Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Fenu EM, Maracaja DLV. BCL6. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsBCL6.html. Accessed January 9th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Transcription factor located at 3q27 that is required for germinal center B cell formation and follicular helper T cell (TFH) differentiation (Immunol Rev 2019;288:214, Trends Immunol 2021;42:336)
- Protects germinal center B cells against DNA damage induced apoptosis during somatic hypermutation and class switch recombination (Trends Mol Med 2014;20:343)
- Translocations help define double or triple hit lymphomas if paired with translocations in MYC or BCL2 (J Clin Pathol 2020;73:126)
Essential features
- Proto-oncogenic transcription factor that is involved in regulating B cell response to DNA damage (Trends Immunol 2021;42:336)
- Marker of germinal center differentiation (Immunol Rev 2019;288:214)
- Responsible for transcriptional regulation and lineage differentiation of follicular helper T cells (Trends Immunol 2021;42:336)
Terminology
- B cell lymphoma 6
Pathophysiology
- Proto-oncogene: normally inhibits germinal center lymphocytes' response to DNA damage to allow for immunoglobulin somatic hypermutation by repressing tumor suppressor TP53 and CDKN1A, ATR and CHEK1 (Blood Cells Mol Dis 2008;41:95)
- Suppresses the expression of antiapoptotic BCL2 (Front Cell Dev Biol 2019;7:272)
Interpretation
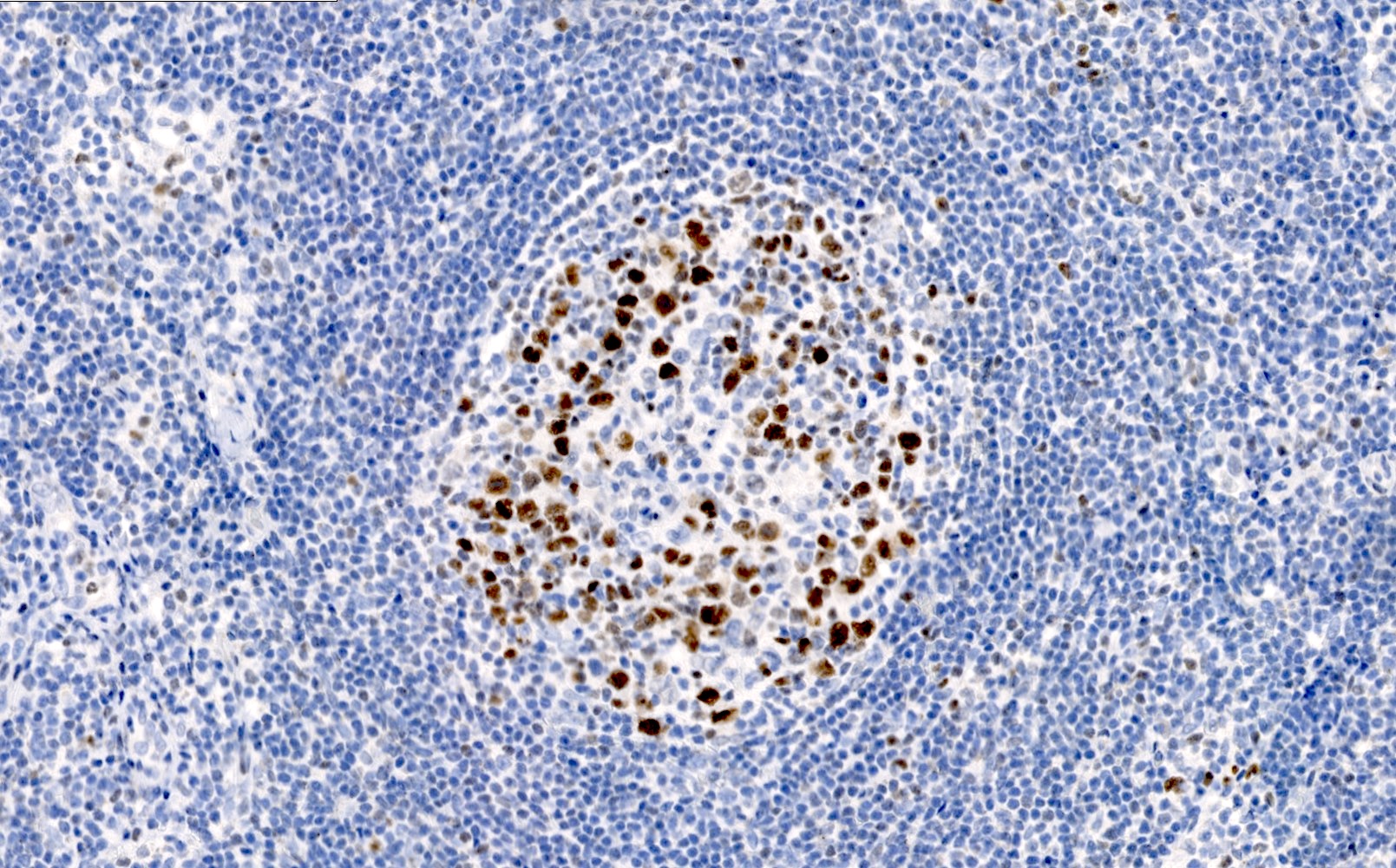
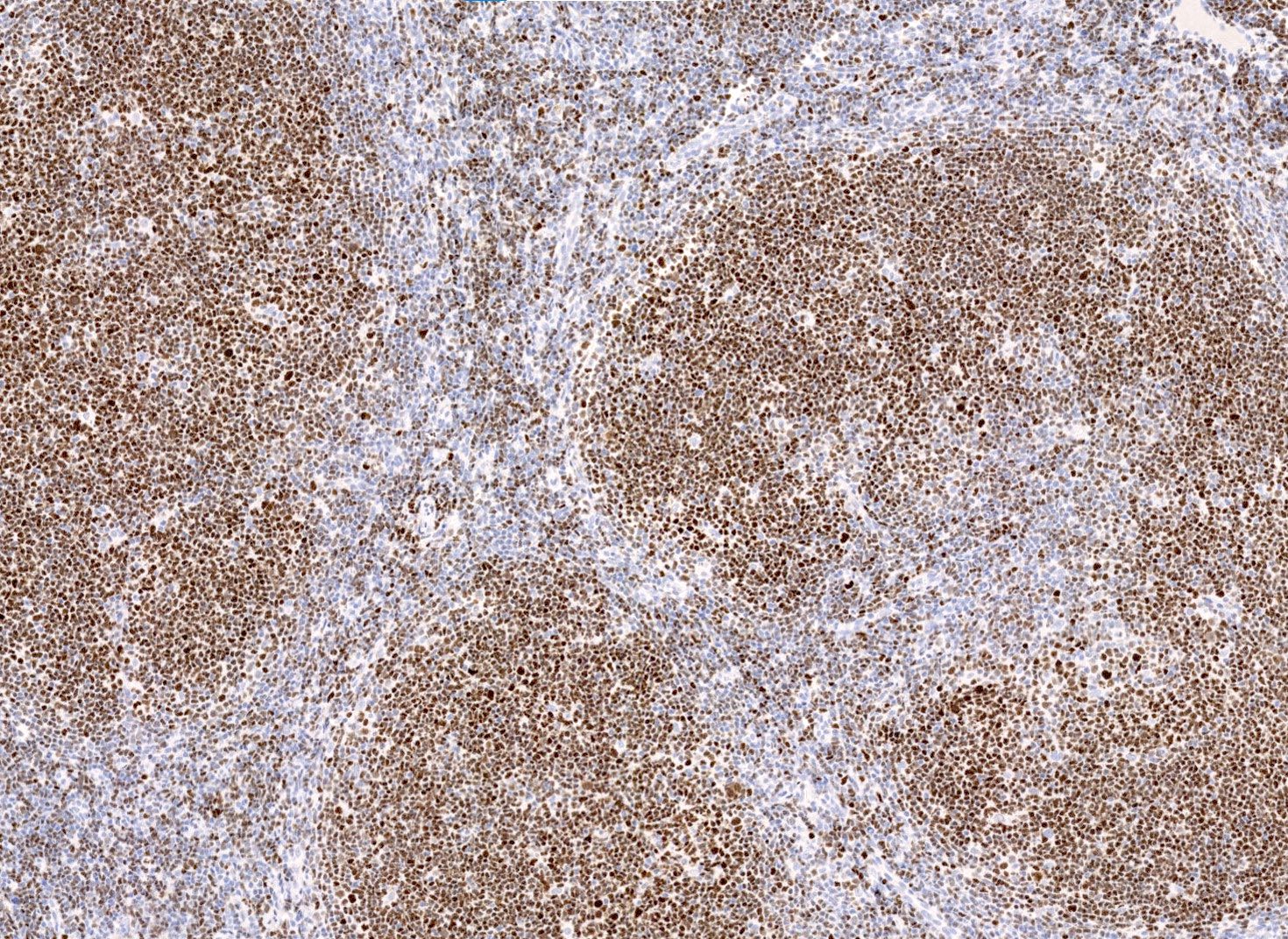
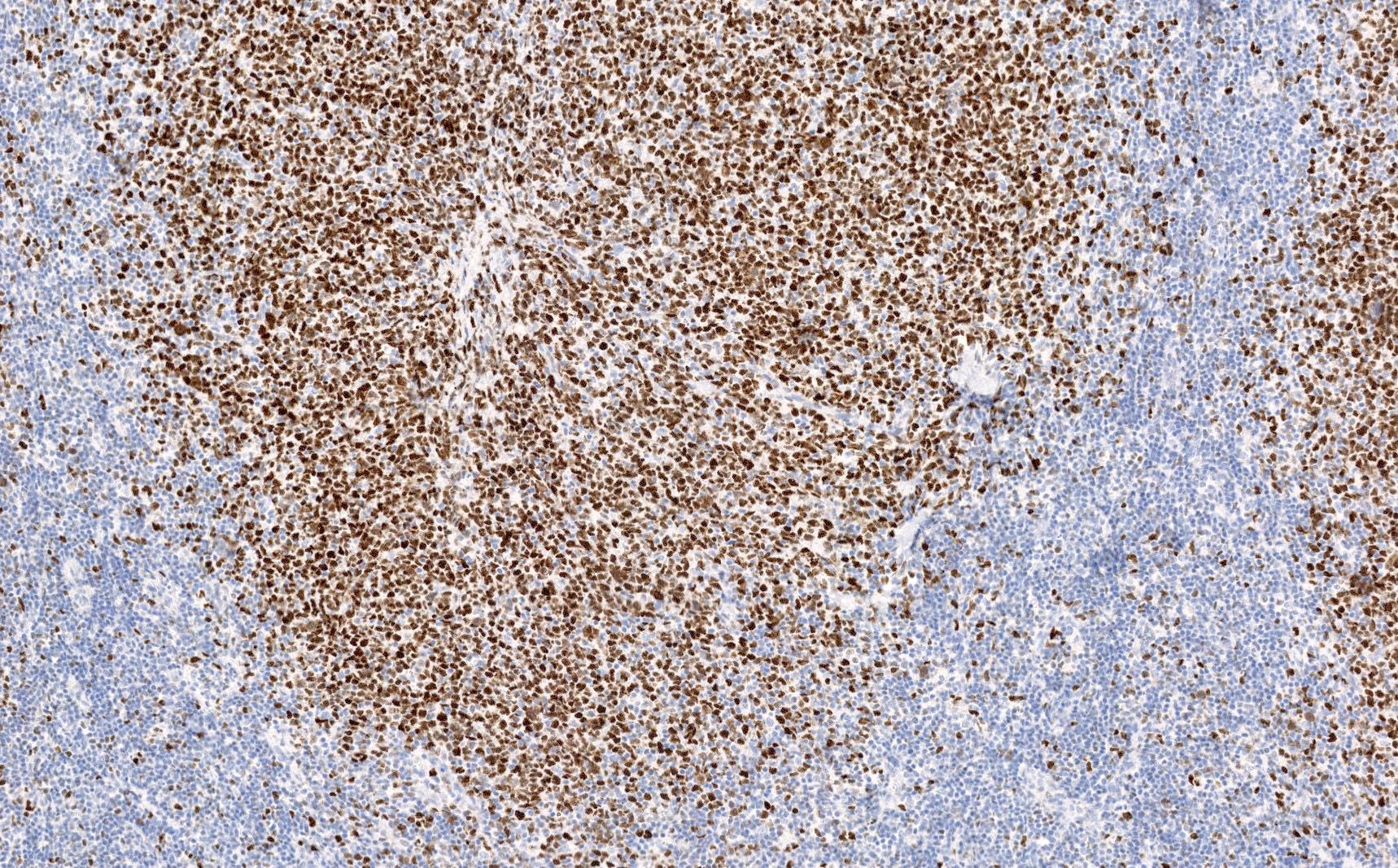
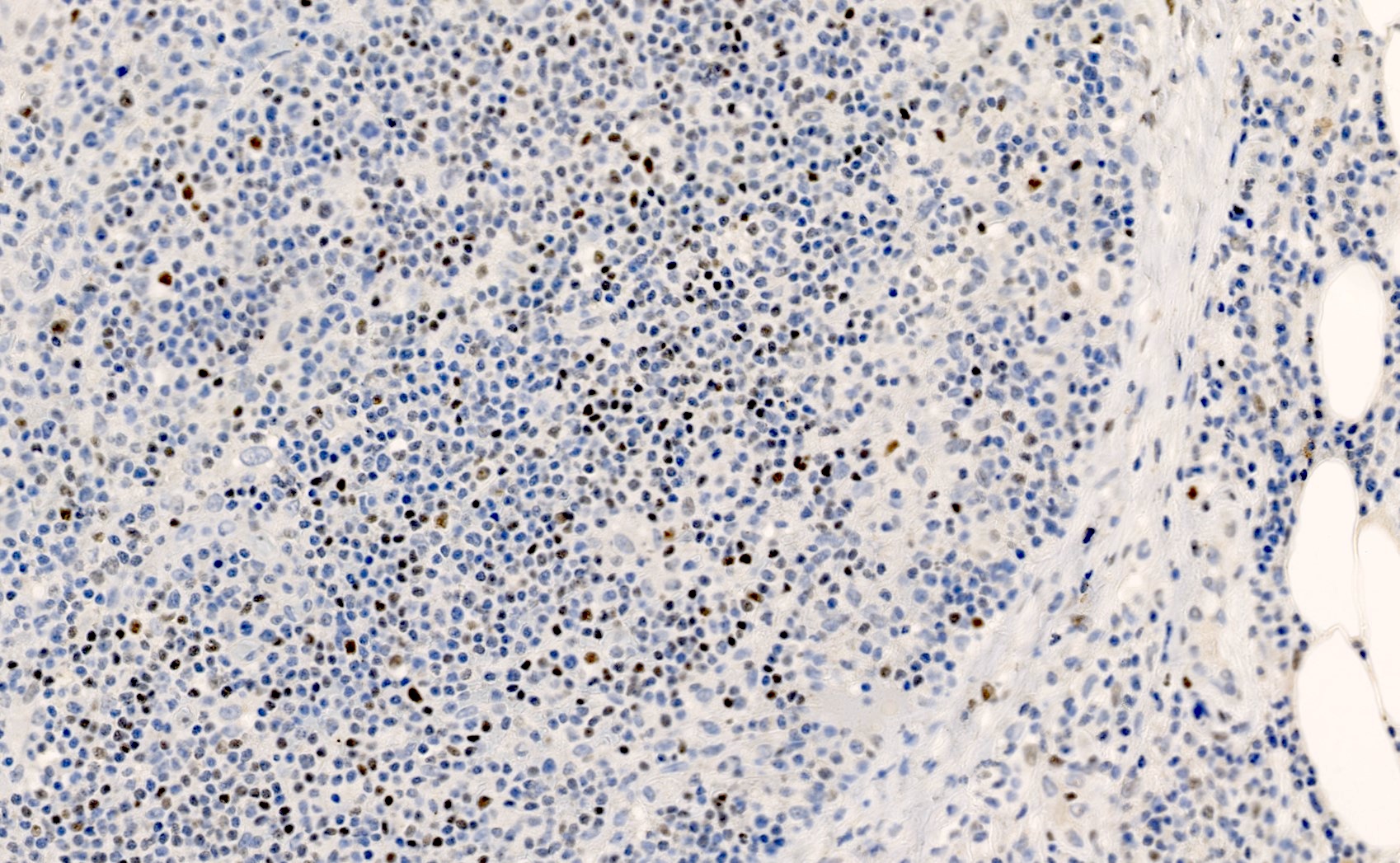
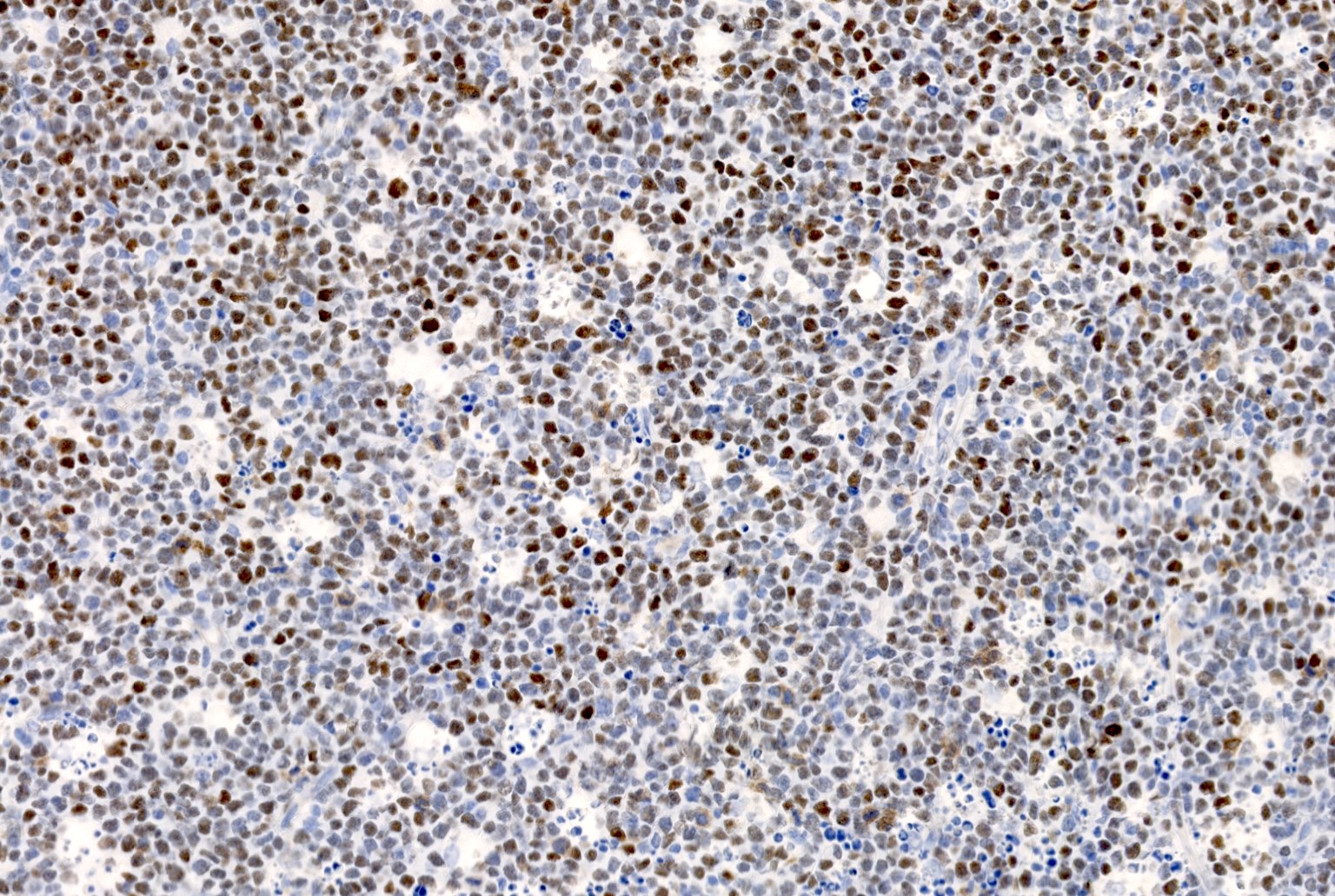
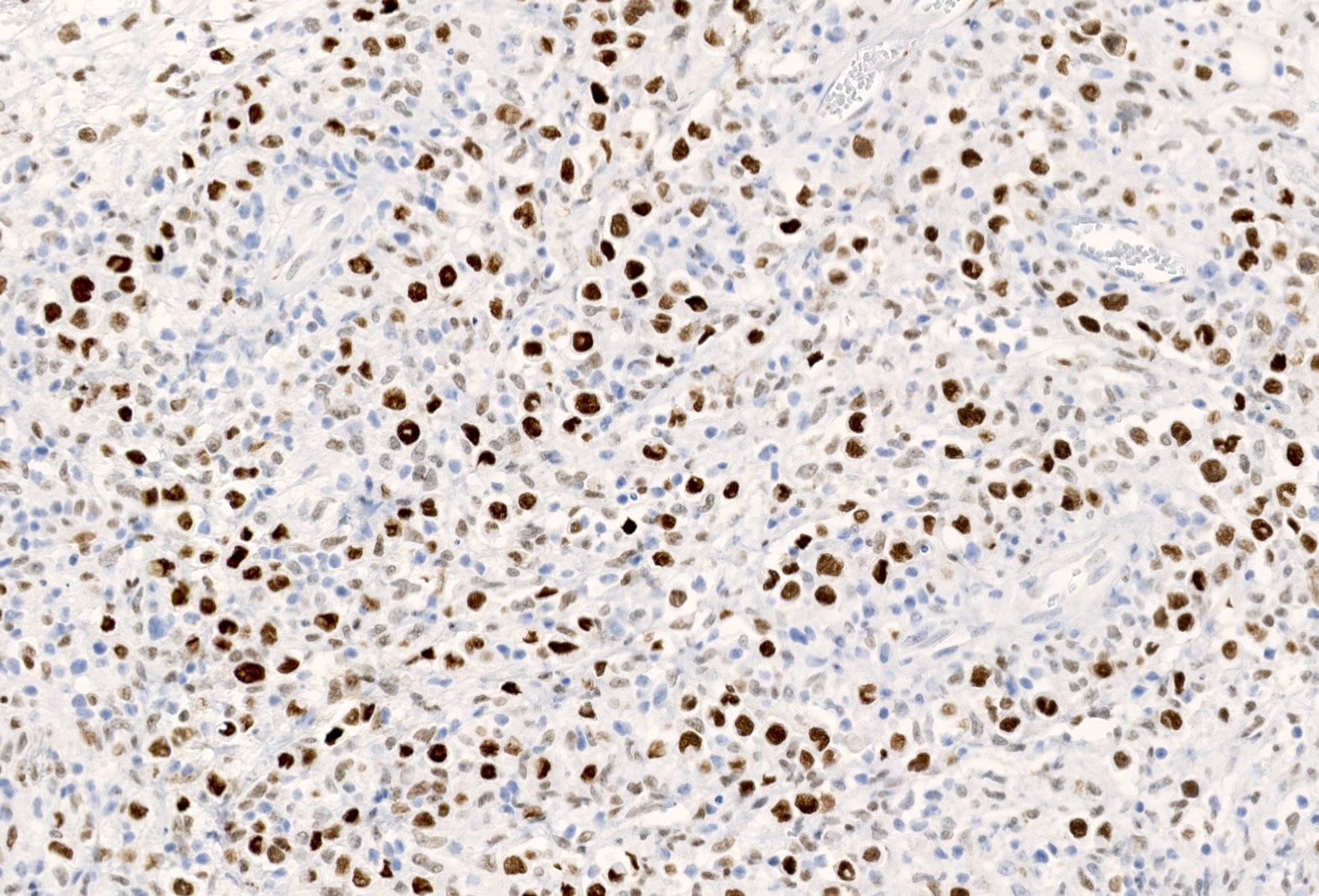
