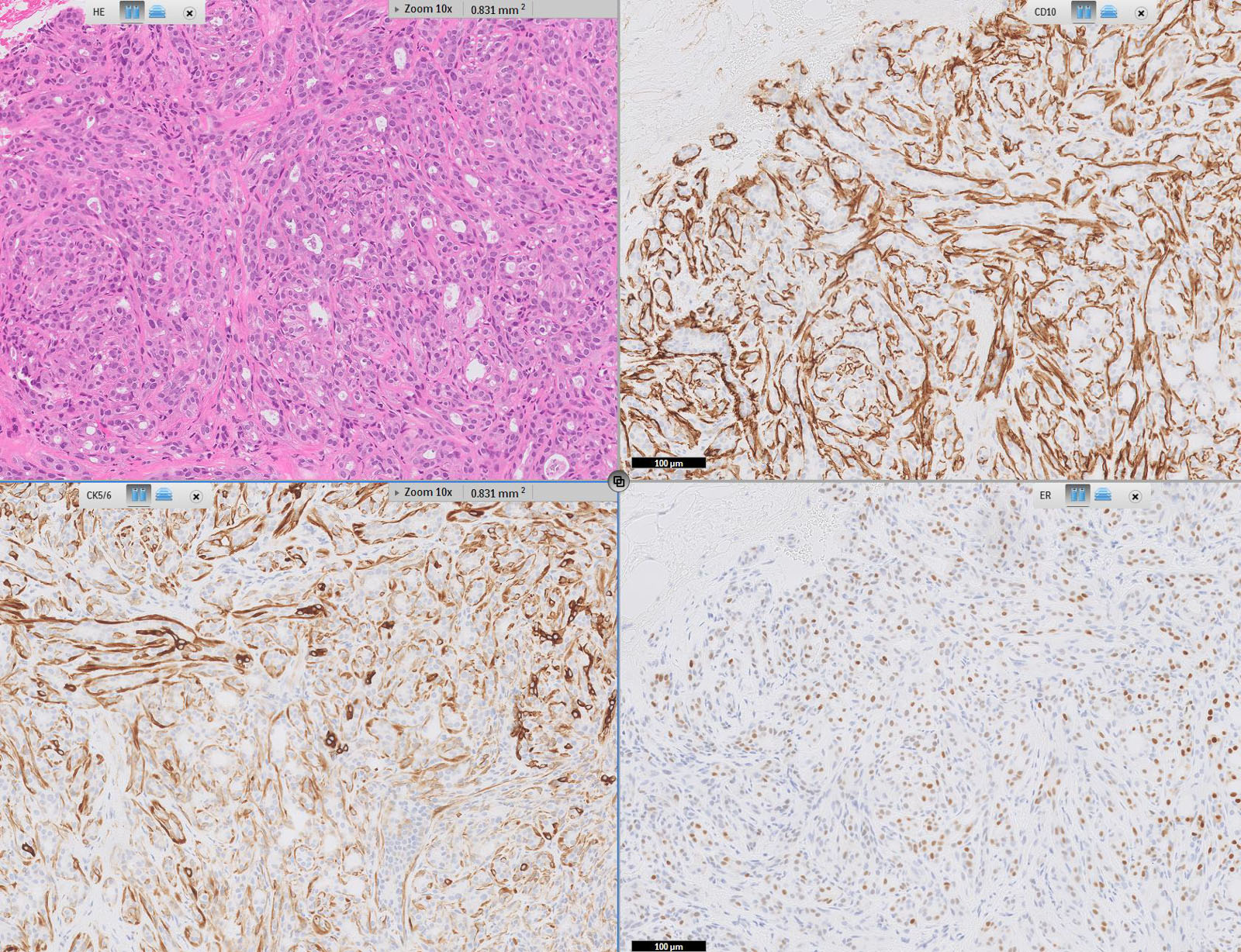
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Julie M. Jorns, M.D., Jijgee Munkhdelger, M.D., Ph.D., Andrey Bychkov, M.D., Ph.D. and Leica Microsystems
Positive staining - normal
- Normal luminal breast epithelium, typically used as internal control staining, demonstrates a broad range of ER expression by immunohistochemistry, which may be influenced by both physiologic and laboratory variables
- ERα is present mainly in mammary gland, uterus, ovary (thecal cells), bone, male reproductive organs (testes and epididymis), prostate (stroma), liver and adipose tissue (Steroids 2014;90:13)