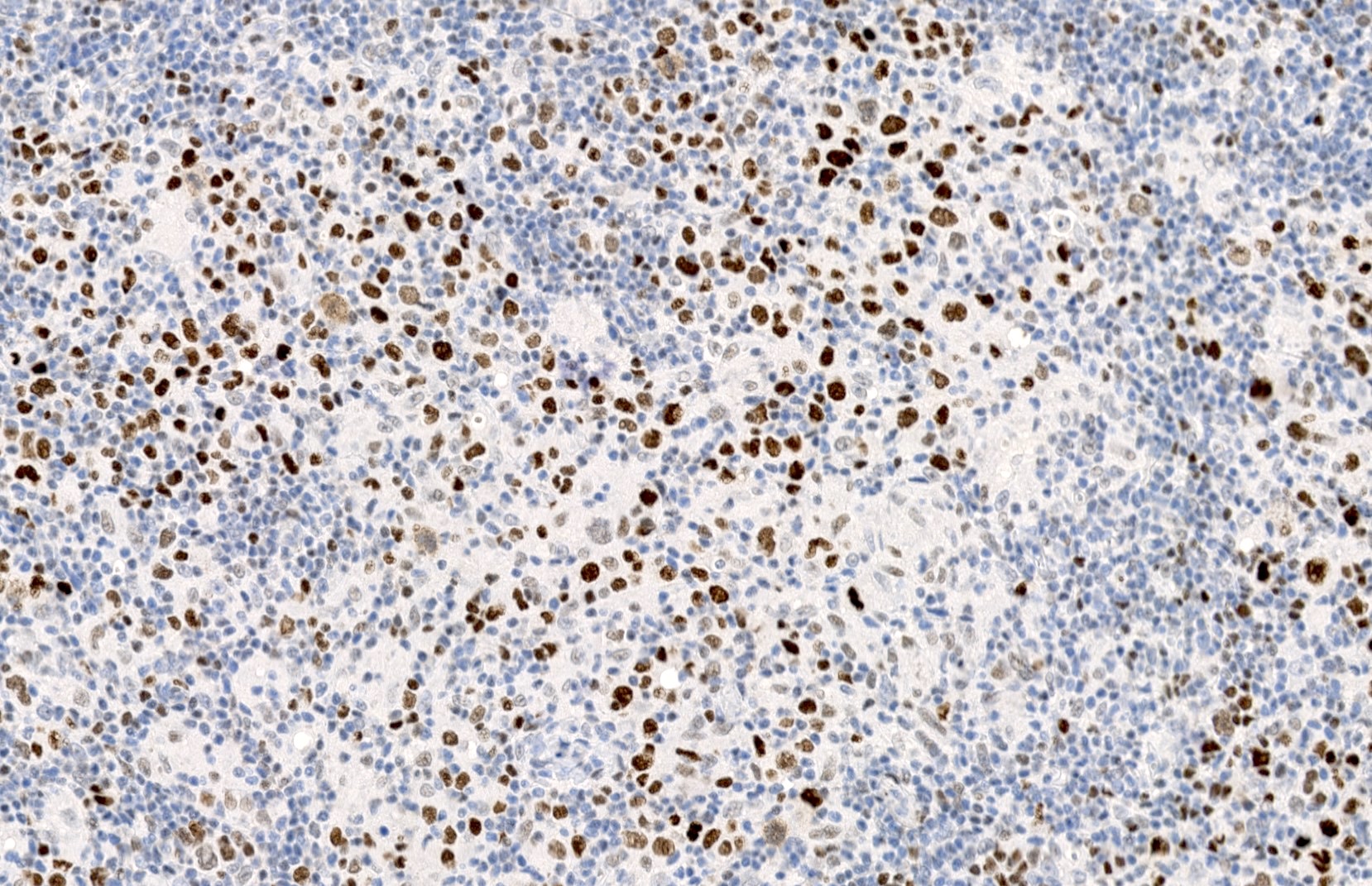
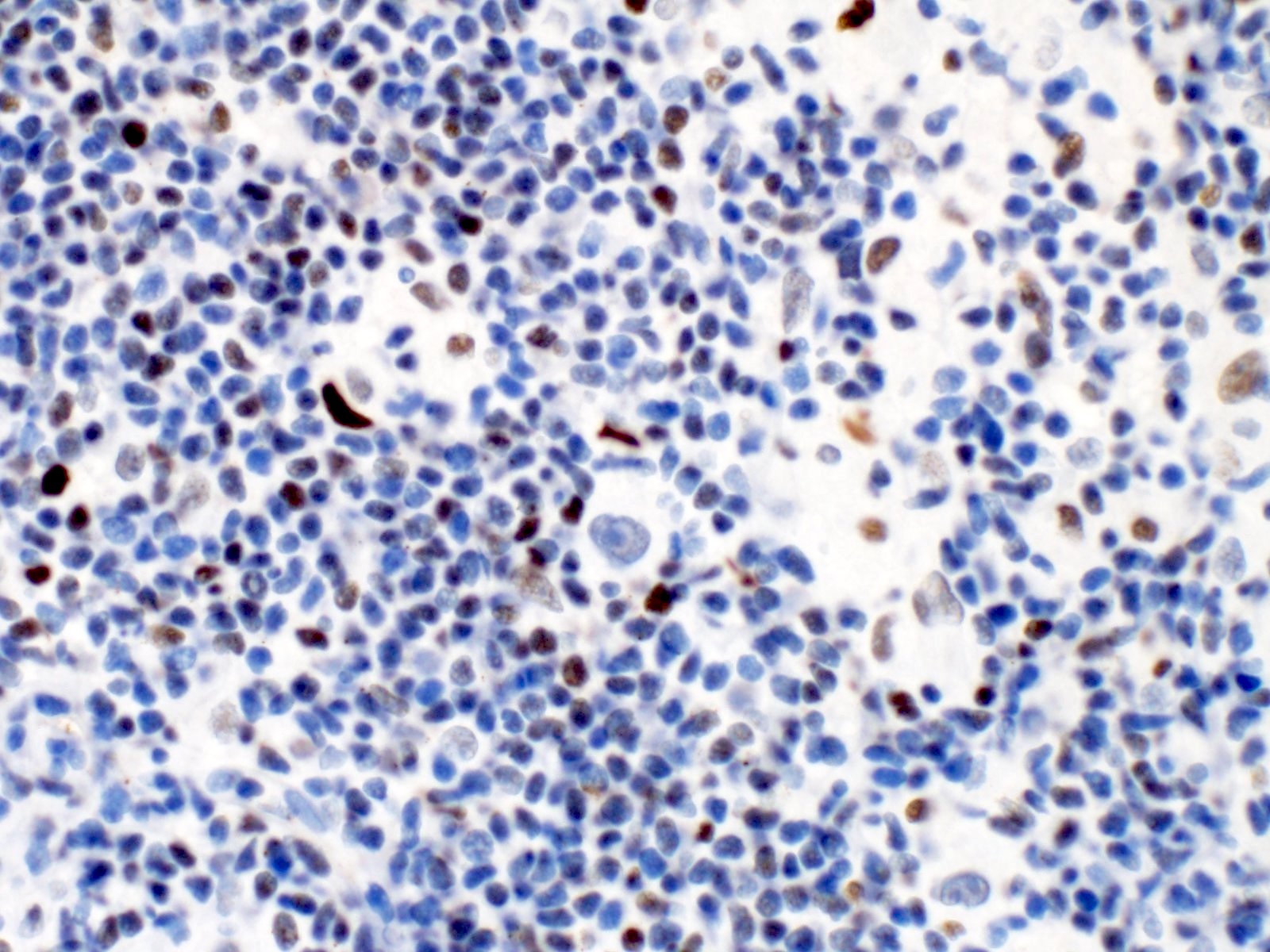
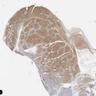
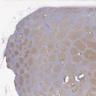
- Nuclear staining
Uses by pathologists
- Marker of germinal center differentiation (also CD10) (Immunol Rev 2019;288:214)
- Can be used together with BCL2 and other stains to distinguish follicular lymphoma from other small B cell lymphomas (World J Gastroenterol 2016;22:1674)
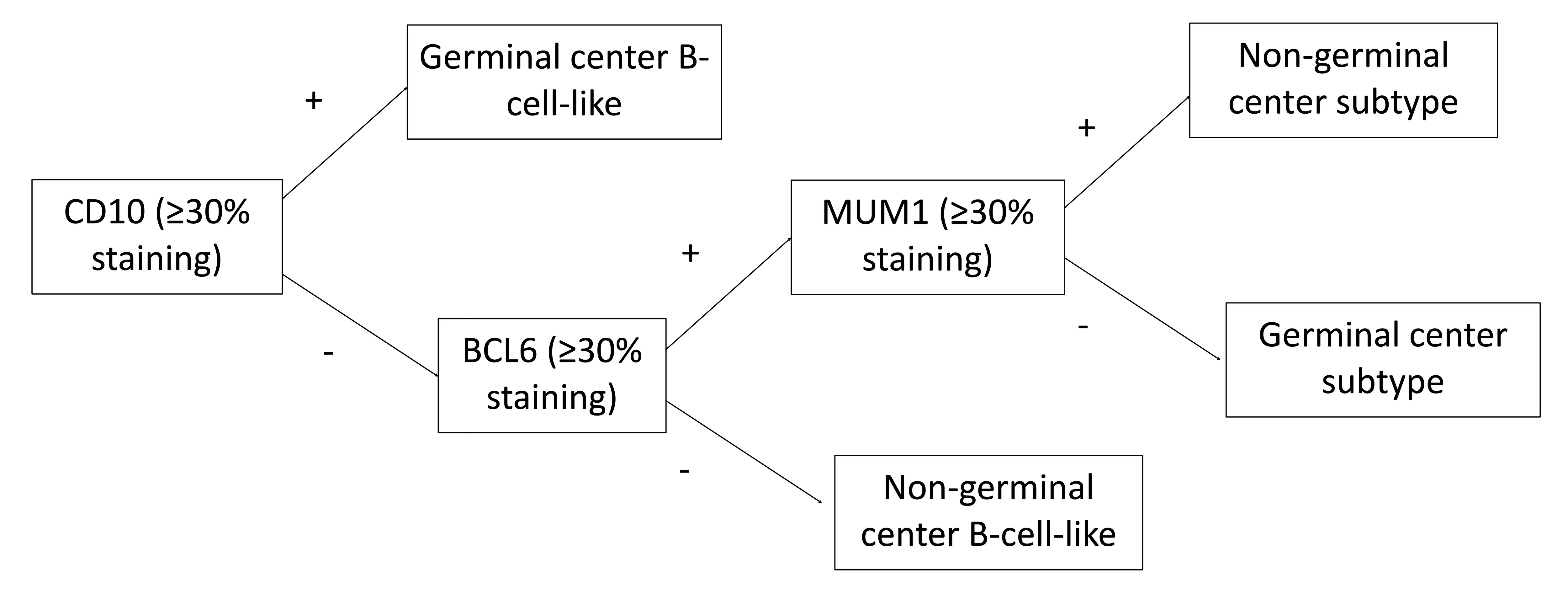
- Used along with CD10 and MUM1 to classify diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) as germinal center or nongerminal center derived (Blood 2004;103:275)
- Can be used in the diagnosis of Burkitt lymphoma (Mod Pathol 2010;23:909)
- Coexpression of BCL6 and BCL2 by immunohistochemistry is abnormal and can help distinguish follicular lymphoma (85 - 90% in grade 1 - 2, < 50% in grade 3) from reactive follicular hyperplasia (Histopathology 2013;62:860, Am J Hematol 2020;95:316)
- Marker of TFH cells used in the diagnosis of angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma (AITL) and other T cell lymphomas of TFH phenotype (also CD10, PD-1, ICOS and CXCL13) (Blood 2017;129:1095)
Prognostic factors
- Large cell lymphomas with rearrangements of MYC, BCL2 or BCL6 (double or triple hit lymphomas) are classified as high grade B cell lymphomas and carry a poor prognosis (Diagn Pathol 2019;14:81)
- DLBCL with a germinal center B cell-like phenotype have better prognosis compared to those that are nongerminal center type (Blood 2004;103:275)
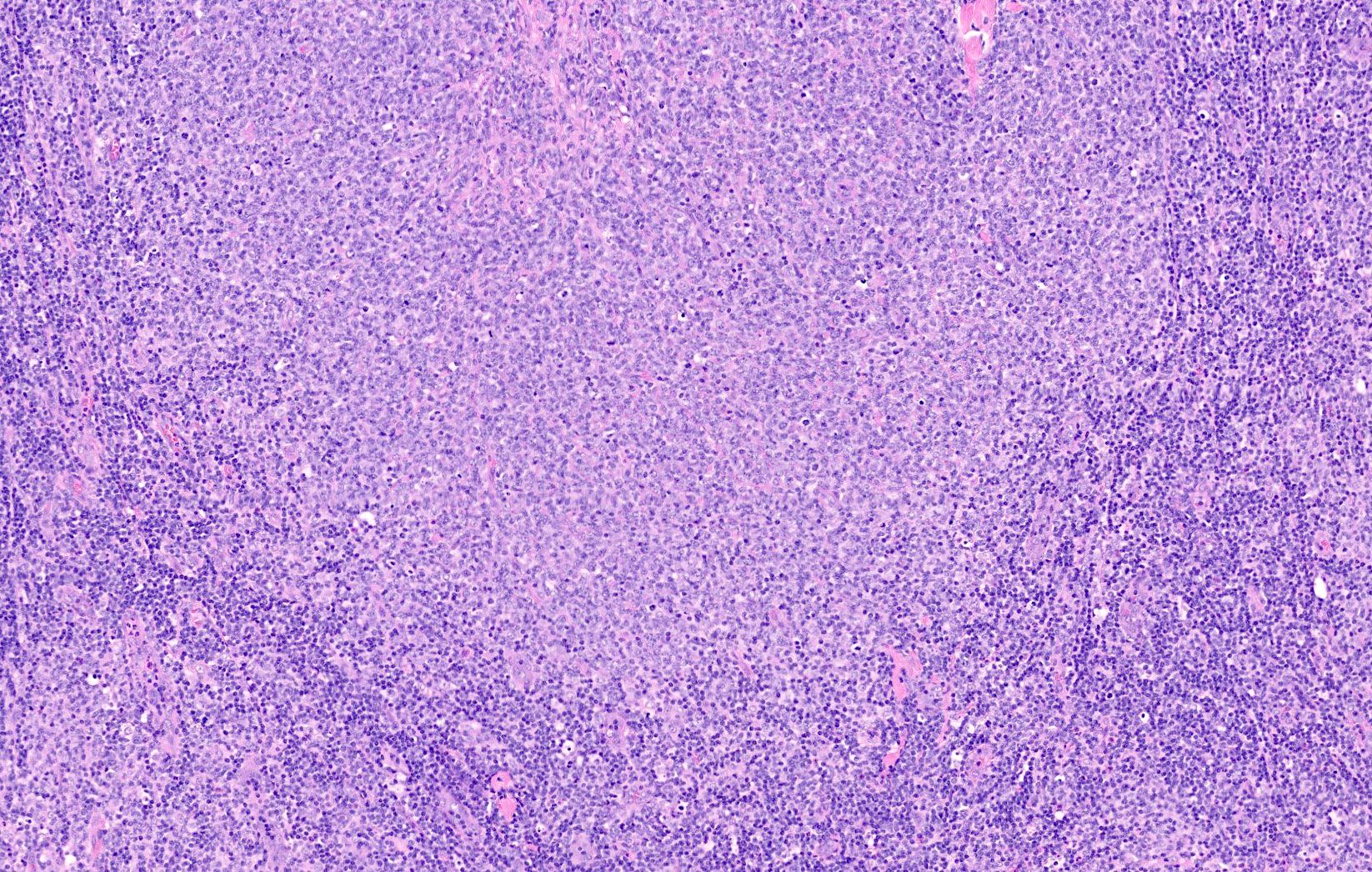
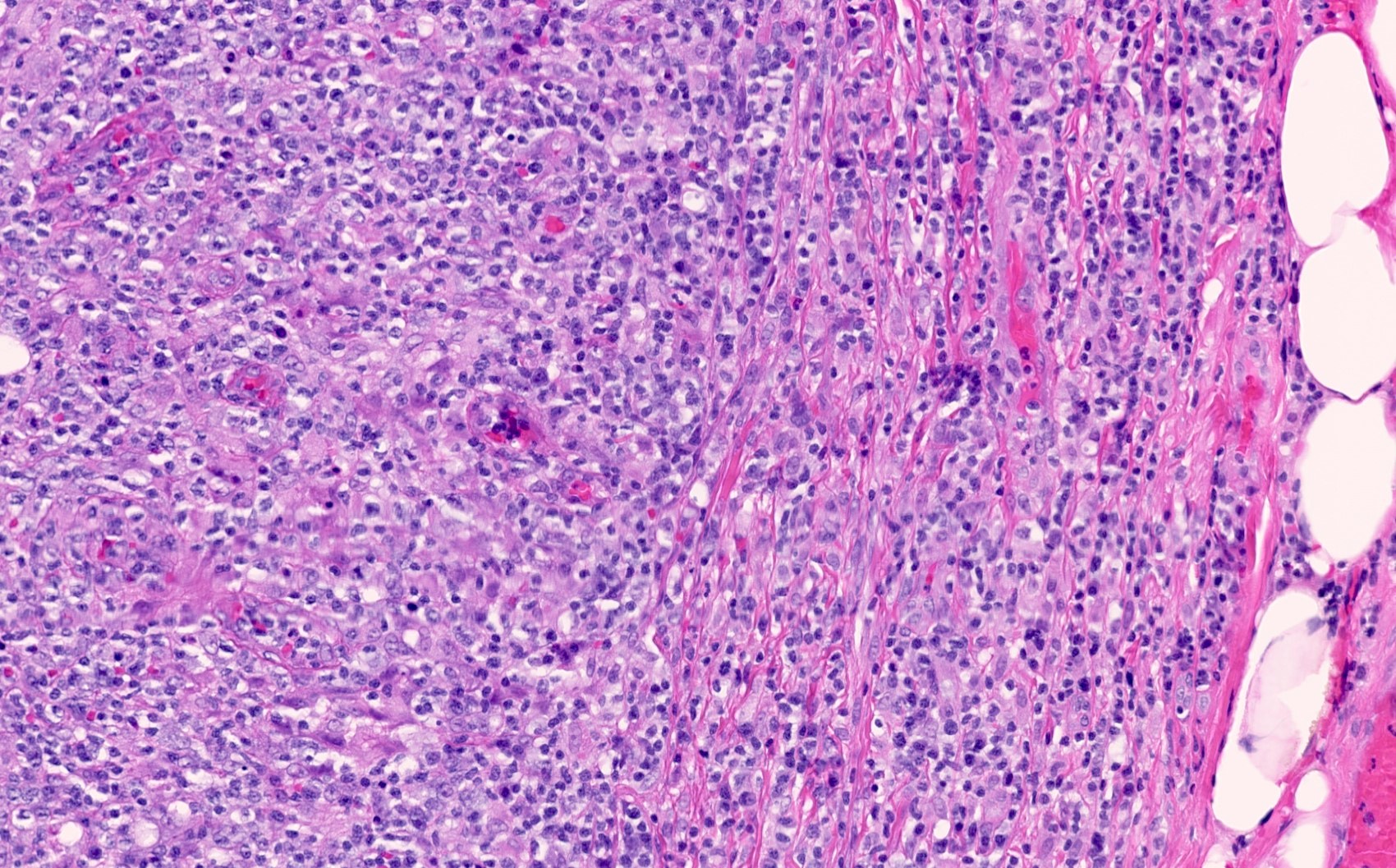
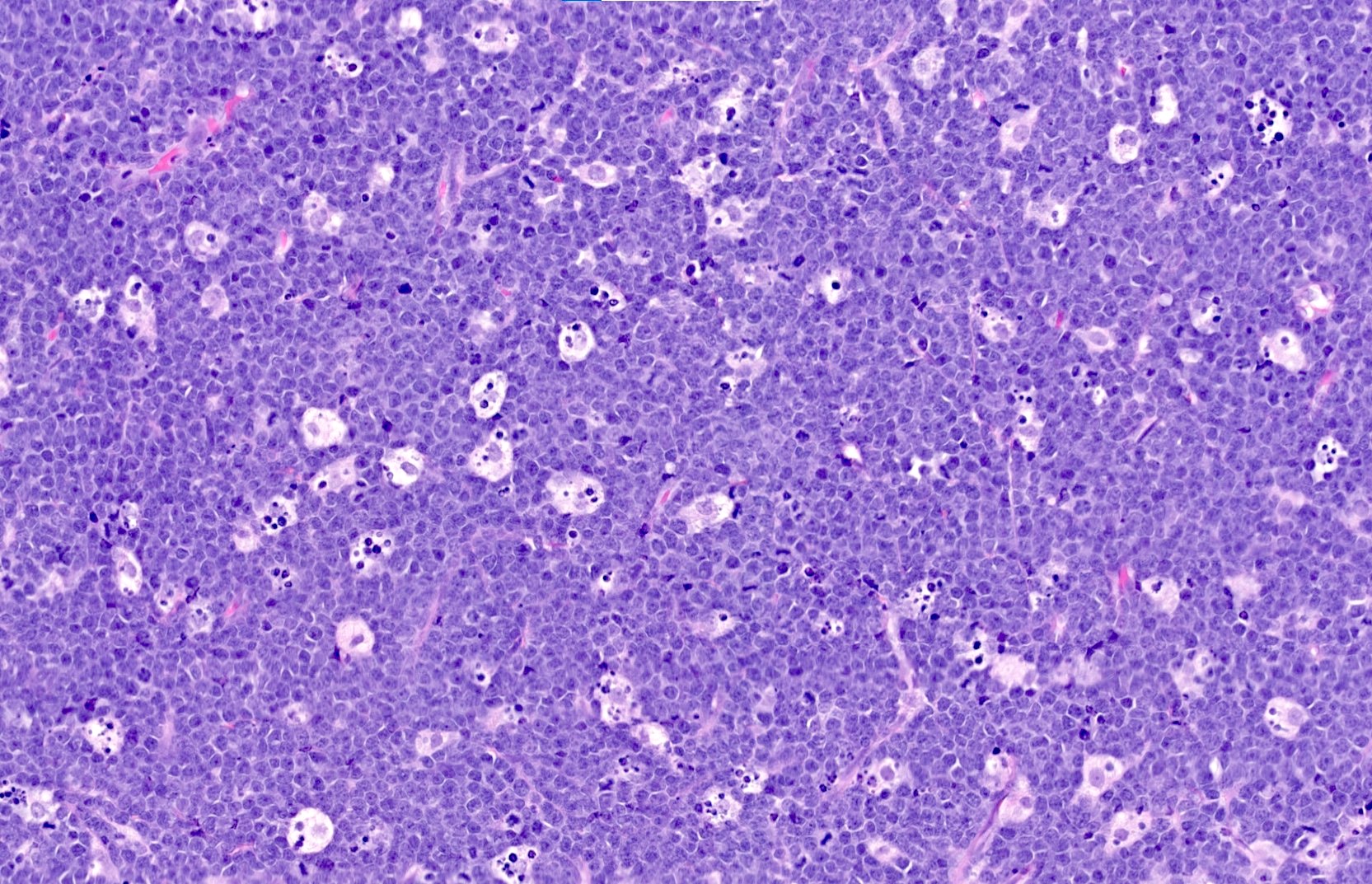