Positive staining - disease
- Breast carcinoma (varies by subtype and tumor grade) (WHO)
- Well differentiated tumors are typically positive
- Overall positivity ~75%
- Breast cancer associated stroma is variably positive (55.6 - 60%) (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2014;143:605, Breast Cancer Res Treat 2022;196:453)
- Endometrial adenocarcinoma (75%)
- Ovarian serous (97.2%), mucinous (70%) and endometrioid adenocarcinomas (100%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:667)
- Ovarian transitional cell carcinoma (90%) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:194)
Negative staining
- Endocervical adenocarcinoma
- Ovarian clear cell carcinoma
- Normal breast stroma (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2014;143:605)
- Papillary urothelial carcinoma of bladder (10 - 20%)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- ESR1 FISH or mRNA expression are potential alternatives for determining ER status (Mol Oncol 2012;6:428, PLoS One 2010;5:e15031)
- ESR1 mutations are associated with resistance to endocrine therapy (J Clin Oncol 2023;41:3423)
- ESR1 mutation testing is recommended at recurrence or progression on endocrine therapy in patients with ER positive, HER2 negative tumors
- Blood based ctDNA ESR1 mutation testing methodology is preferred and has greater sensitivity
Sample pathology report
- Right breast, upper outer quadrant, core biopsy:
- Invasive carcinoma of no special type, preliminary modified Bloom-Richardson (Nottingham) grade 1 (2+1+1), largest continuous focus 0.5 cm (see comment)
- Comment: immunohistochemical stains show invasive carcinoma to be
- Estrogen receptor (91 - 100%, strong) positive
- Progesterone receptor (91 - 100%, strong) positive
- HER2 / neu (0) negative for overexpression
- Controls are appropriate
Additional references
Board review style question #1
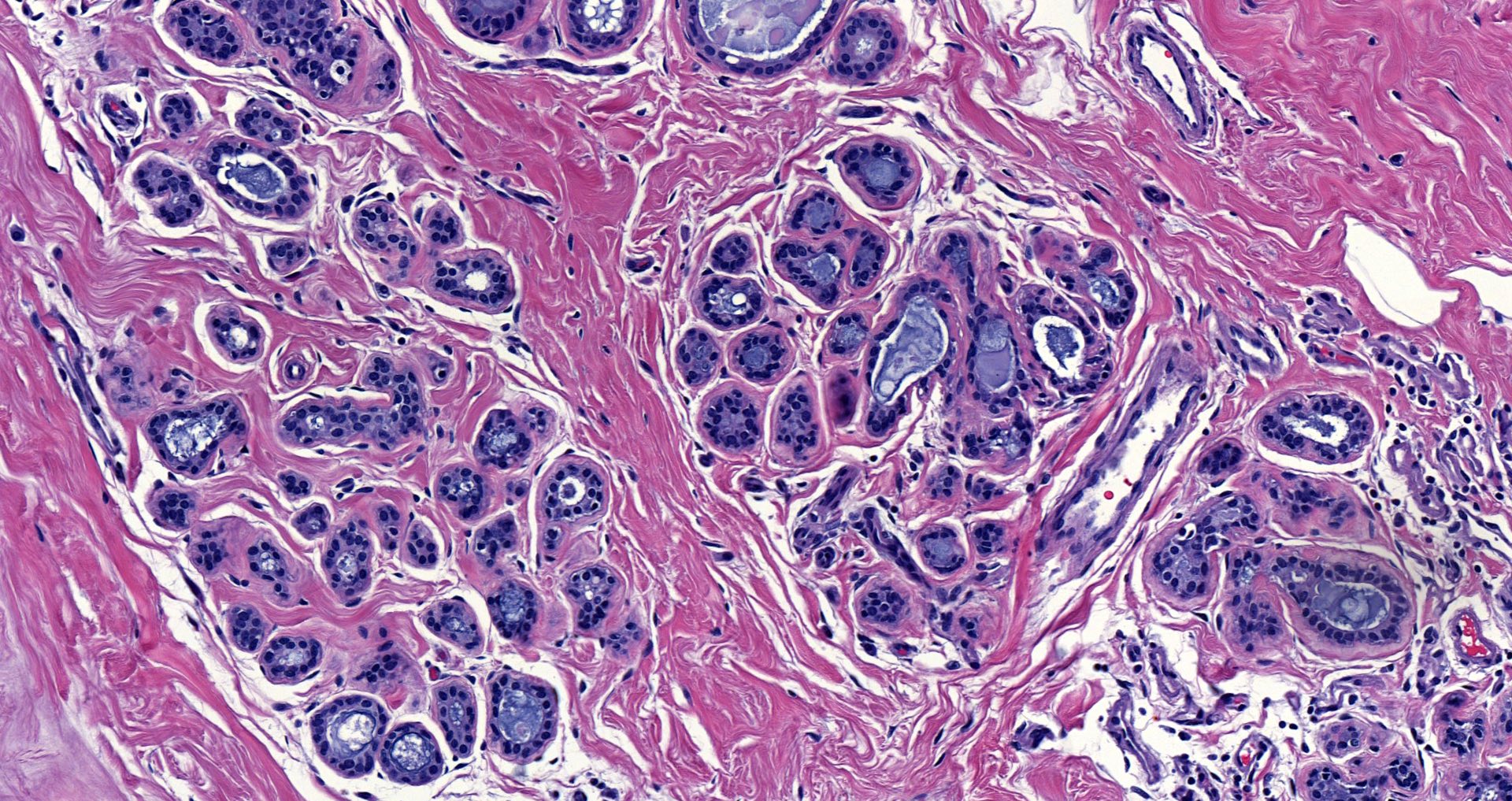
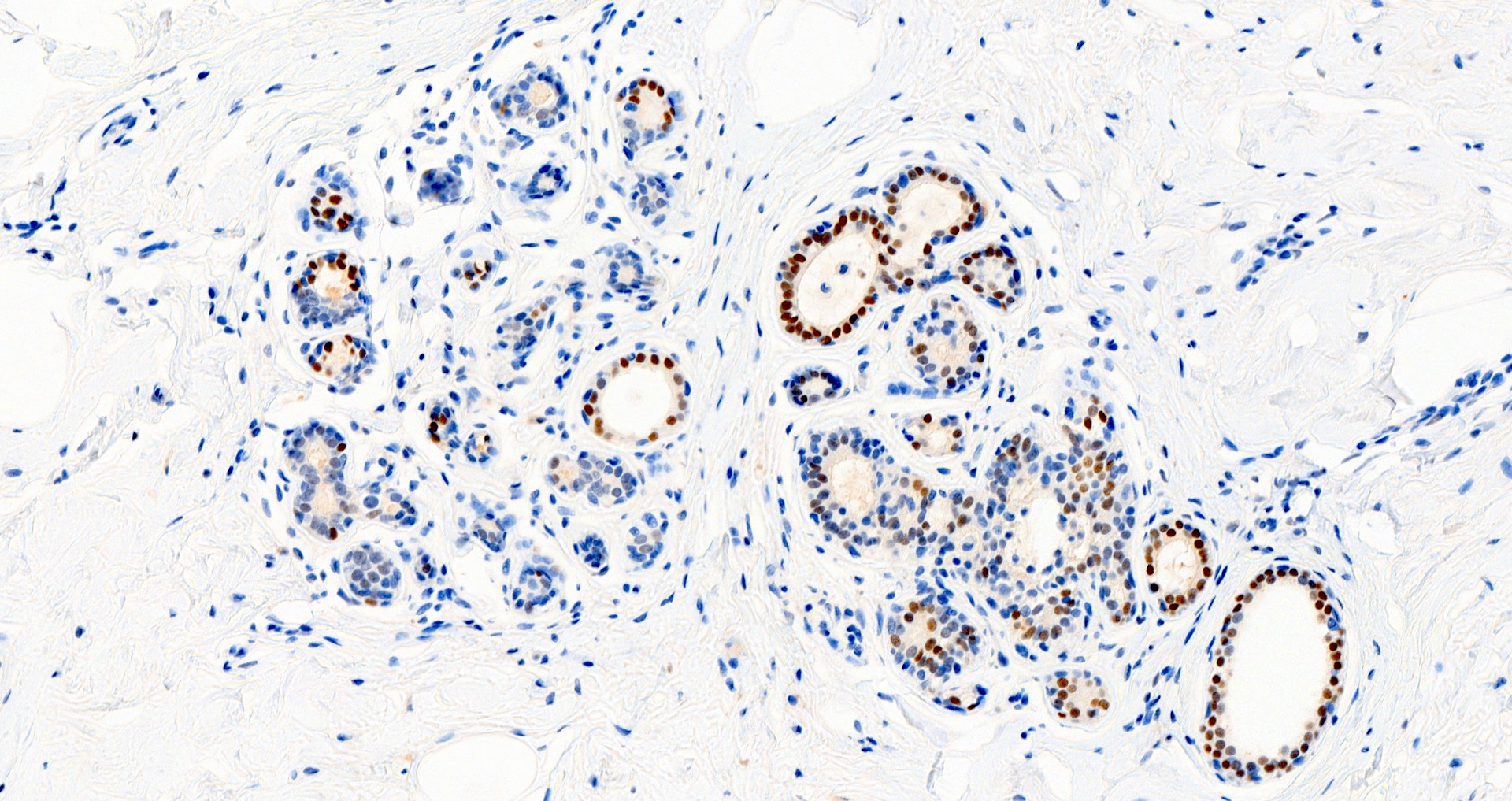
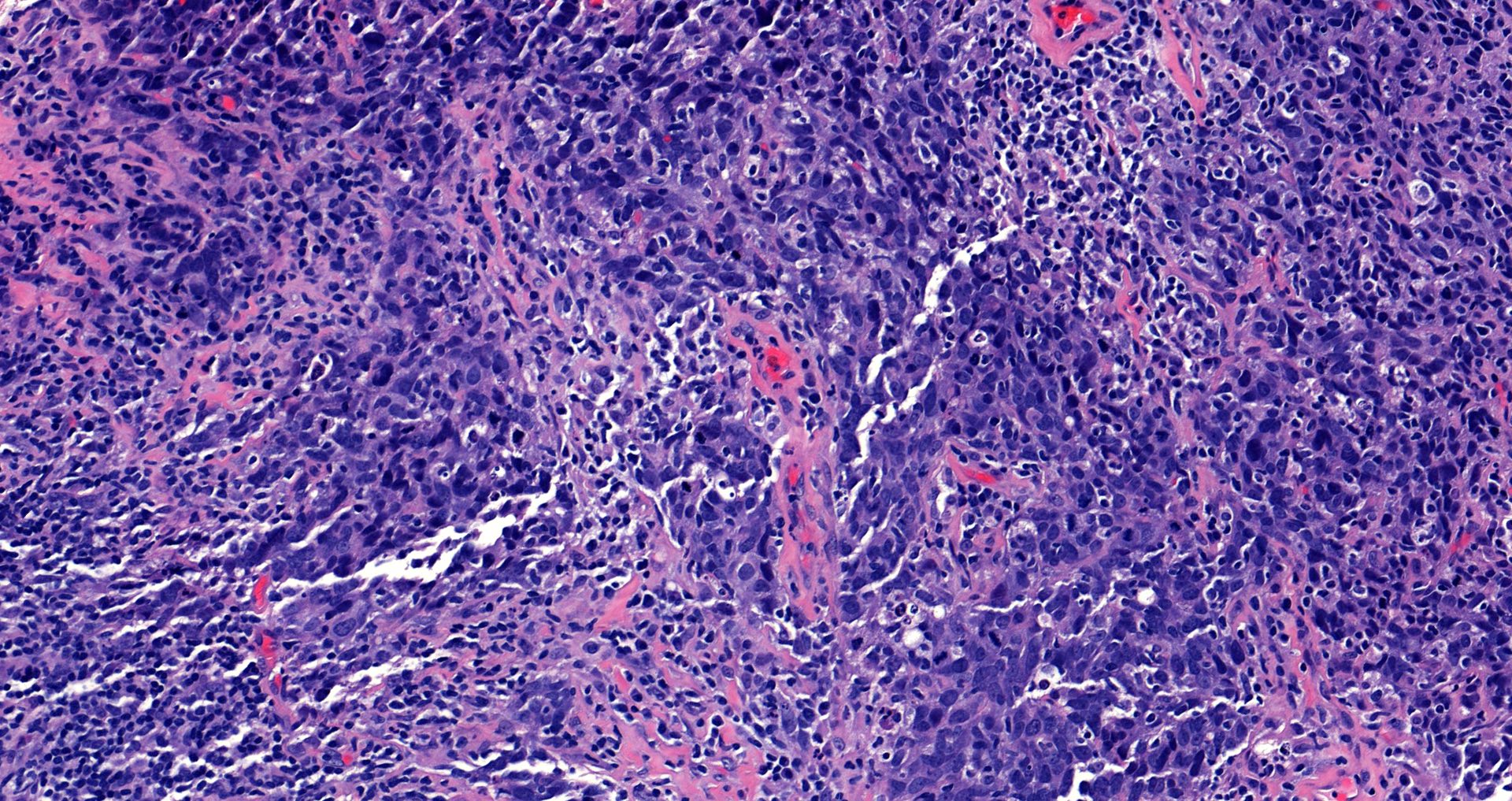
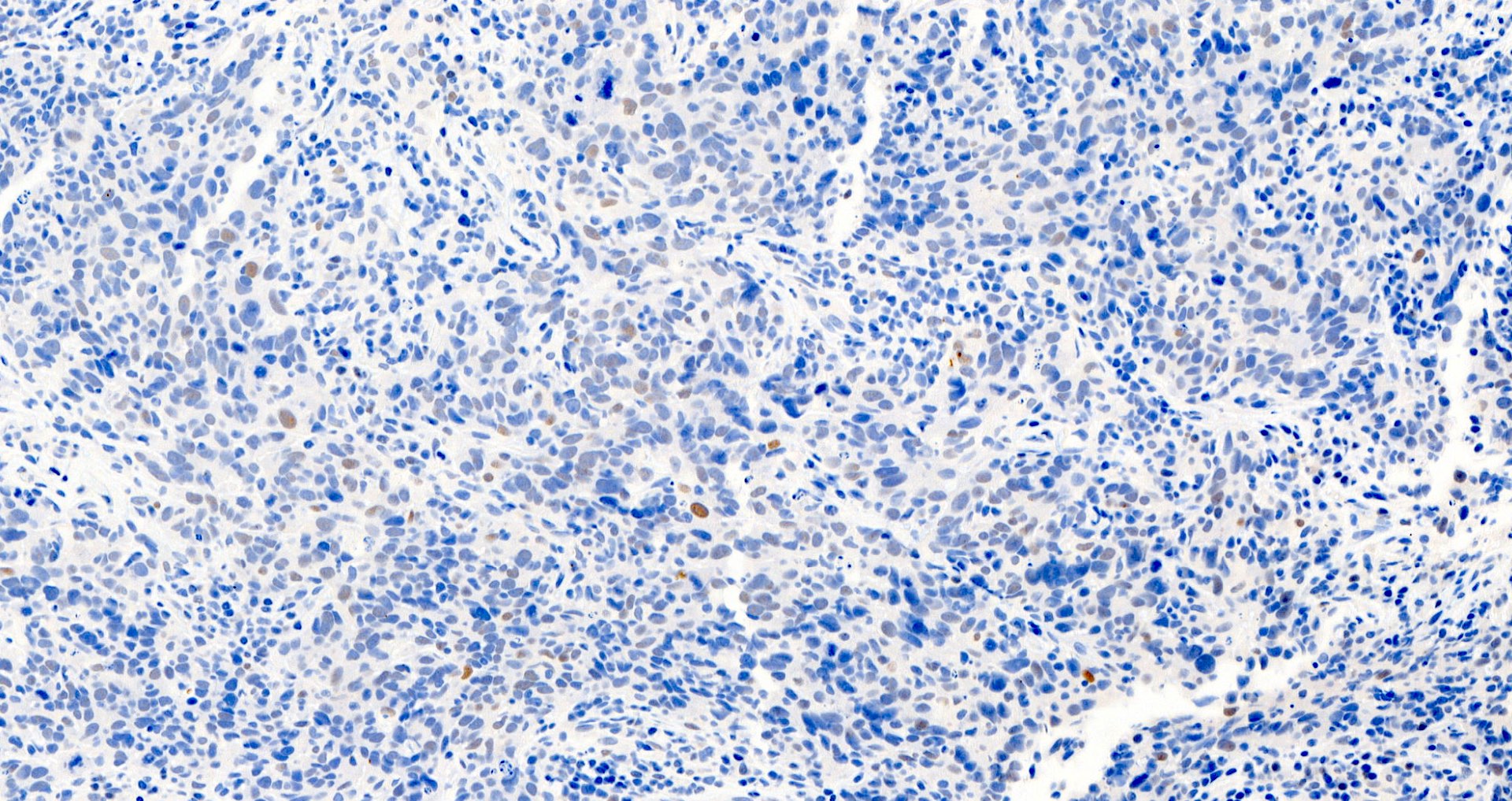
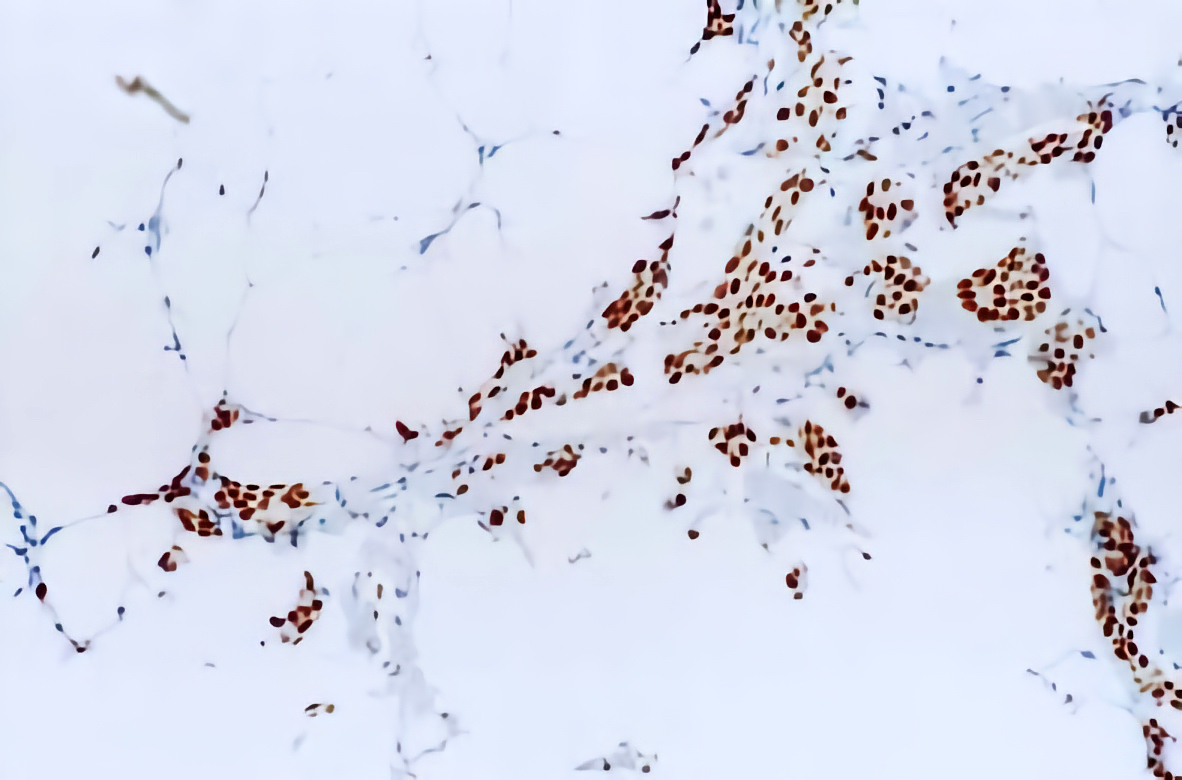
A middle aged woman underwent a core biopsy for a 1 cm (screening detected) breast mass with the pictured estrogen receptor (ER) staining. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Invasive carcinoma, NST, ER low positive
- Invasive carcinoma, NST, ER positive
- Invasive lobular carcinoma, ER low positive
- Invasive lobular carcinoma, ER positive
- Invasive tubular carcinoma, ER positive
Board review style answer #1
D. Invasive lobular carcinoma, ER positive. The tumor cells, highlighted by diffuse, strong positive ER staining, infiltrate as single cells and linear files of cells, supporting the diagnosis of ER positive invasive lobular carcinoma. Answers A, B, C and E are incorrect because the tumor is not infiltrating as cohesive nests or tubules and thus is not morphologically consistent with invasive carcinoma, NST or invasive tubular carcinoma, nor is the tumor showing low positive (1 - 10% staining) with ER.
Comment Here
Reference: Estrogen receptor
Comment Here
Reference: Estrogen receptor