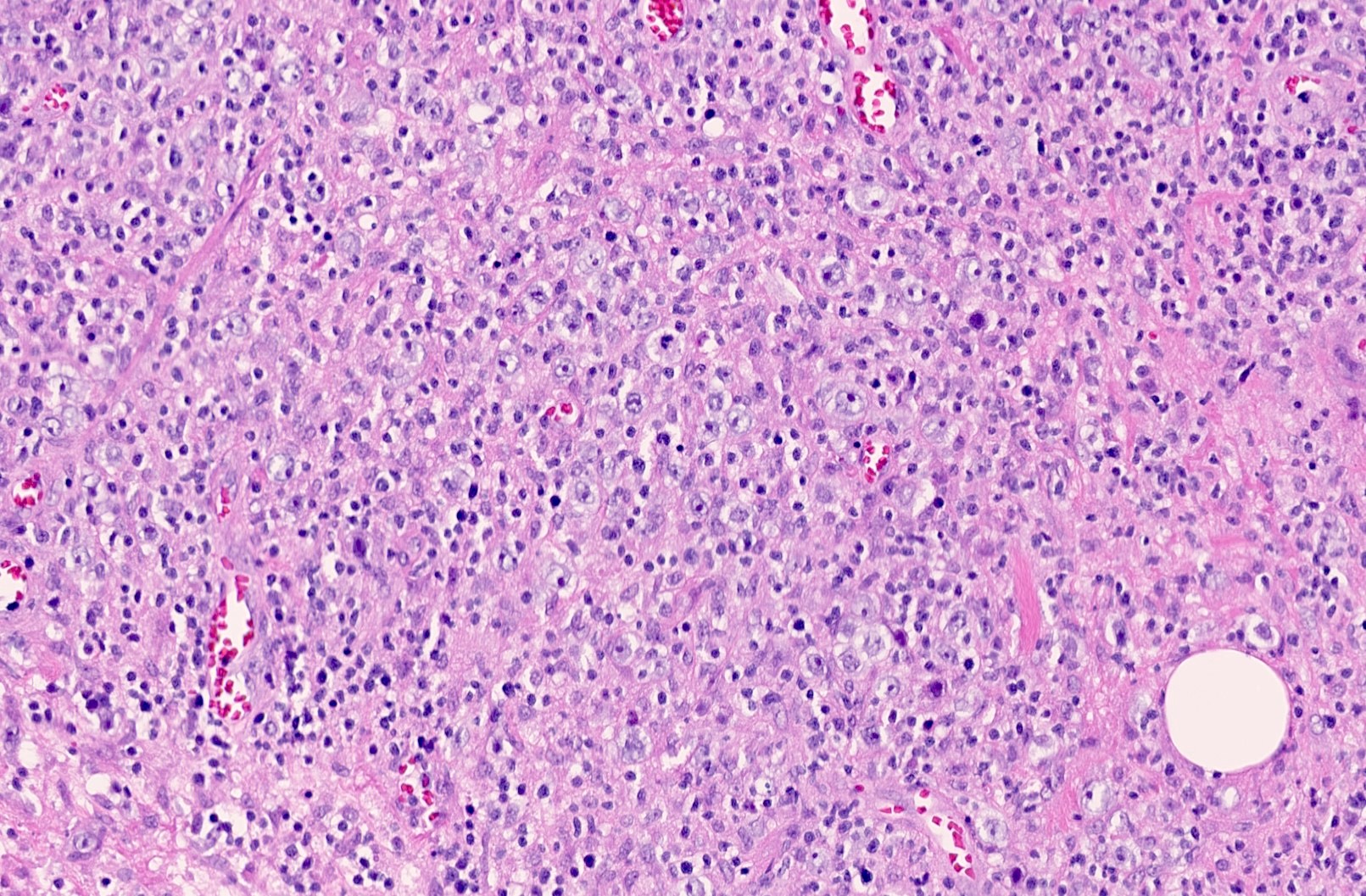
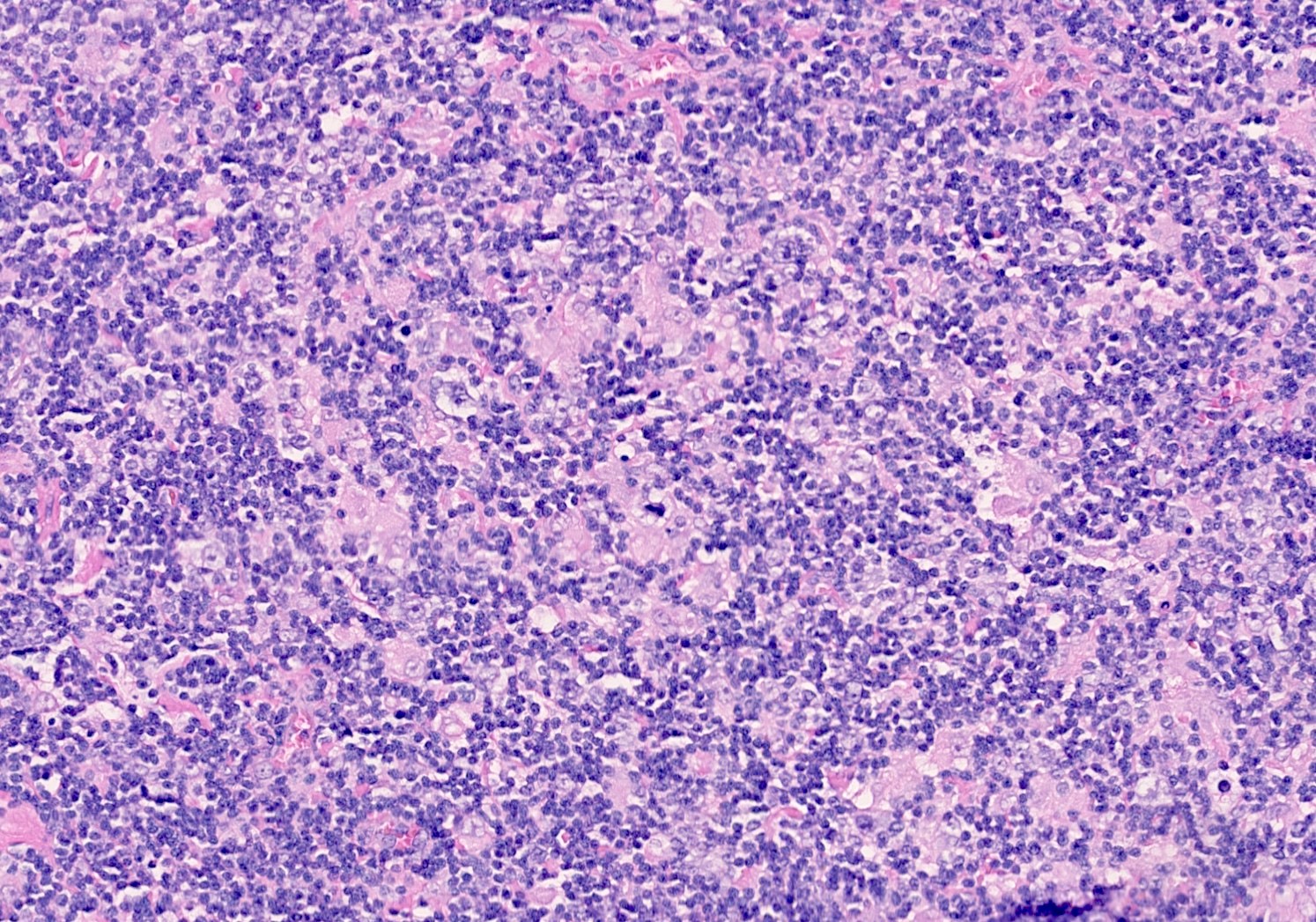
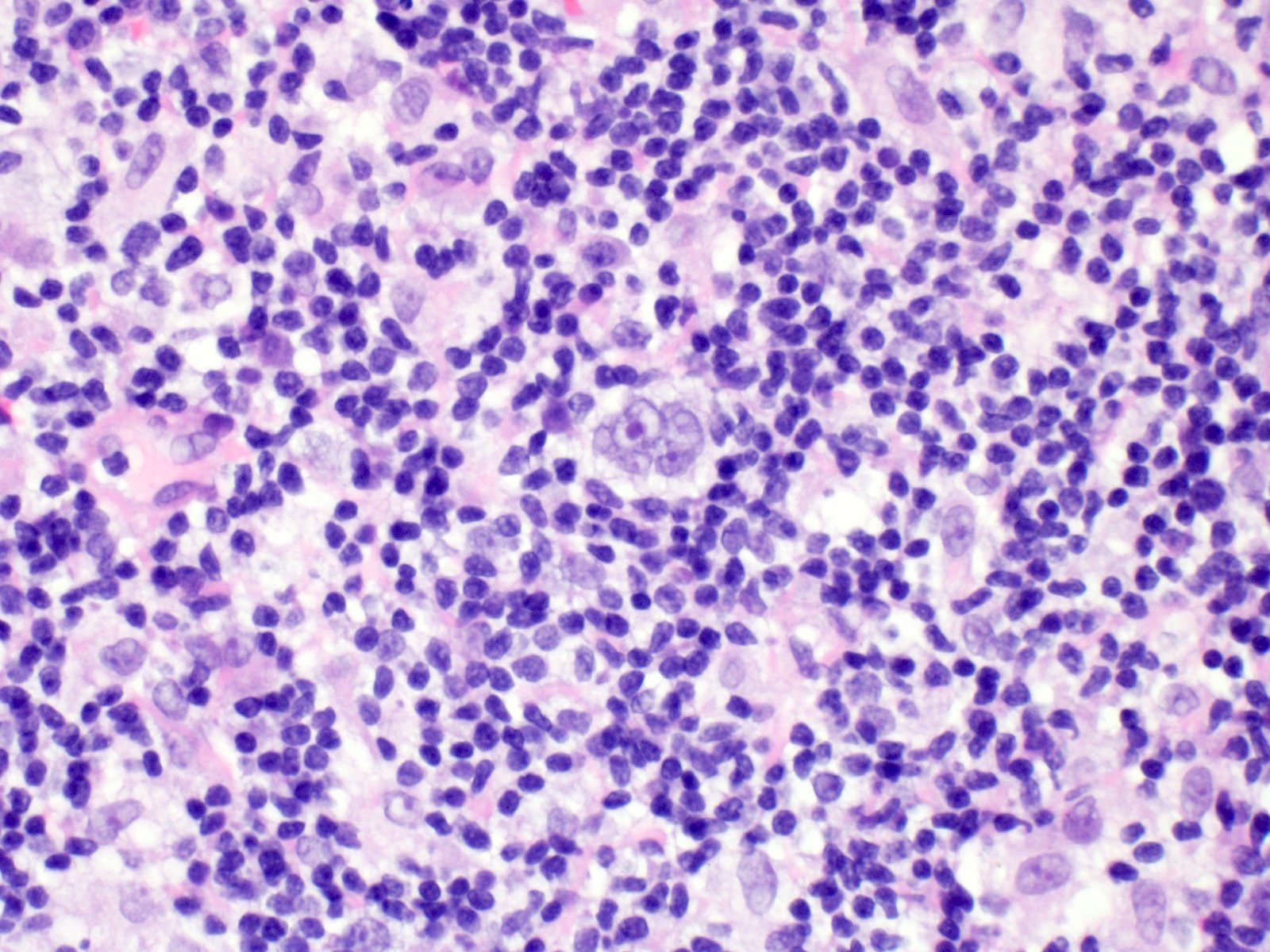
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Elena M. Fenu, M.D.
Virtual slides
Positive staining - normal
- Germinal center B cells, follicular helper T cells (Immunol Rev 2019;288:214, Trends Immunol 2021;42:336)
Positive staining - disease
- Follicular lymphoma (including cutaneous follicle center lymphoma) and germinal center subtype DLBCL (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:732, J Cancer 2020;11:190)
- Burkitt lymphoma (Mod Pathol 2010;23:909)
- Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma, nodal follicular T cell lymphoma and nodal peripheral T cell lymphoma with follicular helper phenotype and follicular helper T cell derived cutaneous T cell lymphomas (Blood 2017;129:1095, Pathology 2020;52:78, Blood 2019;133:1703)
- Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (Case Rep Pathol 2014;2014:956217)
- BCL6 expression may occasionally be seen in solid tumors, including neuroblastoma and mesenchymal tumors (Transl Oncol 2009;2:128, J Clin Pathol 2011;64:866)
Negative staining
- Late germinal center or postgerminal center B cells or plasma cells
- Nongerminal center subtype DLBCL (J Cancer 2020;11:190)
- MALT lymphoma / nodal marginal zone lymphoma (although colonized follicles have BCL6 positive cells), mantle cell lymphoma (usually) (Am J Clin Pathol 2009;132:39, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:103)
- Reed-Sternberg cells of classic Hodgkin lymphoma (usually, ~15% may be positive) (Haematologica 2007;92:1343)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Diagnosis of double or triple hit DLBCL is based on break apart FISH of MYC, BCL2 and BCL6 (Ann Lab Med 2020;40:361)
Sample pathology report
- Lymph node, left inguinal, excision:
- Diffuse large B cell lymphoma, germinal center B cell subtype (see comment)
- Comment: There is total replacement of the nodal architecture by diffuse sheets of large lymphocytes with irregular nuclear contours, open chromatin and distinct nucleoli. The tumor cells are immunoreactive for CD20, CD10, BCL6 and BCL2 and negative for MUM1, MYC and CD30, which confirms the diagnosis. The Ki67 proliferation rate is approximately 60 - 70%.
Board review style question #1
A lymph node biopsy morphologically demonstrates involvement by a large cell lymphoma. The neoplastic cells stain positive for CD20, BCL6, BCL2, MUM1 and MYC and negative for CD3, CD10, CD30 and CD138. What is the diagnosis?
- Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL)
- Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), germinal center subtype
- Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), nongerminal center subtype
- Plasmablastic lymphoma
- T cell / histiocyte rich large B cell lymphoma
Board review style answer #1
C. DLBCL, nongerminal center subtype. The neoplastic cells are positive for CD20, denoting a B cell origin. Following the Hans algorithm, a DLBCL that is negative for CD10 and positive for both BCL6 and MUM1 is nongerminal center subtype. ALCL is a T cell lymphoma and typically positive for CD30. Plasmablastic lymphoma expresses markers of plasmacytic differentiation like CD138 and is negative or only weakly positive for CD20.
Comment Here
Reference: BCL6
Comment Here
Reference: BCL6